Intra-Arterial Injection of Thrombin as Rescue Therapy of Vessel Perforation during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
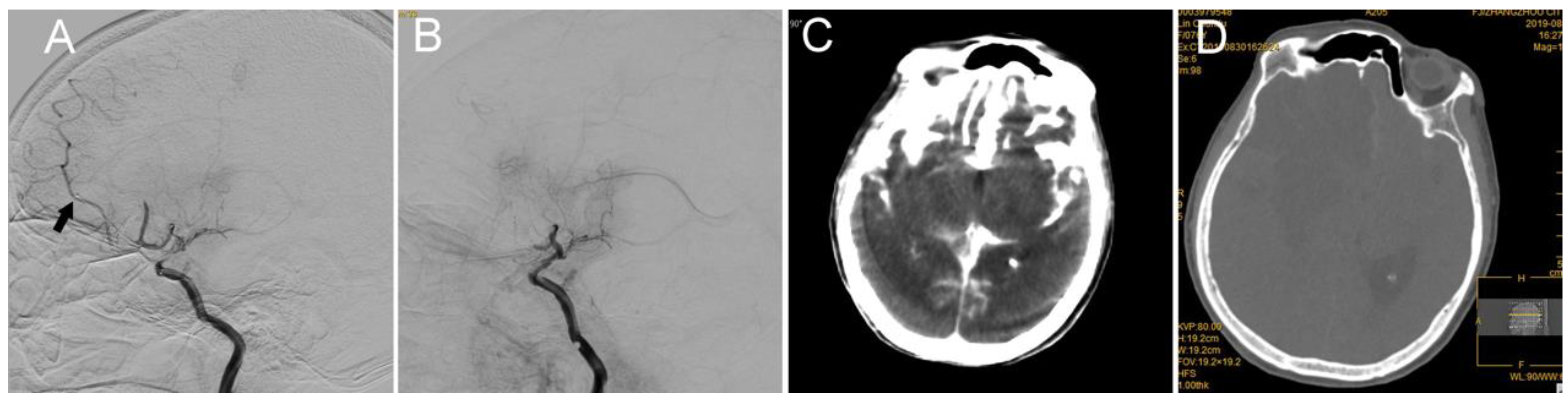
3. Cases 1 and 2: Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) M1 Occlusion
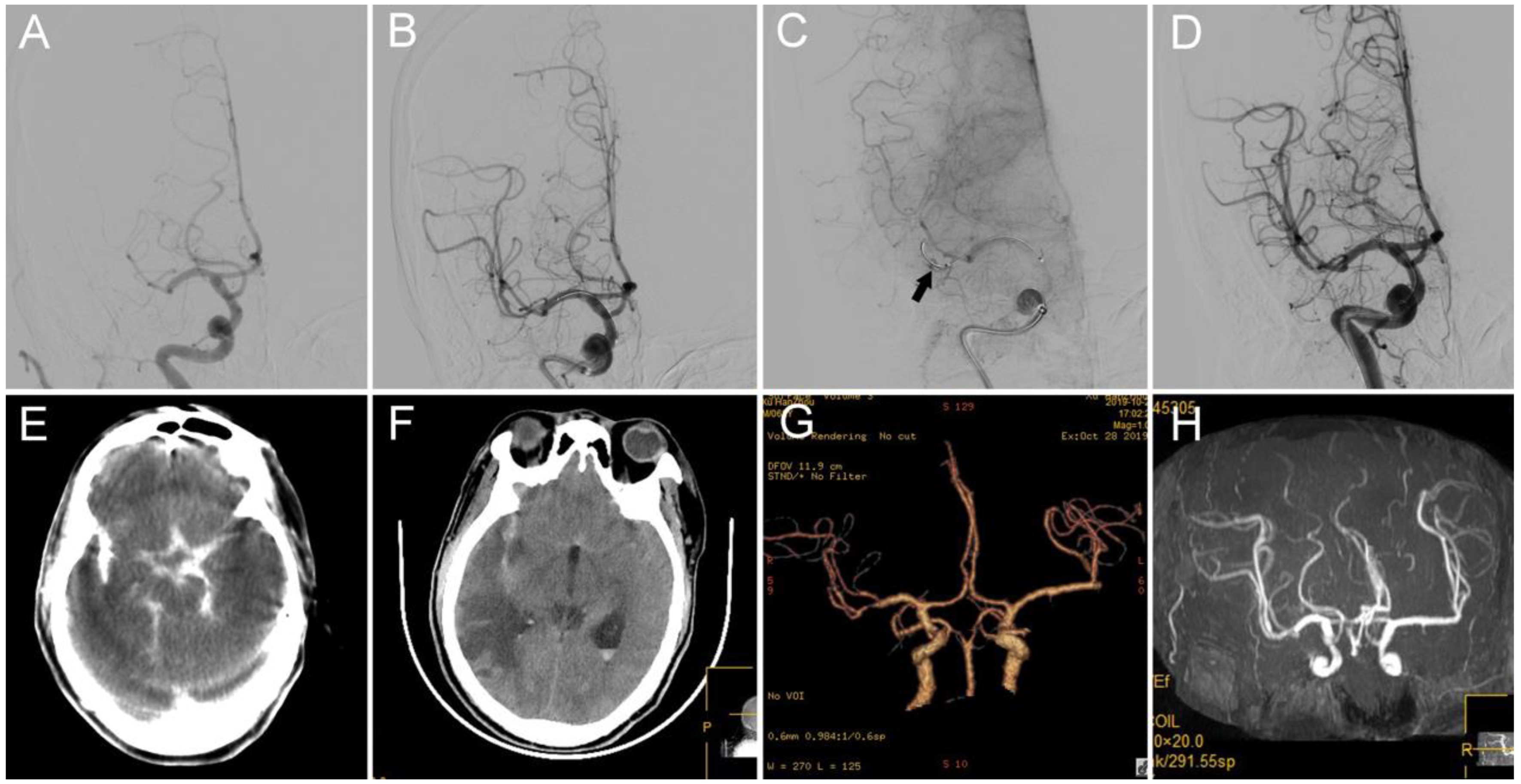
4. Case 3: Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) Terminus Occlusion
5. Case 4: Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA) A2 Segment
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; de Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; San Roman, L.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribo, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 Hours after Symptom Onset in Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver, J.L.; Goyal, M.; Bonafe, A.; Diener, H.-C.; Levy, E.I.; Pereira, V.M.; Albers, G.W.; Cognard, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular Therapy for Ischemic Stroke with Perfusion-Imaging Selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascou, G.; Lobotesis, K.; Machi, P.; Maldonado, I.; Vendrell, J.F.; Riquelme, C.; Eker, O.; Mercier, G.; Mourand, I.; Arquizan, C.; et al. Stent retrievers in acute ischemic stroke: Complications and failures during the perioperative period. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akins, P.T.; Amar, A.P.; Pakbaz, R.S.; Fields, J.D. Complications of endovascular treatment for acute stroke in the SWIFT trial with Solitaire and Merci devices. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.A.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.; Jung, M.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J.T.; Kang, H.K. Subarachnoid hemorrhage in a multimodal approach heavily weighted toward mechanical thrombectomy with solitaire stent in acute stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, P.; Wechsler, L.R.; Broderick, J.P. Intracranial hemorrhage associated with revascularization therapies. Stroke 2007, 38, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Sun, C.H.J.; Rochestie, D.; Owada, K.; Khaldi, A.; Johnson, A.K.; Horn, C.M. Presence of the hyperintense acute reperfusion marker on MRI after mechanical thrombectomy for large vessel occlusion is associated with worse early neurological recovery. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokin, M.; Fargen, K.M.; Primiani, C.T.; Ren, Z.; Dumont, T.M.; Brasiliense, L.B.; Dabus, G.; Linfante, I.; Kan, P.; Srinivasan, V.M.; et al. Vessel perforation during stent retriever thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: Technical details and clinical outcomes. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Jahan, R.; Levy, E.I.; Jovin, T.G.; Baxter, B.; Nogueira, R.G.; Clark, W.; Budzik, R.; Zaidat, O.O. Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci Retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): A randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Lutsep, H.L.; Gupta, R.; Jovin, T.G.; Albers, G.W.; Walker, G.A.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Smith, W.S. Trevo versus Merci retrievers for thrombectomy revascularisation of large vessel occlusions in acute ischaemic stroke (TREVO 2): A randomised trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumbra Pivotal Stroke Trial Investigators. The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: Safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke 2009, 40, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.S. Safety of mechanical thrombectomy and intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke. Results of the multi Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) trial, part I. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhan, A.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chen, B. Microcatheter “First-Pass Effect” Predicts Acute Intracranial Artery Atherosclerotic Disease-Related Occlusion. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshayedi, P.; Desai, S.M.; Jadhav, A.P. Extravasation control with preserved vessel patency after wire perforation during neurothrombectomy: Case report and literature review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 65, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guan, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Han, H.; Quan, T. Rescue Glue Embolization of Vessel Perforation During Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2019, 121, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybody, M.; Madoff, D.C.; Thornton, R.H.; Morales, S.A.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Hsu, M.; Brody, L.A.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M. Catheter-directed endovascular application of thrombin: Report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Clin. Imaging 2017, 42, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Rao, A.; Pimpalwar, Y. Ultrasound guided percutaneous injection of thrombin: Effective technique for treatment of iatrogenic femoral pseudoaneurysms. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, TC04–TC06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padidar, A.M.; Kee, S.T.; Razavi, M.K. Treatment of femoral artery pseudoaneurysms using ultrasound- guided thrombin injection. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 6, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablani, N.; Jain, G.; Hasan, M.M.; Sivakumar, K.; Feuerwerker, S.; Arcot, K.; Farkas, J. A novel approach to the management of carotid blowout syndrome: The use of thrombin in a case of failed covered stenting. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 8, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jargiello, T.; Durakiewicz, M.; Sojka, M.; Czekajska-Chehab, E.; Szczerbo-Trojanowska, M. Saccular aneurysm of superior vena cava treated with percutaneous, transcatheter thrombin injection. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2014, 37, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluenda, G.; Mitulescu, L.; Ben-Dor, I.; Sardi, G.; Romaguera, R.; Satler, L.F.; Pichard, A.D.; Waksman, R.; Bernardo, N.L. Transcatheter “thrombin-blood patch” injection: A novel and effective approach to treat catheterization-related arterial perforation. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 80, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischell, T.A.; Moualla, S.K.; Mannem, S.R. Intracoronary thrombin injection using a microcatheter to treat guidewire-induced coronary artery perforation. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2011, 12, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, C.; Degen, H.; Stoepel, C.; Haude, M. Vorgehen bei einer katheterinduzierten Pulmonalarterienperforation. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2010, 135, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluenda, G.; Waksman, R.; Bernardo, N.L. Accepted TCT challenging case: Common femoral artery perforation after primary percutaneous coronary intervention successfully treated with a novel transcatheter “thrombin-blood patch” injection technique. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 79, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
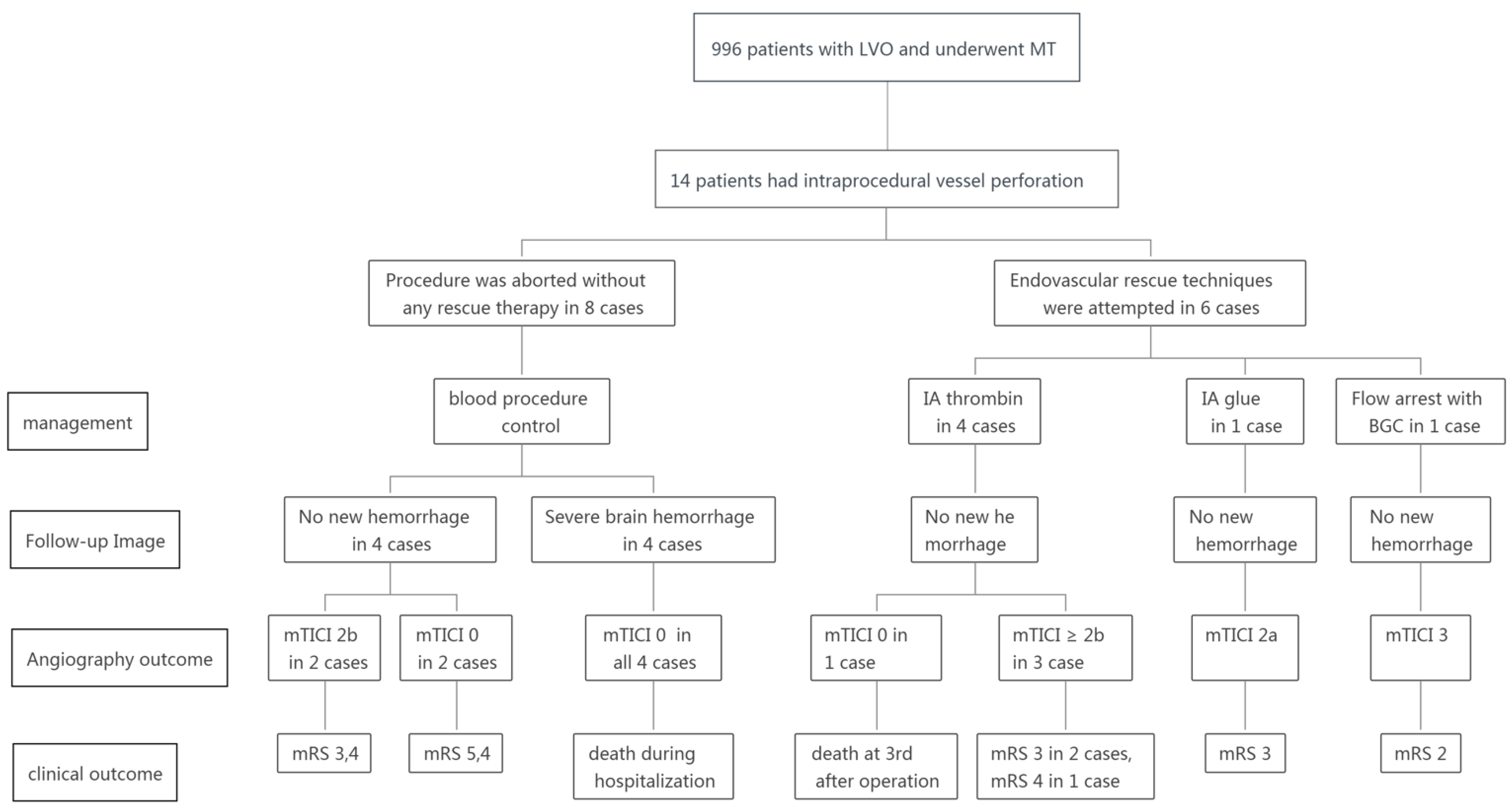


| pt | Occlusion Site TOAST | IV rtPA before; IV Heparin during Thrombectomy | General Anaesthesia Yes/No | Approach to Thrombectomy | Stent Retriever No. of Passes | Location of Perforation | Suspected Cause of Perforation | Rescue Endovascular Treatment | Postprocedure CT | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R-M1P ICAS | IV heparin | No | Stent retriever + Balloon angioplasty | 1 | RM1D | Perforation with microwire/microcatheter when traversing lesion site | IA thrombin | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 3, mRS 4 at 3 months |
| 2 | L-A3 ICAS | IV heparin | No | NA | NA | L-A2 | Perforation with microwire/microcatheter when traversing clot | IA thrombin | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 0; death at 3rd days after operation |
| 3 | L-ICA terminus ICAS | IV heparin | No | Balloon angioplasty | NA | L-ICA terminus | Perforation with microwire/microcatheter when traversing lesion site | IA thrombin | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 3, mRS 3 at discharge |
| 4 | R-M1D ICAS | IV heparin | No | Stent retriever | Solitaire 4 × 20 1 pass | R M1D | Resistance withdrawing stent retriever | IA thrombin | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 2b, mRS 3 at 3 months |
| 5 | L-ICA terminus CE | IV heparin | No | BGC + stent retriever | Solitaire 6 × 30 1 pass | LM1P | Perforation with microwire/microcatheter when traversing clot | Flow arrest with BGC | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 3, mRS 2 at 3 months |
| 6 | L-M1D CE | IV heparin | No | Stent retriever | Solitaire 4 × 20 4 passes | L M3 | Perforation with microcatheter injection to confirm location | IA glue | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 2a, mRS 3 at 3 months |
| 7 | R M2 CE | IV heparin | No | Stent retriever | Solitaire 4 × 20 1 pass | RM3 | Perforation with microwire when traversing clot | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 2b, mRS 3 at 3 months |
| 8 | L-M2 CE | IV heparin | No | NA | NA | L M3 | Perforation with microwire when traversing clot | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 0, mRS 5 at discharge |
| 9 | L-ICA terminus ICAS | IV heparin | No | NA | NA | L-ICA terminus | Perforation with microwire when traversing lesion site | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 0, mRS 4 at 3 months |
| 10 | L-M2 CE | IV heparin | Yes | NA | NA | L M3 | Perforation with microwire when traversing clot | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | No new hemorrhage | mTICI 2b, mRS 4 at 3 months |
| 11 | L-Carotid T * CE | IV heparin | No | NA | NA | L M1P | Perforation with microwire when traversing clot | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | Severe brain hemorrhage | mTICI 0; death in hospital |
| 12 | L-Carotid L ** CE | IV heparin | Yes | NA | NA | L-ICA terminus | Perforation with wire when advancing guiding catheter | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | Severe brain hemorrhage | mTICI 0; death in hospital |
| 13 | R-Carotid-L CE | IV heparin + IV rt-PA | Yes | NA | NA | R M1P | Perforation with microwire when traversing clot | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | Severe brain hemorrhage | mTICI 0; death in hospital |
| 14 | L-M1P CE | IV heparin | Yes | NA | NA | L anterior choroidal artery | Perforation with microcatheter went into anterior choroidal artery | Procedure aborted, blood pressure control | Severe brain hemorrhage | mTICI 0; death in hospital |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, T.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Lin, X.; Lin, D.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X. Intra-Arterial Injection of Thrombin as Rescue Therapy of Vessel Perforation during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060760
Yi T, Chen W, Wu Y, Pan Z, Lin X, Lin D, Chen R, Zheng X. Intra-Arterial Injection of Thrombin as Rescue Therapy of Vessel Perforation during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(6):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060760
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Tingyu, Wenhuo Chen, Yanmin Wu, Zhinan Pan, Xiaohui Lin, Dinglai Lin, Rongcheng Chen, and Xiufeng Zheng. 2022. "Intra-Arterial Injection of Thrombin as Rescue Therapy of Vessel Perforation during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke" Brain Sciences 12, no. 6: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060760
APA StyleYi, T., Chen, W., Wu, Y., Pan, Z., Lin, X., Lin, D., Chen, R., & Zheng, X. (2022). Intra-Arterial Injection of Thrombin as Rescue Therapy of Vessel Perforation during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sciences, 12(6), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060760






