5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a PARP-1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Immune Abnormalities through Upregulation of Anti-Inflammatory and Downregulation of Inflammatory Parameters in T Cells of BTBR Mouse Model of Autism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Animals
2.3. Drug Administration
2.4. Qualitative Intracellular Cytokine and Transcription Factor Detection by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Reverse Transcriptase Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
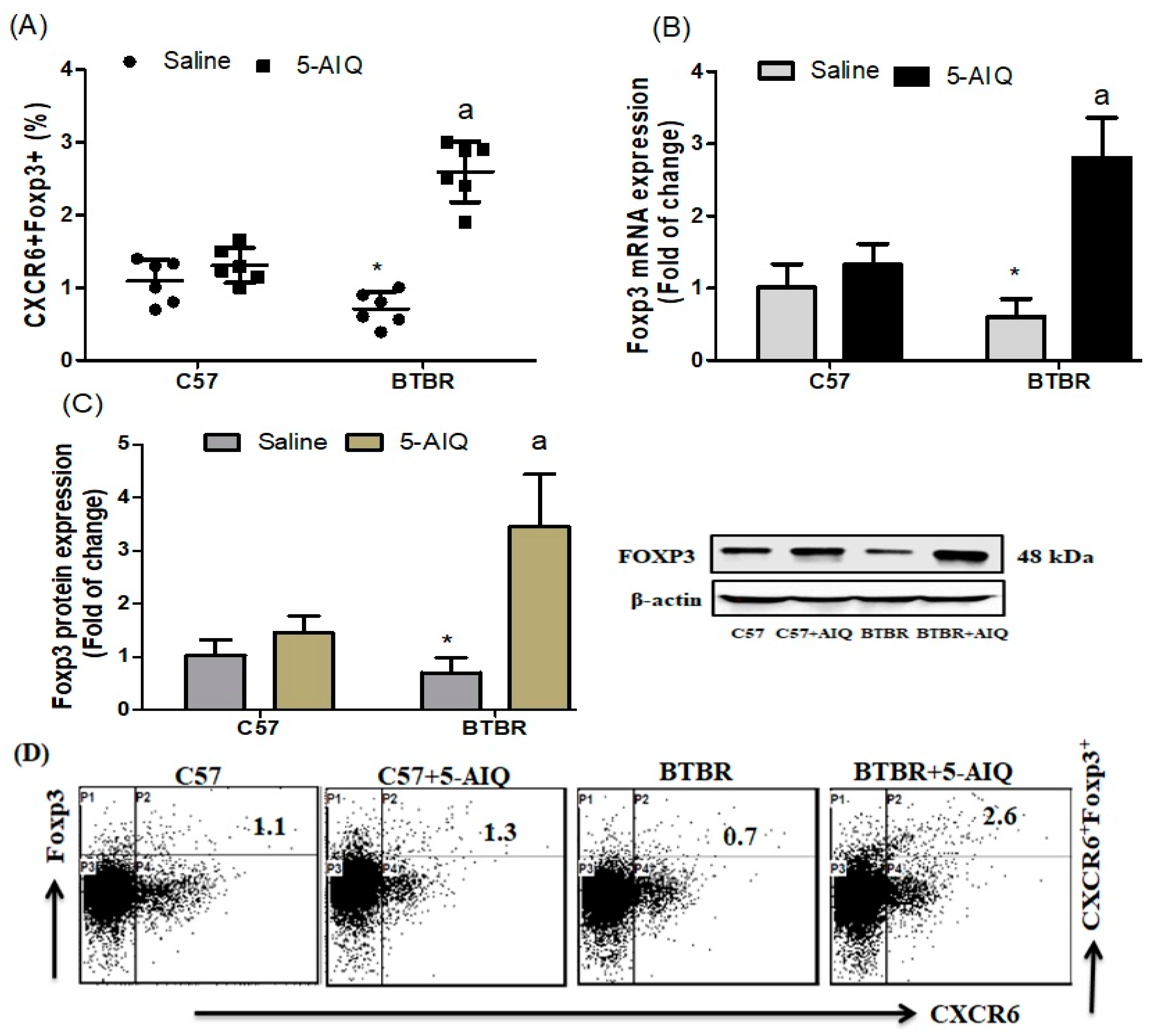
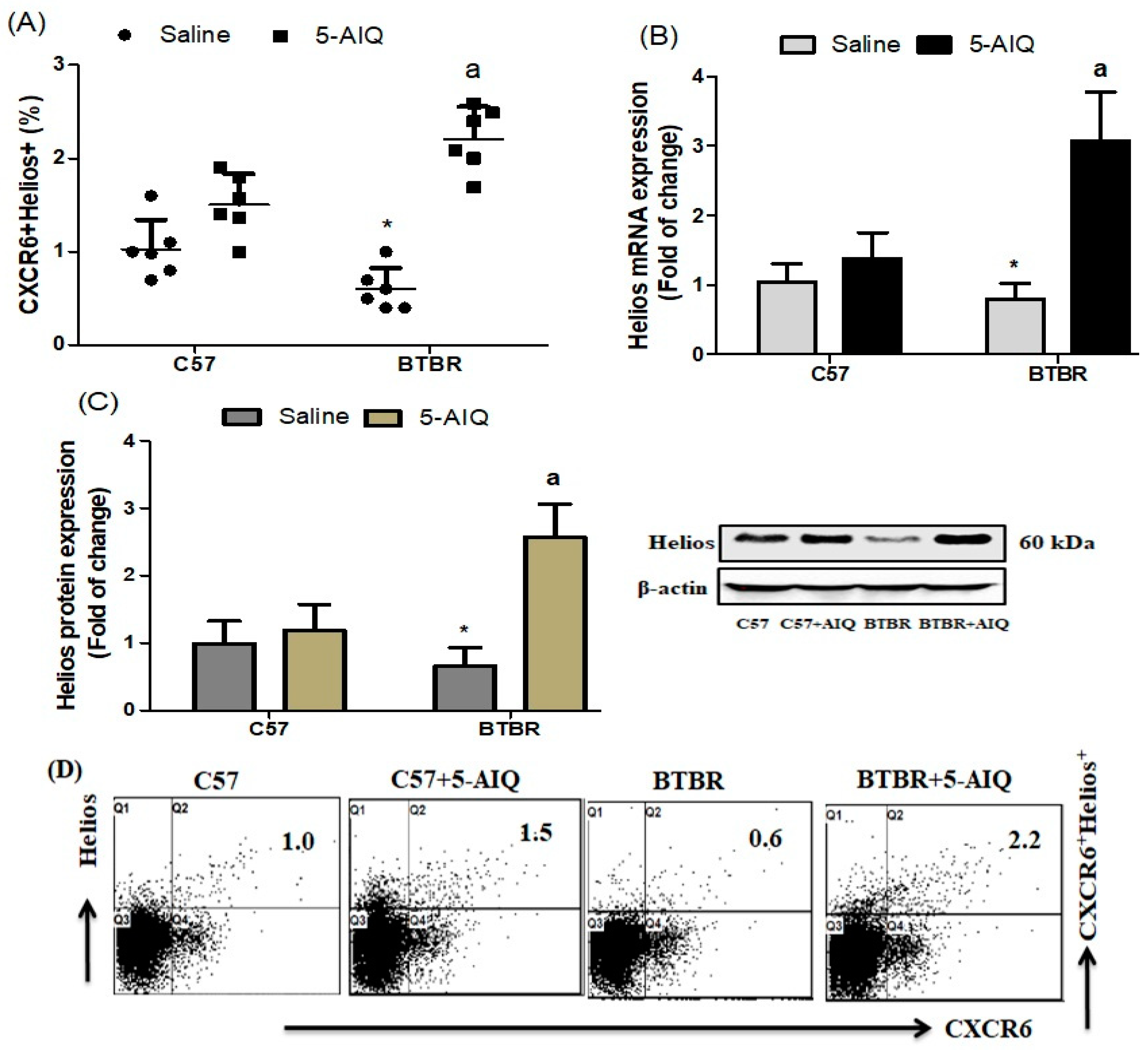
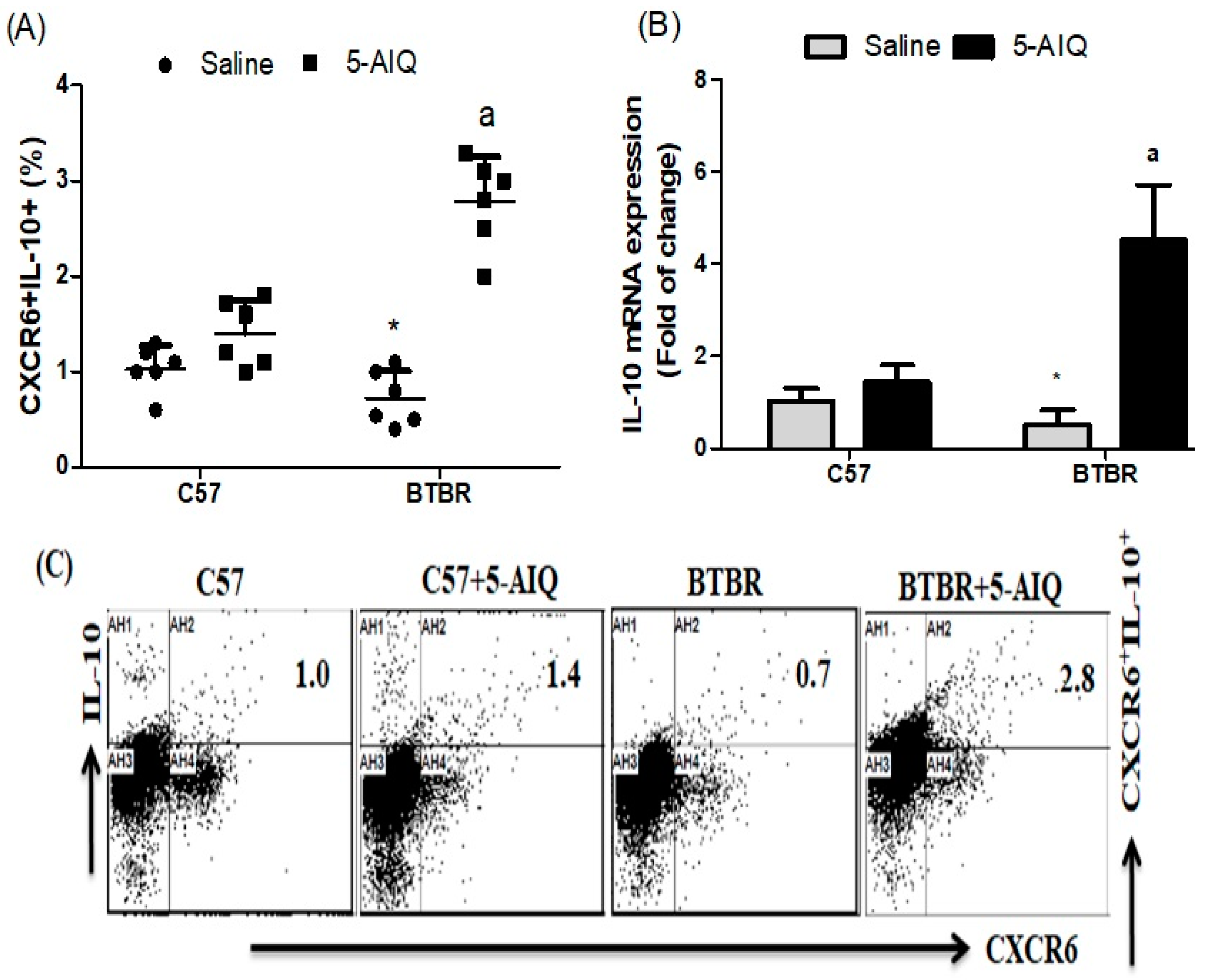
3.1. Treatment with 5-AIQ Upregulates Treg Cells in BTBR Mice
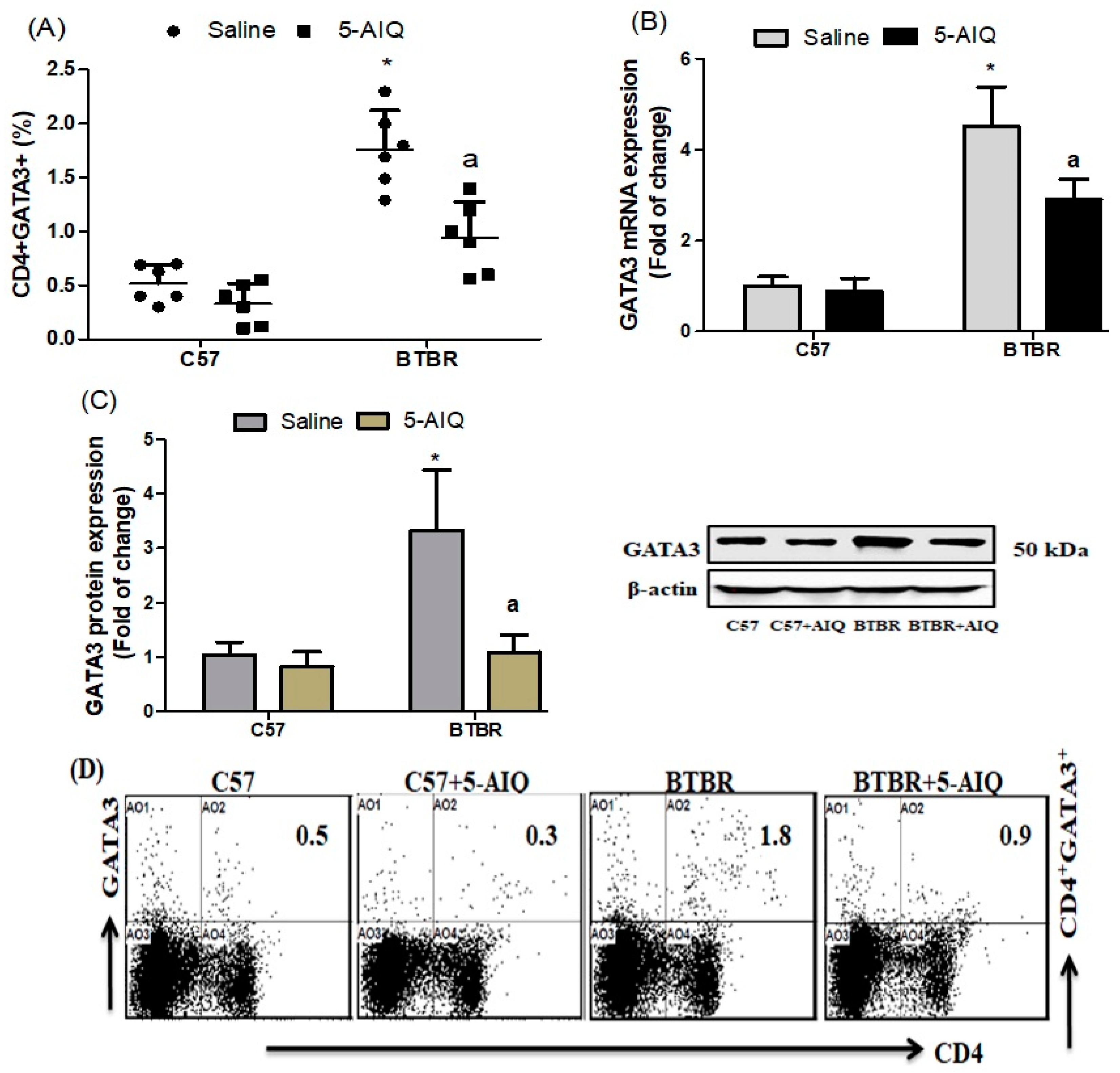
3.2. Effects of 5-AIQ on GATA3 Transcription Factor
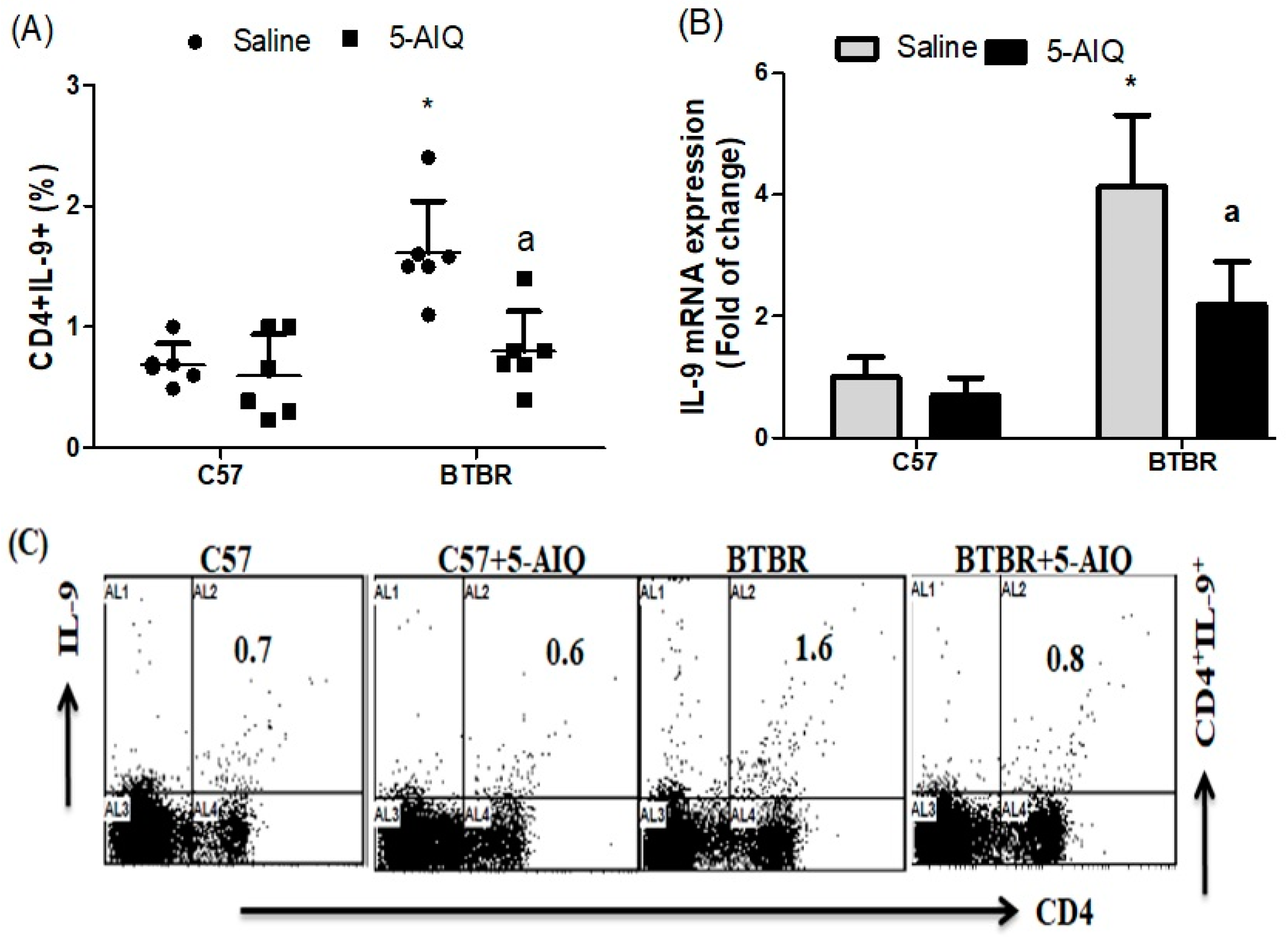
3.3. 5-AIQ Treatment Downregulates Th9 Cells in BTBR Mice
3.4. Effects of 5-AIQ Treatment on Th17 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lord, C.; Risi, S.; Lambrecht, L.; Cook, E.H., Jr.; Leventhal, B.L.; DiLavore, P.C.; Pickles, A.; Rutter, M. The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2000, 30, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Wakefield, A.J. Immune activation of peripheral blood and mucosal CD3+ lymphocyte cytokine profiles in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 173, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.B.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; Ebert, P.J.; Militerni, R.; Bravaccio, C.; Trillo, S.; Elia, M.; Schneider, C.; Melmed, R.; Sacco, R.; et al. A genetic variant that disrupts MET transcription is associated with autism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16834–16839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaar, D.A.; Shao, Y.; Haines, J.L.; Stenger, J.E.; Jaworski, J.; Martin, E.R.; Delong, G.R.; Moore, J.H.; McCauley, J.L.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; et al. Analysis of the RELN gene as a genetic risk factor for autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croonenberghs, J.; Bosmans, E.; Deboutte, D.; Kenis, G.; Maes, M. Activation of the inflammatory response system in autism. Neuropsychobiology 2002, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, U.; Murray, P.J.; Urwyler, A.; Yee, B.K.; Schedlowski, M.; Feldon, J. Adult behavioral and pharmacological dysfunctions following disruption of the fetal brain balance between pro-inflammatory and IL-10-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, N.M.; Servatius, R.; Beck, K.; Marzouk, A.; Kreider, T. Cytokine levels during pregnancy influence immunological profiles and neurobehavioral patterns of the offspring. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1107, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.; Van De Water, J. Elevated plasma cytokines in autism spectrum disorders provide evidence of immune dysfunction and are associated with impaired behavioral outcome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Associations of impaired behaviors with elevated plasma chemokines in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 232, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; A Zoheir, K.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Alzahrani, M.Z.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Attia, S.M. Dysregulation of Th1, Th2, Th17, and T regulatory cell-related transcription factor signaling in children with autism. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4390–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheet, S.A.; Alzahrani, M.Z.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Attia, S.M.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Ahmad, A.M. Resveratrol ameliorates dysregulation of Th1, Th2, Th17, and T regulatory cell-related transcription factor signaling in a BTBR T + tf/J mouse model of autism. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5201–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Anthony, A.; Torrente, F.; Wakefield, A.J. Spontaneous mucosal lymphocyte cytokine profiles in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms: Mucosal immune activation and reduced counter regulatory interleukin 10. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, G.A.; Al Shehab, A.; Fouad, N.R. Frequency of CD4 + CD25 high regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of egyptian children with autism. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Garra, A.; Vieira, P.L.; Vieira, P.; Goldfeld, A.E. IL-10-producing and naturally occurring CD4+ Tregs: Limiting collateral damage. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Garra, A.; Murphy, K.M. From IL-10 to IL-12: How pathogens and their products stimulate APCs to induce T(H)1 development. Nat Immunol. 2009, 10, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getnet, D.; Grosso, J.F.; Goldberg, M.V.; Harris, T.J.; Yen, H.-R.; Bruno, T.C.; Durham, N.M.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Pyle, K.J.; Wada, S.; et al. A role for the transcription factor Helios in human CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-H.; Yang, L.; Cohn, L.; Parkyn, L.; Homer, R.; Ray, P.; Ray, A. Inhibition of allergic inflammation in a murine model of asthma by expression of a dominant-negative mutant of GATA 3. Immunity 1999, 11, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yamane, H.; Cote-Sierra, J.; Guo, L.; Paul, W.E. GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: Induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarovina, K.; Pattyn, A.; Stubbusch, J.; Müller, F.; Van Der Wees, J.; Schneider, C.; Brunet, J.-F.; Rohrer, H. Essential role of GATA transcription factors in sympathetic neuron development. Development 2004, 131, 4775–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorninck, J.H.; Van Der Wees, J.; Karis, A.; Goedknegt, E.; Coesmans, M.; Rutteman, M.; Grosveld, F.; De Zeeuw, C.I. GATA-3 is involved in the development of serotonergic neurons in the caudal raphe nuclei. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, RC12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Schön, M.P.; Wallbrecht, K.; Gruber-Wackernagel, A.; Wang, X.J.; Wolf, P. Involvement of IL-9 in Th17-associated inflammation and angiogenesis of psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sonobe, Y.; Akahori, T.; Jin, S.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Noda, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. IL-9 promotes Th17 cell migration into the central nervous system via CC chemokine ligand-20 produced by astrocytes. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4415–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, G.; Rossi, S.; Motta, C.; Macchiarulo, G.; Barbieri, F.; De Bardi, M.; Borsellino, G.; Finardi, A.; Grasso, M.G.; Ruggieri, S.; et al. T helper 9 cells induced by plasmacytoid dendritic cells regulate interleukin-17 in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donninelli, G.; Saraf-Sinik, I.; Mazziotti, V.; Capone, A.; Grasso, M.G.; Battistini, L.; Reynolds, R.; Magliozzi, R.; Volpe, E. Interleukin-9 regulates macrophage activation in the progressive multiple sclerosis brain. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, M.D.; Yim, Y.S.; Wimmer, R.D.; Kim, H.; Ryu, C.; Welch, G.M.; Andina, M.; King, H.O.; Waisman, A.; Halassa, M.M.; et al. IL-17a promotes sociability in mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders. Nature 2020, 577, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.B.; Yim, Y.S.; Wong, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Littman, D.R.; Huh, J.R. The maternal interleukin-17a pathway in mice promotes autism-like phenotypes in offspring. Science 2016, 351, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Yim, Y.S.; Ha, S.; Atarashi, K.; Tan, T.G.; Longman, R.S.; Honda, K.; Littman, D.R.; Choi, G.B.; et al. Maternal gut bacteria promote neurodevelopmental abnormalities in mouse offspring. Nature 2017, 549, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.; Hoeffer, C. Maternal IL-17A in autism. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veuger, S.J.; Curtin, N.J.; Smith, G.C.M.; Durkacz, B.W. Effects of novel inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and the DNA-dependent protein kinase on enzyme activities and DNA repair. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7322–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Martínez-Romero, R.; O’Valle, F.; Aguilar-Quesada, R.; Conde, C.; Delgado, M.; Oliver, F.J. Therapeutic effect of a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor on experimental arthritis by downregulating inflammation and Th1 response. PLoS ONE 2007, 31, e1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, C.S.; Jangra, A.; Gurjar, S.S.; Hussain, I.; Borah, P.; Lahkar, M.; Mohan, P.; Bezbaruah, B.K. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor, 3-aminobenzamide pretreatment ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurobehavioral and neurochemical anomalies in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 133, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alqahtani, F.; Alhoshani, A.R.; Alasmari, F.; Alsaleh, N.B.; Attia, S.M. 5-aminoisoquinolinone attenuates social behavior deficits and immune abnormalities in the BTBR T + Itpr3tf/J mouse model for autism. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 189, 172859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, H.G.; Kusek, G.K.; Yang, M.; Phoenix, J.L.; Bolivar, V.J.; Crawley, J.N. Autism-like behavioral phenotypes in BTBR T + tf/J mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2008, 7, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, R.; van De Wouw, M.; Moloney, G.M.; Ventura-Silva, A.P.; O’Riordan, K.; Golubeva, A.V.; Dinan, T.G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Strain differences in behaviour and immunity in aged mice: Relevance to Autism. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 399, 113020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Miller, V.M.; Lawrence, D.A. Aberrant immune responses in a mouse with behavioral disorders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onore, C.E.; Careaga, M.; Babineau, B.A.; Schwartzer, J.J.; Berman, R.F.; Ashwood, P. Inflammatory macrophage phenotype in BTBR T + tf/J mice. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankoorikal, G.M.V.; Kaercher, K.A.; Boon, C.J.; Lee, J.K.; Brodkin, E.S. A mouse model system for genetic analysis of sociability: C57BL/6J versus BALB/cJ inbred mouse strains. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Zoheir, A.K.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Ashour, A.E.; Attia, S.M. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor modulates T regulatory and IL-17 cells in the prevention of adjuvant induced arthritis in mice model. Cytokine 2014, 68, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Zoheir, K.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Korashy, H.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Ashour, A.E.; Al-Shabanaha, O.A.; Al-harbi, M.M.; Attia, S.M. The role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor in carrageenan-induced lung inflammation in mice. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Spizzo, I.; Diep, H.; Drummond, G.R.; Widdop, R.E.; Vinh, A. Differential phenotypes of tissue-infiltrating T cells during angiotensin II-induced hypertension in mice. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e114895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Attia, S.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Raish, M.; Ahmad, S.F. Adenosine A2A receptor modulates neuroimmune function through Th17/retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) signaling in a BTBR T + Itpr3tf/J mouse model of autism. Cell Signal. 2017, 36, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, J.Y.; Ding-Zhou, L.; Croci, N.; Plotkine, M.; Margaill, I. 3-aminobenzamide reduces brain infarction and neutrophil infiltration after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 184, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, R.A.; Panizzon, K.L.; Girard, J.M. Traumatic neuroprotection with inhibitors of nitric oxide and ADP-ribosylation. Brain Res. 1996, 710, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lai, Q.; Li, J.; Gordon, V.; Diaz, F.G. Long-term neuroprotective effect of inhibiting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion using a behavioral assessment. Brain Res. 2001, 915, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, V.C.; Croci, N.; Boulu, R.G.; Plotkine, M.; Marchand-Verrecchia, C. Deleterious poly (ADPribose) polymerase-1 pathway activation in traumatic brain injury in rat. Brain Res. 2003, 989, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Lan, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Gu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; et al. Critical role of all-trans retinoic acid in stabilizing human natural regulatory T cells under inflammatory conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3432–E3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, G.; Kanno, Y.; Furumoto, Y.; Jiang, K.; Parker, S.C.J.; Erdos, M.R.; Davis, S.R.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Restifo, N.P.; Gadina, M.; et al. Super-enhancers delineate disease-associated regulatory nodes in T cells. Nature 2015, 520, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, Y.; Takenouchi, N.; Li, H.-C.; Tomaru, U.; Yao, K.; Grant, C.W.; Maric, D.A.; Jacobson, S. Virus-induced dysfunction of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated neuroimmunological disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Sharma, S.; Edwards, J.; Feigenbaum, L.; Zhu, J. Dynamic expression of transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 by regulatory T cells maintains immunotolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, J.D.; Gavin, M.A.; Rudensky, A.Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Chow, J.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Patterson, P.H. Modeling an autism risk factor in mice leads to permanent immune dysregulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12776–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Nadeem, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alshammari, M.A.; Attia, S.M. The PPARdelta agonist GW0742 restores neuroimmune function by regulating Tim-3 and Th17/Treg-related signaling in the BTBR autistic mouse model. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 120, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, E.M.; Bourges, D.; Hogan, T.V.; Van Driel, I.R.; Gleeson, P.A. Helios defines T cells being driven to tolerance in the periphery and thymus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.W.; Lee, J.; Hillsamer, P.; Kim, C.H. Human Th17 cells share major trafficking receptors with both polarized effector T cells and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Nadeem, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Attia, S.M. Downregulation in Helios transcription factor signaling is associated with immune dysfunction in blood leukocytes of autistic children. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 85, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.; Barbieri, I.; Basudev, H.; Brusa, R.; Casati, C.; Lozza, G.; Ongini, E. Interleukin-10 modulates neuronal threshold of vulnerability to ischemic damage. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachis, A.; Colangelo, A.M.; Vicini, S.; Doe, P.P.; De Bernardi, M.A.; Brooker, G.; Mocchetti, I. Interleukin-10 prevents glutamate-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by blocking caspase-3-like activity. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Kluetzman, K.; Mendoza, A.; Bolivar, V.J.; Reilly, A.; Jolly, J.K.; Lawrence, D.A. The maternal autoimmune environment affects the social behavior of offspring. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 258, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chauhan, A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Patil, S.; Chauhan, V.; Li, X.-M.; Ji, L.; Brown, T.; Malik, M. Elevated immune response in the brain of autistic patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 207, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, J.; Thiesson, D.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tsai, F.; Orkin, S.H. Expression and genetic interaction of transcription factors GATA-2 and GATA-3 during development of the mouse central nervous system. Dev. Biol. 1999, 210, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, V.W.; Nguyen, A.; Kim, K.S.; Steinberg, M.E.; Sarachana, T.; Scully, M.A.; Soldin, S.J.; Luu, T.; Lee, N.H. Gene expression profiling of lymphoblasts from autistic and nonaffected sib pairs: Altered pathways in neuronal development and steroid biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.N.; Yao, Y.; Manley, K.; Lawrence, D.A. Development, phenotypes of immune cells in BTBR T(+)Itpr3(tf)/J mice. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 358, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.; Kaplan, M.H. A brief history of IL-9. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3283–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.-F.; Leng, R.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Zheng, S.G.; Ye, D.-Q. Targeting T-helper 9 cells and interleukin-9 in autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, A.; Erickson, A.M.; Banks, A.W. Brain microvascular pericytes are immunoactive in culture: Cytokine, chemokine, nitric oxide, and LRP-1 expression in response to lipopolysaccharide. J. Neuroinflammation 2011, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamali, A.N.; Noorbakhsh, S.M.; Hamedifar, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yazdani, R.; Bautista, J.M.; Azizi, G. A role for Th1-like Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Mostafa, G.A. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-17A in children with autism. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, K.; Kameno, Y.; Shimmura, C.; Kawai, S.; Yoshihara, Y.; Wakuda, T.; Takebayashi, K.; Takagai, S.; et al. Plasma cytokine profiles in subjects with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Zwaag, B.; Franke, L.; Poot, M.; Hochstenbach, R.; Spierenburg, H.A.; Vorstman, J.A.S.; Van Daalen, E.; De Jonge, M.V.; Verbeek, N.E.; Brilstra, E.H.; et al. Gene-network analysis identifies susceptibility genes related to glycobiology in autism. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaaz, M.; Youssry, S.; Elfatatry, A.; El Rahman, M.A. Th17/Treg cells imbalance and their related cytokines (IL-17, IL-10 and TGF-β) in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 337, 577071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akintunde, M.E.; Rose, M.; Krakowiak, P.; Heuer, L.; Ashwood, P.; Hansen, R.H.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Van De Water, J. Increased production of IL-17 in children with autism spectrum disorders and co-morbid asthma. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 286, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhosaini, K.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Attia, S.M.; Alhazzani, K.; Albekairi, T.H.; Al-Mazroua, H.A.; Mahmood, H.M.; Ahmad, S.F. 5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a PARP-1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Immune Abnormalities through Upregulation of Anti-Inflammatory and Downregulation of Inflammatory Parameters in T Cells of BTBR Mouse Model of Autism. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020249
Alhosaini K, Ansari MA, Nadeem A, Bakheet SA, Attia SM, Alhazzani K, Albekairi TH, Al-Mazroua HA, Mahmood HM, Ahmad SF. 5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a PARP-1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Immune Abnormalities through Upregulation of Anti-Inflammatory and Downregulation of Inflammatory Parameters in T Cells of BTBR Mouse Model of Autism. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhosaini, Khaled, Mushtaq A. Ansari, Ahmed Nadeem, Saleh A. Bakheet, Sabry M. Attia, Khalid Alhazzani, Thamer H. Albekairi, Haneen A. Al-Mazroua, Hafiz M. Mahmood, and Sheikh F. Ahmad. 2021. "5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a PARP-1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Immune Abnormalities through Upregulation of Anti-Inflammatory and Downregulation of Inflammatory Parameters in T Cells of BTBR Mouse Model of Autism" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020249
APA StyleAlhosaini, K., Ansari, M. A., Nadeem, A., Bakheet, S. A., Attia, S. M., Alhazzani, K., Albekairi, T. H., Al-Mazroua, H. A., Mahmood, H. M., & Ahmad, S. F. (2021). 5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a PARP-1 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Immune Abnormalities through Upregulation of Anti-Inflammatory and Downregulation of Inflammatory Parameters in T Cells of BTBR Mouse Model of Autism. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020249




