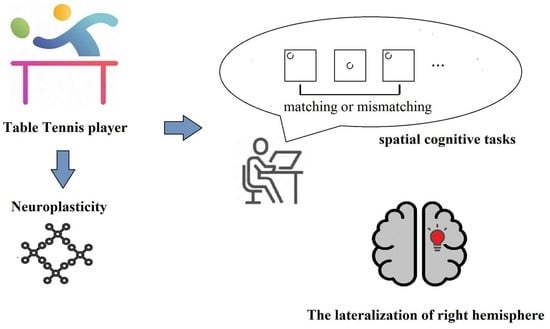
The Lateralization of Spatial Cognition in Table Tennis Players: Neuroplasticity in the Dominant Hemisphere
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Stimuli and Procedure
2.3.1. The Notch Circle Task
2.3.2. The Rotating-Notch Circle Task
2.4. Electroencephalography Recordings
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Performance
3.2. Amplitude
3.3. Latency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGee, M.G. Human spatial abilities: Psychometric studies and environmental, genetic, hormonal, and neurological influences. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, M.C.; Petersen, A.C. Emergence and characterization of sex differences in spatial ability: A meta-analysis. Child Dev. 1985, 56, 1479–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilea, S.L.; Roskos-Ewoldsen, B.; Boles, D. Sex differences in spatial ability: A lateralization of function approach. Brain Cogn. 2004, 56, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. The episodic buffer: A new component of working memory? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Intra- and Inter-hemispheric Connectivity Supporting Hemispheric Specialization. In Micro-, Meso- and Macro-Connectomics of the Brain; Kennedy, H., Van Essen, D.C., Christen, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, L.; Thomas-Antérion, C. Marc Dax and the discovery of the lateralisation of language in the left cerebral hemisphere. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 167, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, S.; Roe, D. Does Gustave Dax deserve to be forgotten? The temporal lobe theory and other contributions of an overlooked figure in the history of language and cerebral dominance. Brain Lang. 1999, 69, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, P.Y.; Zago, L.; Petit, L.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Revisiting human hemispheric specialization with neuroimaging. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, R.; Fox, P.T.; Paus, T. Functional coactivation map of the human brain. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, D.E.; Margulies, D.S.; Shehzad, Z.E.; Reiss, P.; Kelly, A.M.; Uddin, L.Q.; Gee, D.G.; Roy, A.K.; Banich, M.T.; Castellanos, F.X.; et al. Regional variation in interhemispheric coordination of intrinsic hemodynamic fluctuations. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13754–13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raznahan, A.; Lerch, J.P.; Lee, N.; Greenstein, D.; Wallace, G.L.; Stockman, M.; Clasen, L.; Shaw, P.W.; Giedd, J.N. Patterns of coordinated anatomical change in human cortical development: A longitudinal neuroimaging study of maturational coupling. Neuron 2011, 72, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprian, G.; Langs, G.; Brugger, P.C.; Bittner, M.; Weber, M.; Arantes, M.; Prayer, D. The prenatal origin of hemispheric asymmetry: An in utero neuroimaging study. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, P.A.; Scott, J.A.; Roosta, A.; Rajagopalan, V.; Kim, K.; Rousseau, F.; Barkovich, A.J.; Glenn, O.A.; Studholme, C. Early folding patterns and asymmetries of the normal human brain detected from in utero MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iturria-Medina, Y.; Pérez Fernández, A.; Morris, D.M.; Canales-Rodríguez, E.J.; Haroon, H.A.; García Pentón, L.; Augath, M.; Galán García, L.; Logothetis, N.; Parker, G.J.; et al. Brain hemispheric structural efficiency and interconnectivity rightward asymmetry in human and nonhuman primates. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.W. The cognitive laterality battery: Tests of specialized cognitive function. Int. J. Neurosci. 1986, 29, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, R.; Lidzba, K.; Wilke, M.; Kiefer, C.; Mordasini, M.; Schroth, G.; Perrig, W.; Steinlin, M. Strengthening of laterality of verbal and visuospatial functions during childhood and adolescence. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyser, C.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Neil, J.J. Functional connectivity MRI in infants: Exploration of the functional organization of the developing brain. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoma, P.; Soria Bauser, D.; Norra, C.; Brüne, M.; Juckel, G.; Suchan, B. Do you see what I feel?—Electrophysiological correlates of emotional face and body perception in schizophrenia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 125, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Dai, C.; Cai, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Y. Total Sleep Deprivation Impairs Lateralization of Spatial Working Memory in Young Men. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 562035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutas, M.; McCarthy, G.; Donchin, E. Augmenting mental chronometry: The P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science 1977, 197, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, G.L.; Pope, D.L.; Astafiev, S.V.; McAvoy, M.P.; Snyder, A.Z.; Corbetta, M. Right hemisphere dominance during spatial selective attention and target detection occurs outside the dorsal frontoparietal network. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3640–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeo, P.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Chica, A.B. Brain networks of visuospatial attention and their disruption in visual neglect. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, M.D.; Corbetta, M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Raichle, M.E. Spontaneous neuronal activity distinguishes human dorsal and ventral attention systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10046–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Hedden, T.; Buckner, R.L. Evidence from intrinsic activity that asymmetry of the human brain is controlled by multiple factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20499–20503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kucyi, A.; Moayedi, M.; Weissman-Fogel, I.; Hodaie, M.; Davis, K.D. Hemispheric asymmetry in white matter connectivity of the temporoparietal junction with the insula and prefrontal cortex. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, F.; Pi, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y. Neural efficiency in basketball players is associated with bidirectional reductions in cortical activation and deactivation during multiple-object tracking task performance. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 144, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.L.; Jahanshad, N.; McMahon, K.L.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Martin, N.G.; Hickie, I.B.; Toga, A.W.; Wright, M.J.; Thompson, P.M. Development of brain structural connectivity between ages 12 and 30: A 4-Tesla diffusion imaging study in 439 adolescents and adults. NeuroImage 2013, 64, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Fields, R.D.; Johansen-Berg, H. Plasticity in gray and white: Neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, E.J.; Quarta, E.; Bravi, R.; Granato, A.; Minciacchi, D. Neural plasticity and network remodeling: From concepts to pathology. Neuroscience 2017, 344, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttal, D.H.; Meadow, N.G.; Tipton, E.; Hand, L.L.; Alden, A.R.; Warren, C.; Newcombe, N.S. The malleability of spatial skills: A meta-analysis of training studies. Psychol. Bull. 2013, 139, 352–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmer, H.D.; Ecker, U.K. Remembering perceptual features unequally bound in object and episodic tokens: Neural mechanisms and their electrophysiological correlates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Peng, Z.; Song, T.; Wang, L.; Dai, C.; Xu, M.; Shao, Y.; Lv, J. Modafinil ameliorates the decline in pronunciation-related working memory caused by 36-h acute total sleep deprivation: An ERP study. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2022, 192, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Yu, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, M.; Peng, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Shao, Y.; et al. Total Sleep Deprivation Triggers Greater Activation in the Parietal Brain in the Visual Working Memory Updating Processes: An Event-Related Potentials Study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 736437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, W. Enhanced effective connectivity from the middle frontal gyrus to the parietal lobe is associated with impaired mental rotation after total sleep deprivation: An electroencephalogram study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 910618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraskin, J.; Sherwin, J.; Sajda, P. Knowing when not to swing: EEG evidence that enhanced perception-action coupling underlies baseball batter expertise. NeuroImage 2015, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Russo, F.; Taddei, F.; Apnile, T.; Spinelli, D. Neural correlates of fast stimulus discrimination and response selection in top-level fencers. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 408, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.C.; Fink, A. Intelligence and neural efficiency. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 1004–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhozhikashvili, N.; Zakharov, I.; Ismatullina, V.; Feklicheva, I.; Malykh, S.; Arsalidou, M. Parietal Alpha Oscillations: Cognitive Load and Mental Toughness. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöllner, A.; Memmert, D.; von Lehe, M.; Jungilligens, J.; Scharfen, H.E. Specific relations of visual skills and executive functions in elite soccer players. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 960092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, R.H.; Neubauer, A.C.; Stern, E. Superior performance and neural efficiency: The impact of intelligence and expertise. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haier, R.J.; Schandler, S.L.; MacLachlan, A.; Soderling, E.; Buchsbaum, M.S.; Cohen, M.J. Alcohol induced changes in regional cerebral glucose metabolic rate during divided attention. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1999, 26, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkreis, P.; El Tom, S.; Ragert, P.; Pleger, B.; Tegenthoff, M.; Dinse, H.R. Assessment of sensorimotor cortical representation asymmetries and motor skills in violin players. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Percio, C.; Franzetti, M.; De Matti, A.J.; Noce, G.; Lizio, R.; Lopez, S.; Soricelli, A.; Ferri, R.; Pascarelli, M.T.; Rizzo, M.; et al. Football Players Do Not Show “Neural Efficiency” in Cortical Activity Related to Visuospatial Information Processing During Football Scenes: An EEG Mapping Study. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.R.; Chabris, C.F.; Braver, T.S. Neural mechanisms of general fluid intelligence. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, S.D.; Carpenter, P.A.; Varma, S.; Just, M.A. Frontal and parietal participation in problem solving in the Tower of London: fMRI and computational modeling of planning and high-level perception. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiloni, C.; Marzano, N.; Infarinato, F.; Iacoboni, M.; Rizza, G.; Aschieri, P.; Cibelli, G.; Soricelli, A.; Eusebi, F.; Del Percio, C. “Neural efficiency” of experts’ brain during judgment of actions: A high-resolution EEG study in elite and amateur karate athletes. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, H.; Mori, S. Effects of stimulus-response compatibility in mediating expert performance in baseball players. Brain Res. 2008, 1189, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, F.; Weinberg, H.; Wollny, R. The Impact of Practicing Open- vs. Closed-Skill Sports on Executive Functions-A Meta-Analytic and Systematic Review with a Focus on Characteristics of Sports. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Song, T.; Peng, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, L.; Shao, Y.; Wang, L.; Weng, X.; Han, M. Acute Sleep Deprivation Impairs Motor Inhibition in Table Tennis Athletes: An ERP Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, J.; Jung, K.Y. Influence of task difficulty on the features of event-related potential during visual oddball task. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 445, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, J.G.; Pavlenko, E.; Bialystok, E. Bilingualism modifies disengagement of attention networks across the scalp: A multivariate ERP investigation of the IOR paradigm. J. Neurolinguist. 2020, 56, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckert, J.; Ferber, S. Revisiting unilateral neglect. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesulam, M.M. Spatial attention and neglect: Parietal, frontal and cingulate contributions to the mental representation and attentional targeting of salient extrapersonal events. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierard, C.; Liscia, P.; Chauveau, F.; Coutan, M.; Corio, M.; Krazem, A.; Beracochea, D. Differential effects of total sleep deprivation on contextual and spatial memory: Modulatory effects of modafinil. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 97, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, M.W.; Chuah, L.Y.; Venkatraman, V.; Chan, W.Y.; Philip, P.; Dinges, D.F. Functional imaging of working memory following normal sleep and after 24 and 35 h of sleep deprivation: Correlations of fronto-parietal activation with performance. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lythe, K.E.; Williams, S.C.; Anderson, C.; Libri, V.; Mehta, M.A. Frontal and parietal activity after sleep deprivation is dependent on task difficulty and can be predicted by the fMRI response after normal sleep. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 233, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampshire, A.; Highfield, R.R.; Parkin, B.L.; Owen, A.M. Fractionating human intelligence. Neuron 2012, 76, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, R.; Xie, F.; Li, A. Motor expertise and performance in sport-specific priming tasks: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, H.; Yoshie, M.; Miura, A.; Kudo, K. Characteristics of the athletes’ brain: Evidence from neurophysiology and neuroimaging. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 62, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Cai, Q.; Fan, M.; Li, L. Dissociable plasticity of visual-motor system in functional specialization and flexibility in expert table tennis players. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 1973–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Chang, Y.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.; Ryu, K.; Lee, E.; Woo, M.; Janelle, C.M. An fMRI study of differences in brain activity among elite, expert, and novice archers at the moment of optimal aiming. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. Off. J. Soc. Behav. Cogn. Neurol. 2014, 27, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Y.; Pi, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.P.; Zhang, L.L.; Dai, W.; Zhu, H.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y. Morphological and Functional Differences between Athletes and Novices in Cortical Neuronal Networks. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di, X.; Zhu, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, P.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, K.; Zhuo, Y.; Rao, H. Altered resting brain function and structure in professional badminton players. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Seger, C.; Lu, M.; Deng, F.; Wu, X.; He, Y.; Niu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, R. Long-term intensive gymnastic training induced changes in intra- and inter-network functional connectivity: An independent component analysis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Brölz, E.; Scholz, D.; Ramos-Murguialday, A.; Keune, P.M.; Hautzinger, M.; Birbaumer, N.; Strehl, U. Winning the game: Brain processes in expert, young elite and amateur table tennis players. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J. The influence of motor expertise on the brain activity of motor task performance: A meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 15, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarrow, K.; Brown, P.; Krakauer, J.W. Inside the brain of an elite athlete: The neural processes that support high achievement in sports. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overney, L.S.; Blanke, O.; Herzog, M.H. Enhanced temporal but not attentional processing in expert tennis players. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.W.; Kramer, A.F.; Basak, C.; Prakash, R.S.; Roberts, B. Are expert athletes ‘expert’ in the cognitive laboratory? A meta-analytic review of cognition and sport expertise. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2010, 24, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, M.; Dimitrova, A.; Schorn, C.F.; Elles, H.G.; Hein-Kropp, C.; Gizewski, E.R.; Diener, H.C.; Timmann, D. Cerebellar involvement in verb generation: An fMRI study. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 409, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Controls | Table Tennis Athletes |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 28 | 22 |
| Gender | Male | Male |
| Age (y) | 22.79 ± 2.27 | 20.00 ± 1.40 |
| Mass (kg) | 62.81 ± 4.16 | 71.69 ± 1.15 * |
| Height (cm) | 176.32 ± 5.40 | 177.2 ± 6.35 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 20.20 ± 1.15 | 22.83 ± 1.65 * |
| Experience (y) | - | 7.69 ± 4.79 |
| Behavior Indictors | Group | Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) | Rotating-Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Controls | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 0.86 ±0.05 |
| Table tennis athletes | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.88 ±0.04 | |
| Reaction Time | Controls | 635.41 ± 64.10 | 662.45 ± 51.48 |
| Table tennis athletes | 620.28 ± 42.15 | 641.53 ± 32.69 | |
| Correct number/sec | Controls | 1.42 ± 0.21 | 1.31 ± 0.13 |
| Table tennis athletes | 1.51 ± 0.14 | 1.37 ± 0.12 |
| Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) | Rotating-Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | Table Tennis Athletes | Controls | Table Tennis Athletes | |
| F7 | 3.78 ± 3.29 | 5.14 ± 3.70 | 2.30 ± 3.72 | 4.09 ± 3.53 |
| F8 | 5.38 ± 2.70 | 6.49 ± 3.04 | 4.00 ± 2.89 | 6.24 ± 2.94 |
| F3 | 6.02 ± 3.00 | 6.50 ± 3.65 | 4.01 ± 2.91 | 5.87 ± 3.70 |
| F4 | 6.89 ± 3.03 | 7.33 ± 3.14 | 5.58 ± 2.07 | 7.05 ± 3.30 |
| FT7 | 4.56 ± 3.28 | 5.26 ± 3.55 | 2.43 ± 3.06 | 4.33 ± 3.10 |
| FT8 | 5.52 ± 2.16 | 6.32 ± 2.96 | 4.01 ± 2.77 | 5.91 ± 2.82 |
| FC3 | 6.68 ± 2.56 | 7.05 ± 3.17 | 5.35 ± 2.44 | 6.93 ± 4.37 |
| FC4 | 7.61 ± 3.50 | 7.69 ± 3.49 | 6.34 ± 2.23 | 7.71 ± 3.62 |
| CP3 | 5.74± 1.44 | 6.46 ± 2.44 | 5.74 ± 1.93 | 6.85 ± 3.43 |
| CP4 | 6.38± 1.83 | 7.69 ± 2.73 | 6.48 ± 2.09 | 8.63 ± 3.81 |
| P3 | 5.44± 1.56 | 6.24 ± 2.22 | 5.64 ± 2.01 | 6.86 ± 3.05 |
| P4 | 5.69± 1.85 | 6.85 ± 2.64 | 5.97 ± 1.72 | 8.29 ± 3.62 |
| Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) | Rotating-Notch Circle Task (M ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | Table Tennis Athletes | Controls | Table Tennis Athletes | |
| F7 | 344.27 ± 40.96 | 335.45 ± 32.00 | 342.32 ± 40.08 | 328.26 ± 40.71 |
| F8 | 365.42 ± 44.42 | 344.74 ± 51.51 | 330.25 ± 32.50 | 345.89 ± 52.84 |
| F3 | 336.42 ± 47.22 | 322.84 ± 40.51 | 321.95 ± 41.81 | 332.39 ± 37.53 |
| F4 | 350.56 ± 41.68 | 329.66 ± 46.63 | 318.64 ± 41.09 | 335.47 ± 37.01 |
| FT7 | 359.27 ± 43.99 | 342.16 ± 28.52 | 351.17 ± 39.83 | 332.26 ± 45.99 |
| FT8 | 365.83 ± 45.61 | 349.82 ± 49.63 | 351.39 ± 39.52 | 352.79 ± 51.11 |
| FC3 | 346.79 ± 45.37 | 330.66 ± 47.07 | 334.32 ± 38.85 | 335.39 ± 43.54 |
| FC4 | 346.69 ± 41.99 | 330.50 ± 42.90 | 326.77 ± 40.98 | 338.26 ± 38.51 |
| CP3 | 352.96 ± 38.69 | 348.29 ± 37.60 | 354.58 ± 29.77 | 357.76 ± 37.57 |
| CP4 | 355.73 ± 42.87 | 357.84 ± 33.22 | 362.06 ± 32.52 | 357.53 ± 37.95 |
| P3 | 350.46 ± 38.60 | 351.74 ± 37.23 | 362.42 ± 37.15 | 365.45 ± 38.92 |
| P4 | 353.92 ± 44.01 | 358.21 ± 34.89 | 358.35 ± 38.39 | 365.53 ± 38.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Song, T.; Shao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Weng, X. The Lateralization of Spatial Cognition in Table Tennis Players: Neuroplasticity in the Dominant Hemisphere. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121607
Peng Z, Xu L, Wang H, Song T, Shao Y, Liu Q, Weng X. The Lateralization of Spatial Cognition in Table Tennis Players: Neuroplasticity in the Dominant Hemisphere. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121607
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Ziyi, Lin Xu, Haiteng Wang, Tao Song, Yongcong Shao, Qingyuan Liu, and Xiechuan Weng. 2022. "The Lateralization of Spatial Cognition in Table Tennis Players: Neuroplasticity in the Dominant Hemisphere" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121607
APA StylePeng, Z., Xu, L., Wang, H., Song, T., Shao, Y., Liu, Q., & Weng, X. (2022). The Lateralization of Spatial Cognition in Table Tennis Players: Neuroplasticity in the Dominant Hemisphere. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121607