The Insula: A Stimulating Island of the Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Direct Cortical Stimulations (DCSs): General Considerations
3. Functional Mapping of the Insula
4. Functional Connectivity of the Insula
5. DCS-Elicited Insular Seizures
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Howes, O.; Borgwardt, S. Johann Cristian Reil on the 200th anniversary of the first description of the insula (1809). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Economo, C. Eine neue art spezialzellen des Lobus cinguli und Lobus insulae. Z. Ges. Neurol. Psychiatr. 1926, 100, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M. Die inselrinde des menschen und der tiere. J. Psychol. Neurol. 1928, 37, 467–624. [Google Scholar]
- Penfield, W. Some observations on the cerebral cortex of man. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B: Boil. Sci. 1947, 134, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penfield, W.; Faulk, M.E., Jr. The insula; further observations on its function. Brain 1955, 78, 445–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silfvenius, H.; Gloor, P.; Rasmussen, T. Evaluation of insular ablation in surgical treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 1964, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnard, J.; Guénot, M.; Ostrowsky, K.; Sindou, M.; Mauguière, F. The role of the insular cortex in temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, J.; Guenot, M.; Sindou, M.; Mauguiere, F. Clinical manifestations of insular lobe seizures: A stereo-electroencephalographic study. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, F.; Zilles, K.; Fox, P.; Laird, A.; Eickhoff, S.B. A link between the systems: Functional differentiation and integration within the human insula revealed by meta-analysis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deen, B.; Pitskel, N.B.; Pelphrey, K.A. Three systems of insular functional connectivity identified with cluster analysis. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschler, I.; Wieckhorst, B.; Kowalevski, S.; Derix, J.; Wentlandt, J.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Ball, T. Functional organization of the human anterior insular cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 457, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, M.A.; Menon, V.; Walczak, A.; Ahlstrom, J.; Denslow, S.; Horwitz, A.; Dubno, J.R. At the heart of the ventral attention system: The right anterior insula. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2530–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craig, A.D. How do you feel? Interoception: The sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.D. How do you feel—Now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, W.; Jasper, H. Epilepsy and the Functional Anatomy of the Human Brain; Little, Brown and Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- David, O.; Bastin, J.; Chabardès, S.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P. Studying network mechanisms using intracranial stimulation in epileptic patients. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trébuchon, A.; Chauvel, P. Electrical stimulation for seizure induction and functional mapping in stereoelectroencephalography. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afif, A.; Chabardes, S.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P.; Hoffmann, D. Safety and usefulness of insular depth electrodes implanted via an oblique approach in patients with epilepsy. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbeck, W.; Bouthillier, A.; Weil, A.G.; Crevier, L.; Carmant, L.; Lortie, A.; Major, P.; Nguyen, D.K. The combination of subdural and depth electrodes for intracranial EEG investigation of suspected insular (perisylvian) epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, A.G.; Fallah, A.; Lewis, E.C.; Bhatia, S. Medically resistant pediatric insular-opercular/perisylvian epilepsy. Part 1: Invasive monitoring using the parasagittal transinsular apex depth electrode. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouthillier, A.; Surbeck, W.; Weil, A.G.; Tayah, T.; Nguyen, D.K. The hybrid operculo- insular electrode: A new electrode for intracranial investigation of perisylvian/insular refractory epilepsy. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, B.; Lesser, R.P.; Rance, N.E.; Hart, J., Jr.; Webber, R.; Uematsu, S.; Fisher, R.S. Parameters for direct cortical electrical stimulation in the human: Histopathologic confirmation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1990, 75, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.S.; Sinha, S.; Gordon, B.; Lesser, R.P.; Thakor, N. Determination of current density distributions generated by electrical stimulation of the human cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1993, 86, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Gatignol, S.T.P.; Mandonnet, E.; Capelle, L.; Taillandier, L. Intraoperative subcortical stimulation mapping of language pathways in a consecutive series of 115 patients with Grade II glioma in the left dominant hemisphere. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Mandonnet, E. A re-examination of neural basis of language processing: Proposal of a dynamic hodotopical model from data provided by brain stimulation mapping during picture naming. Brain Lang. 2014, 131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmurget, M.; Song, Z.; Mottolese, C.; Sirigu, A. Re-establishing the merits of electrical brain stimulation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowsky, K.; Isnard, J.; Ryvlin, P.; Guenot, M.; Fischer, C.; Mauguiere, F. Functional mapping of the insular cortex: Clinical implication in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Nguyen, D.B.; Malak, R.; Leroux, J.-M.; Carmant, L.; Saint-Hilaire, J.-M.; Giard, N.; Cossette, P.; Bouthillier, A. Revisiting the role of the insula in refractory partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afif, A.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P.; Hoffmann, D. Anatomofunctional organization of the insular cortex: A study using intracerebral electrical stimulation in epileptic patients. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugnaghi, M.; Meletti, S.; Castana, L.; Francione, S.; Nobili, L.; Mai, R.; Tassi, L. Features of somatosensory manifestations induced by intracranial electrical stimulations of the human insula. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephani, C.; Vaca, G.F.-B.; Maciunas, R.; Koubeissi, M.; Lüders, H.O. Functional neuroanatomy of the insular lobe. Brain Struct. Funct. 2011, 216, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzola, L.; Mauguière, F.; Isnard, J. Electrical stimulations of the human insula: Their contribution to the ictal semiology of insular seizures. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, L.; Isnard, J.; Peyron, R.; Guénot, M.; Mauguière, F. Somatotopic organization of pain responses to direct electrical stimulation of the human insular cortex. Pain 2009, 146, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, L.; Isnard, J.; Peyron, R.; Mauguiere, F. Stimulation of the human cortex and the experience of pain: Wilder Penfield’s observations revisited. Brain 2011, 135, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzola, L.; Royet, J.-P.; Catenoix, H.; Montavont, A.; Isnard, J.; Mauguière, F. Gustatory and olfactory responses to stimulation of the human insula. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszynski, C.; Amorim-Leite, R.; Deman, P.; Perrone-Bertolotti, M.; Chabert, F.; Job-Chapron, A.S.; Minotti, L.; Hoffmann, D.; David, O.; Kahane, P. Brain mapping of auditory responses induced by direct electrical stimulation. Submitted for publication.
- Mazzola, L.; Lopez, C.; Faillenot, I.; Chouchou, F.; Mauguière, F.; Isnard, J. Vestibular responses to direct stimulation of the human insular cortex. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouchou, F.; Mauguière, F.; Vallayer, O.; Catenoix, H.; Isnard, J.; Montavont, A.; Jung, J.; Pichot, V.; Rheims, S.; Mazzola, L. How the insula speaks to the heart: Cardiac responses to insular stimulation in humans. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, F.; Lagarde, S.; Scavarda, D.; Carron, R.; Bénar, C.; Picard, F. The role of the dorsal anterior insula in ecstatic sensation revealed by direct electrical brain stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, K.; Terasawa, Y.; Natsume, A.; Iijima, K.; Chalise, L.; Sugiura, J.; Yamamoto, H.; Koyama, K.; Wakabayashi, T.; Umeda, S. Anterior insular cortex stimulation and its effects on emotion recognition. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yih, J.; Beam, D.; Fox, K.C.R.; Parvizi, J. Intensity of affective experience is modulated by magnitude of intracranial electrical stimulation in human orbitofrontal, cingulate and insular cortices. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2019, 14, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, C.; Kahane, P.; Tassi, L.; Francione, S.; Hoffmann, D.; Russo, G.L.; Benabid, A.L. Intracerebral low frequency electrical stimulation: A new tool for the definition of the “epileptogenic area”? Acta Neurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 1993, 58, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, L.; Isnard, J.; Mauguière, F. Electrical stimulation of the human insular cortex. In Insular Epilepsies; Nguyen, D., Isnard, J., Kahane, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D.M. Taste representation in the human insula. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachidi, I. Double dissociation between anterior insula and ventromedial prefrontal cortex in decision-making revealed by direct electrical stimulation. Medical Thesis, Univ. Grenoble Alpes, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Perrone-Bertolotti, M.; Alexandre, S.; Jobb, A.S.; De Palma, L.; Baciu, M.; Mairesse, M.P.; Hoffmann, D.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P.; David, O. Probabilistic mapping of language networks from high frequency activity induced by direct electrical stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, J.R. The insular lobe in primates including humans. Neurol. Res. 1985, 7, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, J.R. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res. Rev. 1996, 22, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.-M.; Mufson, E.J. Insula of the old world monkey. III: Efferent cortical output and comments on function. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 212, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufson, E.J.; Mesulam, M.-M. Insula of the old world monkey. II: Afferent cortical input and comments on the claustrum. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 212, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaziri, J.; Fei, P.; Petit, L.; Nguyen, D.K. Structural connectivity of the insula. In Insular Epilepsies; Nguyen, D., Isnard, J., Kahane, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, R.; Kunieda, T.; Nair, D. Single pulse electrical stimulation to probe functional and pathological connectivity in epilepsy. Seizure 2017, 44, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prime, D.; Rowlands, D.; O’Keefe, S.; Dionisio, S. Considerations in performing and analyzing the responses of cortico-cortical evoked potentials in stereo-EEG. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, O.; Job, A.-S.; De Palma, L.; Hoffmann, D.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P. Probabilistic functional tractography of the human cortex. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubian, L.; Lemaréchal, J.D.; David, O. Functional connectivity of the insula. In Insular Epilepsies; Nguyen, D., Isnard, J., Kahane, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaréchal, J.D.; Jedynak, M.; Trebaul, L.; Tuyisenge, V.; Ayoubian, L.; Hugues, E.; Tadel, F.; Boyer, A.; Chanteloup-Forêt, B.; Saubat, C.; et al. An atlas of human brain axonal and synaptic delays based on causal modeling of cortico-cortical evoked potentials. Brain. in press.
- Trebaul, L.; Deman, P.; Tuyisenge, V.; Jedynak, M.; Hugues, E.; Rudrauf, D.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Tadel, F.; Chanteloup-Foret, B.; Saubat, C.; et al. Probabilistic functional tractography of the human cortex revisited. Neuroimage 2018, 181, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashaikhi, T.; Rheims, S.; Ostrowsky-Coste, K.; Montavont, A.; Jung, J.; De Bellescize, J.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Kosal, P.K.; Guénot, M.; Bertrand, O.; et al. Intrainsular functional connectivity in human. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 35, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, S.; Mayoglou, L.; Cho, S.-M.; Prime, D.; Flanigan, P.M.; Lega, B.; Mosher, J.; Leahy, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Nair, D. Connectivity of the human insula: A Cortico-Cortical Evoked Potential (CCEP) study. Cortex 2019, 120, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacuey, N.; Zonjy, B.; Kahriman, E.S.; Marashly, A.; Miller, J.; Lhatoo, S.D.; Lüders, H.O. Homotopic reciprocal functional connectivity between anterior human insulae. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashaikhi, T.; Rheims, S.; Jung, J.; Ostrowsky-Coste, K.; Montavont, A.; De Bellescize, J.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Kosal, P.K.; Guénot, M.; Bertrand, O.; et al. Functional connectivity of insular efferences. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 5279–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enatsu, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bulacio, J.; Mosher, J.C.; Burgess, R.C.; Najm, I.; Nair, D.R. Connectivity of the frontal and anterior insular network: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovac, S.; Kahane, P.; Diehl, B. Seizures induced by direct electrical cortical stimulation—Mechanisms and clinical considerations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, N. Electro-clinical correlations between seizures induced by direct electrical stimulation and spontaneous seizures: Relevance to define the epileptogenic zone. Medical Thesis, Grenoble-Alpes University, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Oderiz, C.C.; Von Ellenrieder, N.; Dubeau, F.; Eisenberg, A.; Gotman, J.; Hall, J.; Hincapié, A.-S.; Hoffmann, D.; Job, A.-S.; Khoo, H.M.; et al. Association of cortical stimulation-induced seizure with surgical outcome in patients with focal drug-resistant epilepsy. JAMA Neurol 2019, 76, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebuchon, A.; Racila, R.; Cardinale, F.; Lagarde, S.; McGonigal, A.; Russo, G.L.; Scavarda, D.; Carron, R.; Mai, R.; Chauvel, P.; et al. Electrical stimulation for seizure induction during SEEG exploration: A useful predictor of postoperative seizure recurrence? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 92, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, C.; Racz, A.; Quesada, C.M.; Elger, C.E.; Surges, R. Predictive value of electrically induced seizures for postsurgical seizure outcome. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Principe, A.; Tadel, F.; Hoffmann, D.; Chabardes, S.; Minotti, L.; David, O.; Kahane, P. Mapping the insula with stereo-electroencephalography: The emergence of semiology in insula lobe seizures. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dylgjeri, S.; Taussig, D.; Chipaux, M.; Lebas, A.; Fohlen, M.; Bulteau, C.; Ternier, J.; Ferrand-Sorbets, S.; Delalande, O.; Isnard, J.; et al. Insular and insulo-opercular epilepsy in childhood: An SEEG study. Seizure 2014, 23, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartolomei, F.; Lagarde, S.; Wendling, F.; McGonigal, A.; Jirsa, V.; Guye, M.; Bénar, C. Defining epileptogenic networks: Contribution of SEEG and signal analysis. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
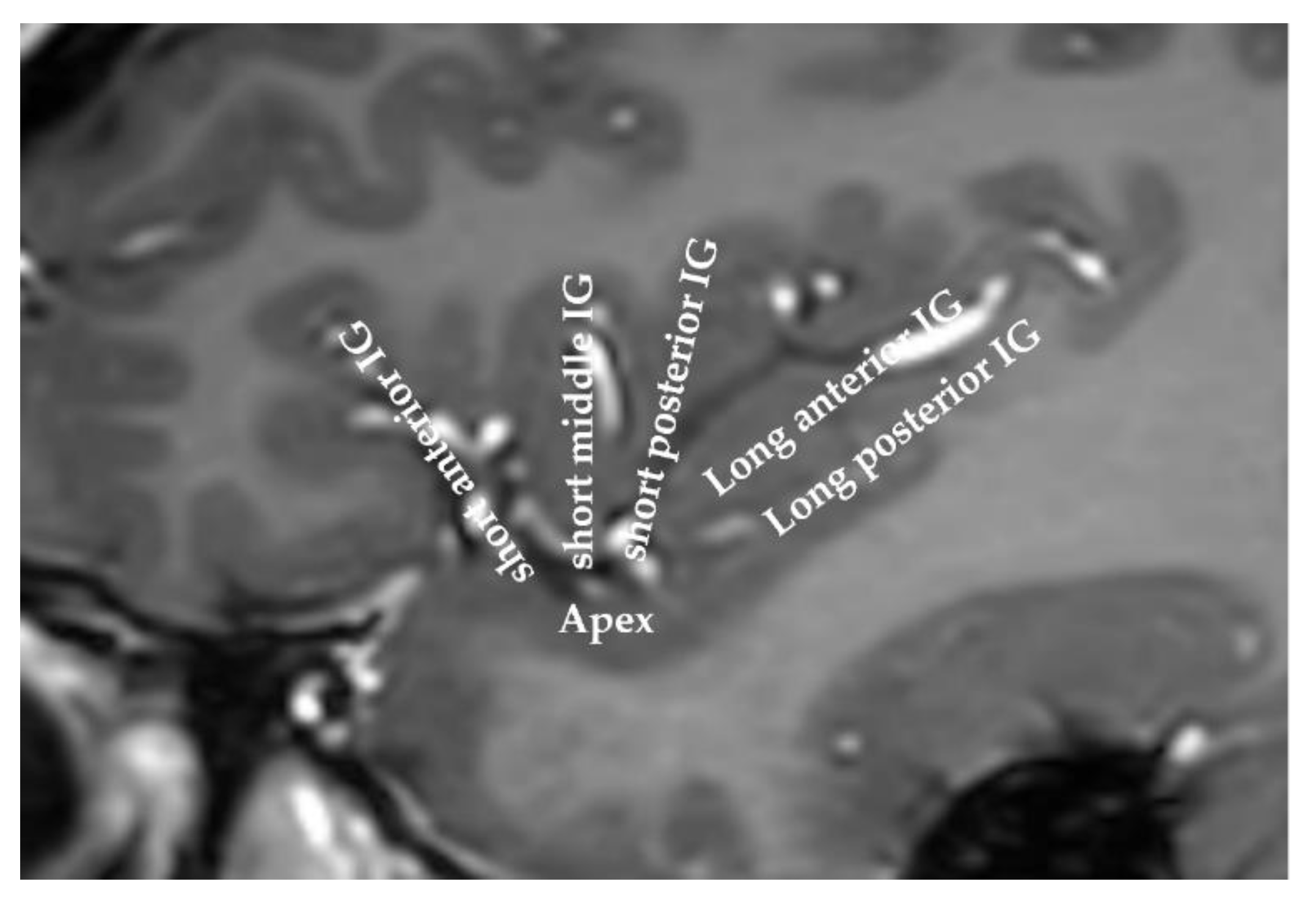
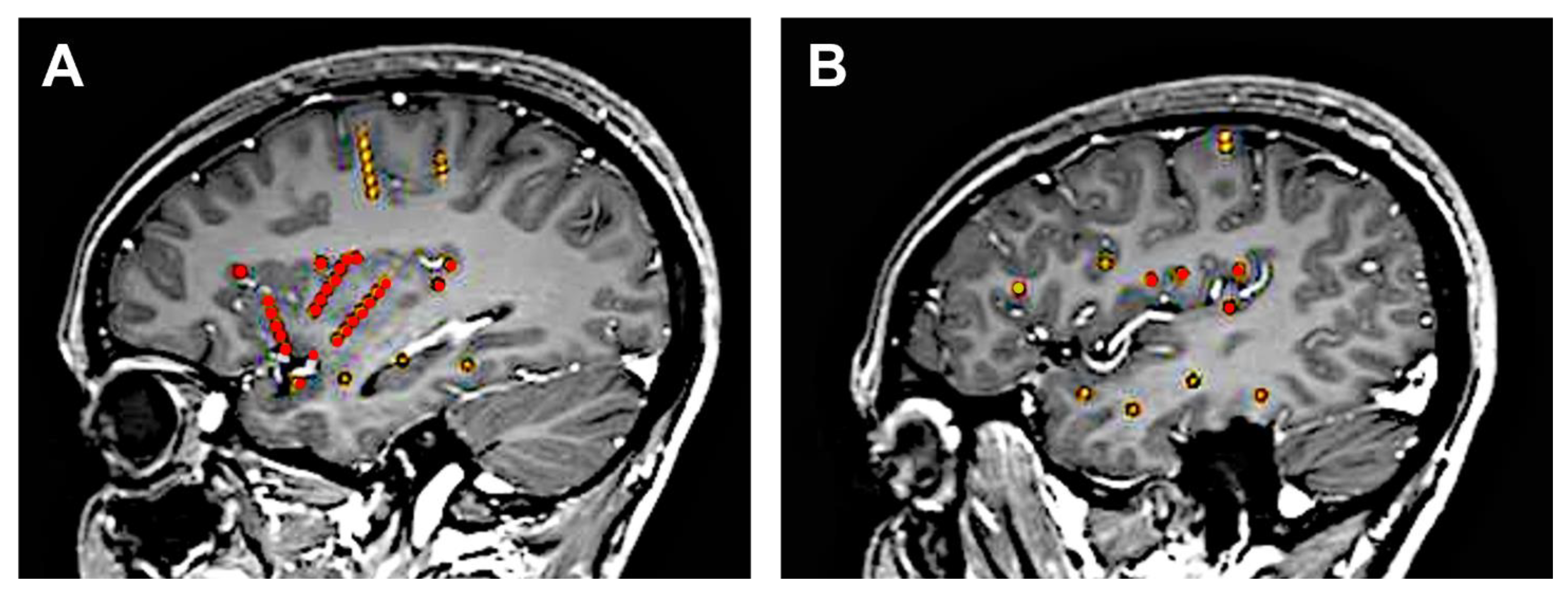


| Study [Reference] | N° of Patients | DCS freq (Hz) | N° of DCS Sites | N° of DCS (+) Sites | N° of DCS | DCS Eliciting Clinical Phenomena Not Recognized by the Patient as Part of the Seizure and Not Accompanied by an Afterdischarge | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° | VisceroS | VisceroM | SomatoS | Gustatory | Olfactory | Auditory | Vestibular | Speech | Motor | Others | ||||||
| Ostrowsky 2000 [27] | 13 | 50–1 | 27 | 20 | 75 | 32 | 17 (53%) | 5 (16%) | 7 (22 %) | 3 (9%) | 1 (3%) | 1 (3%) | 0 | 3 (9%) | 0 | 2 (6%) |
| Isnard 2004 [8] | 50 | 50–1 | 144 | 125 | 139 | 108 | 34 (31%) | 3 (3%) | 58 (54%) | 3 (3%) | 14 (13 %) | 5 (5%) | 9 (8%) | 0 | 6 (6%) | |
| Nguyen 2009 [28] | 9 | 50 | 36 | 32 | 96 | NA | 6% | 0 % | 62 % | 6 % | 0% | 9 % | 3% | 3% | 12% | 0% |
| Afif 2010 [29] | 25 | 50–1 | 25 | 22 | 179 | 67 | 28 (42%) | 19 (28%) | 0 | 0 | 3 (4%) | 4 (6%) | 8 (12%) | 11 (16%) | 3 (4%) | |
| Pugnaghi 2011 [30] | 61 | 50–1 | 165 | NA | 276 | 152 | 2 (1%) | 2 (1 %) | 105 (69%) | 2 (1%) | 0 | 12 (8%) | 3 (2%) | 9 (6%) | 12 (8%) | 2 (1%) |
| Stephani 2011 [31] | 5 | 50 | 113 | 62 | 113 | 54 | 17 (31%) | 0 | 30 (56%) | 7 (13%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mazzola 2017 [32] | 222 | 50 | 669 | NA | 669 | 550 | 82 (15%) | 0 | 335 (61%) | 15 (3%) | 6 (1 %) | 44 (8%) | 41 (8 %) | 27 (5%) | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rachidi, I.; Minotti, L.; Martin, G.; Hoffmann, D.; Bastin, J.; David, O.; Kahane, P. The Insula: A Stimulating Island of the Brain. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111533
Rachidi I, Minotti L, Martin G, Hoffmann D, Bastin J, David O, Kahane P. The Insula: A Stimulating Island of the Brain. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111533
Chicago/Turabian StyleRachidi, Inès, Lorella Minotti, Guillaume Martin, Dominique Hoffmann, Julien Bastin, Olivier David, and Philippe Kahane. 2021. "The Insula: A Stimulating Island of the Brain" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111533
APA StyleRachidi, I., Minotti, L., Martin, G., Hoffmann, D., Bastin, J., David, O., & Kahane, P. (2021). The Insula: A Stimulating Island of the Brain. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111533






