Changes in CSF Surface Tension in Relation to Surfactant Proteins in Children with Intraventricular Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
- (i)
- Group 1: IVH without/before primary intervention (N = 24);
- (ii)
- Group 2: IVH 4–28 days after primary intervention (N = 14);
- (iii)
- Group 3: IVH 44–357 days after primary intervention (N = 14);
- (iv)
- Group 4: Hydrocephalus (N = 14);
- (v)
- Group 5: Sepsis (N = 7);
- (vi)
- Group 6: Control group (N = 37).
2.2. CSF Surface Tension
2.3. Quantification of Surfactant Proteins
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Analyses
3.2. Variance Analyses and Non-Parametric Tests
3.3. Post Hoc Analyses
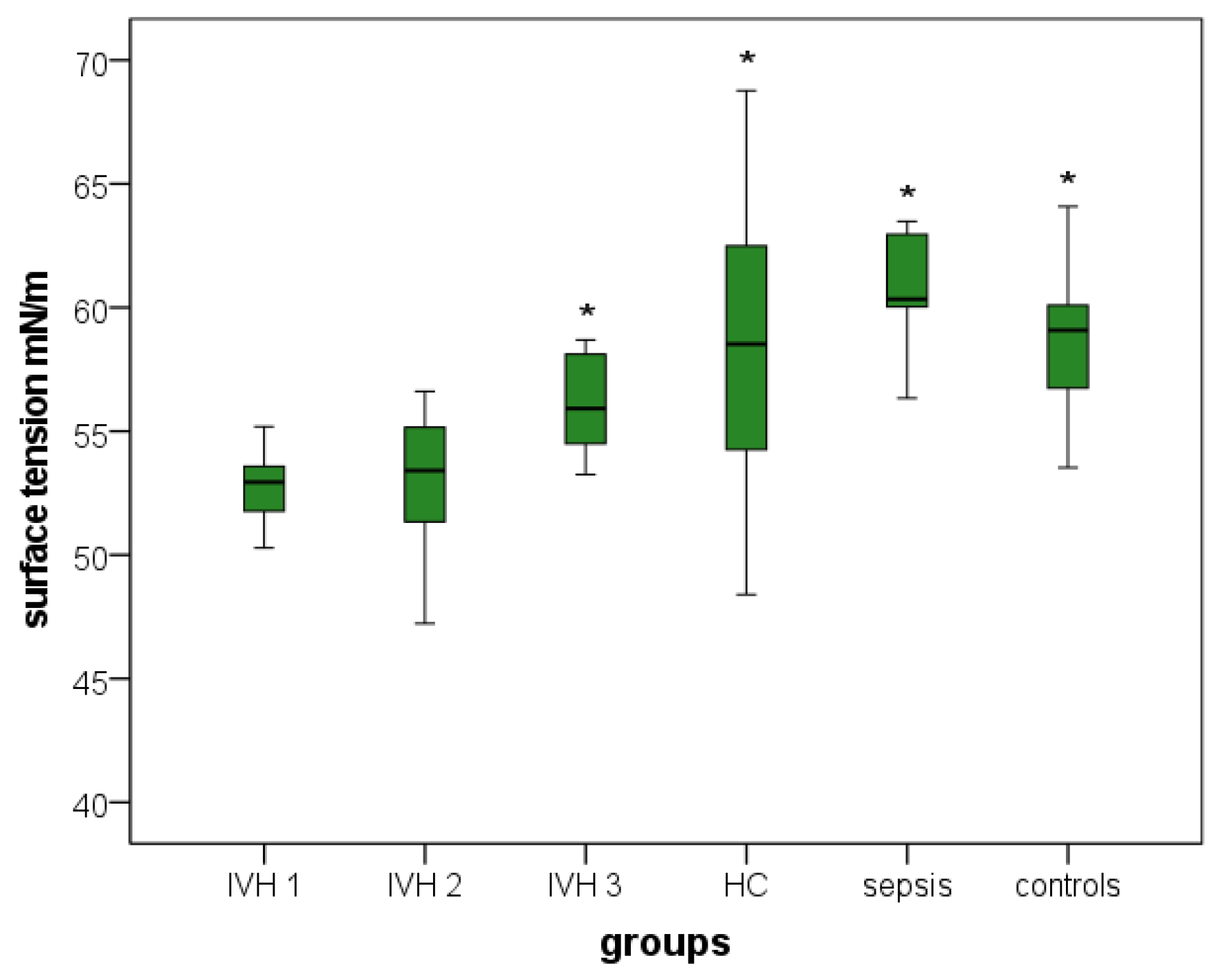
3.3.1. Surface Tension
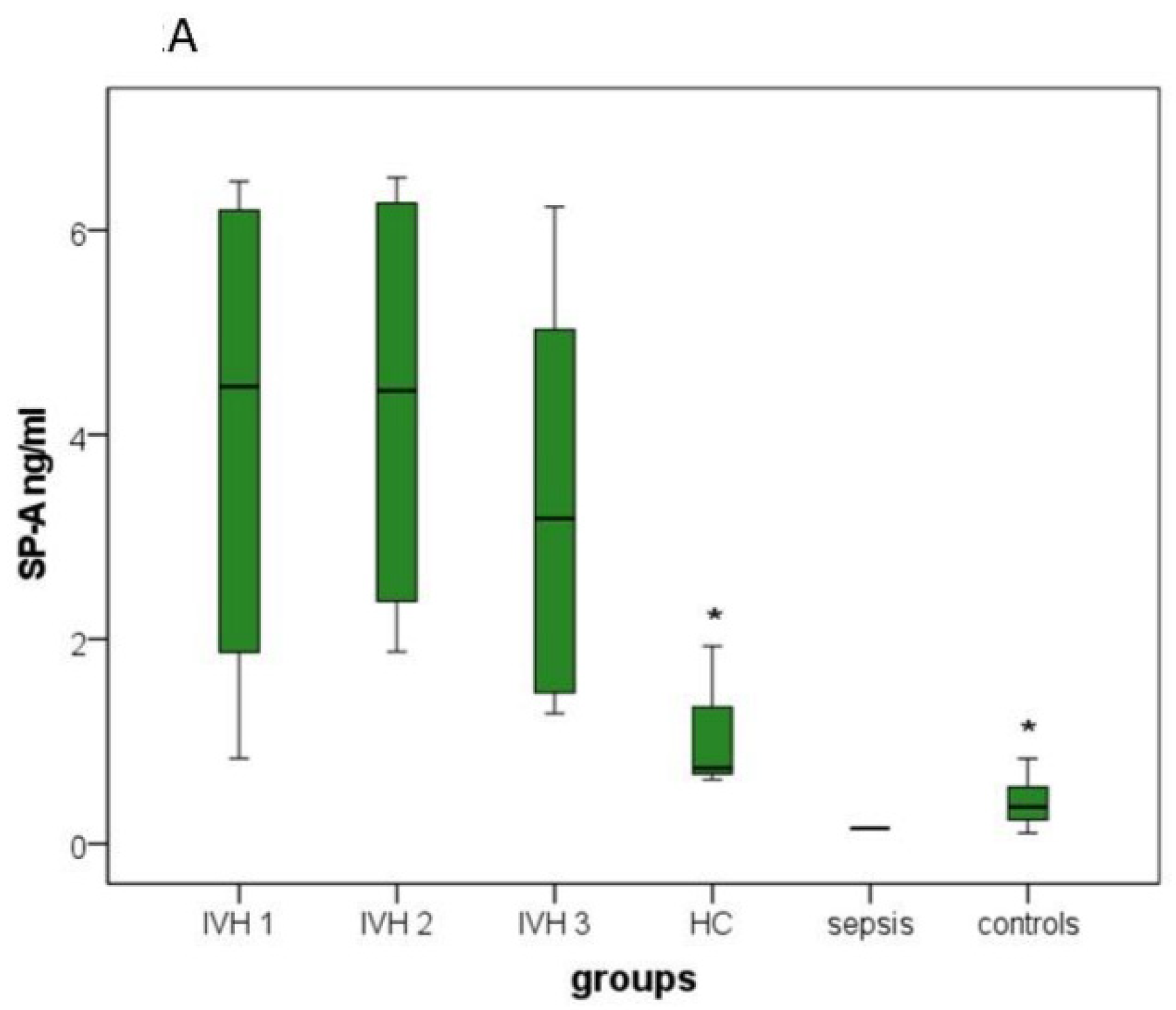
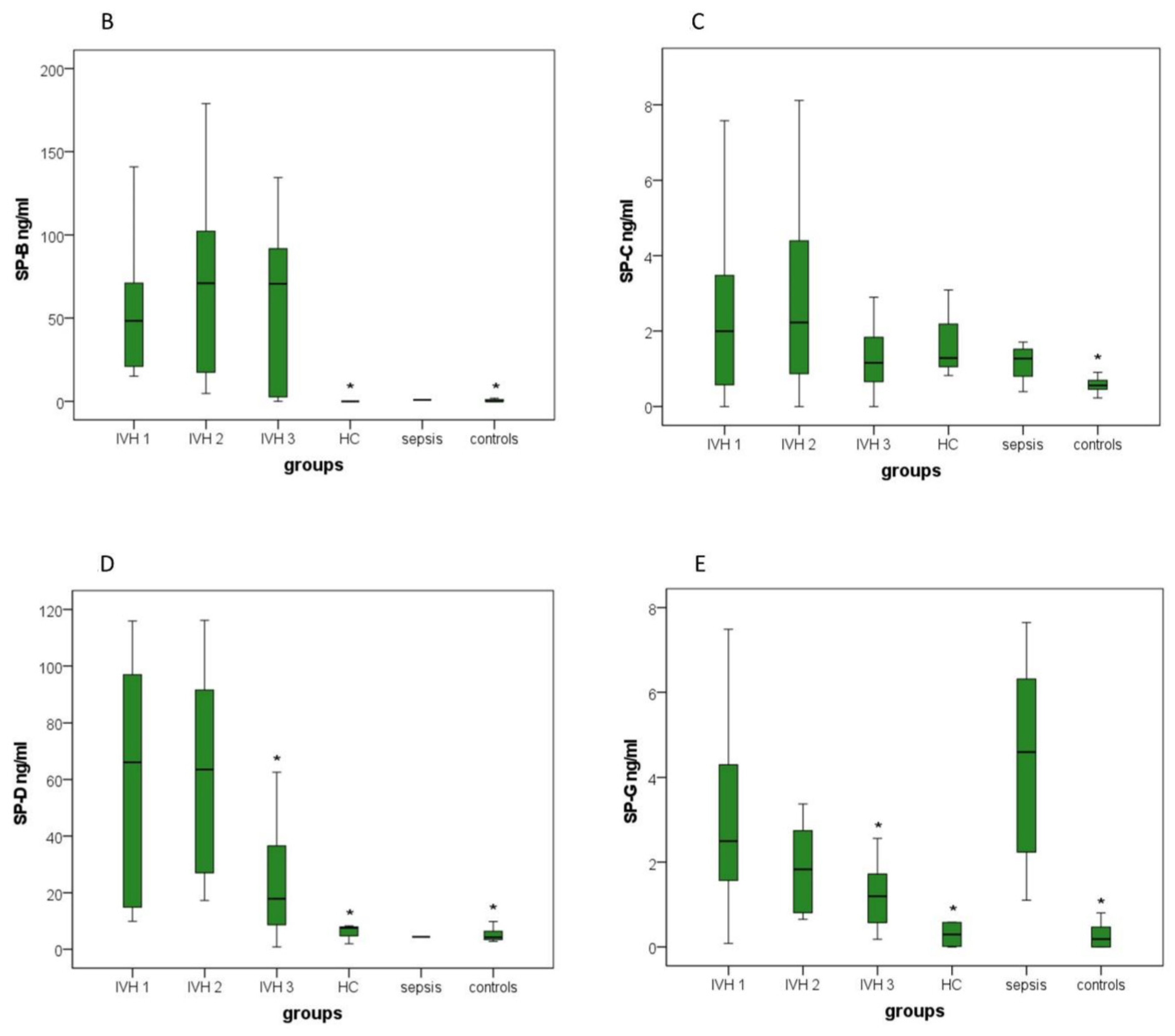
3.3.2. SP-A, SP-B and SP-D
3.3.3. SP-C
3.3.4. SP-G
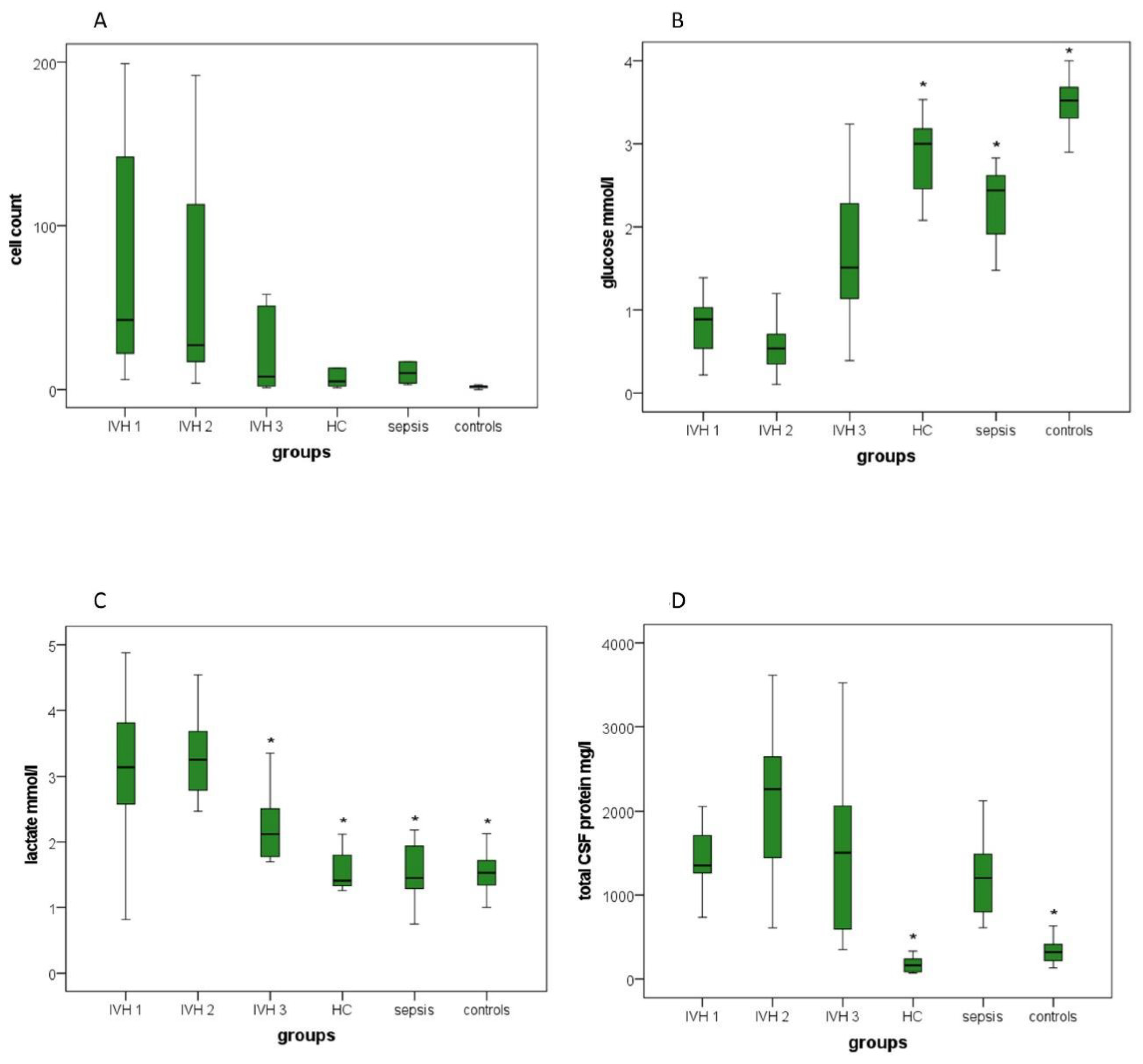
3.3.5. Cell Count
3.3.6. Lactate, Glucose and Total CSF Protein Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cañadas, O.; Olmeda, B.; Alonso, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Lipid-Protein and Protein-Protein Interactions in the Pulmonary Surfactant System and Their Role in Lung Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgeig, S.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Casals, C.; Clark, H.W.; Haczku, A.; Knudsen, L.; Possmayer, F. Recent advances in alveolar biology: Evolution and function of alveolar proteins. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 173, S43–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikaar, J.C.; Voorhout, W.F.; van Golde, L.M.; Verhoef, J.; van Strijp, J.A.; van Iwaarden, J.F. Opsonic activities of surfactant proteins A and D in phagocytosis of gram-negative bacteria by alveolar macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniyar, N. Antibody equivalent molecules of the innate immune system: Parallels between innate and adaptive immune proteins. Innate Immun. 2010, 16, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.R. P63 (CKAP4) as an SP-A receptor: Implications for surfactant turnover. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 25, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, M.; Grant, S.; Korfhagen, T.; Scheule, R.K.; Whitsett, J.A. Surfactant protein-D regulates the postnatal maturation of pulmonary surfactant lipid pool sizes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, C. Role of surfactant protein A (SP-A)/lipid interactions for SP-A functions in the lung. Pediatr. Pathol. Mol. Med. 2001, 20, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawgood, S. Surfactant protein B: Structure and function. Biol. Neonate 2004, 85, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, S.; Beers, M.F. Surfactant protein C: Its unique properties and emerging immunomodulatory role in the lung. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J. Structure and properties of surfactant protein C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1408, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, F.; Schicht, M.; Paulsen, F.; Ngueya, I.; Bräuer, L.; Brandt, W. “SP-G”, a putative new surfactant protein--tissue localization and 3D structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.A.; Hammel, M.; Schwarz, J.; Heschl, K.M.; Bretschneider, N.; Flemmer, A.W.; Herber-Jonat, S.; Königshoff, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Holzinger, A. SFTA2—A novel secretory peptide highly expressed in the lung--is modulated by lipopolysaccharide but not hyperoxia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Peukert, N.; Härtig, W.; Emmer, A.; Mahr, C.V.; Richter, C.; Dieckow, J.; Puchta, J.; Pirlich, M.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; et al. Localization, Occurrence, and CSF Changes of SP-G, a New Surface Active Protein with Assumable Immunoregulatory Functions in the CNS. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamvas, A.; Cole, F.S.; Nogee, L.M. Genetic disorders of surfactant proteins. Neonatology 2007, 91, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, N.; Taytard, J.; Duquesnoy, P.; Thouvenin, G.; Corvol, H.; Amselem, S.; Clement, A. Surfactant protein A: A key player in lung homeostasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, S.; Lobsien, D.; Friedrich, B.; Bernhard, M.K.; Gebauer, C.; Dieckow, J.; Gawlitza, M.; Pirlich, M.; Saur, D.; Bräuer, L.; et al. The Cerebral Surfactant System and Its Alteration in Hydrocephalic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Härtig, W.; Mahr, C.V.; Richter, C.; Schob, J.; Puchta, J.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Nestler, U.; Thome, U.; Knüpfer, M.; et al. CSF Surfactant Protein Changes in Preterm Infants After Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 572851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubarth, L.B.; Quinn, J. Respiratory Development and Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Neonatal Netw. 2015, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, S.; Dieckow, J.; Fehrenbach, M.; Peukert, N.; Weiss, A.; Kluth, D.; Thome, U.; Quäschling, U.; Lacher, M.; Preuß, M. Occurrence and colocalization of surfactant proteins A, B, C and D in the developing and adult rat brain. Ann. Anat. 2017, 210, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özek, E.; Kersin, S.G. Intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm babies. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 55, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, S.; Schicht, M.; Sel, S.; Stiller, D.; Kekulé, A.S.; Kekulé, A.; Paulsen, F.; Maronde, E.; Bräuer, L. The detection of surfactant proteins A, B, C and D in the human brain and their regulation in cerebral infarction, autoimmune conditions and infections of the CNS. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, A.W.; Helmke, B.P.; Blackman, B.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanisms of mechanotransduction. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinicke, A.; Härtig, W.; Winter, K.; Puchta, J.; Mages, B.; Michalski, D.; Emmer, A.; Otto, M.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Reimann, W.; et al. Surfactant Protein-G in Wildtype and 3xTg-AD Mice: Localization in the Forebrain, Age-Dependent Hippocampal Dot-like Deposits and Brain Content. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Calle, M.; Olmeda, B.; Dietl, P.; Frick, M.; Pérez-Gil, J. Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-B promotes exocytosis of lamellar bodies in alveolar type II cells. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4600–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, W.R.; Ross, G.F.; Singleton, F.M.; Dingle, S.; Whitsett, J.A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 1987, 63, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochvíl, A.; Hrncír, E. Correlations between the cerebrospinal fluid surface tension value and 1. Concentration of total proteins 2. Number of cell elements. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2002, 21, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Brydon, H.L.; Hayward, R.; Harkness, W.; Bayston, R. Physical properties of cerebrospinal fluid of relevance to shunt function. 2: The effect of protein upon CSF surface tension and contact angle. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 9, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, O. Die Oberflächenspannung in Serum und Liquor. In Ergebnisse der Inneren Medizin und Kinderheilkund; Czerny, A., Müller, F., Pfaundler, M., Schittenhelm, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosina, J.; Kvasnák, E.; Suta, D.; Kolárová, H.; Málek, J.; Krajci, L. Temperature dependence of blood surface tension. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56 (Suppl. S1), S93–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Ariki, S.; Sohma, H.; Nishitani, C.; Inoue, K.; Ebata, N.; Takahashi, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kuronuma, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Pulmonary surfactant protein A protects lung epithelium from cytotoxicity of human β-defensin 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15034–15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Nag, K.; Booth, V.; Smyth, E.; Dueck, H.; Fritzen-Garcia, M.; Ghosh, C.; Panda, A.K. Paradoxical Bactericidal Effects of Hydrophobic Lung Surfactant Proteins and Their Peptide Mimics Using Liposome Molecular Trojan. J. Oleo Sci. 2018, 67, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group Description | IVH 1 without/before Intervention | IVH 1 4–28 Days after Intervention | IVH 1 44–357 Days after Intervention | Hydrocephalus | Sepsis and Brain Infection | Controls |
| N | 24 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 7 | 37 |
| Mean age (days) |
3–29
(15.46) |
11–49
(31.29) |
59–389
(115.21) |
2–5416
(637.92) |
2–16
(7.57) | 2–30,698 (12,093.81) |
| CSF surface tension (mN/m) |
39.2–57.50
(52.06) |
47.23–56.62
(52.87) |
53.25–58.70
(56.23) | 48.40–68.77 (58.32) | 56.34–63.49 (60.88) | 50.66–68.27 (58.55) |
| SP-A (ng/mL) |
0.83–6.48
(3.87) |
1.88–6.52
(4.32) |
1.27–6.23
(3.39) |
0.63–1.93
(1.10) | 0.15 2 | 0.11–0.83 (0.41) |
| SP-B (ng/mL) |
15.14–176.06
(64.31) |
4.75–178.92
(74.24) |
0.00–134.54
(59.92) | 0.00 | 0.92 2 | 0.00–1.92 (0.47) |
| SP-C (ng/mL) |
0.00–17.02
(3.17) |
0.00–9.92
(3.28) |
0.00–5.80
(1.60) |
0.82–3.09
(1.73) |
0.40–1.71
(1.16) | 0.23–2.26 (0.65) |
| SP-D (ng/mL) |
9.91–115.94
(59.18) |
17.3–116.14
(63.18) |
0.83–62.61
(24.07) |
1.96–8.32
(5.96) | 4.40 2 | 2.81–9.85 (5.01) |
| SP-G (ng/mL) |
0.09–9.38
(3.44) |
0.65–8.42
(2.28) |
0.18–2.56
(1.22) |
0.00–4.06
(0.69) |
1.11–7.65
(4.35) | 0.00–2.79 (0.37) |
| Cell count |
6–5729
(394.86) |
4–724
(110.07) |
1–551
(63.71) |
1–68
(14.50) | 3–7772 (1302.67) | 0–58 (3.80) |
| Glucose (mmol/L) |
0.22–4.34
(1.07) |
0.11–1.28
(0.63) |
0.39–3.24
(1.62) |
2.08–3.53
(2.86) |
1.48–2.83
(2.26) | 2.59–4.84 (3.48) |
| Lactate (mmol/L) |
0.82–4.88
(3.15) |
1.40–4.54
(3.19) |
1.70–3.65
(2.27) |
1.26–2.12
(1.56) |
0.75–2.18
(1.52) | 1.00–4.90 (1.74) |
| Total CSF protein (mg/L) | 383.30–5640.90 (1860.71) | 607.60–3615.10 (2138.71) | 350.40–3525.40 (1528.07) | 73.00–864.80 (221.93) | 610.00–2121.80 (1216.66) | 137.00–4150.00 (492.62) |
| SP-A ng/mL | SP-B ng/mL | SP-C ng/mL | SP-D ng/mL | SP-G ng/mL | Cell Count | Glucose | Lactose | Protein mg/L | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST mN/m | Corr. coeff. | −0.663 | −0.577 | −0.381 | −0.450 | −0.385 | −0.476 | 0.521 | −0.565 | −0.504 |
| Sig. (2-side) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| N | 58 | 57 | 79 | 58 | 106 | 100 | 99 | 92 | 100 | |
| SP-A ng/mL | Corr. coeff. | 0.754 | 0.271 | 0.736 | 0.728 | 0.698 | −0.605 | 0.662 | 0.743 | |
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | 0.041 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| N | 57 | 57 | 58 | 57 | 50 | 49 | 48 | 51 | ||
| SP-B ng/mL | Corr. coeff. | 0.265 | 0.778 | 0.754 | 0.634 | −0.644 | 0.520 | 0.788 | ||
| Sig. (2-sided) | 0.049 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| N | 56 | 57 | 56 | 49 | 48 | 47 | 50 | |||
| SP-C ng/mL | Corr. coeff. | 0.302 | 0.424 | 0.341 | −0.436 | 0.295 | 0.332 | |||
| Sig. (2-sided) | 0.022 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.016 | 0.005 | ||||
| N | 57 | 78 | 71 | 69 | 66 | 71 | ||||
| SP-D ng/mL | Corr. coeff. | 0.672 | 0.547 | −00.659 | 0.521 | 0.748 | ||||
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| N | 57 | 50 | 49 | 48 | 51 | |||||
| SP-G ng/mL | Corr. coeff. | 0.574 | −0.607 | 0.489 | 0.738 | |||||
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| N | 97 | 96 | 90 | 97 | ||||||
| Cell Count | Corr. coeff. | −0.658 | 0.492 | 0.635 | ||||||
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| N | 96 | 90 | 97 | |||||||
| Glucose | Corr. coeff. | −0.669 | −0.668 | |||||||
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| N | 90 | 96 | ||||||||
| Lactate | Corr. coeff. | 0.634 | ||||||||
| Sig. (2-sided) | <0.001 | |||||||||
| N | 89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reger, R.M.; Meinicke, A.; Härtig, W.; Knüpfer, M.; Thome, U.; Schob, S.; Krause, M. Changes in CSF Surface Tension in Relation to Surfactant Proteins in Children with Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111440
Reger RM, Meinicke A, Härtig W, Knüpfer M, Thome U, Schob S, Krause M. Changes in CSF Surface Tension in Relation to Surfactant Proteins in Children with Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111440
Chicago/Turabian StyleReger, Rieka M., Anton Meinicke, Wolfgang Härtig, Matthias Knüpfer, Ulrich Thome, Stefan Schob, and Matthias Krause. 2022. "Changes in CSF Surface Tension in Relation to Surfactant Proteins in Children with Intraventricular Hemorrhage" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111440
APA StyleReger, R. M., Meinicke, A., Härtig, W., Knüpfer, M., Thome, U., Schob, S., & Krause, M. (2022). Changes in CSF Surface Tension in Relation to Surfactant Proteins in Children with Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111440







