Serum Vitamin D as a Marker of Impaired Information Processing Speed and Early Disability in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Vitamin D and Cognitive Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
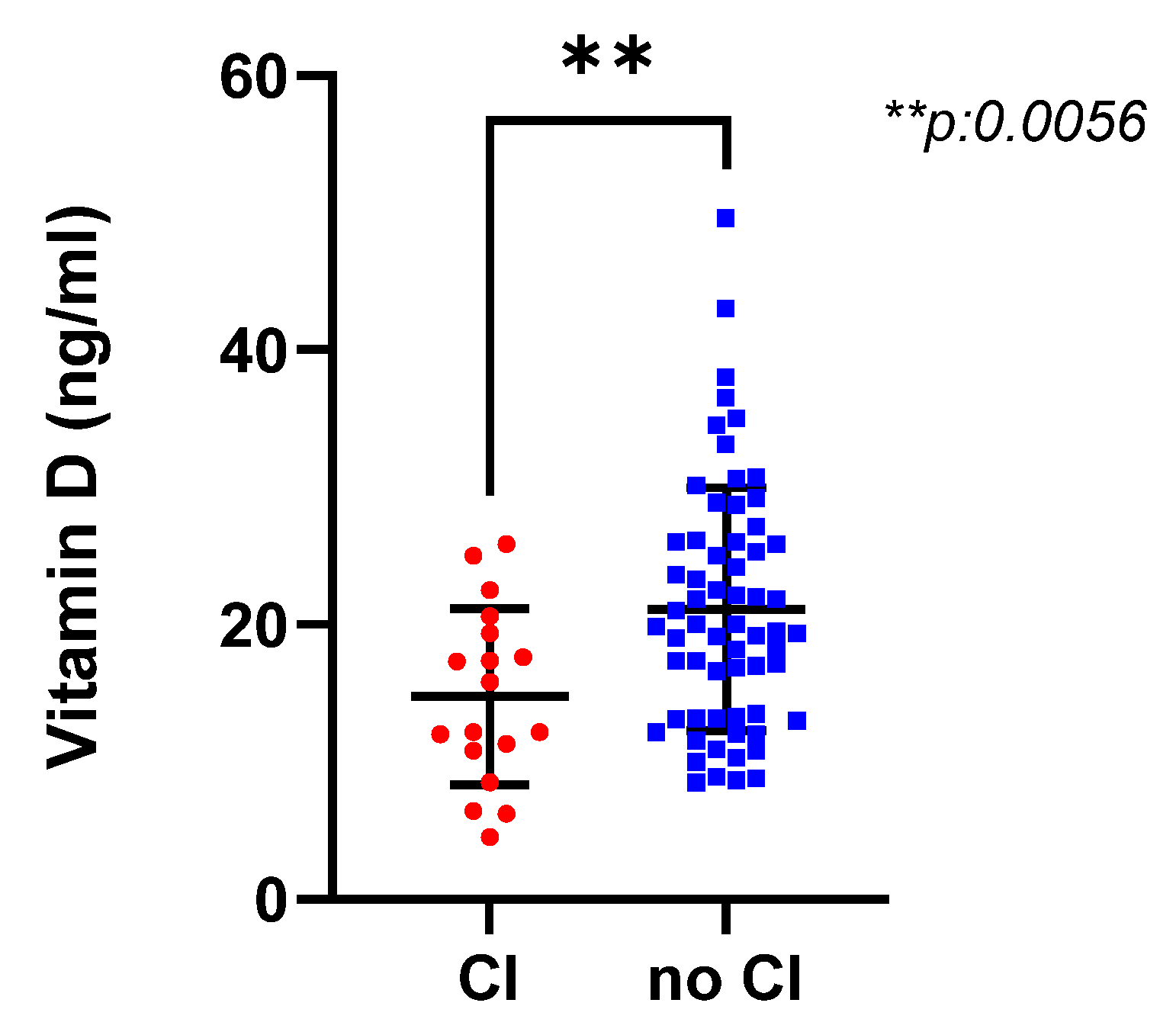
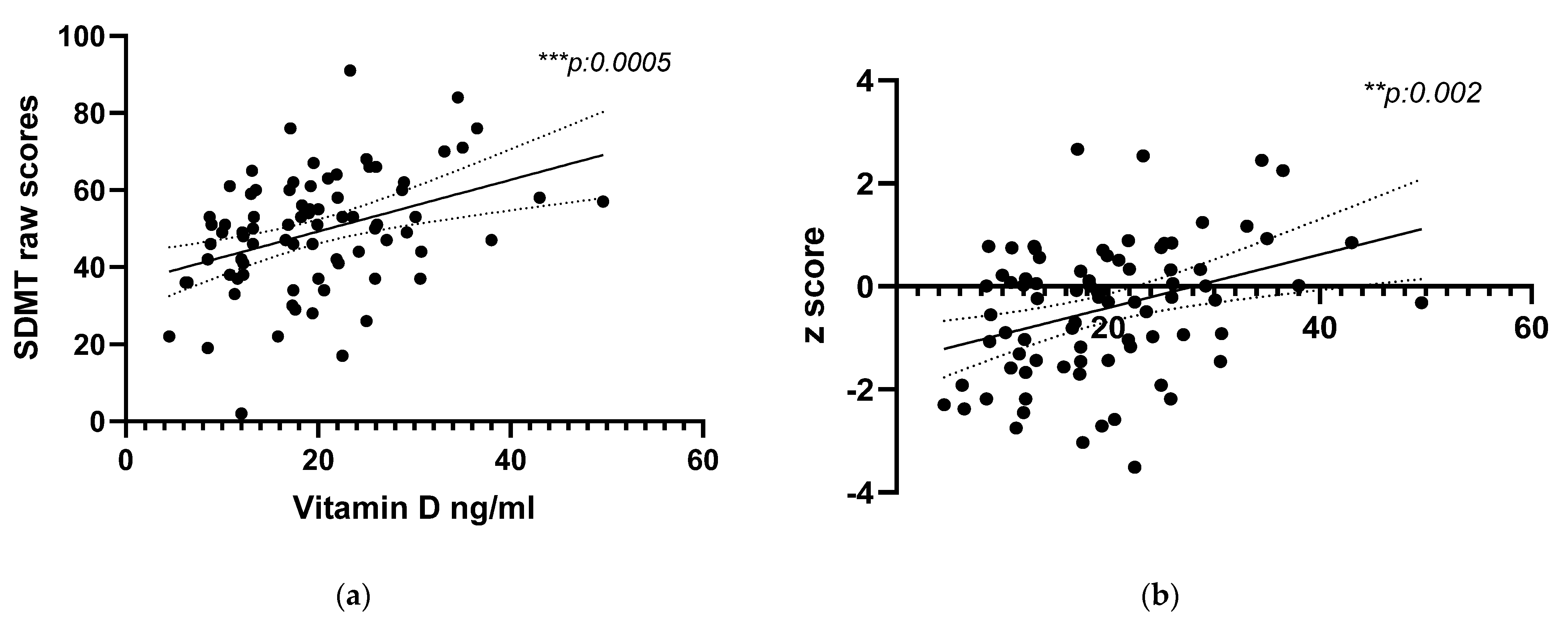
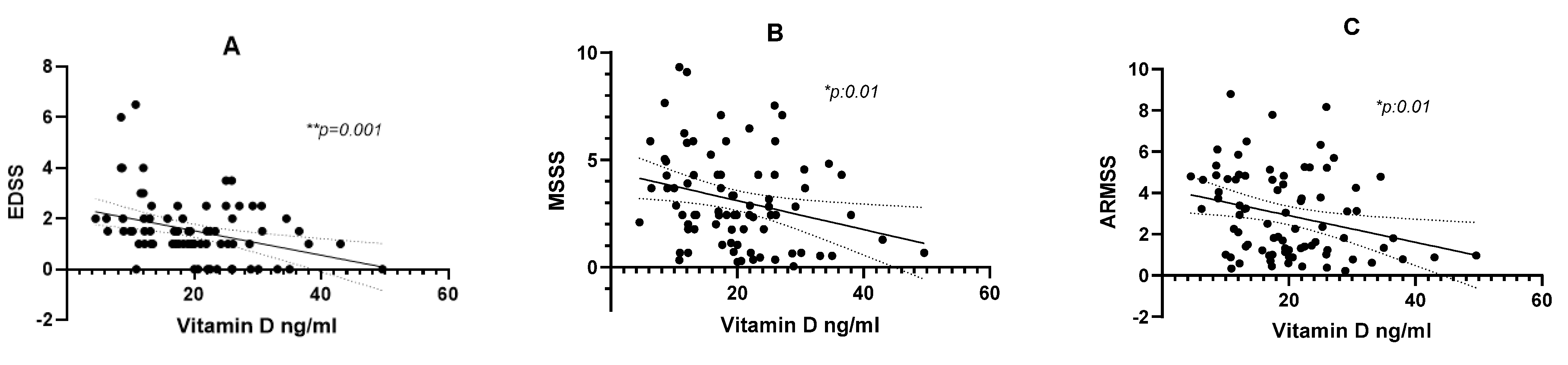
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalb, R.; Beier, M.; Benedict, R.H.; Charvet, L.; Costello, K.; Feinstein, A.; Gingold, J.; Goverover, Y.; Halper, J.; Harris, C.; et al. Recommendations for cognitive screening and management in multiple sclerosis care. Mult. Scler. 2018, 24, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goretti, B.; Niccolai, C.; Hakiki, B.; Sturchio, A.; Falautano, M.; Minacapelli, E.; Martinelli, V.; Incerti, C.; Nocentini, U.; Murgia, M.; et al. The Brief International Cognitive Assessment for Multiple Sclerosis (BICAMS): Normative values with gender, age and education corrections in the Italian population. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brochet, B.; Ruet, A. Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis With Regards to Disease Duration and Clinical Phenotypes. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Góngora, M.; Querol, L.; Escartín, A. A one-year follow-up study of the Symbol Digit Modalities Test (SDMT) and the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test (PASAT) in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: An appraisal of comparative longitudinal sensitivity. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deloire, M.S.; Ruet, A.; Hamel, D.; Bonnet, M.; Dousset, V.; Brochet, B. MRI predictors of cognitive outcome in early multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2011, 76, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moroso, A.; Ruet, A.; Lamargue-Hamel, D.; Munsch, F.; Deloire, M.; Coupé, P.; Ouallet, J.-C.; Planche, V.; Moscufo, N.; Meier, D.S.; et al. Posterior lobules of the cerebellum and information processing speed at various stages of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patti, F.; De Stefano, M.; Lavorgna, L.; Messina, S.; Chisari, C.G.; Ippolito, D.; Lanzillo, R.; Vacchiano, V.; Realmuto, S.; Valentino, P.; et al. Lesion load may predict long-term cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, G.; Arru, M.; Lorefice, L.; Frau, J.; Coghe, G.; Fronza, M.; Loi, L.; Barracciu, M.A.; Marrosu, M.G.; Cocco, E. Does focal inflammation have an impact on cognition in multiple sclerosis? An MRI study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 23, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.P.; Hakiki, B.; Goretti, B.; Rossi, F.; Stromillo, M.L.; Giorgio, A.; Roscio, M.; Ghezzi, A.; Guidi, L.; Bartolozzi, M.L.; et al. Association of MRI metrics and cognitive impairment in radiologically isolated syndromes. Neurology 2012, 78, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petracca, M.; Pontillo, G.; Moccia, M.; Carotenuto, A.; Cocozza, S.; Lanzillo, R.; Brunetti, A.; Brescia Morra, V. Neuroimaging Correlates of Cognitive Dysfunction in Adults with Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Amato, M.P.; DeLuca, J.; Geurts, J.J.G. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: Clinical management, MRI, and therapeutic avenues. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmeyer, N.C.; Bürkner, P.C.; Wiendl, H.; Ruck, T.; Hartung, H.P.; Holling, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Johnen, A. Disease-modifying treatments and cognition in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 94, e2373–e2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, P.J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, A.C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belbasis, L.; Bellou, V.; Evangelou, E.; Tzoulaki, I. Environmental factors and risk of multiple sclerosis: Findings from meta-analyses and Mendelian randomization studies. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclea, A.; Bagnoud, M.; Chan, A.; Hoepner, R. A Brief Review of the Effects of Vitamin D on Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivona, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Iacolino, G.; Ciaccio, M. Vitamin D and the nervous system. Neurol. Res. 2019, 41, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Munger, K.L. Epidemiology of Multiple Sclerosis: From Risk Factors to Prevention-An Update. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Mahatanan, R.; Lee, C.H.; Charoenpong, P.; Hong, J.P. Associations of serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels with clinical and radiological outcomes in multiple sclerosis, a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 411, 116668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Ragonese, P.; Bivona, G.; Realmuto, S.; Iacolino, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Bellia, C.; Salemi, G.; et al. Klotho and vitamin D in multiple sclerosis: An Italian study. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzone, C.; Agnello, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Salemi, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Ragonese, P.; Candore, G.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Giglio, R.V.; Bivona, G.; et al. FOXP3 and GATA3 Polymorphisms, Vitamin D3 and Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.C.; Munger, K.L.; Köchert, K.; Arnason, B.G.; Comi, G.; Cook, S.; Goodin, D.S.; Filippi, M.; Hartung, H.P.; Jeffery, D.R.; et al. Association of Vitamin D Levels With Multiple Sclerosis Activity and Progression in Patients Receiving Interferon Beta-1b. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ascherio, A.; Munger, K.L.; White, R.; Köchert, K.; Simon, K.C.; Polman, C.H.; Freedman, M.S.; Hartung, H.P.; Miller, D.H.; Montalbán, X.; et al. Vitamin D as an early predictor of multiple sclerosis activity and progression. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, M.; Munger, K.L.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Barro, C.; Edan, G.; Freedman, M.S.; Hartung, H.P.; Montalbán, X.; Foley, F.W.; Penner, I.K.; et al. Vitamin D, smoking, EBV, and long-term cognitive performance in MS: 11-year follow-up of BENEFIT. Neurology 2020, 94, e1950–e1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, J.; Torkildsen, Ø.; Camu, W.; Holmøy, T. An Update on Vitamin D and Disease Activity in Multiple Sclerosis. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piędel, F.; Rocka, A.; Piwek, M.; Jasielski, P.P.; Petit, V.; Rejdak, K. Correlation between vitamin D and alterations in MRI among patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, V.; Dalla Costa, G.; Colombo, B.; Dalla Libera, D.; Rubinacci, A.; Filippi, M.; Furlan, R.; Comi, G. Vitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. Mult. Scler. 2014, 20, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, H.; Farran, N.; Hannoun, S.; Tadros, N.; Yamout, B.; El Ayoubi, N.K.; Khoury, S.J. Serum vitamin D level is associated with speed of processing in multiple sclerosis patients. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 200, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, H.; Haddad, R.; Osman, S.; Ghassan, S.; Yamout, B.; Tamim, H.; Khoury, S. Effect of Vitamin D Replacement on Cognition in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhussain, F.; Alomar, M.; Alenazi, A.; Aldraihem, M.; Alshiha, L.; Bashir, S. The relationship between vitamin D levels and cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannath, V.A.; Filippini, G.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Asokan, G.V.; Robak, E.W.; Whamond, L.; Robinson, S.A. Vitamin D for the management of multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, Cd008422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Gao, F.; Wu, R.; Dong, T.; Gu, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y. Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: An updated meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wu, P.; Gao, D.M.; Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, N.F.; Tong, S.Q.; Rao, L.; Liu, J. The Impact of Vitamin D on Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 4716–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.O.W.; Thiel, A.; Lauer, A.A.; Winkler, J.; Lehmann, J.; Regner, L.; Nelke, C.; Janitschke, D.; Benoist, C.; Streidenberger, O.; et al. Vitamin D and Its Analogues Decrease Amyloid-β (Aβ) Formation and Increase Aβ-Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Bastianello, S.; Comi, G.; Gallo, P.; Gallucci, M.; Ghezzi, A.; Marrosu, M.G.; Minonzio, G.; Pantano, P.; et al. Guidelines from The Italian Neurological and Neuroradiological Societies for the use of magnetic resonance imaging in daily life clinical practice of multiple sclerosis patients. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxburgh, R.H.; Seaman, S.R.; Masterman, T.; Hensiek, A.E.; Sawcer, S.J.; Vukusic, S.; Achiti, I.; Confavreux, C.; Coustans, M.; le Page, E.; et al. Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score: Using disability and disease duration to rate disease severity. Neurology 2005, 64, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehrinia, A.; Westerlind, H.; Kingwell, E.; Zhu, F.; Carruthers, R.; Ramanujam, R.; Ban, M.; Glaser, A.; Sawcer, S.; Tremlett, H.; et al. Age Related Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score: Disability ranked by age. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesareo, R.; Attanasio, R.; Caputo, M.; Castello, R.; Chiodini, I.; Falchetti, A.; Guglielmi, R.; Papini, E.; Santonati, A.; Scillitani, A.; et al. Italian Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AME) and Italian Chapter of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) Position Statement: Clinical Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lips, P. Vitamin D status and nutrition in Europe and Asia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Pilz, S.; Hoffmann, H.; März, W. Vitamin D and airway infections: A European perspective. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2016, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson, R.; Cock, H.R.; Brex, P.; Giovannoni, G. Vitamin D supplementation. Pract. Neurol. 2018, 18, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yildiz, M.; Tettenborn, B.; Putzki, N. Vitamin D levels in Swiss multiple sclerosis patients. Swiss Med. Wkly 2011, 141, w13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt, A.; Boleixa, D.; Reguengo, H.; Samões, R.; Santos, E.; Oliveira, J.C.; Silva, B.; Costa, P.P.; da Silva, A.M. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in multiple sclerosis patients from the north of Portugal. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 180, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, L.; Langdon, D. How does cognition relate to employment in multiple sclerosis? A systematic review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 26, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardini, M.; Uccelli, A.; Grafman, J.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Mancardi, G.; Roccatagliata, L. Isolated cognitive relapses in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano, L.; Portaccio, E.; Goretti, B.; Niccolai, C.; Severo, M.; Patti, F.; Cilia, S.; Gallo, P.; Grossi, P.; Ghezzi, A.; et al. Age and disability drive cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis across disease subtypes. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruet, A.; Deloire, M.; Charré-Morin, J.; Hamel, D.; Brochet, B. Cognitive impairment differs between primary progressive and relapsing-remitting MS. Neurology 2013, 80, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sonneville, L.M.; Boringa, J.B.; Reuling, I.E.; Lazeron, R.H.; Adèr, H.J.; Polman, C.H. Information processing characteristics in subtypes of multiple sclerosis. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 1751–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergendal, G.; Fredrikson, S.; Almkvist, O. Selective decline in information processing in subgroups of multiple sclerosis: An 8-year longitudinal study. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 57, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients with Low Vitamin D | (3) Patients with Normal Vitamin D ≥30 ng/mL N = 10 | p-Values (1) + (2) vs. (3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Deficiency < 20 ng/mL N = 46 | (2) Insufficiency ≥ 20 ng/mL N = 25 | (1) vs. (2) vs. (3) | ||
| Age at diagnosis Mean ± SD | 37.63 ± 12.07 | 37.50 ± 9.82 | 0.9 | |
| 39.56 ± 12.31 | 34.08 ± 10.99 | 0.2 | ||
| Age at onset Mean ± SD | 35.01 ± 11.84 | 36.80 ± 9.58 | 0.5 | |
| 37.61 ± 12.32 | 30.24 ± 9.37 | 0.04 | ||
| Gender F/M | 47/24 | 7/3 | 0.8 | |
| 31/15 | 16/9 | 0.9 | ||
| Edss at diagnosis Mean ± SD | 1.58 ± 0.85 | 0.85 ± 0.62 | 0.01 | |
| 1.67 ± 0.79 | 1.42 ± 0.94 | 0.009 | ||
| MRI high brain LL yes/no | 32/39 | 3/7 | 0.3 | |
| 20/26 | 12/13 | 0.6 | ||
| MRI spinal yes/no | 44/27 | 9/1 | 0.08 | |
| 29/17 | 15/10 | 0.2 | ||
| MRI Gd+ yes/no | 35/36 | 5/5 | 0.9 | |
| 23/23 | 12/13 | 0.9 | ||
| Vitamin D Mean ± SD | 17.29 ± 6.25 | 36.11 ± 6.16 | <0.0001 | |
| 13.71 ± 4.15 | 24.15 ± 2.78 | <0.0001 | ||
| SDMT raw score Mean ± SD | 47.58 ± 14.74 | 59.7 ± 15.16 | 0.03 | |
| 45.5 + 14.15 | 52.45 ±14.69 | 0.02 | ||
| Z-score Mean ± SD | −0.55 ± 1.26 | 0.47 ± 1.28 | 0.02 | |
| −0.67 ± 1.21 | −0.26 ± 1.32 | 0.03 | ||
| EDSSS last fu Mean ± SD | 1.62 ± 1.26 | 0.95 ± 0.92 | 0.09 | |
| 1.84 ± 1.29 | 1.22 ± 1.12 | 0.03 | ||
| MSSS at last fu Mean ± SD | 3.23 ± 2.22 | 2.35 ± 1.82 | 0.3 | |
| 3.59 ± 2.15 | 2.58 ± 2.23 | 0.07 | ||
| ARMSS at last fu Mean ± SD | 3.06 ± 2.10 | 1.93 ± 1.55 | 0.1 | |
| 3.23 ± 2.07 | 2.74 ± 2.16 | 0.1 | ||
| SDMT Raw Scores Mean ± SD | p-Value | |
| Gd+ lesion (N = 40) Gd− lesion (N = 41) | 51.33 ± 14.41 | 0.29 |
| 46.88 ± 15.85 | ||
| High brain LL yes (N = 46) High brain LL no (N = 23) | 46.09 ± 16.59 53.0 ± 12.41 | 0.02 |
| MRI spinal yes (N = 53) MRI spinal no (N = 28) | 49.53 ± 14.29 | 0.56 |
| 48.21 ± 17.13 | ||
| SDMT Z-Scores Mean ±SD | p-Value | |
| Gd+ lesion (N = 40) Gd− lesion (N = 41) | −0.25 ± 1.24 −0.6 ± 1.34 | 0.22 |
| High brain LL yes (N = 46) High brain LL no (N = 23) | −0.65 ± 1.4 −0.13 ± 1.07 | 0.049 |
| MRI spinal yes (N = 53) MRI spinal no (N = 28) | −0.38 ± 1.22 | 0.59 |
| −0.50 ± 1.44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virgilio, E.; Vecchio, D.; Crespi, I.; Barbero, P.; Caloni, B.; Naldi, P.; Cantello, R.; Dianzani, U.; Comi, C. Serum Vitamin D as a Marker of Impaired Information Processing Speed and Early Disability in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111521
Virgilio E, Vecchio D, Crespi I, Barbero P, Caloni B, Naldi P, Cantello R, Dianzani U, Comi C. Serum Vitamin D as a Marker of Impaired Information Processing Speed and Early Disability in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111521
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirgilio, Eleonora, Domizia Vecchio, Ilaria Crespi, Paolo Barbero, Beatrice Caloni, Paola Naldi, Roberto Cantello, Umberto Dianzani, and Cristoforo Comi. 2021. "Serum Vitamin D as a Marker of Impaired Information Processing Speed and Early Disability in Multiple Sclerosis Patients" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111521
APA StyleVirgilio, E., Vecchio, D., Crespi, I., Barbero, P., Caloni, B., Naldi, P., Cantello, R., Dianzani, U., & Comi, C. (2021). Serum Vitamin D as a Marker of Impaired Information Processing Speed and Early Disability in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111521







