Emotional Valence in the Eye Region Modulates the Attentional Blink in a Task-Dependent Manner: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
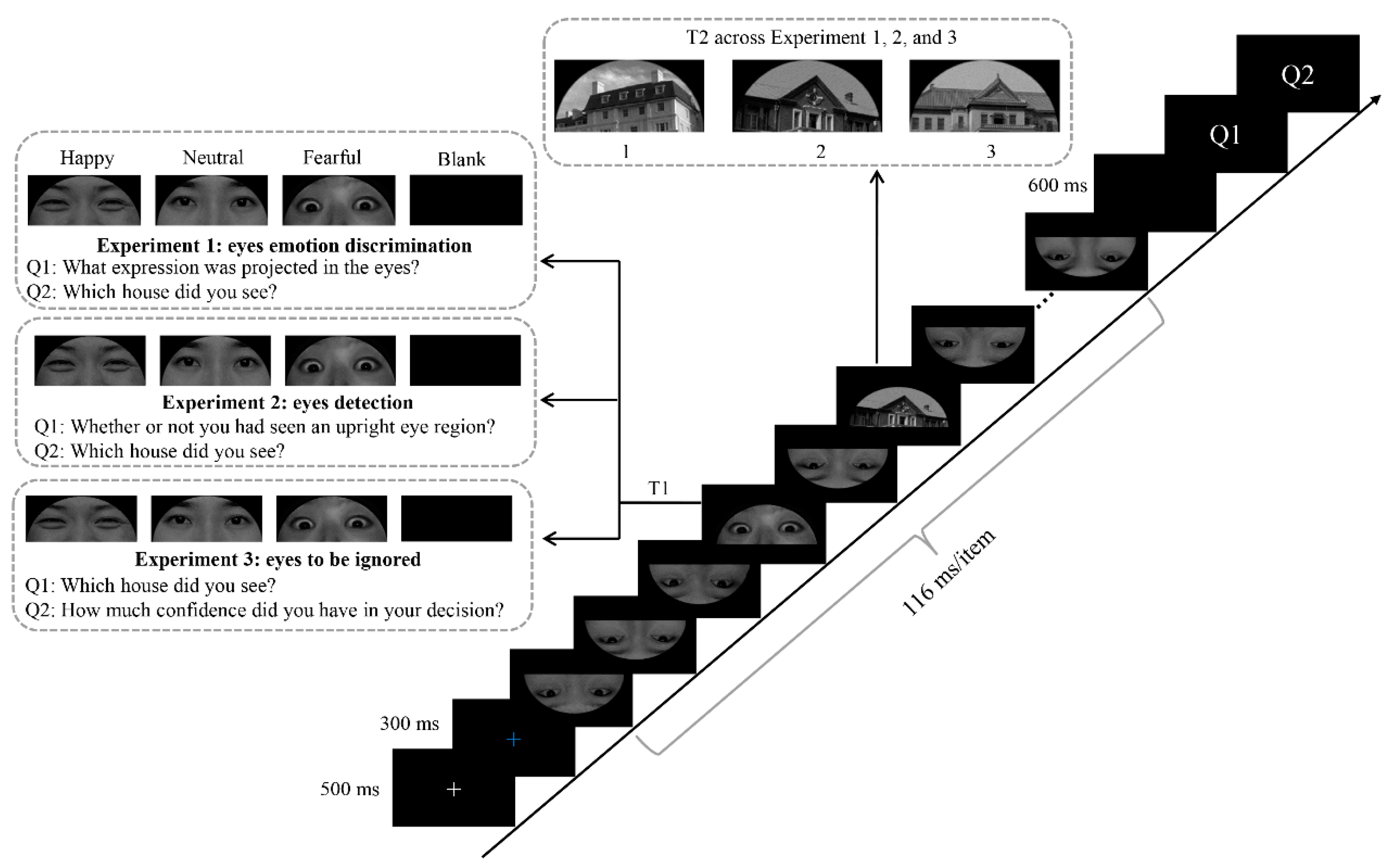
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Recording and Analysis of EEG Data
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1
3.1.1. Behavioral Results
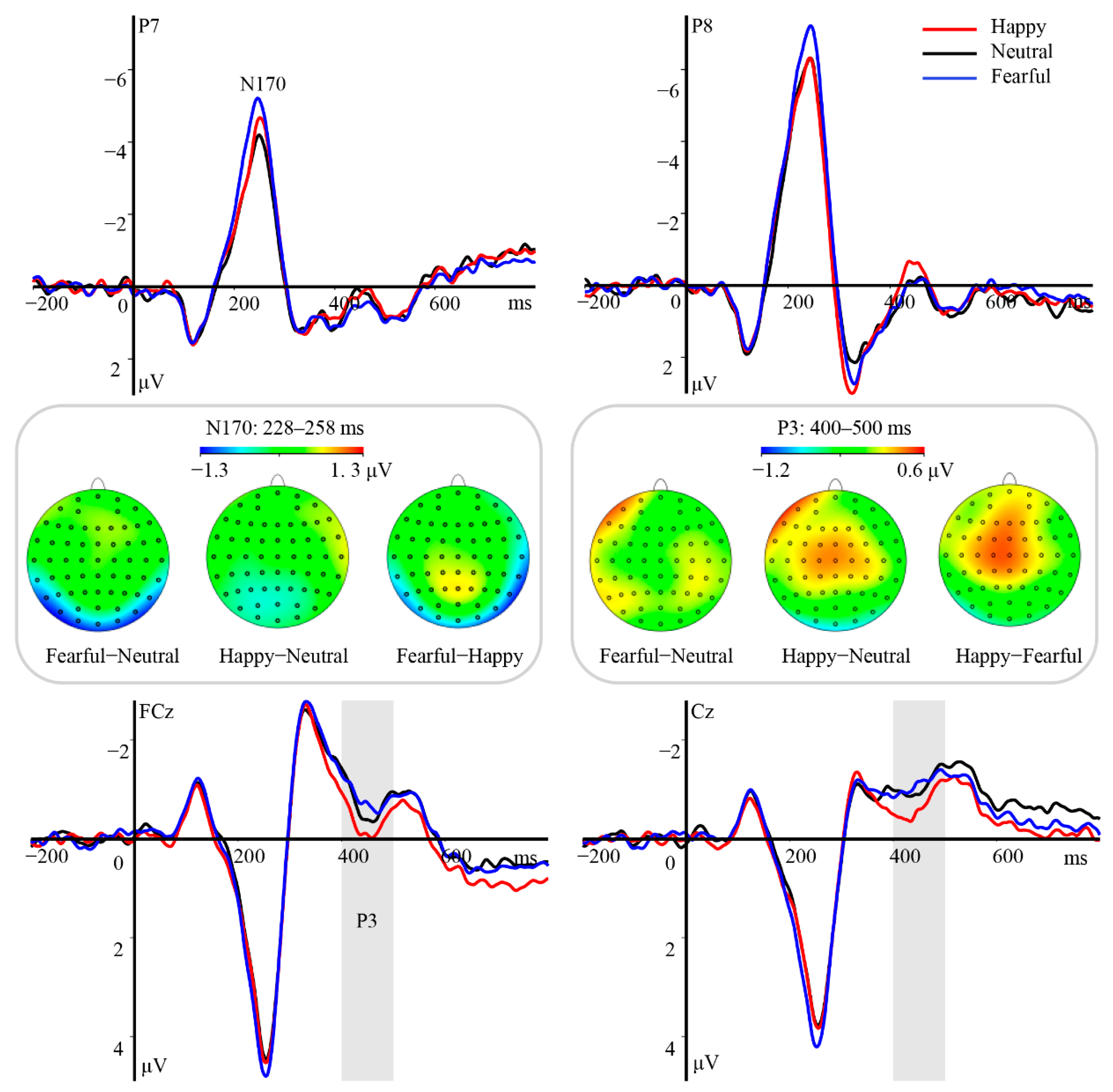
3.1.2. ERP Results
ERPs Related to the T1 Eye Region
ERPs Related to T2 Houses
3.2. Experiment 2
3.2.1. Behavioral Results
3.2.2. ERP Results
ERPs Related to the T1 Eye Region
ERPs Related to T2 Houses
3.3. Experiment 3
3.3.1. Behavioral Results
3.3.2. ERP Results
ERPs Related to the T1 Eye Region
ERPs Related to T2 Houses
4. Discussion
4.1. The Neural Correlates of Eye Region Processing
4.2. Effect of T1 Emotional Task Relevance on AB
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Happy | Neutral | Fearful | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotion discrimination task | 2.07 (0.31) | 2.01 (0.31) | 1.86 (0.28) |
| Eyes detection task | 1.78 (0.24) | 1.88 (0.21) | 1.84 (0.26) |
| Eyes to be ignored task | 1.82 (0.34) | 2.07 (0.28) | 2.04 (0.29) |
References
- Durston, A.J.; Itier, R.J. The early processing of fearful and happy facial expressions is independent of task demands—Support from mass univariate analyses. Brain Res. 2021, 1765, 147505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegna, A.J.; Landis, T.; Khateb, A. Electrophysiological evidence for early non-conscious processing of fearful facial expressions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2008, 70, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, H.T.; Flaisch, T.; Stockburger, J.; Junghöfer, M. Emotion and attention: Event-related brain potential studies. In Progress in Brain Research; Anders, S., Ende, G., Junghofer, M., Kissler, J., Wildgruber, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 156, pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Jolliffe, T. Is There a “Language of the Eyes”? Evidence from Normal Adults, and Adults with Autism or Asperger Syndrome. Vis. Cogn. 1997, 4, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.G.; Fernández-Martín, A.; Nummenmaa, L. Facial expression recognition in peripheral versus central vision: Role of the eyes and the mouth. Psychol. Res. 2014, 78, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; He, W.Q.; Luo, W.B. The neural mechanisms of the processing of facial expressions based on cues from eye region. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 25, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, P.J.; Kagan, J.; Cook, R.G.; Davis, F.C.; Kim, H.; Polis, S.; McLaren, D.G.; Somerville, L.H.; McLean, A.A.; Maxwell, J.S. Human amygdala responsivity to masked fearful eye whites. Science 2004, 306, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Luo, W.; Liao, Y.; Wang, N.; Gan, T.; Luo, Y. Human brain responsivity to different intensities of masked fearful eye whites: An ERP study. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.; Damjanovic, L. The eyes are sufficient to produce a threat superiority effect. Emotion 2006, 6, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.M.; Reinke, K.S. Attending to the fear in your eyes: Facilitated orienting and delayed disengagement. Cogn. Emot. 2014, 28, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.M.; Torrence, R.D.; Vander Hyde, M.R. Beware the eyes behind the mask: The capture and hold of selective attention by backward masked fearful eyes. Motiv. Emot. 2016, 40, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, M.; Maddux, W.W.; Masuda, T. Are the windows to the soul the same in the East and West? Cultural differences in using the eyes and mouth as cues to recognize emotions in Japan and the United States. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2007, 43, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Wyble, B. The attentional blink: Past, present, and future of a blind spot in perceptual awareness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, J.E.; Shapiro, K.L.; Arnell, K.M. Temporary suppression of visual processing in an RSVP task: An attentional blink? J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1992, 18, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.K. Affective influences on the attentional dynamics supporting awareness. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2005, 134, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.; Ihssen, N. Identification facilitation for emotionally arousing verbs during the attentional blink. Emotion 2004, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Ding, R.; Zhao, D.F.; Zhou, X.; Zhan, B.; Luo, W.B. Processing of emotions expressed through eye regions attenuates attentional blink. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 182, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.J.; Koster, E.H.W.; van Wees, R.; Martens, S. Emotional facial expressions and the attentional blink: Attenuated blink for angry and happy faces irrespective of social anxiety. Cogn. Emot. 2009, 23, 1640–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Feng, W.; He, W.; Wang, N.Y.; Luo, Y.J. Three stages of facial expression processing: ERP study with rapid serial visual presentation. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, S.; Iwasaki, S. Do happy faces capture attention? The happiness superiority effect in attentional blink. Emotion 2010, 10, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oca, B.M.; Villa, M.; Cervantes, M.; Welbourne, T. Emotional modulation of the attentional blink by pleasant and unpleasant pictures. J. Gen. Psychol. 2012, 139, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.T.; Duan, H.J.; Kan, Y.C.; Qi, S.Q.; Hu, W.P. Influence of emotional task relevancy on the temporal dynamic of attentional bias in people with high-trait anxiety. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2020, 32, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.J.; Koster, E.H.; van Wees, R.; Martens, S. Angry facial expressions hamper subsequent target identification. Emotion 2010, 10, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, Q.L. Cognitive mechanisms of the emotional attentional blink: Evidence from behavior and ERPs. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2016, 48, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, K.J.; Arnell, K.M.; Mansfield, C.A. Capturing and holding attention: The impact of emotional words in rapid serial visual presentation. Mem. Cogn. 2008, 36, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, I.; Botella, J. Emotional stimuli reduce the attentional blink in sub-clinical anxious subjects. Psicothema 2002, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- de Jong, P.J.; Koster, E.H.; Wessel, I.; Martens, S. Distinct temporal processing of task-irrelevant emotional facial expressions. Emotion 2014, 14, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Lan, J.; Duan, H. Acute stress reduces the emotional attentional blink: Evidence from human electrophysiology. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 21, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T.; Zwickel, J.; Ritter, J.; Kitzmantel, M.; Schneider, W.X. The effect of fearful faces on the attentional blink is task dependent. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2009, 16, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, J.A.; Mercado, F.; Carretié, L. N170 sensitivity to facial expression: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 55, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Bublatzky, F. Attention and emotion: An integrative review of emotional face processing as a function of attention. Cortex 2020, 130, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eimer, M. The face-sensitive N170 component of the event-related brain potential. In The Oxford Handbook of Face Perception; Rhodes, G., Calder, A., Johnson, M., V.Haxby, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 329–344. [Google Scholar]
- Bentin, S.; Allison, T.; Puce, A.; Perez, E.; McCarthy, G. Electrophysiological studies of face perception in humans. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itier, R.J.; Alain, C.; Sedore, K.; McIntosh, A.R. Early Face Processing Specificity: It’s in the Eyes! J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itier, R.J.; Latinus, M.; Taylor, M.J. Face, eye and object early processing: What is the face specificity? NeuroImage 2006, 29, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemrodov, D.; Anderson, T.; Preston, F.F.; Itier, R.J. Early sensitivity for eyes within faces: A new neuronal account of holistic and featural processing. NeuroImage 2014, 97, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Bruchmann, M.; Steinweg, A.-L.; Moeck, R.; Straube, T. Attentional conditions differentially affect early, intermediate and late neural responses to fearful and neutral faces. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchmann, M.; Schindler, S.; Dinyarian, M.; Straube, T. The role of phase and orientation for ERP modulations of spectrum-manipulated fearful and neutral faces. Psychophysiology 2022, 59, e13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppänen, J.M.; Hietanen, J.K.; Koskinen, K. Differential early ERPs to fearful versus neutral facial expressions: A response to the salience of the eyes? Biol. Psychol. 2008, 78, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyns, P.G.; Petro, L.S.; Smith, M.L. Dynamics of visual information integration in the brain for categorizing facial expressions. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Wang, J.; Xia, T.; Zhao, W.S.; Xu, Q.R.; He, W.Q. The influence of spatial frequency content on facial expression processing: An ERP study using rapid serial visual presentation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Caldarone, F.; Bruchmann, M.; Moeck, R.; Straube, T. Time-dependent effects of perceptual load on processing fearful and neutral faces. Neuropsychologia 2020, 146, 107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Tirloni, C.; Bruchmann, M.; Straube, T. Face and emotional expression processing under continuous perceptual load tasks: An ERP study. Biol. Psychol. 2021, 161, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajcak, G.; MacNamara, A.; Olvet, D.M. Event-related potentials, emotion, and emotion regulation: An integrative review. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2010, 35, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Ren, J.; He, W. Neural correlates of facial expression processing during a detection task: An ERP study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.G.; Beltran, D. Brain lateralization of holistic versus analytic processing of emotional facial expressions. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.L.; Rawding, J.; Most, S.B.; Hoffman, J.E. Emotion-induced blindness reflects competition at early and late processing stages: An ERP study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 14, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergent, C.; Baillet, S.; Dehaene, S. Timing of the brain events underlying access to consciousness during the attentional blink. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, M.; Revonsuo, A. Comparison of event-related potentials in attentional blink and repetition blindness. Brain Res. 2008, 1189, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranczioch, C.; Debener, S.; Maye, A.; Engel, A.K. Temporal dynamics of access to consciousness in the attentional blink. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.J. Revision of the Chinese facial affective picture system. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2011, 25, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Ma, H.; Huang, Y.X.; Luo, Y.J. The development of native chinese affective picture system—A pretest in 46 college students. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2005, 19, 719–722. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, M.M.; Potter, M.C. A two-stage model for multiple target detection in rapid serial visual presentation. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1995, 21, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, E.K.; Luck, S.J.; Shapiro, K.L. Electrophysiological evidence for a postperceptual locus of suppression during the attentional blink. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1998, 24, 1656–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Makeig, S.; Humphries, C.; Lee, T.H.; Mckeown, M.J.; Iragui, V.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, A.; Debener, S.; Gratton, G.; Junghofer, M.; Kappenman, E.S.; Luck, S.J.; Luu, P.; Miller, G.A.; Yee, C.M. Committee report: Publication guidelines and recommendations for studies using electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography. Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, J.K.; Nordin, S.; Sequeira, H.; Polich, J. Affective picture processing: An integrative review of ERP findings. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 77, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.R.; Luo, W.B. The effect of emotionally valenced eye region images on visuocortical processing of surprised faces. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchmann, M.; Schindler, S.; Straube, T. The spatial frequency spectrum of fearful faces modulates early and mid-latency ERPs but not the N170. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rellecke, J.; Sommer, W.; Schacht, A. Does processing of emotional facial expressions depend on intention? Time-resolved evidence from event-related brain potentials. Biol. Psychol. 2012, 90, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Bruchmann, M.; Gathmann, B.; Moeck, R.; Straube, T. Effects of low-level visual information and perceptual load on P1 and N170 responses to emotional expressions. Cortex 2021, 136, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.G.; Nummenmaa, L.; Avero, P. Recognition advantage of happy faces in extrafoveal vision: Featural and affective processing. Vis. Cogn. 2010, 18, 1274–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ge, Y.; Luo, W.B.; Luo, Y.J. Show your teeth or not: The role of the mouth and eyes in smiles and its cross-cultural variations. Behav. Brain Sci. 2010, 33, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronka, E.; Walentowska, W. Attention modulates emotional expression processing. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.X.; Zhu, X.R.; Ding, R.; Ren, J.; Luo, W.B. The effect of emotional and self-referential contexts on ERP responses towards surprised faces. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 146, 107728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinweg, A.-L.; Schindler, S.; Bruchmann, M.; Moeck, R.; Straube, T. Reduced early fearful face processing during perceptual distraction in high trait anxious participants. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, F.; Cui, L.; Wei, P.; Zhang, Q. The effect of fearful faces on the attentional blink is modulated by emotional task relevance: An event-related potential study. Neuropsychologia 2021, 162, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardelli, P.; Lugli, L.; Pellicano, A.; Iani, C.; Nicoletti, R. Interactive effects between gaze direction and facial expression on attentional resources deployment: The task instruction and context matter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenbreth, C.; Rieger, J.; Heinze, H.J.; Zaehle, T. Seeing emotions in the eyes-inverse priming effects induced by eyes expressing mental states. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- MacLeod, J.; Stewart, B.M.; Newman, A.J.; Arnell, K.M. Do emotion-induced blindness and the attentional blink share underlying mechanisms? An event-related potential study of emotionally-arousing words. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 592–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.L.; Caldwell, J.; Sorensen, R.E. Personal names and the attentional blink: A visual “cocktail party” effect. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1997, 23, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, C.; Saija, J.D.; Akyürek, E.G.; Martens, S. An individual differences approach to temporal integration and order reversals in the attentional blink task. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, C.; Wierda, S.M.; van Viegen, E.; Martens, S. Individual differences in the attentional blink: The temporal profile of blinkers and non-blinkers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Raymond, J.E. Familiarity effects on face recognition in the attentional blink. J. Vis. 2003, 3, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Raymond, J.E. The role of attention and familiarity in face identification. Percept. Psychophys. 2006, 68, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; He, W.; Luo, W. Emotional Valence in the Eye Region Modulates the Attentional Blink in a Task-Dependent Manner: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121665
Li S, Li Y, Liu S, He W, Luo W. Emotional Valence in the Eye Region Modulates the Attentional Blink in a Task-Dependent Manner: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121665
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuaixia, Yiwen Li, Shuaicheng Liu, Weiqi He, and Wenbo Luo. 2022. "Emotional Valence in the Eye Region Modulates the Attentional Blink in a Task-Dependent Manner: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121665
APA StyleLi, S., Li, Y., Liu, S., He, W., & Luo, W. (2022). Emotional Valence in the Eye Region Modulates the Attentional Blink in a Task-Dependent Manner: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121665






