Patient Experience of Flunarizine for Vestibular Migraine: Single Centre Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Side Effects
4.2. VM Pathophysiology
4.3. Use of Flunarizine in the UK
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuhauser, H.K. Epidemiology of vertigo. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2007, 20, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempert, T.; Olesen, J.; Furman, J.; Waterston, J.; Seemungal, B.; Carey, J.; Bisdorff, A.; Versino, M.; Evers, S.; Newman-Toker, D. Vestibular migraine: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2012, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byun, Y.J.; Levy, D.A.; Nguyen, S.A.; Brennan, E.; Rizk, H.G. Treatment of Vestibular Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmito, M.C.; Duarte, J.A.; Morganti, L.O.G.; Brandão, P.V.C.; Nakao, B.H.; Villa, T.R.; Ganança, F.F. Prophylactic treatment of vestibular migraine. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Zhuang, J.; Li, F. The efficacy of topiramate and flunarizine hydrochloride for prophylactic treatment of vestibular migraine. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 35, 784–787, 795. [Google Scholar]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [CrossRef]
- Amery, W.K. Flunarizine, a calcium channel blocker: A new prophylactic drug in migraine. Headache 1983, 23, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepcha, A.; Amalanathan, S.; Augustine, A.M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Balraj, A. Flunarizine in the prophylaxis of migrainous vertigo: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 2931–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, L.; Amery, W.; Towse, G. Flunarizine in the treatment of vertigo. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1983, 97, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, B.; Winkenwerder, E.; Dieterich, M. “Vestibular migraine”: Effects of prophylactic therapy with various drugs. A retrospective study. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 436–442. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Ma, T.; Che, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, S. The Efficacy of Venlafaxine, Flunarizine, and Valproic Acid in the Prophylaxis of Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domínguez-Durán, E.; Montilla-Ibáñez, M.A.; De Sande, M.G.-M.; Domènech-Vadillo, E.; Bécares-Martínez, C.; Gonzalez-Aguado, R.; Guerra-Jiménez, G. Analysis of the effectiveness of the prophylaxis of vestibular migraine depending on the diagnostic category and the prescribed drug. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbanti, P.; Brighina, F.; Egeo, G.; di Stefano, V.; Silvestro, M.; Russo, A. Migraine as a Cortical Brain Disorder. Headache 2020, 60, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Tamayo, A.; Perez-Carpena, P.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Systematic Review of Prevalence Studies and Familial Aggregation in Vestibular Migraine. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucci, V.; Hamid, M.; Jacquemyn, Y.; Browne, C.J. Influence of sex hormones on vestibular disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jen, J.C.; Cha, Y.H.; Nelson, S.F.; Baloh, R.W. Phenotypic and genetic analysis of a large family with migraine-associated vertigo. Headache 2008, 48, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jen, J.C.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Mamsa, H.; Sabatti, C.; Baloh, R.W.; Nelson, S.F. A genome-wide linkage scan of familial benign recurrent vertigo: Linkage to 22q12 with evidence of heterogeneity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T. Episodic vertigo related to migraine (90 cases): Vestibular migraine? J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, H.; Leopold, M.; von Brevern, M.; Arnold, G.; Lempert, T. The interrelations of migraine, vertigo, and migrainous vertigo. Neurology 2001, 56, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Shiao, A.S.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, S.J. Migraine is a risk factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, D.; Rota, E.; Morelli, N.; Immovilli, P. Migraine and stroke: “vascular” comorbidity. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Sanchez, J.M.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. New insights into pathophysiology of vestibular migraine. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Altered brain metabolism in vestibular migraine: Comparison of interictal and ictal findings. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, M.; Wurthmann, S.; Steinberg, B.S.; Theysohn, N.; Diener, H.C.; Naegel, S. Central vestibular system modulation in vestibular migraine. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Tang, M.; Yan, X.; Bai, F.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Altered structure of the vestibular cortex in patients with vestibular migraine. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furman, J.M.; Marcus, D.A.; Balaban, C.D. Vestibular migraine: Clinical aspects and pathophysiology. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Klever, R.R.; Terwindt, G.M.; Ayata, C.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M. Migraine pathophysiology: Lessons from mouse models and human genetics. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qiu, E.; Dong, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, S.; Yu, S. Protection of flunarizine on cerebral mitochondria injury induced by cortical spreading depression under hypoxic conditions. J. Headache Pain. 2011, 12, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belforte, J.E.; Magarinos-Azcone, C.; Armando, I.; Buno, W.; Pazo, J.H. Pharmacological involvement of the calcium channel blocker flunarizine in dopamine transmission at the striatum. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2001, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva, A.F.; Nascimento, T.D.; Jassar, H.; Heffernan, J.; Toback, R.L.; Lucas, S.; DosSantos, M.F.; Bellile, E.L.; Boonstra, P.S.; Taylor, J.M.; et al. Dopamine D2/D3 imbalance during migraine attack and allodynia in vivo. Neurology 2017, 88, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Stefano, V.; Rispoli, M.G.; Pellegrino, N.; Graziosi, A.; Rotondo, E.; Napoli, C.; Pietrobon, D.; Brighina, F.; Parisi, P. Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of hemiplegic migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciullacci, M.; Alessandri, M.; Del Rosso, A. Dopamine involvement in the migraine attack. Funct. Neurol. 2000, 15 (Suppl. 3), 171–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marmura, M.J. Use of dopamine antagonists in treatment of migraine. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2012, 14, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado Fernández, M.; Birdi, J.S.; Irving, G.J.; Murdin, L.; Kivekäs, I.; Strupp, M. Pharmacological agents for the prevention of vestibular migraine. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, Cd010600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
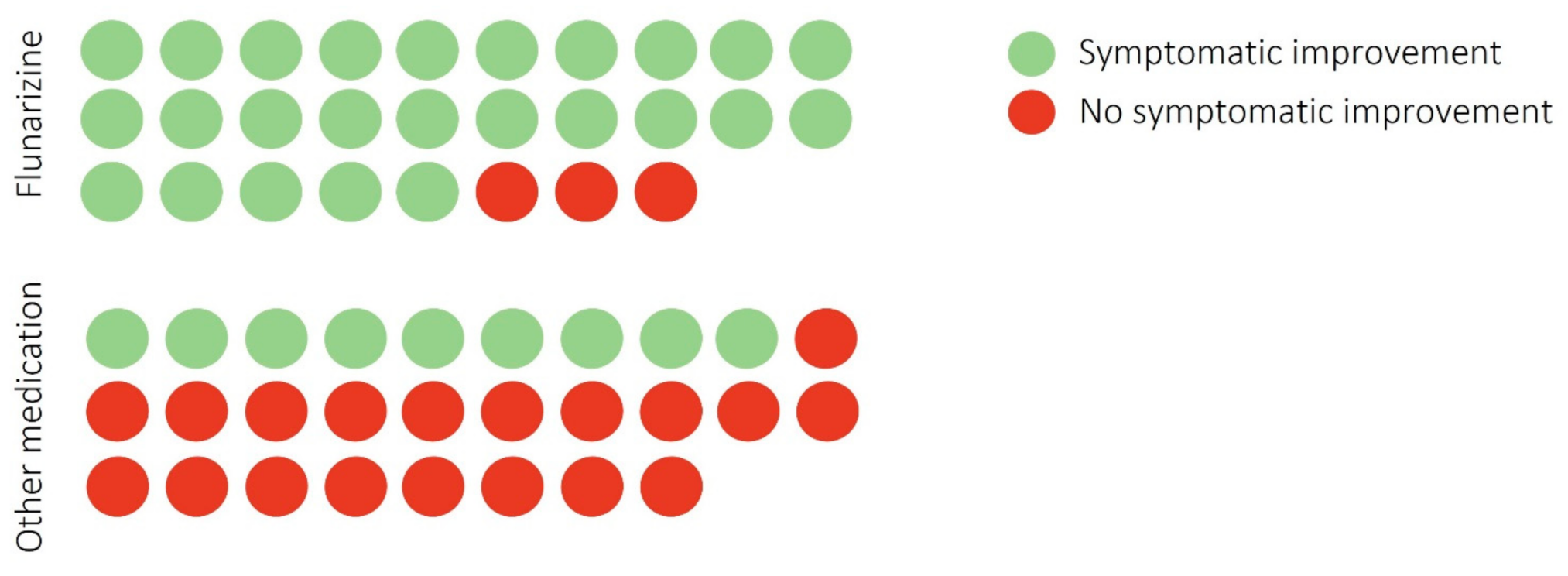
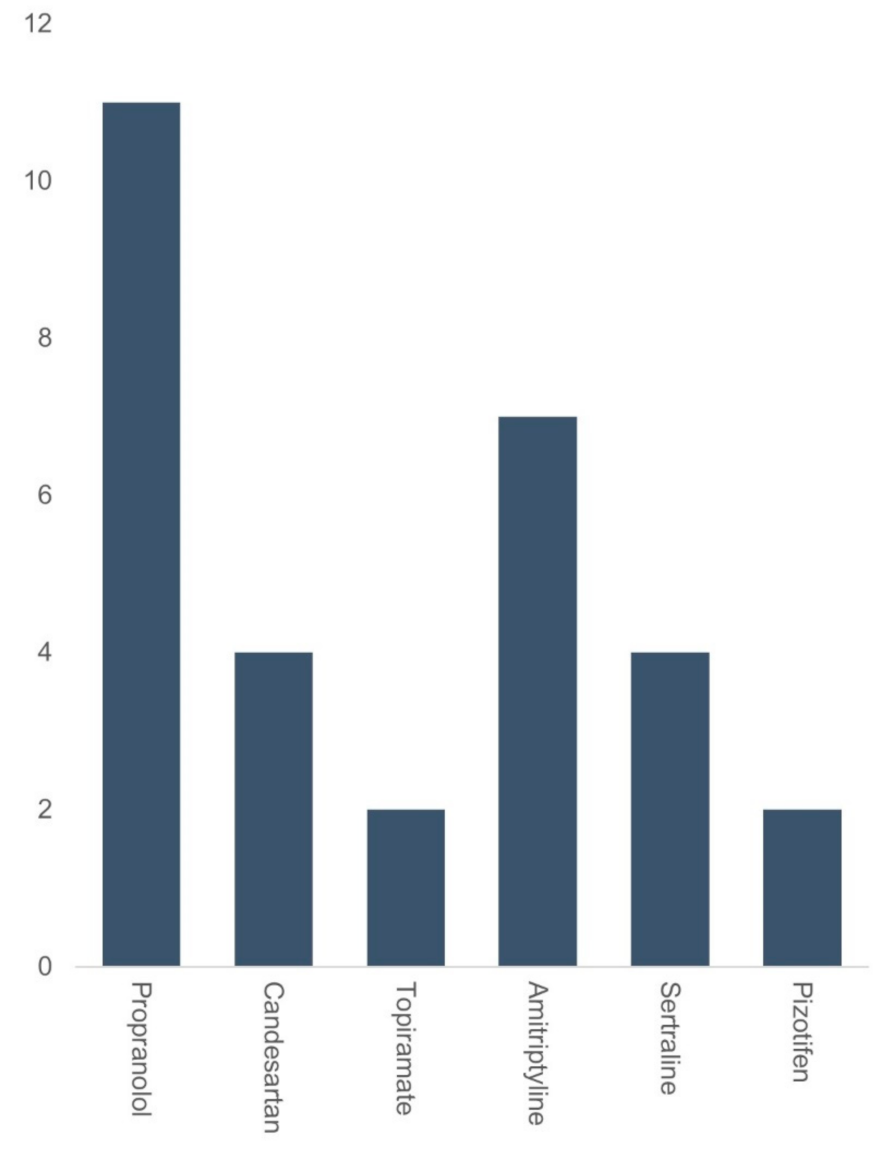
| Groups | Flunarizine | Other Medications | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age in yrs (range) | 44.6 (24–70) | 50.1 (25–71) | 0.11 |
| Gender F/M | 24/4 | 23/5 | - |
| Disease Duration in yrs (SD) | 5.6 (3.5) | 4.7 (3.4) | 0.33 |
| Average monthly vertigo attacks (days) | 6.0 (4.0) | 5.5 (3.3) | 0.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, S.M.U.; Sumaria, S.; Koohi, N.; Arshad, Q.; Kaski, D. Patient Experience of Flunarizine for Vestibular Migraine: Single Centre Observational Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12040415
Rashid SMU, Sumaria S, Koohi N, Arshad Q, Kaski D. Patient Experience of Flunarizine for Vestibular Migraine: Single Centre Observational Study. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(4):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12040415
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Sk Mamun Ur, Sheetal Sumaria, Nehzat Koohi, Qadeer Arshad, and Diego Kaski. 2022. "Patient Experience of Flunarizine for Vestibular Migraine: Single Centre Observational Study" Brain Sciences 12, no. 4: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12040415
APA StyleRashid, S. M. U., Sumaria, S., Koohi, N., Arshad, Q., & Kaski, D. (2022). Patient Experience of Flunarizine for Vestibular Migraine: Single Centre Observational Study. Brain Sciences, 12(4), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12040415







