Variations of Brain Functional Connectivity in Alcohol-Preferring and Non-Preferring Rats with Consecutive Alcohol Training or Acute Alcohol Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Animals
2.2. Alcohol Preference Training
2.3. Resting-State fMRI Experiments
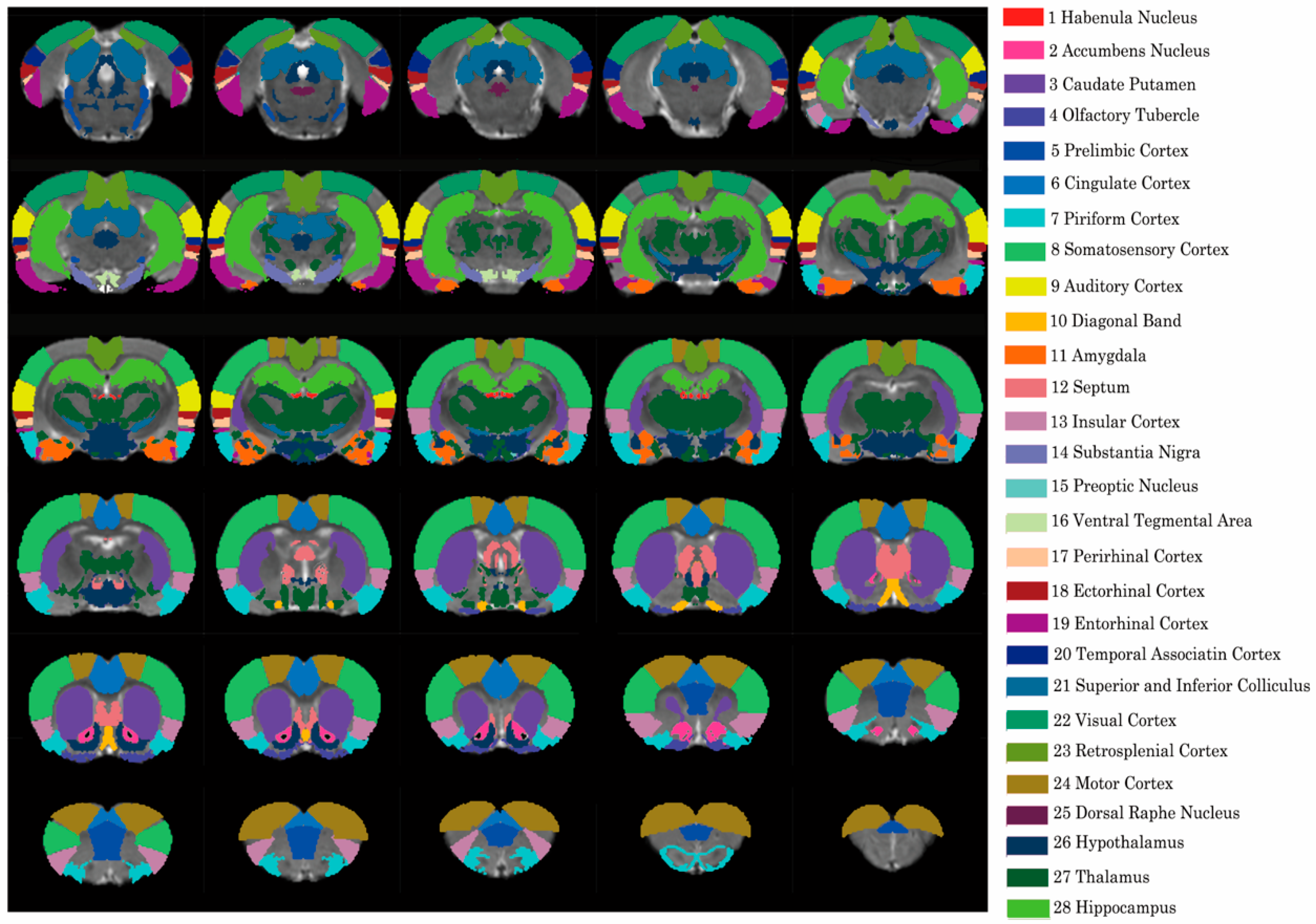
2.4. Resting-State fMRI Analysis
Data Analysis
- (1)
- Data screening: The first 10 volumes of each scan were discarded to allow for magnetization equilibrium.
- (2)
- Slice timing: The differences in slice acquisition times of each scan were corrected using the slice timing approach.
- (3)
- Realignment: The temporal processed volumes of each subject were realigned to the first volume to remove the head motion, and a mean image was created over the 310 realigned volumes. All the participants had less than 1 mm of translation in the x-, y-, or z-axis and 1° of rotation in each axis.
- (4)
- Spatial normalization: The realigned volumes were spatially standardized into the Paxinos and Watson space by normalizing with the EPI template of rat brain via their corresponding mean image. Then, all the normalized images were resliced by 1.0 × 1.5 × 1.0 mm3 voxels.
- (5)
- Smooth: The normalized functional series were smoothed with a Gaussian kernel of 2 × 4 × 2 mm3 FWHM (full width at half-maximum).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
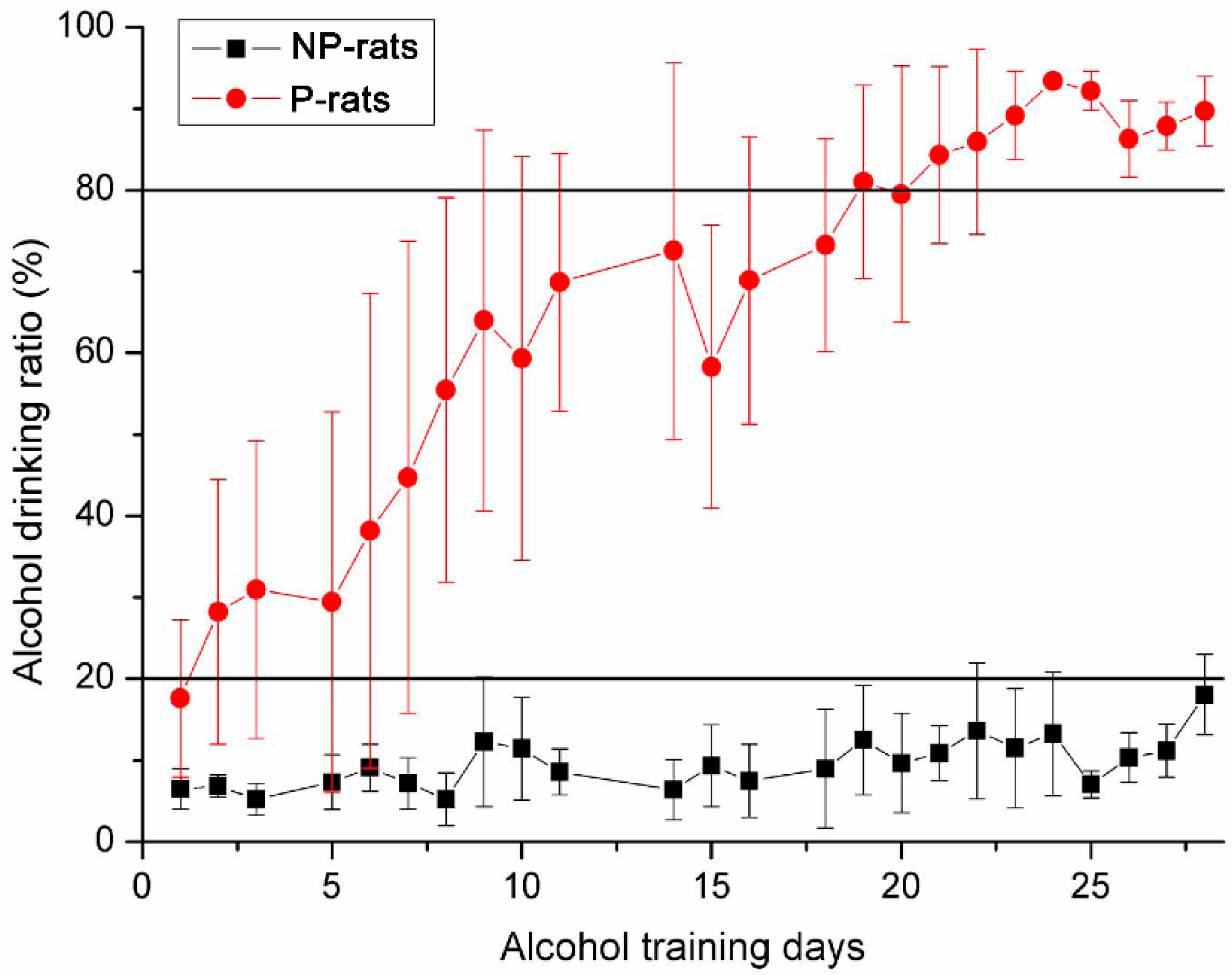
3.1. Detection of Alcohol Preference Using Two-Bottle Free Choice
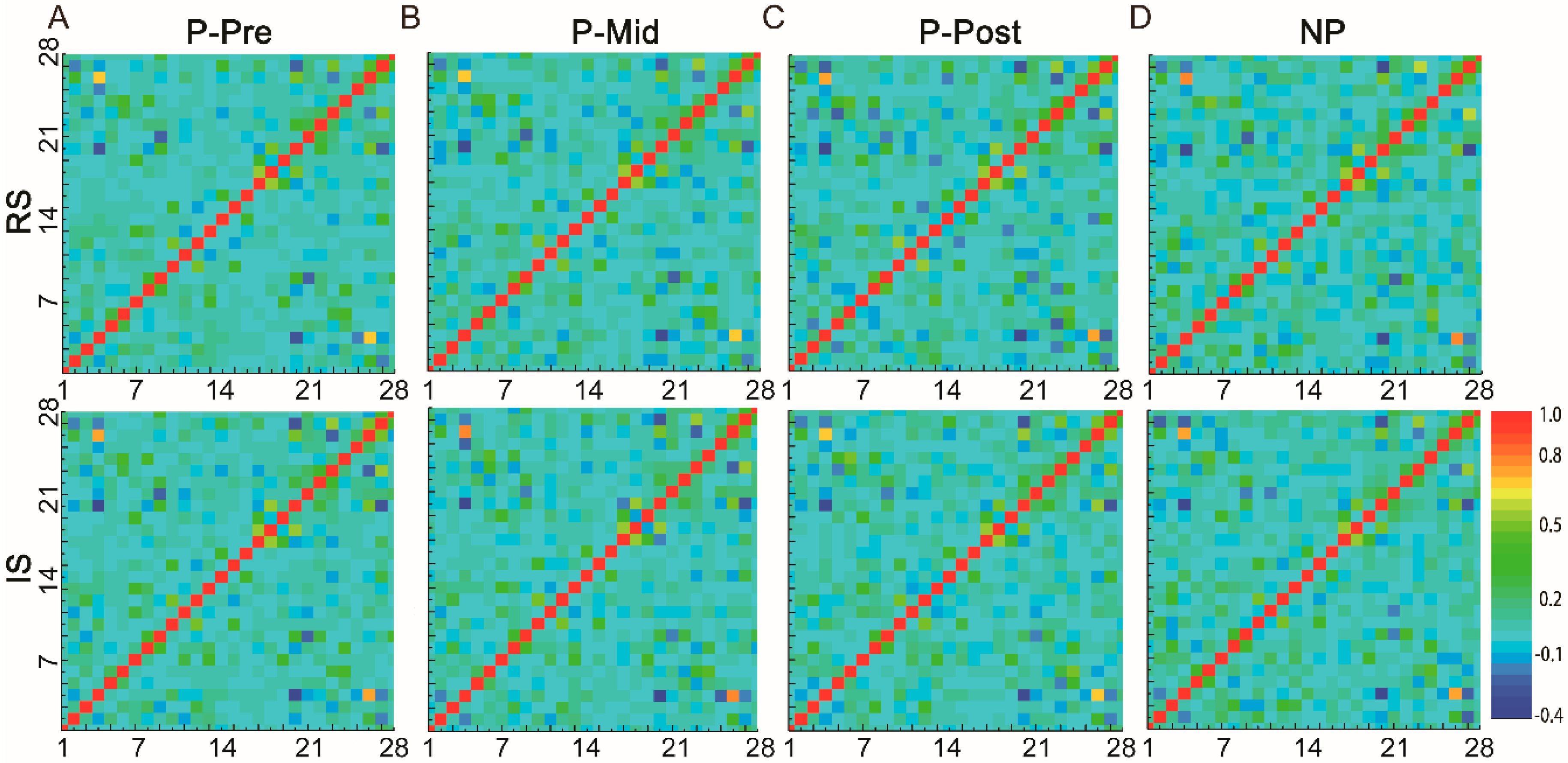
3.2. Whole-Brain Network Analysis of the Resting State
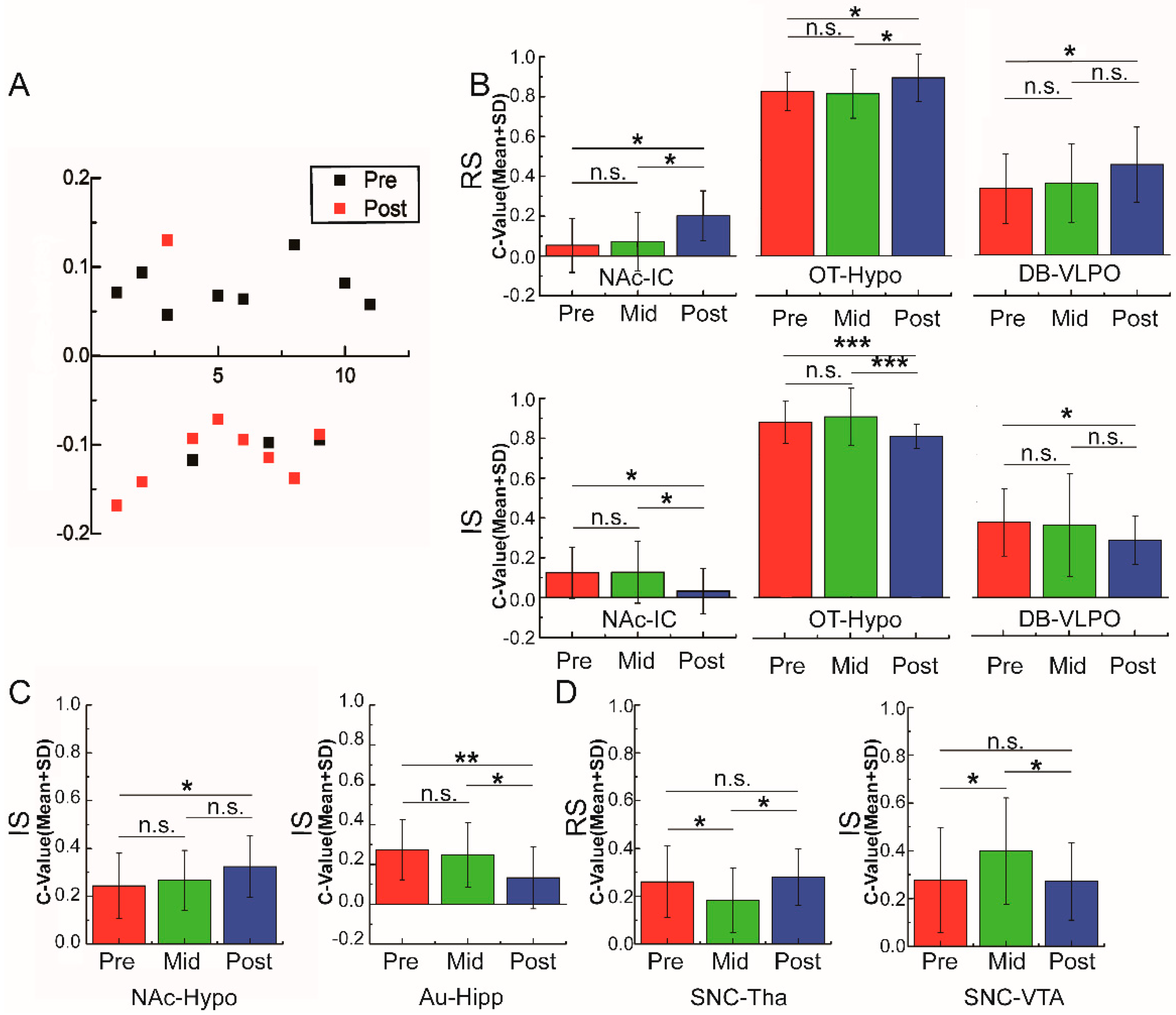
3.3. Variations of Functional Connectivity with Alcohol Stimulation and Alcohol Preference
3.4. Different Patterns of Functional Connectivity Related to Various Alcohol Conditions
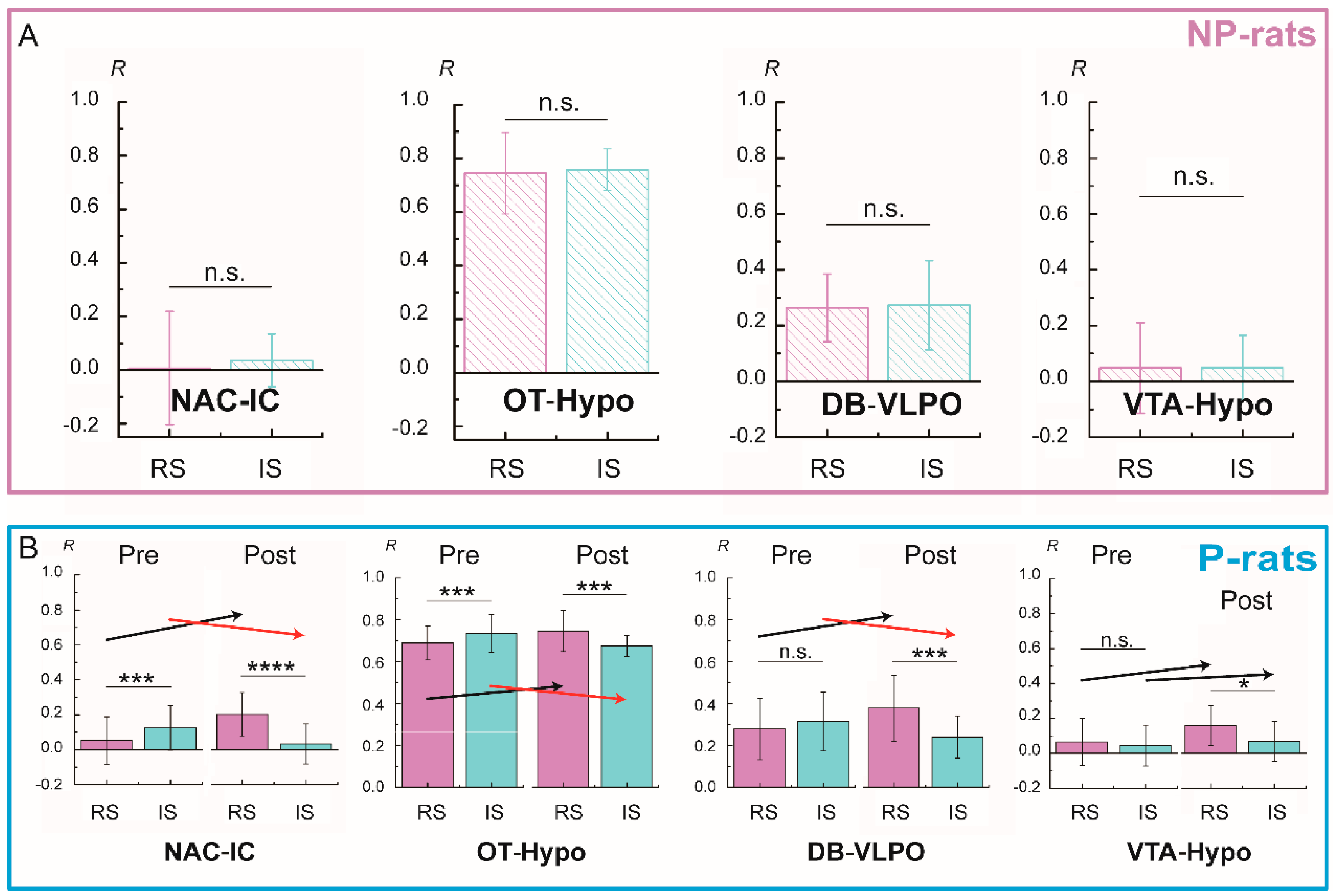
3.5. Functional Connectivity Related to Different Alcohol Preferences
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Alcohol Stimulation on the Brain Functional Connectivity
4.2. Functional and Structural Connections of Brain Regions
4.3. Functional Connectivity and Alcohol Preference
4.4. Comparison of the Genetic and Alcohol Drinking Factors on the Alcohol Preference
4.5. Limitations and Perspective
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garbutt, J.C.; West, S.L.; Carey, T.S.; Lohr, K.N.; Crews, F.T. Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: A review of the evidence. JAMA 1999, 281, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, J.-E. Impact of drinking alcohol on gut microbiota: Recent perspectives on ethanol and alcoholic beverage. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannoy, S.; Duka, T.; Carbia, C.; Billieux, J.; Fontesse, S.; Dormal, V.; Gierski, F.; López-Caneda, E.; Sullivan, E.V.; Maurage, P. Emotional processes in binge drinking: A systematic review and perspective. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 84, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Smith, T.L. The relationships of a family history of alcohol dependence, a low level of response to alcohol and six domains of life functioning to the development of alcohol use disorders. J. Stud. Alcohol 2000, 61, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurnberger, J.I.; Wiegand, R.; Bucholz, K.; O’Connor, S.; Meyer, E.T.; Reich, T.; Rice, J.; Schuckit, M.; King, L.; Petti, T.; et al. A family study of alcohol dependence—Coaggregation of multiple disorders in relatives of alcohol-dependent probands. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, A.C.; Bernardy, N.C.; Hauner, K. Stressful events, personality, and mood disturbance: Gender differences in alcoholics and problem drinkers. Addict. Behav. 2003, 28, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.B.; Salvatore, J.E.; Maes, H.; Aliev, F.; Latvala, A.; Viken, R.; Rose, R.J.; Kaprio, J.; Dick, D.M. Education and alcohol use: A study of gene-environment interaction in young adulthood. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 162, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prescott, C.A.; Kendler, K.S. Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol abuse and dependence in a population-based sample of male twins. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohman, M.; Cloninger, C.R.; Vonknorring, A.L.; Sigvardsson, S. An Adoption Study of Somatoform Disorders: III. Cross-Fostering Analysis and Genetic-Relationship to Alcoholism and Criminality. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1984, 41, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Caneda, E.; Cadaveira, F.; Crego, A.; Doallo, S.; Corral, M.; Gomez-Suarez, A.; Holguin, S.R. Effects of a Persistent Binge Drinking Pattern of Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Follow-Up Study Using Event-Related Potentials. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013, 48, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parada, M.; Corral, M.; Caamano-Isorna, F.; Mota, N.; Crego, A.; Holguin, S.R.; Cadaveira, F. Binge Drinking and Declarative Memory in University Students. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E.; MacLeod, A.M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Powers, W.J.; Gusnard, D.A.; Shulman, G.L. A default mode of brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, J.L.; Patel, G.H.; Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Baker, J.T.; Van Essen, D.C.; Zempel, J.M.; Snyder, L.H.; Corbetta, M.; Raichle, M.E. Intrinsic functional architecture in the anaesthetized monkey brain. Nature 2007, 447, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhás, M.; Sun, H.; Brown, M.R.G.; MacKay, M.B.; Mann, K.F.; Sommer, W.H.; Wilman, A.H.; Dursun, S.M.; Greenshaw, A.J. Deep grey matter iron accumulation in alcohol use disorder. NeuroImage 2017, 148, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Zhao, Q.; Pohl, K.M.; Zahr, N.M.; Pfefferbaum, A. Attenuated cerebral blood flow in frontolimbic and insular cortices in Alcohol Use Disorder: Relation to working memory. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 136, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Smith, T.L.; Paulus, M.P.; Tapert, S.F.; Simmons, A.N.; Tolentino, N.J.; Shafir, A. The Ability of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Predict Heavy Drinking and Alcohol Problems 5 Years Later. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milne, E.; Greenop, K.R.; Scott, R.J.; de Klerk, N.H.; Bower, C.; Ashton, L.J.; Heath, J.A.; Armstrong, B.K. Parental alcohol consumption and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and brain tumors. Cancer Cause Control. 2013, 24, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweinhardt, P.; Fransson, P.; Olson, L.; Spenger, C.; Andersson, J.L.R. A template for spatial normalisation of MR images of the rat brain. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2003, 129, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.; Chen, K.W.; Zhao, S.J.; Liu, J.H.; Gu, X.C.; Yao, Q.L.; Hui, J.J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Teng, G.J.; Zhao, C.J.; et al. A rat brain MRI template with digital stereotaxic atlas of fine anatomical delineations in paxinos space and its automated application in voxel-wise analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchison, R.M.; Mirsattari, S.M.; Jones, C.K.; Gati, J.S.; Leung, L.S. Functional Networks in the Anesthetized Rat Brain Revealed by Independent Component Analysis of Resting-State fMRI. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 3398–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenczi, E.A.; Zalocusky, K.A.; Liston, C.; Grosenick, L.; Warden, M.R.; Amatya, D.; Katovich, K.; Mehta, H.; Patenaude, B.; Ramakrishnan, C.; et al. Prefrontal cortical regulation of brainwide circuit dynamics and reward-related behavior. Science 2016, 351, aac9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, M.J.; Dzemidzic, M.; Lurito, J.T.; Mathews, V.P.; Phillips, M.D. Correlations in low-frequency BOLD fluctuations reflect cortico-cortical connections. Neuroimage 2000, 12, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.P.; Li, Y.L.; Gong, Q.; Liang, H.; Liu, Q.; Bernardi, R.E.; Zhang, H.T.; Chen, F.; Lawrence, A.J.; Liang, J.H. Brucine N-Oxide Reduces Ethanol Intake and Preference in Alcohol-Preferring Male Fawn-Hooded Rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore-Langton, J.K.; Spear, L.P. Prenatal ethanol exposure attenuates sensitivity to the aversive effects of ethanol in adolescence and increases adult preference for a 5% ethanol solution in males, but not females. Alcohol 2019, 79, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.B.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.W.; Jiang, X.F.; Shan, B.C. A Statistical Parametric Mapping Toolbox Used for Voxel-Wise Analysis of FDG-PET Images of Rat Brain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.F.; King, J.; Zhang, N.Y. Anticorrelated resting-state functional connectivity in awake rat brain. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homanics, G.E.; Ferguson, C.; Quinlan, J.J.; Daggett, J.; Snyder, K.; Lagenaur, C.; Mi, Z.-P.; Wang, X.-H.; Grayson, D.R.; Firestone, L.L. Gene Knockout of the α6 Subunit of the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor: Lack of Effect on Responses to Ethanol, Pentobarbital, and General Anesthetics. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dölen, G.; Darvishzadeh, A.; Huang, K.W.; Malenka, R.C. Social reward requires coordinated activity of nucleus accumbens oxytocin and serotonin. Nature 2013, 501, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schultz, W.; Dayan, P.; Montague, P.R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 1997, 275, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempadoo, K.A.; Tourino, C.; Cho, S.L.; Magnani, F.; Leinninger, G.M.; Stuber, G.D.; Zhang, F.; Myers, M.G.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L.; et al. Hypothalamic Neurotensin Projections Promote Reward by Enhancing Glutamate Transmission in the VTA. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7618–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, M.E.; Kesner, R.P. The role of the agranular insular cortex in working memory for food reward value and allocentric space in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 98, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farb, N.A.S.; Anderson, A.K.; Segal, Z.V. The Mindful Brain and Emotion Regulation in Mood Disorders. Can. J. Psychiatry 2012, 57, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindler, S.; Geyer, S.; Strauss, M.; Anwander, A.; Hegerl, U.; Turner, R.; Schonknecht, P. Structural studies of the hypothalamus and its nuclei in mood disorders. Psychiatry Res. -Neuroimaging 2012, 201, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Olie, J.P. Neurobiology of mood, anxiety, and emotions as revealed by studies of a unique antidepressant: Tianeptine. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, P.M.; Gooley, J.J.; Saper, C.B. Neurobiology of the sleep-wake cycle: Sleep architecture, circadian regulation, and regulatory feedback. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2006, 21, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squire, L.R.; Zolamorgan, S. The Medial Temporal-Lobe Memory System. Science 1991, 253, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riekkinen, P.; Sirvio, J.; Riekkinen, P. Similar Memory Impairments Found in Medial Septal-Vertical Diagonal Band of Broca and Nucleus Basalis Lesioned Rats—Are Memory Defects Induced by Nucleus Basalis Lesions Related to the Degree of Nonspecific Subcortical Cell Loss. Behav. Brain Res. 1990, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, M.J.; Dawson, L.G.; Duty, S. Changes in metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-8 gene expression in the rodent basal ganglia motor loop following lesion of the nigrostriatal tract. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgens, U. The Efferent and Afferent Connections of the Supplementary Motor Area. Brain Res. 1984, 300, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Li, J.; Ye, J.H. Histamine regulates activities of neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus. J. Physiol-Lond. 2010, 588, 4103–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.A. The role of the thalamus in motor control. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottfried, J.A. Smell: Central nervous processing. In Taste and Smell; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 63, pp. 44–69. [Google Scholar]
- Benarroch, E.E. Olfactory system functional organization and involvement in neurodegenerative disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, S.N.; Knutson, B. The reward circuit: Linking primate anatomy and human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Li, A.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Xue, G. The coupling of BOLD signal variability and degree centrality underlies cognitive functions and psychiatric diseases. NeuroImage 2021, 237, 118187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, I.; Assaad, J.M.; Pihl, R.O.; Benkelfat, C.; Leyton, M.; Diksic, M.; Tremblay, R.E.; Dagher, A. Alcohol promotes dopamine release in the human nucleus accumbens. Synapse 2003, 49, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, A.S.; Srivastava, A. Structural Changes in the Insular Cortex in Alcohol Dependence: A cross sectional study. Iran. J. Psychiatry 2011, 6, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Larson, M.P.; Bogorodzki, P.; Rogowska, J.; McGlade, E.; King, J.B.; Terry, J.; Yurgelun-Todd, D. Altered prefrontal and insular cortical thickness in adolescent marijuana users. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 220, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matthews, D.B.; Criswell, H.E.; Grobin, A.C.; Morrow, A.L. Chronic Ethanol Consumption Alters Recovery of Spontaneously Active Medial Septal/Diagonal Band of Broca Neurons From GABA-Microiontophoresis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgin, D.V. Perinatal alcohol exposure leads to prolonged upregulation of hypothalamic GABA A receptors and increases behavioral sensitivity to gaboxadol. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 439, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartley, T.; Lever, C.; Burgess, N.; O’Keefe, J. Space in the brain: How the hippocampal formation supports spatial cognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20120510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, K.T.; Steinberg, E.E.; DeLoach, K.E.; Xie, S.; Miyamichi, K.; Schwarz, L.; Gao, X.J.; Kremer, E.J.; Malenka, R.C.; Luo, L. Circuit architecture of VTA dopamine neurons revealed by systematic input-output mapping. Cell 2015, 162, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendler, K.S.; Neale, M.C.; Heath, A.C.; Kessler, R.C.; Eaves, L.J. A Twin-Family Study of Alcoholism in Women. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, L.; Hawkins, T.D.; Li, T.K. New strains of rats with alcohol preference and nonpreference. In Alcohol and Aldehyde Metabolizing Systems; Thurman, R.G., Williamson, J.R., Drott, H., Chance, B., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 3, pp. 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.M.; Mcbride, W.J.; Lumeng, L.; Li, T.K. Contents of Monoamines in Forebrain Regions of Alcohol-Preferring (P) and Alcohol-Nonpreferring (Np) Lines of Rats. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 1987, 26, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, H.L.; Du, H.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, T.T.; Hu, T.; Kamal, G.M.; Li, X.H.; Liu, H.L.; et al. Evaluation of metabolites extraction strategies for identifying different brain regions and their relationship with alcohol preference and gender difference using NMR metabolomics. Talanta 2018, 179, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, G.; Lobina, C.; Lorrai, I.; Acciaro, C.; Maccioni, P.; Gessa, G.L. Binge drinking and anxiety at the end of the nocturnal period in alcohol-preferring sP rats. Alcohol 2017, 63, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, B.; Colombo, G.; Maccioni, P.; Carai, M.A.M.; Franconi, F.; Gessa, G.L. High alcohol intake in female Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 2014, 48, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
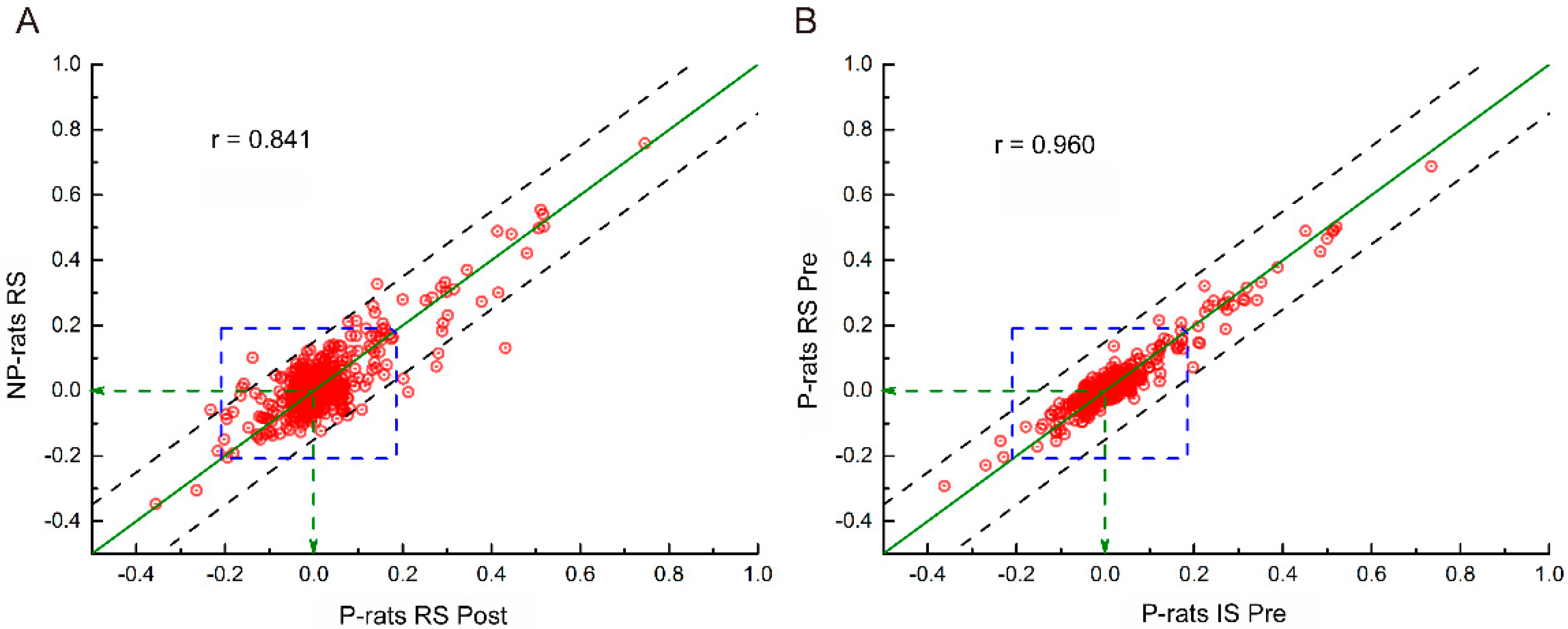

| RS, P-Pre | IS, P-Pre | RS, P-Mid | IS, P-Mid | RS, P-Post | IS, P-Post | RS, NP | IS, NP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS, P-Pre | 1 | 0.96 | 0.940 | 0.934 | 0.920 | 0.919 | 0.856 | 0.860 |
| IS, P-Pre | 0.960 | 1 | 0.942 | 0.942 | 0.924 | 0.919 | 0.863 | 0.878 |
| RS, P-Mid | 0.940 | 0.942 | 1 | 0.931 | 0.936 | 0.920 | 0.862 | 0.863 |
| IS, P-Mid | 0.934 | 0.942 | 0.931 | 1 | 0.913 | 0.910 | 0.850 | 0.870 |
| RS, P-Post | 0.920 | 0.924 | 0.936 | 0.913 | 1 | 0.925 | 0.841 | 0.848 |
| IS, P-Post | 0.919 | 0.919 | 0.920 | 0.910 | 0.925 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.869 |
| RS, NP | 0.856 | 0.863 | 0.862 | 0.850 | 0.841 | 0.857 | 1 | 0.908 |
| IS, NP | 0.860 | 0.878 | 0.863 | 0.870 | 0.848 | 0.869 | 0.908 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Nie, B.; Liu, T.; Zheng, N.; Liu, Z.; Shan, B.; Jiang, L.; Manyande, A.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; et al. Variations of Brain Functional Connectivity in Alcohol-Preferring and Non-Preferring Rats with Consecutive Alcohol Training or Acute Alcohol Administration. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111474
Liu Y, Nie B, Liu T, Zheng N, Liu Z, Shan B, Jiang L, Manyande A, Li X, Xu F, et al. Variations of Brain Functional Connectivity in Alcohol-Preferring and Non-Preferring Rats with Consecutive Alcohol Training or Acute Alcohol Administration. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111474
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yue, Binbin Nie, Taotao Liu, Ning Zheng, Zeyuan Liu, Baoci Shan, Lihong Jiang, Anne Manyande, Xihai Li, Fuqiang Xu, and et al. 2021. "Variations of Brain Functional Connectivity in Alcohol-Preferring and Non-Preferring Rats with Consecutive Alcohol Training or Acute Alcohol Administration" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111474
APA StyleLiu, Y., Nie, B., Liu, T., Zheng, N., Liu, Z., Shan, B., Jiang, L., Manyande, A., Li, X., Xu, F., & Wang, J. (2021). Variations of Brain Functional Connectivity in Alcohol-Preferring and Non-Preferring Rats with Consecutive Alcohol Training or Acute Alcohol Administration. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111474






