Functional Gait Recovery after a Combination of Conventional Therapy and Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Muscle Activation Pattern: An EMG Preliminary Study on Subjects Subacute Post Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. The Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training
2.3. Outcome Measurements
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, T.; Cempini, M.; Oddo, C.M.; Vitiello, N. Review of assistive strategies in powered lower-limb orthoses and exoskeletons. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 64, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártolo, P.; Bidanda, B. Bio-Materials and Prototyping Applications in Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 139–164. [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau, H. Locomotor Training in Neurorehabilitation: Emerging Rehabilitation Concepts. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2003, 17, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiero, S.; Poli, P.; Rosati, G.; Zanotto, D.; Iosa, M.; Paolucci, S.; Morone, G. The value of robotic systems in stroke rehabilitation. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2013, 11, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morone, G.; Paolucci, S.; Cherubini, A.; De Angelis, D.; Venturiero, V.; Coiro, P.; Iosa, M. Robot-assisted gait training for stroke patients: Current state of the art and perspectives of robotics. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chan, C.K.; Guo, Z.; Yu, H. A Review of Lower Extremity Assistive Robotic Exoskeletons in Rehabilitation Therapy. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, D.R.; Eng, J.J. Powered robotic exoskeletons in post-stroke rehabilitation of gait: A scoping review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2016, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Gasperini, G.; Cannaviello, G.; Guanziroli, E. Exoskeleton and End-Effector Robots for Upper and Lower Limbs Rehabilitation: Narrative Review. PM&R 2018, 10, S174–S188. [Google Scholar]
- Tedla, J.S.; Dixit, S.; Gular, K.; Abohashrh, M. Robotic-Assisted Gait Training Effect on Function and Gait Speed in Subacute and Chronic Stroke Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 81, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, T.B.; Thrift, A.G.; Collier, J.M.; Churilov, L.; Dewey, H.M.; Donnan, G.A.; Bernhardt, J. Very early mobilization after stroke fast-tracks return to walking: Further results from the phase II AVERT randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2011, 42, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesing, C.; Fisch, G.; O’Donnell, M.; Shahidi, I.; Thomas, L.; Mummidisetty, C.K.; Williams, K.J.; Takahashi, H.; Rymer, W.Z.; Jayaraman, A. Effects of a wearable exoskeleton stride management assist system (SMA®) on spatiotemporal gait characteristics in individuals after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ding, L.; Chen, N.; Mao, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, L. Improved walking ability with wearable robot-assisted training in patients suffering chronic stroke. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, S329–S340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, G.; Gaffuri, M.; Guanziroli, E.; Goffredo, M.; Puornajaf, S.; Galafate, D.; Russo, E.; Filoni, S.; Franceschini, M.; Molteni, F. Recovery of gait function with a wearable powered exoskeleton in sub-acute stroke patients using SEMG for fine tuning: Preliminary results. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Guanziroli, E.; Pournajaf, S.; Gaffuri, M.; Gasperini, G.; Filoni, S.; Baratta, S.; Damiani, C.; Franceschini, M.; Molteni, F.; et al. Overground wearable powered exoskeleton for gait training in subacute stroke subjects: Clinical and gait assessments. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 55, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffredo, M.; Iacovelli, C.; Russo, E.; Pournajaf, S.; Di Blasi, C.; Galafate, D.; Pellicciari, L.; Agosti, M.; Filoni, S.; Aprile, I.; et al. Stroke Gait Rehabilitation: A Comparison of End-Effector, Overground Exoskeleton, and Conventional Gait Training. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Guanziroli, E.; Goffredo, M.; Calabrò, R.; Pournajaf, S.; Gaffuri, M.; Gasperini, G.; Filoni, S.; Baratta, S.; Galafate, D.; et al. Gait Recovery with an Overground Powered Exoskeleton: A Randomized Controlled Trial on Subacute Stroke Subjects. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournajaf, S.; Goffredo, M.; Agosti, M.; Massucci, M.; Ferro, S.; Franceschini, M. The Italian Study Group on Implementation of Stroke Care (ISC Study) Community ambulation of stroke survivors at 6 months follow-up: An observational study on sociodemographic and sub-acute clinical indicators. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 55, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, K.; Lee, M.; Chang, W.H.; Choi, B.O.; Ryu, G.-H.; Kim, Y.-H. Training for walking efficiency with a wearable hip-assist robot in patients with stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2019, 50, 3545–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capecci, M.; Pournajaf, S.; Galafate, D.; Sale, P.; Le Pera, D.; Goffredo, M.; Franceschini, M. Clinical effects of robot-assisted gait training and treadmill training for Parkinson’s disease. A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, S.; Meloni, F.; Bracalenti, M.; De Filippis, M.L. The effectiveness of powered, active lower limb exoskeletons in neurorehabilitation: A systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Carter, J.N.; Nixon, M.S. 2D markerless gait analysis. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, Antwerp, Belgium, 23–27 November 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Goffredo, M.; Carli, M.; Conforto, S.; Bibbo, D.; Neri, A.; D’Alessio, T. Evaluation of Skin and Muscular Deformations in a non-rigid motion analysis. In Medical Imaging 2005: Physiology, Function, and Structure from Medical Images; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5746, pp. 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Arippa, F.; Pau, M.; Cimolin, V.; Stocchi, F.; Goffredo, M.; Franceschini, M.; Galli, M. A novel summary kinematic index for postural characterization in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, L.; Nielsen, J.F.; Felici, F.; Moreno, J.C.; Pons, J.L.; Farina, D. Motor modules in robot-aided walking. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.C.; Barroso, F.; Farina, D.; Gizzi, L.; Santos, C.; Molinari, M.; Pons, J.L. Effects of robotic guidance on the coordination of locomotion. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, G.; Iosa, M.; Tamburella, F.; Muzzioli, L.; Pisotta, I.; Moreno, J.C.; Molinari, M. An EMG pattern comparison of exoskeleton vs. end-effector robotic device for assisted walking training. In Replace, Repair, Restore, Relieve–Bridging Clinical and Engineering Solutions in Neurorehabilitation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Torricelli, D.; Barroso, F.; Coscia, M.; Alessandro, C.; Lunardini, F.; Esteban, E.B.; d’Avella, A. Muscle synergies in clinical practice: Theoretical and practical implications. In Emerging Therapies in Neurorehabilitation II; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 251–272. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asseldonk, E.H.F.; Veneman, J.F.; Ekkelenkamp, R.; Buurke, J.H.; Van Der Helm, F.C.T.; Van Der Kooij, H. The Effects on Kinematics and Muscle Activity of Walking in a Robotic Gait Trainer during Zero-Force Control. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2008, 16, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Bellitto, A.; Mandraccia, S.; Marchesi, G.; Pellegrino, L.; Coscia, M.; Casadio, M. Exoskeleton for Gait Rehabilitation: Effects of Assistance, Mechanical Structure, and Walking Aids on Muscle Activations. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swank, C.; Wang-Price, S.; Gao, F.; Almutairi, S.; Bogey, R.; Peng, Y.; Osgouei, R.H. Walking With a Robotic Exoskeleton Does Not Mimic Natural Gait: A Within-Subjects Study. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2019, 6, e11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, I.; Iacovelli, C.; Goffredo, M.; Cruciani, A.; Galli, M.; Simbolotti, C.; Pecchioli, C.; Padua, L.; Galafate, D.; Pournajaf, S.; et al. Efficacy of end-effector Robot-Assisted Gait Training in subacute stroke patients: Clinical and gait outcomes from a pilot bi-centre study. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 45, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kammen, K.; Boonstra, A.M.; Van Der Woude, L.H.V.; Reinders-Messelink, H.A.; Otter, R.D. Differences in muscle activity and temporal step parameters between Lokomat guided walking and treadmill walking in post-stroke hemiparetic patients and healthy walkers. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hu, G.; Ran, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of bodyweight support and guidance force on muscle activation during Locomat walking in people with stroke: A cross-sectional study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androwis, G.J.; Pilkar, R.; Ramanujam, A.; Nolan, K.J. Electromyography Assessment during Gait in a Robotic Exoskeleton for Acute Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, R.S.; Naro, A.; Russo, M.; Bramanti, P.; Carioti, L.; Balletta, T.; Buda, A.; Manuli, A.; Filoni, S.; Bramanti, A. Shaping neuroplasticity by using powered exoskeletons in patients with stroke: A randomized clinical trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylos-Labini, F.; La Scaleia, V.; D’Avella, A.; Pisotta, I.; Tamburella, F.; Scivoletto, G.; Molinari, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Van Asseldonk, E.; et al. EMG patterns during assisted walking in the exoskeleton. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.K.; Kadone, H.; Watanabe, H.; Marushima, A.; Yamazaki, M.; Sankai, Y.; Suzuki, K. Lateral Symmetry of Synergies in Lower Limb Muscles of Acute Post-stroke Patients After Robotic Intervention. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.H. The evolution of clinical gait analysis part l: Kinesiological EMG. Gait Posture 2001, 14, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwarts, M.J.; Stegeman, D.F. Multichannel surface EMG: Basic aspects and clinical utility. Muscle Nerve 2003, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogrel, J.-Y. Clinical applications of surface electromyography in neuromuscular disorders. Neurophysiol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 35, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Feldner, H.A.; Howell, D.; Kelly, V.E.; McCoy, S.W.; Steele, K.M. “Look, Your Muscles Are Firing!” A Qualitative Study of Clinician Perspectives on the Use of Surface Electromyography in Neurorehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigo, C.; Crenna, P. Multichannel SEMG in clinical gait analysis: A review and state-of-the-art. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, R.; Boresta, M.; Fusco, F.; Tronci, E.; Di Gemma, E.; Palagi, L.; Franceschini, M. Data of patients undergoing rehabilitation programs. Data Brief 2020, 30, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, C.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M.; Goffredo, M.; Franceschini, M.; Servidio, M.; Bernetti, A. Trade-Offs with rehabilitation Effectiveness (REs) and Efficiency (REy) in a sample of Italian disabled persons in a in post-acuity rehabilitation unit. Ann Ig 2020, 32, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, D.L.; Quinlivan, J.M.; Owen, B.F.; Payne, P.; Nelson, K.C.; Abel, M.F. What does the Ashworth scale really measure and are instrumented measures more valid and precise? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Infarinato, F.; Pournajaf, S.; Romano, P.; Ottaviani, M.; Pellicciari, L.; Galafate, D.; Gabbani, D.; Gison, A.; Franceschini, M. Barriers to sEMG Assessment During Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Subacute Stroke Patients. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater Reliability of a Modified Ashworth Scale of Muscle Spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.; Bohannon, R.W. Criterion validity of lower extremity Motricity Index scores. Clin. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M.K.; Gill, K.M.; Magliozzi, M.R.; Nathan, J.; Piehl-Baker, L. Clinical Gait Assessment in the Neurologically Impaired. Phys. Ther. 1984, 64, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchignoni, F.P.; Tesio, L.; Ricupero, C.; Martino, M.T. Trunk Control Test as an Early Predictor of Stroke Rehabilitation Outcome. Stroke 1997, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, S.; Connell, L. The psychometric properties and clinical utility of measures of walking and mobility in neurological conditions: A systematic review. Clin. Rehabil. 2009, 23, 1018–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B.; Merletti, R.; Stegeman, D.; Blok, J.; Rau, G.; Hägg, G. European recommendations for surface electromyography. Roessingh Res. Dev. 1999, 8, 13–54. [Google Scholar]
- Alemi, M.M.; Geissinger, J.; Simon, A.A.; Chang, S.E.; Asbeck, A.T. A passive exoskeleton reduces peak and mean EMG during symmetric and asymmetric lifting. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 47, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoloni, M.; Mangone, M.; Scettri, P.; Procaccianti, R.; Cometa, A.; Santilli, V. Segmental muscle vibration improves walking in chronic stroke patients with foot drop: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, T.A.; Do, K.P.; Rethlefsen, S.A.; Healy, B. Cross-correlation as a method for comparing dynamic electromyography signals during gait. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2714–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, F.; Mengarelli, A.; Burattini, L.; Maranesi, E.; Agostini, V.; Nascimbeni, A.; Knaflitz, M.; Fioretti, S. Normative EMG patterns of ankle muscle co-contractions in school-age children during gait. Gait Posture 2016, 46, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.A.; Corona, F.; Pilloni, G.; Porta, M.; Fastame, M.C.; Hitchcott, P.K.; Penna, M.P.; Pau, M.; Côté, J.N. Sex-dependent and sex-independent muscle activation patterns in adult gait as a function of age. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.L.; Huang, H.J.; Little, V.L.; Patten, C. Electromyography Exposes Heterogeneity in Muscle Co-Contraction following Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buurke, J.H.; Nene, A.V.; Kwakkel, G.; Erren-W olters, V.; Ijzerman, M.J.; Hermens, H.J. Recovery of Gait after Stroke: What Changes? Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

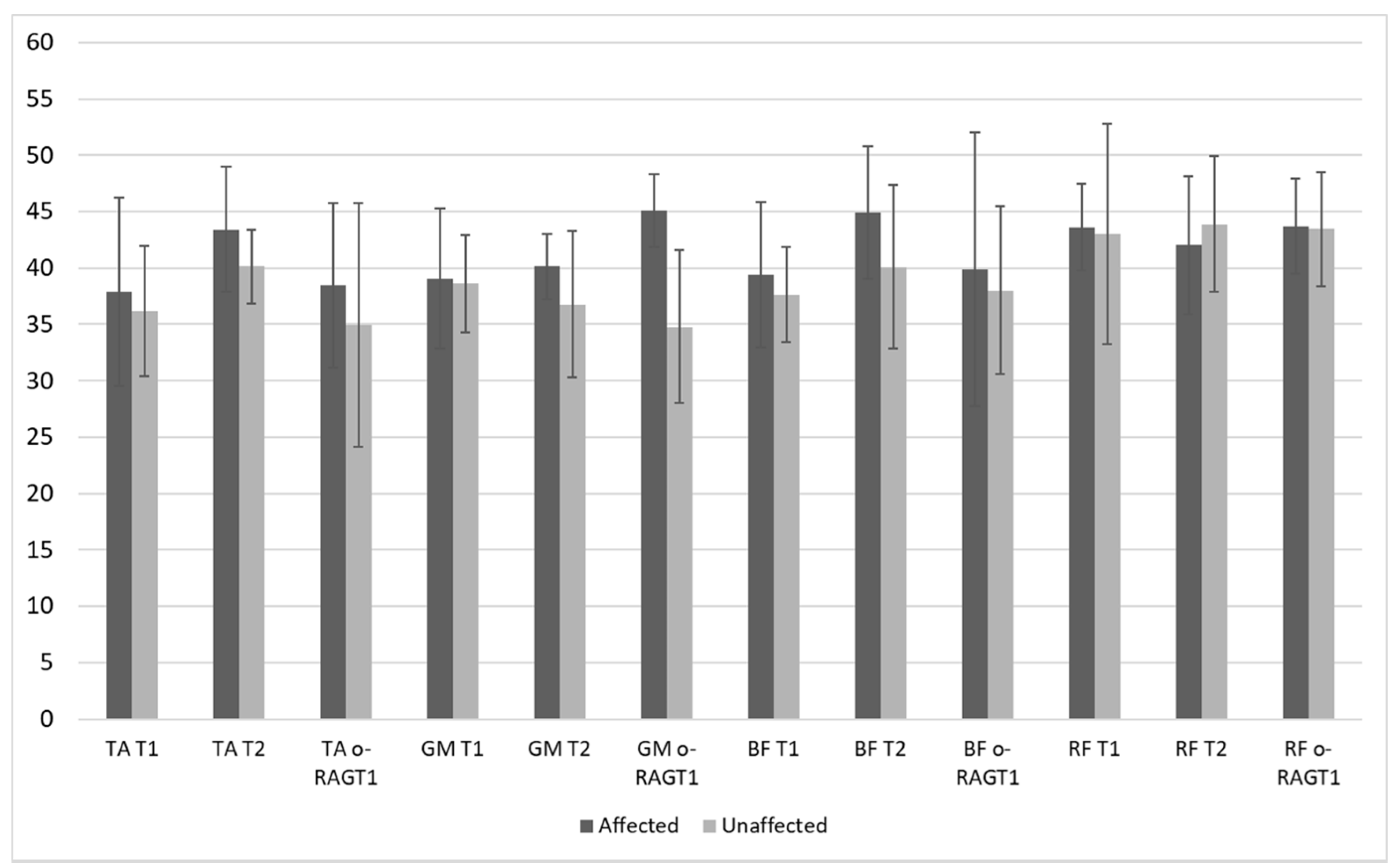
| ID | Age (Years) | Gender | AS | AOT (Days) | MAS-AL | MI-AL | FAC | TCT | 10MWT (m/s) and Type of Assistive Device | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | |||||
| S02 | 64 | M | R | 11 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 60 | 76 | 2 | 4 | 87 | 100 | 0.44 Wa | 0.62 NoS |
| S03 | 69 | M | L | 13 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 64 | 76 | 1 | 3 | 74 | 100 | 0.34 Wa | 0.48 TC |
| S06 | 54 | F | L | 29 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 48 | 65 | 1 | 3 | 61 | 100 | 0.16 AW | 0.32 TC |
| S09 | 50 | M | R | 23 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 43 | 76 | 1 | 4 | 74 | 100 | 0.91 AW | 0.67 NoS |
| S11 | 76 | F | R | 30 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 64 | 76 | 2 | 4 | 87 | 100 | 0.45 Wa | 0.56 NoS |
| S14 | 44 | F | R | 26 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 53 | 76 | 2 | 4 | 74 | 100 | 0.38 Wa | 0.53 NoS |
| S18 | 66 | M | R | 12 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 76 | 82 | 4 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 0.44 NoS | 1.41 No |
| S20 | 66 | M | R | 75 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 70 | 100 | 3 | 4 | 100 | 100 | 1.09 TC | 1.38 NoS |
| ID | TA | GM | BF | RF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | |
| S02 | 0.64 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.71 |
| S03 | 0.83 | n.a. | 0.80 | 0.75 | n.a. | 0.46 | 0.77 | n.a. | 0.82 | 0.87 | n.a. | 0.80 |
| S06 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.59 | 0.91 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.87 | 0.78 |
| S09 | 0.65 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| S11 | 0.68 | n.a. | 0.71 | 0.68 | n.a. | 0.80 | 0.70 | n.a. | 0.68 | 0.85 | n.a. | 0.71 |
| S14 | 0.73 | n.a. | 0.73 | 0.79 | n.a. | 0.75 | 0.81 | n.a. | 0.83 | 0.86 | n.a. | 0.73 |
| S18 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.67 |
| S20 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87 |
| ID | TA-GM_AL | TA-GM_UL | BF-RF_AL | BF-RF_UL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | T1 | o-RAGT1 | T2 | |
| S02 | 12.51 | 12.10 | 20.52 | 18.44 | 22.39 | 38.09 | 32.51 | 15.54 | 22.85 | 43.81 | 33.26 | 36.42 |
| S03 | 24.40 | n.a. | 11.90 | 26.01 | n.a. | 10.02 | 21.45 | n.a. | 29.71 | 23.30 | n.a. | 33.56 |
| S06 | 17.95 | 11.16 | 34.60 | 11.01 | 7.39 | 11.02 | 25.48 | 14.38 | 30.01 | 10.78 | 32.74 | 38.64 |
| S09 | 23.40 | 26.80 | 33.73 | 22.45 | 26.46 | 27.13 | 15.42 | 45.62 | 27.78 | 23.57 | 32.64 | 38.47 |
| S11 | 11.71 | n.a. | 31.30 | 37.81 | n.a. | 30.33 | 31.27 | n.a. | 29.05 | 41.36 | n.a. | 35.27 |
| S14 | 27.33 | n.a. | 35.96 | 24.36 | n.a. | 35.88 | 40.03 | n.a. | 52.33 | 43.86 | n.a. | 36.58 |
| S18 | 18.58 | 25.64 | 22.82 | 10.01 | 22.40 | 21.28 | 36.39 | 32.88 | 29.43 | 30.82 | 49.11 | 23.20 |
| S20 | 15.76 | 25.42 | 25.59 | 24.51 | 28.40 | 39.99 | 22.06 | 17.48 | 31.68 | 26.67 | 18.22 | 28.90 |
| N = 8 | Mean Change Score ± SD | Wilcoxon Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect Size | p-Value | |||||
| BS | ||||||
| TA | 0.04 | ± | 0.11 | 0.83 | 0.04 | |
| GM | −0.08 | ± | 0.16 | −0.39 | 0.38 | |
| BF | 0.04 | ± | 0.13 | 0.33 | 0.46 | |
| RF | −0.05 | ± | 0.12 | −0.22 | 0.64 | |
| CC | ||||||
| TA-GM_AL | 8.10 | ± | 9.66 | 0.50 | 0.25 | |
| TA-GM_UL | 4.89 | ± | 12.12 | 0.39 | 0.38 | |
| BF-RF_AL | 3.53 | ± | 8.72 | 0.33 | 0.46 | |
| BF-RF_UL | 3.36 | ± | 13.21 | 0.11 | 0.84 | |
| RMS | ||||||
| TA_AL | 0.04 | ± | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.38 | |
| GM_AL | −0.01 | ± | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| BF_AL | 0.05 | ± | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.31 | |
| RF_AL | −0.02 | ± | 0.09 | −0.33 | 0.46 | |
| TA_UL | 0.02 | ± | 0.06 | 0.44 | 0.31 | |
| GM_UL | −0.03 | ± | 0.05 | −0.50 | 0.25 | |
| BF_UL | 0.01 | ± | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.95 | |
| RF_UL | 0.00 | ± | 0.08 | −0.11 | 0.84 | |
| N = 5 | Mean Change Score ± SD | Wilcoxon Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect Size | p-Value | |||||
| BS | ||||||
| TA | 0.08 | ± | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.44 | |
| GM | 0.10 | ± | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.44 | |
| BF | 0.08 | ± | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.44 | |
| RF | 0.04 | ± | 0.11 | −0.07 | 1.00 | |
| CC | ||||||
| TA-GM_AL | 2.58 | ± | 6.47 | 0.73 | 0.19 | |
| TA-GM_UL | 4.12 | ± | 5.67 | 0.87 | 0.13 | |
| BF-RF_AL | −1.19 | ± | 18.37 | −0.33 | 0.63 | |
| BF-RF_UL | 6.06 | ± | 14.98 | 0.47 | 0.44 | |
| RMS | ||||||
| TA_AL | 0.03 | ± | 0.04 | 0.73 | 0.19 | |
| GM_AL | 0.05 | ± | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.81 | |
| BF_AL | 0.01 | ± | 0.13 | −0.07 | 1.00 | |
| RF_AL | 0.00 | ± | 0.04 | −0.07 | 1.00 | |
| TA_UL | 0.02 | ± | 0.13 | 0.07 | 1.00 | |
| GM_UL | −0.05 | ± | 0.06 | −0.87 | 0.13 | |
| BF_UL | 0.02 | ± | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.44 | |
| RF_UL | 0.02 | ± | 0.13 | −0.07 | 1.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Infarinato, F.; Romano, P.; Goffredo, M.; Ottaviani, M.; Galafate, D.; Gison, A.; Petruccelli, S.; Pournajaf, S.; Franceschini, M. Functional Gait Recovery after a Combination of Conventional Therapy and Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Muscle Activation Pattern: An EMG Preliminary Study on Subjects Subacute Post Stroke. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040448
Infarinato F, Romano P, Goffredo M, Ottaviani M, Galafate D, Gison A, Petruccelli S, Pournajaf S, Franceschini M. Functional Gait Recovery after a Combination of Conventional Therapy and Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Muscle Activation Pattern: An EMG Preliminary Study on Subjects Subacute Post Stroke. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(4):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040448
Chicago/Turabian StyleInfarinato, Francesco, Paola Romano, Michela Goffredo, Marco Ottaviani, Daniele Galafate, Annalisa Gison, Simone Petruccelli, Sanaz Pournajaf, and Marco Franceschini. 2021. "Functional Gait Recovery after a Combination of Conventional Therapy and Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Muscle Activation Pattern: An EMG Preliminary Study on Subjects Subacute Post Stroke" Brain Sciences 11, no. 4: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040448
APA StyleInfarinato, F., Romano, P., Goffredo, M., Ottaviani, M., Galafate, D., Gison, A., Petruccelli, S., Pournajaf, S., & Franceschini, M. (2021). Functional Gait Recovery after a Combination of Conventional Therapy and Overground Robot-Assisted Gait Training Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Muscle Activation Pattern: An EMG Preliminary Study on Subjects Subacute Post Stroke. Brain Sciences, 11(4), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040448










