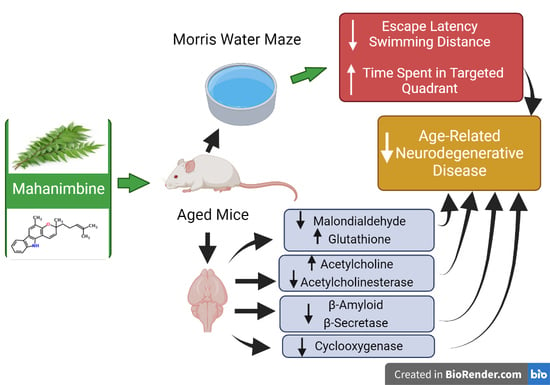
Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction and Isolation of Mahanimbine
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Mahanimbine Administration
2.4. Behavioral Assessment of Memory by the Morris Water Maze (MWM)
2.5. Collection of Brain Samples
2.6. Evaluation of Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Glutathione (GSH) Levels
2.7. Estimation of Acetylcholine (ACh) and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activities
2.8. Measurement of β-Amyloid Levels
2.9. Assessment of β-Secretase (BACE-1) Activity in Mouse Brain
2.10. Measurement of Total Cyclooxygenase (COX) Activity
2.11. Gene Expression of BACE-1 and COX-2
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mahanimbine-Enhanced Memory in Aged Mice
3.2. Effect of Mahanimbine on MDA and GSH Levels in the Aged Mouse Brain
3.3. Mahanimbine Improved the Cholinergic Activity in the Aged Mouse Brain
3.4. Mahanimbine Inhibited Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 in the Aged Mouse Brain
3.5. Mahanimbine Inhibited BACE-1 Activity and Expression in the Aged Mouse Brain
3.6. Effects of Mahanimbine on Total Cyclooxygenase (COX) Activity and COX-2 Expression in the Aged Mouse Brain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piskovatska, V.; Strilbytska, O.; Koliada, A.; Vaiserman, A.; Lushchak, O. Health benefits of anti-aging drugs. Subcell. Biochem. 2019, 91, 339–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenzweig, E.S.; Barnes, C.A. Impact of aging on hippocampal function: Plasticity, network dynamics, and cognition. Prog. Neurobiol. 2003, 69, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.R.; Wilhelm, E.A.; Jesse, C.R.; Brandão, R.; Nogueira, C.W. Protective effect of caffeine and a selective A2A receptor antagonist on impairment of memory and oxidative stress of aged rats. Exp. Geront. 2011, 46, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.; Zheng, S.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Protective effects of taurine against inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in brain injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Kalra, J.; Mani, V.; Ramasamy, K.; Majeed, A.B. Pharmacological approaches for Alzheimer’s disease: Neurotransmitter as drug targets. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I. β-Amyloid: The known unknowns. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.R.; Holler, C.J.; Webb, R.L.; Li, F.; Beckett, T.L.; Murphy, M.P. BACE1 and BACE2 enzymatic activities in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H.; Bohr, V.A. Signaling by cGAS-STING in neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and aging. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, R.M.; Kitt, M.M.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. Neuroinflammation in the normal aging hippocampus. Neuroscienece 2015, 309, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, V.; Jaafar, S.M.; Azahan, N.S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; Ming, L.C.; Majeed, A.B.A. Ciproxifan improves cholinergic transmission, attenuates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress but does not reduce amyloid level in transgenic mice. Life Sci. 2017, 180, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, Y.; Kikuzaki, H.; Lajis, N.H.; Nakatani, N. Comparison of antioxidative properties of carbazole alkaloids from Murraya koenigii leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6461–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saied, S.; Hassan, F.; Naz, S.; Siddiqi, H. Carbazole alkaloids from stem bark of Murraya koenigii (L.) Spreng. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 11, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dineshkumar, B.; Mitra, A.; Manjunatha, M. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effects of mahanimbine (carbazole alkaloid) from Murraya koenigii (Rutaceae) Leaves. Int. J. Phytomed. 2010, 2, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, T.; Yang, N.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Anticancer effects of Mahanimbine alkaloid on the human bladder cancer cells are due to the induction of G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy. JBUON 2020, 25, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Knolker, H.J.; Reddy, K.R. Biological and pharmacological activities of carbazole alkaloids. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2008, 65, 181–193. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, M.; Parle, M. Antiamnesic potential of Murraya koenigii leaves. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Ramasamy, K.; Ahmad, A.; Parle, M.; Shah, S.A.; Majeed, A.B. Protective effects of total alkaloidal extract from Murraya koenigii leaves on experimentally induced dementia. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Azahan, N.S.; Mani, V.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; Johari James, R.M.; Alsharidah, M.; Alhowail, A.; Abdul Majeed, A.B. Mahanimbine-induced neuroprotection via cholinergic system and attenuated amyloidogenesis as well as neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharides-induced mice. Phcog. Mag. 2020, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Azahan, N.S.; Mani, V.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; Alhowail, A.; Sajid, S.; Majeed, A.A. Neuroprotective potential of mahanimbine against lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced neuronal deficits on SK-N-SH cells and antioxidant potentials in ICR mice brain. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2019, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakurta, I.G.; Banerjee, P.; Bagh, M.B.; Ghosh, A.; Sahoo, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chakrabarti, S. Combination of N-acetylcysteine, α-lipoic acid and α-tocopherol substantially prevents the brain synaptosomal alterations and memory and learning deficits of aged rats. Exp. Geront. 2014, 50, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallaberry, C.; Nunes, F.; Costa, M.S.; Fioreze, G.T.; Ardais, A.P.; Botton, P.H.; Klaudat, B.; Forte, T.; Souza, D.O.; Elisabetsky, E.; et al. Chronic caffeine prevents changes in inhibitory avoidance memory and hippocampal BDNF immunocontent in middle-aged rats. Neuropharmacolgy 2013, 64, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaola, D.; Tijana, M.; Andrea, C.; Angela, L.; Domenico, D. ROS, cell senescence, and novel molecular mechanisms in aging and age-related diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 3565127. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateshappa, C.; Harish, G.; Mythri, R.B.; Mahadevan, A.; Bharath, M.M.; Shankar, S.K. Increased oxidative damage and decreased antioxidant function in aging human substantia nigra compared to striatum: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, D.; Colloca, G.; Monaco, M.R.L.; Cesari, M. Effects of antioxidant supplementation on the aging process. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. Food sources of selenium and its relationship with chronic diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrola, M.J.; de Castro, A.J.; Pitombeira, M.H.; Barbosa, M.C.; Quixadá, A.T.; Duarte, F.B.; Gonçalves, R.P. Serum concentrations of nitrite and malondialdehyde as markers of oxidative stress in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2012, 34, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.M.; Hasan, S.M.; Alam, T.; Hasan, A.T.; Hossain, I.; Didar, R.R.; Alam, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Taladafil enhances working memory and reduces hippocampal oxidative stress in both young and aged mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 745, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Wu, Q.P.; Yang, X.F.; Wei, M.K.; Zhang, J.M.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, X.Y. l-Malate reverses oxidative stress and antioxidative defenses in liver and heart of aged rats. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, Y.; Kikuzaki, H.; Lajis, N.H.; Nakatani, N. Antioxidative activity of carbazoles from Murraya koenigii leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5589–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmo, M.E. The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartus, R.T.; Dean, R.3; Beer, B.; Lippa, A.S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 1982, 217, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Choi, S.H.; Koo, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, H. Novel cognitive improving and neuroprotective activities of Polygala Tenuifolia willdenow extract, BT-11. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 70, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGleenon, B.M.; Dynan, K.B.; Passmore, A.P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Pharm. 1999, 48, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Bhadra, S.; Saha, B.P.; Pal, B.C. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of a carbazole alkaloid, mahanimbine, from Murraya koenigii. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xekardaki, A.; Kovari, E.; Gold, G.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Giacobini, E.; Herrmann, F.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Bouras, C. Neuropathological changes in aging brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 821, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Hwang, B.R.; Lee, M.H.; Cho, E.J. Perilla frutescens var. japonica and rosmarinic acid improve amyloid-β25–35 induced impairment of cognition and memory function. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthias, S.; Carsten, S.; Walter, R.; Chen, X.; Marcus, F.; Nikolaus, G. Comparison of Alzheimer Aβ(1-40) and Aβ(1-42) amyloid fibrils reveals similar protofilament structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19813–19818. [Google Scholar]
- Vassar, R. BACE1: The beta-secretase enzyme in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 23, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, S.L.; Vassar, R. The role of amyloid precursor protein processing by BACE1, the beta-secretase, in Alzheimer disease pathophysiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29621–29625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.U.; de Vellis, J. Microglia in health and disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mani, V.; Mohd Azahan, N.S.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; Abdul Majeed, A.B. Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010012
Mani V, Mohd Azahan NS, Ramasamy K, Lim SM, Abdul Majeed AB. Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMani, Vasudevan, Nur Syamimi Mohd Azahan, Kalavathy Ramasamy, Siong Meng Lim, and Abu Bakar Abdul Majeed. 2022. "Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation" Brain Sciences 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010012
APA StyleMani, V., Mohd Azahan, N. S., Ramasamy, K., Lim, S. M., & Abdul Majeed, A. B. (2022). Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation. Brain Sciences, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010012