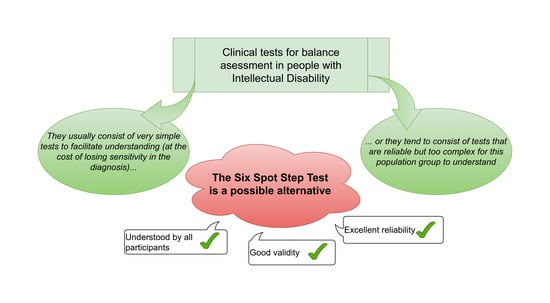
Reliability and Validity of the Six Spot Step Test in People with Intellectual Disability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. The SSST
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
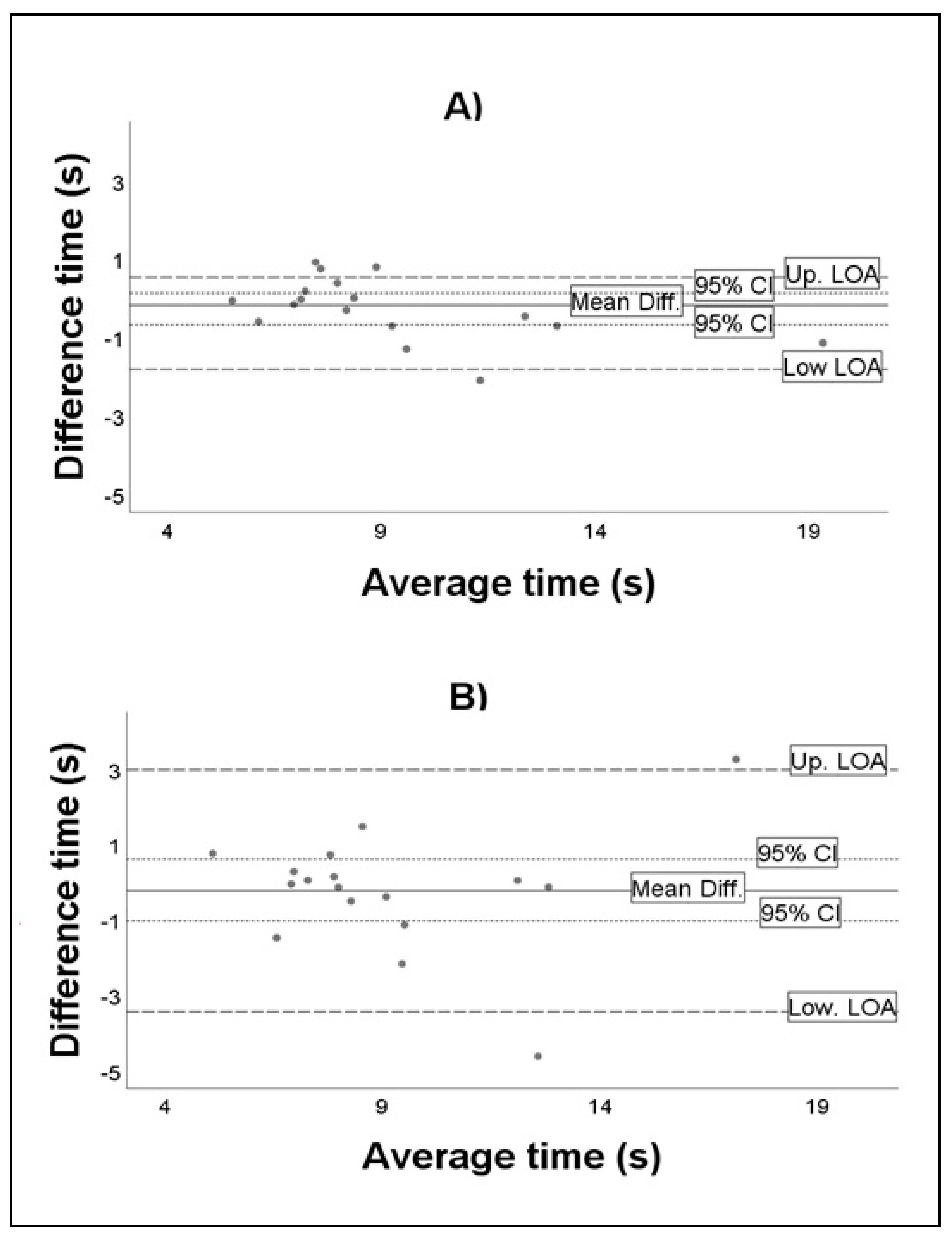
3.2. Test–Retest within-Day and Day-to-Day Reliability Analyses
3.3. Validity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eichstaedt, C.B. Physical Activity for Individuals with Mental Retardation: Infancy through Adulthood; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, L.; Miller, R.; Barach, A.; Skinner, M.; Gray, A. Motor Control Test responses to balance perturbations in adults with an intellectual disability. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2009, 34, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Woollacott, M.H. Motor Control: Translating Research into Clinical Practice; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Enkelaar, L.; Smulders, E.; Valk, H.V.S.L.-D.; Geurts, A.C.; Weerdesteyn, V. A review of balance and gait capacities in relation to falls in persons with intellectual disability. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C. Motor proficiency differences among students with intellectual disabilities, autism, and developmental disability. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2018, 14, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeli, E.; Bar-Yossef, T.; Ariav, C.; Levy, R.; Liebermann, D.G. Perceptual-motor coordination in persons with mild intellectual disability. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; Romo-Pérez, V.; García-Soidán, J.L.; García-Liñeira, J. Percentiles and Reference Values for the Accelerometric Assessment of Static Balance in Women Aged 50–80 Years. Sensors 2020, 20, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.M.; Thomas, M.J. Promoting Physical Activity and Exercise in Older Adults with Developmental Disabilities. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2008, 24, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaver, S.; Hunter, D.; Ouellette-Kuntz, H. Physical mobility limitations in adults with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2009, 53, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Mooney, A.J.; Schmitt, F.A.; Head, E.; Lott, I.T.; Heilman, K.M. Gait dyspraxia as a clinical marker of cognitive decline in Down syndrome: A review of theory and proposed mechanisms. Brain Cogn. 2016, 104, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Ms, R.M.B.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Bs, H.C.F.; Gahan, W.P.; Correa, J.B.; Bs, D.M.N.; Keller, J.N. Assessment of Cognition, Physical Performance, and Gait in the Context of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppewal, A.; Hilgenkamp, T.I.M.; Van Wijck, R.; Evenhuis, H.M. Feasibility and outcomes of the Berg Balance Scale in older adults with intellectual disabilities. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, S.; Wester, A.; Sundelin, G.; Rehn, B. Test–retest reliability, smallest real difference and concurrent validity of six different balance tests on young people with mild to moderate intellectual disability. Physiotherapy 2012, 98, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, L.; Bray, A.; Littmann, A. Assessing the balance capabilities of people with profound intellectual disabilities who have experienced a fall. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2007, 51, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; García-Soidán, J.L.; Romo-Pérez, V. Analyzing the Use of Accelerometers as a Method of Early Diagnosis of Alterations in Balance in Elderly People: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.M.; Van Tongeren, H.; Sørensen, P.S.; Ravnborg, M. The Six Spot Step Test: A new measurement for walking ability in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2006, 12, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, J.; Richter, C.; Kristensen, C.; Sunesen, I.; Næsby, M.; Dalgas, U.; Skjerbæk, A.G. Test–retest agreement and reliability of the Six Spot Step Test in persons with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 25, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, N.E.; Jiang, A.; Keller, J.; Zackowski, K.M. Utility of the Six-Spot Step Test as a Measure of Walking Performance in Ambulatory Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindvall, M.A.; Anderzén-Carlsson, A.; Appelros, P.; Forsberg, A. Validity and test–retest reliability of the six-spot step test in persons after stroke. Physiother. Theory Pr. 2018, 36, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutzfeldt, M.; Andersen, H.; Jensen, H.B.; Markvardsen, L.H.; Sindrup, S.H.; Ravnborg, M. The six-spot-step test—A new method for monitoring walking ability in patients with chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2017, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanish Institute of Statistics. Survey on Disabilities, Personal Autonomy and Dependency Situations; Spanish Institute of Statistics: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Langford, Z. The Four Square Step Test. J. Physiother. 2015, 61, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed “Up & Go”: A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, A.; Kraft, E.; Olenick, H.; Kiesling, R.; Doty, A. The reliability and validity of the Timed Up and Go as a clinical tool in individuals with and without disabilities across a lifespan: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dite, W.; Temple, V.A. A clinical test of stepping and change of direction to identify multiple falling older adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, S.L.; Marchetti, G.F.; Morris, L.O.; Sparto, P.J. The Reliability and Validity of the Four Square Step Test for People With Balance Deficits Secondary to a Vestibular Disorder. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.; Barker, K. The validity and reliability of the four square step test in different adult populations: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeza-Ruiz, R.; Alcántara-Cordero, F.J.; Ruiz-Gavilán, I.; Sánchez-López, A.M. Feasibility and Reliability of a Physical Fitness Test Battery in Individuals with Down Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, P.W.; Weiner, D.K.; Chandler, J.; Studenski, S. Functional Reach: A New Clinical Measure of Balance. J. Gerontol. 1990, 45, M192–M197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Leurer, M.; Fisher, I.; Neeb, M.; Schwartz, I.; Carmeli, E. Reliability and validity of the modified functional reach test at the sub-acute stage post-stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2009, 31, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán-Baeza, J.A.; González-Sánchez, M.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Reliability in the Parameterization of the Functional Reach Test in Elderly Stroke Patients: A Pilot Study. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, S.G.; Burns, Y.; Galley, P. Lateral reach: A clinical measure of medio-lateral postural stability. Physiother. Res. Int. 1999, 4, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K. Measuring balance in the elderly: Preliminary development of an instrument. Physiother. Can. 1989, 41, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.O.; Maki, B.E.; Williams, J.; Holliday, P.J.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.L. Clinical and laboratory measures of postural balance in an elderly population. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1992, 73, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Godi, M.; Franchignoni, F.; Caligari, M.; Giordano, A.; Turcato, A.M.; Nardone, A. Comparison of Reliability, Validity, and Responsiveness of the Mini-BESTest and Berg Balance Scale in Patients with Balance Disorders. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, G.; Nevill, A.M. Statistical Methods for Assessing Measurement Error (Reliability) in Variables Relevant to Sports Medicine. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, I.C. The misinterpretation of the standard error of measurement in medical education: A primer on the problems, pitfalls and peculiarities of the three different standard errors of measurement. Med. Teach. 2012, 34, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, K.; Tilbery, C.P.; Lianza, S.; Marangoni, B.E.M. Validation of the “Six Step Spot Test” for gait among patients with multiple sclerosis in Brazil. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2010, 68, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brincks, J.; Callesen, J.; Dalgas, U.; Johnsen, E. Test–retest reliability and limits of agreement of the Six-Spot Step Test in people with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexell, J.; Flansbjer, U.-B.; Holmbäck, A.M.; Downham, D.; Patten, C. Reliability of Gait Performance Tests in Men and Women with Hemiparesis after Stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2005, 37, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valet, M.; Lejeune, T.; Devis, M.; Van Pesch, V.; El Sankari, S.; Stoquart, G. Timed Up-and-Go and 2-Minute Walk Test in patients with multiple sclerosis with mild disability: Reliability, responsiveness and link with perceived fatigue. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 55, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandroff, B.M.; Motl, R.W.; Sosnoff, J.J.; Pula, J.H. Further validation of the Six-Spot Step Test as a measure of ambulation in multiple sclerosis. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddle, D.L.; Stratford, P.W. Interpreting Validity Indexes for Diagnostic Tests: An Illustration Using the Berg Balance Test. Phys. Ther. 1999, 79, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergquist, R.; Kröger, I.; Taraldsen, K.; Mellone, S.; Ihlen, E.A.; Vereijken, B.; Helbostad, J.; Becker, C.; Mikolaizak, A.S. Predicting Advanced Balance Ability and Mobility with an Instrumented Timed Up and Go Test. Sensors 2020, 20, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | All (n = 18) | Men (n = 11) | Women (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.8 ± 9.9 | 30.5 ± 9.3 | 34.1 ± 10.7 |
| Height (cm) | 163.7 ± 0.1 | 165.6 ± 0.1 | 162 ± 0.1 |
| Weight (kg) | 74.1 ± 24.5 | 65.6 ± 14.4 * | 88.4 ± 31.9 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.4 ± 8 | 23.7 ± 3.9 * | 33 ± 9.6 * |
| MMSE (points) | 25.2 ± 6 | 27.9 ± 6.4 | 23.4 ± 5.7 |
| TUG (s) | 8.4 ± 2.4 | 7.7 ± 2.6 | 9.3 ± 2.1 |
| FST (s) | 9.3 ± 3.7 | 8.1 ± 2.9 | 11.2 ± 4.4 |
| FRT (cm) | 22.2 ± 11.5 | 22.8 ± 12.4 | 21.2 ± 11.1 |
| LRT–R (cm) | 11.8 ± 5.2 | 13.6 ± 4.4 | 8.5 ± 5.4 |
| LRT–L (cm) | 12.6 ± 5.1 | 14.3 ± 4.9 | 10 ± 4.8 |
| BBS (points) | 49.9 ± 6.4 | 50.8 ± 6.8 | 48.6 ± 6.2 |
| ICAP–GF (points) | 81.4 ± 6.8 | 81.1 ± 7.1 | 81.9 ± 6.4 |
| All (n = 18) | Men (n = 11) | Women (n = 7) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ± SD | 95% CI | ± SD | 95% CI | ± SD | 95% CI | |
| Chronometer | ||||||
| First test | 9.1 ± 3.2 | [7.4–10.7] | 8.3 ± 2.1 | [6.8–9.9] | 10.1 ± 4.2 | [6.2–14] |
| Second test | 9.4 ± 3.6 | [7.5–11.2] | 8.9 ± 2.6 | [7–10.7] | 10.1 ± 4.8 | [5.6–14.5] |
| Third test | 9.3 ± 3 | [7.8–10.9] | 9.3 ± 3 | [7.2–11.5] | 9.3 ± 3.3 | [6.2–12.3] |
| Video Camera | ||||||
| First test | 8.4 ± 3.3 | [6.7–10.1] | 7.8 ± 2.4 | [6.1–9.5] | 9.2 ± 4.4 | [5.2–13.3] |
| Second test | 8.5 ± 3.2 | [6.9–10.1] | 8.2 ± 2.4 | [6.2–10.2] | 8.9 ± 3.8 | [5.4–12.3] |
| Third test | 8.8 ± 3.1 | [7.1–10.4] | 8.7 ± 3 | [6.5–10.8] | 9 ± 3.5 | [5.3–12.6] |
| ICC | 95% CI | CV (%) | SEM | Mean Difference | 95% CI | Upper LOA | Lower LOA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronometer | ||||||||
| Within-day agreement | 0.97 | 0.92–0.99 | 4.69 | 0.59 | −0.3 | −0.4–0.11 | 1.26 | −1.85 |
| Day-to-day agreement | 0.86 | 0.66–0.95 | 7.3 | 1.16 | −0.26 | −1.1–0.59 | 2.96 | −3.47 |
| Video Camera | ||||||||
| Within-day agreement | 0.96 | 0.9–0.99 | 6.71 | 0.62 | −0.99 | −0.59–0.4 | 0.83 | −2.8 |
| Day-to-day agreement | 0.88 | 0.71–0.96 | 6.79 | 1.07 | −0.32 | −1.17–0.52 | 2.77 | −3.42 |
| Chronometer | Video Camera | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First Test | Second Test | Third Test | |
| First test | 0.976 * | 0.941 * | 0.876 * |
| Second test | 0.973 * | 0.975 * | 0.930 * |
| Third test | 0.844 * | 0.928 * | 0.984 * |
| Variables Included | Chronometer | Video | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | R2 | B | SE | R2 | |
| TUG | 0.652 | 0.302 | 0.25 * | 0.731 | 0.307 | 0.29 * |
| FSST | 0.765 | 0.123 | 0.76 *** | 0.837 | 0.107 | 0.83 *** |
| FRT | −0.143 | 0.06 | 0.27 * | −0.148 | 0.064 | 0.26 * |
| LRT–R | −0.329 | 0.133 | 0.29 * | −0.283 | 0.149 | 0.19 |
| LRT–L | −0.068 | 0.16 | 0.01 | −0.082 | 0.168 | 0.02 |
| BBS | −0.303 | 0.1 | 0.38 ** | −0.315 | 0.105 | 0.33 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reguera-García, M.M.; Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; Fernández-Baro, E.; Álvarez-Barrio, L. Reliability and Validity of the Six Spot Step Test in People with Intellectual Disability. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020201
Reguera-García MM, Leirós-Rodríguez R, Fernández-Baro E, Álvarez-Barrio L. Reliability and Validity of the Six Spot Step Test in People with Intellectual Disability. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020201
Chicago/Turabian StyleReguera-García, María Mercedes, Raquel Leirós-Rodríguez, Eva Fernández-Baro, and Lorena Álvarez-Barrio. 2021. "Reliability and Validity of the Six Spot Step Test in People with Intellectual Disability" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020201
APA StyleReguera-García, M. M., Leirós-Rodríguez, R., Fernández-Baro, E., & Álvarez-Barrio, L. (2021). Reliability and Validity of the Six Spot Step Test in People with Intellectual Disability. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020201