Brain Network Research of Skilled Shooters in the Shooting Preparation Stage under the Condition of Limited Sensory Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
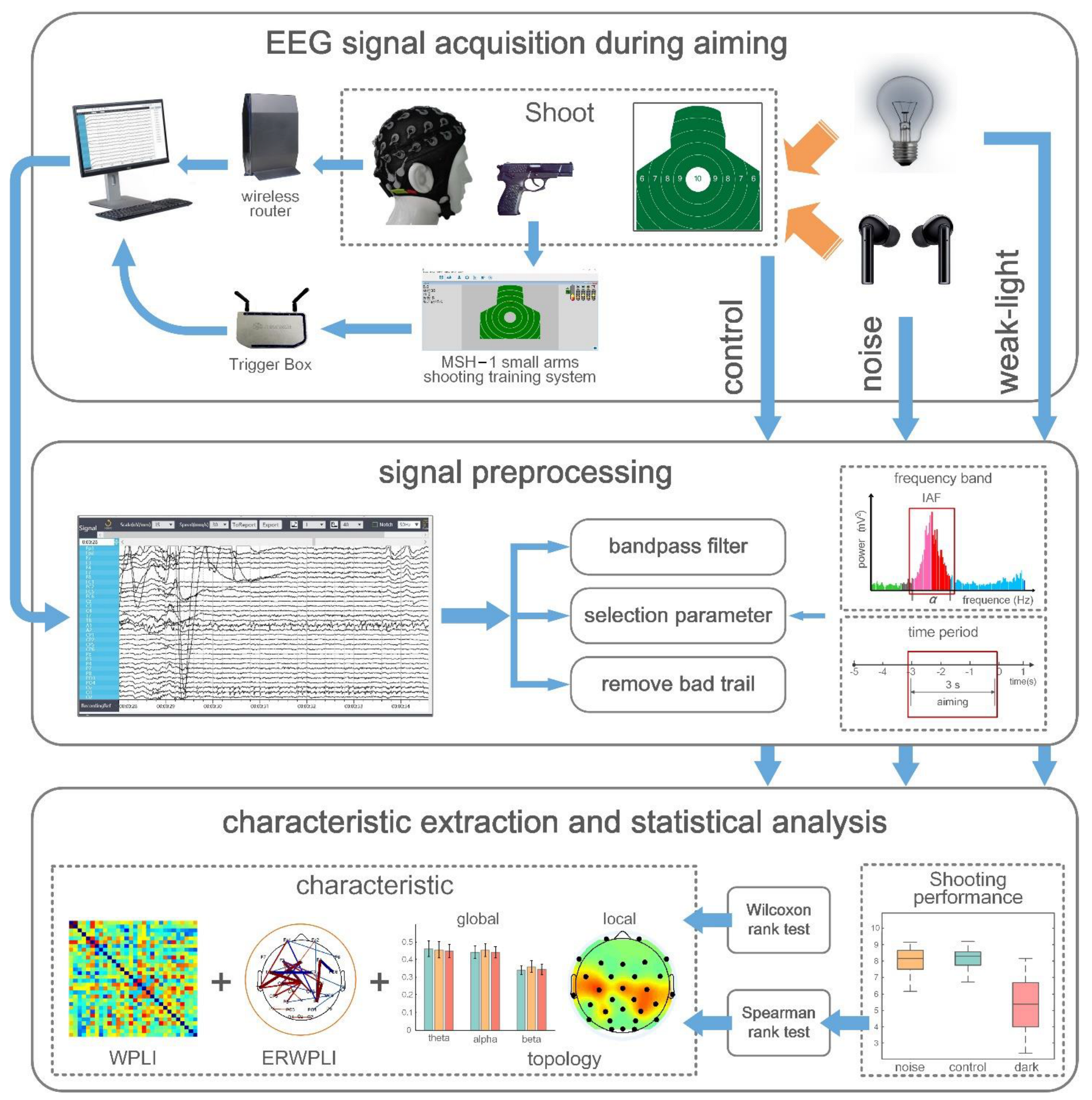
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Environment Setting
2.3. EEG Acquisition
2.4. Signal Preprocessing
2.5. EEG Functional Connectivity Based on WPLI
2.6. Functional Brain Network Characteristics during Aiming
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Shooting Performance Differences
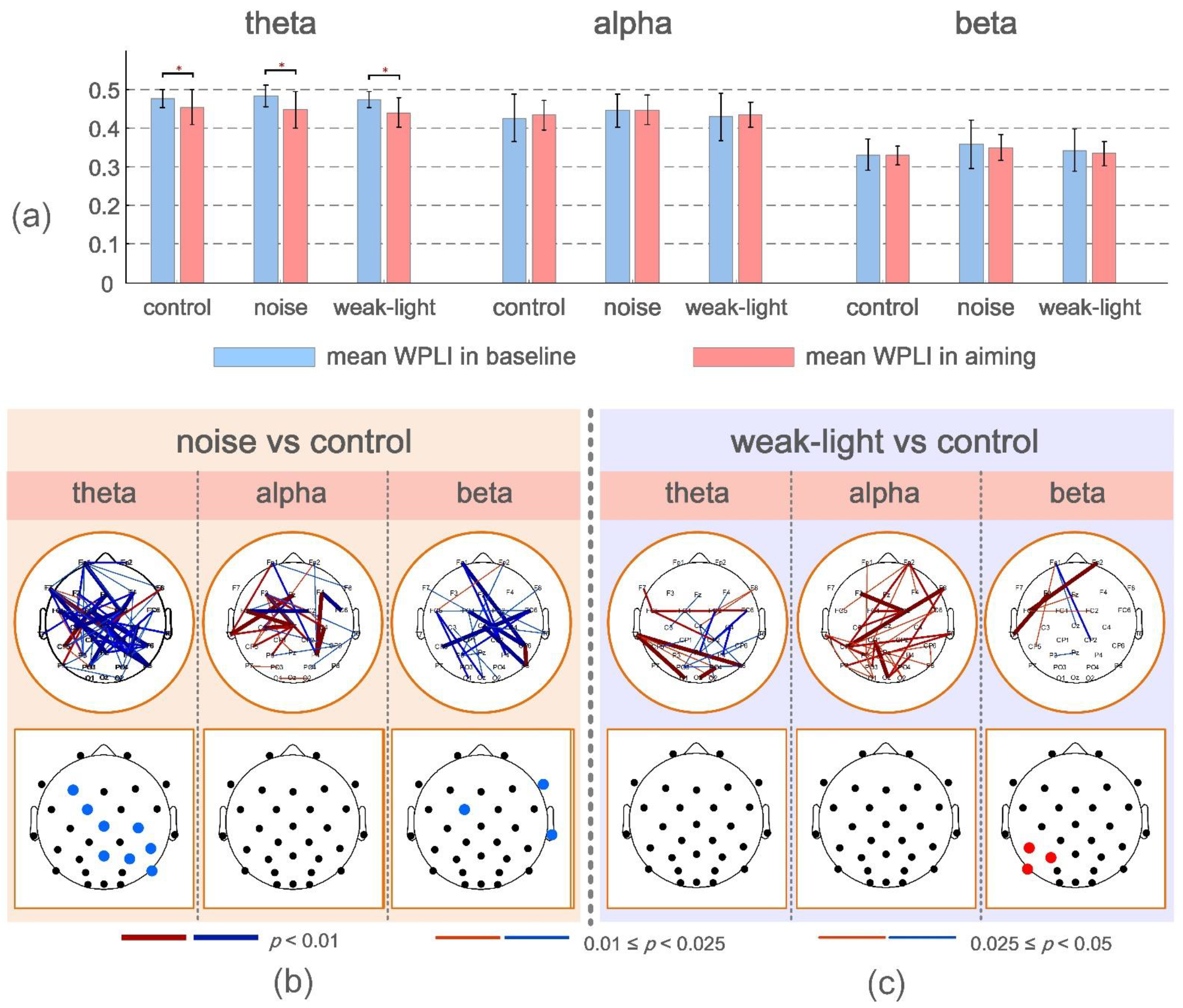
3.2. Functional Connectivity Differences during Aiming
3.3. Differences in Functional Connectivity Changes
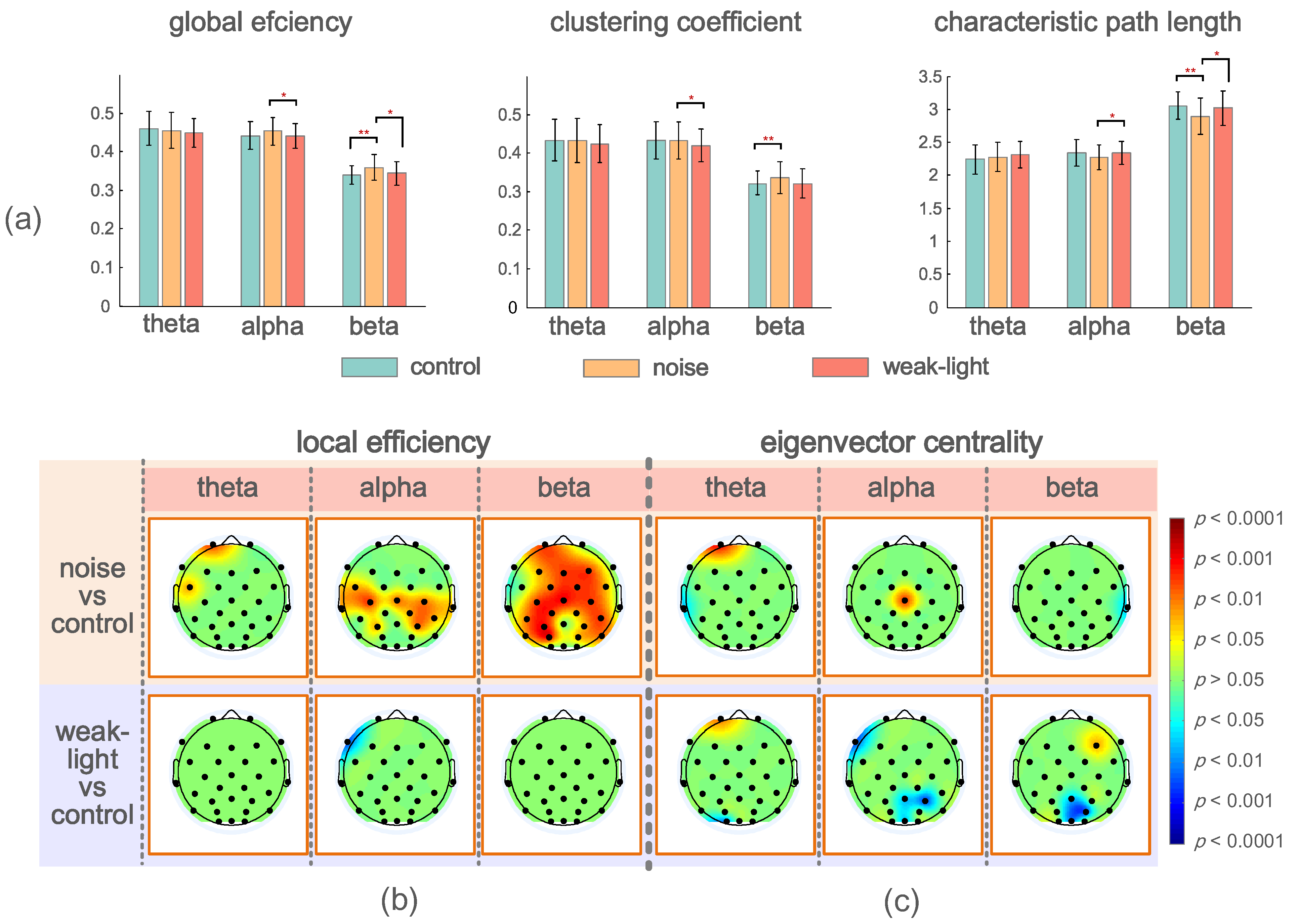
3.4. Differences in Topological Characteristics of Brain Networks
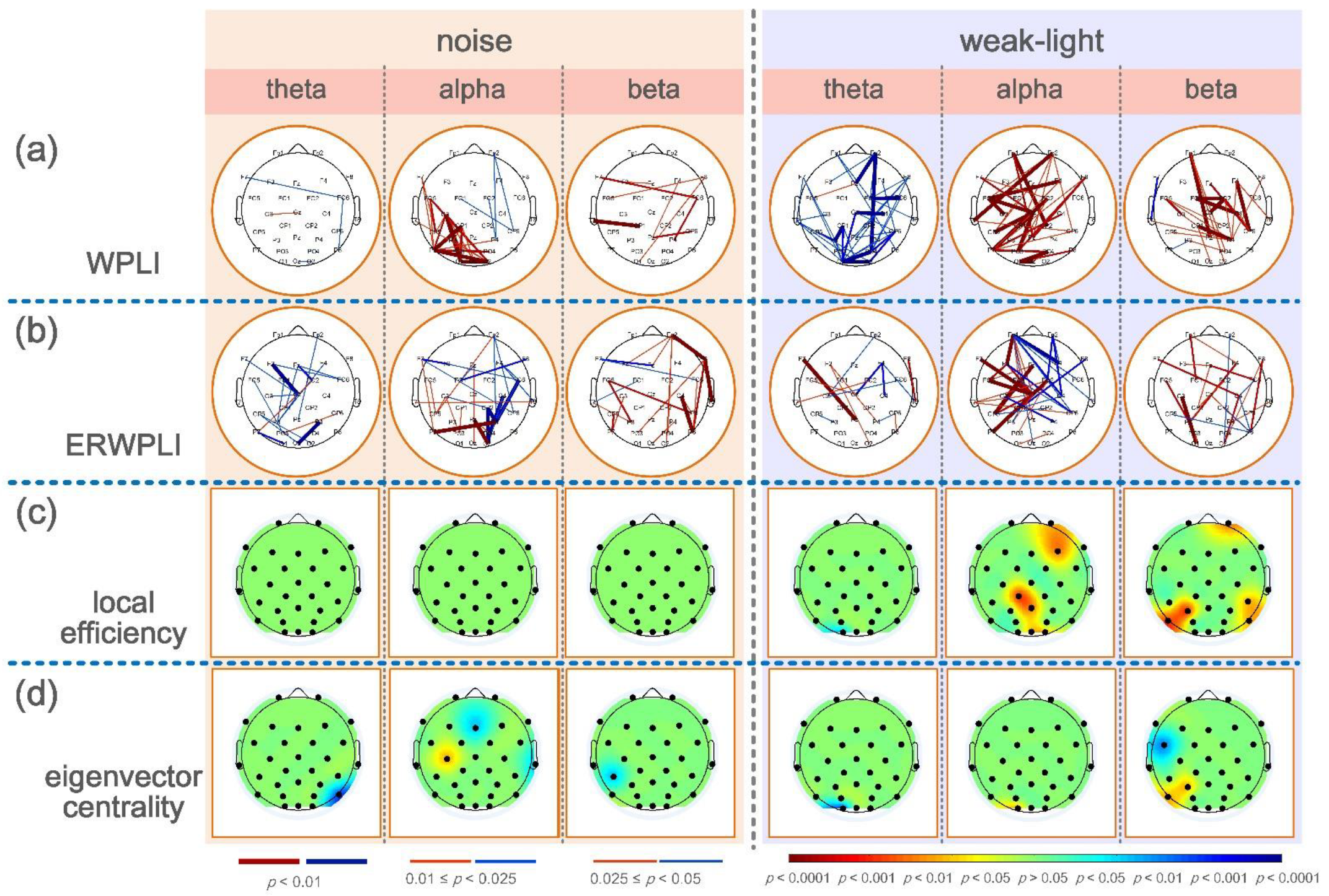
3.5. Correlation between Brain Network Characteristics and Shooting Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Functional Connection Difference during Aiming
4.2. Analysis of the Dynamic Change of Function Connection in the Shooting Preparation Stage
4.3. Analysis of Differences in Brain Network Topology during Aiming
4.4. Correlation Analysis between Brain Network Characteristics and Firing Performance in the Shooting Preparation Stage
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, F.L. EEG: Origin and measurement. In EEg-fMRI; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, G.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. Characteristic differences between the brain networks of high-level shooting athletes and non-athletes calculated using the phase-locking value algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 51, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gu, R.; Peng, W.; Hu, L. Demystifying signal processing techniques to extract task-related EEG responses for psychologists. Brain Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorghis, C.I.; Terry, P.C. Inside Sport Psychology; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Loze, G.M.; Collins, D.; Holmes, P.S. Pre-shot EEG alpha-power reactivity during expert air-pistol shooting: A comparison of best and worst shots. J. Sports Sci. 2001, 19, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Li, P.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y. Efficiency and enhancement in attention networks of elite shooting and archery athletes. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, B.D.; Daniel, M.L.; William, J.R. Cognitive processes during self-paced motor performance: An electroencephalographic profile of skilled marksmen. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1984, 6, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallicchio, G.; Finkenzeller, T.; Sattlecker, G.; Lindinger, S.; Hoedlmoser, K. Shooting under cardiovascular load: Electroencephalographic activity in preparation for biathlon shooting. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 109, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, H.; Sandbakk, Ø.; Schubert, M.; Ettema, G.; Baumeister, J. A Comparison of Frontal Theta Activity During Shooting among Biathletes and Cross-Country Skiers before and after Vigorous Exercise. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Yujin, K. Inter-and intrahemispheric EEG coherence and visuomotor performance during shooting competition and practice. Sens. Mot. Ski. 2017, 124, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; Ji, L.; Cheng, J.; Wu, F. Preshooting electroencephalographic activity of professional shooters in a competitive state. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6639865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, W.; Yan, T.; Song, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, B.; Go, R.; Huang, Q.; Wu, J. Beta-band functional connectivity influences audiovisual integration in older age: An EEG study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekelenburg, J.J.; Vroomen, J.; de Gelder, B. Illusory sound shifts induced by the ventriloquist illusion evoke the mismatch negativity. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 357, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.M.G.; Foxe, J.J.; Murray, M.M.; Higgins, B.A.; Javitt, D.C.; Schroeder, C.E. Attention-dependent suppression of distracter visual input can be cross-modally cued as indexed by anticipatory parieto–occipital alpha-band oscillations. Cogn. Brain Res. 2001, 12, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkowski, D.; Molholm, S.; Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Foxe, J.J. Oscillatory beta activity predicts response speed during a multisensory audiovisual reaction time task: A high-density electrical mapping study. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Benjamin, W. Noise and occupational health and safety. In Proceedings of the First European Forum on Efficient Solutions for Managing Occupational Noise Risks, Noise at Work, Lille, France, 3–5 July 2007; pp. 851–856. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, J.; Jing, D.; Xiaowei, L. The effect of noise content and level on cognitive performance measured by electroencephalography (EEG). Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, D.E. The current state of noise research: Reply to Poulton. Psychol. Bull. 1978, 85, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, M.; Lachmann, T.; Schlittmeier, S.; Hellbruck, J. The irrelevant sound effect in short-term memory: Is there developmental change? Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2010, 22, 1168–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marois, A.; Marsh, J.E.; Vachon, F. Is auditory distraction by changing-state and deviant sounds underpinned by the same mechanism? Evidence from pupillometry. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 14, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, M.K.; Unsworth, N. Working memory capacity offers resistance to mind-wandering and external distraction in a context-specific manner. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2015, 29, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, F.B.R. The cognitive determinants of behavioral distraction by deviant auditory stimuli: A review. Psychol. Res. 2014, 78, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppeney, U. The effects of visual deprivation on functional and structural organization of the human brain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, J.C.B.; VanRullen, R.; Bremmer, F. Dynamics of visual sensory echoes following short-term visual deprivation. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2020, 1, tgaa012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroojerdi, B.; Bushara, K.O.; Corwell, B.; Immisch, I.; Battaglia, F.; Muellbacher, W.; Cohen, L.G. Enhanced excitability of the human visual cortex induced by short-term light deprivation. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisser, V.; Stilla, R.; Peltier, S.; Hu, X.; Sathian, K. Short-term visual deprivation alters neural processing of tactile form. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 166, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeny, S.P.; Haufler, A.J.; Saffer, M.; Hatfield, B.D. Electroencephalographic coherence during visuomotor performance: A comparison of cortico-cortical communication in experts and novices. J. Mot. Behav. 2009, 41, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.R.S.; de Melo Rocha, K.; Gupta, D.; Marinho, V.; Moura, I.; Fernandes, J.R.N.; Magalhães, F.E.X.; da Silva, V.N.C.; Alves, E.H.P.; Ribeiro, P.; et al. Bromazepam changes performance during target shooting but does not affect the interhemispheric coupling in the theta rhythm of the electroencephalography. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e33110918174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, Y. Time–frequency cross mutual information analysis of the brain functional networks underlying multiclass motor imagery. J. Mot. Behav. 2018, 50, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Percio, C.; Iacoboni, M.; Lizio, R.; Marzano, N.; Infarinato, F.; Vecchio, F.; Bertollo, M.; Robazza, C.; Comani, S.; Limatola, C.; et al. Functional coupling of parietal alpha rhythms is enhanced in athletes before visuomotor performance: A coherence electroencephalographic study. Neuroscience 2011, 175, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. Rifle shooting performance correlates with electroencephalogram beta rhythm network activity during aiming. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 4097561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, K.A.; Hoffman, R.R.; Kozbelt, A.; Williams, A.M. The Cambridge Handbook of Expertise and Expert Performance; Cambridge University Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. Memory processes, brain oscillations and EEG synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1996, 24, 61–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Percio, C.; Infarinato, F.; Marzano, N.; Iacoboni, M.; Aschieri, P.; Lizio, R.; Soricelli, A.; Limatola, C.; Rossini, P.M.; Babiloni, C. Reactivity of alpha rhythms to eyes opening is lower in athletes than non-athletes: A high-resolution EEG study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 82, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, C.; Scherer, R.; Graimann, B.; Supp, G.; Pfurtscheller, G. Online control of a brain-computer interface using phase synchronization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinck, M.; Oostenveld, R.; Van Wingerden, M.; Battaglia, F.; Pennartz, C.M. An improved index of phase-synchronization for electrophysiological data in the presence of volume-conduction, noise and sample-size bias. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scally, B.; Burke, M.R.; Bunce, D.; Delvenne, J.F. Resting-state EEG power and connectivity are associated with alpha peak frequency slowing in healthy aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, F.; Gong, A.; Qu, Y.; Bao, A.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. From Expert to Elite?—Research on Top Archer’s EEG Network Topology. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 759330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinov, M.; Kötter, R.; Hagmann, P.; Sporns, O. Brain connectivity toolbox: A collection of complex network measurements and brain connectivity datasets. Neuroimage 2009, 47, S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Network-based statistic: Identifying differences in brain networks. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumbley, J.R.; Friston, K.J. False discovery rate revisited: FDR and topological inference using Gaussian random fields. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Liu, F.; Jiang, C.; Fu, Y. Correlation Between Resting-state Electroencephalographic Characteristics and Shooting Performance. Neuroscience 2017, 366, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O. Brain connectivity. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, D.A.; Lynch, C.J.; Cheng, K.M.; Menon, V. Underconnectivity between voice-selective cortex and reward circuitry in children with autism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 9, 12060–12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N. Oscillatory interactions between sensorimotor cortex and the periphery. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.B.; Warm, J.S.; Dember, W.N.; Hancock, P.A. Effects of jet engine noise and performance feedback on perceived workload in a monitoring task. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1995, 5, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzbani, H.; Marateb, H.R.; Mansourian, M. Neurofeedback: A comprehensive review on system design, methodology and clinical applications. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, L.J. Brain lateralization and cognitive capacity. Animals 2021, 11, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheron, G.; Petit, G.; Cheron, J.; Leroy, A.; Cebolla, A.; Cevallos, C.; Petieau, M.; Hoellinger, T.; Zarka, D.; Clarinval, A.-M.; et al. Brain oscillations in sport: Toward EEG biomarkers of performance. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Hwang, G.; Curran, T.; Kahana, M.J. EEG oscillations and recognition memory: Theta correlates of memory retrieval and decision making. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.F.; Zambrano-Vazquez, L.; Allen, J.J. Theta lingua franca: A common mid-frontal substrate for action monitoring processes. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.F.; Zambrano-Vazquez, L.; Allen, J.J. Frontal theta as a mechanism for cognitive control. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 18, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, J.; Mario, B.; Boualem, M. Effect of neurofeedback training on the neural substrates of selective attention in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 394, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, H.; Holger, G.; Ute, S. Annotation: Neurofeedback–train your brain to train behaviour. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhiguo, Z. EEG Signal Processing and Feature Extraction; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onnela, J.P.; Saramäki, J.; Kertész, J.; Kaski, K. Intensity and coherence of motifs in weighted complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 065103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Rao, N.; Lin, P. The reorganization of human brain networks modulated by driving mental fatigue. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 21, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. Network attributes for segregation and integration in the human brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, D.; Nadeau, L.; Kröger, H. Fastest learning in small-world neural networks. Phys. Lett. 2005, A 336, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.S.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Achard, S.; Duke, T.; Bullmore, E. Adaptive reconfiguration of fractal small-world human brain functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19518–19523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufler, A.J.; Spalding, T.W.; Santa Maria, D.L.; Hatfield, B.D. Neuro-cognitive activity during a self-paced visuospatial task: Comparative EEG profiles in marksmen and novice shooters. Biol. Psychol. 2000, 53, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelle, C.M.; Hatfield, B.D. Visual attention and brain processes that underlie expert performance: Implications for sport and military psychology. Mil. Psychol. 2008, 20 (Suppl. S1), S39–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, F.; Gong, A.; Qu, Y.; Lu, L.; Shi, Q.; Fu, Y. Brain Network Research of Skilled Shooters in the Shooting Preparation Stage under the Condition of Limited Sensory Function. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101373
Gu F, Gong A, Qu Y, Lu L, Shi Q, Fu Y. Brain Network Research of Skilled Shooters in the Shooting Preparation Stage under the Condition of Limited Sensory Function. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(10):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101373
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Feng, Anmin Gong, Yi Qu, Ling Lu, Qidi Shi, and Yunfa Fu. 2022. "Brain Network Research of Skilled Shooters in the Shooting Preparation Stage under the Condition of Limited Sensory Function" Brain Sciences 12, no. 10: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101373
APA StyleGu, F., Gong, A., Qu, Y., Lu, L., Shi, Q., & Fu, Y. (2022). Brain Network Research of Skilled Shooters in the Shooting Preparation Stage under the Condition of Limited Sensory Function. Brain Sciences, 12(10), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12101373




