Cerebellum-Cortical Interaction in Spatial Navigation and Its Alteration in Dementias
Abstract
1. Introduction
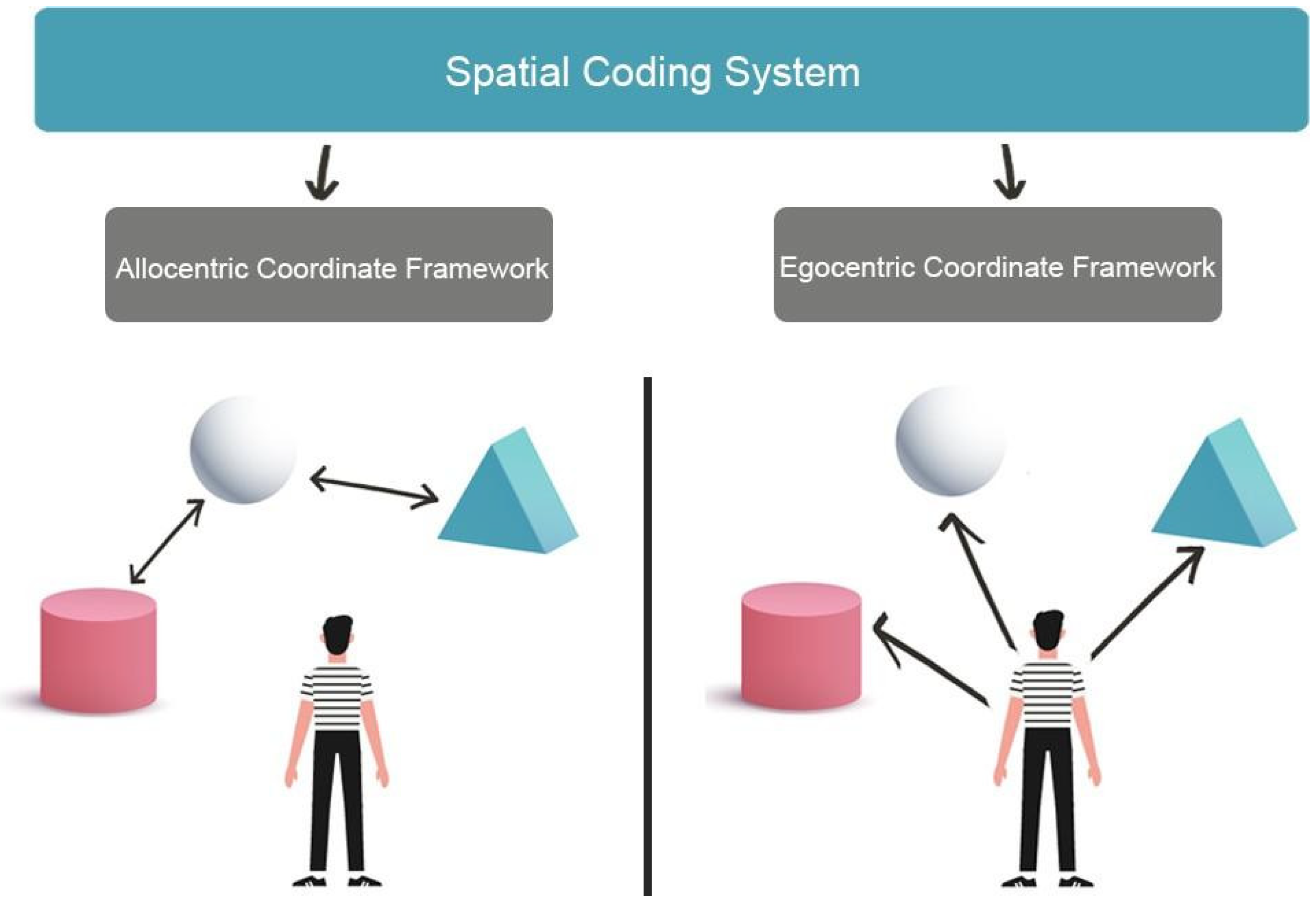
2. Visuospatial Skills and Spatial Navigation
3. The Role of the Cerebellum in Spatial Navigation
Cerebellum as Part of a Complex Network
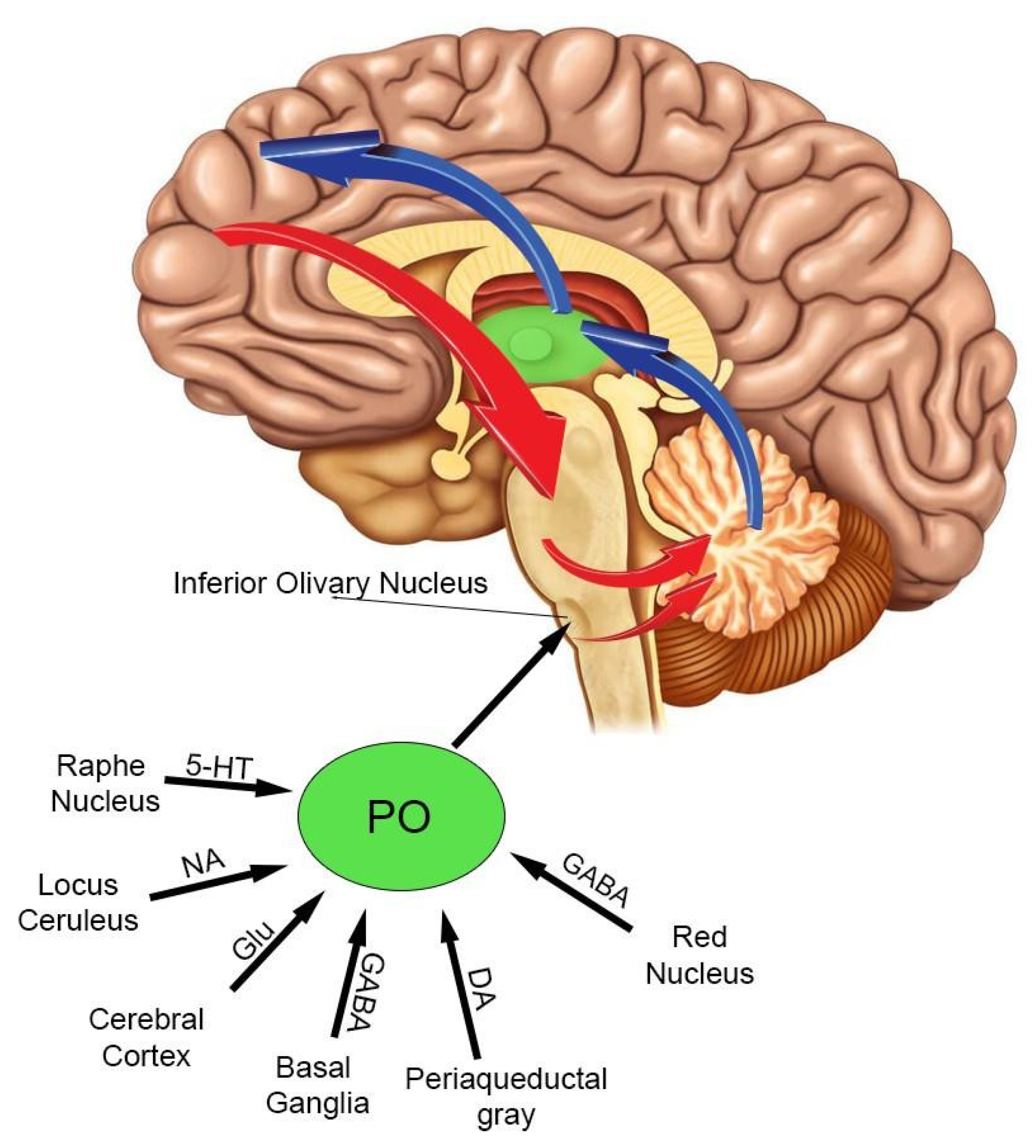
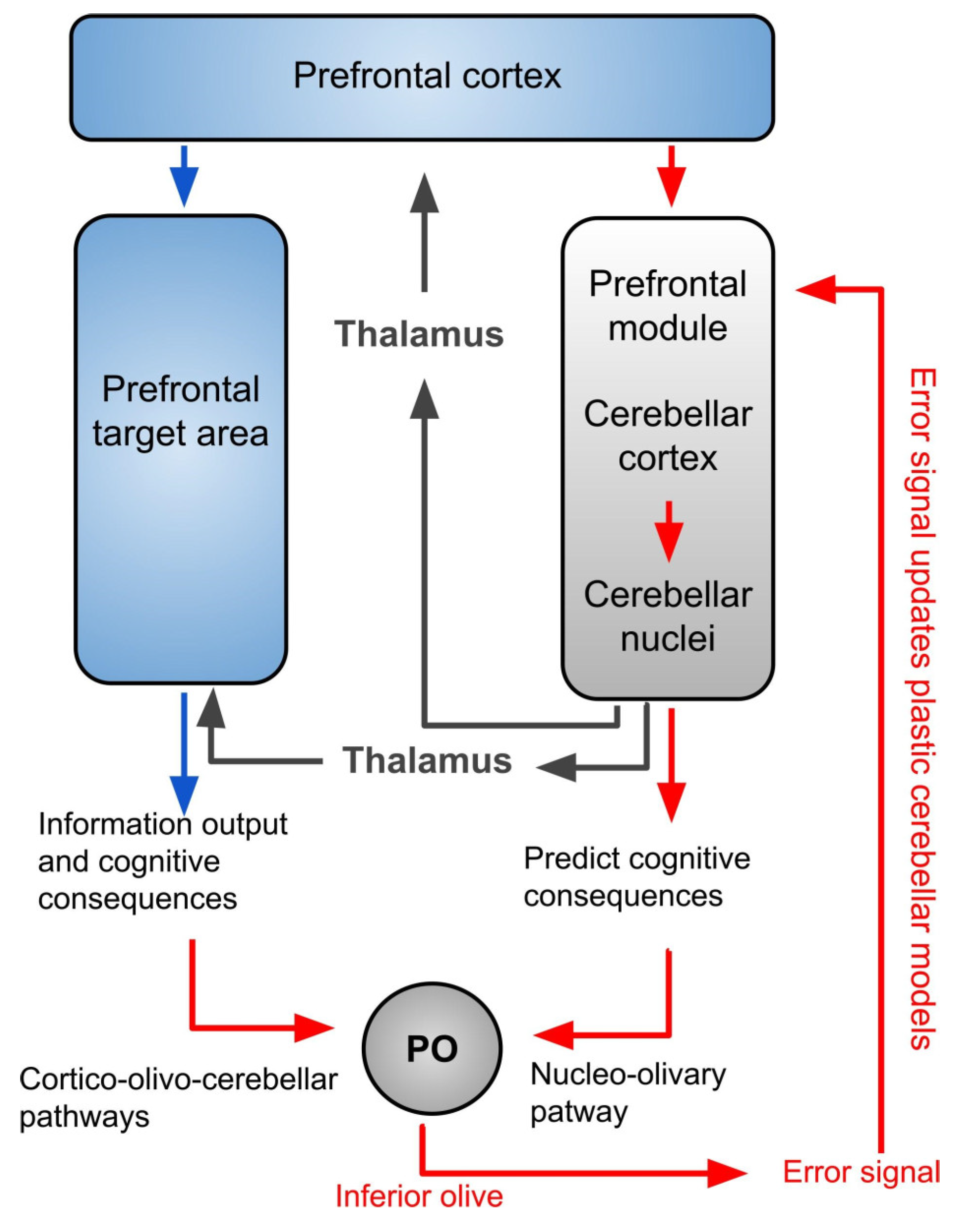
4. The Inferior Olivary Complex: A Complex Hub in the Brainstem to Regulate the Cerebellar Activity
5. Cerebellum and Spatial Navigation Disorders Involved in Dementia
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Selection Criteria
References
- Diedrichsen, J.; King, M.; Hernandez-Castillo, C.; Sereno, M.; Ivry, R.B. Universal Transform or Multiple Functionality? Understanding the Contribution of the Human Cerebellum across Task Domains. Neuron 2019, 102, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, F.; Di Vita, A.; Palermo, L.; Piccardi, L.; Blundo, C.; Guariglia, C. A Selective Egocentric Topographical Working Memory Deficit in the Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preliminary Study. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2014, 29, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeIpolyi, A.R.; Rankin, K.P.; Mucke, L.; Miller, B.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. Spatial Cognition and the Human Navigation Network in AD and MCI. Neurology 2007, 69, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirasic, K.C. Spatial Cognition and Behavior in Young and Elderly Adults: Implications for Learning New Environments. Psychol. Aging 1991, 6, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.A.; Steinberg, M.; Galik, E.; Steele, C.; Sheppard, J.M.; Warren, A.; Rosenblatt, A.; Lyketsos, C.G. Wandering Behaviour in Community-Residing Persons with Dementia. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1999, 14, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monacelli, A.M.; Cushman, L.A.; Kavcic, V.; Duffy, C.J. Spatial Disorientation in Alzheimer’s Disease: The Remembrance of Things Passed. Neurology 2003, 61, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbeck, D.R.; Tanninen, S.E. Place Learning and Spatial Navigation. In Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 2639–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, A.; Carrieri, M.; Lancia, S.; Quaresima, V.; Piccardi, L. The Key of the Maze: The Role of Mental Imagery and Cognitive Flexibility in Navigational Planning. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 651, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, L.; Iaria, G.; Ricci, M.; Bianchini, F.; Zompanti, L.; Guariglia, C. Walking in the Corsi Test: Which Type of Memory Do You Need? Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 432, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariglia, C.; Palermo, L.; Piccardi, L.; Iaria, G.; Incoccia, C. Neglecting the Left Side of a City Square but Not the Left Side of Its Clock: Prevalence and Characteristics of Representational Neglect. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Alireza, A. Dementia: Comprehensive Principles and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Galati, G.; Lobel, E.; Vallar, G.; Berthoz, A.; Pizzamiglio, L.; Bihan, D. Le The Neural Basis of Egocentric and Allocentric Coding of Space in Humans: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Study. Exp. Brain Res. 2000, 133, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbers, T.; Hegarty, M. What Determines Our Navigational Abilities? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.; Becker, S.; Burgess, N. Remembering the Past and Imagining the Future: A Neural Model of Spatial Memory and Imagery. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 114, 340–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The Hippocampus as a Spatial Map. Preliminary Evidence from Unit Activity in the Freely-Moving Rat. Brain Res. 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.W.; White, S.H. The Development of Spatial Representations of Large-Scale Environments. Adv. Child Dev. Behav. 1975, 10, 9–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montello, D.R. Navigation. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Egenhofer, M.J., Golledge, R.G., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Spelke, E. Human Spatial Representation: Insights from Animals. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6613, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, L.; Bianchini, F.; Zompanti, L.; Guariglia, C. Pure Representational Neglect and Navigational Deficits in a Case with Preserved Visuo-Spatial Working Memory. Neurocase 2008, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teghil, A.; Bonavita, A.; Guariglia, C.; Boccia, M. Commonalities and Specificities between Environmental Navigation and Autobiographical Memory: A Synthesis and a Theoretical Perspective. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H.; Sauvage, M.; Fortin, N.; Komorowski, R.; Lipton, P. Towards a Functional Organization of Episodic Memory in the Medial Temporal Lobe. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, M.; Leggio, M.G. Cerebellar Information Processing and Visuospatial Functions. Cerebellum 2007, 6, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.P.; Ulmer, J.L.; Quinet, S.A.; Mathews, V.; Mark, L.P. Nonmotor Functions of the Cerebellum: An Introduction. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.; Nemmi, F.; Guariglia, C. Neuropsychology of Environmental Navigation in Humans: Review and Meta-Analysis of FMRI Studies in Healthy Participants. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014, 24, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Schmahmann, J.D. Functional Topography in the Human Cerebellum: A Meta-Analysis of Neuroimaging Studies. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochefort, C.; Lefort, J.; Rondi-Reig, L. The Cerebellum: A New Key Structure in the Navigation System. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochefort, C.; Arabo, A.; André, M.; Poucet, B.; Save, E.; Rondi-Reig, L. Cerebellum Shapes Hippocampal Spatial Code. Science 2011, 334, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; McAfee, S.S.; Van Der Heijden, M.E.; Dhamala, M.; Sillitoe, R.V.; Heck, D.H. Causal Evidence for a Role of Cerebellar Lobulus Simplex in Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interaction in Spatial Working Memory Decision-Making. Cerebellum, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itō, M. The Cerebellum and Neural Control; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0890041062. [Google Scholar]
- Schmahmann, J.D. The Role of the Cerebellum in Affect and Psychosis. J. Neurolinguistics 2000, 13, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D. The Role of the Cerebellum in Cognition and Emotion: Personal Reflections since 1982 on the Dysmetria of Thought Hypothesis, and Its Historical Evolution from Theory to Therapy. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 236–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol, L.F.; Budding, D.; Andreasen, N.; D’Arrigo, S.; Bulgheroni, S.; Imamizu, H.; Ito, M.; Manto, M.; Marvel, C.; Parker, K.; et al. Consensus Paper: The Cerebellum’s Role in Movement and Cognition. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillieux, H.; De Smet, H.J.; Dobbeleir, A.; Paquier, P.F.; De Deyn, P.P.; Mariën, P. Cognitive and Affective Disturbances Following Focal Cerebellar Damage in Adults: A Neuropsychological and SPECT Study. Cortex 2010, 46, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, M.; Ferlazzo, F.; Aloise, F.; Di Nocera, F.; Tedesco, A.M.; Cardillo, C.; Leggio, M. New Protocol for Dissociating Visuospatial Working Memory Ability in Reaching Space and in Navigational Space. Behav. Res. Methods 2018, 50, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahhaoui, M.; Lannou, J.; Stelz, T.; Caston, J.; Guastavinot, J.M. Role of the Cerebellum in Spatial Orientation in the Rat. Behav. Neural Biol. 1992, 58, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondi-Reig, L.; Le Marec, N.; Caston, J.; Mariani, J. The Role of Climbing and Parallel Fibers Inputs to Cerebellar Cortex in Navigation. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 132, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, D.J.; Saleem, K.S.; Baker, C.I.; Mishkin, M. A New Neural Framework for Visuospatial Processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, M.; Sulpizio, V.; Nemmi, F.; Guariglia, C.; Galati, G. Direct and Indirect Parieto-Medial Temporal Pathways for Spatial Navigation in Humans: Evidence from Resting-State Functional Connectivity. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 1945–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, F.A.; Strick, P.L. Cerebellar Projections to the Prefrontal Cortex of the Primate. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolkan, S.S.; Stujenske, J.M.; Parnaudeau, S.; Spellman, T.J.; Rauffenbart, C.; Abbas, A.I.; Harris, A.Z.; Gordon, J.A.; Kellendonk, C. Thalamic Projections Sustain Prefrontal Activity during Working Memory Maintenance. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Pandya, D.N. Prefrontal Cortex Projections to the Basilar Pons in Rhesus Monkey: Implications for the Cerebellar Contribution to Higher Function. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 199, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Pandya, D.N. Anatomic Organization of the Basilar Pontine Projections from Prefrontal Cortices in Rhesus Monkey. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palesi, F.; De Rinaldis, A.; Castellazzi, G.; Calamante, F.; Muhlert, N.; Chard, D.; Tournier, J.D.; Magenes, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.G. Contralateral Cortico-Ponto-Cerebellar Pathways Reconstruction in Humans in Vivo: Implications for Reciprocal Cerebro-Cerebellar Structural Connectivity in Motor and Non-Motor Areas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D. From Movement to Thought: Anatomic Substrates of the Cerebellar Contribution to Cognitive Processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1996, 4, 174–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; McColl, R.; Barnard, H.; Ringe, W.K.; Fleckenstein, J.; Cullum, C.M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cerebellar-Prefrontal and Cerebellar-Parietal Functional Connectivity. Neuroimage 2005, 28, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, A.M.; Bianchini, F.; Piccardi, L.; Clausi, S.; Berthoz, A.; Molinari, M.; Guariglia, C.; Leggio, M. Does the Cerebellum Contribute to Human Navigation by Processing Sequential Information? Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrochon, A.; Kemoun, G.; Dugué, B.; Berthoz, A. Cognitive Impairment Assessment through Visuospatial Memory Can Be Performed with a Modified Walking Corsi Test Using the “Magic Carpet”. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2014, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardi, L.; Bianchini, F.; Argento, O.; De Nigris, A.; Maialetti, A.; Palermo, L.; Guariglia, C. The Walking Corsi Test (WalCT): Standardization of the Topographical Memory Test in an Italian Population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilinger, T.; Berthoz, A.; Wiener, J.M. The Integration of Spatial Information across Different Viewpoints. Mem. Cognit. 2011, 39, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.M.C.; Ivry, R.B. Sequence Learning Is Preserved in Individuals with Cerebellar Degeneration When the Movements Are Directly Cued. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi, L.; Leggio, M.G.; Spirito, F.; Petrosini, L. Cerebellar Contribution to Spatial Event Processing: Do Spatial Procedures Contribute to Formation of Spatial Declarative Knowledge? Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2618–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, T.; Ashe, J.; Bushara, K.O. Role of the Olivo-Cerebellar System in Timing. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5990–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standring, S. Anatomia Del Gray 41 Ed.: 2 Volumi; Edra: Palm Beach Gardens, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-8821441479. [Google Scholar]
- Glickstein, M.; Sultan, F.; Voogd, J. Functional Localization in the Cerebellum. Cortex 2011, 47, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinas, R. Eighteenth Bowditch Lecture. Motor Aspects of Cerebellar Control. Physiologist 1974, 17, 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Szteyn, S. Types of Neurons in Nucleus Olivaris Inferior of the European Bison. J. Hirnforsch. 1988, 29, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Fredette, B.J.; Adams, J.C.; Mugnaini, E. GABAergic Neurons in the Mammalian Inferior Olive and Ventral Medulla Detected by Glutamate Decarboxylase Immunocytochemistry. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 321, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.M. Functional Significance of Connections of the Inferior Olive. Physiol. Rev. 1974, 54, 358–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinta, G.; Casabona, A.; Valle, M.S.; Bosco, G.; Perciavalle, V. On the Relation of Rat’s External Cuneate Activity to Global Parameters of Forelimb Posture. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, P.M.; Lodge, D.; Duggan, A.W. Drug-Induced Rhythmical Activity in the Inferior Olivary Complex of the Rat. Brain Res. 1976, 101, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodal, P.; Brodal, A. The Olivocerebellar Projection in the Monkey. Experimental Studies with the Method of Retrograde Tracing of Horseradish Peroxidase. J. Comp. Neurol. 1981, 201, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.E.; O’Connor, D.T.; Price, D.L. Noradrenergic Innervation of Human Inferior Olivary Complex. Brain Res. 1990, 523, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton-Provencher, V.; Drummond, G.T.; Sur, M. Locus Coeruleus Norepinephrine in Learned Behavior: Anatomical Modularity and Spatiotemporal Integration in Targets. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 638007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Waterhouse, B. Locus Coeruleus: From Global Projection System to Adaptive Regulation of Behavior. Brain Res. 2016, 1645, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gruijl, J.R.; Bosman, L.W.J.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; De Jeu, M.T.G. Inferior Olive: All Ins and Outs. In Handbook of the Cerebellum and Cerebellar Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1013–1058. ISBN 9789400713338. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, G.A.; McCrea, R.A.; Kitai, S.T. A Horseradish Peroxidase Study of the Cortico-Olivary Projection in the Cat. Brain Res. 1976, 116, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinta, G.; Casabona, A.; Smecca, G.; Bosco, G.; Perciavalle, V. Cortical Control of Cerebellar Dentato-Rubral and Dentato-Olivary Neurons. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 3009–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szteyn, S.; Robak, A. Types of Neurons in Nucleus Gracilis and Nucleus Cuneatus of the European Bison. J. Hirnforsch. 1989, 30, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulfig, N.; Chan, W.Y. Differential Expression of Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Red Nucleus of the Developing and Adult Human Brain. Anat. Embryol. 2001, 203, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, J.C.; Llinás, R.; Sasaki, K. The Excitatory Synaptic Action of Climbing Fibres on the Purkinje Cells of the Cerebellum. J. Physiol. 1966, 182, 268–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, E.R. The Organization and Planning of Movement. In Principles of Neural Science, 5th ed.; McGraw Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0071390118. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, F.; Hesslow, G. Cerebellar Control of the Inferior Olive. Cerebellum 2006, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnani, N. The Primate Cortico-Cerebellar System: Anatomy and Function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, D.; Ashe, J.; Bushara, K. Specificity of Inferior Olive Response to Stimulus Timing. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Nestrasil, I.; Ashe, J.; Tuite, P.; Bushara, K. Inferior Olive Response to Passive Tactile and Visual Stimulation with Variable Interstimulus Intervals. Cerebellum 2010, 9, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teghil, A.; Boccia, M.; D’Antonio, F.; Di Vita, A.; de Lena, C.; Guariglia, C. Neural Substrates of Internally-Based and Externally-Cued Timing: An Activation Likelihood Estimation (ALE) Meta-Analysis of FMRI Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 96, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Bases and Implications of Learning in the Cerebellum--Adaptive Control and Internal Model Mechanism. Prog. Brain Res. 2005, 148, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiore, D.; Mirino, P. How the Cerebellum and Prefrontal Cortex Cooperate During Trace Eyeblinking Conditioning. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 2050041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willson, M.L.; Bower, A.J.; Sherrard, R.M. Developmental Neural Plasticity and Its Cognitive Benefits: Olivocerebellar Reinnervation Compensates for Spatial Function in the Cerebellum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willson, M.L.; McElnea, C.; Mariani, J.; Lohof, A.M.; Sherrard, R.M. BDNF Increases Homotypic Olivocerebellar Reinnervation and Associated Fine Motor and Cognitive Skill. Brain 2008, 131, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrard, R.M.; Bower, A.J.; Payne, J.N. Innervation of the Adult Rat Cerebellar Hemisphere by Fibres from the Ipsilateral Inferior Olive Following Unilateral Neonatal Pedunculotomy: An Autoradiographic and Retrograde Fluorescent Double-Labelling Study. Exp. Brain Res. 1986, 62, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.M.; Salmon, D.P.; Galasko, D.; Raman, R.; Emond, J.; Hansen, L.A.; Masliah, E.; Thal, L.J. Visuospatial Deficits Predict Rate of Cognitive Decline in Autopsy-Verified Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neuropsychology 2008, 22, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckman, L.; Small, B.J. Cognitive Deficits in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia: Patterns of Findings from the Kungsholmen Project. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Biswas, A.; Pandit, A.; Roy, A.; Guin, D.; Gangopadhyay, G.; Senapati, A.K. Study of Visuospatial Skill in Patients with Dementia. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2016, 19, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, G.K.; D’Esposito, M. Topographical Disorientation: A Synthesis and Taxonomy. Brain 1999, 122, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.; Di Vita, A.; Diana, S.; Margiotta, R.; Imbriano, L.; Rendace, L.; Campanelli, A.; D’Antonio, F.; Trebbastoni, A.; De Lena, C.; et al. Is Losing One’s Way a Sign of Cognitive Decay? Topographical Memory Deficit as an Early Marker of Pathological Aging. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 68, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Wong, S.; Hodges, J.R.; Irish, M.; Piguet, O.; Hornberger, M. Lost in Spatial Translation—A Novel Tool to Objectively Assess Spatial Disorientation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Cortex 2015, 67, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Herman, M.; Emrani, S.; Nahmani, E.; Barrett, G.; Figueroa, H.Y.; Goldberg, E.; Hussaini, S.A.; Duff, K.E. Tau Pathology Induces Excitatory Neuron Loss, Grid Cell Dysfunction, and Spatial Memory Deficits Reminiscent of Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2017, 93, 533–541.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, G.; Laczó, J.; Hort, J.; Minihane, A.M.; Hornberger, M. Spatial Navigation Deficits—Overlooked Cognitive Marker for Preclinical Alzheimer Disease? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological Stageing of Alzheimer-Related Changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redish, A.D. Beyond the Cognitive Map: From Place Cells to Episodic Memory. Available online: https://books.google.nl/books?hl=it&lr=&id=vrnagI06NMIC&oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=Redish,+A.+D.+(1999).+Beyond+the+cognitive+map:+From+place+cells+to+episodic+memory.+The+MIT+Press.&ots=OohMlzJOIY&sig=mpYFG_wppy9Euzic3hQujkbk1pI&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Redish%2CA (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- Pai, M.C.; Jacobs, W.J. Topographical Disorientation in Community-Residing Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2004, 19, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.; Silveri, M.C.; Sabatini, U.; Guariglia, C.; Nemmi, F. Neural Underpinnings of the Decline of Topographical Memory in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2016, 31, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosini, L.; Leggio, M.G.; Molinari, M. The Cerebellum in the Spatial Problem Solving: A Co-Star or a Guest Star? Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, M.G.; Neri, P.; Graziano, A.; Mandolesi, L.; Molinari, M.; Petrosini, L. Cerebellar Contribution to Spatial Event Processing: Characterization of Procedural Learning. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayan, B.M.; Watilliaux, A.; Viejo, G.; Paradis, A.L.; Girard, B.; Rondi-Reig, L. A Hippocampo-Cerebellar Centred Network for the Learning and Execution of Sequence-Based Navigation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivito, G.; Serra, L.; Marra, C.; Di Domenico, C.; Caltagirone, C.; Toniolo, S.; Cercignani, M.; Leggio, M.; Bozzali, M. Cerebellar Dentate Nucleus Functional Connectivity with Cerebral Cortex in Alzheimer’s Disease and Memory: A Seed-Based Approach. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 89, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Testa, C.; Sabattoli, F.; Beltramello, A.; Soininen, H.; Laakso, M.P. Structural Correlates of Early and Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: Voxel Based Morphometric Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Anderson, V.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Whitwell, J.; Barnes, J.; Scahill, R.; Stevens, J.M.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Rossor, M.N.; et al. The Clinical Profile of Right Temporal Lobe Atrophy. Brain 2009, 132, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadel, L.; Hoscheidt, S.; Ryan, L.R. Spatial Cognition and the Hippocampus: The Anterior–Posterior Axis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, F. Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Loops: Motor and Cognitive Circuits. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 31, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.C.; Tan, R.; Hodges, J.R.; Hu, X.; Sami, S.; Hornberger, M. Network-Selective Vulnerability of the Human Cerebellum to Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain 2016, 139, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, H.I.L.; Hopkins, D.A.; Mayrhofer, H.C.; Bruner, E.; van Leeuwen, F.W.; Raaijmakers, W.; Schmahmann, J.D. The Cerebellum in Alzheimer’s Disease: Evaluating Its Role in Cognitive Decline. Brain 2018, 141, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toniolo, S.; Serra, L.; Olivito, G.; Marra, C.; Bozzali, M.; Cercignani, M. Patterns of Cerebellar Gray Matter Atrophy across Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habas, C.; Kamdar, N.; Nguyen, D.; Prater, K.; Beckmann, C.F.; Menon, V.; Greicius, M.D. Distinct Cerebellar Contributions to Intrinsic Connectivity Networks. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8586–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levisohn, L.; Cronin-Golomb, A.; Schmahmann, J.D. Neuropsychological Consequences of Cerebellar Tumour Resection in Children: Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome in a Paediatric Population. Brain 2000, 123 Pt 5, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Sherman, J.C. The Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome. Brain 1998, 121 Pt 4, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirino, P.; Pecchinenda, A.; Boccia, M.; Capirchio, A.; D’Antonio, F.; Guariglia, C. Cerebellum-Cortical Interaction in Spatial Navigation and Its Alteration in Dementias. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050523
Mirino P, Pecchinenda A, Boccia M, Capirchio A, D’Antonio F, Guariglia C. Cerebellum-Cortical Interaction in Spatial Navigation and Its Alteration in Dementias. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(5):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050523
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirino, Pierandrea, Anna Pecchinenda, Maddalena Boccia, Adriano Capirchio, Fabrizia D’Antonio, and Cecilia Guariglia. 2022. "Cerebellum-Cortical Interaction in Spatial Navigation and Its Alteration in Dementias" Brain Sciences 12, no. 5: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050523
APA StyleMirino, P., Pecchinenda, A., Boccia, M., Capirchio, A., D’Antonio, F., & Guariglia, C. (2022). Cerebellum-Cortical Interaction in Spatial Navigation and Its Alteration in Dementias. Brain Sciences, 12(5), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12050523








