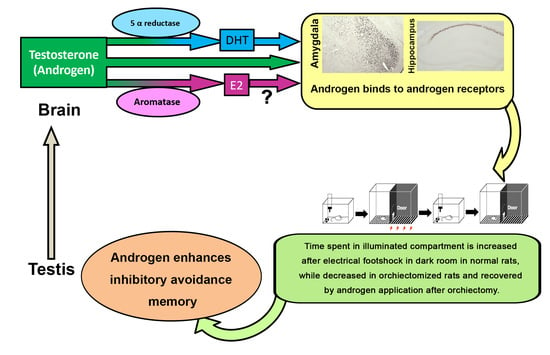
Androgen Affects the Inhibitory Avoidance Memory by Primarily Acting on Androgen Receptor in the Brain in Adolescent Male Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rats and Ethical Statement
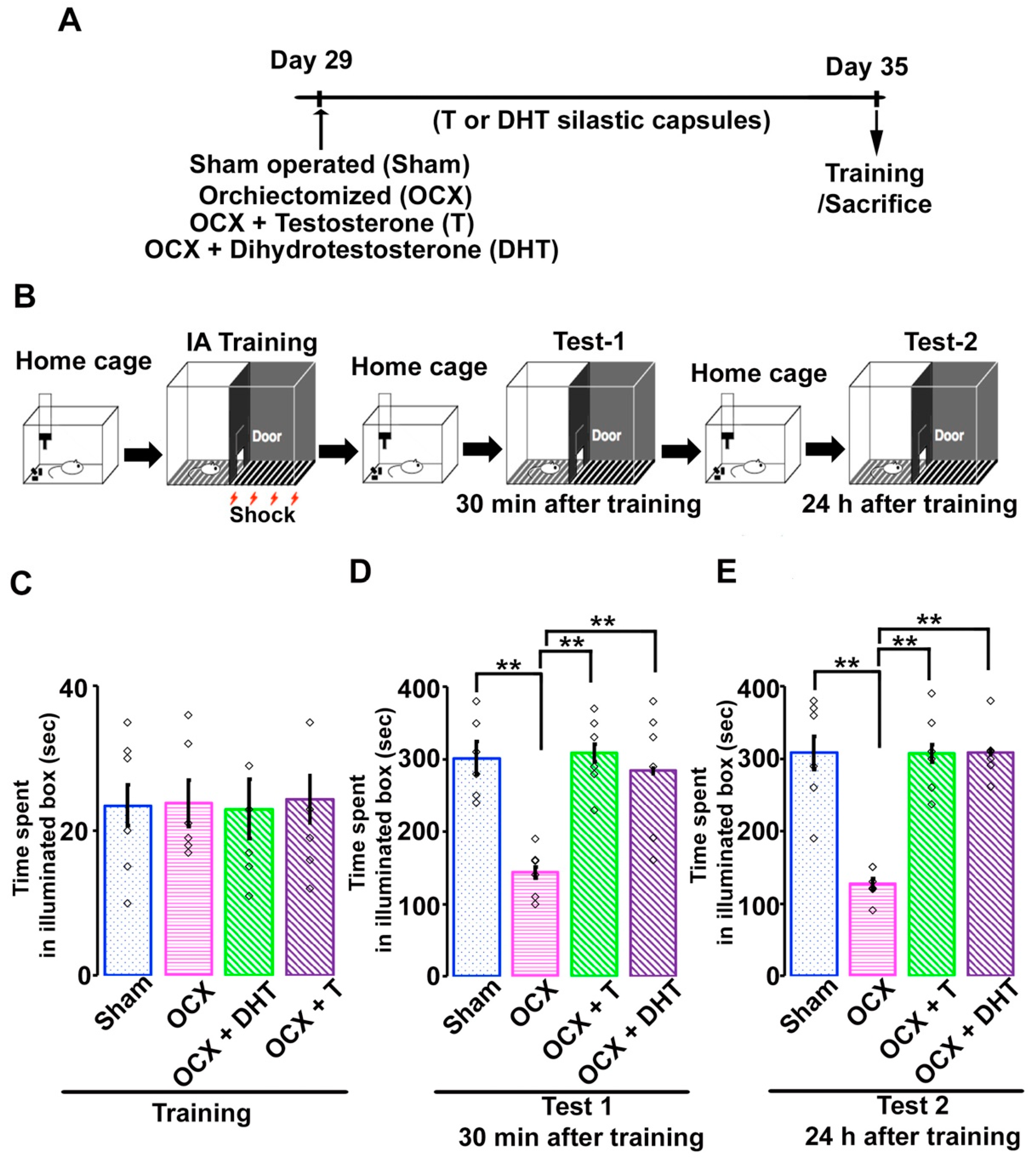
2.2. Surgical Procedure and Steroidal Manipulation
2.3. Inhibitory Avoidance Task
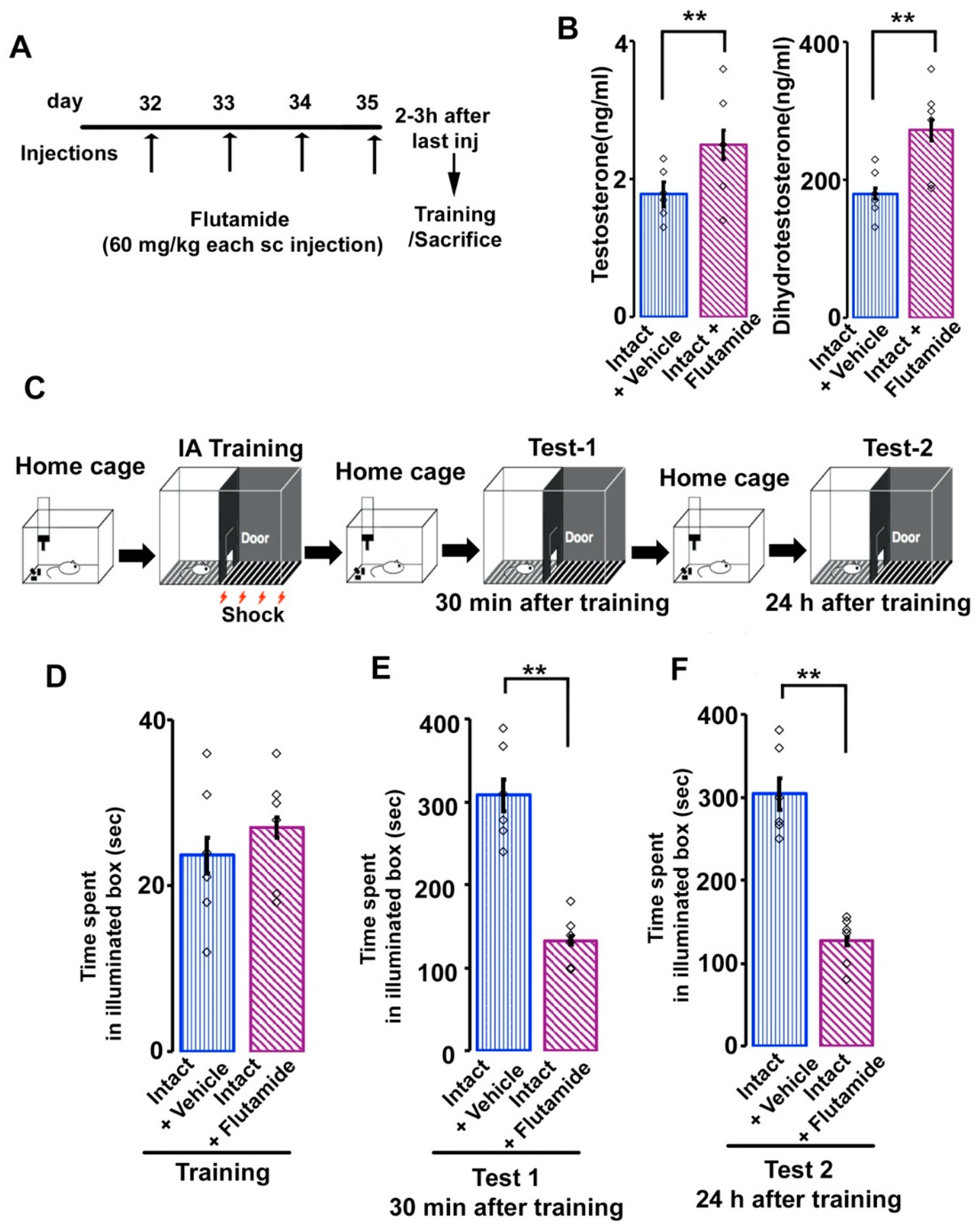
2.4. Serum Steroid Hormone Assay
2.5. Primary Antibodies
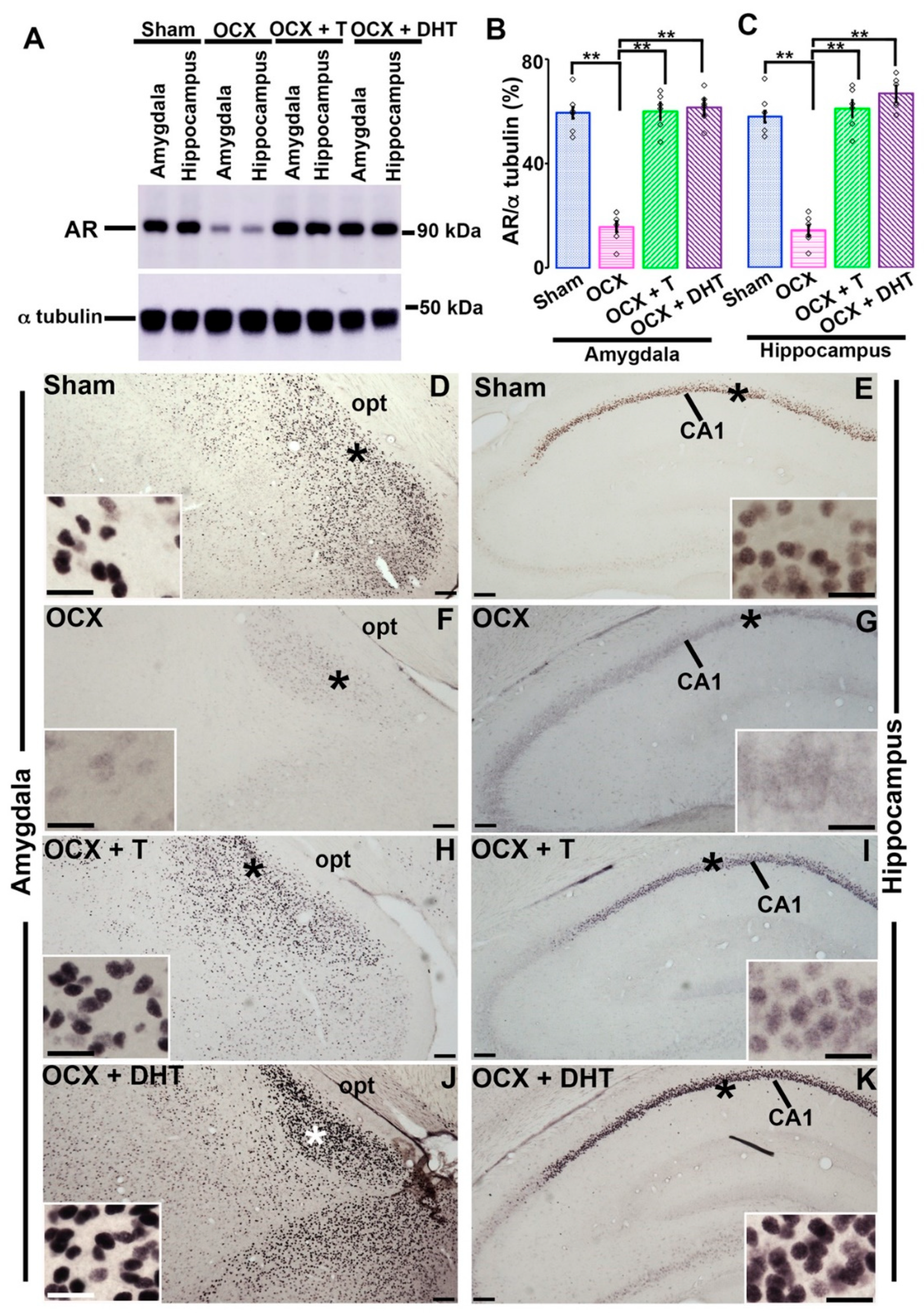
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Serum Steroid Levels after Manipulations of T and DHT
3.2. Effects of Gonadal Steroids on Inhibitory Avoidance Memory in Adolescent Male Rats
3.3. Effects of Gonadal Steroids on the Expression of AR in the Amygdala and Hippocampus in Adolescent Male Rats
3.4. Effects of Flutamide on Serum Androgen Concentration and Inhibitory Avoidance Memory in Adolescent Male Rats
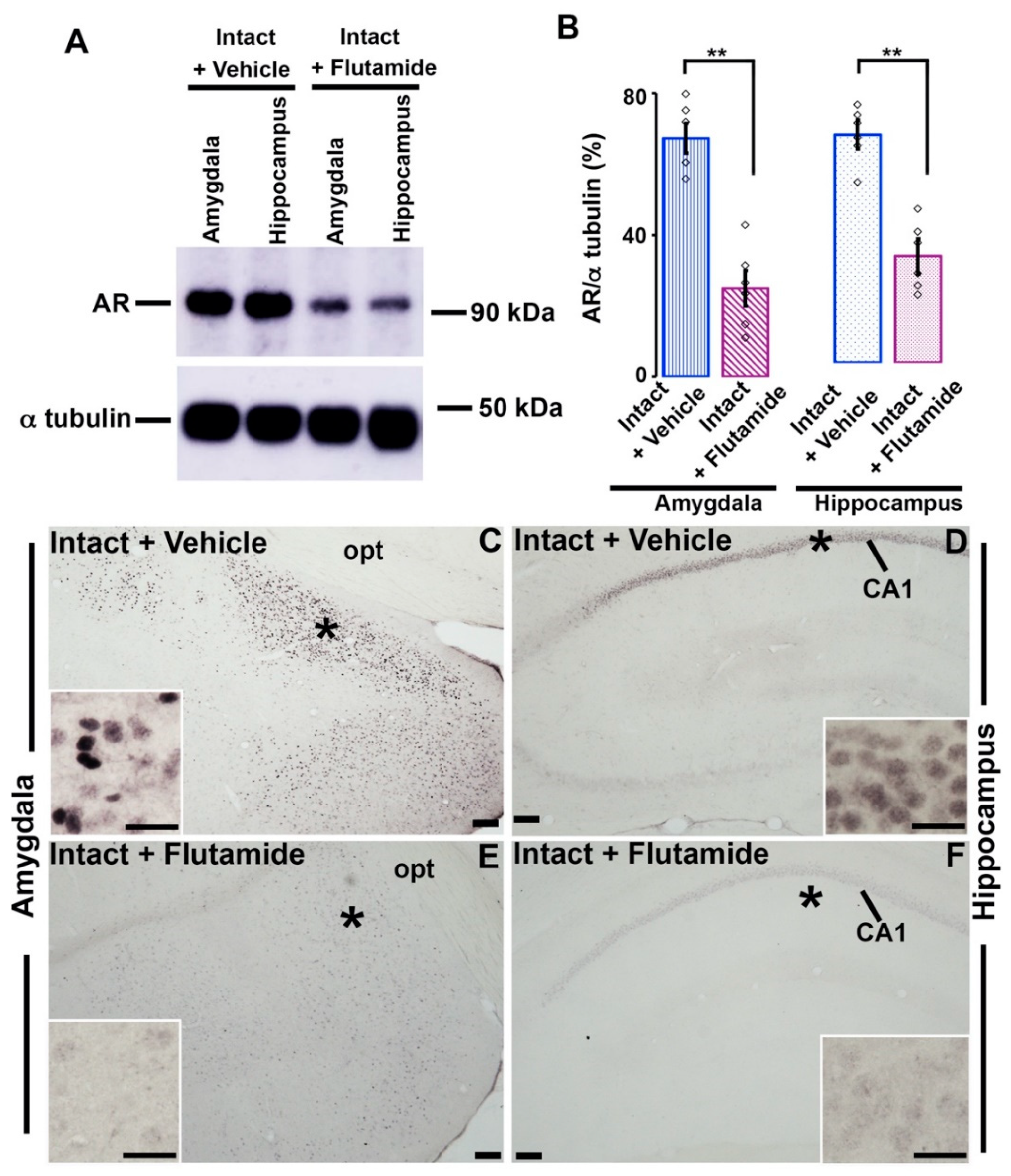
3.5. Effects of Flutamide on AR-immunoreactivity in the Amygdala and Hippocampus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinoda, K.; Nagano, M.; Osawa, Y. Neuronal aromatase expression in preoptic, strial, and amygdaloid regions during late prenatal and early postnatal development in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 343, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Washburn, T.F.; Taylor, J.; Lubahn, D.B.; Korach, K.S.; Pfaff, D.W. Modifications of testosterone-dependent behaviors by estrogen receptor-alpha gene disruption in male mice. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 5058–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLusky, N.J.; Hajszan, T.; Leranth, C. Effects of dehydroepiandrosterone and flutamide on hippocampal CA1 spine synapse density in male and female rats: Implications for the role of androgens in maintenance of hippocampal structure. Endocrinology. 2004, 145, 4154–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajszan, T.; MacLusky, N.J.; Johansen, J.A.; Jordan, C.L.; Leranth, C. Effects of androgens and estradiol on spine synapse formation in the prefrontal cortex of normal and testicular feminization mutant male rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Fujinaga, R.; Tanaka, M.; Yanai, A.; Nakahama, K.; Shinoda, K. Region-specific expression and sex-steroidal regulation on aromatase and its mRNA in the male rat brain: Immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization analyses. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 500, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, R.J.; Pak, T.R.; Kudwa, A.E.; Lund, T.D.; Hinds, L. An alternate pathway for androgen regulation of brain function: Activation of estrogen receptor beta by the metabolite of dihydrotestosterone, 5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foradori, C.D.; Weiser, M.J.; Handa, R.J. Non-genomic actions of androgens. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simerly, R.B.; Chang, C.; Muramatsu, M.; Swanson, L.W. Distribution of androgen and estrogen receptor mRNA-containing cells in the rat brain: An in situ hybridization study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 294, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, S.M.; McGinnis, M.Y. Effects of testosterone in the VMN on copulation, partner preference, and vocalizations in male rats. Horm. Behav. 2003, 43, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaney, W.T.; Dubose, B.N.; Curley, J.P.; Champagne, F.A. Sexual experience affects reproductive behavior and preoptic androgen receptors in male mice. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.R.; Kokubu, K.; Islam, M.N.; Matsuo, C.; Yanai, A.; Wroblewski, G.; Fujinaga, R.; Shinoda, K. Species differences in androgen receptor expression in the medial preoptic and anterior hypothalamic areas of adult male and female rodents. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 943–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Guterman, P.; Lieblich, S.E.; Wainwright, S.R.; Chow, C.; Chaiton, J.A.; Watson, N.V.; Galea, L. Androgens enhance adult hippocampal neurogenesis in males but not females in an age-dependent manner. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Fujinaga, R.; Yanai, A.; Jahan, M.R.; Takeshita, Y.; Kokubu, K.; Shinoda, K. Characterization of the “sporadically lurking HAP1-immunoreactive (SLH) cells” in the hippocampus, with special reference to the expression of steroid receptors, GABA, and progenitor cell markers. Neuroscience 2012, 210, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Sakimoto, Y.; Jahan, M.R.; Ishida, M.; Tarif, A.M.M.; Nozaki, K.; Masumoto, K.H.; Yanai, A.; Mitsushima, D.; Shinoda, K. Androgen Affects the Dynamics of Intrinsic Plasticity of Pyramidal Neurons in the CA1 Hippocampal Subfield in Adolescent Male Rats. Neuroscience 2020, 440, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.M.; Schulz, K.M.; Sisk, C.L.; Wood, R.I. Adolescents and androgens, receptors and rewards. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, L. Modeling adolescent development and alcohol use in animals. Alcohol Res. Health 2000, 24, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shaughnessy, P.J.; Baker, P.J.; Heikkilä, M.; Vainio, S.; McMahon, A.P. Localization of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/17-ketosteroid reductase isoform expression in the developing mouse testis--androstenedione is the major androgen secreted by fetal/neonatal leydig cells. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Arumugam, R.; Zhang, N.; Lee, M.M. Androgen profiles during pubertal Leydig cell development in mice. Reproduction 2010, 140, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Nakata, M.; Musatov, S.; Morishita, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Tsukahara, S.; Ogawa, S. Pubertal activation of estrogen receptor α in the medial amygdala is essential for the full expression of male social behavior in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7632–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashon, M.L.; Arbogast, J.A.; Sisk, C.L. Distribution and hormonal regulation of androgen receptor immunoreactivity in the forebrain of the male European ferret. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 376, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, L.R.; Romeo, R.D.; Novak, C.M.; Sisk, C.L. Actions of testosterone in prepubertal and postpubertal male hamsters: Dissociation of effects on reproductive behavior and brain androgen receptor immunoreactivity. Horm. Behav. 1997, 31, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, T.; Lattal, K.M. Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, C.A.; Seliga, A.M. Testosterone increases analgesia, anxiolysis, and cognitive performance of male rats. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2001, 1, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinger, K.L.; Frye, C.A. Testosterone’s analgesic, anxiolytic, and cognitive-enhancing effects may be due in part to actions of its 5alpha-reduced metabolites in the hippocampus. Behav. Neurosci. 2004, 118, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwi, S.; McMahon, D.; Scharfman, H.; MacLusky, N.J. Androgen Modulation of Hippocampal Structure and Function. Neuroscientist 2016, 22, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.A.; Watson, N.V. Spatial memory performance in androgen insensitive male rats. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, A.; Robertson, J.; Raber, J. Behavioral performance of tfm mice supports the beneficial role of androgen receptors in spatial learning and memory. Brain Res. 2005, 1034, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, W.R.; Grissom, E.M.; Martin, R.C.; Halmos, M.B.; Bart, C.L.; Dohanich, G.P. Testosterone modulates spatial recognition memory in male rats. Horm. Behav. 2013, 63, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubele, T.; Kaufman, R.; Montalmant, F.; Kritzer, M.F. Effects of gonadectomy and hormone replacement on a spontaneous novel object recognition task in adult male rats. Horm. Behav. 2008, 54, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot, M.; Billard, J.M.; Dombret, C.; Albac, C.; Karameh, N.; Daumas, S.; Hardin-Pouzet, H.; Mhaouty-Kodja, S. Neural Androgen Receptor Deletion Impairs the Temporal Processing of Objects and Hippocampal CA1-Dependent Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, A.L.; Creighton, S.D.; Wilson, H.A.; Jardine, K.H.; Isaacs, L.; Winters, B.D.; MacLusky, N.J. Inhibition of 5α reductase impairs cognitive performance, alters dendritic morphology and increases tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus of male 3xTg-AD mice. Neuroscience 2020, 429, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinger, K.L.; Frye, C.A. Testosterone’s anti-anxiety and analgesic effects may be due in part to actions of its 5alpha-reduced metabolites in the hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinger, K.L.; Frye, C.A. Intrahippocampal administration of an androgen receptor antagonist, flutamide, can increase anxiety-like behavior in intact and DHT-replaced male rats. Horm. Behav. 2006, 50, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baarendse, P.J.; van Grootheest, G.; Jansen, R.F.; Pieneman, A.W.; Ogren, S.O.; Verhage, M.; Stiedl, O. Differential involvement of the dorsal hippocampus in passive avoidance in C57bl/6J and DBA/2J mice. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atucha, E.; Roozendaal, B. The inhibitory avoidance discrimination task to investigate accuracy of memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, C.A.; Edinger, K.L.; Seliga, A.M.; Wawrzycki, J.M. 5alpha-reduced androgens may have actions in the hippocampus to enhance cognitive performance of male rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2004, 29, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinger, K.L.; Frye, C.A. Androgens’ performance-enhancing effects in the inhibitory avoidance and water maze tasks may involve actions at intracellular androgen receptors in the dorsal hippocampus. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 87, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, C.A.; McCormick, C.M. The neurosteroid, 3alpha-androstanediol, prevents inhibitory avoidance deficits and pyknotic cells in the granule layer of the dentate gyrus induced by adrenalectomy in rats. Brain Res. 2000, 855, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Hintz, T.M.; Gomez, J.; Stormes, K.A.; Barouk, S.; Malthankar-Phatak, G.H.; McCloskey, D.P.; Luine, V.N.; Maclusky, N.J. Changes in hippocampal function of ovariectomized rats after sequential low doses of estradiol to simulate the preovulatory estrogen surge. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 2595–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsushima, D.; Ishihara, K.; Sano, A.; Kessels, H.W.; Takahashi, T. Contextual learning requires synaptic AMPA receptor delivery in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12503–12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsushima, D.; Sano, A.; Takahashi, T. A cholinergic trigger drives learning-induced plasticity at hippocampal synapses. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimoto, Y.; Mizuno, J.; Kida, H.; Kamiya, Y.; Ono, Y.; Mitsushima, D. Learning Promotes Subfield-Specific Synaptic Diversity in Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Maeda, N.; Miyasato, E.; Jahan, M.R.; Tarif, A.; Ishino, T.; Nozaki, K.; Masumoto, K.H.; Yanai, A.; Shinoda, K. Expression of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in adult mouse dorsal root ganglia and its neurochemical characterization in reference to sensory neuron subpopulations. IBRO Rep. 2020, 9, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Takeshita, Y.; Yanai, A.; Imagawa, A.; Jahan, M.R.; Wroblewski, G.; Nemoto, J.; Fujinaga, R.; Shinoda, K. Immunohistochemical analysis of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in adult rat spinal cord and its regional relationship with androgen receptor. Neuroscience 2017, 340, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, G.; Islam, M.N.; Yanai, A.; Jahan, M.R.; Masumoto, K.H.; Shinoda, K. Distribution of HAP1-immunoreactive Cells in the Retrosplenial-retrohippocampal Area of Adult Rat Brain and Its Application to a Refined Neuroanatomical Understanding of the Region. Neuroscience 2018, 394, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, A.; Islam, M.N.; Hayashi-Okada, M.; Jahan, M.R.; Tarif, A.; Nozaki, K.; Masumoto, K.H.; Shinoda, K. Immunohistochemical relationships of huntingtin-associated protein 1 with enteroendocrine cells in the pyloric mucosa of the rat stomach. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, I.; Scaramuzzino, A.; Aloisi, A.M. Effects of gonadal hormones and persistent pain on non-spatial working memory in male and female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 123, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, M.F.; McLaughlin, P.J.; Smirlis, T.; Robinson, J.K. Gonadectomy impairs T-maze acquisition in adult male rats. Horm. Behav. 2001, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, J.F.; Farr, S.A.; Kaiser, F.E.; La Regina, M.; Morley, J.E. Age-related decrease of plasma testosterone in SAMP8 mice: Replacement improves age-related impairment of learning and memory. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 57, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbach, H. Age-associated testosterone decline in men: Clinical issues for psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 1998, 155, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.S. Memory loss as a reported symptom of andropause. Arch. Androl. 2001, 47, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhu, J.C.; Dou, J.T.; Bai, W.J.; Deng, S.M.; Li, M.; Huang, W.; Jin, H. Effects of androgen supplementation therapy on partial androgen deficiency in the aging male: A preliminary study. Aging Male 2002, 5, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, B.C.; Bever-Stille, K.A.; Perry, P.J. Testosterone and andropause: The feasibility of testosterone replacement therapy in elderly men. Pharmacotherapy 1999, 19, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Kaiser, F.E.; Sih, R.; Hajjar, R.; Perry, H.M., III. Testosterone and frailty. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 1997, 13, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowsky, J.S.; Oviatt, S.K.; Orwoll, E.S. Testosterone influences spatial cognition in older men. Behav. Neurosci. 1994, 108, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowsky, J.S.; Chavez, B.; Orwoll, E. Sex steroids modify working memory. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, S.; Shalet, S. Testosterone deficiency and replacement. Horm. Res. 2001, 56 (Suppl. 1), 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.M.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wang, C.; Davidson, T.; McDonald, V.; Steiner, B.; Hines, M. Androgen-behavior correlations in hypogonadal men and eugonadal men. II. Cognitive abilities. Horm. Behav. 1998, 33, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Jordan, C.L. Sex differences, laterality, and hormonal regulation of androgen receptor immunoreactivity in rat hippocampus. Horm. Behav. 2002, 42, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.W.; Taniguchi, S.; Samoza, J.; Ridder, A. Age- and Sex-Dependent Changes in Androgen Receptor Expression in the Developing Mouse Cortex and Hippocampus. Neurosci. J. 2015, 2015, 525369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babstock, D.M.; Walling, S.G.; Harley, C.W.; Malsbury, C.W. Androgen receptor ontogeny in the dorsal hippocampus of male and female rats. Horm. Behav. 2018, 100, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.F.; McKenna, S.E.; Cologer-Clifford, A.; Nau, E.A.; Simon, N.G. Androgen receptor in mouse brain: Sex differences and similarities in autoregulation. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M. The role of the amygdala in conditioned and unconditioned fear and anxiety. In The Amygdala, 2nd ed.; Aggleton, J.P., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 213–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, R.A.; Zhou, L.; Vierk, R.; Brandt, N.; Keller, A.; Gee, C.E.; Schäfer, M.K.; Rune, G.M. Sex-Dependent Regulation of Aromatase-Mediated Synaptic Plasticity in the Basolateral Amygdala. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkänen, A. Connectivity of the rat amygdaloid complex. In The Amygdala, 2nd ed.; Aggleton, J.P., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 31–115. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, A.J.; Mascagni, F. Projections of the lateral entorhinal cortex to the amygdala: A phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin study in the rat. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdakov, D.; Peleg-Raibstein, D. The hypothalamus as a primary coordinator of memory updating. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 223, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leranth, C.; Hajszan, T.; MacLusky, N.J. Androgens increase spine synapse density in the CA1 hippocampal subfield of ovariectomized female rats. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLusky, N.J.; Hajszan, T.; Prange-Kiel, J.; Leranth, C. Androgen modulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 2006, 138, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, Y.; Hojo, Y.; Mukai, H.; Murakami, G.; Komatsuzaki, Y.; Kim, J.; Ikeda, M.; Hiragushi, A.; Kimoto, T.; Kawato, S. Rapid increase of spines by dihydrotestosterone and testosterone in hippocampal neurons: Dependence on synaptic androgen receptor and kinase networks. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Liang, K.C.; Yen, C.T. Inhibitory avoidance learning altered ensemble activity of amygdaloid neurons in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsushima, D.; Takase, K.; Funabashi, T.; Kimura, F. Gonadal steroid hormones maintain the stress-induced acetylcholine release in the hippocampus: Simultaneous measurements of the extracellular acetylcholine and serum corticosterone levels in the same subjects. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Simon, N.G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S. Neural androgen receptor regulation: Effects of androgen and antiandrogen. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 41, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Lane, M.V.; Kemppainen, J.A.; French, F.S.; Wilson, E.M. Specificity of ligand-dependent androgen receptor stabilization: Receptor domain interactions influence ligand dissociation and receptor stability. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Farla, P.; Hersmus, R.; Trapman, J.; Houtsmuller, A.B. Antiandrogens prevent stable DNA-binding of the androgen receptor. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, T.R.; Chung, W.C.; Lund, T.D.; Hinds, L.R.; Clay, C.M.; Handa, R.J. The androgen metabolite, 5alpha-androstane-3beta, 17beta-diol, is a potent modulator of estrogen receptor-beta1-mediated gene transcription in neuronal cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.S.; Jian, K. The testosterone-derived neurosteroid androstanediol is a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Du, J.; Cui, H. Detecting the presence of hippocampus membrane androgen receptors in male SAMP8 mice and their induced synaptic plasticity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 414, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Immunogen | Clonality/Host | Source | Dilution | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Androgen receptor | Mouse androgen receptor | Polyclonal Rabbit | RRID: AB_1563391, Cat# sc-816, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA | 1:2000 | [11,14] |
| Androgen receptor | Androgen Receptor from Human (N terminal, aa 1–10) | Monoclonal Rabbit | RRID: AB_11156085, Cat# ab133273, Abcam, Cambridge, UK | 1:5000 | [14] |
| α-tubulin | chicken embryonic brain derived microtubule | Monoclonal Mouse | RRID: AB_477583,Cat# T6199, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | 1:200,000 | [43] |
| Group | Number of Rats | T (ng/mL) | DHT (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham-operated | 18 | 1.71 ± 0.25 | 171.35 ± 12.29 |
| OCX | 18 | 0.29 ± 0.09 a | 41.03 ± 8.27 a |
| OCX + T | 18 | 2.21 ± 0.27 b | 221.35 ± 31.13 b |
| OCX + DHT | 18 | 0.41 ± 0.15 a | 233.62 ± 28.21 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.N.; Sakimoto, Y.; Jahan, M.R.; Miyasato, E.; Tarif, A.M.M.; Nozaki, K.; Masumoto, K.-h.; Yanai, A.; Mitsushima, D.; Shinoda, K. Androgen Affects the Inhibitory Avoidance Memory by Primarily Acting on Androgen Receptor in the Brain in Adolescent Male Rats. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020239
Islam MN, Sakimoto Y, Jahan MR, Miyasato E, Tarif AMM, Nozaki K, Masumoto K-h, Yanai A, Mitsushima D, Shinoda K. Androgen Affects the Inhibitory Avoidance Memory by Primarily Acting on Androgen Receptor in the Brain in Adolescent Male Rats. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Nabiul, Yuya Sakimoto, Mir Rubayet Jahan, Emi Miyasato, Abu Md Mamun Tarif, Kanako Nozaki, Koh-hei Masumoto, Akie Yanai, Dai Mitsushima, and Koh Shinoda. 2021. "Androgen Affects the Inhibitory Avoidance Memory by Primarily Acting on Androgen Receptor in the Brain in Adolescent Male Rats" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020239
APA StyleIslam, M. N., Sakimoto, Y., Jahan, M. R., Miyasato, E., Tarif, A. M. M., Nozaki, K., Masumoto, K.-h., Yanai, A., Mitsushima, D., & Shinoda, K. (2021). Androgen Affects the Inhibitory Avoidance Memory by Primarily Acting on Androgen Receptor in the Brain in Adolescent Male Rats. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020239