18F–THK–5351, Fluorodeoxyglucose, and Florbetaben PET Images in Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pictorial Insight into Disease Pathophysiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. 18F–THK–5351 PET Imaging Acquisition
2.4. 18F–Fluorodeoxyglucose PET Imaging Acquisition
2.5. 18F–Florbetaben PET Imaging Acquisition
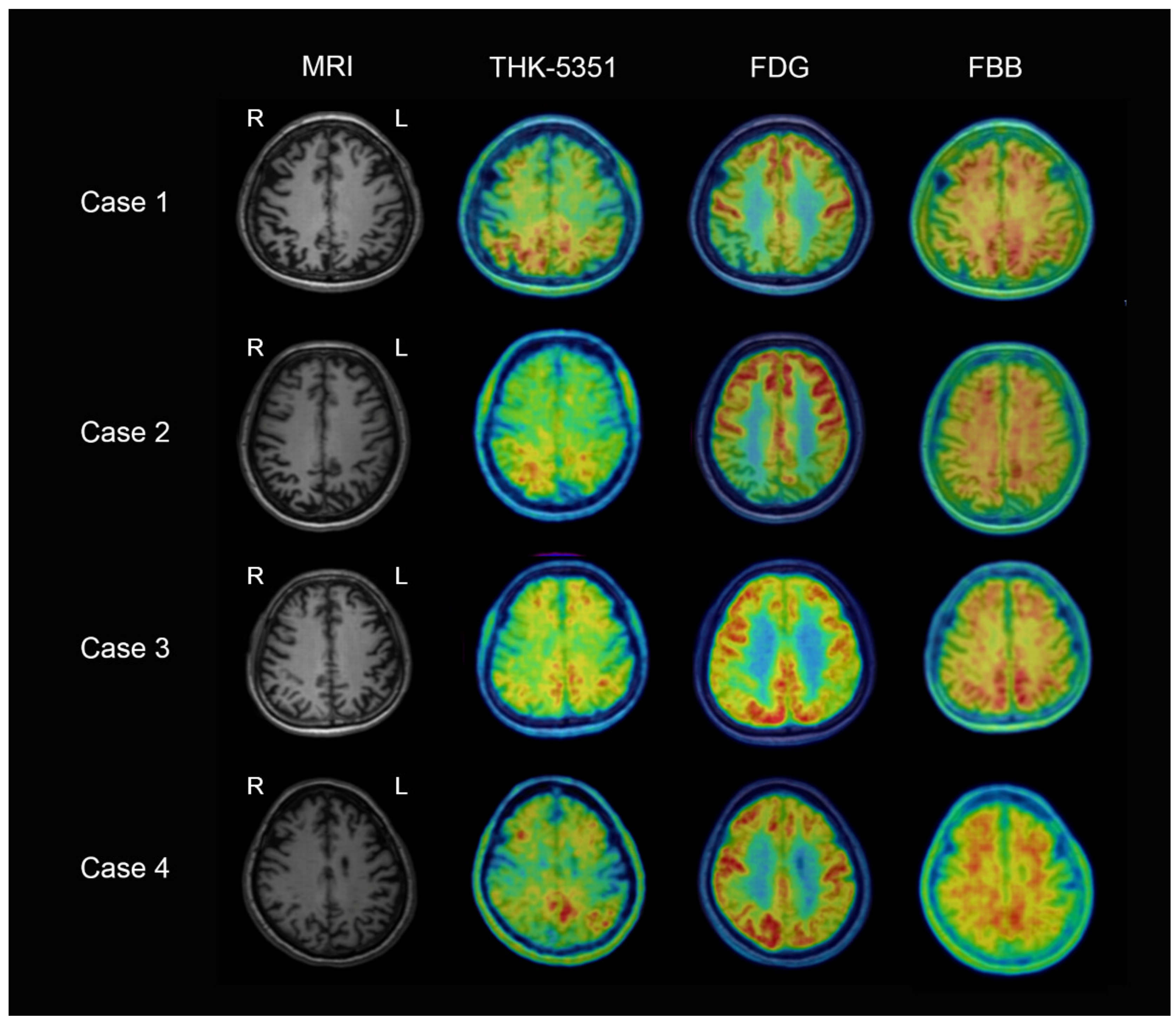
3. Results
3.1. Case 1 (PCA)
3.2. Case 2 (PCA)
3.3. Case 3 (lpvPPA)
3.4. Case 4 (lpvPPA)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuzy, A.; Chiotis, K.; Lemoine, L.; Gillberg, P.G.; Almkvist, O.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Nordberg, A. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies-still a challenge. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1112–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.; Chalkidou, A.; Hammers, A.; Peacock, J.; Summers, J.; Keevil, S. Diagnostic accuracy of (18)F amyloid PET tracers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, J.C.; Li, C.; Bodea, L.G.; Martinez-Marmol, R.; Meunier, F.A.; Gotz, J. Amyloid-beta and tau complexity—Towards improved biomarkers and targeted therapies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, J.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Schneider, J.A.; Abisambra, J.F.; Abner, E.L.; Alafuzoff, I.; Arnold, S.E.; Attems, J.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; et al. Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): A common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutch, S.J.; Schott, J.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Murray, M.; Snowden, J.S.; van der Flier, W.M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Vandenberghe, R.; Ahmed, S.; Bak, T.H.; et al. Consensus classification of posterior cortical atrophy. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, R.; Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Furukawa, K.; Ishiki, A.; Tomita, N.; Tago, T.; Hiraoka, K.; Watanuki, S.; Shidahara, M.; et al. 18F-THK5351: A Novel PET Radiotracer for Imaging Neurofibrillary Pathology in Alzheimer Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.P.; Pascoal, T.A.; Mathotaarachchi, S.; Therriault, J.; Kang, M.S.; Shin, M.; Guiot, M.C.; Guo, Q.; Harada, R.; Comley, R.A.; et al. Monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, selegiline, reduces (18)F-THK5351 uptake in the human brain. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Harada, R.; Ishiki, A.; Kikuchi, A.; Nakamura, T.; Kudo, Y. The development and validation of tau PET tracers: Current status and future directions. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2018, 6, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.J.; Oh, J.S.; Oh, M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Roh, J.H.; Kim, J.S. The clinical feasibility of deep learning-based classification of amyloid PET images in visually equivocal cases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Chin, J.; Park, A.; Lee, B.H.; Suh, M.K.; Seo, S.W.; Na, D.L. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): A useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Schonhaut, D.R.; Baker, S.L.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Ghosh, P.M.; Santos, M.; Miller, Z.A.; Bettcher, B.M.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; et al. Tau, amyloid, and hypometabolism in a patient with posterior cortical atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Schonhaut, D.R.; Scholl, M.; Lockhart, S.N.; Ayakta, N.; Baker, S.L.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Lazaris, A.; Cantwell, A.; et al. Tau PET patterns mirror clinical and neuroanatomical variability in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 1551–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Ghosh, P.M.; Madison, C.; Laforce, R., Jr.; Corbetta-Rastelli, C.; Weiner, M.W.; Greicius, M.D.; Seeley, W.W.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Rosen, H.J.; et al. Diverging patterns of amyloid deposition and hypometabolism in clinical variants of probable Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2013, 136, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Graff-Radford, J.; Tosakulwong, N.; Weigand, S.D.; Machulda, M.M.; Senjem, M.L.; Spychalla, A.J.; Vemuri, P.; Jones, D.T.; Drubach, D.A.; et al. Imaging correlations of tau, amyloid, metabolism, and atrophy in typical and atypical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintini, I.; Schwarz, C.G.; Martin, P.R.; Graff-Radford, J.; Machulda, M.M.; Senjem, M.L.; Reid, R.I.; Spychalla, A.J.; Drubach, D.A.; Lowe, V.J.; et al. Regional multimodal relationships between tau, hypometabolism, atrophy, and fractional anisotropy in atypical Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintini, I.; Martin, P.R.; Graff-Radford, J.; Senjem, M.L.; Schwarz, C.G.; Machulda, M.M.; Spychalla, A.J.; Drubach, D.A.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Longitudinal tau-PET uptake and atrophy in atypical Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, N.J.; Perrin, R.J.; Franklin, E.E.; Carter, D.; Vincent, B.; Xie, M.; Bateman, R.J.; Benzinger, T.; Friedrichsen, K.; Brooks, W.S.; et al. Neuropathologic assessment of participants in two multi-center longitudinal observational studies: The Alzheimer Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN). Neuropathology 2015, 35, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Dickson, D.W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jack, C.R.; Boyle, P.A.; Arfanakis, K.; Rademakers, R.; Alafuzoff, I.; Attems, J.; Brayne, C.; et al. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): Consensus working group report. Brain 2019, 142, 1503–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E. New insights into atypical Alzheimer’s disease in the era of biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, J.S.; Roh, J.H.; Chung, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, J.S. Clinical Evaluation of 18F-PI-2620 as a Potent PET Radiotracer Imaging Tau Protein in Alzheimer Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases Compared With 18F-THK-5351. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/Sex | 49/F | 47/F | 58/M | 56/F |
| Onset age | 47 | 44 | 53 | 54 |
| Disease duration (years) | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| Education (years) | 9 | 16 | 14 | 8 |
| Initial presentation | Losing directions, dressing apraxia | Visual agnosia | Word finding difficulty | Language disturbance |
| Clinical diagnosis | PCA | PCA | lpvPPA | lpvPPA |
| MMSE | 21(<0.01%ile) | 23 (<0.01%ile) | 8 (<0.01%ile) | 17 (<0.01%ile) |
| SNSB subdomain (percentile (z-score)) | ||||
| Stroop CR | <0.01 (−5.89) | < 0.01 (−5.15) | N.A. | <0.01 (−5.34) |
| K-BNT | 1.3 (−2.23) | <0.01 (−11.75) | <0.01 (−11.77) | <0.01 (−3.98) |
| DS-F | 63.89 (0.36) | 41.99 (−0.20) | 0.17 (−2.93) | 5.49 (−1.60) |
| DS-B | 1.5 (−2.17) | 9.40 (−1.32) | N.A. | <0.01 (−4.00) |
| SVLT-immediate | 43.64 (−0.16) | 0.08 (−3.17) | <0.01 (−5.91) | 0.73 (−2.44) |
| SVLT-delayed | 1.04 (−2.31) | 1.07 (−2.30) | 0.02 (−3.61) | 0.30 (−2.75) |
| SVLT-recognition | 24.39 (−0.69) | 8.97 (−1.34) | 21.94 (−0.77) | 59.73 (0.25) |
| RCFT-immediate | 0.4 (−2.65) | 0.03 (−3.45) | 0.44 (−2.62) | 0.85 (−2.39) |
| RCFT-delayed | 0.19 (−2.89) | 0.02 (−3.60) | 0.02 (−3.49) | 1.66 (−2.13) |
| RCFT-recognition | 0.01 (−3.70) | 0.85 (−2.39) | <0.01 (−5.15) | 11.43 (−1.20) |
| RCFT copy | <0.01 (−14.24) | <0.01 (−23.49) | 39.76 (−0.26) | <0.01 (−7.16) |
| COWAT (Animal) | 6.63 (−1.50) | 12.85 (−1.13) | N.A. | 0.59 (−2.52) |
| COWAT (Supermarket) | 3.59 (−1.80) | 13.40 (−1.11) | N.A. | 1.16 (−2.27) |
| COWAT phonemic total | 3.9 (−1.76) | 40.82 (−0.23) | N.A. | N.A. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Oh, M.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, Y.W.; Roh, J.-H. 18F–THK–5351, Fluorodeoxyglucose, and Florbetaben PET Images in Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pictorial Insight into Disease Pathophysiology. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040465
Park S, Oh M, Kim JS, Lee J-H, Yoon YW, Roh J-H. 18F–THK–5351, Fluorodeoxyglucose, and Florbetaben PET Images in Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pictorial Insight into Disease Pathophysiology. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(4):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040465
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sohee, Minyoung Oh, Jae Seung Kim, Jae-Hong Lee, Young Wook Yoon, and Jee-Hoon Roh. 2021. "18F–THK–5351, Fluorodeoxyglucose, and Florbetaben PET Images in Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pictorial Insight into Disease Pathophysiology" Brain Sciences 11, no. 4: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040465
APA StylePark, S., Oh, M., Kim, J. S., Lee, J.-H., Yoon, Y. W., & Roh, J.-H. (2021). 18F–THK–5351, Fluorodeoxyglucose, and Florbetaben PET Images in Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pictorial Insight into Disease Pathophysiology. Brain Sciences, 11(4), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040465





