Elevated Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Reflect Inflammatory MRI Activity in Neurosarcoidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Validation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Neurofilament Light Chain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byg, K.E.; Milman, N.; Hansen, S. Sarcoidosis in Denmark 1980–1994. A registry-based incidence study comprising 5536 patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2003, 20, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.P.; Teirstein, A.S.; Judson, M.A.; Rossman, M.D.; Yeager, H., Jr.; Bresnitz, E.A.; DePalo, L.; Hunninghake, G.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Johns, C.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1885–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; White, J.R., Jr.; Espahbodi, M.; Haynes, D.S.; Driscoll, C.L.; Aksamit, A.J.; Pawate, S.; Lane, J.I.; Link, M.J. Cranial base manifestations of neurosarcoidosis: A review of 305 patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D.P. Sarcoidosis of the central nervous system: Clinical features, imaging, and CSF results. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengert, O.; Rothenfusser-Korber, E.; Vollrath, B.; Bohner, G.; Scheibe, F.; Otto, C.; Hofmann, J.; Angstwurm, K.; Ruprecht, K. Neurosarcoidosis: Correlation of cerebrospinal fluid findings with diffuse leptomeningeal gadolinium enhancement on MRI and clinical disease activity. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 335, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazal, T.; Costopoulos, M.; Maillart, E.; Fleury, C.; Psimaras, D.; Legendre, P.; Pineton de Chambrun, M.; Haroche, J.; Lubetzki, C.; Amoura, Z.; et al. The cerebrospinal fluid CD4/CD8 ratio and interleukin-6 and -10 levels in neurosarcoidosis: A multicenter, pragmatic, comparative study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.; Wengert, O.; Unterwalder, N.; Meisel, C.; Ruprecht, K. Analysis of soluble interleukin-2 receptor as CSF biomarker for neurosarcoidosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.P.; Patel, D.C.; Tavee, J.O.; Culver, D.A. Evaluating S100B as a serum biomarker for central neurosarcoidosis. Respir Med. 2020, 162, 105855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiottino, J.; Norgren, N.; Dobson, R.; Topping, J.; Nissim, A.; Malaspina, A.; Bestwick, J.P.; Monsch, A.U.; Regeniter, A.; Lindberg, R.L.; et al. Increased neurofilament light chain blood levels in neurodegenerative neurological diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Mukerji, S.S.; Chettimada, S.; Misra, V.; Lorenz, D.R.; Morgello, S.; Gabuzda, D. Cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles and neurofilament light protein as biomarkers of central nervous system injury in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy. Aids 2019, 33, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahim, P.; Tegner, Y.; Marklund, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light and tau as blood biomarkers for sports-related concussion. Neurology 2018, 90, e1780–e1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Costabel, U.; Ando, M.; Baughman, R.; Cordier, J.F.; du Bois, R. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 1999, 16, 149–173. [Google Scholar]
- Judson, M.A.; Costabel, U.; Drent, M.; Wells, A.; Maier, L.; Koth, L.; Shigemitsu, H.; Culver, D.A.; Gelfand, J.; Valeyre, D.; et al. The WASOG Sarcoidosis Organ Assessment Instrument: An update of a previous clinical tool. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2014, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, T.; Pattison, L.; Palace, J. Distinguishing neurosarcoidosis from multiple sclerosis based on CSF analysis: A retrospective study. Neurology 2020, 94, e2545–e2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Vuilleumier, N.; Lalive, P.H. Cerebrospinal fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme for diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 285, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petereit, H.F.; Reske, D.; Tumani, H.; Jarius, S.; Markus Leweke, F.; Woitalla, D.; Pfister, H.-W.; Rubbert, A. Soluble CSF interleukin 2 receptor as indicator of neurosarcoidosis. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.A.; Leite, M.C.; Nardin, P. Biological and methodological features of the measurement of S100B, a putative marker of brain injury. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjensvoll, A.B.; Lauvsnes, M.B.; Zetterberg, H.; Kvaløy, J.T.; Kvivik, I.; Maroni, S.S.; Greve, O.J.; Beyer, M.K.; Hirohata, S.; Putterman, C.; et al. Neurofilament light is a biomarker of brain involvement in lupus and primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Michalak, Z.; Isobe, N.; Barro, C.; Leppert, D.; Matsushita, T.; Hayashi, F.; Yamasaki, R.; Kuhle, J.; et al. Serum GFAP and neurofilament light as biomarkers of disease activity and disability in NMOSD. Neurology 2019, 93, e1299–e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Disanto, G.; Tsagkas, C.; Amann, M.; Naegelin, Y.; Leppert, D.; Gobbi, C.; Granziera, C.; Yaldizli, Ö.; et al. Serum neurofilament as a predictor of disease worsening and brain and spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2018, 141, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disanto, G.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Naegelin, Y.; Schädelin, S.; Giardiello, A.; Zecca, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Leppert, D.; et al. Serum Neurofilament light: A biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sejbaek, T.; Mendoza, J.P.; Penner, N.; Madsen, J.S.; Olsen, D.A.; Illes, Z. Comparison of neurofilament light chain results between two independent facilities. BMJ Neurol. Open 2020, 2, e000063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Pirpamer, L.; Hofer, E.; Voortman, M.M.; Barro, C.; Leppert, D.; Benkert, P.; Ropele, S.; Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Serum neurofilament light levels in normal aging and their association with morphologic brain changes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
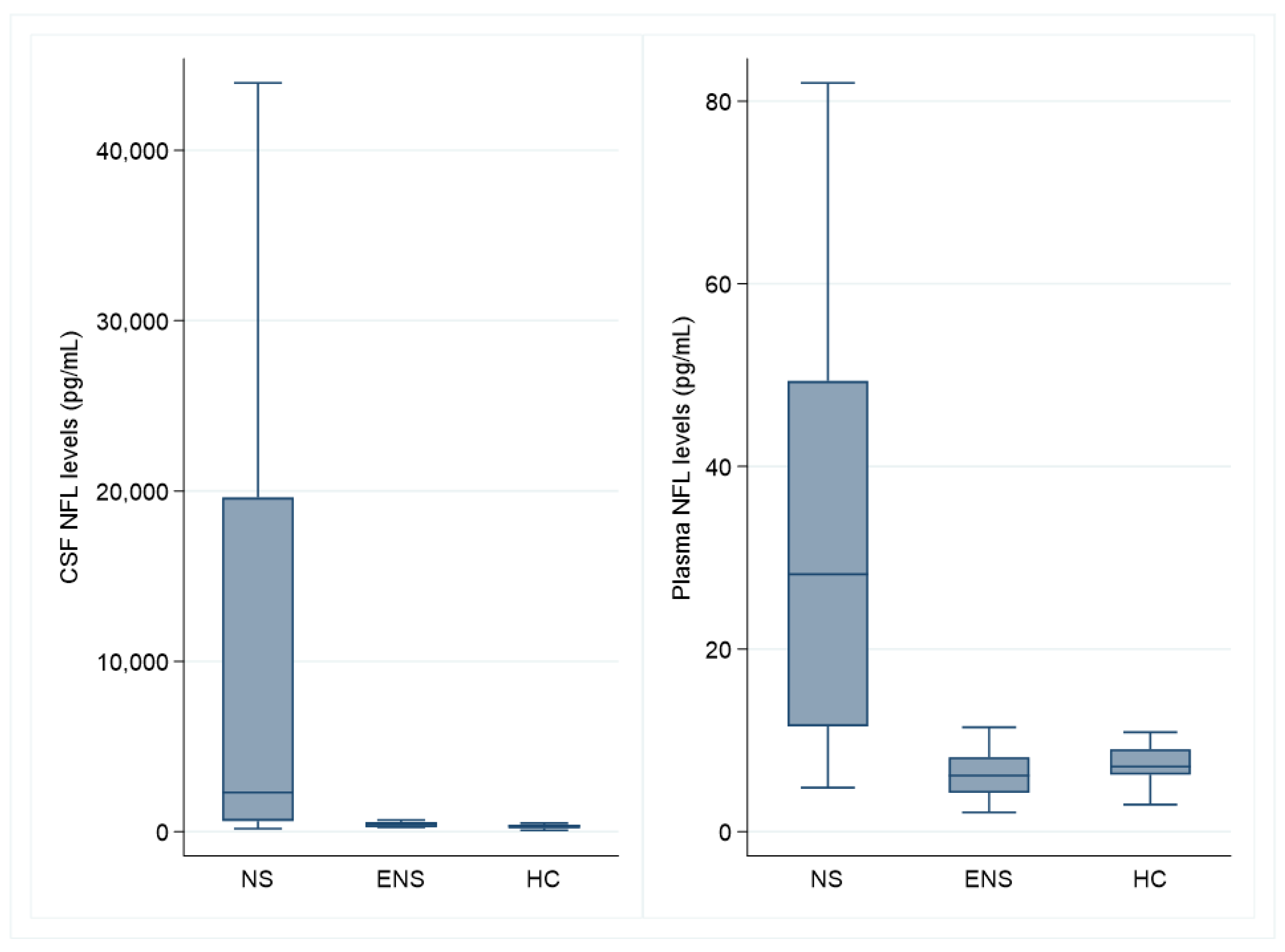
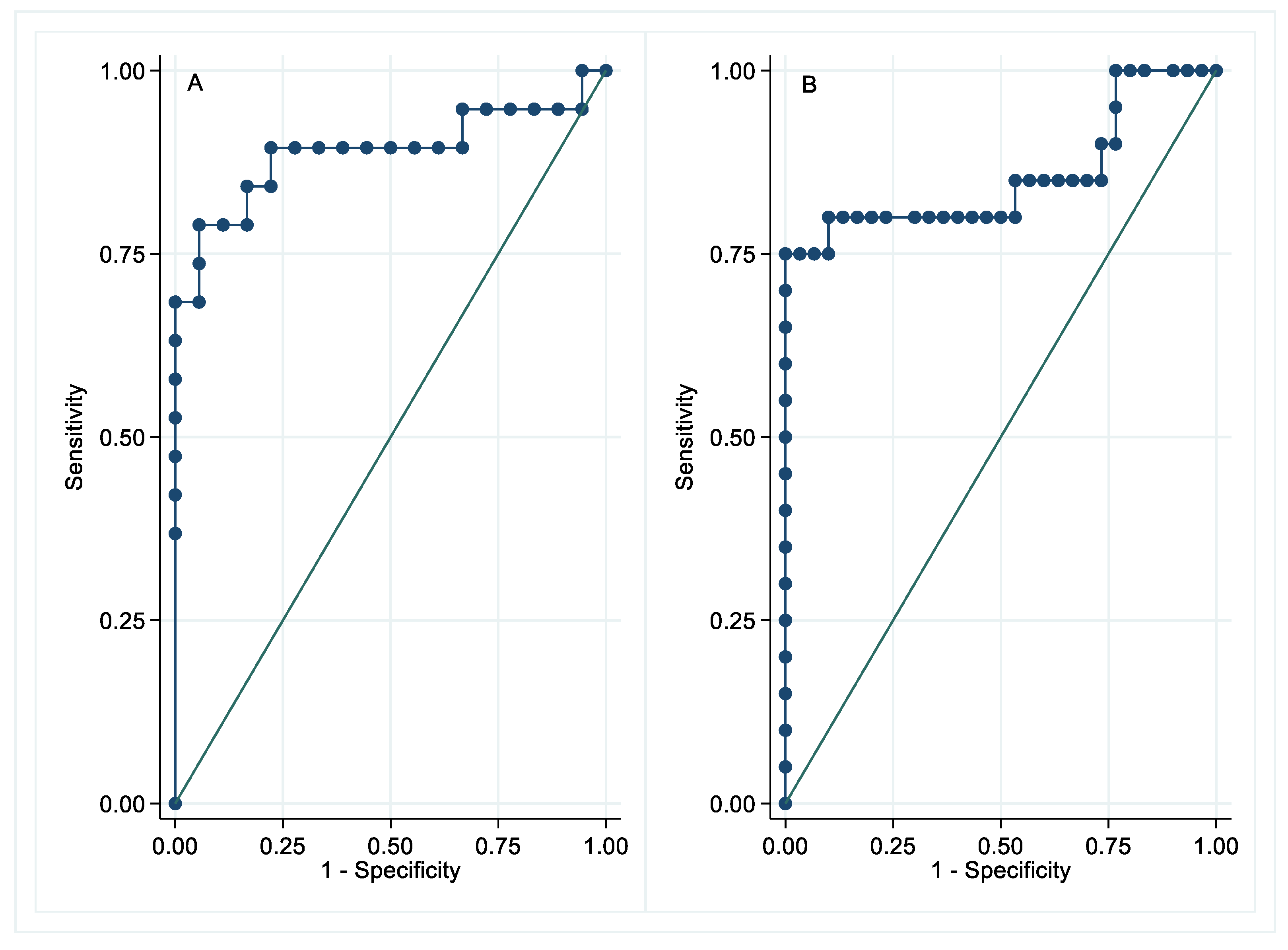
| Neurosarcoidosis | Extra-Neurologic Sarcoidosis | Healthy Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 20 | 20 | 11 |
| Age, years (median, IQR) | 51.6 (43.0–56.4) | 44.5 (40.2–54.6) | 37.0 (25.8–44.5) |
| Female (%) | 9 (45) | 14 (70) | 10 (91) |
| Duration of symptoms, months (median, IQR) | 8 (4–16) | 33 (13–45) | |
| Neurological symptoms | |||
| Headache (%) | 12 (60) | 6 (30) | |
| Tinnitus (%) | 10 (50) | 2 (10) | |
| Vertigo (%) | 11 (55) | 1 (5) | |
| Cranial nervous affection (%) | 6 (30) | 1 (5) | |
| Peripheral motor symptoms (%) | 8 (40) | 0 | |
| Peripheral sensory symptoms (%) | 10 (50) | 0 | |
| Chest X-ray (%) | |||
| Stage 0 | 8 (40) | 4 (20) | |
| Stage 1 | 9 (45) | 12 (60) | |
| Stage 2 | 3 (15) | 3 (15) | |
| Stage 3–4 | 0 | 1 (5) | |
| Immunosuppression (%) | |||
| Glycocorticosteroid | 4 (20) | 5 (25) | |
| Methotrexate/Azatrioprin | 2 (10) | 5 (25) |
| No Enhancement | Mild Enhancement | Moderate/Severe Enhancement | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 8 | 5 | 7 | |
| NFL in CSF (median, IQR) | 820 (449–2635) | 689 (514–2070) | 28977 (19,612–30,239) | 0.004 |
| NFL in plasma (median, IQR) | 9.5 (5.2–28.9) | 16.8 (16.0–16.8) | 62.7 (47.2–82.0) | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byg, K.-E.; Nielsen, H.H.; Sejbaek, T.; Madsen, J.S.; Olsen, D.A.; Nguyen, N.; Kindt, A.; Grauslund, J.; Illes, Z.; Ellingsen, T. Elevated Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Reflect Inflammatory MRI Activity in Neurosarcoidosis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020238
Byg K-E, Nielsen HH, Sejbaek T, Madsen JS, Olsen DA, Nguyen N, Kindt A, Grauslund J, Illes Z, Ellingsen T. Elevated Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Reflect Inflammatory MRI Activity in Neurosarcoidosis. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020238
Chicago/Turabian StyleByg, Keld-Erik, Helle H. Nielsen, Tobias Sejbaek, Jonna Skov Madsen, Dorte Aalund Olsen, Nina Nguyen, Astrid Kindt, Jakob Grauslund, Zsolt Illes, and Torkell Ellingsen. 2021. "Elevated Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Reflect Inflammatory MRI Activity in Neurosarcoidosis" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020238
APA StyleByg, K.-E., Nielsen, H. H., Sejbaek, T., Madsen, J. S., Olsen, D. A., Nguyen, N., Kindt, A., Grauslund, J., Illes, Z., & Ellingsen, T. (2021). Elevated Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Reflect Inflammatory MRI Activity in Neurosarcoidosis. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020238






