Laser Induced Nano and Micro Structures of Molybdenum Surface Applied in Multistage Depressed Collector for Secondary Electron Suppression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
2.1. Laser Parameters
2.2. Characterization Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Processing Patterns
3.2. Average Power
3.3. Pitch Spacing
3.4. Scanning Speed
3.5. The Effect of Incidence Angle on SEY
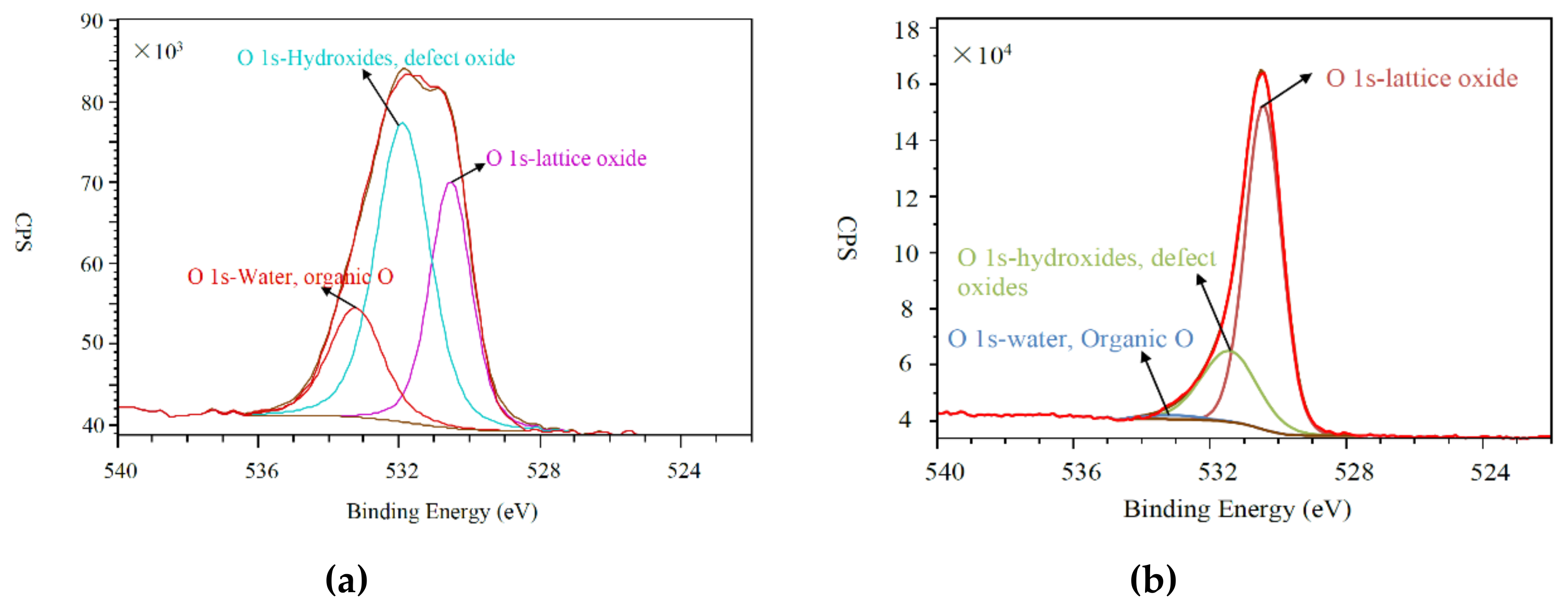
3.6. Chemical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.; Pagonakis, I.G.; Illy, S.; Gantenbein, G.; Jelonnek, J. 3D simulation of a realistic multistage depressed collector for high-power fusion gyrotrons. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Monterey, CA, USA, 19–21 April 2016; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Pagonakis, I.G.; Illy, S.; Thumm, M.; Gantenbein, G.; Jelonnek, J. Preliminary studies on multistage depressed collectors for fusion gyrotrons. In Proceedings of the 2016 German Microwave Conference (GeMiC), Bochum, Germany, 14–16 March 2016; pp. 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Curren, A.N.; Long, K.J.; Jensen, K.A.; Roman, R.F. An effective secondary electron emission suppression treatment for copper MDC electrodes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 December 1993; pp. 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Kussmaul, M.; Mirtich, M.J.; Curren, A.N. Ion beam treatment of potential space materials at the NASA Lewis Research Center. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1992, 51, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramins, P. Performance of computer designed small-size multistage depressed collectors for a high-perveance traveling wave tube. NASA Tech. Pap. 1984, 2248, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kenneth, A.; Curren, A.N.; Jensen, A.; Roman, R.F. Secondary emission electron characteristics of molybdenum-masked, ion-textured OFHC Copper. NASA Tech. Pap. 1990, 2967, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.Q.; Huang, M.G.; Feng, J.J.; Bai, G.D.; Yan, T.C. Ion surface modification for space TWT multistage depressed collectors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2196–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Cao, Q.; Liu, J.; Gong, D.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, B. A multistage depressed collectors design tool for traveling wave tubes based on non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Monterey, CA, USA, 24–26 April 2018; pp. 175–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Arya, S.; Latha, A.M.; Roy, A.; Ghosh, S.K. A Study of Thermal Behavior of Travelling Wave Tube. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Monterey, CA, USA, 24–26 April 2018; pp. 133–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pagonakis, I.G.; Wul, C.; Ell, B.; Avramidis, K.A.; Gantenbein, G.; Illy, S.; Thumm, M.; Jelonnek, J. Progress in the development of a multistage depressed collector system for high power gyrotrons. In Proceedings of the 2018 43rd International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Nagoya, Japan, 9–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Glyavin, M.; Manuilov, V.; Morozkin, M. Two-stage Energy Recovery System for DEMO Gyrotron. In Proceedings of the 2018 43rd International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Nagoya, Japan, 9–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Gong, Y.; Duan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Gong, H.; Liu, H. A non-axisymmetric structure multistage depressed collector for sheet beam VEDs. In Proceedings of the 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS-FALL), Singapore, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Mingqin, D.; Mingsuang, H.; Jinjun, F.; Guodong, B.; Xinghuil, L.; Qingping, Z.; Minghuil, L.; Yujuan, G.; Qilue, C. Secondary electron emission suppression of multistage vacuum depressed collector in space traveling tube by Mo ion deposition. Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- James, J.; Dayton, A. A review of the suppression of secondary electron emission from the electrodes of multistage collectors. In Proceedings of the ISDEIV. 18th International Symposium on Discharges and Electrical Insulation in Vacuum (Cat. No. 98CH36073), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 17–21 August 1998; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadeh, R.; Malyshev, O.B.; Wang, S.; Zolotovskaya, S.A.; Gillespie, W.A.; Abdolvand, A. Low secondary electron yield engineered surface for electron cloud mitigation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 231605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sian, T.; Valizadeh, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. The effect of air exposure on SEY and surface composition of laser treated copper applied in accelerators. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2018, 65, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, C.; Gilmore, M.; Schamiloglu, E. Effects of laser surface modification on secondary electron emission of copper. IEEE Trans. Plasma. Sci. 2011, 39, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J.; You, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z. Study on the effect of laser parameters on the SEY of aluminum alloy. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2019, 66, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.J. Secondary electron emission. In Solid State Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1958; Volume 6, pp. 251–331. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Joy, D.C. A new examination of secondary electron yield data. Surf. Interface Anal. 2005, 37, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, H. Secondary electron emission in the scanning electron microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, R1–R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.G.H.; El-Gomati, M.M.; Assa’D, A.M.D.; Zadrazil, M. The secondary electron emission yield for 24 solid elements excited by primary electrons in the range 250–5000 eV: A theory/experiment comparison. Scanning 2008, 30, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Pattinson, E.B. Automatic measurement of secondary electron emission characteristics of TaC, TiC and ZrC. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1969, 2, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.; Holmén, G.; Burén, A. Angular dependence of the ion-induced secondary-electron yield from solids. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 24, 3749–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieberger, P.; Hanson, A.L.; Steski, D.B.; Zajic, V.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ludewig, H. Secondary-electron yields and their dependence on the angle of incidence on stainless-steel surfaces for three energetic ion beams. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 61, 042901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.E.; King, F.K. Secondary electron emission yields from PEP-II accelerator materials. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2001, 469, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcon, N.; Payan, D.; Belhaj, M.; Tondu, T.; Inguimbert, V. Secondary electron emission on space materials: Evaluation of the total secondary electron yield from surface potential measurements. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, D.; Laperriere, G. Electrochromic Molybdenum Trioxide thin film preparation and characterization. Chem. Mater. 1990, 2, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerfi, A.; Paynter, R.W.; Dao, H. Characterization and stability of electrochromic MoO3 thin films prepared by electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Gopinath, C.S.; Jayachandran, M.; Sanjeeviraja, C. An electrochromic device (ECD) cell characterization on electron beam evaporated MoO3 films by intercalating/deintercalating the H+ ions. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2007, 7, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, M.; Wertheim, G.K.; Shanks, H.R.; Zumsteg, F.; Banks, E. Local character of many-body effects in X-ray photoemission from transition-metal compounds: NaxWO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, 34, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, G.K.; Kufner, S. Many-body line shape in x-ray photoemission from metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, 35, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Watson, G.W.; Payne, D.J.; Atkinson, G.R.; Egdell, R.G.; Law, D.S.L. Theoretical and Experimental Study of the Electronic Structures of MoO3 and MoO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, R.; Malyshev, O.B.; Wang, S.; Sian, T.; Gurran, L.; Goudket, P.; Cropper, M.D.; Sykes, N. Low secondary electron yield of laser treated surfaces of copper, aluminium and stainless steel. In Proceedings of the 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC’16), Busan, Korea, 1 June 2016; pp. 1089–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadeh, R.; Malyshev, O.B.; Wang, S.; Sian, T.; Cropper, M.D.; Sykes, N. Reduction of secondary electron yield for E-cloud mitigation by laser ablation surface engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 404, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Shibata, T.; Ogiwara, N.; Kinsho, M. Secondary electron emission yields from the J-PARC RCS vacuum components. Vacuum 2007, 81, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Hatched Pattern | Average Power /W | Spot /μm | Pitch Spacing /μm | Scanning Speed /mm s−1 | δmax | Emax /eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Cross | 10 | 15 | 15 | 100 | 1.13 | 400 |
| #2 | Cross | 10 | 15 | 15 | 1000 | 1.11 | 2400 |
| #3 | Line | 10 | 15 | 15 | 100 | 0.96 | 1500 |
| #4 | Line | 10 | 15 | 20 | 100 | 0.95 | 2000 |
| #5 | Line | 10 | 15 | 15 | 1000 | 1.35 | 300 |
| #6 | Line | 13.3 | 15 | 15 | 100 | 0.82 | 1200 |
| #7 | Line | 13.3 | 15 | 15 | 1000 | 1.07 | 300 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; You, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z. Laser Induced Nano and Micro Structures of Molybdenum Surface Applied in Multistage Depressed Collector for Secondary Electron Suppression. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204374
Wang J, Gao Y, You Z, Fan J, Zhang J, Wang S, Xu Z. Laser Induced Nano and Micro Structures of Molybdenum Surface Applied in Multistage Depressed Collector for Secondary Electron Suppression. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204374
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jie, Yong Gao, Zhiming You, Jiakun Fan, Jing Zhang, Sheng Wang, and Zhanglian Xu. 2019. "Laser Induced Nano and Micro Structures of Molybdenum Surface Applied in Multistage Depressed Collector for Secondary Electron Suppression" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204374
APA StyleWang, J., Gao, Y., You, Z., Fan, J., Zhang, J., Wang, S., & Xu, Z. (2019). Laser Induced Nano and Micro Structures of Molybdenum Surface Applied in Multistage Depressed Collector for Secondary Electron Suppression. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204374







