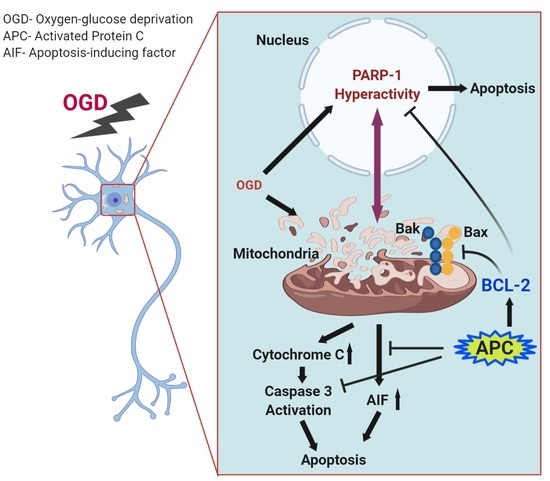
Neuroprotective Effects of Activated Protein C Involve the PARP/AIF Pathway against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Cell Viability Assessment
2.3. Electron Microscope Assay
2.4. PAR1, PAR3, and EPCR Expression by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide (PI) Double-Staining Assay
2.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.7. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
2.8. Analysis of BCL-2, Bax, PARP-1 and AIF mRNA Expression
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
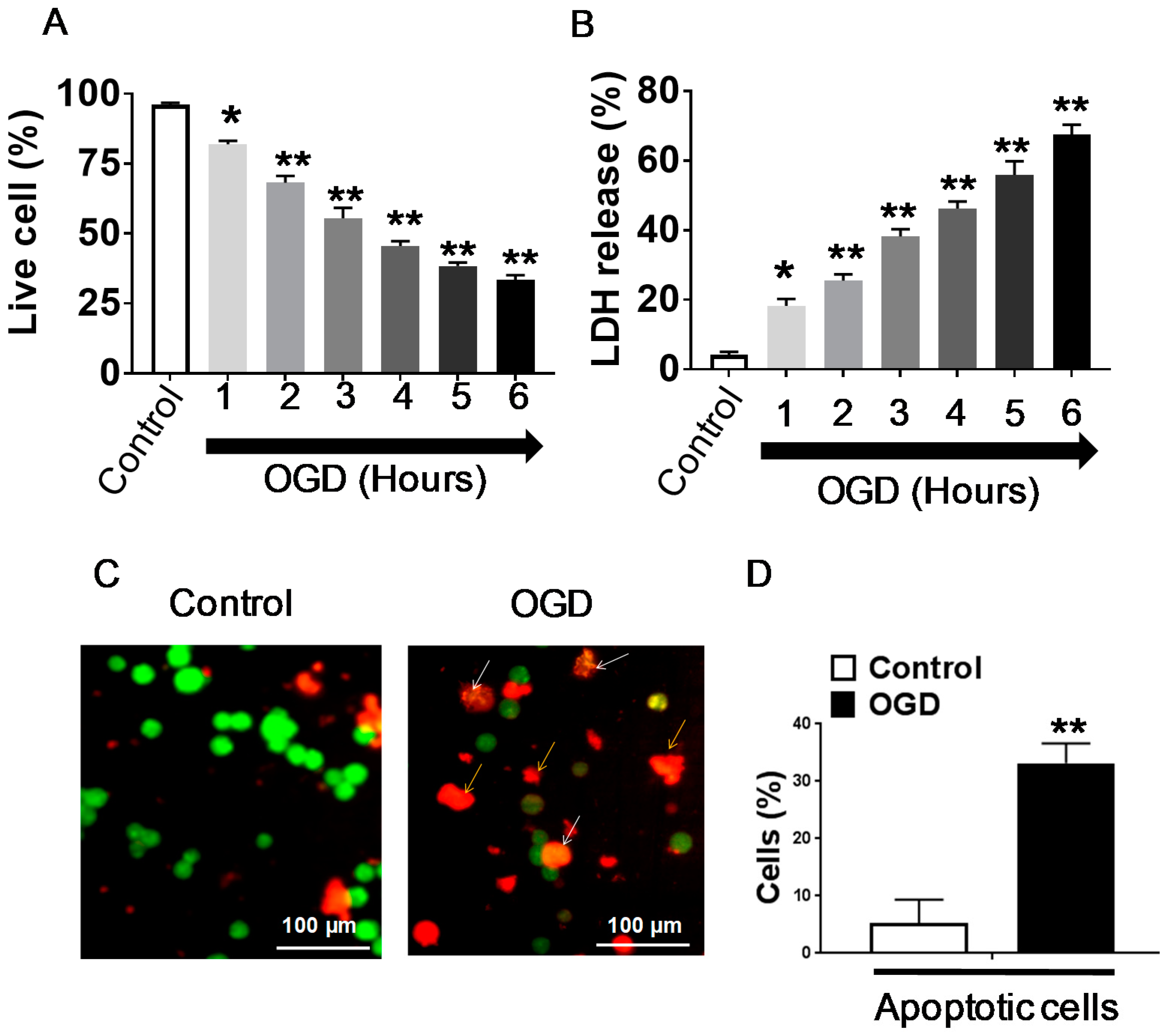
3.1. Effect of OGD Exposure in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
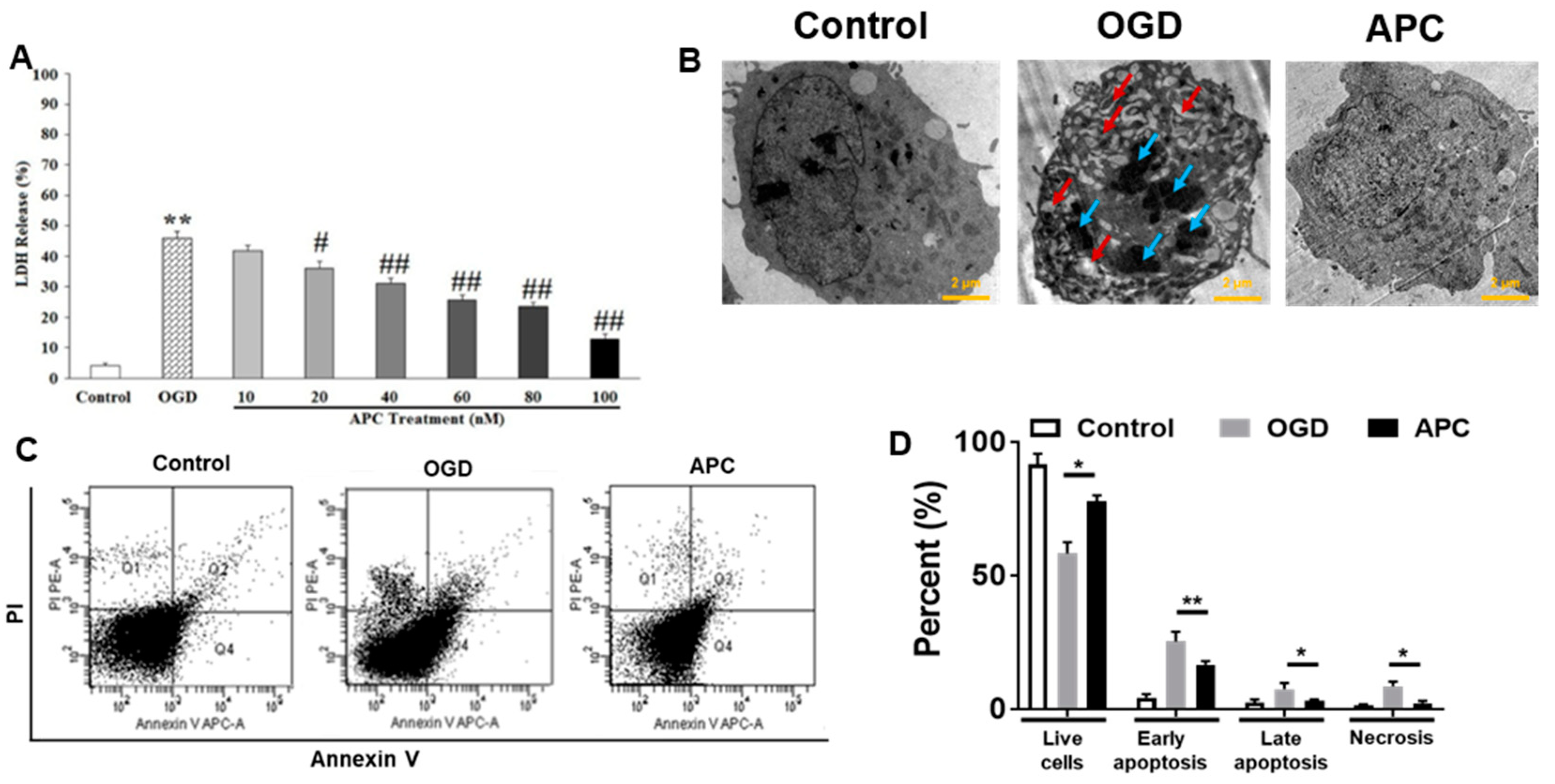
3.2. Effect of APC Treatment on OGD Induced Cell Death
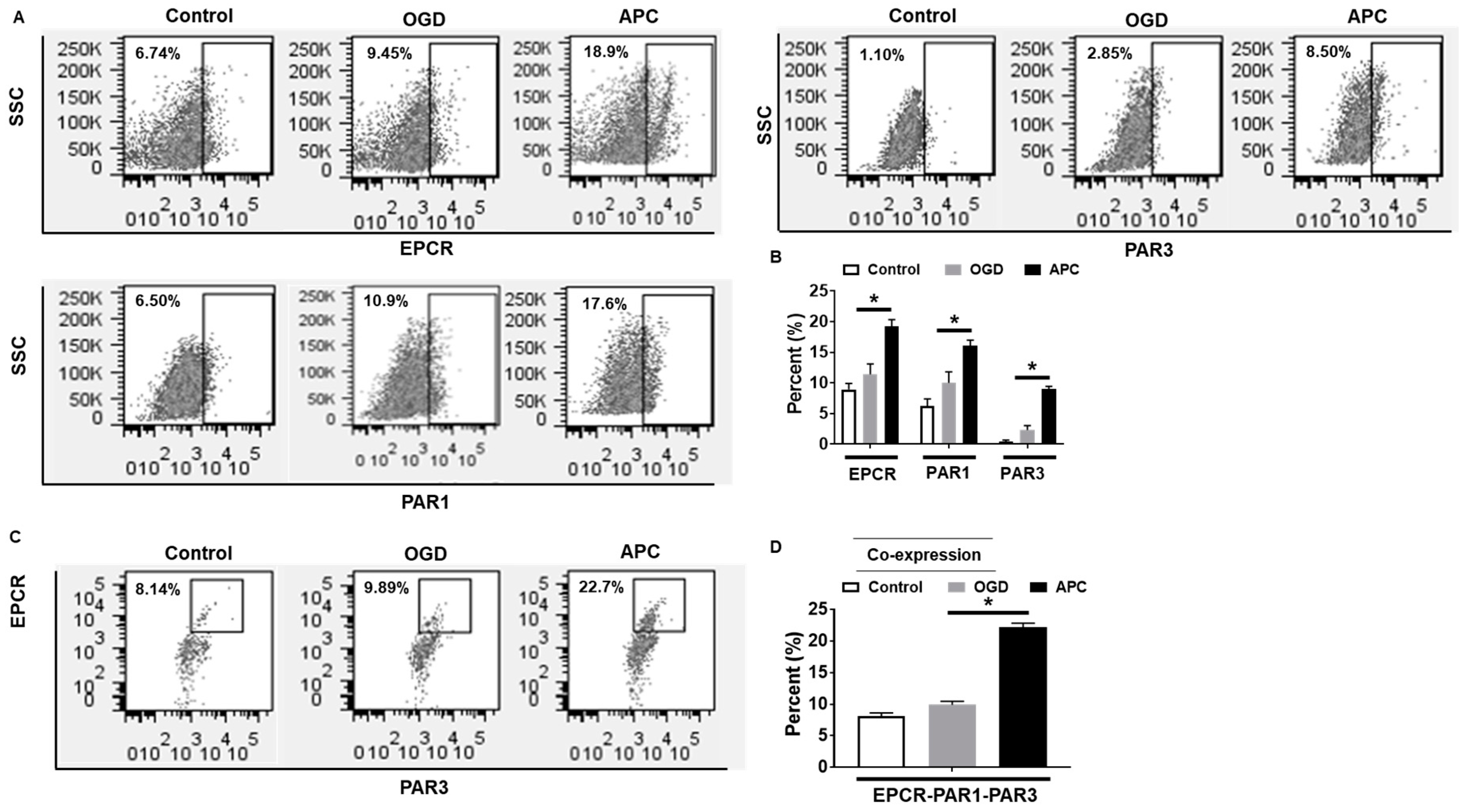
3.3. Effect of APC on the Expression of EPCR, PAR1, and PAR3
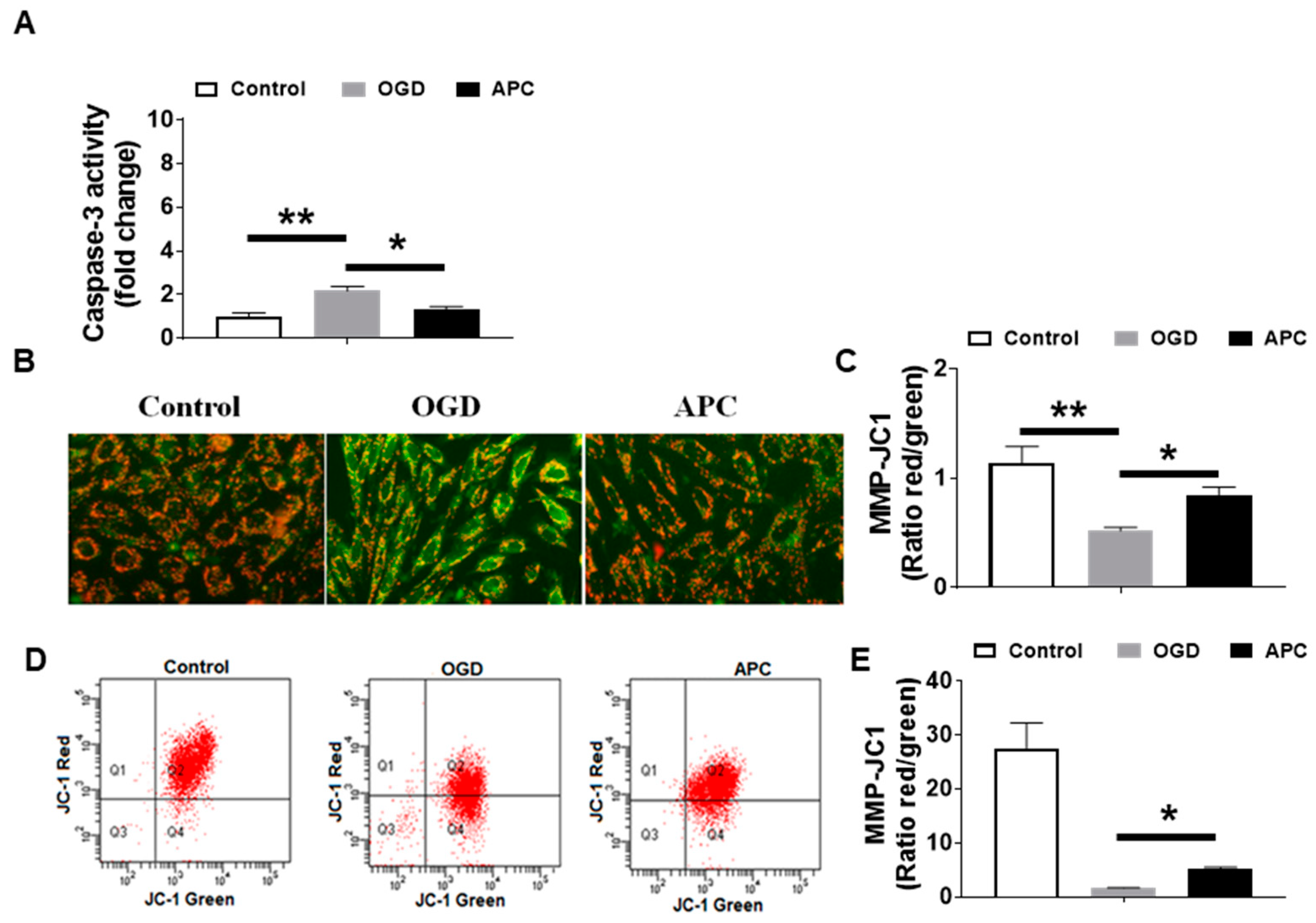
3.4. Effect of APC on Caspase-3 Activity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
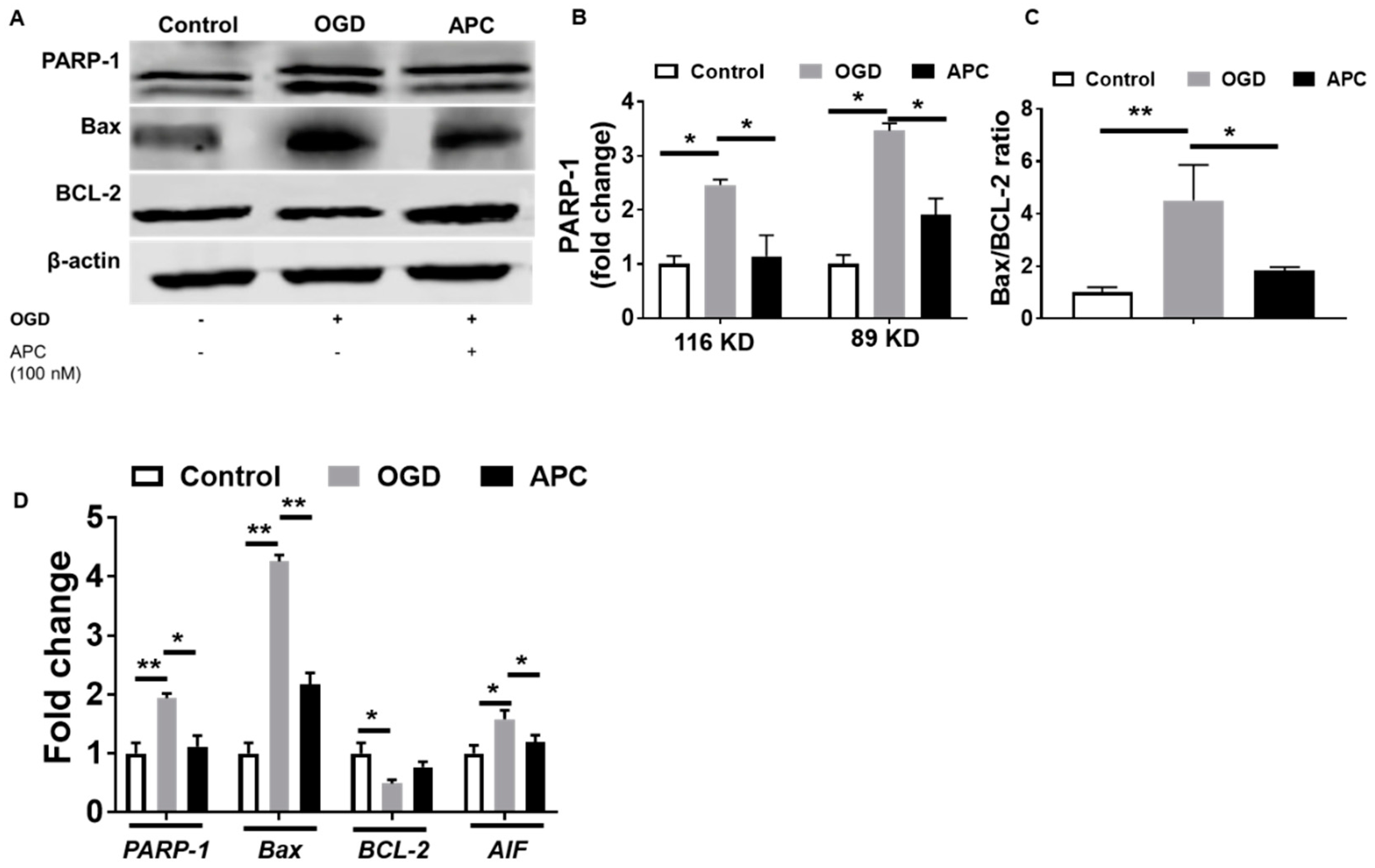
3.5. Expression of PARP-1 and AIF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2014, 383, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrial.gov/ (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Foster, D.; Davie, E.W. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human protein C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4766–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.; Whitmont, K.; Tritton, S.; March, L.; Sambrook, P.; Xue, M. New therapeutic applications for the anticoagulant, activated protein C. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008, 8, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlbäck, B.; Villoutreix, B.O. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C anticoagulant pathway: Novel insights into structure-function relationships and molecular recognition. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, G.R.; Vincent, J.L.; Laterre, P.F.; LaRosa, S.P.; Dhainaut, J.F.; Lopez-Rodriguez, A.; Steingrub, J.S.; Garber, G.E.; Helterbrand, J.D.; Ely, E.W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folsom, A.R.; Ohira, T.; Yamagishi, K.; Cushman, M. Low protein C and incidence of ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2009, 7, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D.E.; Gelbert, L.; Ciaccia, A.; DeHoff, B.; Grinnell, B.W. Gene expression profile of antithrombotic protein c defines new mechanisms modulating inflammation and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 11199–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gerlitz, B.; Richardson, M.A.; Bull, C.; Berg, D.T.; Syed, S.; Galbreath, E.J.; Swanson, B.A.; Jones, B.E.; Grinnell, B.W. Distinct Functions of Activated Protein C Differentially Attenuate Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2009, 20, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Liu, D.; Griffin, J.H.; Fernández, J.A.; Castellino, F.; Rosen, E.D.; Fukudome, K.; Zlokovic, B.V. Activated protein C blocks p53-mediated apoptosis in ischemic human brain endothelium and is neuroprotective. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.R. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 2000, 407, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dömötör, E.; Benzakour, O.; Griffin, J.H.; Yule, D.; Fukudome, K.; Zlokovic, B.V. Activated protein C alters cytosolic calcium flux in human brain endothelium via binding to endothelial protein C receptor and activation of protease activated receptor-1. Blood 2003, 101, 4797–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Liu, D.; Gelbard, H.; Cheng, T.; Insalaco, R.; Fernández, J.A.; Griffin, J.H.; Zlokovic, B.V. Activated protein C prevents neuronal apoptosis via protease activated receptors 1 and 3. Neuron 2004, 41, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosnier, L.O.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Griffin, J.H. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood 2007, 109, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, L.O.; Griffin, J.H. Inhibition of staurosporine-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells by activated protein C requires protease-activated receptor-1 and endothelial cell protein C receptor. Biochem. J. 2003, 373, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.J.; Molino, M.; Kahn, M.; Brass, L.F. Protease activated receptors: Theme and variations. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riewald, M.; Petrovan, R.J.; Donner, A.; Mueller, B.M.; Ruf, W. Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamby, A.M.; Suh, S.W.; Kauppinen, T.M.; Swanson, R.A. Use of a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor to suppress inflammation and neuronal death after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2007, 38, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, R.; Kraus, W.L. The PARP Side of the Nucleus: Molecular Actions, Physiological Outcomes, and Clinical Targets. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Chu, G.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y. Role of p300 in regulating neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene expression through nuclear factor-κB-mediated way in neuronal cells. Neuroscience 2013, 248, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Yuan, J. Expansion and evolution of cell death programmes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, N.J.; Szabo, C. Therapeutic applications of PARP inhibitors: Anticancer therapy and beyond. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komjáti, K.; Besson, V.C.; Szabó, C. Poly (adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents in stroke and neurotrauma. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkarim, G.E.; Gertz, K.; Harms, C.; Katchanov, J.; Dirnagl, U.; Szabó, C.; Endres, M. Protective effects of PJ34, a novel, potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in in vitro and in vivo models of stroke. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, M.; Rhinn, H.; Bloquel, C.; Coqueran, B.; Szabó, C.; Plotkine, M.; Scherman, D.; Margaill, I. Anti-inflammatory effects of PJ34, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, in transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-M.; Cho, S.; Frys, K.; Racchumi, G.; Zhou, P.; Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Interaction between inducible nitric oxide synthase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2004, 35, 2896–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, N.; Ogawa, S.; Takagi, T.; Wanaka, A.; Mori, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Pinsky, D.J.; Stern, D.M.; Tohyama, M. Cloning of a putative vesicle transport-related protein, RA410, from cultured rat astrocytes and its expression in ischemic rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16438–16444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Sano, K.; Takakura, K.; Saito, I.; Shinohara, Y.; Asano, T.; Yasuhara, H. Ebselen in acute ischemic stroke: A placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Ebselen Study Group. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 1998, 29, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Xie, K.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L. Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury: Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Brain Res. 2012, 1452, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGahon, A.J.; Martin, S.J.; Bissonnette, R.P.; Mahboubi, A.; Shi, Y.; Mogil, R.J.; Nishioka, W.K.; Green, D.R. The end of the (cell) line: Methods for the study of apoptosis in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 1995, 46, 153–185. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods San Diego Calif. 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, M.D. Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 363–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendioroz, M.; Fernández-Cadenas, I.; Alvarez-Sabín, J.; Rosell, A.; Quiroga, D.; Cuadrado, E.; Delgado, P.; Rubiera, M.; Ribó, M.; Molina, C.; et al. Endogenous activated protein C predicts hemorrhagic transformation and mortality after tissue plasminogen activator treatment in stroke patients. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Basel Switz. 2009, 28, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlokovic, B.V.; Griffin, J.H. Cytoprotective protein C pathways and implications for stroke and neurological disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwens, E.A.; Stavenuiter, F.; Mosnier, L.O. Mechanisms of anticoagulant and cytoprotective actions of the protein C pathway. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11 (Suppl. 1), 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Vetrano, S.; Zhang, L.; Poplis, V.A.; Castellino, F.J. The protein C pathway in tissue inflammation and injury: Pathogenic role and therapeutic implications. Blood 2010, 115, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmon, C.T. Protein C anticoagulant system—Anti-inflammatory effects. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, T.; Guo, H.; Fernández, J.A.; Griffin, J.H.; Song, X.; Zlokovic, B.V. Tissue plasminogen activator neurovascular toxicity is controlled by activated protein C. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, N.; Larochette, N.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondrial permeability transition in apoptosis and necrosis. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12 (Suppl. 2), 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrabi, S.A.; Kim, N.S.; Yu, S.-W.; Wang, H.; Koh, D.W.; Sasaki, M.; Klaus, J.A.; Otsuka, T.; Zhang, Z.; Koehler, R.C.; et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer is a death signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18308–18313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-W.; Andrabi, S.A.; Wang, H.; Kim, N.S.; Poirier, G.G.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer-induced cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18314–18319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, L.L.; Sensi, S.L.; Canzoniero, L.M.; Handran, S.D.; Rothman, S.M.; Lin, T.S.; Goldberg, M.P.; Choi, D.W. Mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species in cortical neurons following exposure to N-methyl-D-aspartate. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6377–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandir, A.S.; Poitras, M.F.; Berliner, A.R.; Herring, W.J.; Guastella, D.B.; Feldman, A.; Poirier, G.G.; Wang, Z.Q.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. NMDA but not non-NMDA excitotoxicity is mediated by Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8005–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Meli, E.; Peruginelli, F.; Chiarugi, A.; Cozzi, A.; Picca, R.; Romagnoli, P.; Pellicciari, R.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors attenuate necrotic but not apoptotic neuronal death in experimental models of cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosznajder, R.P.; Gadamski, R.; Czapski, G.A.; Jesko, H.; Strosznajder, J.B. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during reperfusion after transient forebrain ischemia: Its role in brain edema and cell death. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2003, 20, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.W.; Aoyama, K.; Chen, Y.; Garnier, P.; Matsumori, Y.; Gum, E.; Liu, J.; Swanson, R.A. Hypoglycemic neuronal death and cognitive impairment are prevented by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors administered after hypoglycemia. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10681–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culmsee, C.; Zhu, C.; Landshamer, S.; Becattini, B.; Wagner, E.; Pellecchia, M.; Pellechia, M.; Blomgren, K.; Plesnila, N. Apoptosis-inducing factor triggered by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and Bid mediates neuronal cell death after oxygen-glucose deprivation and focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10262–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moubarak, R.S.; Yuste, V.J.; Artus, C.; Bouharrour, A.; Greer, P.A.; Menissier-de Murcia, J.; Susin, S.A. Sequential activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, calpains, and Bax is essential in apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated programmed necrosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4844–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| BCL2 | F: GTGCCACCTGTGGTCCACCT |
| R: CTTCACTTGTGGCCCAGATAGG | |
| Bax | F: GCTTCAGGGTTTCATCCAGG |
| R: AACATGTCAGCTGCCACTCG | |
| PARP-1 | F: TTGAAAAAGCCCTAAAGGCTCA |
| R: CTACTCGGTCCAAGATCGCC | |
| AIF | F: AAATCTCTCCACTACACT |
| R: AATTTTAGCAGATTAAGAAGC | |
| GAPDH | F: AACAGCGACACCCATCCTC |
| R: CATACCAGGAAATGAGCTTGACAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sriwastva, M.K.; Kunjunni, R.; Andrabi, M.; Prasad, K.; Saxena, R.; Subbiah, V. Neuroprotective Effects of Activated Protein C Involve the PARP/AIF Pathway against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120959
Sriwastva MK, Kunjunni R, Andrabi M, Prasad K, Saxena R, Subbiah V. Neuroprotective Effects of Activated Protein C Involve the PARP/AIF Pathway against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120959
Chicago/Turabian StyleSriwastva, Mukesh Kumar, Remesh Kunjunni, Mutahar Andrabi, Kameshwar Prasad, Renu Saxena, and Vivekanandhan Subbiah. 2020. "Neuroprotective Effects of Activated Protein C Involve the PARP/AIF Pathway against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120959
APA StyleSriwastva, M. K., Kunjunni, R., Andrabi, M., Prasad, K., Saxena, R., & Subbiah, V. (2020). Neuroprotective Effects of Activated Protein C Involve the PARP/AIF Pathway against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120959