Risk Factors of the First-Time Stroke in the Southwest of Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorelick, P.B. The global burden of stroke: Persistent and disabling. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams-Vahdati, S.; Ala, A.; Sadeghi-Hokmabad, E.; Parnianfard, N.; Sepehri, N.A.; Gheybi, M. The Relationship between Demographic Factors in Adult Patients with Stroke. Adv. Biosci. Clin. Med. 2020, 7, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, K.; Wang, H.; Xie, Y.; Xu, P.; Dai, Z.; Gu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, M. Impact of smoking status on stroke recurrence. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, M.; Mansournia, M.A.; Kaufman, J.S. Estimating Effect of Obesity on Stroke Using G-Estimation: The ARIC study. Obesity 2019, 27, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Borlongan, C.V.; Tajiri, N. A brief physical activity protects against ischemic stroke. Brain Circ. 2019, 5, 112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alloubani, A.; Saleh, A.; Abdelhafiz, I. Hypertension and diabetes mellitus as a predictive risk factors for stroke. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-rawi, W.W.; Sulaiman, M.A. Profile of stroke patients admitted to Azadi Teaching Hospital in Duhok. Duhok Med. J. 2017, 11, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Benamer, H.T.; Grosset, D. Stroke in Arab countries: A systematic literature review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 284, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, M.M.; Adeuja, A.O.G.; El-Nahrawy, E.; Olaish, M.A. Characteristics of stroke in Hofuf, Saudi Arabia. Ann. Saudi Med. 1999, 19, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoola, A.E.; Banzal, S.S.; Elamin, A.K.; Godour, M.; Elsammani, E.W.; Al-Hazmi, M.H. Profile of stroke in Gizan, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Neurosci. J. 2003, 8, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Central Authority of Statistics, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In Statistical Yearbook of 2016; Issue Number 52. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa/en/866-0 (accessed on 22 January 2018).
- World Health Organization. WHO STEPS Surveillance Manual: The WHO STEP Wise Approach to Chronic Disease Risk Factor Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Härdle, W.; Mori, Y.; Vieu, P. Statistical Methods for Biostatistics and Related Fields; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hatim, M.; Sha’ar, M.; AlQurashi, Q.Z.; Abdulrahem, A.M.; AlOsaimi, F.F.; Basharaheel, S.S.; Alharthi, S.J. Epidemiology of stroke in hypobaric oxygen environment in Taif city, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Med. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 3, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, N.; Alassaf, H.; Alhaysuni, A.; AlTbenawi, A.; Alateeq, L.; Alkhalaf, A.; Alshammari, K.; Alghassab, T.; Alshammari, O.; Alshammari, S. Prevalence and Prognosis of Cerebrovascular Accidents and its Subtypes: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Hail Region, Saudi Arabia. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. CPhysiol. Mol. Biol. 2019, 11, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, N.; Alrasheedi, M.S.; Alshammari, S.T. Hemoglobin level is associated with severe stroke among stroke patients in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Health Sci. 2020, 14, 18. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hajj, M.; Salameh, P.; Rachidi, S.; Hosseini, H. The epidemiology of stroke in the Middle East. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistoia, F.; Sacco, S.; Degan, D.; Tiseo, C.; Ornello, R.; Carolei, A. Hypertension and stroke: Epidemiological aspects and clinical evaluation. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2016, 23, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nozha, M.; Abdullah, M.; Arafah, M.; Khalil, M.; Khan, N.; Al-Mazrou, Y.; Al-Maatouq, M.; Al-Marzouki, K.; Al-Khadra, A.; Nouh, M.; et al. Hypertension in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2007, 28, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Alhazzani, A.A.; Mahfouz, A.A.; Abolyazid, A.Y.; Awadalla, N.J.; Ahmed, R.A.; Siddiqui, A.F.; Khalil, S.N. Awareness of stroke among patients attending primary healthcare services in Abha, Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Neurosci. J. 2019, 24, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- James, P.A.; Oparil, S.; Carter, B.L.; Cushman, W.C.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.; Handler, J.; Lackland, D.T.; LeFevre, M.L.; MacKenzie, T.D.; Ogedegbe, O. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014, 311, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, R. Risk factors and subtypes of ischemic stroke in young patients: An observational study from a teaching hospital in Saudi Arabia. Funct. Neurol. 2019, 34, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, M.N.; Alharbi, A.K.; Alamri, M.A.; Alharthi, A.A.S.; Alqerafi, A.M.; Alharbi, M.N. Ischemic stroke: Prevalence of modifiable risk factors in the Saudi population. Age (Years) 2019, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, G.R.; Lewis, C.E. The Look AHEAD Trial: Implications for lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tun, N.N.; Arunagirinathan, G.; Munshi, S.K.; Pappachan, J.M. Diabetes mellitus and stroke: A clinical update. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dawish, M.A.; Robert, A.A.; Braham, R.; Al Hayek, A.A.; Al Saeed, A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Al Sabaan, F.S. Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: A Review of the Recent Literature. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nozha, M.M.; Al-Maatouq, M.A.; Al-Mazrou, Y.Y.; Al-Harthi, S.S.; Arafah, M.R.; Khalil, M.Z.; Khan, N.B.; Al-Khadra, A.; Al-Marzouki, K.; Nouh, M.S.; et al. Diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2004, 11, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robert, A.A.; Al Dawish, M.A.; Braham, R.; Musallam, M.A.; Al Hayek, A.A.; Al Kahtany, N.H. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: Major Challenges and Possible Solutions. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2017, 13, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubeaan, K.; Al-Hussain, F.; Youssef, A.M.; Subhani, S.N.; Al-Sharqawi, A.H.; Ibrahim, H.M. Ischemic stroke and its risk factors in a registry-based large cross-sectional diabetic cohort in a country facing a diabetes epidemic. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SS, M.A. A review of prevalence of obesity in Saudi Arabia. J. Obes. Eat Disord. 2016, 2, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Memish, Z.A.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Tuffaha, M.; Robinson, M.; Daoud, F.; Jaber, S.; Mikhitarian, S.; Al Saeedi, M.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Mokdad, A.H. Peer reviewed: Obesity and associated factors—Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2013. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nozha, M.M.; Arafah, M.R.; Al-Maatouq, M.A.; Khalil, M.Z.; Khan, N.B.; Al-Marzouki, K.; Al-Mazrou, Y.Y.; Abdullah, M.; Al-Khadra, A.; Al-Harthi, S.S.; et al. Hyperlipidemia in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2008, 29, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R. Heart disease and stroke Statistics—2019 update a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.D.; Folsom, A.R.; Blair, S.N. Physical activity and stroke risk: A meta-analysis. Stroke 2003, 34, 2475–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Saudi Arabia Diabetes Country Profiles 2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Chin, S.L.; Rangarajan, S.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Zhang, X.; Pais, P.; Agapay, S. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): A case-control study. Lancet 2016, 388, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
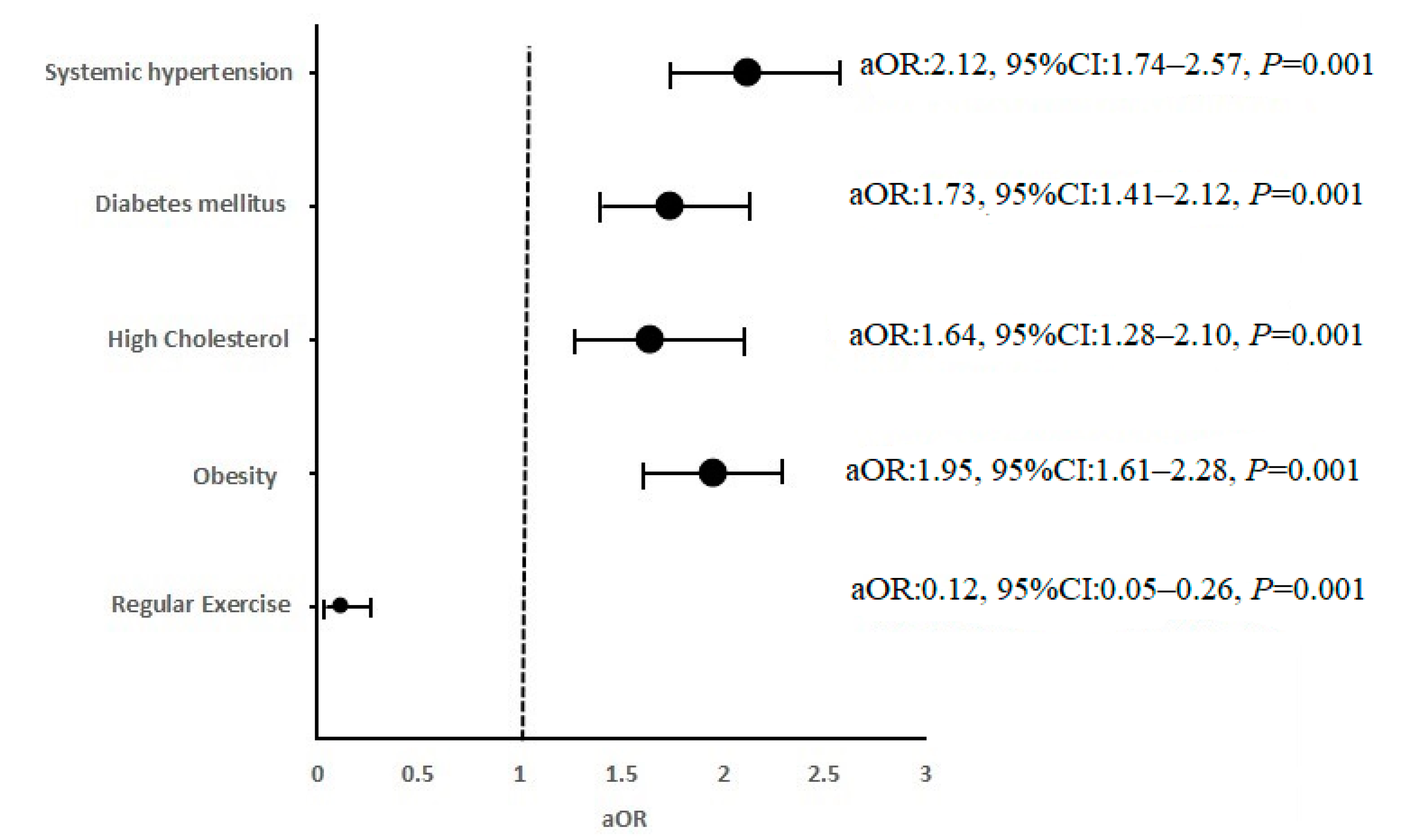
| Factors | Cases N (%) | Controls N (%) | cOR (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationality | Saudi | 1157 (92.6) | 1170 (93.7) | Ref. |
| Non-Saudi | 92 (7.4) | 79 (6.3) | 0.85 (0.62–1.15) | |
| Marital Status | Married | 892 (71.4) | 908 (72.7) | Ref. |
| Single/widowed | 357 (28.6) | 341 (27.3) | 1.07 (0.89–1.13) | |
| Education | Illiterate | 576 (46.1) | 524 (42) | Ref. |
| Primary | 376 (30.1) | 367 (29.4) | 0.93 (0.77–1.12) | |
| Intermediate | 114 (9.1) | 145 (11.6) | 0.72 (0.54–0.98) | |
| Secondary | 106 (8.5) | 115 (9.2) | 0.84 (0.63–1.12) | |
| University | 77 (6.2) | 98 (7.8) | 0.71 (0.52–0.99) | |
| Consanguinity | No | 706 (56.5) | 707 (56.6) | Ref |
| Yes | 543 (43.5) | 542 (43.4) | 1.00 (0.86–1.18) | |
| Family History | No | 1107 (88.6) | 1133 (90.7) | Ref. |
| Yes | 142 (11.4) | 116 (9.3) | 1.25 (0.97–1.62) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 632 (50.6) | 926 (74.1) | Ref. |
| Yes | 617 (49.4) | 323 (25.9) | 2.80 (2.36–3.31) | |
| Systemic hypertension | No | 528 (42.3) | 852 (68.2) | Ref. |
| Yes | 721 (57.7) | 397 (31.8) | 2.93 (2.48–3.45) | |
| High cholesterol | No | 882 (70.6) | 1098 (87.9) | Ref. |
| Yes | 367 (29.4) | 151 (12.1) | 3.30 (2.45–3.73) | |
| Current Smoking | No | 1121 (89.7) | 1136 (91.0) | Ref. |
| Yes | 128 (10.3) | 113 (9.0) | 1.15 (0.88–1.50) | |
| Regular Exercise | No | 1085 (86.9) | 875 (70.1) | Ref. |
| Yes | 164 (13.1) | 374 (29.9) | 0.35 (0.29–0.43) | |
| Obesity | No | 724 (58.2) | 864 (69.2) | Ref. |
| Yes | 525 (42.0) | 385 (30.8) | 1.63 (1.38–1.92) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhazzani, A.A.; Mahfouz, A.A.; Abolyazid, A.Y.; Awadalla, N.J. Risk Factors of the First-Time Stroke in the Southwest of Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020222
Alhazzani AA, Mahfouz AA, Abolyazid AY, Awadalla NJ. Risk Factors of the First-Time Stroke in the Southwest of Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhazzani, Adel A., Ahmed A. Mahfouz, Ahmed Y. Abolyazid, and Nabil J. Awadalla. 2021. "Risk Factors of the First-Time Stroke in the Southwest of Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020222
APA StyleAlhazzani, A. A., Mahfouz, A. A., Abolyazid, A. Y., & Awadalla, N. J. (2021). Risk Factors of the First-Time Stroke in the Southwest of Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020222






