Effects of Ten Different Exercise Interventions on Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Patients—A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Risk of Bias of Individual Studies
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study and Identification and Selection
3.2. Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
3.3. Characteristics of the Included Studies
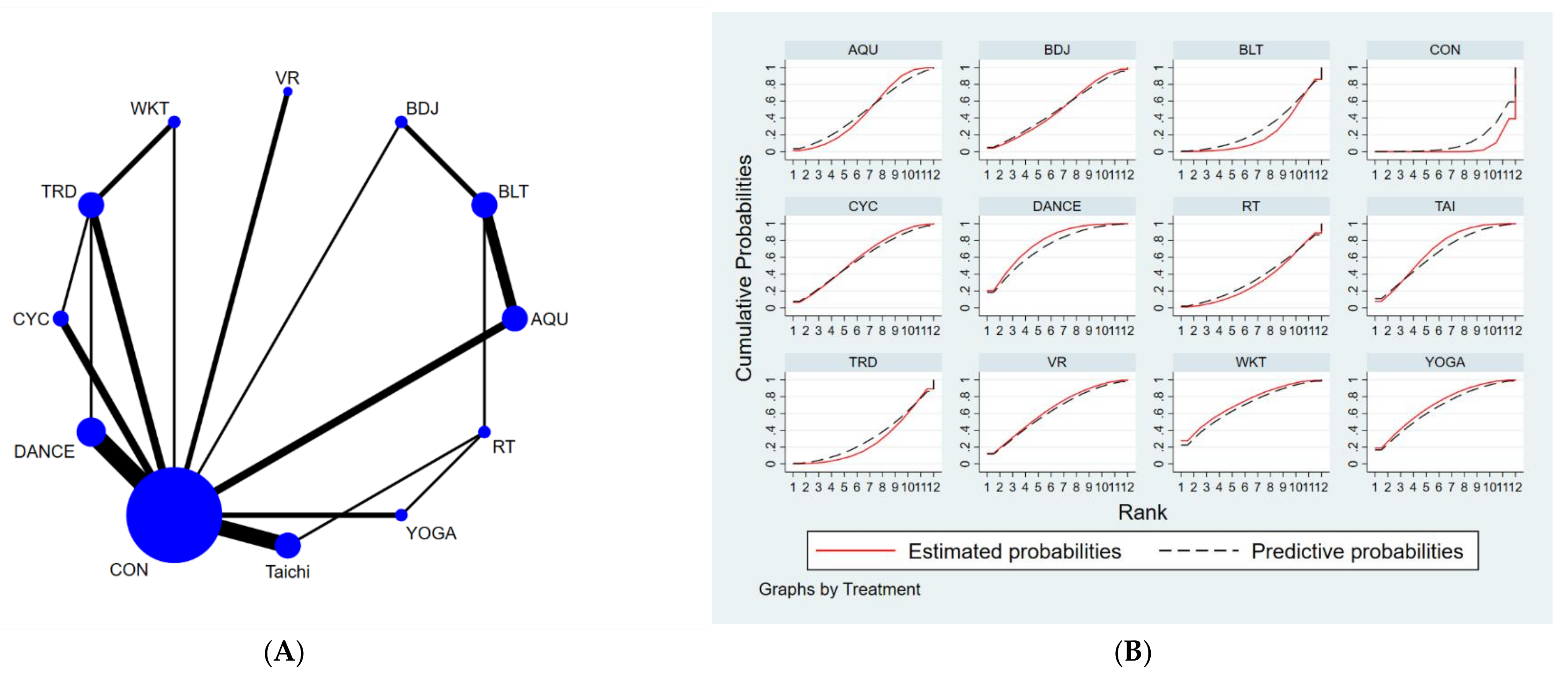
3.4. Network Meta-Analysis
3.4.1. Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale-Motor (UPDRS-Motor)
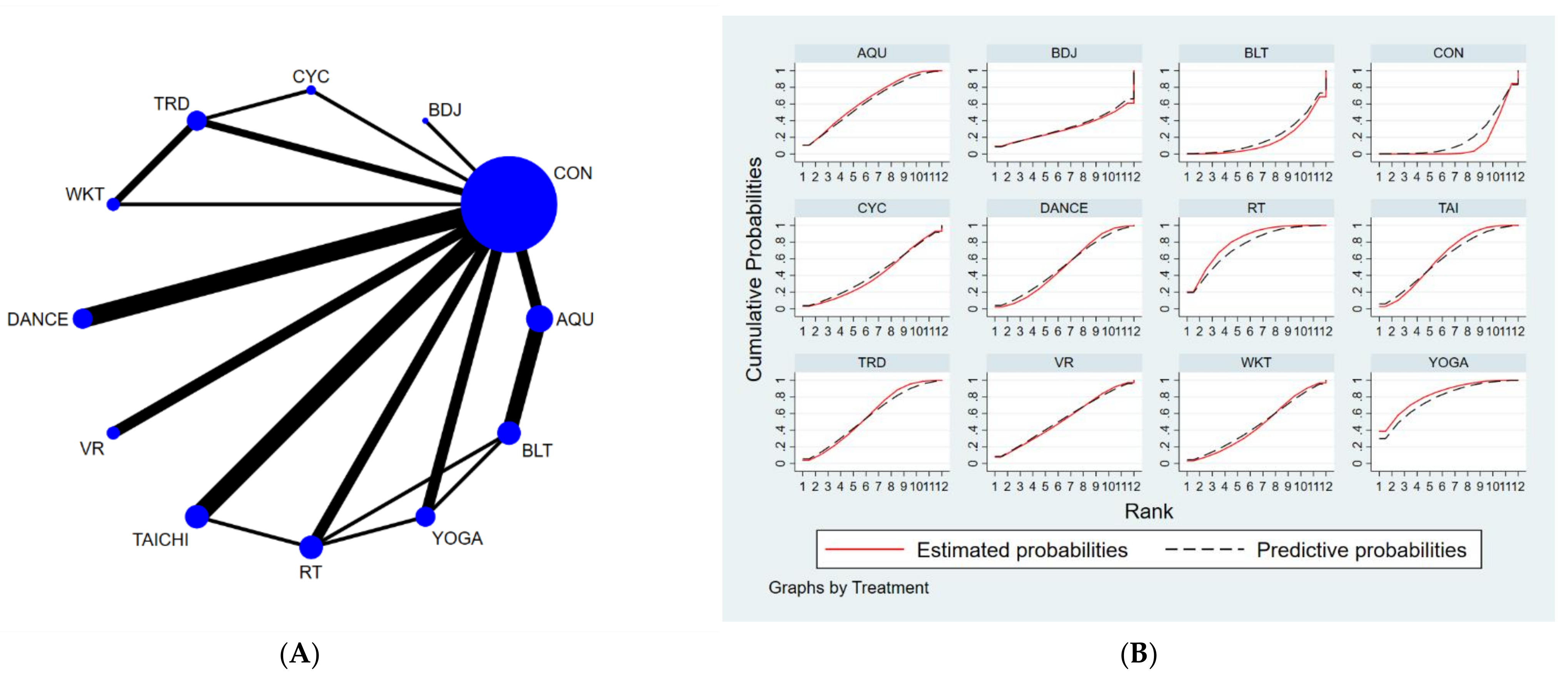
3.4.2. Timed-Up-and-Go Test (TUGT)
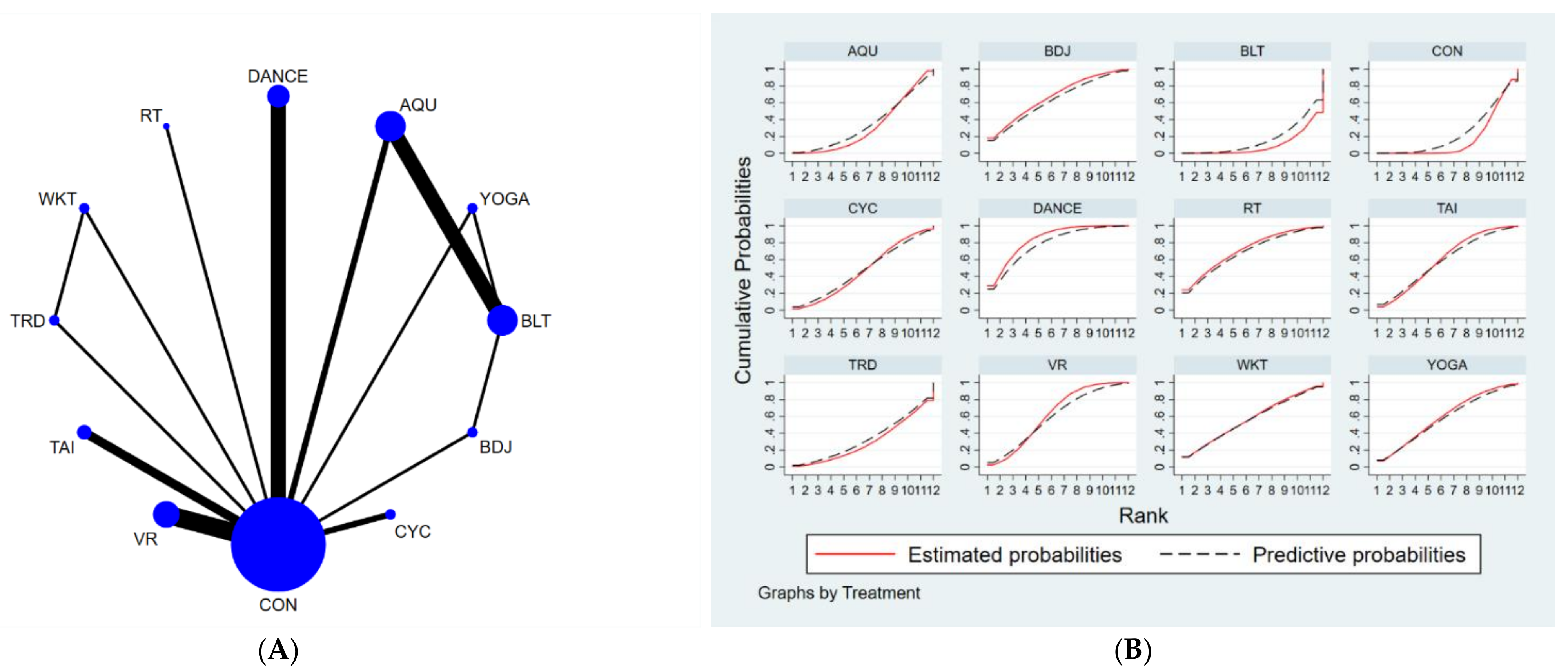
3.4.3. Berge Balance Scale
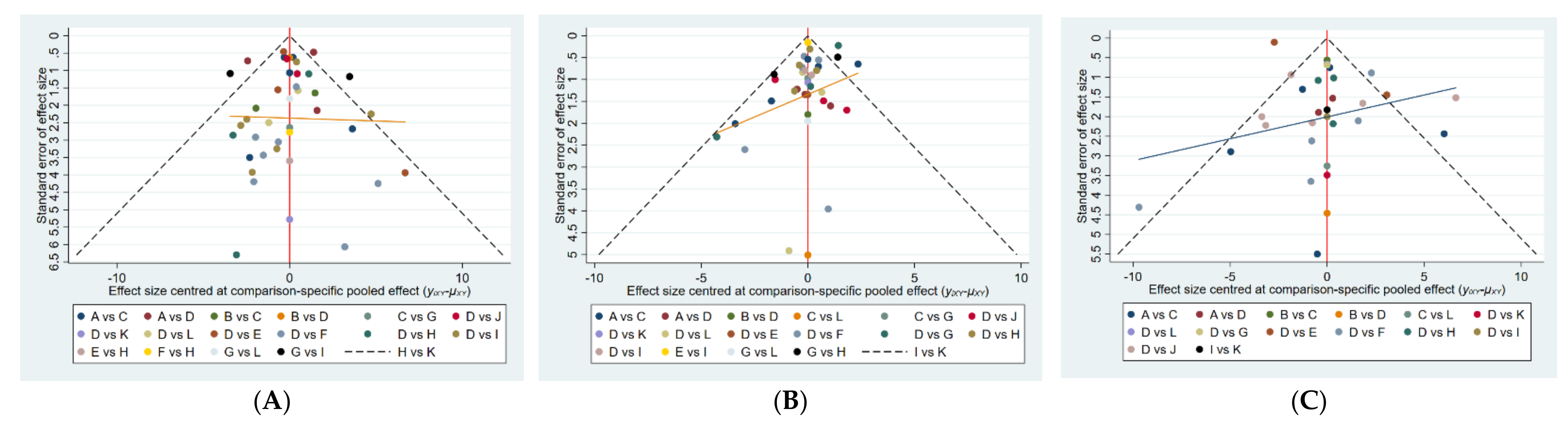
3.5. Publication Bias Test
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, D.; Lawson, K.D.; Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; van Mechelen, W.; Pratt, M. The Economic Burden of Physical Inactivity: A Global Analysis of Major Non-Communicable Diseases. Lancet 2016, 388, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators Global, Regional, and National Burden of Neurological Disorders, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeso, J.A.; Stamelou, M.; Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Lang, A.E.; Weintraub, D.; Burn, D.; Halliday, G.M.; Bezard, E.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Past, Present, and Future of Parkinson’s Disease: A Special Essay on the 200th Anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1264–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuepbach, W.M.M.; Rau, J.; Knudsen, K.; Volkmann, J.; Krack, P.; Timmermann, L.; Haelbig, T.D.; Hesekamp, H.; Navarro, S.M.; Meier, N.; et al. Neurostimulation for Parkinson’s Disease with Early Motor Complications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, R.; Li, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, R. Exercise as a Prescription for Patients with Various Diseases. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 422–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Siqueira, T.C.; D’Oliveira, A.; Dominski, F.H. Effects of Exercise in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Tsang, R.C.C.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Gao, Q. Effects of Exercise in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.K.; Wong-Yu, I.S.; Shen, X.; Chung, C.L. Long-Term Effects of Exercise and Physical Therapy in People with Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwan, M.; Begemann, M.J.H.; Slot, M.I.E.; Lee, E.H.M.; Scheltens, P.; Sommer, I.E.C. Physical Exercise Improves Quality of Life, Depressive Symptoms, and Cognition across Chronic Brain Disorders: A Transdiagnostic Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1222–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, X.; Song, W.; Du, X. The Effect of Qigong-Based Therapy on Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.O.; Scianni, A.; Rodrigues-de-Paula, F. Progressive Resistance Exercise Improves Strength and Physical Performance in People with Mild to Moderate Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Physiother. 2013, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, A.; Jaegers, L.; Krieger, M.; Bixler, E.; Kelly, P.; Weiss, E.P.; Ahmad, S.O. Endurance Exercise Improves Function in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 659, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, K.; Hewitt, J. Dance as an Intervention for People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, B.; Chaimani, A.; Li, T. Network Meta-Analysis: An Introduction for Clinicians. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Jueni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ-Br. Med. J. 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, P. Effects of Aquatic Exercise and Land-Based Exercise on Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Motor Function, Balance, and Functional Independence in Stroke Patients—A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.; Riley, R.; White, I.R. Multivariate Meta-Analysis: Potential and Promise. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. PRISMA-P Group Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, D.; Flegal, J.M.; Jones, G.L. Multivariate Output Analysis for Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Biometrika 2019, 106, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Graphical Methods and Numerical Summaries for Presenting Results from Multiple-Treatment Meta-Analysis: An Overview and Tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaimani, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Mavridis, D.; Spyridonos, P.; Salanti, G. Graphical Tools for Network Meta-Analysis in STATA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, N.; Demeco, A.; Moggio, L.; Marinaro, C.; Pino, I.; Barletta, M.; Petraroli, A.; Pepe, D.; Lavano, F.; Ammendolia, A. Comparative Effectiveness of Breathing Exercises in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Complementary Ther. Clin. Pract. 2020, 41, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Murad, M.H.; Chandar, A.K.; Dulai, P.S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Loomba, R.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S. Association of Pharmacological Treatments for Obesity with Weight Loss and Adverse Events A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Kang, Y. Effect of Health Qigong Baduanjin on Fall Prevention in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, e227–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, Q.; Dong, S.; Cai, Z. Effects of Baduanjin and Balancer Exercise on Motor and Non-motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. 2021, 27, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, X.; Yang, W.; Jie, W. Effects of Baduanjin combined with balance mat training on lower limb motor function and trunk balance strength in elderly Parkinson’s patients. Pract. Clin. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2021, 21, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugusi, L.; Solla, P.; Serpe, R.; Carzedda, T.; Piras, L.; Oggianu, M.; Gabba, S.; Di Blasio, A.; Bergamin, M.; Cannas, A.; et al. Effects of a Nordic Walking Program on Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms, Functional Performance and Body Composition in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, D.-H.; Shin, W.-S. Effects of an Intensive Nordic Walking Intervention on the Balance Function and Walking Ability of Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.; Sanchez, J.A.; Lopez-Alonso, V.; Márquez, G.; Morenilla, L.; Castro, X.; Giraldez, M.; Santos-García, D.; Fernandez-del-Olmo, M. The Effects of Treadmill or Overground Walking Training Program on Gait in Parkinson’s Disease. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Barbirato, D.; Araujo, N.; Martins, J.V.; Cavalcanti, J.L.S.; Santos, T.M.; Coutinho, E.S.; Laks, J.; Deslandes, A.C. Comparison of Strength Training, Aerobic Training, and Additional Physical Therapy as Supplementary Treatments for Parkinson’s Disease: Pilot Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, L.M.; Katzel, L.I.; Ivey, F.M.; Sorkin, J.D.; Favors, K.; Anderson, K.E.; Smith, B.A.; Reich, S.G.; Weiner, W.J.; Macko, R.F. Randomized Clinical Trial of 3 Types of Physical Exercise for Patients with Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage, M.D.; Almeida, Q.J. Symptom and Gait Changes after Sensory Attention Focused Exercise vs Aerobic Training in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-de la Cruz, S. A Bicentric Controlled Study on the Effects of Aquatic Ai Chi in Parkinson Disease. Complementary Ther. Med. 2018, 36, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.M.; Volpe, D.; Morris, M.E.; Saunders, J.; Clifford, A.M. Aquatic Exercise Therapy for People with Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, J.; Arias, P.; Cudeiro, J. Aquatic Therapy versus Conventional Land-Based Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: An Open-Label Pilot Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, D.; Giantin, M.G.; Maestri, R.; Frazzitta, G. Comparing the Effects of Hydrotherapy and Land-Based Therapy on Balance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Feng, S.; Hou, W.; Zhang, Y. Effect of water—Based exercise on motor function, balance function and walking ability in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 17, 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, E.E.; Büyükturan, B.; Büyükturan, Ö.; Erdem, H.R.; Tuncay, F. Effects of Ai Chi on Balance, Quality of Life, Functional Mobility, and Motor Impairment in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamara, G.; Gotti, F.; Maestri, R.; Bera, R.; Gargantini, R.; Bossio, F.; Zivi, I.; Volpe, D.; Ferrazzoli, D.; Frazzitta, G. Land Plus Aquatic Therapy Versus Land-Based Rehabilitation Alone for the Treatment of Balance Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study With 6-Month Follow-Up. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, I.; Maestri, R.; Bonetti, F.; Ortelli, P.; Volpe, D.; Ferrazzoli, D.; Frazzitta, G. Land Plus Aquatic Therapy Versus Land-Based Rehabilitation Alone for the Treatment of Freezing of Gait in Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2019, 99, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, D.; Giantin, M.G.; Manuela, P.; Filippetto, C.; Pelosin, E.; Abbruzzese, G.; Antonini, A. Water-Based vs. Non-Water-Based Physiotherapy for Rehabilitation of Postural Deformities in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J. Effects of Therapeutic Tai Chi on Functional Fitness and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Parkinson Disease. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2016, 12, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; She, J. Observation on the effectiveness of group therapy of Tai Chi balance exercise in improving the balance function and depressive state of Parkinson’s disease patients. Guizhou Med. J. 2020, 44, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Harmer, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Eckstrom, E.; Stock, R.; Galver, J.; Maddalozzo, G.; Batya, S.S. Tai Chi and Postural Stability in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Diaz, G.; Osypiuk, K.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Bonato, P.; Gow, B.J.; Miranda, J.G.; Sudarsky, L.R.; Tarsy, D.; Fox, M.D.; Gardiner, P.; et al. Tai Chi for Reducing Dual-Task Gait Variability, a Potential Mediator of Fall Risk in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2018, 7, 2164956118775385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, M.E.; Earhart, G.M. Tai Chi Improves Balance and Mobility in People with Parkinson Disease. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, M. Tai Chi Improves Balance and Prevents Falls in People with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Physiother. 2014, 61, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amano, S.; Nocera, J.R.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Juncos, J.L.; Gregor, R.J.; Waddell, D.E.; Wolf, S.L.; Hass, C.J. The Effect of Tai Chi Exercise on Gait Initiation and Gait Performance in Persons with Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Garber, C.E.; Jun, T.-W.; Jin, Y.-S.; Chung, S.-J.; Kang, H.-J. Therapeutic Effects of Tai Chi in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. ISRN Neurol. 2013, 2013, 548240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, D.; Signorini, M.; Marchetto, A.; Lynch, T.; Morris, M.E. A Comparison of Irish Set Dancing and Exercises for People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Phase II Feasibility Study. BMC Geriatr. 2013, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P. Analysis of the effects of rhythmic auditory stimulation combined with motor training on motor function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mod. Diagn. Treat. 2020, 31, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Michels, K.; Dubaz, O.; Hornthal, E.; Bega, D. “Dance Therapy” as a Psychotherapeutic Movement Intervention in Parkinson’s Disease. Complementary Ther. Med. 2018, 40, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, J.; Morris, M.E.; Bhriain, O.N.; Volpe, D.; Lynch, T.; Clifford, A.M. Dancing for Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Trial of Irish Set Dancing Compared with Usual Care. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackney, M.E.; Earhart, G.M. Effects of Dance on Movement Control in Parkinson’s Disease: A Comparison of Argentine Tango and American Ballroom. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, K.S.; McNeely, M.E.; Duncan, R.P.; Pickett, K.A.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Earhart, G.M. Exercise and Parkinson Disease: Comparing Tango, Treadmill and Stretching. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2019, 43, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Paul, S.; Caetano, M.J.; Smith, S.; Dibble, L.; Love, R.; Schoene, D.; Menant, J.; Sherrington, C.; Lord, S.; et al. Home-Based Step Training Using Videogame Technology in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Blinded Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 32, 0269215517721593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.P.; Earhart, G.M. Randomized Controlled Trial of Community-Based Dancing to Modify Disease Progression in Parkinson Disease. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair. 2012, 26, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, P.; Cugusi, L.; Bertoli, M.; Cereatti, A.; Della Croce, U.; Pani, D.; Fadda, L.; Cannas, A.; Marrosu, F.; Defazio, G.; et al. Sardinian Folk Dance for Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J. Altern. Complementary 2019, 25, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Romenets, S.; Anang, J.; Fereshtehnejad, S.-M.; Pelletier, A.; Postuma, R. Tango for Treatment of Motor and Non-Motor Manifestations in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study. Complementary Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Robbins, K.; Wagner, K.; Colgrove, Y. A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study of the Therapeutic Effects of Yoga in People with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Yoga 2015, 8, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Mooney, K.; Richards, L.; Balachandran, A.; Sun, M.; Harriell, K.; Potiaumpai, M.; Signorile, J.F. Comparative Impacts of Tai Chi, Balance Training, and a Specially-Designed Yoga Program on Balance in Older Fallers. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuzema, A.; Brammatha, A.; Arul Selvan, V. Effect of Home-Based Tai Chi, Yoga or Conventional Balance Exercise on Functional Balance and Mobility among Persons with Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: An Experimental Study. Hong Kong Physiother. J. 2020, 40, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.Y.Y.; Kwan, J.C.Y.; Auyeung, M.; Mok, V.C.T.; Lau, C.K.Y.; Choi, K.C.; Chan, H.Y.L. Effects of Mindfulness Yoga vs Stretching and Resistance Training Exercises on Anxiety and Depression for People with Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.; Bhimani, R.; Wyman, J.F.; Konczak, J.; Zhang, L.; Mishra, U.; Terluk, M.; Kartha, R.V.; Tuite, P. Effects of Yoga on Oxidative Stress, Motor Function, and Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puymbroeck, M.; Walter, A.; Hawkins, B.; Sharp, J.; Woschkolup, K.; Urrea-Mendoza, E.; Revilla, F.; Adams, E.; Schmid, A. Functional Improvements in Parkinson’s Disease Following a Randomized Trial of Yoga. Evid. -Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8516351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kolk, N.M.; de Vries, N.M.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Joosten, H.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Post, B.; Bloem, B.R. Effectiveness of Home-Based and Remotely Supervised Aerobic Exercise in Parkinson’s Disease: A Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacheli, M.A.; Neva, J.L.; Lakhani, B.; Murray, D.K.; Vafai, N.; Shahinfard, E.; English, C.; McCormick, S.; Dinelle, K.; Neilson, N.; et al. Exercise Increases Caudate Dopamine Release and Ventral Striatal Activation in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgel, A.L.; Ault, D.L. High-Cadence Cycling Promotes Sustained Improvement in Bradykinesia, Rigidity, and Mobility in Individuals with Mild-Moderate Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2019, 2019, 4076862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcolin, I.; Pisano, F.; Delconte, C.; Godi, M.; Schieppati, M.; Mezzani, A.; Picco, D.; Grasso, M.; Nardone, A. Intensive Cycle Ergometer Training Improves Gait Speed and Endurance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Comparison with Treadmill Training. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2016, 34, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollár, J.; Nagy, F.; Hortobágyi, T. Vastly Different Exercise Programs Similarly Improve Parkinsonian Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Gerontology 2019, 65, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Mei, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Effect of resistance training on the improvement of lower extremity muscle strength and balance function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2019, 39, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, L.C.; Abrahin, O.; Rodrigues, R.P.; da Silva, M.C.; Araújo, A.P.; de Sousa, E.C.; Pimentel, C.P.; Cortinhas-Alves, E.A. Low-Volume Resistance Training Improves the Functional Capacity of Older Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira de Moraes Filho, A.; Chaves, S.N.; Martins, W.R.; Tolentino, G.P.; de Cássia Pereira Pinto Homem, R.; Landim de Farias, G.; Fischer, B.L.; Oliveira, J.A.; Pereira, S.K.A.; Vidal, S.E.; et al. Progressive Resistance Training Improves Bradykinesia, Motor Symptoms and Functional Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, T.A.; Ferreira-Moraes, R.; da Alves, W.M.G.C.; Alves, T.G.G.; Pimentel, C.P.; Sousa, E.C.; Abrahin, O.; Cortinhas-Alves, E.A. Resistance Training Reduces Depressive Symptoms in Elderly People with Parkinson Disease: A Controlled Randomized Study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenstedt, C.; Paschen, S.; Kruse, A.; Raethjen, J.; Weisser, B.; Deuschl, G. Resistance versus Balance Training to Improve Postural Control in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Rater Blinded Controlled Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, C.; Imbimbo, I.; Tranchita, E.; Minganti, C.; Ricciardi, D.; Lo Monaco, R.; Parisi, A.; Padua, L. Comparison of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation and Conventional Rehabilitation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Physiotherapy 2020, 106, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhen, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Lin, Z. Effect of somatosensory games on cognition and gait of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Focus 2020, 35, 900–903. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.-Y.; Lee, D.-K.; Song, H.-S. Effect of Virtual Reality Dance Exercise on the Balance, Activities of Daily Living, and Depressive Disorder Status of Parkinson’s Disease Patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Peng, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-N.; Chang, Y.-T.; Lai, C.-H. Effects of Interactive Video-Game–Based Exercise on Balance in Older Adults with Mild-to-Moderate Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Machado, T.; Santos, L.; Ribeiro, N.; Melo, A. Efficacy of the Nintendo Wii Combination with Conventional Exercises in the Rehabilitation of Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 45, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, B.C.; Schmid, C.H.; Lau, J.; Trikalinos, T.A. Meta-Analyst: Software for Meta-Analysis of Binary, Continuous and Diagnostic Data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2009, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickenbrock, H.M.; Diel, A.; Zapf, A. A Comparison between the Static Balance Test and the Berg Balance Scale: Validity, Reliability, and Comparative Resource Use. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repp, B.H.; Su, Y.-H. Sensorimotor Synchronization: A Review of Recent Research (2006–2012). Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2013, 20, 403–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpert, D.M.; Diedrichsen, J.; Flanagan, J.R. Principles of Sensorimotor Learning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Agudo, R.D.; Lucena-Anton, D.; Luque-Moreno, C.; Marcos Heredia-Rizo, A.; Moral-Munoz, J.A. Additional Physical Interventions to Conventional Physical Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, H.S.; Porto, F.; Porretti, M.; Lopes, G.; Fiorot, D.; dos Bunn, P.S.; da Silva, E.B. Effect of Dance on Postural Control in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis Review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 29, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirnberger, G.; Jahanshahi, M. Executive Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. J. Neuropsychol. 2013, 7, 193–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinbjornsdottir, S. The Clinical Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, G.T.; Goetz, C.G.; Burn, D.J.; Jankovic, J.; Khoo, T.K.; Tilley, B.C. How to Identify Tremor Dominant and Postural Instability/Gait Difficulty Groups with the Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale: Comparison with the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.M.; Alshafie, S.; Hasabo, E.A.; Saleh, M.; Elnaiem, W.; Qasem, A.; Alzu’bi, Y.O.; Khaled, A.; Zaazouee, M.S.; Ragab, K.M.; et al. Efficacy of Dance for Parkinson’s Disease: A Pooled Analysis of 372 Patients. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Bueno, C.; Deeks, J.J.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Jolly, K.; Torres-Costoso, A.I.; Price, M.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, R.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V. Effect of Exercise on Motor Symptoms in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, B.; Paris-Garcia, F. Influence of Dance Programmes on Gait Parameters and Physical Parameters of the Lower Body in Older People: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Krause, J.; Krause, M.; Reischak-Oliveira, A. Dancing for Healthy Aging: Functional and Metabolic Perspectives. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2019, 25, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Machado, L.; Arida, R.M.; de Jesus Mari, J. Dance for Neuroplasticity: A Descriptive Systematic Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 96, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap, L.A.; Koster, A.; Visser, M. Adiposity, Muscle Mass, and Muscle Strength in Relation to Functional Decline in Older Persons. Epidemiol. Rev. 2013, 35, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.E.; Jang, W.; Shin, D.W.; Jeong, S.-M.; Jung, H.-W.; Youn, J.; Han, K.; Kim, B. Timed Up and Go Test and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Nation-Wide Retrospective Cohort Study. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.; Chen, D.; Zhu, M. Effects of Aerobic Exercise and Mind-Body Exercise in Parkinson’s Disease: A Mixed-Treatment Comparison Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 739115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henwood, T.; Tuckett, A.; Edelstein, O.; Bartlett, H. Exercise in Later Life: The Older Adults’ Perspective about Resistance Training. Ageing Soc. 2011, 31, 1330–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneen, L.J.; Moore, R.A.; Clarke, C.; Martin, D.; Colvin, L.A.; Smith, B.H. Physical Activity and Exercise for Chronic Pain in Adults: An Overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 4, CD011279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| #1 | “Parkinson disease”[MeSH] |
| #2 | (((((Parkinson disease[Title/Abstract])OR Parkinson′s disease[Title/Abstract]) OR idiopathic Parkinson′s disease[Title/Abstract]) OR lewy body Parkinson′s disease[Title/Abstract]) OR primary Parkinsonism[Title/Abstract]) OR paralysis agitans[Title/Abstract] |
| #3 | #1 OR #2 |
| #4 | “exercise”[MeSH] |
| #5 | (((((((exercise[Title/Abstract]) OR exercise intervention[Title/Abstract]) OR exercise training[Title/Abstract]) OR training[Title/Abstract]) OR physical training[Title/Abstract]) OR physical exercise[Title/Abstract]) OR sports training[Title/Abstract]) OR nurse intervention[Title/Abstract] |
| #6 | #4 OR #5 |
| #7 | randomzied controlled trials[Publication Type] |
| #8 | #3 AND #6 AND #7 |
| Author | Country | Year | Population | Age (Mean + SD) | Total/Male/Female | Intervention | Control | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuan | Taiwan | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T:67.8 (5.5) C:66.5 (8.8) | T:12/2/10 C:12/9/3 | VR training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 30 min | CON | BBS |
| Pazzaglia | Italy | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T:72 (7) C:70 (10) | T: 25/15/7 C: 26/17/9 | VR training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 40 min | CON | BBS |
| Xia | China | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.99 (4.3) C: 66 (8.55) | T: 15/11/4 C: 15/12/3 | VR training Length of Intervention: four weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 15–20 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS |
| Santos | Brazil | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 61.7 (7.3) C: 64.5 (9.8) | T: 13/11/2 C: 14/11/3 | VR training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 50 min | CON | TUG, BBS |
| Tollar | Hungary | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 70 (4.69) C:67.5 (4.28) | T: 25/12/13 C: 24/13/11 | VR training Length of Intervention: five weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS |
| Song | Australia | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 68 (7) C: 65 (7) | T: 28/12/16 C: 25/5/20 | VR training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: Minimum 15 min each time | CON | TUG |
| Lee | Korea | 2015 | NA | T: 68.4 (2.9) C: 70.1 (3.3) | T: 10/5/5 C: 10/5/5 | VR training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 45 min | CON | BBS |
| Li | China | 2020 | NA | T: 70.1 (3.24) C: 68.72 (3.26) | T: 40/24/16 C: 40/27/13 | Dance training (Dance to the rhythm of music) Length of Intervention: four weeks Freq: seven times a week Duration: 40 min | CON | BBS |
| Vivas | Spain | 2011 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.67 (3.67) C: 68.33 (6.92) | T: 12/3/3 C: 12/4/2 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: four weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 45 min | BLT (balance training) | BBS |
| Carroll | Italy | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 69.5 (1.75) C: 74 (6.01) | T: 10/7/3 C: 8/5/3 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 45 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Volpe | Italy | 2014 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 68 (7) C: 66 (8) | T: 17/NA/NA C: 17/NA/NA | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | BLT | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Volpe | Italy | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 70.6 (7.8) C: 70 (7.8) | T: 15/9/6 C: 15/10/5 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | BLT | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Perez-de | Spain | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.87 (7.09) C: 66.44 (5.73) | T: 14/NA/NA C: 15/NA/NA | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: 11 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 45 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Kurt | Turkey | 2017 | NA | T: 62.41 (6.76) C: 63.61 (7.18) | T: 20/11/9 C: 20/13/7 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: five weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | BLT | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Wang | China | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 63.4 (7.22) C: 64.45 (6.82) | T: 20/12/8 C: 20/14/6 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 50 min | BLT | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Palamara | Italy | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 70.9 (5.7) C: 70.8 (5.3) | T: 15/9/8 C: 15/11/6 | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: four weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Clerici | Italy | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 67 (8) C: 67 (11) | T: 27/NA/NA C: 25/NA/NA | Aquatic training Length of Intervention: four weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS, TUG |
| Vieira | UK | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 64.7 (1.8) C: 64.4 (3.7) | T: 25/20/5 C: 15/10/5 | resistance training Length of Intervention: nine weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 50–60 min | CON | TUG |
| De lima | Brazil | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 66.2 (5.5) C: 67.2 (5.2) | T: 17/NA/NA C: 16/NA/NA | resistance training Length of Intervention: 20 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 30–40 min | CON | TUG |
| Kwok | China | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 63.7 (8.2) C: 63.5 (9.3) | T: 71/347/34 C: 67/28/39 | resistance training Length of Intervention: 20 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | TUG, UPDRS |
| Leal | Brazil | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.2 (2.05) C: 64.9 (2.32) | T: 27/13/14 C: 27/14/13 | resistance training Length of Intervention: six MOs Freq: two times a week Duration: 20 min | CON | TUG |
| Schlenstedt | Germany | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 75.7 (5.5) C: 75.7 (7.2) | T: 17/12/5 C: 15/9/6 | resistance training Length of Intervention: seven weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | TUG, UPDRS |
| Tang | China | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 67.76 (5.23) C: 69.64 (4.58) | T: 31/24/7 C: 31/19/12 | resistance training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 20 min | CON | BBS |
| Choi | Korea | 2013 | NA | T: 60.81 (7.6) C: 65.54 (6.8) | T: 11/NA/NA C: 9/NA/NA | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | TUG, UPDRS |
| Amano | USA | 2013 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 66 (11) C: 66 (7) | T: 15/8/7 C: 9/2/7 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 16 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Hackney | USA | 2008 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1.5-3 | T: 64.9 (8.3) C: 62.6 (10.2) | T: 13/2/11 C: 13/3/10 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Vergara-Diaz | USA | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 65.7 (3.86) C: 62 (7.77) | T: 16/7/9 C: 16/9/7 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG |
| Li | USA | 2012 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T: 68 (9) C: 69 (8) | T: 65/20/45 C: 65/27/38 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 24 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | RT | UPDRS, TUG |
| Choi | Korea | 2016 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 60.81 (7.6) C: 65.54 (6.8) | T: 11/NA/NA C: 9/NA/NA | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: one time a week Duration: 30 min | CON | TUG |
| Gao | Australia | 2014 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T: 69.54 (7.3) C: 68.28 (8.5) | T: 37/14/23 C: 37/10/27 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| You | China | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T: 68.81 (5.02) C: 68.48 (5.27) | T: 35/18/17 C: 35/19/16 | Taichi training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | BBS, UPDRS |
| Xiao | China | 2016 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T + C: 67.8 (9.4) | T: 49/NA/NA C: 49/NA/NA | Baduanjin training Length of Intervention: six MOs Freq: four times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Shi | China | 2021 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 67.89 (4.63) C: 67.48 (4.52) | T: 65/34/31 C: 64/34/30 | Baduanjin training Length of Intervention: two MOs Freq: four times a week Duration: 30 min | BLT | BBS, UPDRS |
| Wang | China | 2021 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T + C:65.52 (7.29) | T: 27/NA/NA C: 24/NA/NA | Baduanjin training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: seven times a week Duration: 30 min | BLT | UPDRS |
| Marieke | USA | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.53 (6.1) C: 70.5 (4.4) | T: 15/5/10 C: 15/8/7 | Yoga training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Cheung | USA | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 63.5 (8.5) C: 65.8 (6.6) | T: 50/45/5 C: 50/45/5 | Yoga training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Kwok | Hong Kong | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T + C: 63.6 (8.7) | T: 71/37/34 C: 67/28/39 | Yoga training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: one time a week Duration: 90 min | RT | UPDRS, TUG |
| Khuzema | India | 2020 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr2.5-3 | T: 68.11 (4.2) C: 72 (5.2) | T: 9/NA/NA C: 9/NA/NA | Yoga training Length of Intervention: eight weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 30–40 min | CON | TUG, BBS |
| Ni | USA | 2016 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T + C: 72.2 (6.5) | T: 13/2/11 C: 14/5/9 | Yoga training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Sharma | USA | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 62.8 (13.2) C: 73.4 (6.5) | T: 8/6/2 C: 8/3/5 | Yoga training Length of Intervention: six weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Song | Australia | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 68 (7) C: 65 (7) | T: 31/16/15 C: 30/21/9 | Walking training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 15 min | CON | TUG |
| Michels | USA | 2018 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr2-2.5 | T + C: 69.2 (8.7) | T: 7/NA/NA C: 6/NA/NA | Dance training (Dance to the rhythm of music) Length of Intervention: 10 weeks Freq: one time a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Volpe | Italy | 2013 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2.5 | T: 61.6 (4.5) C: 65.0 (5.3) | T: 12/5/7 C: 12/6/6 | Dance training (Irish set dancing) Length of Intervention: 24 weeks Freq: one times a week Duration: 90 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS |
| Shanahan | Ireland | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2.5 | T: 69 (10) C: 69 (8) | T: 20/7/13 C: 20/7/13 | Dance training (Irish set dancing) Length of Intervention: 10 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 20 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Hackney | USA | 2009 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T: 68.2 (1.4) C: 66.5 (2.8) | T: 14/3/11 C: 17/5/12 | Dance training (Tango) Length of Intervention: 13 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Rawson | USA | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T + C: 67.2 (8.9) | T: 39/NA/NA C: 31/NA/NA | Dance training (Tango) Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | TRD | UPDRS |
| Duncan | USA | 2012 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-4 | T: 69.3 (1.9) C: 69.0 (1.5) | T: 26/11/15 C: 26/11/15 | Dance training (community-based dancing) Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Solla | Italy | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 67.8 (5.9) C: 67.1 (6.3) | T: 10/4/6 C: 10/3/7 | Dance training (Folk dance) Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 90 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Romenets | Canada | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 63.2 (9.9) C: 64.3 (8.1) | T: 18/6/12 C: 16/9/7 | Dance training (Tango) Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG |
| Shulman | USA | 2013 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 66.1 (9.7) C: 65.3 (11.3) | T: 70/54/16 C: 80/62/18 | Treadmill training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 80 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG |
| Carvalho | Brazil | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 64.8 (11.9) C: 64.1 (9.9) | T: 6/2/4 C: 8/2/6 | Treadmill training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 30 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS |
| Sage | USA | 2009 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 65.1 (9.3) C: 64.2 (10.3) | T: 13/7/6 C: 15/11/7 | Treadmill training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 20 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG |
| Cugusia | Italy | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 68.1 (8.7) C: 66.6 (7.3) | T: 10/2/8 C: 10/2/8 | Walking training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 60 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Bang | Korea | 2017 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 58.3 (7.7) C: 60.6 (6.7) | T: 10/5/5 C: 10/6/4 | Walking training Length of Intervention: five weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | TRD | UPDRS, TUG, BBS |
| Bello | Spain | 2013 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 58 (9.4) C: 59.5 (11.3) | T: 11/4/7 C: 11/5/6 | Walking training Length of Intervention: five weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: NA | TRD | UPDRS, TUG |
| Kolk | Korea | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-2 | T: 59.3 (8.3) C: 59.4 (9.3) | T: 65/23/42 C: 65/27/38 | Cycling training Length of Intervention: 24 weeks Freq: two times a week Duration: 30 min | CON | UPDRS, BBS |
| Sacheli | Canada | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 66.76 (5.9) C: 67.85 (8.5) | T: 20/7/13 C: 20/11/9 | Cycling training Length of Intervention: 12 weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 50 min | CON | UPDRS |
| Ridgel | USA | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1-3 | T: 69.9 (7.4) C: 70 (6.4) | T: 8/4/4 C: 8/3/5 | Cycling training Length of Intervention: two weeks Freq: three times a week Duration: 40 min | CON | UPDRS, TUG |
| Arcolin | Italy | 2015 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr1.5-3 | T: 68.7 (8.3) C: 67.8 (8.8) | T: 18/9/9 C: 13/7/6 | Cycling training Length of Intervention: three weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 60 min | TRD | UPDRS, TUG |
| Tollar | Hungary | 2019 | Parkinson disease Hoehn & Yahr2-3 | T: 70.6 (4.1) C: 70 (4.69) | T: 25/13/12 C: 25/14/11 | Cycling training Length of Intervention: five weeks Freq: five times a week Duration: 45 min | CON | BBS |
| DANCE | WKT | YOGA | TAI | VR | CYC | BDJ | AQU | RT | TRD | BLT | CON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DANCE | 0.11 (−4.66,4.88) | 0.39 (−4.02,4.80) | 0.64 (−2.93,4.22) | 0.78 (−3.40,4.96) | 1.20 (−2.74,5.14) | 1.81 (−2.48,6.10) | 1.97 (−1.66,5.59) | 2.91 (−1.62,7.45) | 3.20 (−0.51,6.91) | 3.50 (−0.49,7.49) | 4.90 (2.23,7.57) |
| −0.11 (−4.88,4.66) | WKT | 0.28 (−5.23,5.79) | 0.53 (−4.34,5.40) | 0.67 (−4.67,6.01) | 1.09 (−3.91,6.09) | 1.70 (−3.72,7.11) | 1.86 (−3.04,6.76) | 2.80 (−2.80,8.40) | 3.09 (−0.13,6.32) | 3.39 (−1.79,8.57) | 4.79 (0.53,9.05) |
| −0.39 (−4.80,4.02) | −0.28 (−5.79,5.23) | YOGA | 0.25 (−3.73,4.23) | 0.39 (−4.37,5.15) | 0.81 (−3.79,5.41) | 1.42 (−3.33,6.17) | 1.58 (−2.59,5.74) | 2.52 (−1.51,6.55) | 2.81 (−1.82,7.45) | 3.11 (−1.28,7.51) | 4.51 (1.00,8.02) |
| −0.64 (−4.22,2.93) | −0.53 (−5.40,4.34) | −0.25 (−4.23,3.73) | TAI | 0.14 (−3.86,4.14) | 0.56 (−3.23,4.35) | 1.16 (−2.87,5.20) | 1.33 (−2.00,4.65) | 2.27 (−1.34,5.88) | 2.56 (−1.30,6.42) | 2.86 (−0.79,6.50) | 4.26 (1.88,6.63) |
| −0.78 (−4.96,3.40) | −0.67 (−6.01,4.67) | −0.39 (−5.15,4.37) | −0.14 (−4.14,3.86) | VR | 0.42 (−3.94,4.78) | 1.03 (−3.62,5.67) | 1.19 (−2.85,5.23) | 2.13 (−2.74,7.01) | 2.42 (−2.01,6.86) | 2.72 (−1.66,7.10) | 4.12 (0.91,7.34) |
| −1.20 (−5.14,2.74) | −1.09 (−6.09,3.91) | −0.81 (−5.41,3.79) | −0.56 (−4.35,3.23) | −0.42 (−4.78,3.94) | CYC | 0.61 (−3.87,5.08) | 0.77 (−3.08,4.62) | 1.71 (−3.02,6.44) | 2.00 (−2.01,6.01) | 2.30 (−1.90,6.50) | 3.70 (0.75,6.65) |
| −1.81 (−6.10,2.48) | −1.70 (−7.11,3.72) | −1.42 (−6.17,3.33) | −1.16 (−5.20,2.87) | −1.03 (−5.67,3.62) | −0.61 (−5.08,3.87) | BDJ | 0.16 (−3.33,3.65) | 1.11 (−3.57,5.78) | 1.40 (−3.13,5.92) | 1.69 (−1.52,4.90) | 3.09 (−0.26,6.45) |
| −1.97 (−5.59,1.66) | −1.86 (−6.76,3.04) | −1.58 (−5.74,2.59) | −1.33 (−4.65,2.00) | −1.19 (−5.23,2.85) | −0.77 (−4.62,3.08) | −0.16 (−3.65,3.33) | AQU | 0.94 (−3.15,5.04) | 1.23 (−2.66,5.13) | 1.53 (−0.85,3.92) | 2.93 (0.48,5.38) |
| −2.91 (−7.45,1.62) | −2.80 (−8.40,2.80) | −2.52 (−6.55,1.51) | −2.27 (−5.88,1.34) | −2.13 (−7.01,2.74) | −1.71 (−6.44,3.02) | −1.11 (−5.78,3.57) | −0.94 (−5.04,3.15) | RT | 0.29 (−4.45,5.03) | 0.59 (−3.55,4.73) | 1.99 (−1.68,5.65) |
| −3.20 (−6.91,0.51) | −3.09 (−6.32,0.13) | −2.81 (−7.45,1.82) | −2.56 (−6.42,1.30) | −2.42 (−6.86,2.01) | −2.00 (−6.01,2.01) | −1.40 (−5.92,3.13) | −1.23 (−5.13,2.66) | −0.29 (−5.03,4.45) | TRD | 0.30 (−3.94,4.54) | 1.70 (−1.35,4.75) |
| −3.50 (−7.49,0.49) | −3.39 (−8.57,1.79) | −3.11 (−7.51,1.28) | −2.86 (−6.50,0.79) | −2.72 (−7.10,1.66) | −2.30 (−6.50,1.90) | −1.69 (−4.90,1.52) | −1.53 (−3.92,0.85) | −0.59 (−4.73,3.55) | −0.30 (−4.54,3.94) | BLT | 1.40 (−1.57,4.37) |
| −4.90 (−7.57,−2.23) | −4.79 (−9.05,−0.53) | −4.51 (−8.02,−1.00) | −4.26 (−6.63,−1.88) | −4.12 (−7.34,−0.91) | −3.70 (−6.65,−0.75) | −3.09 (−6.45,0.26) | −2.93 (−5.38,−0.48) | −1.99 (−5.65,1.68) | −1.70 (−4.75,1.35) | −1.40 (−4.37,1.57) | CON |
| YOGA | RT | AQU | TAI | TRD | VR | DANCE | WKT | CYC | BDJ | BLT | CON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOGA | 0.21 (−1.79,2.21) | 0.73 (−1.61,3.07) | 0.83 (−1.16,2.83) | 0.98 (−1.28,3.25) | 1.09 (−1.48,3.66) | 1.15 (−0.98,3.29) | 1.33 (−1.17,3.83) | 1.52 (−1.12,4.15) | 2.30 (−2.07,6.67) | 2.50 (0.04,4.96) | 2.40 (0.65,4.14) |
| −0.21 (−2.21,1.79) | RT | 0.52 (−1.32,2.37) | 0.63 (−0.76,2.01) | 0.77 (−1.12,2.67) | 0.88 (−1.38,3.14) | 0.95 (−0.77,2.67) | 1.12 (−1.02,3.27) | 1.31 (−0.99,3.61) | 2.09 (−2.10,6.28) | 2.30 (0.42,4.18) | 2.19 (0.97,3.41) |
| −0.73 (−3.07,1.61) | −0.52 (−2.37,1.32) | AQU | 0.10 (−1.78,1.99) | 0.25 (−1.93,2.43) | 0.36 (−2.13,2.85) | 0.43 (−1.62,2.48) | 0.60 (−1.83,3.03) | 0.79 (−1.78,3.36) | 1.57 (−2.76,5.90) | 1.78 (0.42,3.14) | 1.67 (0.03,3.30) |
| −0.83 (−2.83,1.16) | −0.63 (−2.01,0.76) | −0.10 (−1.99,1.78) | TAI | 0.15 (−1.62,1.92) | 0.26 (−1.89,2.40) | 0.32 (−1.28,1.92) | 0.50 (−1.56,2.56) | 0.69 (−1.54,2.91) | 1.46 (−2.67,5.60) | 1.67 (−0.37,3.72) | 1.56 (0.54,2.59) |
| −0.98 (−3.25,1.28) | −0.77 (−2.67,1.12) | −0.25 (−2.43,1.93) | −0.15 (−1.92,1.62) | TRD | 0.11 (−2.27,2.48) | 0.17 (−1.73,2.08) | 0.35 (−1.13,1.83) | 0.54 (−1.18,2.25) | 1.32 (−2.94,5.58) | 1.52 (−0.83,3.88) | 1.42 (−0.03,2.86) |
| −1.09 (−3.66,1.48) | −0.88 (−3.14,1.38) | −0.36 (−2.85,2.13) | −0.26 (−2.40,1.89) | −0.11 (−2.48,2.27) | VR | 0.07 (−2.19,2.33) | 0.24 (−2.37,2.85) | 0.43 (−2.32,3.18) | 1.21 (−3.22,5.64) | 1.42 (−1.25,4.08) | 1.31 (−0.57,3.19) |
| −1.15 (−3.29,0.98) | −0.95 (−2.67,0.77) | −0.43 (−2.48,1.62) | −0.32 (−1.92,1.28) | −0.17 (−2.08,1.73) | −0.07 (−2.33,2.19) | DANCE | 0.17 (−1.99,2.34) | 0.36 (−1.96,2.69) | 1.14 (−3.05,5.34) | 1.35 (−0.86,3.56) | 1.24 (0.01,2.48) |
| −1.33 (−3.83,1.17) | −1.12 (−3.27,1.02) | −0.60 (−3.03,1.83) | −0.50 (−2.56,1.56) | −0.35 (−1.83,1.13) | −0.24 (−2.85,2.37) | −0.17 (−2.34,1.99) | WKT | 0.19 (−1.99,2.37) | 0.97 (−3.42,5.36) | 1.18 (−1.38,3.73) | 1.07 (−0.73,2.86) |
| −1.52 (−4.15,1.12) | −1.31 (−3.61,0.99) | −0.79 (−3.36,1.78) | −0.69 (−2.91,1.54) | −0.54 (−2.25,1.18) | −0.43 (−3.18,2.32) | −0.36 (−2.69,1.96) | −0.19 (−2.37,1.99) | CYC | 0.78 (−3.69,5.25) | 0.99 (−1.70,3.68) | 0.88 (−1.10,2.86) |
| −2.30 (−6.67,2.07) | −2.09 (−6.28,2.10) | −1.57 (−5.90,2.76) | −1.46 (−5.60,2.67) | −1.32 (−5.58,2.94) | −1.21 (−5.64,3.22) | −1.14 (−5.34,3.05) | −0.97 (−5.36,3.42) | −0.78 (−5.25,3.69) | BDJ | 0.21 (−4.21,4.62) | 0.10 (−3.91,4.11) |
| −2.50 (−4.96,−0.04) | −2.30 (−4.18,−0.42) | −1.78 (−3.14,−0.42) | −1.67 (−3.72,0.37) | −1.52 (−3.88,0.83) | −1.42 (−4.08,1.25) | −1.35 (−3.56,0.86) | −1.18 (−3.73,1.38) | −0.99 (−3.68,1.70) | −0.21 (−4.62,4.21) | BLT | −0.11 (−1.96,1.75) |
| −2.40 (−4.14,−0.65) | −2.19 (−3.41,−0.97) | −1.67 (−3.30,−0.03) | −1.56 (−2.59,−0.54) | −1.42 (−2.86,0.03) | −1.31 (−3.19,0.57) | −1.24 (−2.48,−0.01) | −1.07 (−2.86,0.73) | −0.88 (−2.86,1.10) | −0.10 (−4.11,3.91) | 0.11 (−1.75,1.96) | CON |
| DANCE | RT | BDJ | VR | TAI | YOGA | WKT | CYC | AQU | TRD | CON | BLT |
| DANCE | −0.91 (−7.48,5.66) | −1.56 (−8.43,5.30) | −2.21 (−6.47,2.05) | −2.31 (−7.20,2.58) | −2.37 (−8.27,3.53) | −2.49 (−9.72,4.73) | −3.45 (−8.79,1.89) | −4.85 (−10.06,0.36) | −5.07 (−11.71,1.57) | −5.81 (−9.17,−2.45) | −7.07 (−12.68,−1.47) |
| 0.91 (−5.66,7.48) | RT | −0.65 (−8.92,7.61) | −1.30 (−7.53,4.93) | −1.40 (−8.07,5.27) | −1.46 (−8.96,6.05) | −1.58 (−10.12,6.96) | −2.54 (−9.52,4.44) | −3.94 (−10.85,2.96) | −4.16 (−12.21,3.89) | −4.90 (−10.54,0.74) | −6.16 (−13.37,1.04) |
| 1.56 (−5.30,8.43) | 0.65 (−7.61,8.92) | BDJ | −0.64 (−7.22,5.94) | −0.75 (−7.75,6.26) | −0.80 (−7.91,6.30) | −0.93 (−9.72,7.86) | −1.89 (−9.21,5.43) | −3.29 (−8.89,2.31) | −3.51 (−11.83,4.82) | −4.25 (−10.28,1.79) | −5.51 (−10.55,−0.46) |
| 2.21 (−2.05,6.47) | 1.30 (−4.93,7.53) | 0.64 (−5.94,7.22) | VR | −0.10 (−4.53,4.33) | −0.16 (−5.76,5.44) | −0.29 (−7.22,6.64) | −1.24 (−6.13,3.65) | −2.64 (−7.42,2.13) | −2.86 (−9.18,3.45) | −3.60 (−6.24,−0.96) | −4.87 (−10.07,0.34) |
| 2.31 (−2.58,7.20) | 1.40 (−5.27,8.07) | 0.75 (−6.26,7.75) | 0.10 (−4.33,4.53) | TAI | −0.06 (−6.15,6.04) | −0.18 (−7.51,7.15) | −1.14 (−6.57,4.29) | −2.54 (−7.88,2.80) | −2.76 (−9.51,3.99) | −3.50 (−7.05,0.06) | −4.76 (−10.48,0.96) |
| 2.37 (−3.53,8.27) | 1.46 (−6.05,8.96) | 0.80 (−6.30,7.91) | 0.16 (−5.44,5.76) | 0.06 (−6.04,6.15) | YOGA | −0.13 (−8.21,7.95) | −1.08 (−7.55,5.38) | −2.48 (−8.14,3.17) | −2.70 (−10.27,4.87) | −3.44 (−8.39,1.51) | −4.71 (−10.38,0.97) |
| 2.49 (−4.73,9.72) | 1.58 (−6.96,10.12) | 0.93 (−7.86,9.72) | 0.29 (−6.64,7.22) | 0.18 (−7.15,7.51) | 0.13 (−7.95,8.21) | WKT | −0.96 (−8.58,6.66) | −2.36 (−9.90,5.19) | −2.58 (−8.21,3.06) | −3.32 (−9.73,3.09) | −4.58 (−12.40,3.24) |
| 3.45 (−1.89,8.79) | 2.54 (−4.44,9.52) | 1.89 (−5.43,9.21) | 1.24 (−3.65,6.13) | 1.14 (−4.29,6.57) | 1.08 (−5.38,7.55) | 0.96 (−6.66,8.58) | CYC | −1.40 (−7.12,4.32) | −1.62 (−8.68,5.44) | −2.36 (−6.47,1.75) | −3.62 (−9.70,2.46) |
| 4.85 (−0.36,10.06) | 3.94 (−2.96,10.85) | 3.29 (−2.31,8.89) | 2.64 (−2.13,7.42) | 2.54 (−2.80,7.88) | 2.48 (−3.17,8.14) | 2.36 (−5.19,9.90) | 1.40 (−4.32,7.12) | AQU | −0.22 (−7.20,6.77) | −0.96 (−4.94,3.02) | −2.22 (−5.20,0.75) |
| 5.07 (−1.57,11.71) | 4.16 (−3.89,12.21) | 3.51 (−4.82,11.83) | 2.86 (−3.45,9.18) | 2.76 (−3.99,9.51) | 2.70 (−4.87,10.27) | 2.58 (−3.06,8.21) | 1.62 (−5.44,8.68) | 0.22 (−6.77,7.20) | TRD | −0.74 (−6.48,5.00) | −2.00 (−9.29,5.28) |
| 5.81 (2.45,9.17) | 4.90 (−0.74,10.54) | 4.25 (−1.79,10.28) | 3.60 (0.96,6.24) | 3.50 (−0.06,7.05) | 3.44 (−1.51,8.39) | 3.32 (−3.09,9.73) | 2.36 (−1.75,6.47) | 0.96 (−3.02,4.94) | 0.74 (−5.00,6.48) | CON | −1.26 (−5.75,3.22) |
| 7.07 (1.47,12.68) | 6.16 (−1.04,13.37) | 5.51 (0.46,10.55) | 4.87 (−0.34,10.07) | 4.76 (−0.96,10.48) | 4.71 (−0.97,10.38) | 4.58 (−3.24,12.40) | 3.62 (−2.46,9.70) | 2.22 (−0.75,5.20) | 2.00 (−5.28,9.29) | 1.26 (−3.22,5.75) | BLT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. Effects of Ten Different Exercise Interventions on Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Patients—A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060698
Hao Z, Zhang X, Chen P. Effects of Ten Different Exercise Interventions on Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Patients—A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(6):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060698
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Zikang, Xiaodan Zhang, and Ping Chen. 2022. "Effects of Ten Different Exercise Interventions on Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Patients—A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Brain Sciences 12, no. 6: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060698
APA StyleHao, Z., Zhang, X., & Chen, P. (2022). Effects of Ten Different Exercise Interventions on Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Patients—A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sciences, 12(6), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060698






