Presenting Psychiatric and Neurological Symptoms and Signs of Brain Tumors before Diagnosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
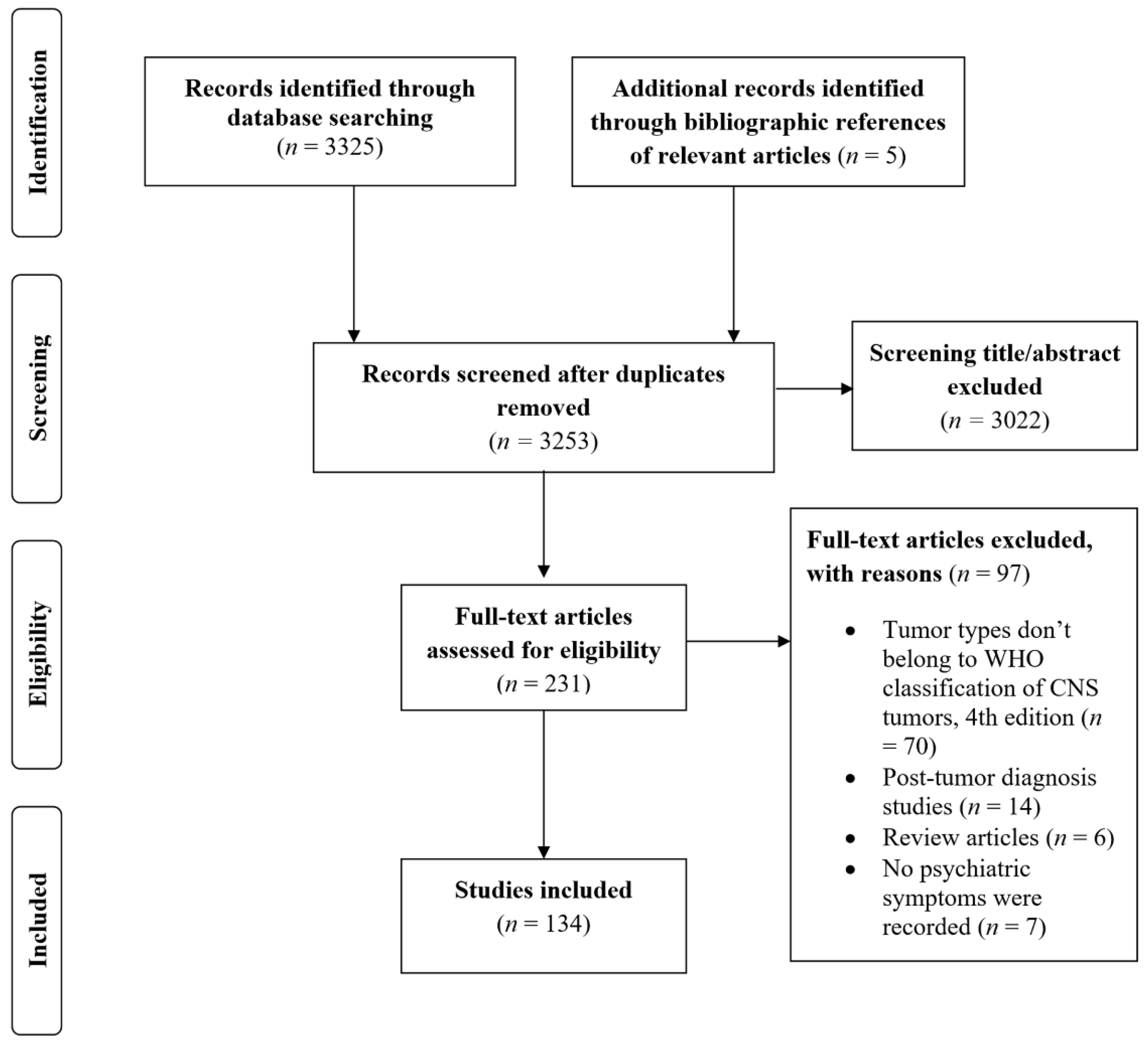
2.1. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
2.2. Analysis of Features of Included Studies
3. Results
3.1. Cases Characteristics
3.2. Onset of Neurological Symptoms Compared to Psychiatric Symptoms in Pediatric Cases
3.3. Onset of Neurological Symptoms Compared to Psychiatric Symptoms in Adult Cases
3.4. Onset of Neurological Symptoms Compared to Psychiatric Symptoms in Older Adult Cases
3.5. Symptoms Associated with Delay in Diagnosis
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Affecting the Clinical Presentation of Brain Tumors
4.2. Which Symptoms and Signs Must Raise Suspicion about A Possible Brain Tumor?
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, V.; Kochar, P. Brain Cancer: Implication to Disease, Therapeutic Strategies and Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery Approaches. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, P. Brain tumours: Incidence, survival, and aetiology. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, ii12–ii17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, G. Number of Diagnoses | CureSearch. Available online: https://curesearch.org/Number-of-Diagnoses (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Halperin, E.C.; Friedman, H.S. Is There a Correlation between Duration of Presenting Symptoms and Stage of Medulloblastoma at the Time of Diagnosis? Cancer 1996, 78, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimi, M.; Peretz Nahum, M.; Ben Arush, M.W. Delay in Diagnosis of Children with Cancer: A Retrospective Study of 315 Children. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2004, 21, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.; Chapman, A.; McNeely, P.D.; Walling, S.; Howes, W.J. Latency between Symptom Onset and Diagnosis of Pediatric Brain Tumors: An Eastern Canadian Geographic Study. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 365–372; discussion 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgeworth, J.; Bullock, P.; Bailey, A.; Gallagher, A.; Crouchman, M. Why Are Brain Tumours Still Being Missed? Arch. Dis. Child. 1996, 74, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, G.; Sosa, F.; Cuccia, V.; Lubieniecky, F.; Monges, J. Lateral Ventricle Tumors in Children: A Series of 54 Cases. Childs Nerv. Syst. 1999, 15, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.; Clarke, C. Early Symptoms of Brain Tumours. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1205–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dobrovoljac, M.; Hengartner, H.; Boltshauser, E.; Grotzer, M.A. Delay in the Diagnosis of Paediatric Brain Tumours. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2002, 161, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keschner, M.; Bender, M.B.; Strauss, I. MENTAL SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH BRAIN TUMOR: A STUDY OF 530 VERIFIED CASES. JAMA 1938, 110, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F.M. The First CT Scan of the Brain: Entering the Neurologic Information Age. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 28, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, W.R. Current Therapy for Brain Tumors: Back to the Future. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reilly, K.M. Brain Tumor Susceptibility: The Role of Genetic Factors and Uses of Mouse Models to Unravel Risk. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLOS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhusoodanan, S.; Ting, M.B.; Farah, T.; Ugur, U. Psychiatric Aspects of Brain Tumors: A Review. World J. Psychiatry 2015, 5, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkstein, S.E.; Petracca, G.; Chemerinski, E.; Kremer, J. Syndromic Validity of Apathy in Alzheimer’s Disease. AJP 2001, 158, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Yasumoto, Y.; Ito, M. Pathological Laughter Caused by Frontal Glioblastoma: Case Report. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2008, 48, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.M.; Swerdlow, R.H. Right Orbitofrontal Tumor With Pedophilia Symptom and Constructional Apraxia Sign. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. Childhood Central Nervous System Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, R.L. Neurologically Silent Brain Tumors in Psychiatric Hospital Admissions: Three Cases and a Review. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1983, 44, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.A.; Williams, D.J.; Stack, B.H. Meningioma in a Chronic Schizophrenic. Scott. Med. J. 1987, 32, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, A.; Giannuzzi, R.; Daini, S.; Bernardini, L.; Petrongolo, L.; Gentiloni Silveri, N. Psychiatric Emergencies (Part III): Psychiatric Symptoms Resulting from Organic Diseases. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17 (Suppl. 1), 86–99. [Google Scholar]
- Blustein, J.; Seeman, M.V. Brain Tumors Presenting as Functional Psychiatric Disturbances. Can. Psychiatr. Assoc. J. 1972, 17, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautricourt, S.; Marzloff, V.; Dollfus, S. Meningiomatosis Revealed by a Major Depressive Syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, I.; Ben Ammar, H.; Nefzi, R.; Mhedhbi, N.; Khelifa, E.; Aissa, A.; El Hechmi, Z. Frontal Meningioma and Bipolar Disorder: Etiopathogenic Link or Co-Morbidity? A Case Report. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selecki, B.R. Intracranial space-occupying lesions among patients admitted to mental hospitals. Med. J. Aust. 1965, 1, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.S.; Shade, M.Y.; Breton, G.; Gilbert, M.R.; Mahajan, A.; Scheurer, M.E.; Vera, E.; Berger, A.M. Sleep-Wake Disturbance in Patients with Brain Tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, L.M. Brain Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, S. Imaging the Brain. Second of Two Parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.; Sadock, B. Mental disorders due to general medical condition. In Synopsis of Psychiatry; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 350–364. [Google Scholar]
- Mardaga, S.; Bassir, M.A.; Bracke, J.; Dutilleux, A.; Born, J.D. Psychiatric Symptoms in Patients with Brain Tumors. Eur. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, N.; Kato, E.; Kanemoto, K. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Associated with Posterior Cranial Fossa Meningioma. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/crips/2017/8164537/ (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Gupta, R.K.; Kumar, R. Benign Brain Tumours and Psychiatric Morbidity: A 5-Years Retrospective Data Analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2004, 38, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Das, A.; Behere, P. Psychiatric Symptoms in Brain Tumor. East. J. Psychiatry 2017, 18, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Starkstein, S.E.; Robinson, R.G.; Price, T.R. Comparison of Cortical and Subcortical Lesions in the Production of Poststroke Mood Disorders. Brain 1987, 110 Pt 4, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusoodanan, S.; Opler, M.G.A.; Moise, D.; Gordon, J.; Danan, D.M.; Sinha, A.; Babu, R.P. Brain Tumor Location and Psychiatric Symptoms: Is There Any Association? A Meta-Analysis of Published Case Studies. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusoodanan, S.; Danan, D.; Moise, D. Psychiatric Manifestations of Brain Tumors: Diagnostic Implications. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.; Hugo, P.; Stapleton, S.; Lask, B. “Anorexia Saved My Life”: Coincidental Anorexia Nervosa and Cerebral Meningioma. Int. J. Eat Disord. 2001, 30, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakhmi, S.; Sidhu, B.S.; Kaur, J.; Kaur, A. Diagnosis of Frontal Meningioma Presenting with Psychiatric Symptoms. Indian J. Psychiatry 2015, 57, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, S.T.; Carey, T.G.; Owens, J.M.; Owens, A.P. Psychiatric Presentation of Frontal Meningiomas. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 1995, 12, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.; Henry, S. Meningioma and Psychosis – Cause or Coincidence? PProg. Neurol. Psychiatry 2020, 24, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undurraga, J.; Baeza, I.; Valentí, M.; Lázaro, M.L. Brain Germinoma Presenting as a First Psychotic Episode in an Adolescent Male. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 741–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Distelmaier, F.; Janssen, G.; Mayatepek, E.; Schaper, J.; Göbel, U.; Rosenbaum, T. Disseminated Pilocytic Astrocytoma Involving Brain Stem and Diencephalon: A History of Atypical Eating Disorder and Diagnostic Delay. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 79, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakula-Juchnowicz, H.; Morylowska-Topolska, J.; Juchnowicz, D.; Korzeniowska, A.; Krukow, P.; Rola, R. Paranoid Syndrome as the First Sign of Central Neurocytoma: A Case Report. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2018, 24, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.G.; Perl, M. Psychiatric Presentations of Cancer. Psychosomatics 1982, 23, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, J.D.; Duncan, G.; Caird, F.I. Psychiatric Presentation of Intracranial Tumour in the Elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1992, 7, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.M.; Kok, L.P. Cerebral Tumours Presenting with Psychiatric Symptoms. Singap. Med. J. 1989, 30, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lampl, Y.; Barak, Y.; Achiron, A.; Sarova-Pinchas, I. Intracranial Meningiomas: Correlation of Peritumoral Edema and Psychiatric Disturbances. Psychiatry Res. 1995, 58, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.C.; Dirven, L.; Koekkoek, J.A.; Numans, M.E.; Taphoorn, M.J. Prediagnostic Presentations of Glioma in Primary Care: A Case-Control Study. CNS Oncol. 2019, 8, CNS44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M. History and Evolution of Brain Tumor Imaging: Insights through Radiology. Radiology 2014, 273, S111–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowosielski, M.; Radbruch, A. The Emerging Role of Advanced Neuroimaging Techniques for Brain Metastases. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyratzopoulos, G.; Neal, R.D.; Barbiere, J.M.; Rubin, G.P.; Abel, G.A. Variation in Number of General Practitioner Consultations before Hospital Referral for Cancer: Findings from the 2010 National Cancer Patient Experience Survey in England. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, M.; Brennan, P.M.; Zienius, K.; Kurian, K.M.; Hollingworth, W.; Weller, D.; Hamilton, W.; Grant, R.; Ben-Shlomo, Y. Symptoms in Primary Care with Time to Diagnosis of Brain Tumours. Fam. Pract. 2018, 35, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, A.; Salford, L.G. Early Mental Changes in Patients with Astrocytomas with Special Reference to Anxiety and Epilepsy. PSP 1997, 30, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilanakis, N.; Vratsista, A.; Siorou, S. A Brain Ependymoma with Psychiatric Manifestation. J. BUON 2017, 22, 1604–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Gondwal, R.; Saxena, V.; Avinash, P.R. Godot Syndrome: A Rare Presentation of Anxiety in a Young Male with Glioblastoma Multiforme. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2019, 40, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vile, C.J.; Sufraz, R.; Lask, B.D.; Stanhope, R. Occult Intracranial Tumours Masquerading as Early Onset Anorexia Nervosa. BMJ 1995, 311, 1359–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berek, K.; Aichner, F.; Schmutzhard, E.; Kofler, M.; Langmayr, J.; Gerstenbrand, F. Intracranial Germ Cell Tumor Mimicking Anorexia Nervosa. Klin Wochenschr 1991, 69, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, A.P.; Barnard, D.; D’Souza, G.; Shad, A.; Sherlala, K.; Sidhu, J.; Singh, S.P. Pineal Germinoma Presenting as Anorexia Nervosa: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Int. J. Eat Disord. 2006, 39, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, T.R.; Fahlbusch, R.; Buchfelder, M.; Dörr, H.G. Craniopharyngioma in a Female Adolescent Presenting with Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa. Klin Padiatr. 2006, 218, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunevicius, A.; Deltuva, V.P.; Deltuviene, D.; Tamasauskas, A.; Bunevicius, R. Brain Lesions Manifesting as Psychiatric Disorders: Eight Cases. CNS Spectr. 2008, 13, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensgens, T.B.; Bloemer, E.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.Y.N.; Zwaan, C.M.; Van den Bos, C.; Huyser, C.; Kaspers, G.J.L. Psychiatric Symptoms Causing Delay in Diagnosing Childhood Cancer: Two Case Reports and Literature Review. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 22, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazzi, M.A.; Luby, E.D. The Neurobiology of Anorexia Nervosa: An Auto-Addiction? In The Brain as an Endocrine Organ; Cohen, M.P., Foà, P.P., Eds.; Endocrinology and Metabolism; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 46–95. ISBN 978-1-4612-3480-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pavesi, G.; Berlucchi, S.; Feletti, A.; Opocher, G.; Scienza, R. Hemangioblastoma of the Obex Mimicking Anorexia Nervosa. Neurology 2006, 67, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldney, R.D. CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA SIMULATING ANOREXIA NERVOSA. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1978, 166, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8. [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel, R.S.; Meyers, C.A.; Levin, V.A. Cognitive Dysfunction Following Surgery for Intracerebral Glioma: Influence of Histopathology, Lesion Location, and Treatment. J. Neurooncol. 1996, 30, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovagnoli, A.R. Investigation of Cognitive Impairments in People with Brain Tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 108, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douw, L.; van Dellen, E.; de Groot, M.; Heimans, J.J.; Klein, M.; Stam, C.J.; Reijneveld, J.C. Epilepsy Is Related to Theta Band Brain Connectivity and Network Topology in Brain Tumor Patients. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahana, M.J. The Cognitive Correlates of Human Brain Oscillations. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouma, J. Psychotic Manifestations in Brain Tumour Patients: 2 Case Reports from South Africa. Afr. Health Sci. 2004, 4, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nadvi, S.S.; van Dellen, J.R. Transient Peduncular Hallucinations Secondary to Brain Stem Compression by a Medulloblastoma. Surg. Neurol. 1994, 41, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.S.; Craig, J.J.; McKinstry, C.S. Bilateral Astrocytoma Involving the Limbic System Precipitating Disabling Amnesia and Seizures. Seizure 2000, 9, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, J.; Severus, E.; Meyer, S.; Bauer, M.; Daubner, D.; Krex, D.; Juratli, T.A. Glioblastoma Multiforme Presenting as Postpartum Depression: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanphear, J.; Sarnaik, S. Presenting Symptoms of Pediatric Brain Tumors Diagnosed in the Emergency Department. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2014, 30, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, M.P. Symptom Management of Brain Tumor Patients. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2004, 20, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SONIAT, T.L.L. PSYCHIATRIC SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH INTRACRANIAL NEOPLASMS. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.C.M.; Dirven, L.; Koekkoek, J.A.F.; Gortmaker, E.G.; Fritz, L.; Vos, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B. Prediagnostic Symptoms and Signs of Adult Glioma: The Patients’ View. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 146, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, K.A. Sleep and Sleep Treatments in Bipolar Disorder. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 34, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, D.; Wilson, S.; Paterson, L. Sleep Disorders as Core Symptoms of Depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staner, L. Sleep and Anxiety Disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 5, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mainio, A.; Hakko, H.; Niemelä, A.; Koivukangas, J.; Räsänen, P. Insomnia among Brain Tumor Patients: A Population-Based Prospective Study of Tumor Patients in Northern Finland. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2013, 31, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, R.; Yin, H. Health-Related Quality of Life in Glioma Patients in China. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, L.; Shpirer, I.; Rabey, J.M.; Klein, C.; Schiffer, J. Polysomnography in Patients with Intracranial Tumors before and after Operation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2004, 109, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavas, C.; Zorlu, F.; Ozyigit, G.; Gurkaynak, M.; Yavas, G.; Yuce, D.; Cengiz, M.; Yildiz, F.; Akyol, F. Health-Related Quality of Life in High-Grade Glioma Patients: A Prospective Single-Center Study. Support Care Cancer 2012, 20, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulrooney, D.A.; Ness, K.K.; Neglia, J.P.; Whitton, J.A.; Green, D.M.; Zeltzer, L.K.; Robison, L.L.; Mertens, A.C. Fatigue and Sleep Disturbance in Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS). Sleep 2008, 31, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprathi, M.; Jayashree, M. Child with Vomiting. Indian J. Pediatr. 2017, 84, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, R.F.; Ramaker, C.; van Ouwerkerk, W.J.R.; Linssen, W.H.J.P.; Wolf, B.H.M. [Vomiting as a first neurological sign of brain tumors in children]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2002, 146, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mučić-Pucić, B.; Cvitanović-Šojat, L.; Hajnžić, T.; Mataija, M. Neurologic Symptoms as First Signs of Brain Tumor in Children. Acta Clin. Croat. 2001, 40, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender Male Female | 165 77 (46.7) 88 (53.3) |
| Age Pediatric (< 18 years) Adult (18 ≤ age <65) Older Adult (≥ 65 years) | 165 33 (20%) 108 (65.5%) 24 (14.5%) |
| Tumor Location Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital Parieto-occipital Parieto-temporal Parieto-frontal Fronto-temporal Ventricular Posterior Fossa Pineal Suprasellar Parasellar Hypothalamus Thalamus Corpus Callosum Basal Ganglia Cingulated area Multi-localized | 163 35 (21.2%) 23 (13.9%) 4 (2.4%) 4 (2.4%) 3 (1.8%) 5 (3%) 6 (3.6%) 5 (3%) 19 (11.5%) 22 (13.3%) 7 (4.2%) 8 (4.8%) 1 (0.6%) 4 (2.4%) 2 (1.2%) 3 (1.8%) 1 (0.6%) 1 (0.6%) 10 (6.1%) |
| Tumor Type Categorization Diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors Meningiomas Germ cell tumors Mesenchymal, non-meningothelial tumors Tumors of the sellar region Neuronal and mixed neuronal glial tumors Ependymal tumors Choroid plexus tumors Tumors of the pineal region Embryonal tumors Other astrocytic tumors Other gliomas | 165 48 (29.1%) 54 (32.7%) 12 (7.3%) 11 (6.7%) 9 (5.5%) 10 (6.1%) 4 (2.4%) 4 (2.4%) 2 (1.2%) 1 (0.6%) 8 (4.8%) 2 (1.2%) |
| Pediatric Cases | Adult Cases | Older Adult Cases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Generalized Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 18) | Generalized Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 9) | Stat | p | Generalized Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 39) | Generalized Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 40) | Stat | p | Generalized Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 18) | Generalized Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 5) | Stat | p |
| Age, years a | 10 (8, 14) | 14 (11, 16) | 42.5 | 0.046 | 50 (35, 55) | 42 (32, 53) | 699.5 | 0.43 | 68 (66, 74) | 69 (66, 75) | 41.5 | 0.80 |
| Gender, n (%F) | 7 (38.9 %) | 4 (44.4%) | 0.08 | 1.00 | 23 (59.0%) | 20 (50.0%) | 0.64 | 0.50 | 11 (61.1%) | 4 (80.0%) | 0.62 | 0.62 |
| Type of tumor (n, % of the three most frequent types) b | Diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (7, 39%); meningiomas (6, 33%); mesenchimal (2, 11%); | Diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (4, 44%); meningiomas (3, 33%); mesenchimal (1, 11%) | 1.30 | 0.94 | Meningiomas (10, 26%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (7, 18%); tumors of the sellar region (6, 15%) | Diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (11, 28%); meningiomas (8, 20%), germ cell (7, 18%) | 18.07 | 0.05 | Meningiomas (10, 56%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (7, 39%); mesenchimal (1, 6%) | Meningiomas (3, 60%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (2, 40%) | 0.29 | 0.86 |
| Location, n (% infratentorial) c | 4 (25%) | 2 (25%) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 4 (10%) | 10 (25%) | 2.94 | 0.14 | 3 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 1.02 | 1.00 |
| Time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis, months a | 12 (4, 30) | 14 (3, 30) | 76.5 | 1.00 | 5 (2, 18) | 24 (7, 60) | 381.5 | 0.002 | 4 (2, 8) | 6 (6, 78) | 18.00 | 0.08 |
| Resolution of psychiatric symptoms after tumor treatment, n (%) | 15 (94%) d | 4 (80%) d | 0.84 | 0.43 | 17 (85%) e | 28 (93%) e | 0.93 | 0.38 | 4 (100%) f | 3 (100%) f | - f | - f |
| Psychiatric Symptoms | ||||||||||||
| Anxiety, n (%) | 7 (39%) | 0 (0%) | 4.73 | 0.06 | 10 (26%) | 6 (15%) | 1.38 | 0.27 | 3 (17%) | 3 (60%) | 3.81 | 0.09 |
| Apathy, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (11%) | 2.08 | 0.33 | 3 (8%) | 7 (18%) | 1.72 | 0.31 | 7 (39%) | 1 (20%) | 0.62 | 0.62 |
| Depression, n (%) | 4 (22%) | 4 (44%) | 1.42 | 0.38 | 19 (49%) | 13 (33%) | 2.16 | 0.17 | 4 (22%) | 2 (40%) | 0.64 | 0.58 |
| Eating disorder, n (%) | 10 (56%) | 5 (56%) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 3 (8%) | 4 (10%) | 0.13 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Manic symptoms, n (%) | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 1.08 | 0.54 | 1 (3%) | 6 (15%) | 3.78 | 0.11 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Miscellaneous, n (%) | 3 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 1.69 | 0.53 | 2 (5%) | 3 (3%) | 0.19 | 1.00 | 1 (6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.29 | 1.00 |
| Personality changes, n (%) | 2 (11%) | 1 (11%) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 10 (26%) | 10 (26%) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 6 (33%) | 2 (40%) | 0.08 | 1.00 |
| Psychotic symptoms, n (%) | 4 (22%) | 4 (44%) | 1.42 | 0.38 | 16 (41%) | 15 (36%) | 0.10 | 0.82 | 5 (28%) | 2 (40%) | 0.28 | 0.62 |
| Neurological Symptoms | ||||||||||||
| Cognitive deficits, n (%) | 3 (17%) | 5 (56%) | 4.35 | 0.07 | 26 (67%) | 15 (38%) | 6.73 | 0.013 | 11 (31%) | 5 (100%) | 2.80 | 0.27 |
| Delayed puberty, n (%) | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 1.08 | 0.54 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Dizziness, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 2 (22%) | 1.69 | 0.25 | 4 (10%) | 8 (20%) | 1.46 | 0.35 | 3 (17%) | 2 (40%) | 1.25 | 0.29 |
| Growth retardation, n (%), n (%) | 5 (28%) | 0 (0%) | 3.07 | 0.14 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Headache, n (%) | 7 (39%) | 2 (22%) | 0.75 | 0.67 | 18 (46%) | 23 (58%) | 1.02 | 0.37 | 6 (33%) | 2 (40%) | 0.08 | 1.00 |
| Motor deficits, n (%) | 8 (44%) | 5 (56%) | 0.30 | 0.70 | 17 (44%) | 16 (40%) | 0.11 | 0.82 | 8 (44%) | 2 (40%) | 0.03 | 1.00 |
| Nausea/Vomiting, n (%) | 11 (61%) | 5 (56%) | 0.08 | 1.00 | 8 (21%) | 11 (28%) | 0.53 | 0.60 | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 0.61 | 1.00 |
| Ocular impairments, n (%) | 5 (28%) | 3 (33%) | 0.09 | 1.00 | 13 (33%) | 7 (118%) | 2.62 | 0.13 | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) | 7.89 | 0.04 |
| Seizures, n (%) | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 1.08 | 0.54 | 5 (13%) | 6 (15%) | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) | 7.89 | 0.04 |
| Sleep disturbances, n (%) | 5 (28%) | 4 (44%) | 0.75 | 0.42 | 21 (54%) | 11 (28%) | 5.69 | 0.022 | 4 (22%) | 1 (20%) | 0.01 | 1.00 |
| Speech impediments, n (%) | 1 (6%) | 1 (11%) | 0.27 | 1.00 | 5 (13%) | 9 (23%) | 1.27 | 0.38 | 2 (11%) | 1 (20%) | 0.27 | 0.54 |
| Urinary incontinence, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 2 (5%) | 6 (15%) | 2.23 | 0.26 | 3 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| Pediatric cases | Adult Cases | Older Adult Cases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Focal Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 4) | Focal Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 19) | Stat | p | Focal Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 16) | Focal Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 49) | Stat | p | Focal Neurological Symptoms along with Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 6) | Focal Neurological Symptoms after Psychiatric Symptoms (n = 8) | Stat | p |
| Age, years a | 8 (4, 14) | 13 (10, 15) | 22.00 | 0.22 | 49 (30, 59) | 41 (33, 55) | 361.0 | 0.64 | 72 (68, 79) | 68 (65, 73) | 14.00 | 0.23 |
| Gender, n (%F) | 1 (25%) | 7 (37%) | 0.20 | 1.00 | 11 (69%) | 26 (57%) | 1.21 | 0.39 | 2 (33%) | 5 (63%) | 1.17 | 0.59 |
| Type of tumor (n, % of the three most frequent types) b | Diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (2, 50%); mesenchimal (1, 25%); germ cell (1, 25%) | Meningiomas (9, 47%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (6, 32%); mesenchimal (2, 11%) | 7.92 | 0.10 | Meningiomas (5, 27%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (4, 27%); tumors of the sellar region (2, 13%) | Meningiomas (14, 29%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (13, 27%); neuronal and mixed neuronal glia (6, 12%) | 5.49 | 0.70 | Meningiomas (5, 83%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (1, 17%) | Meningiomas (4, 50%); diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial (4, 50%) | 1.66 | 0.30 |
| Location, n (% infratentorial) c | 1 (25%) | 6 (38%) | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1 (7%) | 9 (18%) | 1.36 | 0.43 | 1 (17%) | 2 (25%) | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis, months a | 4 (1, 8) | 13 (4, 36) | 15.00 | 0.07 | 3 (1, 18) d | 18 (6, 48) d | 161.5 | 0.012 | 4 (1, 68) | 18 (5, 57) | 11.00 | 0.31 |
| Resolution of psychiatric symptoms after tumor treatment, n (%) | 4 (100%) e | 13 (100%) e | - | - | 7 (86%) f | 28 (90%) f | 0.06 | 1.00 | 1 (100%) g | 2 (100%) g | - | - |
| Psychiatric Symptoms | ||||||||||||
| Anxiety, n (%) | 1 (25%) | 5 (26%) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 2 (13%) | 10 (20%) | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0 (0%) | 4 (50%) | 4.20 | 0.09 |
| Apathy, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (5%) | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 9 (18%) | 3.41 | 0.10 | 2 (33%) | 2 (25%) | 0.12 | 1.00 |
| Depression, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 7 (37%) | 2.12 | 0.27 | 5 (31%) | 13 (27%) | 0.13 | 0.75 | 0 (0%) | 3 (38%) | 2.86 | 0.21 |
| Eating disorder, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (53%) | 3.73 | 0.10 | 0 (0%) | 5 (10%) | 1.77 | 0.32 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Manic Symptoms, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (5%) | 0.22 | 1.00 | 1 (6%) | 5 (10%) | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Miscellaneous, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 3 (16%) | 2.27 | 0.19 | 3 (19%) | 3 (6%) | 2.30 | 0.15 | 2 (33%) | 0 (0%) | 3.11 | 0.17 |
| Personality changes, n (%) | 1 (25%) | 3 (16%) | 0.20 | 1.00 | 3 (19%) | 14 (29%) | 0.60 | 0.53 | 3 (50%) | 2 (25%) | 0.93 | 0.58 |
| Psychotic symptoms, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 5 (26%) | 0.88 | 0.56 | 10 (63%) | 21 (43%) | 1.87 | 0.25 | 1 (17%) | 2 (25%) | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Neurological Symptoms | ||||||||||||
| Cognitive deficits, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (26%) | 1.35 | 0.54 | 9 (56%) | 16 (33%) | 2.84 | 0.14 | 3 (50%) | 6 (75%) | 0.93 | 0.58 |
| Delayed puberty, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (11%) | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Dizziness, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (16%) | 0.73 | 1.00 | 1 (6%) | 5 (10%) | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 3 (38%) | 2.86 | 0.21 |
| Growth retardation, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (21%) | 1.02 | 1.00 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - |
| Headache, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 4 (21%) | 1.44 | 0.27 | 5 (31%) | 26 (53%) | 2.30 | 0.16 | 3 (50%) | 3 (38%) | 0.22 | 1.00 |
| Motor deficits, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 15 (79%) | 1.44 | 0.27 | 13 (81%) | 23 (47%) | 5.75 | 0.02 | 5 (83%) | 6 (75%) | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Nausea/Vomiting, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 10 (53%) | 0.01 | 1.00 | 2 (13%) | 11 (22%) | 0.75 | 0.49 | 0 (0%) | 2 (25%) | 1.75 | 0.47 |
| Ocular impairments, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 7 (37%) | 0.24 | 1.00 | 6 (38%) | 15 (31%) | 0.26 | 0.76 | 1 (17%) | 2 (25%) | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Seizures, n (%) | 2 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 10.41 | 0.024 | 5 (31%) | 13 (27%) | 0.13 | 0.75 | 0 (0%) | 2 (25%) | 1.75 | 0.47 |
| Sleep disturbances, n (%) | 3 (75%) | 3 (16%) | 6.01 | 0.04 | 5 (31%) | 14 (29%) | 0.04 | 1.00 | 1 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 1.44 | 0.43 |
| Speech impediments, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (11%) | 0.46 | 1.00 | 4 (25%) | 14 (29%) | 0.07 | 1.00 | 1 (17%) | 2 (25%) | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Urinary incontinence, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | 1 (6%) | 8 (17%) h | 1.08 | 0.43 | 2 (33%) | 1 (13%) | 0.88 | 0.54 |
| Pediatric Cases (n = 32) | Adult Cases (n = 100) | Older Adult Cases (n = 22) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Statistics | p | Statistics | p | Statistics | p |
| Age at diagnosis | 0.2 | 0.21 | −0.2 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.42 |
| Female gender | 87.5 | 0.17 | 1224.0 | 0.90 | 32.5 | 0.11 |
| Type of tumor | 3.4 | 0.64 | 9.5 | 0.58 | 1.5 | 0.46 |
| Tumor location | 82.0 | 0.94 | 584.5 | 0.41 | 4.5 | 0.09 |
| Psychiatric Symptoms | ||||||
| Anxiety | 94.5 | 0.95 | 665.5 | 0.25 | 25.5 | 0.19 |
| Apathy | 6.5 | 0.44 | 555.5 | 0.27 | 44.0 | 0.58 |
| Depression | 71.5 | 0.18 | 892.0 | 0.19 | 40.5 | 0.59 |
| Eating disorders | 63.5 | 0.014 | 246.5 | 0.007 | - | - |
| Manic symptoms | 26.0 | 0.79 | 327.5 | 0.61 | - | - |
| Miscellaneous symptoms | 66.5 | 0.96 | 368.5 | 0.62 | 4.0 | 0.08 |
| Personality changes | 19.0 | 0.009 | 893.0 | 0.88 | 43.5 | 0.54 |
| Psychotic symptoms | 98.0 | 0.65 | 1200.5 | 0.95 | 36.5 | 0.27 |
| Neurological symptoms | ||||||
| Cognitive deficits | 69.0 | 0.25 | 619.5 | <0.0001 | 51.0 | 0.95 |
| Delayed puberty | 1.5 | 0.40 | - | - | - | - |
| Dizziness | 42.0 | 0.95 | 470.0 | 0.83 | 22.5 | 0.26 |
| Growth retardation | 40.0 | 0.17 | - | - | - | - |
| Headache | 95.0 | 0.74 | 1141.5 | 0.73 | 47.0 | 0.57 |
| Motor deficits | 117.5 | 0.71 | 1017.5 | 0.60 | 53.5 | 0.74 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 104.5 | 0.39 | 558.0 | 0.11 | 4.5 | 0.46 |
| Ocular Impairments | 89.0 | 0.56 | 743.0 | 0.62 | 7.0 | 0.04 |
| Seizures | 15.0 | 0.29 | 612.5 | 0.44 | 2.0 | 0.04 |
| Sleep disturbances | 59.0 | 0.06 | 975.0 | 0.48 | 21.0 | 0.10 |
| Speech impediments | 27.5 | 0.85 | 613.0 | 0.26 | 11.0 | 0.11 |
| Urinary incontinence | - | - | 324.5 | 0.61 | 26.0 | 0.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghandour, F.; Squassina, A.; Karaky, R.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Fadda, P.; Pisanu, C. Presenting Psychiatric and Neurological Symptoms and Signs of Brain Tumors before Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030301
Ghandour F, Squassina A, Karaky R, Diab-Assaf M, Fadda P, Pisanu C. Presenting Psychiatric and Neurological Symptoms and Signs of Brain Tumors before Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(3):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030301
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhandour, Fatima, Alessio Squassina, Racha Karaky, Mona Diab-Assaf, Paola Fadda, and Claudia Pisanu. 2021. "Presenting Psychiatric and Neurological Symptoms and Signs of Brain Tumors before Diagnosis: A Systematic Review" Brain Sciences 11, no. 3: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030301
APA StyleGhandour, F., Squassina, A., Karaky, R., Diab-Assaf, M., Fadda, P., & Pisanu, C. (2021). Presenting Psychiatric and Neurological Symptoms and Signs of Brain Tumors before Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Brain Sciences, 11(3), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030301








