Adsorption of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Solutions by Unmodified Iron-Ore Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Adsorbent and Solutions
2.2. Experiments
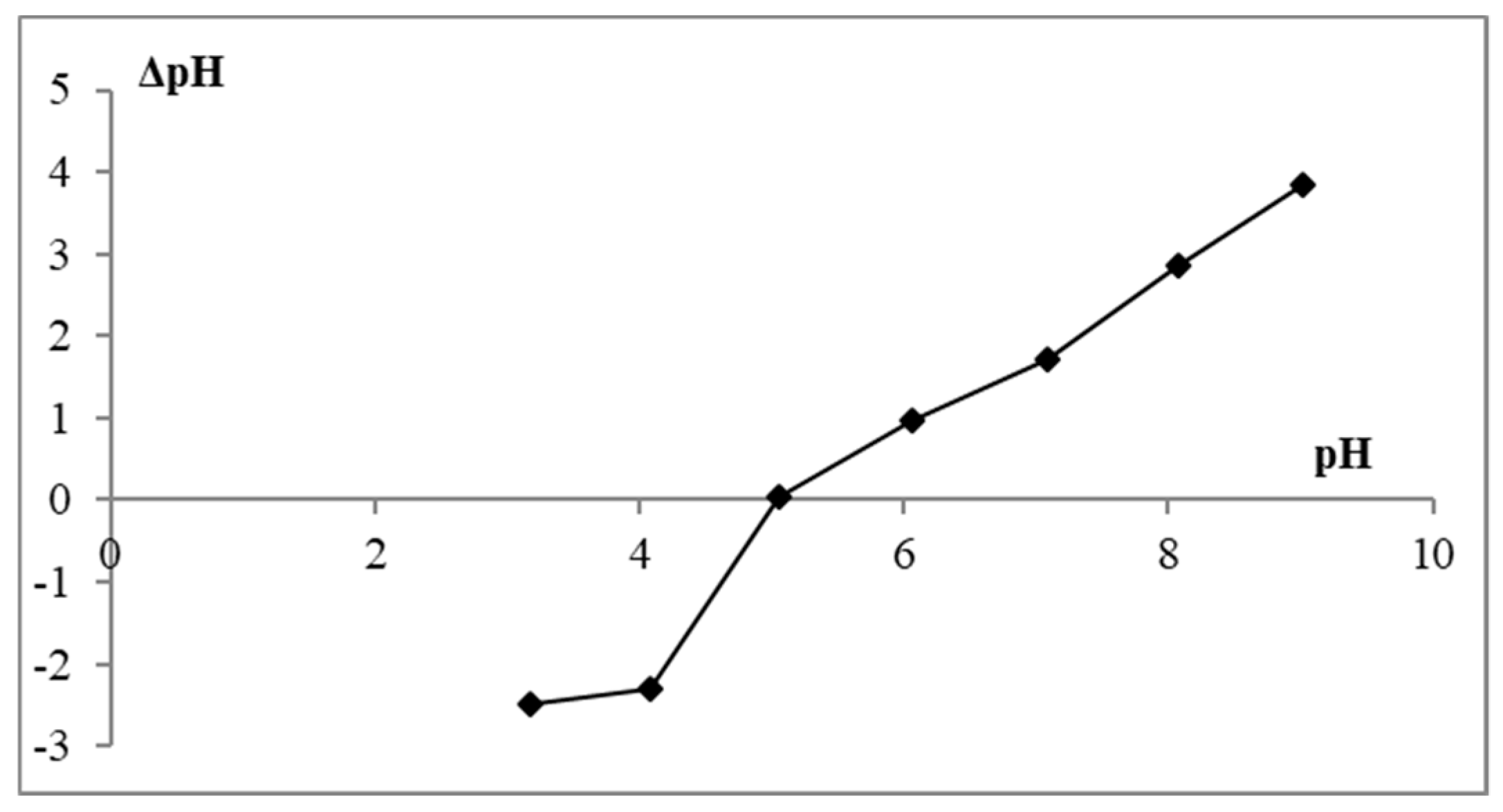
2.2.1. Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC)
2.2.2. Adsorption Study
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
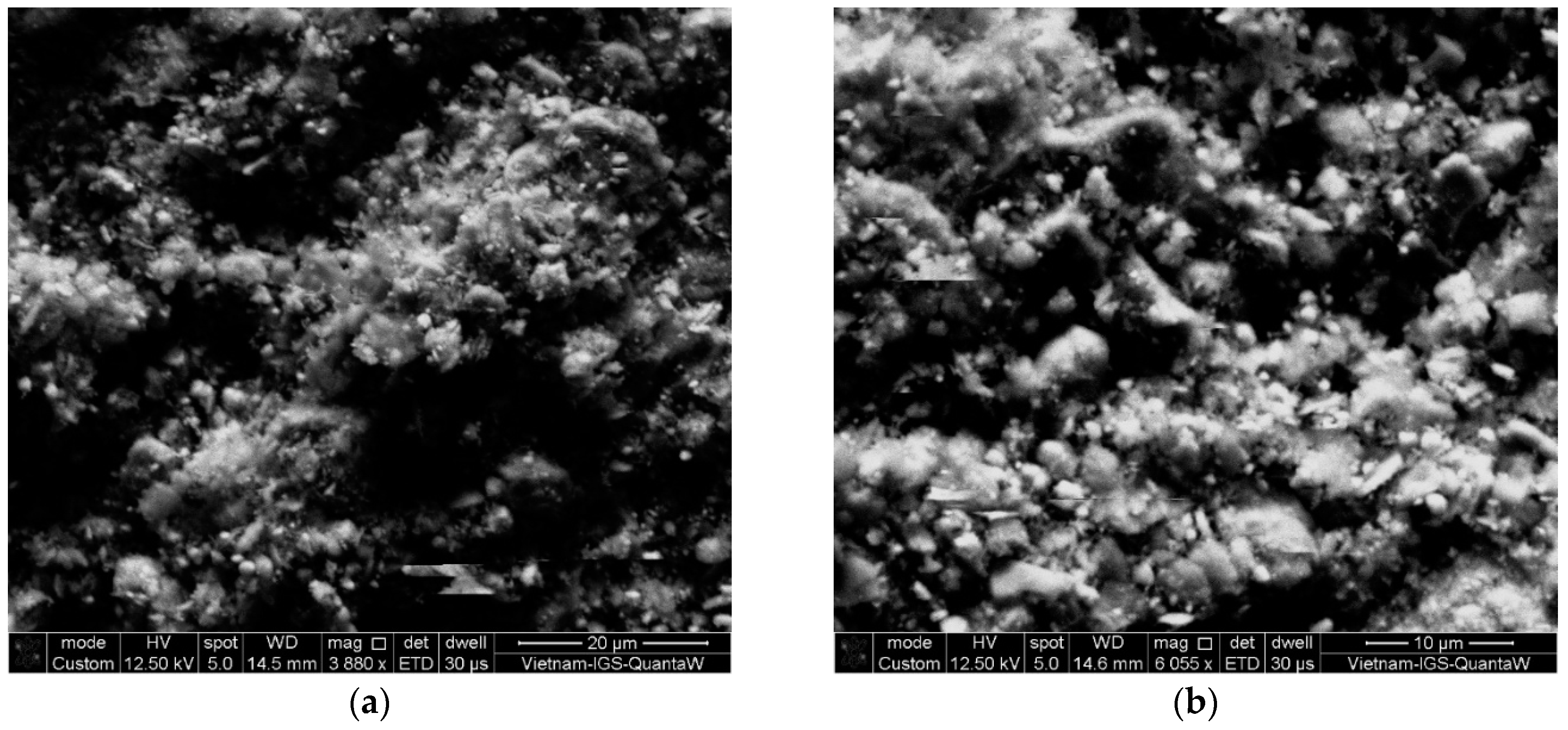
3.1. Characteristics of Materials
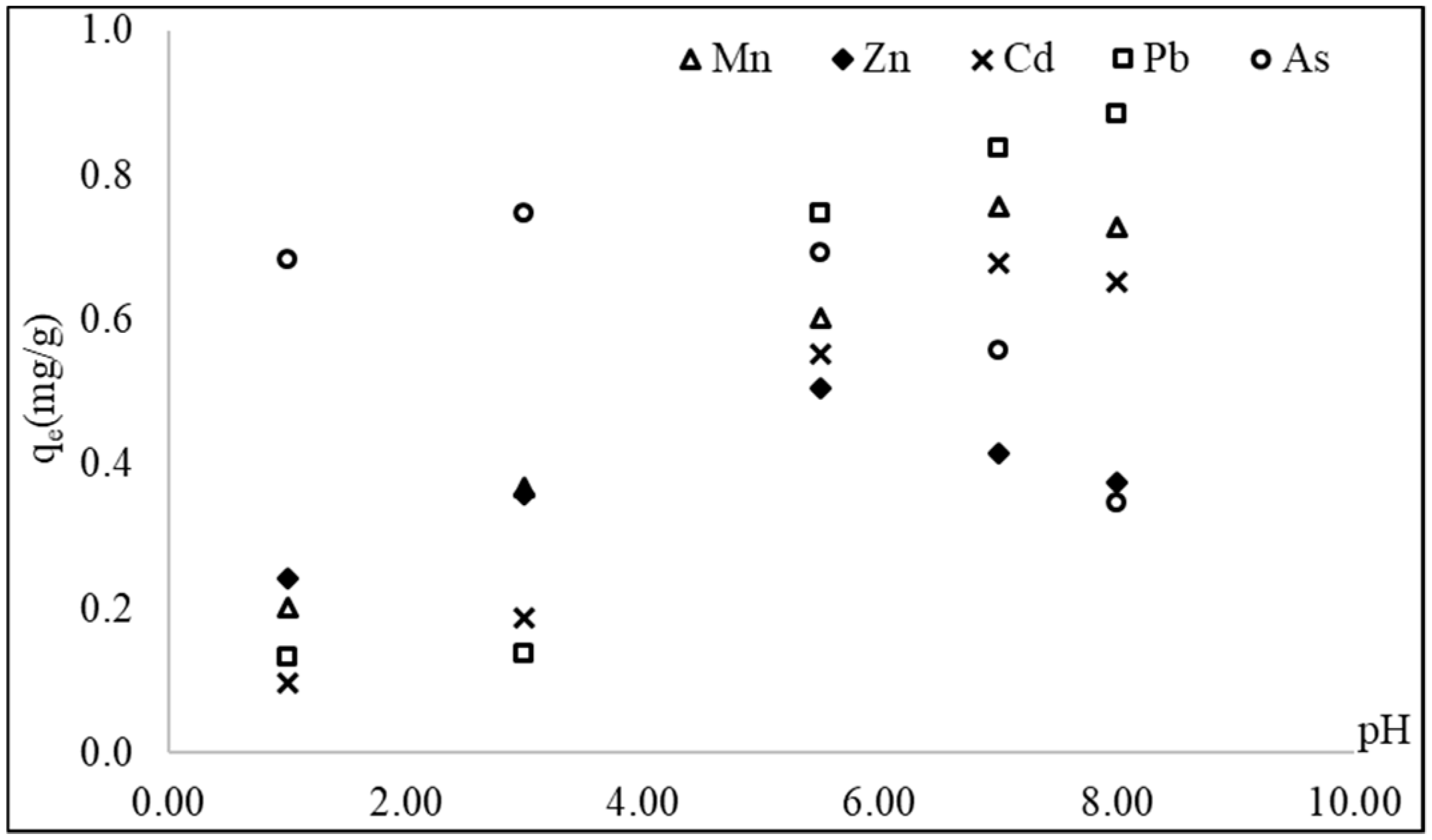
3.2. Effect of pH on Adsorption
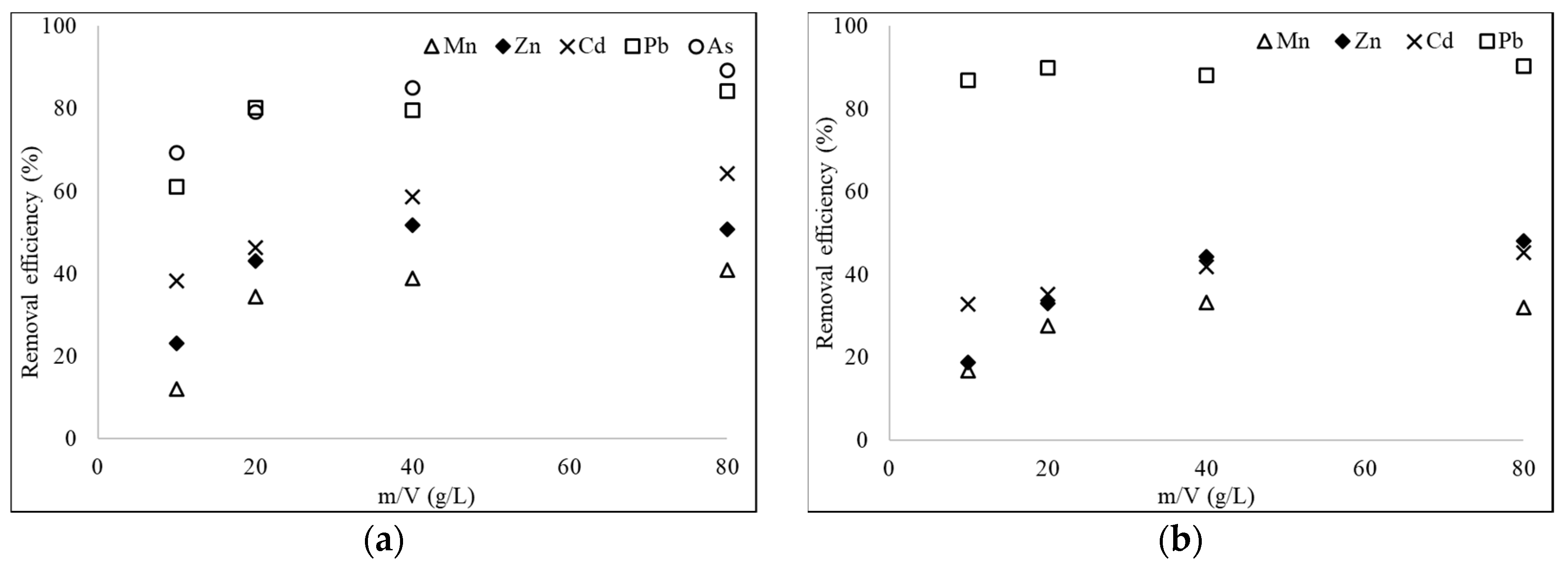
3.3. Effect of Doses of the Adsorbent on Adsorption
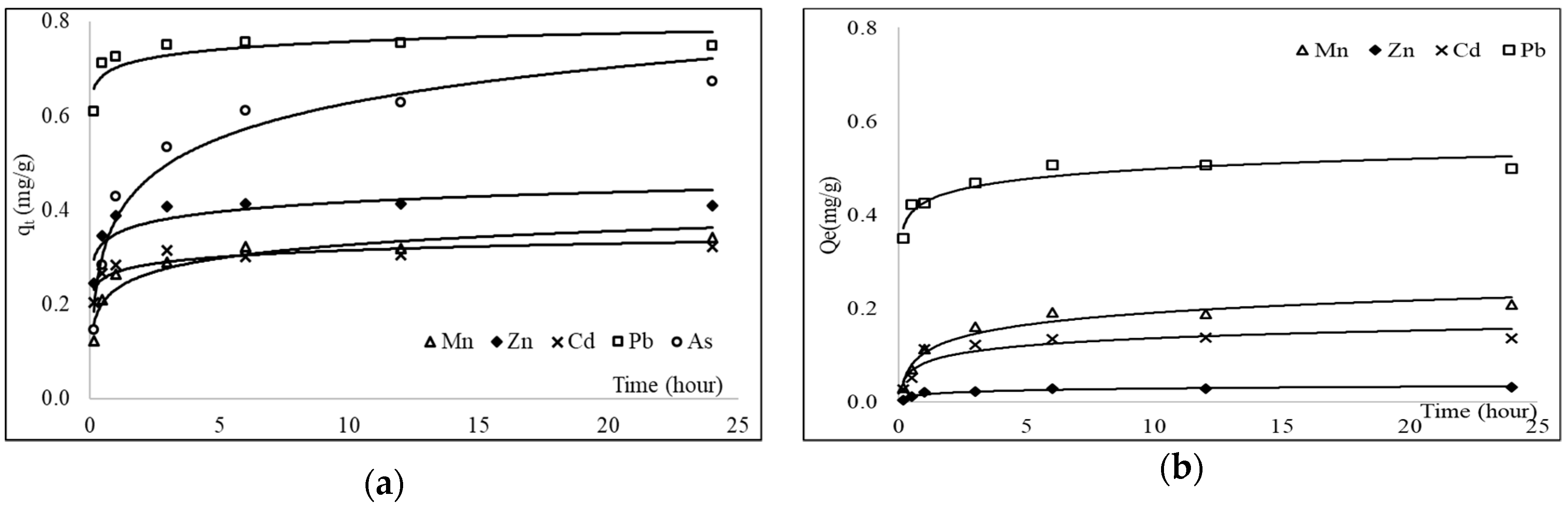
3.4. Batch Adsorption Kinetics
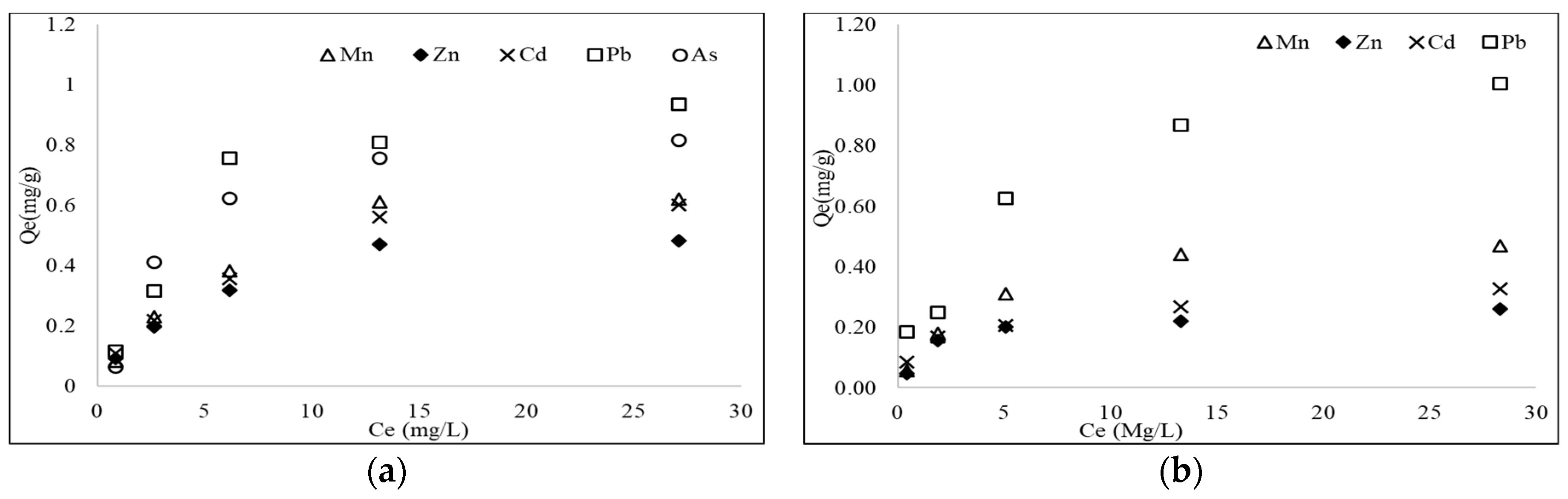
3.5. Batch Equilibrium Adsorption
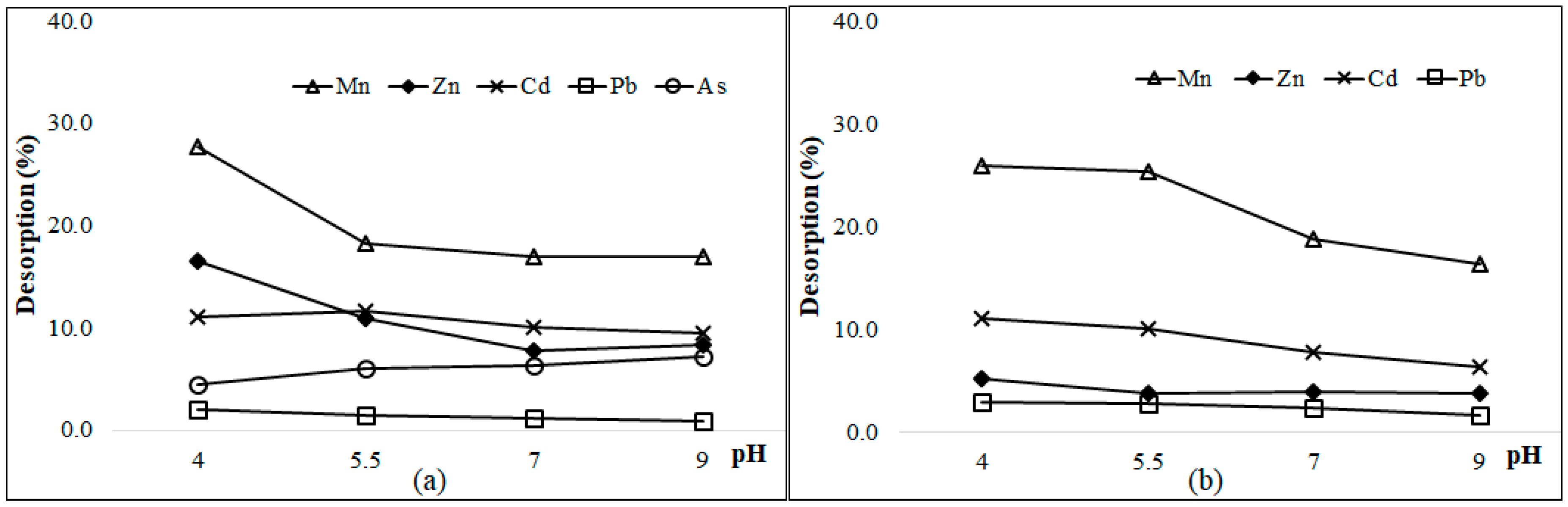
3.6. Desorption of As and Heavy Metals at Different pH Values
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gosar, M. Environmental impacts of metal mining. Mater. Geoenviron. 2004, 51, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Z. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2017, 141, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancha, A.M. Review of coagulation technology for removal of arsenic: Case of Chile. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2006, 24, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Zhanga, F.Z.; Chena, Y.; Chena, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of arsenic on soils: Kinetics, equilibrium, and effect of Fe(OH)2 colloid, H2SiO3 colloid and phosphate. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A.; Ismat Shah, S. Utilization of anion exchange resin Spectra/Gel for separation of arsenic from water. Arab. J. Chem. 2013, 6, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, P.; Khilar, S.; Mahajan, K.C. Removal of arsenic from water by electro coagulation. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsonyannis, I.A.; Zhouboulis, A.I. Application of biological processes for the removal of arsenic from groundwaters. Water Res. 2004, 38, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.H.; Sakakibara, M.; Sano, S. Accumulation of Indium and other heavy metals by Eleocharis acicularis: An option for phytoremediation and phytomining. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R.T. COD and BOD removal from Textile wastewater using naturally prepared adsorbents and their activation forms using sulphuric acid. In Wastewater Engineering: Advanced Wastewater Treatment Systems; IJSR Publication: Chhattisgarh, India, 2014; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Utilization of sludge based adsorbents for the removal of various pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, H.A. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural and industrial wastes as adsorbents. HBRC Journal 2013, 9, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovleva, E.; Sillanpaa, M. The use of low-cost adsorbents for wastewater purification in mining industries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7878–7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çoruh, S.; Ergun, O.N. Copper Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Using Red Mud—An Aluminium Industry Waste; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Aldrich, C. Removal of pollutants from acid mine wastewater using metallurgical by-product slags. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovleva, E.; Philipp, M.; Tatiana, V.I.; Mika, S.; Walter, Z.T.; Ermei, M.; Jarno, S.; Anna, G.; Alexander, A.G.; Khanita, K.; et al. Modified and unmodified low-cost iron-containing solid wastes as adsorbents for efficient removal of As(III) and As(V) from mine water. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdes, D.; Gundogdu, A.; Kemer, B.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.B.; Soylak, M. Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by a waste mud from copper mine industry: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, L.; Das, B.; Rao, D.S. Studies on removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions using iron ore slimes as adsorbent. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeltrauda, H.R.; Rafał, W. Competitive sorption/desorption of Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni, Cu, and Cr by clay-bearing mining wastes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 65–66, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hülya, G.; Jens, C.T.; David, M.; Olaf, S. Adsorption of arsenate from water using neutralized red mud. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Pepper, R.A.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Millar, G.J. A novel akaganeite sorbent synthesised from waste red mud: Application for treatment of arsenate in aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6308–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, P.T.; Mai, N.T.T.; Khai, N.M. Production of adsorbent from red mud for the removal of arsenic in aqueous environment. VNU J. Sci. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 32, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, D.D. Assess the Possibility of Using Some Coal Mine Sludge in Treating Wastewater Contaminated with Heavy Metals; Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST05.04/12-13): Hanoi, Vietnam, 2004. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A.; Nayak, A. Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 342, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General Statistics Office of Vietnam. Social-economic report of Vietnam; Statistics Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2016. (In Vietnamese)
- Khoi, N.N. Mineral resources potential of Vietnam and current state of mining activity. Applied Environmental Research 2014, 36, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. News. Available online: http://kttvqg.gov.vn/tin-tuc/3075/Bac-Kan:-Vo-h%C3%B4-chua-bun-do,-chat-thai-nguy-hai.html (accessed on 10 November 2018). (In Vietnamese)
- Nhan, N.V. Mineral Mines; Vietnam National University Express: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2004. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Bac Kan Department of Natural Resources and Environment. Report on the Assessment of Environmental Impacts of the Project on Investment in the Construction of Iron Ore Exploitation and Processing Projects in Ban Cuon Commune; Ngoc Phai Commune: Bac Kan, Vietnam, 2010. (In Vietnamese)
- Mellah, A.; Chegrouchethe, S. The removal of zinc from aqueous solutions by natural bentonite. Water Res. 1996, 31, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, A.; Higashi, T.; Hatta, T.; Jamoussi, F.; Tase, N. Mineralogical and spectroscopic characterization, and potential environmental use of limestone from the Abiod formation, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Chao, H.P. Adsorption and desorption of potentially toxic metals on modified biosorbents through new green grafting process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12808–12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, S.K.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Arsenic removal from real-life groundwater by adsorption on laterite soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thao, N.P.H.; Ha, N.T.H.; Anh, B.T.K. Sorption of heavy metals by laterite from Vinh Phuc and Hanoi. Vietnam. J. Viet. Env. 2016, 8, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kayode, O.A.; Iyayi, E.U.; Bamidele, I.O. The effect of some operating variables on the adsorption of lead and cadmium ions on kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B134, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, S.; Jaouali, I.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Cadmium sorption and desorption in soils: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 489–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.; O’Day, P.A.; Vlassopoulos, D.; Garc´ıa-Gonzalez, M.T.; Garrido, F. A surface complexation and ion exchange model of Pb and Cd competitive sorption on natural soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Wei, G.; Qian, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C. A designed nanoporous material for phosphate removal with high efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, T.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.C.; Vigneswaran, S.; Singh, G.; Kandasamy, J. Batch and column adsorption and desorption of fluoride using hydrous ferric oxide: Solution chemistry and modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn by an iron-coated Australian zeolite in batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 270, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasastjerna, J.A. On the radii of ions. Comm. Phys. Math. Soc. Sci. Fenn. 1923, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W. Arsenate and cadmium co-adsorption and co-precipitation on goethite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raul, P.K.; Devi, R.R.; Umlong, I.M.; Thakur, A.J.; Banerjee, S.; Veer, V. Iron oxide hydroxide nanoflower assisted removal of arsenic from water. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 49, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glocheux, Y.; Pasarin, M.M.; Albadarin, A.B.; Allen, S.J.; Walker, G.M. Removal of arsenic from groundwater by adsorption onto an acidified laterite by-product. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 228, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, E.; Tran, H.T.; Ouédraogo, W.K.I.; Schmidt, C.; Zachmann, D.; Bahadir, M. Sugarcane bagasse treated with hydrous ferric oxide as a potential adsorbent for the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, B.R.C.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Santos, S.C.R. Arsenic removal from water using iron-coated seaweeds. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 192, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, N.T. Research on Adsorbent Based on Natural Mineral Materials: Basalt, Laterite, Clay to Remove Heavy Metal and Arsenic from Contaminated Wastewater; Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (KC-02.25/06-10): Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Giménez, J.; De Pablo, J.; Martínez, M.; Rovira, M.; Valderrama, C. Reactive transport of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) on natural hematite: Experimental and modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.C.; Rosemberg, R.S.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Monteiro, D.S.; Barbosa, F.; Oliveira, L.C.; Rodriguez, M.; Pereira, M.C.; Rodrigues, J.L. Arsenic removal from contaminated water by ultrafine δ-FeOOH adsorbents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 237, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Immobilization of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 87, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Lee, C.K.; Han, Y.L.; Chao, W.C.; Chao, H.P. Preparation of activated carbon using micro-nano carbon spheres through chemical activation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, D.K.V.; Jamuna, K.; Satyanarayana, B.; Venkateswarlu, B.; Rao, M.M.; Seshaiah, K. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from Cicer arietinum. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 92, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-El-Enein, S.A.; Shebl, A.; El-Dahab, S.A. Drinking water treatment sludge as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metals removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolali, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, J.L.; Du, B.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Nguyen, P.D. Characterization of a multi-metal binding biosorbent: Chemical modification and desorption studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| SBET (m2/g) | CEC (mmolc(−).Kg−1) | Authors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBC | 47.4 | 75 | This study |
| Laterite | 15.365 | - | [33] |
| Laterite (Hanoi, Vietnam) | - | 66 | [34] |
| Clay | 10–20 | 15–75 | [35,36] |
| Red mud | 30 | 37 | [19] |
| Heavy Metals | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | K2 (g.mg−1.min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| Single-metal experiments | |||||||
| Mn | 0.035 | 0.318 | 0.931 | 0.121 | 0.345 | 0.957 | |
| Zn | 0.066 | 0.406 | 0.897 | 0.653 | 0.427 | 0.941 | |
| Cd | 0.125 | 0.305 | 0.995 | 0.565 | 0.321 | 0.940 | |
| Pb | 0.177 | 0.737 | 0.902 | 0.451 | 0.761 | 0.947 | |
| As | 0.018 | 0.641 | 0.954 | 0.039 | 0.692 | 0.985 | |
| Mixed-metal experiments | |||||||
| Mn | 0.013 | 0.202 | 0.969 | 0.073 | 0.220 | 0.991 | |
| Zn | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.882 | 0.862 | 0.030 | 1.000 | |
| Cd | 0.028 | 0.110 | 0.956 | 0.512 | 0.120 | 0.778 | |
| Pb | 0.124 | 0.460 | 0.596 | 0.483 | 0.486 | 0.881 | |
| Heavy Metals | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/g)/(mg/L)n | n | R2 | |||
| Single-metal experiments | |||||||
| Mn | 0.710 | 0.154 | 0.951 | 0.143 | 0.459 | 0.874 | |
| Zn | 0.745 | 0.121 | 0.952 | 0.124 | 0.477 | 0.894 | |
| Cd | 0.771 | 0.154 | 0.980 | 0.157 | 0.431 | 0.936 | |
| Pb | 1.305 | 0.131 | 0.923 | 0.222 | 0.476 | 0.833 | |
| As | 1.113 | 0.455 | 0.993 | 0.220 | 0.426 | 0.843 | |
| Mixed-metal experiments | |||||||
| Mn | 0.370 | 0.217 | 0.975 | 0.100 | 0.350 | 0.854 | |
| Zn | 0.447 | 0.263 | 0.955 | 0.109 | 0.402 | 0.949 | |
| Cd | 0.484 | 0.338 | 0.982 | 0.136 | 0.229 | 0.910 | |
| Pb | 1.059 | 1.913 | 0.902 | 0.577 | 0.261 | 0.870 | |
| Heavy Metals | Adsorbent | Authors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| As | SBC | 1.113 | This study |
| Laterite (Tam Duong) | 0.756 | [34] | |
| Laterite (OBY) | 0.702 | [51] | |
| Laterite soil | 1.384 | [33] | |
| Modified red mud | 1.08 | [52] | |
| δ-FeOOH | 37.3 | [53] | |
| Pb | SBC | 1.305 | This study |
| Laterite (Tam Duong) | 1.553 | [34] | |
| Laterite (OBY) | 0.658 | [51] | |
| Activated carbon | 20.7 | [57] | |
| Kaolinite | 4.730 | [36] | |
| Montmorillonite | 31.1 | [55] | |
| Glucose AC | 28.2 | [56] | |
| Cd | SBC | 0.771 | This study |
| Laterite (Tam Duong) | 0.397 | [34] | |
| Montmorillonite | 4.700 | [54] | |
| 30.7 | [55] | ||
| Activated carbon | 17.8 | [57] | |
| Modified biosorbents | > 45.4 | [32] | |
| Zn | SBC | 0.745 | This study |
| Laterite (Tam Duong) | 0.281 | [34] | |
| Activated carbon | 19.9 | [57] | |
| ICZ (Iron-coated zeolite) | 6.22 | [44] | |
| Mn | SBC | 0.710 | This study |
| Laterite (Tam Duong) | 0.143 | [34] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, K.M.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, H.T.H. Adsorption of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Solutions by Unmodified Iron-Ore Sludge. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040619
Nguyen KM, Nguyen BQ, Nguyen HT, Nguyen HTH. Adsorption of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Solutions by Unmodified Iron-Ore Sludge. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(4):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040619
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Khai M., Bien Q. Nguyen, Hai T. Nguyen, and Ha T.H. Nguyen. 2019. "Adsorption of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Solutions by Unmodified Iron-Ore Sludge" Applied Sciences 9, no. 4: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040619
APA StyleNguyen, K. M., Nguyen, B. Q., Nguyen, H. T., & Nguyen, H. T. H. (2019). Adsorption of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Solutions by Unmodified Iron-Ore Sludge. Applied Sciences, 9(4), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040619





