Semantic Mediation Model to Promote Improved Data Sharing Using Representation Learning in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a semantic mediation model to support interoperability provisioning for healthcare data integration, sharing, and exchange;
- A base ontology model has been developed with a standard healthcare vocabularies catalog, supporting the reuse of semantic ontologies across applications;
- We utilize deep representation learning-based mechanisms to mitigate the heterogeneity of semantic data models.
- Ontology models have been developed to describe and maintain healthcare knowledge.
- The development of interoperable healthcare applications has been simplified by devising Web of objects enabled features with semantic interoperability provisioning capabilities.
- We formulated a semantic annotation algorithm and semantic alignment procedures to enhance overall interoperability provisioning.
2. Background and Related Work
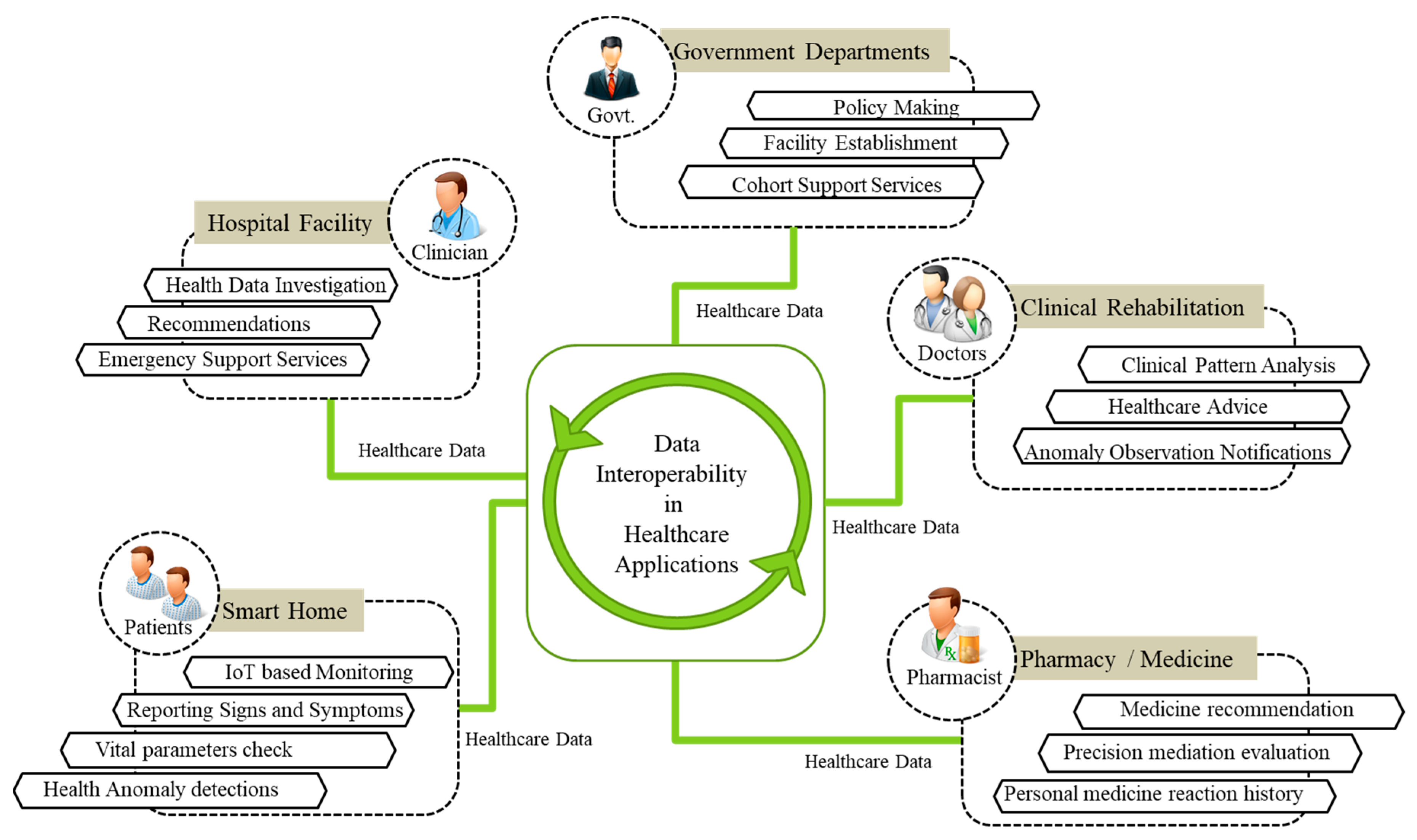
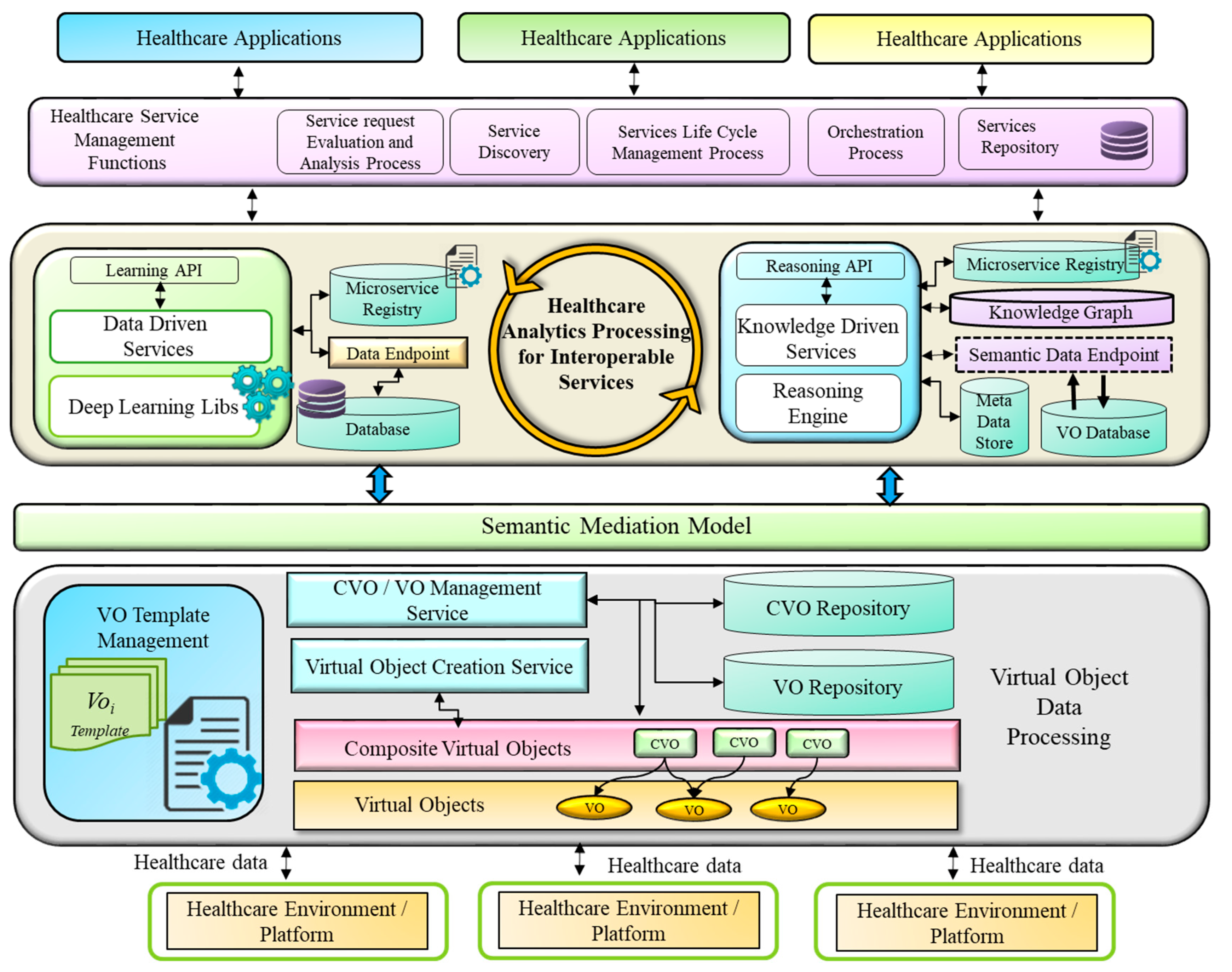
3. Data Interoperability Provisioning with Web of Objects
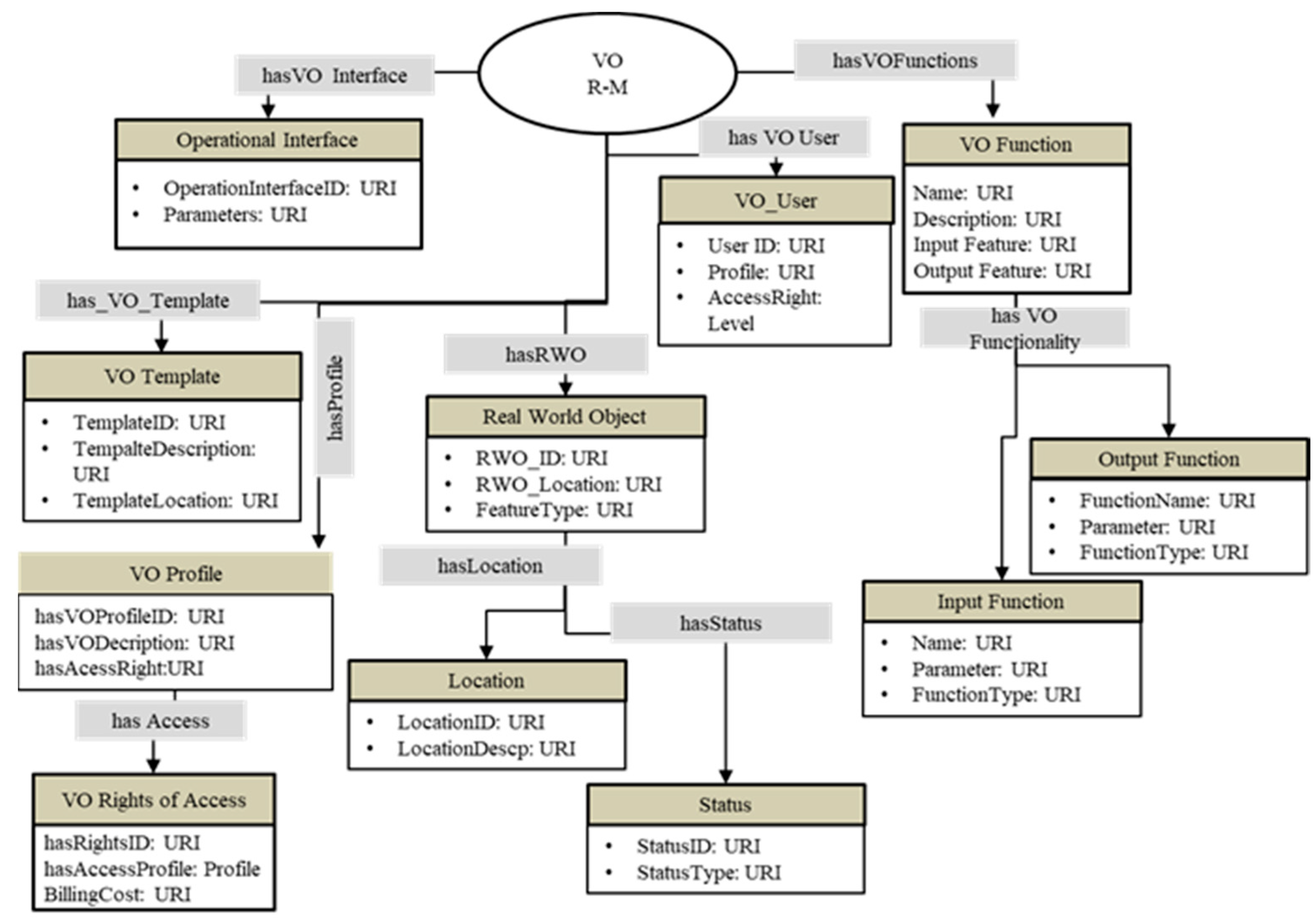
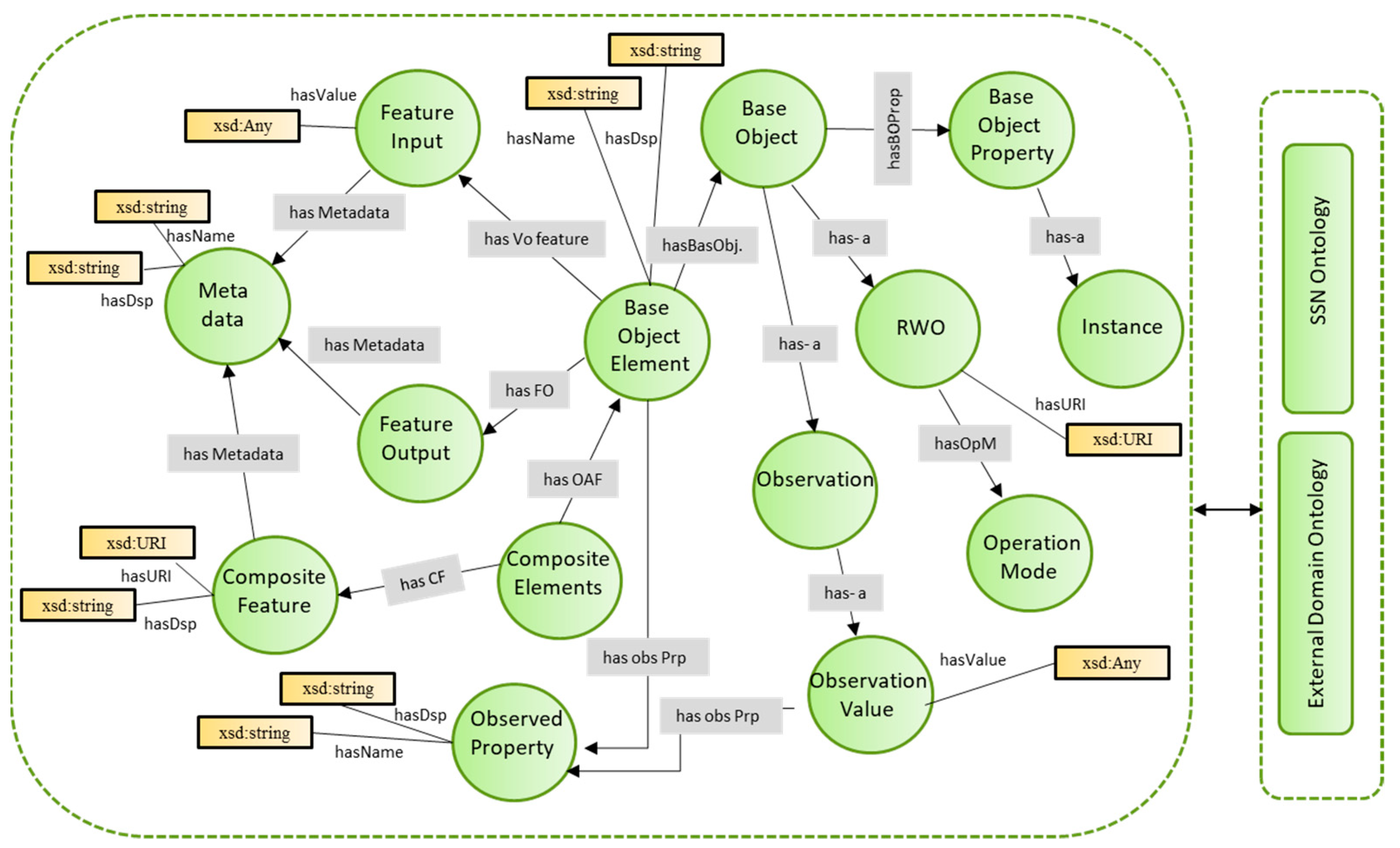
3.1. Web of Objects Model
3.2. Modeling Interoperable Healthcare Services with WoO
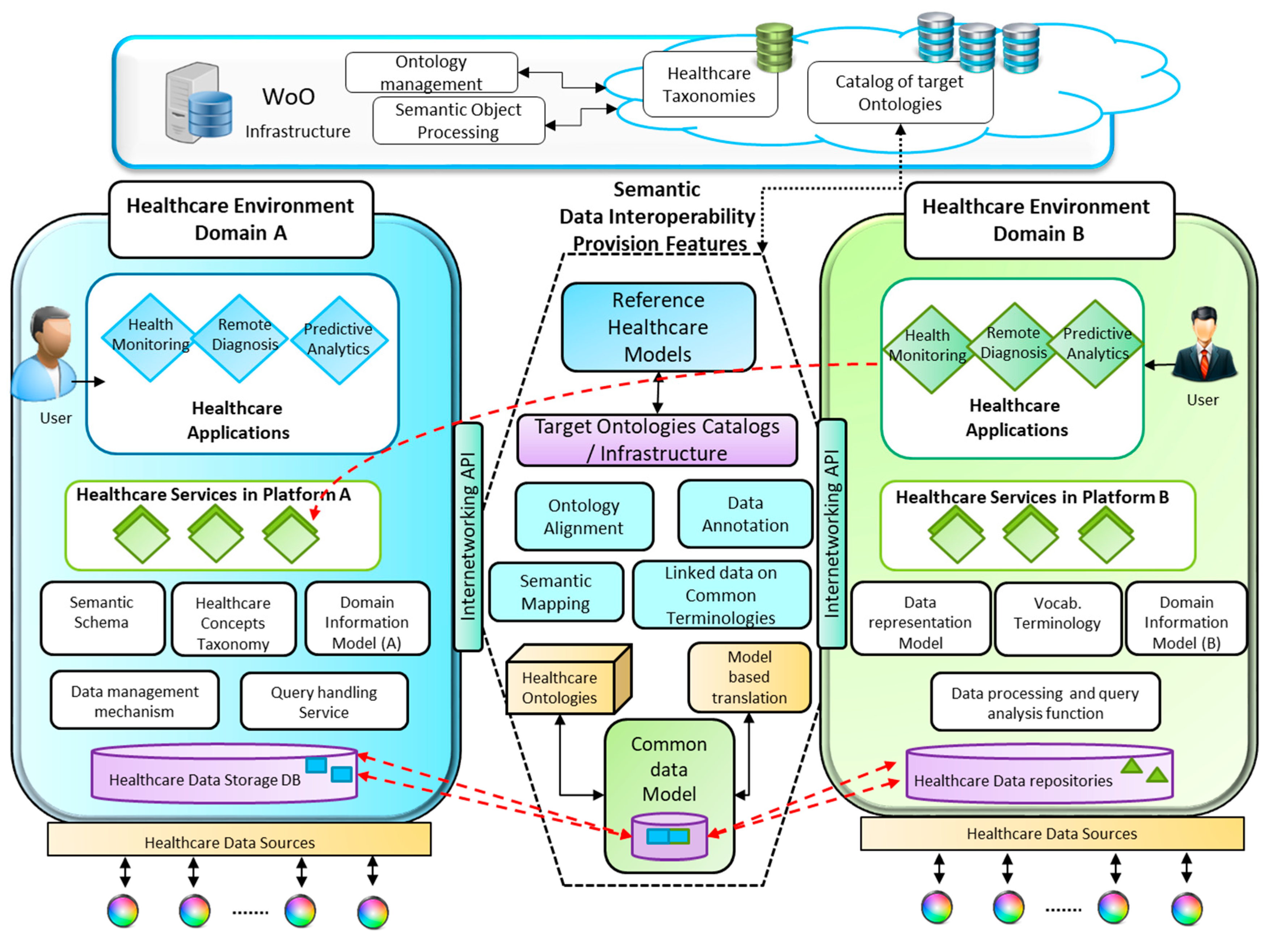
4. Semantic Interoperability Provision in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments
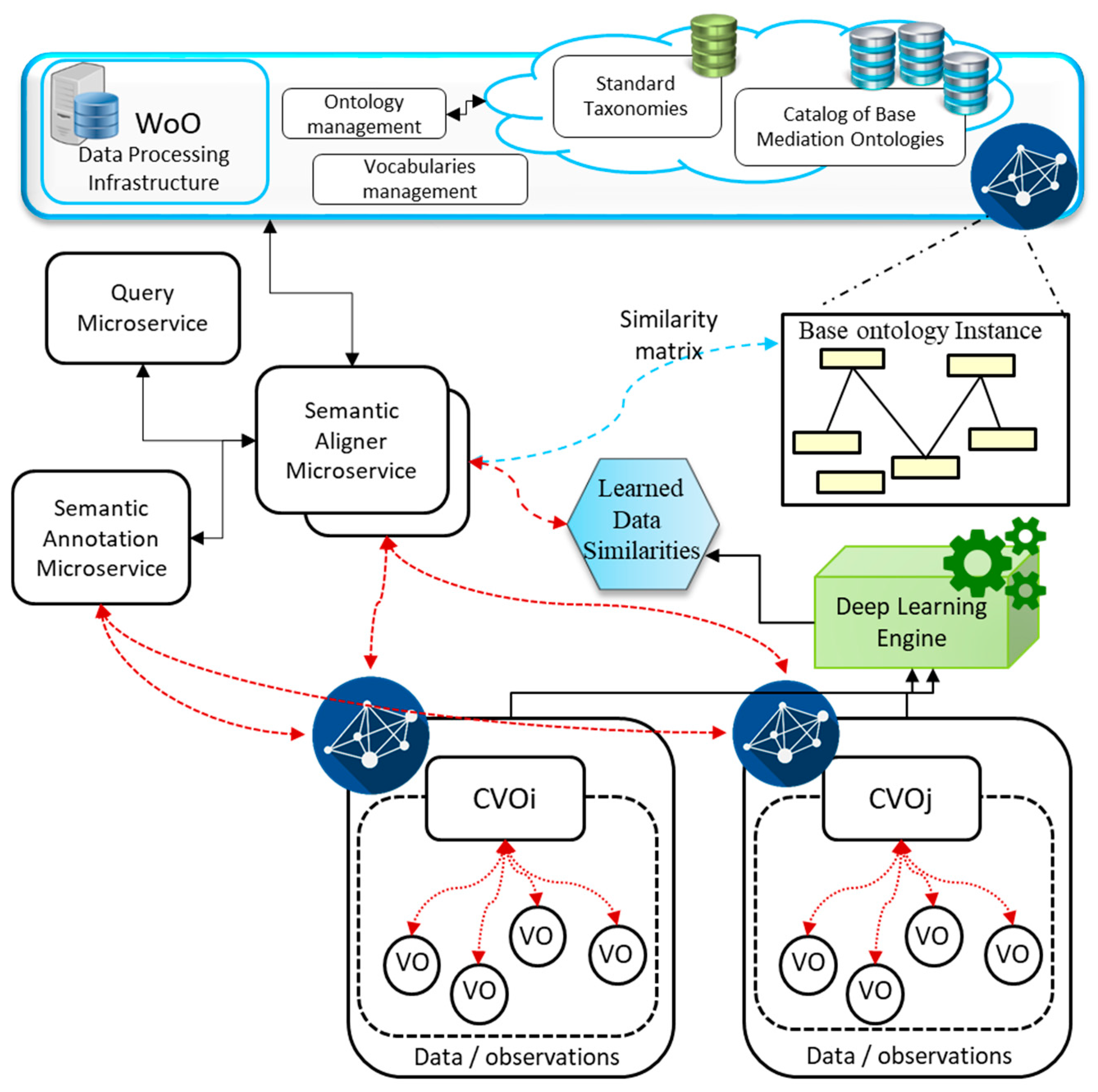
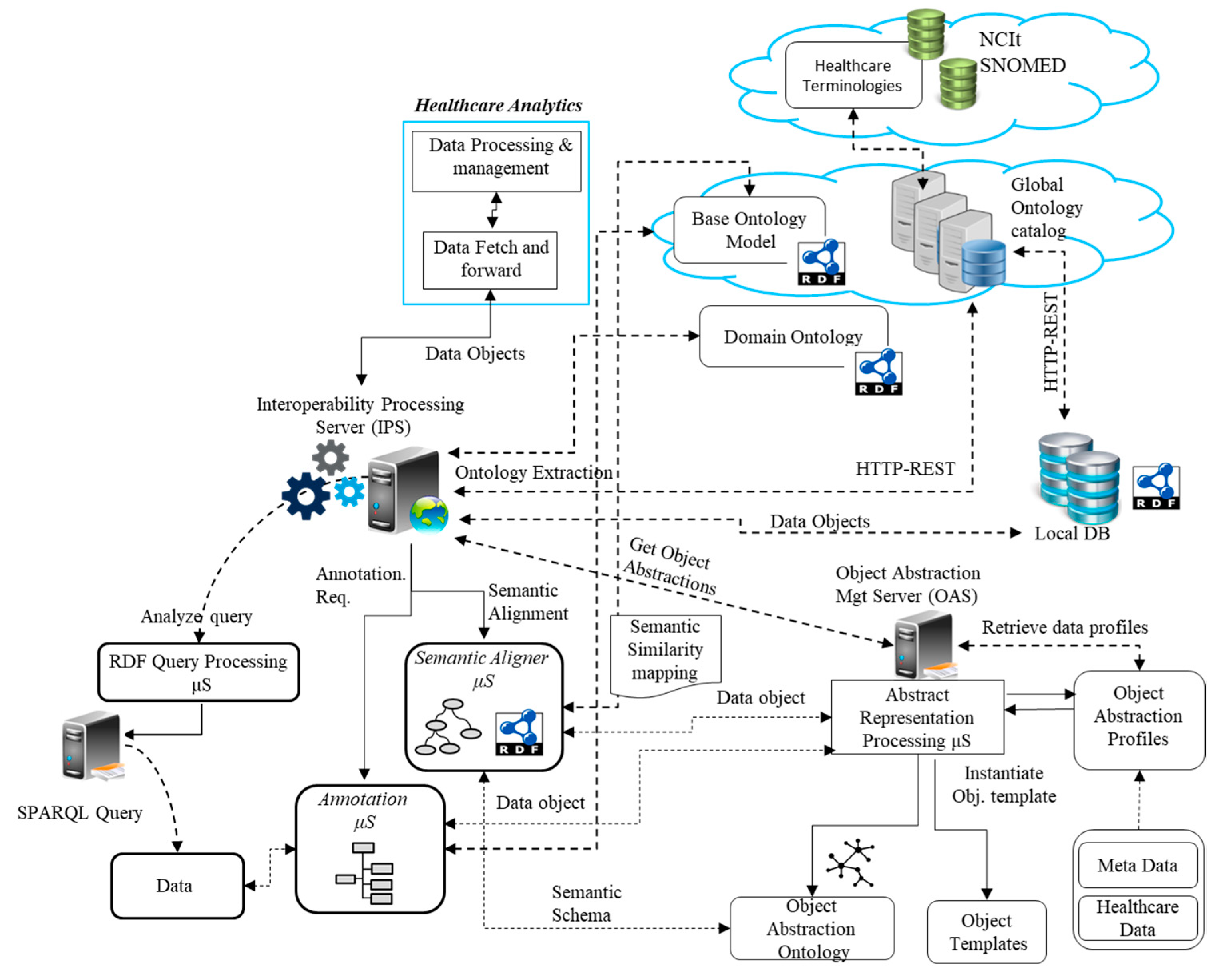
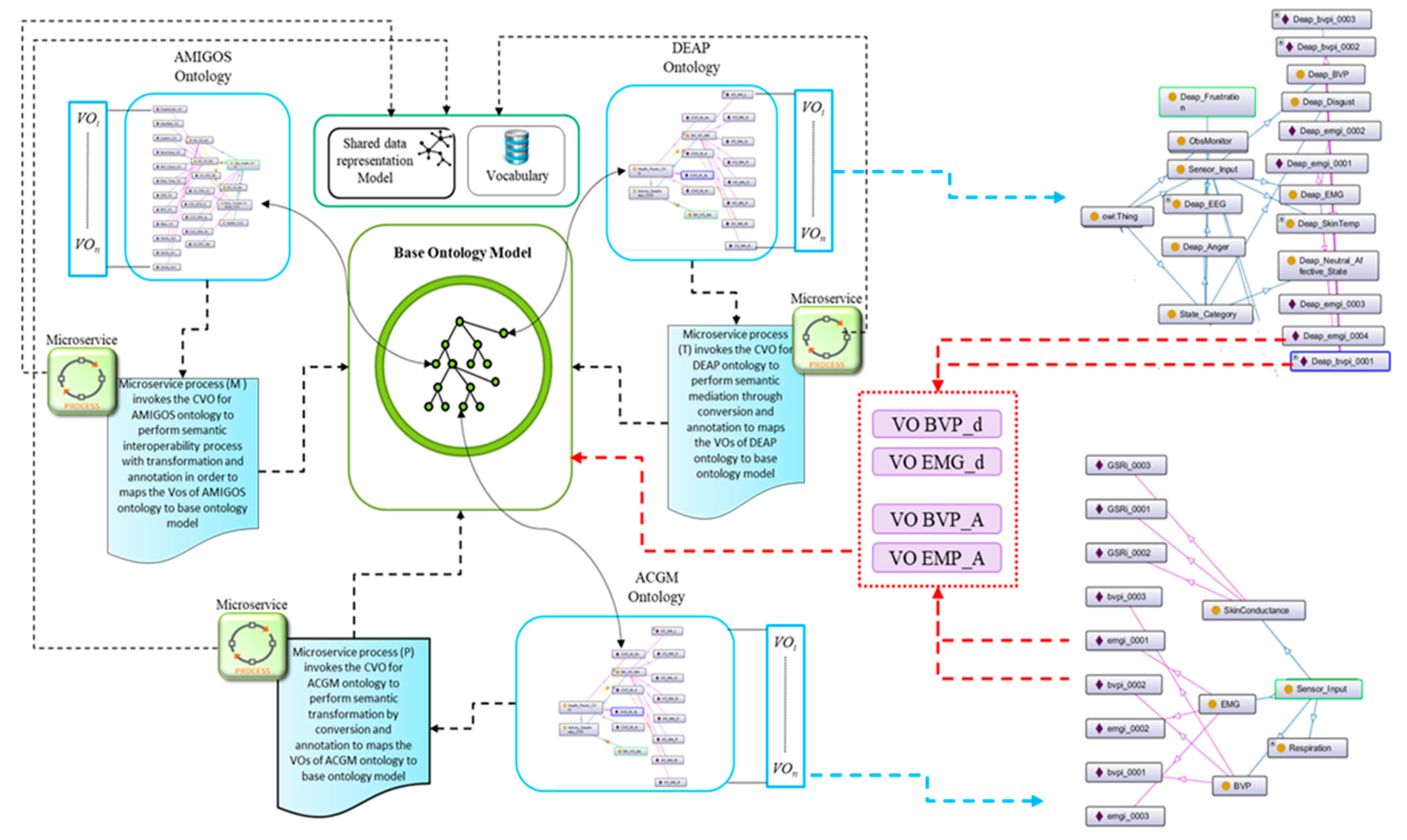
4.1. Semantic Mediation Model
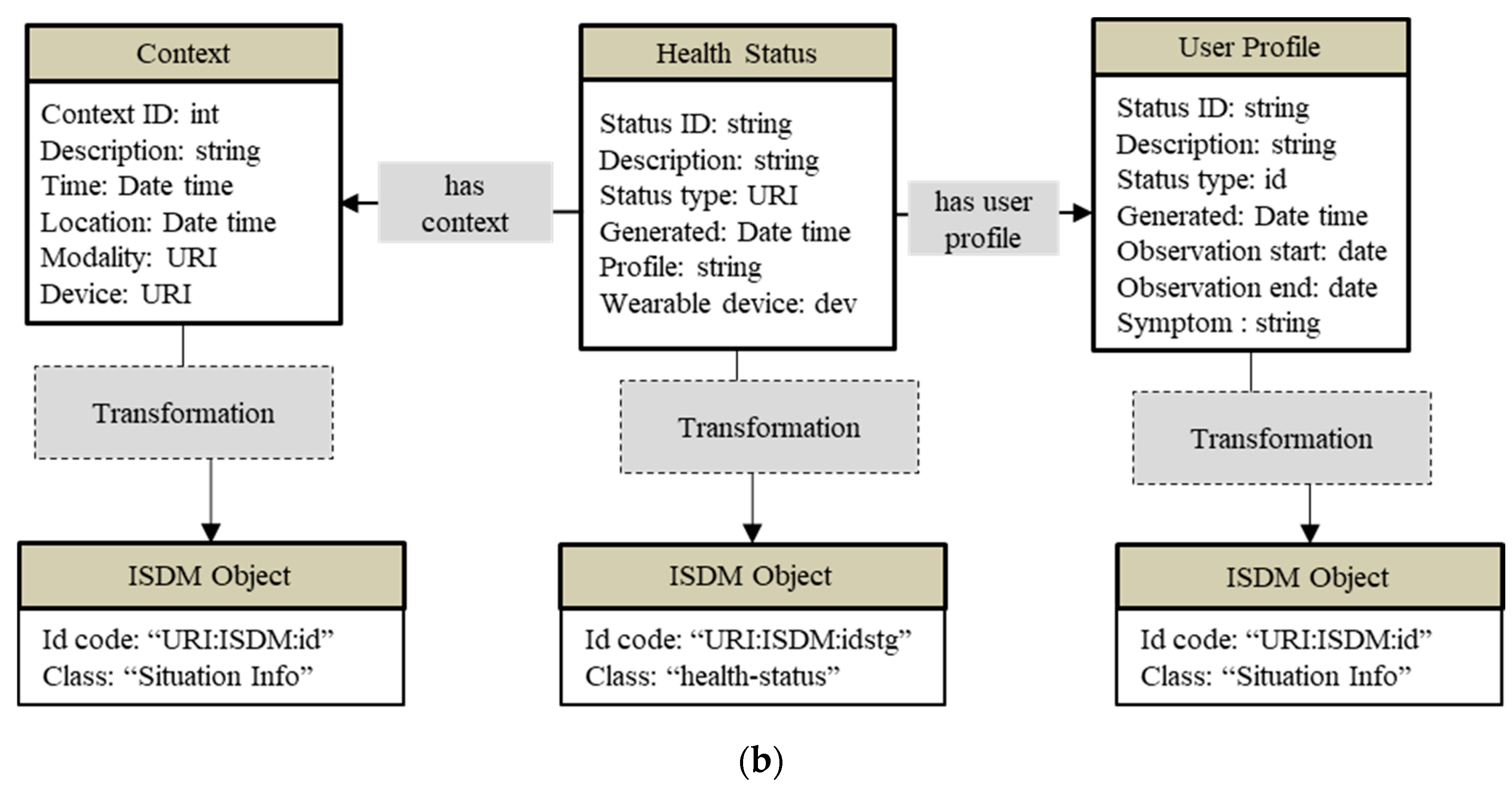
4.2. Semantic Interoperability in Healthcare Data Models
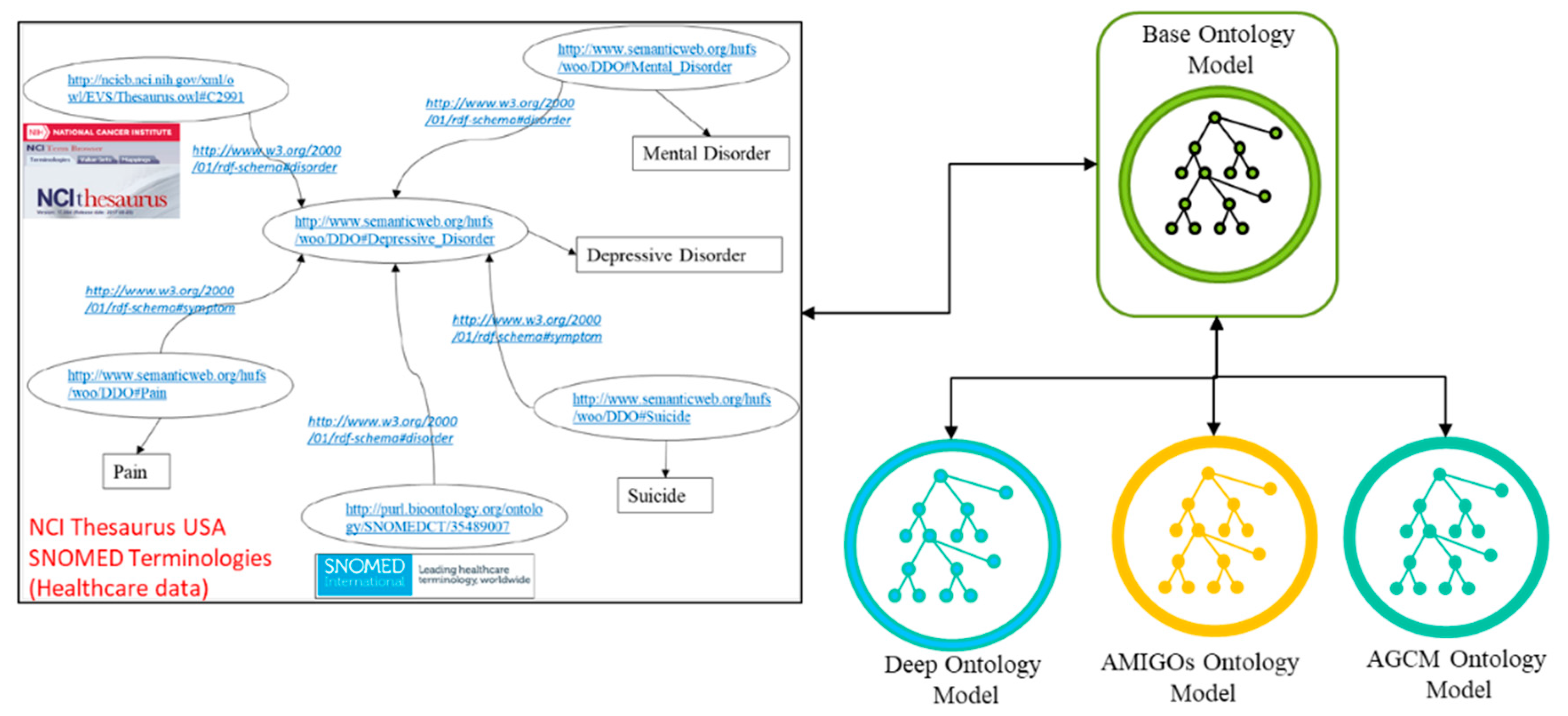
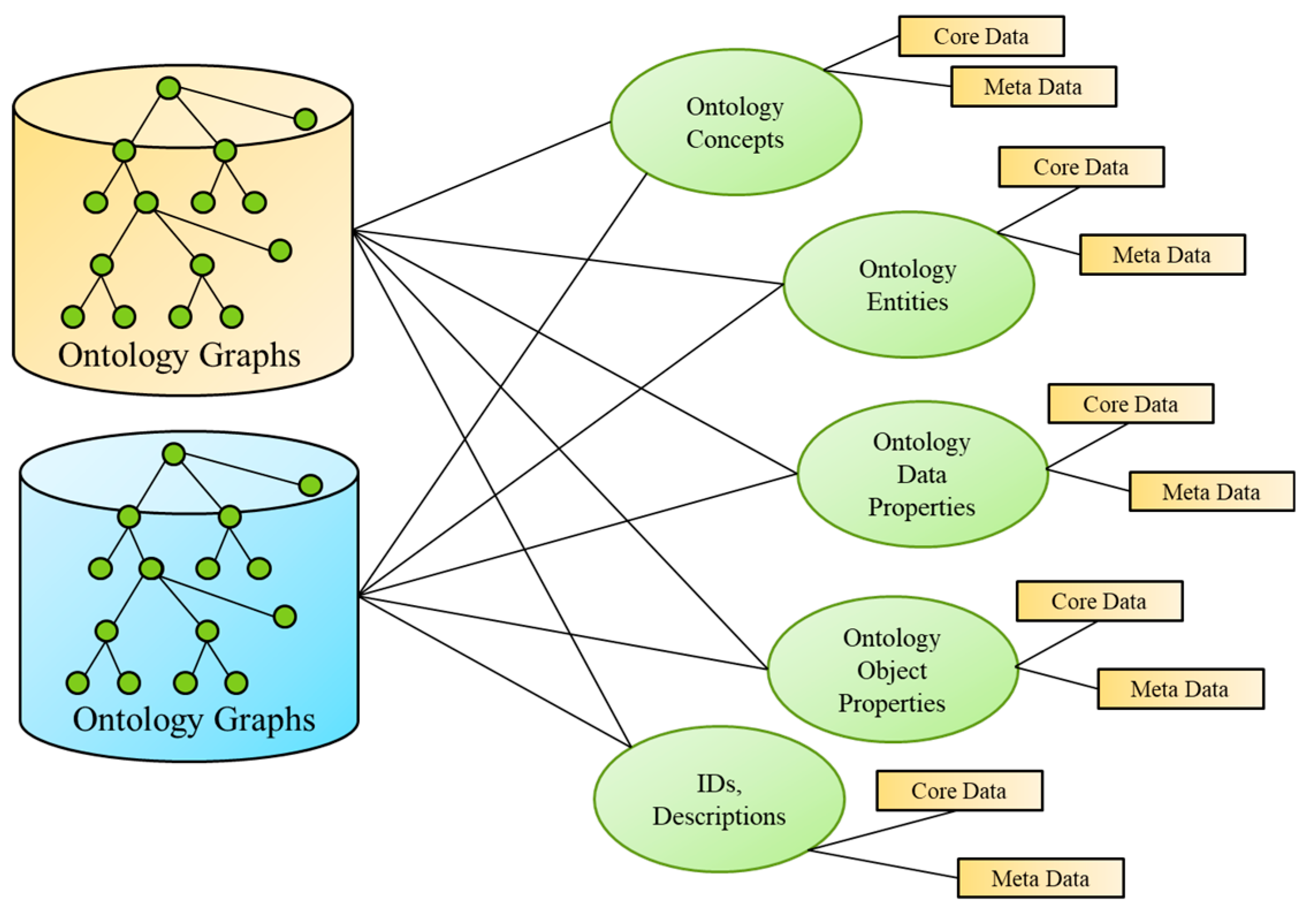
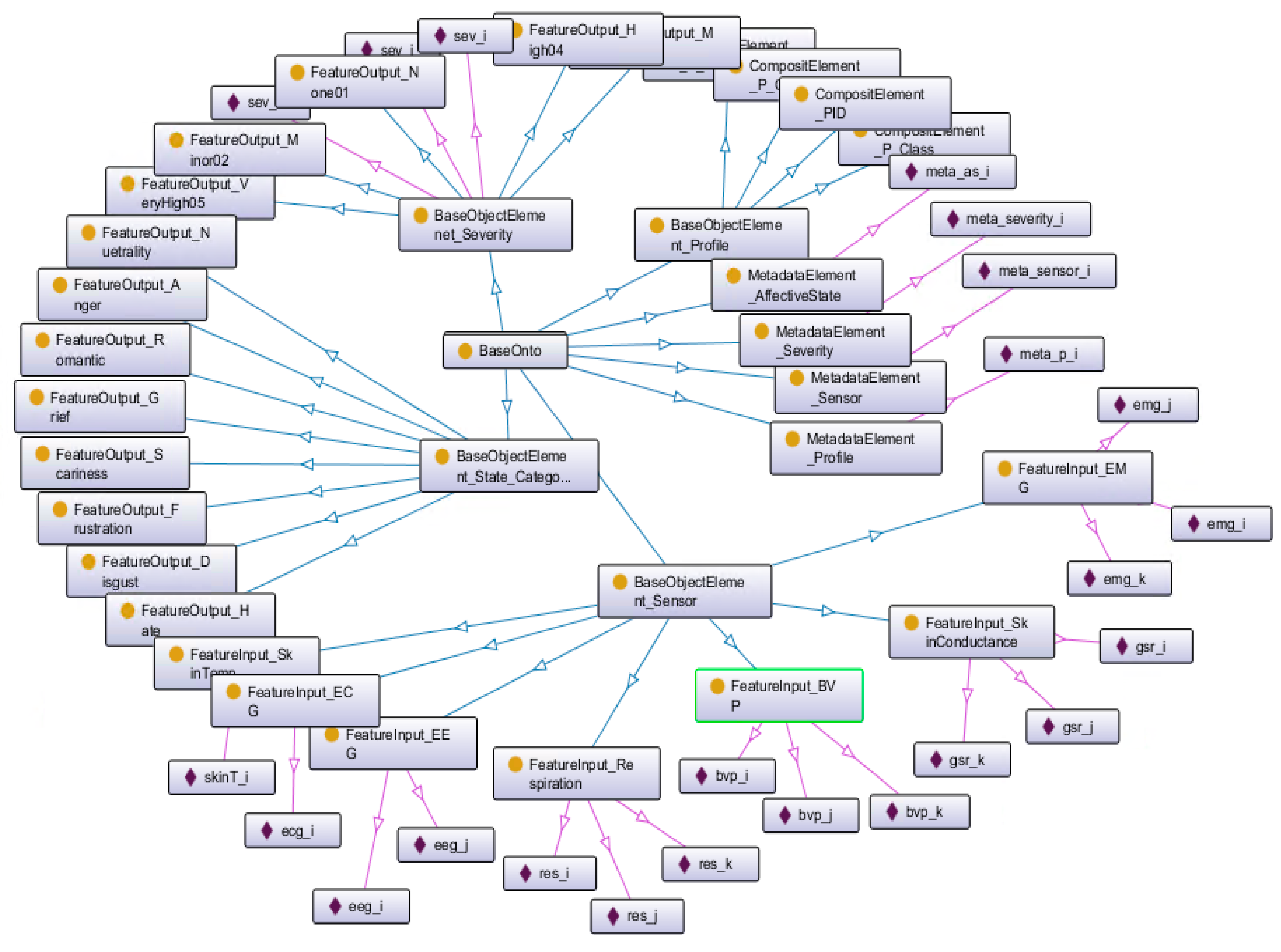
4.2.1. Development of Ontology Models for Semantic Alignments
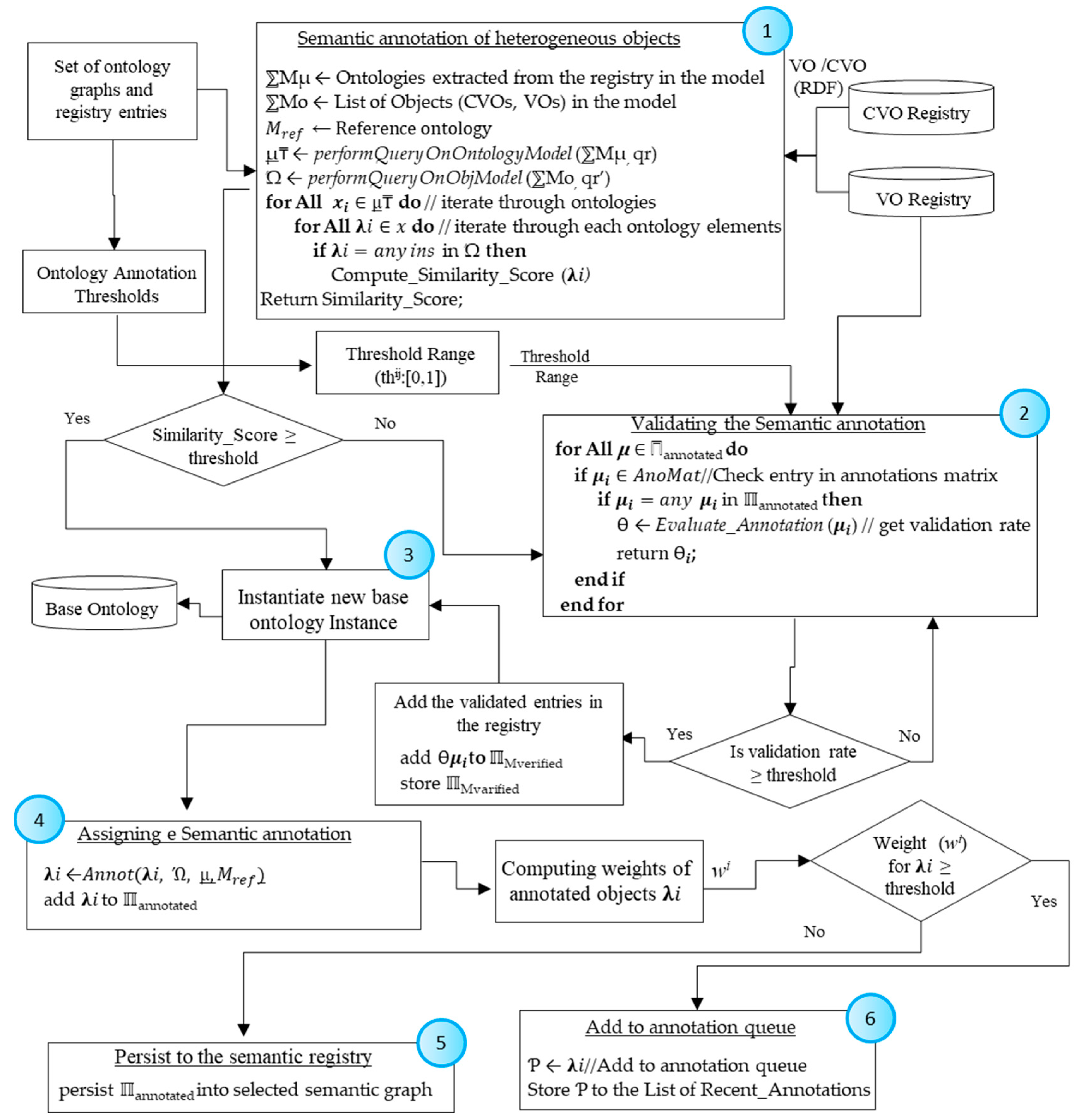
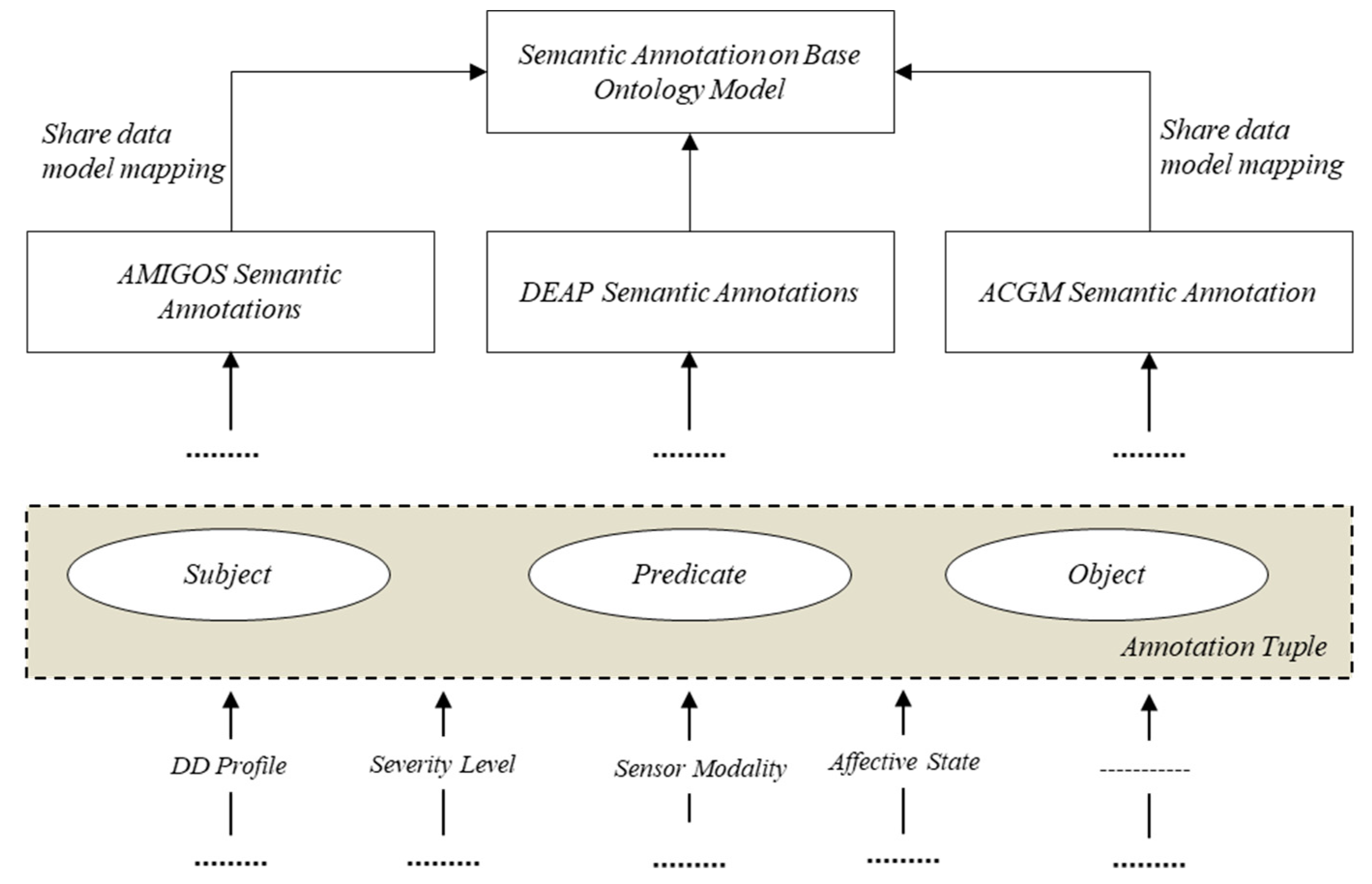
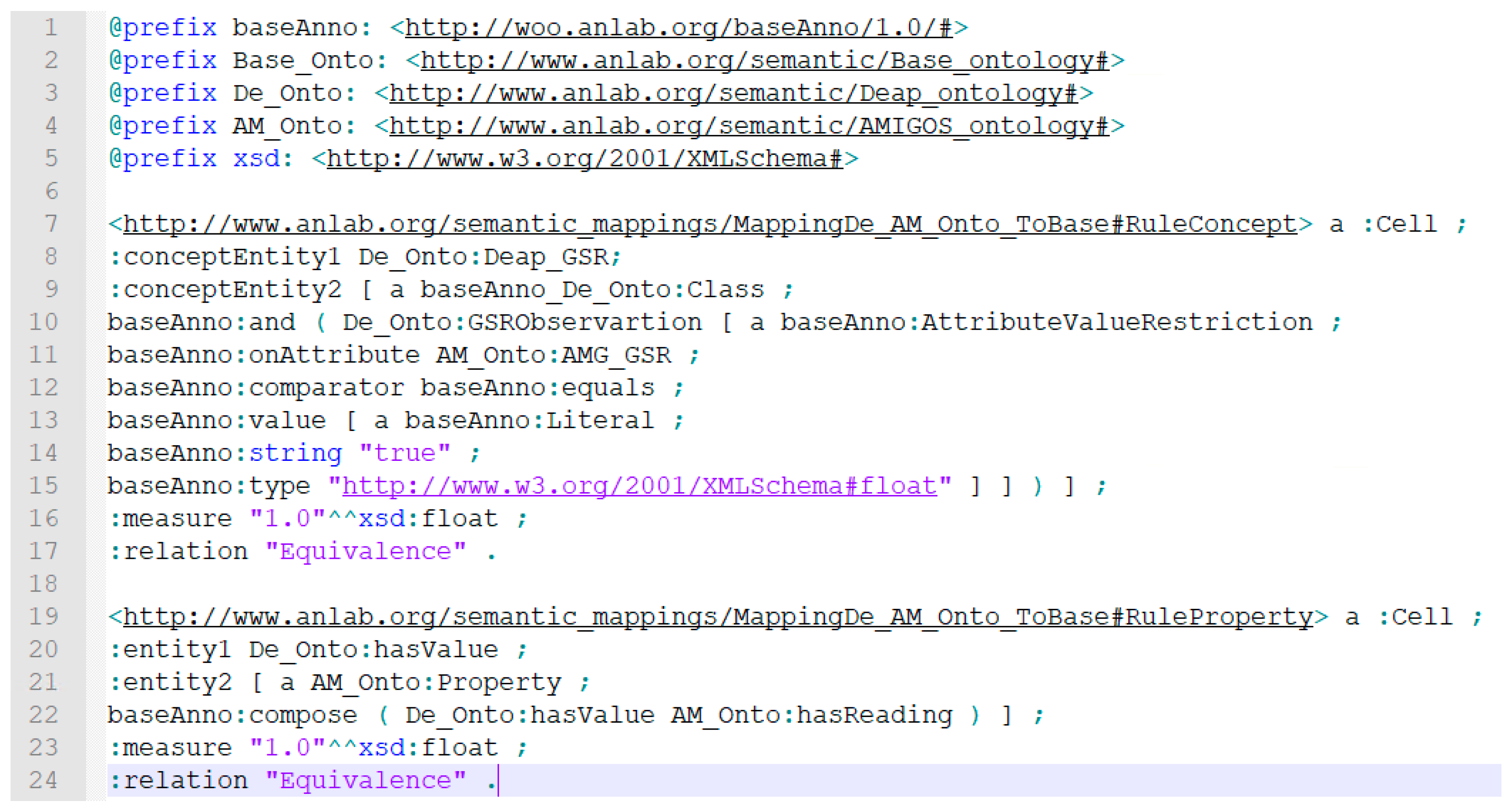
4.2.2. Semantic Annotation of Data Generated from Heterogeneous Sources
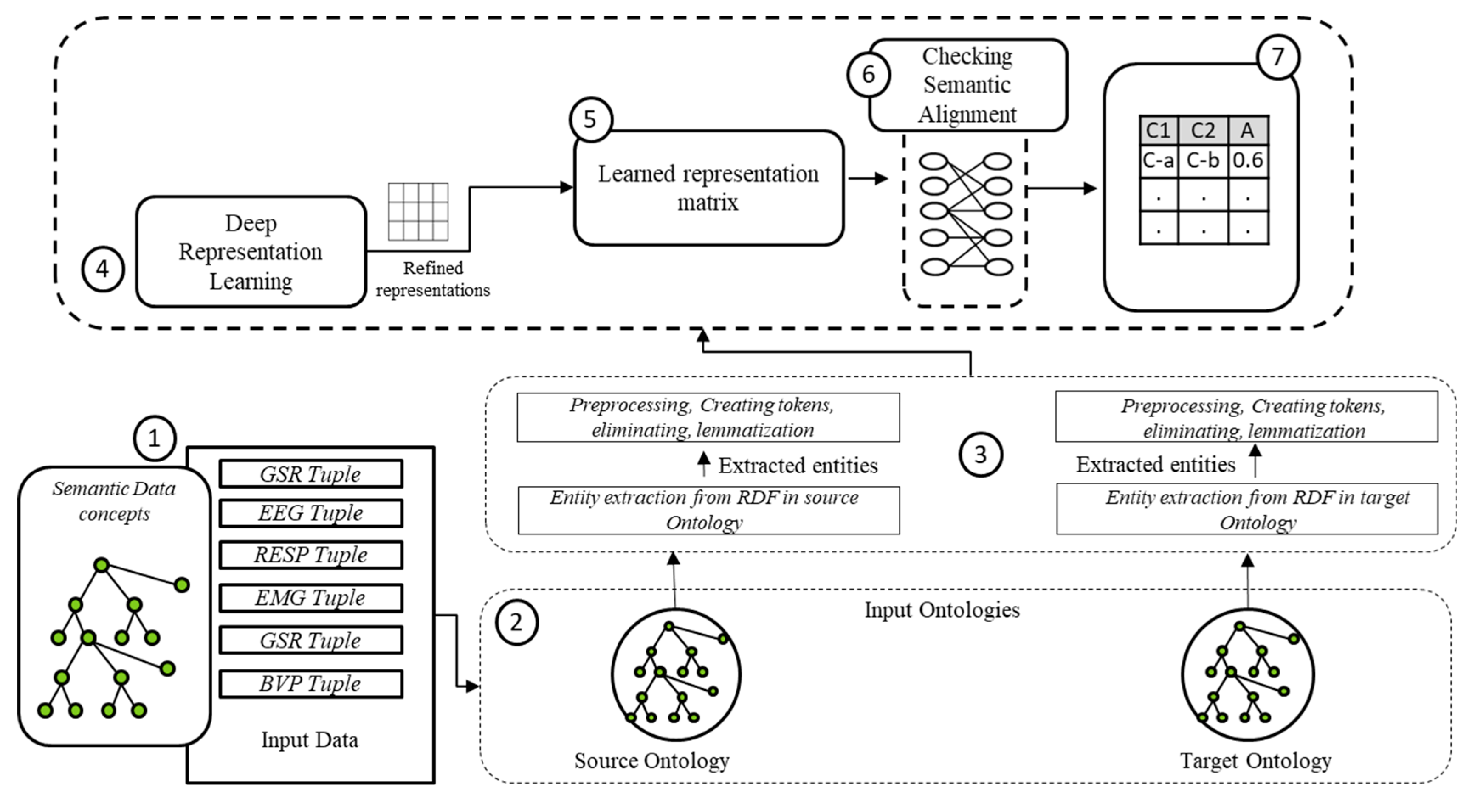
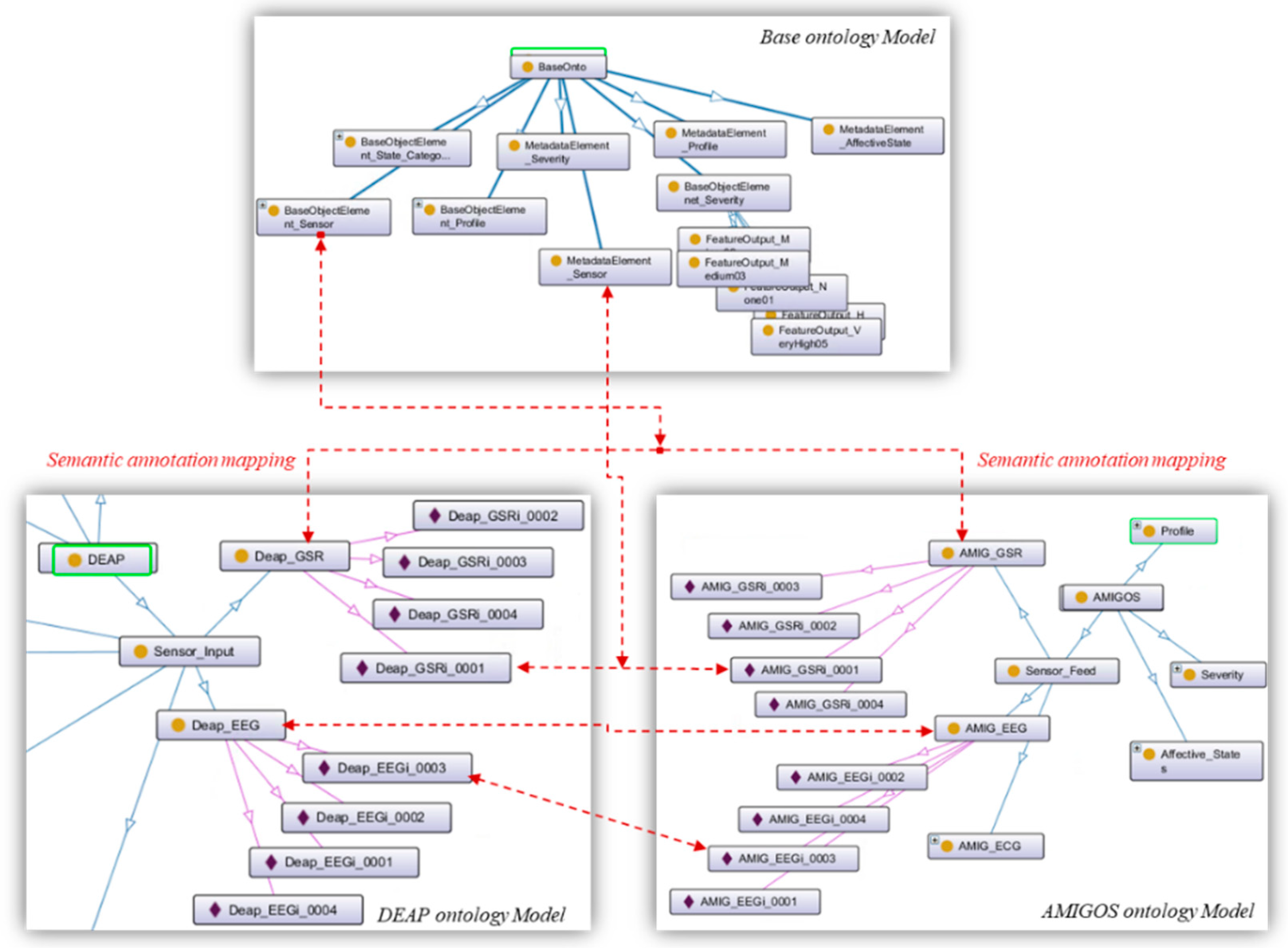
4.2.3. Semantic Ontology Alignment using Deep Representation Learning
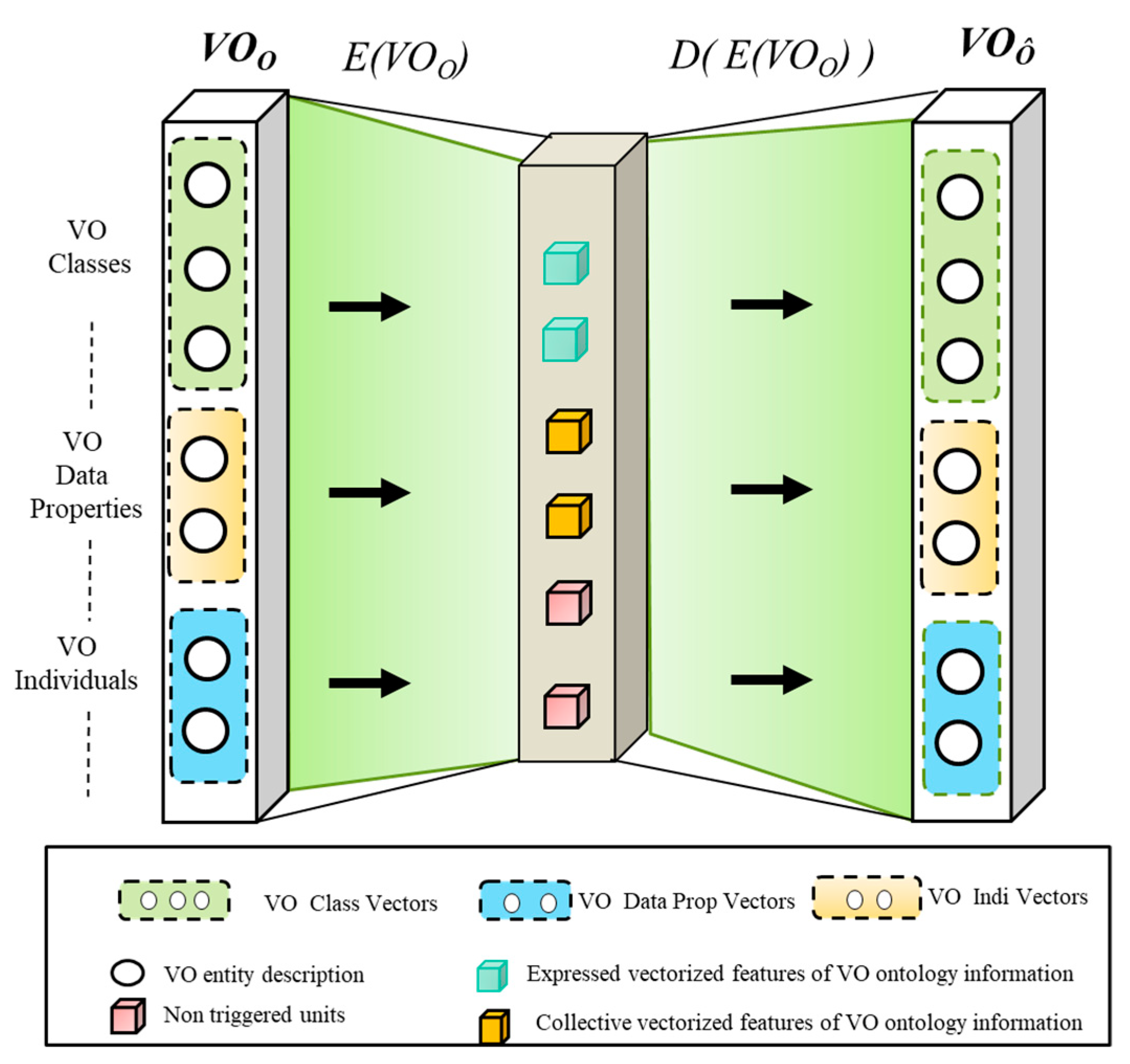
Learning VO Ontology Representations
Procedure for Learning Representations
4.2.4. Deployment of Learned Semantic Alignments in the Target Ontology Catalog
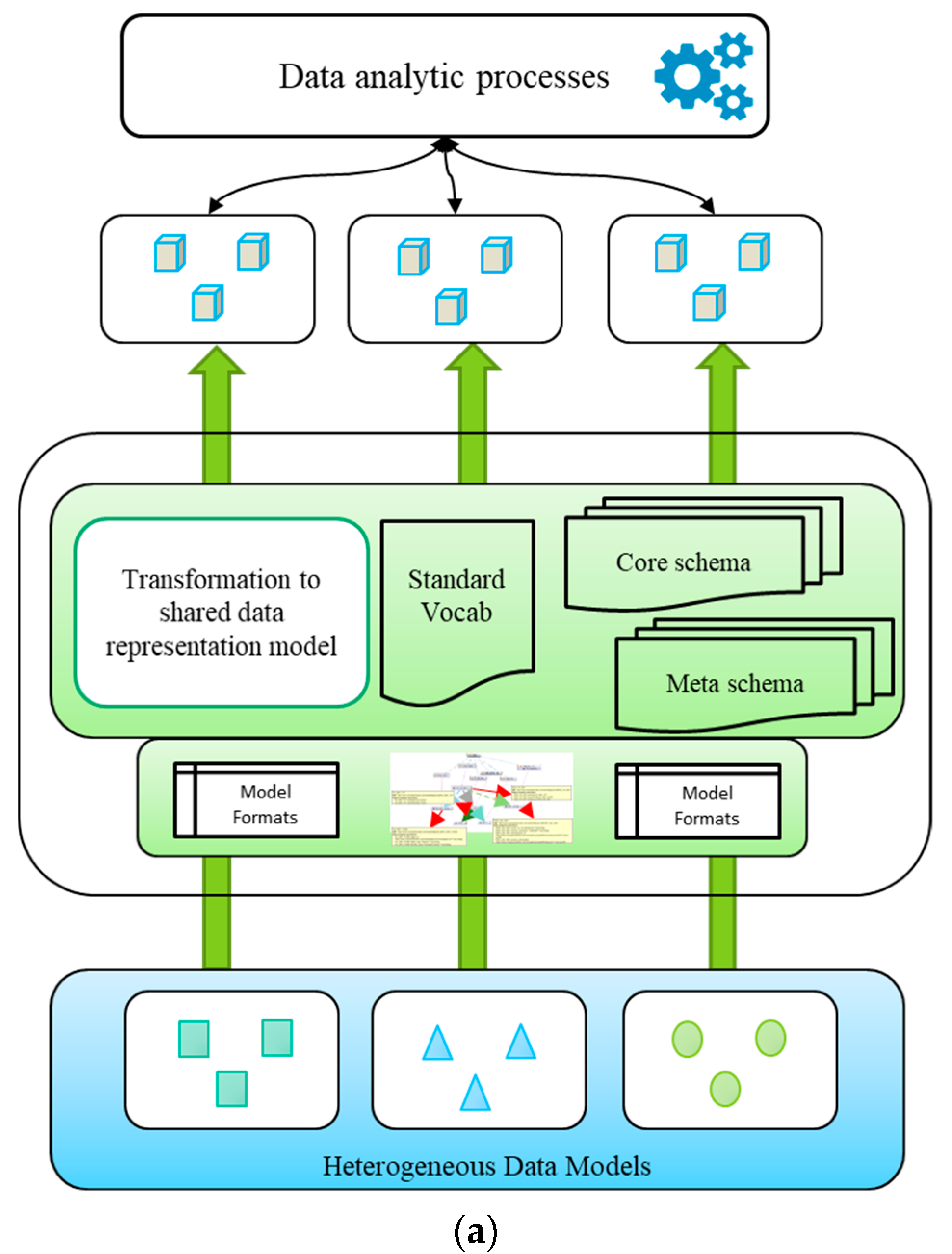
4.2.5. Common Data Model
5. Experimental Analysis and Implementation
5.1. Implementation Setup
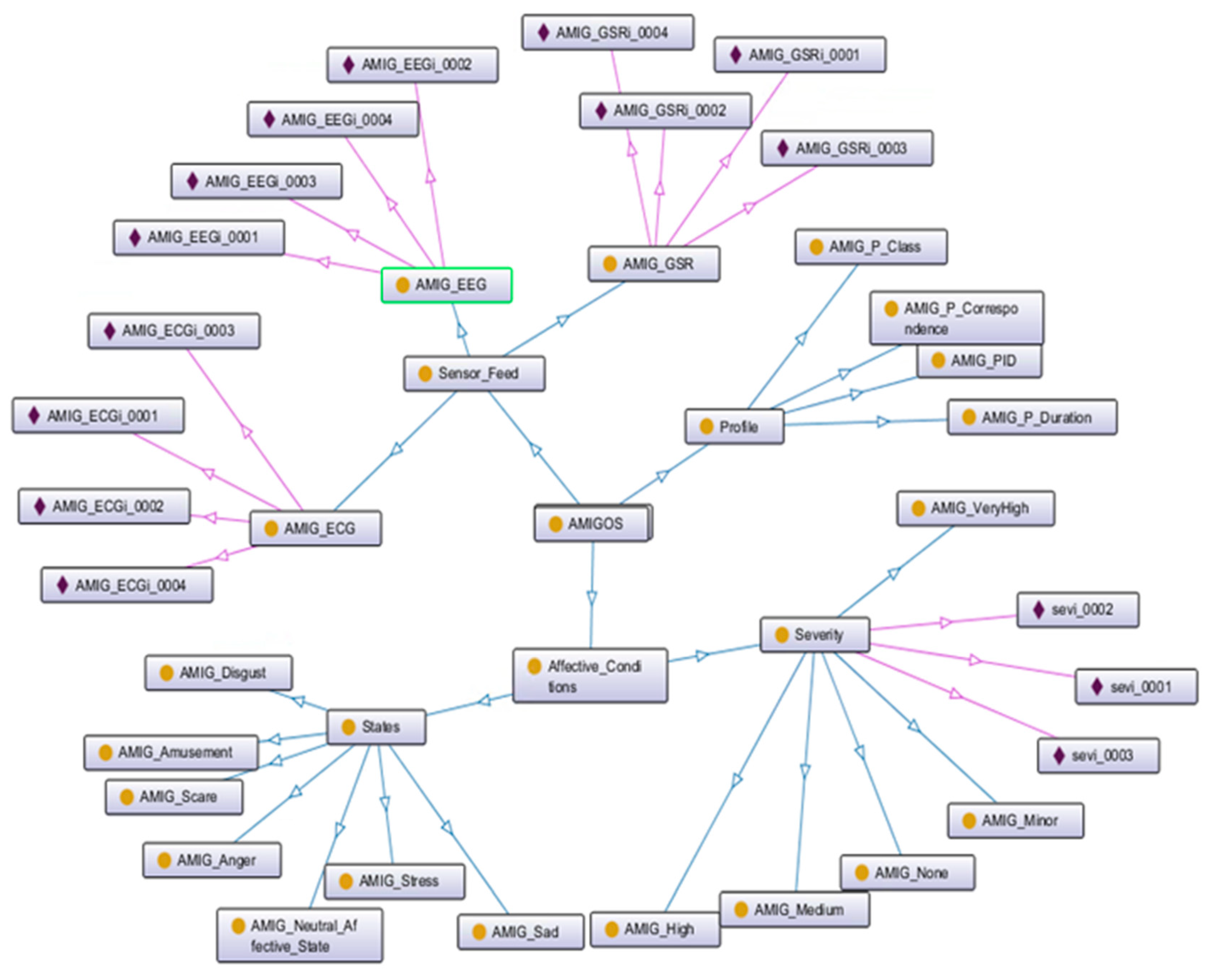
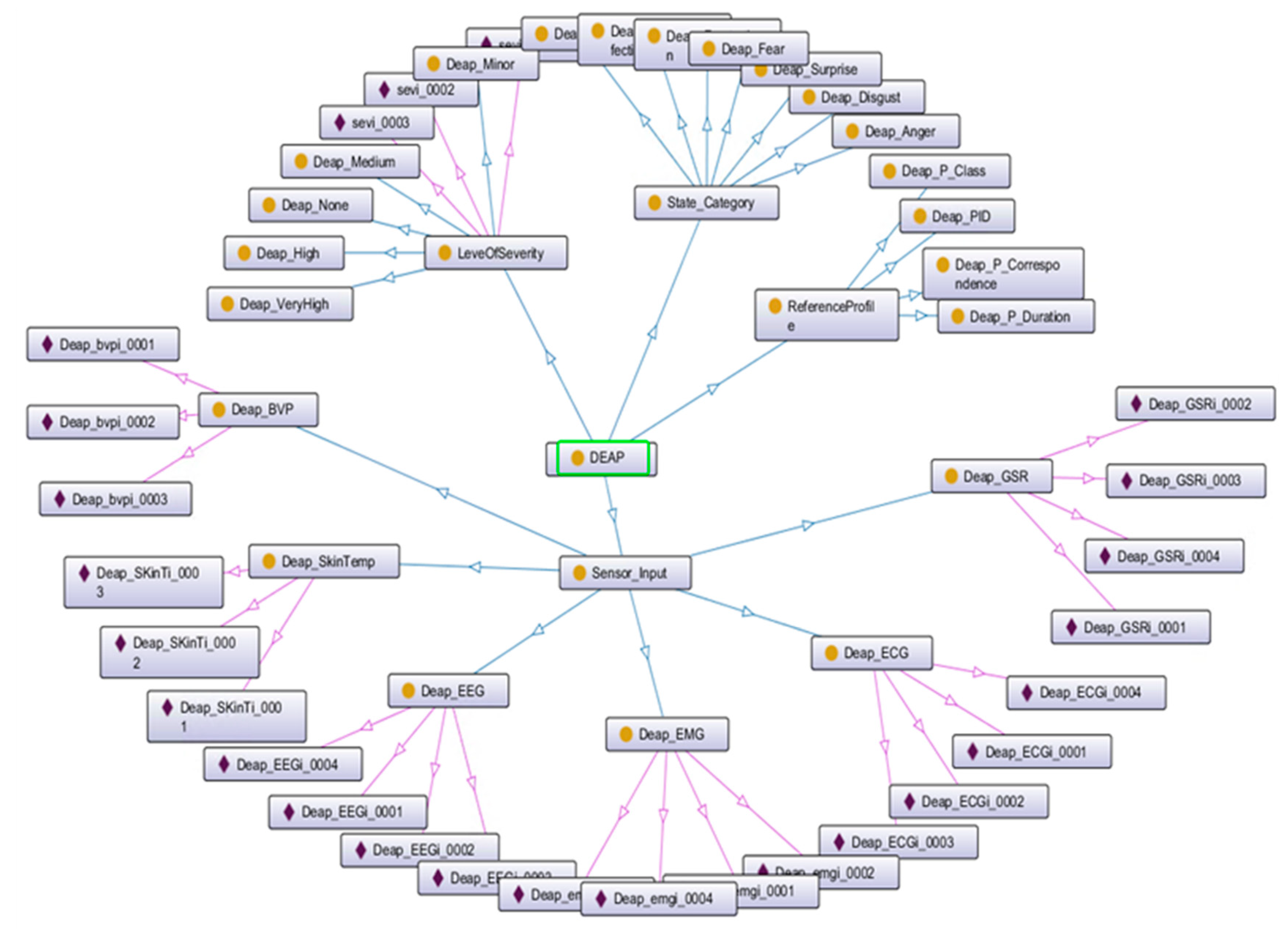
5.2. Semantic Ontology Development
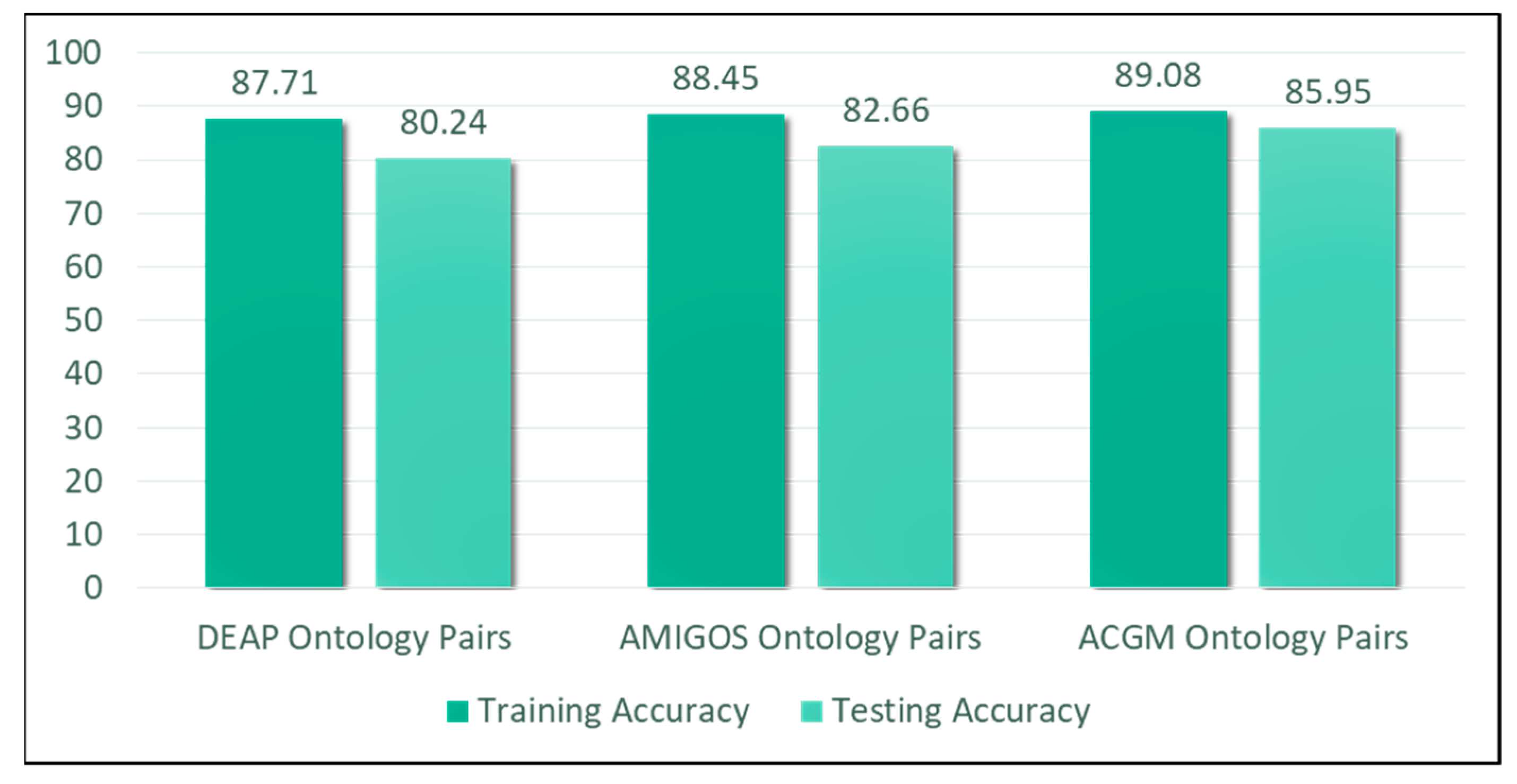
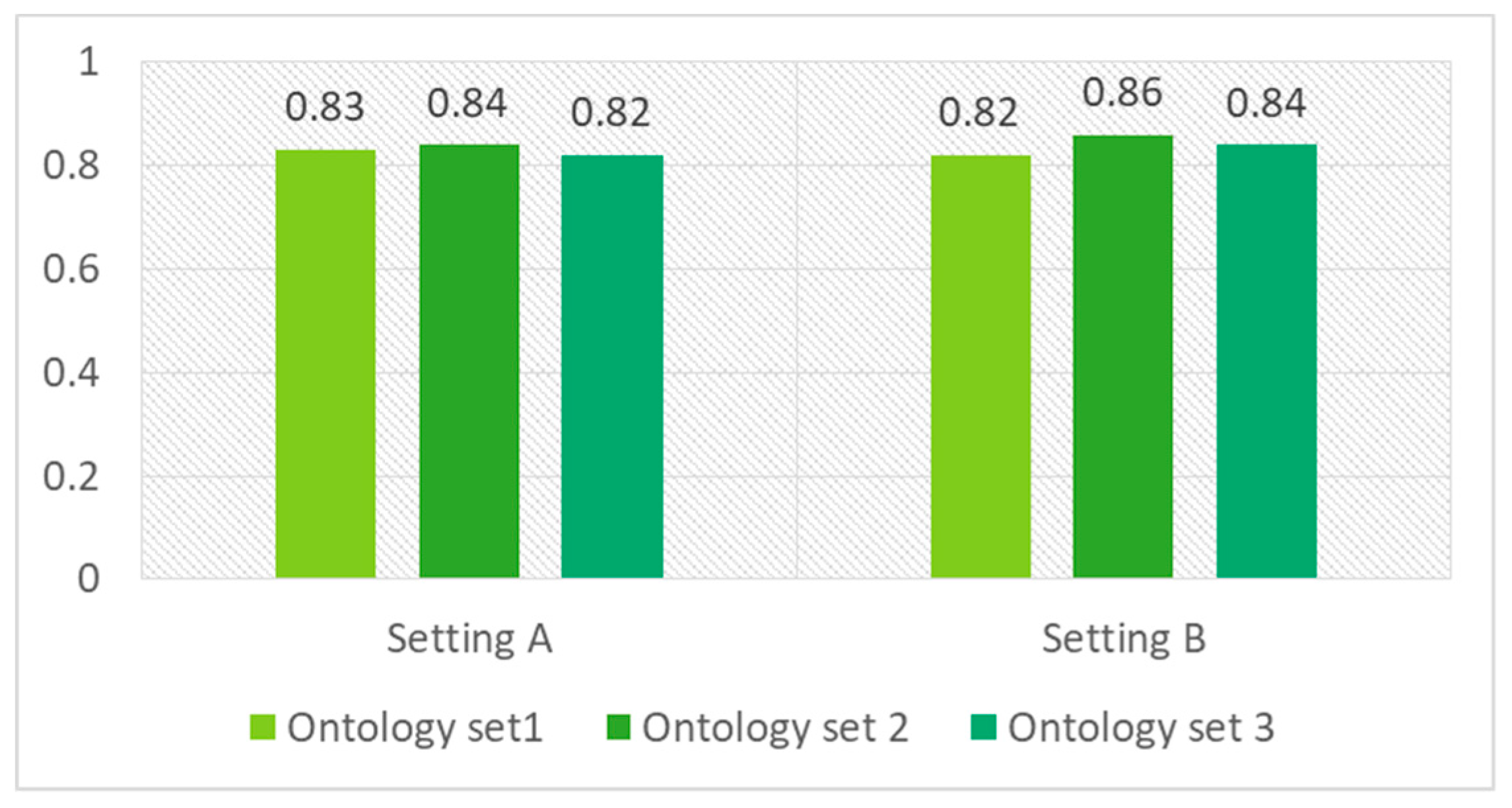
5.3. Semantic Alignment of the Affective States Ontology Models
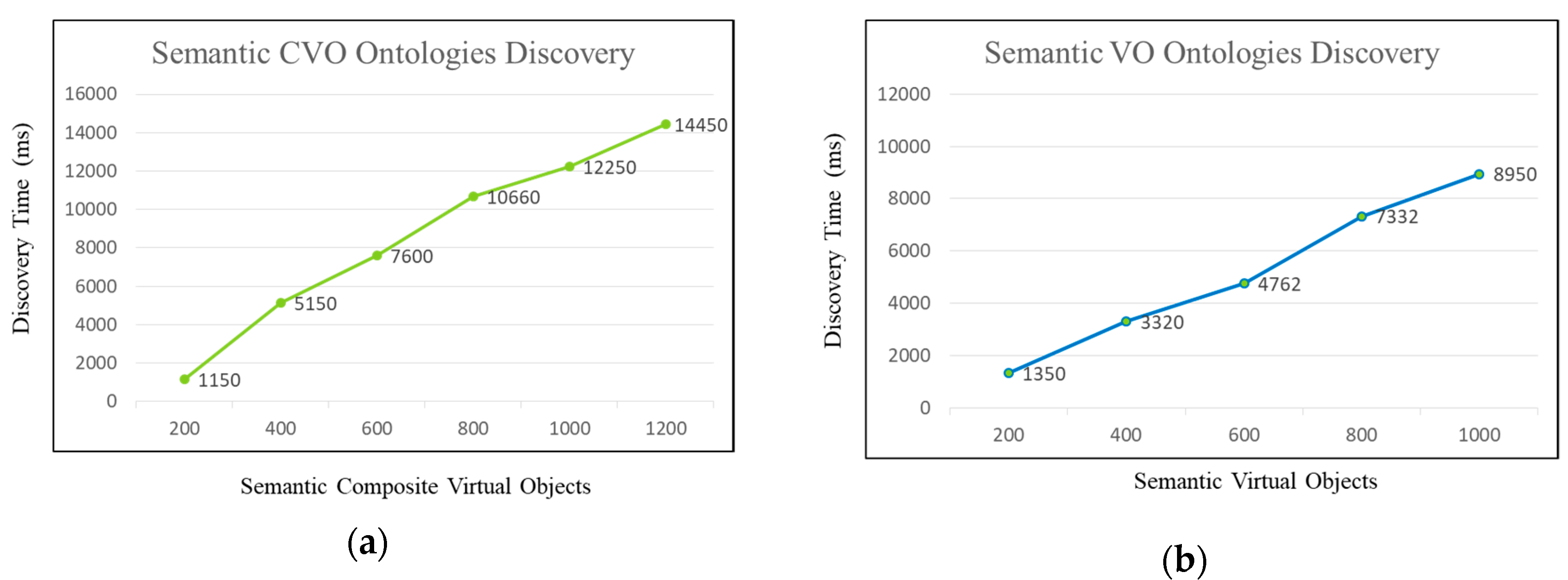
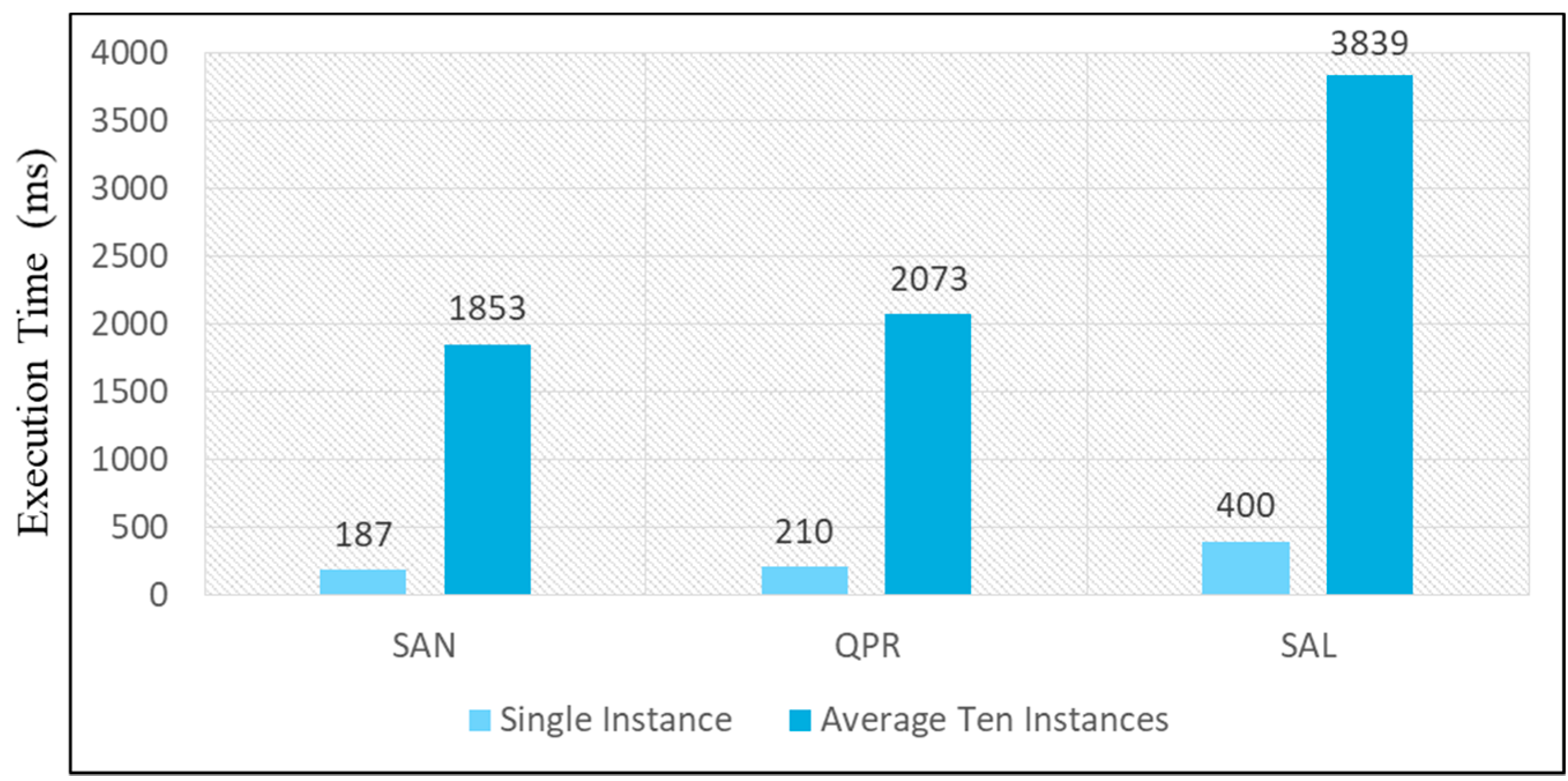
5.4. Evaluation and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haluza, D.; Jungwirth, D. ICT and the future of healthcare: Aspects of pervasive health monitoring. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2018, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iroju, O.; Soriyan, A.; Gambo, I.; Olaleke, J. Interoperability in Healthcare: Benefits, Challenges and Resolutions. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2013, 3, 2028–9324. [Google Scholar]
- Interoperability: The Key To The Future Health Care System: Interoperability will bind together a wide network of real-time, life-critical data that not only transform but become health care. Health Aff. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.E.; Vreeman, D.J.; Grannis, S.J. The long road to semantic interoperability in support of public health: Experiences from two states. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, T.N. Semantic interoperability in healthcare. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2014, 202, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Qu, Y.; Cheng, G. Matching large ontologies: A divide-and-conquer approach. Data Knowl. Eng. 2008, 67, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, E.; El-Sappagh, S.; Barakat, S.; Elmogy, M. Ontology-based electronic health record semantic interoperability: A survey. In U-Healthcare Monitoring Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 315–352. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 30182: 2017-Smart City Concept Model—Guidance for Establishing a Model for Data Interoperability. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53302.html (accessed on 12 April 2018).
- Serrano, M.; Barnaghi, P.; Carrez, F.; Cousin, P.; Vermesan, O.; Friess, P. Internet of Things, IoT Semantic Interoperability: Research Challenges, Best Practices, Recommendations and Next Steps, European Research Cluster on the Internet of Things. 2015. Available online: http://www.eglobalmark.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/2015-03-IoT-Semantic-Interoperability-Research-Challenges-Best-Practices-Recommendations-and-Next-Steps.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Yang, J.J.; Li, J.; Mulder, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.; Pan, H. Emerging information technologies for enhanced healthcare. Comput. Ind. 2015, 69, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, S.J.; Hasan, J.; Gammack, J.G. On-Cloud Healthcare Clinic: An e-health consultancy approach for remote communities in a developing country. Telemat. Inform. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, S.J.; Hasan, N.; Hasan, R.; Gammack, J. Healthcare support for underserved communities using a mobile social media platform. Inf. Syst. 2017, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zou, C.; Ullah, S.; Lai, C.F.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X. Cloud-Enabled wireless body area networks for pervasive healthcare. IEEE Netw. 2013, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Street, W.N.; Xu, E. Healthcare information systems: Data mining methods in the creation of a clinical recommender system. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2011, 5, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, U.; Sachdeva, S.; Mukherjee, S. Implementing healthcare interoperability utilizing SOA and data interchange agent. Health Policy Technol. 2015, 4, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.A.; Jiang, N. Effective behavioral intervention strategies using mobile health applications for chronic disease management: A systematic review. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mano, L.Y.; Faiçal, B.S.; Nakamura, L.H.V.; Gomes, P.H.; Libralon, G.L.; Meneguete, R.I.; Filho, G.P.R.; Giancristofaro, G.T.; Pessin, G.; Krishnamachari, B.; et al. Exploiting IoT technologies for enhancing Health Smart Homes through patient identification and emotion recognition. Comput. Commun. 2016, 89–90, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, X. A Review of Emotion Recognition Using Physiological Signals. Sensors 2018, 8, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Jang, E.H.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.W.; Jeon, H.J.; Yu, H.Y.; Byun, S. Automatic detection of major depressive disorder using electrodermal activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ceja, E.; Riegler, M.; Nordgreen, T.; Jakobsen, P.; Oedegaard, K.J.; Tørresen, J. Mental health monitoring with multimodal sensing and machine learning: A survey. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2018, 51, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noura, M.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Gaedke, M. Interoperability in Internet of Things: Taxonomies and Open Challenges. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2019, 24, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzirakis, P.; Trigeorgis, G.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Schuller, B.W.; Zafeiriou, S. End-to-End Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zualkernan, I.; Aloul, F.; Shapsough, S.; Hesham, A.; El-Khorzaty, Y. Emotion recognition using mobile phones. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y.4452: Functional Framework of Web of Objects. Available online: http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Y.4452-201609-P (accessed on 24 January 2017).
- Pan, E.; Walker, J.; Johnston, D.; Adler-Milstein, J.; Bates, D.W.; Middleton, B. The Value of Health Care Information Exchange and Interoperability. Health Aff. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaulent, M.C.; Leprovost, D.; Charlet, J.; Choquet, R. Semantic interoperability challenges to process large amount of data perspectives in forensic and legal medicine. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2018, 57, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.A.; Khattak, A.M.; Hussain, M.; Amin, M.B.; Afzal, M.; Nugent, C.; Lee, S. An adaptive semantic based mediation system for data interoperability among health information systems systems-level quality improvement. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, E.; El-Sappagh, S.; Barakat, S.; Elmogy, M. Distributed electronic health record based on semantic interoperability using fuzzy ontology: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 40, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, E.; Exposito, E.; Drira, K.; da Silveira, M.; Pruski, C. A Semantic Big Data Platform for Integrating Heterogeneous Wearable Data in Healthcare. J. Med. Syst. 2015, 39, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Cerdeira, L.; Rodríguez-Martínez, F.J.; Gómez-Rodríguez, A. Ontology matching: A literature review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 949–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, E.; El-Sappagh, S.; Barakat, S.; Elmogy, M.; Adel, E.; El-Sappagh, S.; Barakat, S.; Elmogy, M. A unified fuzzy ontology for distributed electronic health record semantic interoperability. In U-Healthcare Monitoring Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sensor Ontology 2009-Semantic Sensor Network Incubator Group. Available online: https://www.w3.org/2005/Incubator/ssn/wiki/SensorOntology2009 (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- Underbrink, A.; Witt, K.; Stanley, J.; Mandl, D. Autonomous Mission Operations for Sensor Webs. In American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting 2008, Abstract IN33C-05; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, S.J.D. Ontology for observations and sampling features, with alignments to existing models. Semant. Web 2016, 8, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- oneM2M-oneM2M Ontologies. Available online: http://www.onem2m.org/technical/onem2m-ontologies (accessed on 8 February 2019).
- Lambrix, P.; Tan, H. SAMBO—A system for aligning and merging biomedical ontologies. J. Web Semant. 2006, 4, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Vargas-Vera, M.; Motta, E. DSSim-ontology mapping with uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Ontology Matching (OM-2006), Athens, GA, USA, 5 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q. RiMOM: A Dynamic Multistrategy Ontology Alignment Framework. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1218–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Mary, Y.R.; Shironoshita, E.P.; Kabuka, M.R. Ontology matching with semantic verification. J. Web Semant. 2009, 7, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OHDSI–Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics. Available online: https://www.ohdsi.org/ (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Gardner, D.; Knuth, K.H.; Abato, M.; Erde, S.M.; White, T.; DeBellis, R.; Gardner, E.P. Common Data Model for Neuroscience Data and Data Model Exchange. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2001, 8, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Common Data Model (CDM) Specification. In The Book of OHDSI; Chapter 4; Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- NCI Thesaurus (NCIt). Available online: https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ (accessed on 16 March 2019).
- SNOMED CT Terminilogies. Available online: http://bioportal.bioontology.org/ontologies/SNOMEDCT?p=classes&conceptid=285854004 (accessed on 22 March 2019).
- Mao, M.; Peng, Y.; Spring, M. Ontology Mapping: As a Binary Classification Problem. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fourth International Conference on Semantics, Knowledge and Grid, Beijing, China, 3–5 December 2008; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, D.H.; Bellahsene, Z.; Ngo, D. YAM++: A multi-strategy based approach for Ontology matching task. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management, Galway, Ireland, 8–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, A.; Madhavan, J.; Domingos, P.; Halevy, A. Ontology Matching: A Machine Learning Approach. In Handbook on Ontologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lai, S.; He, S.; Liu, K.; Zhao, J.; Lv, X. Ontology Matching with Word Embeddings. In Chinese Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing Based on Naturally Annotated Big Data. NLP-NABD 2014, CCL 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kolyvakis, P.; Kalousis, A.; Kiritsis, D. DeepAlignment: Unsupervised Ontology Matching with Refined Word Vectors. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 787–798. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E. Learning multiple layers of representation. Rev. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2007, 11, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibria, M.G.; Ali, S.; Jarwar, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Chong, I. Logistic Model to Support Service Modularity for the Promotion of Reusability in a Web Objects-Enabled IoT Environment. Sensors 2017, 17, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolyvakis, P.; Kalousis, A.; Smith, B.; Kiritsis, D. Biomedical ontology alignment: An approach based on representation learning. J. Biomed. Semant. 2018, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apache Jena. A Free and Open Source Java Framework for Building Semantic Web and Linked Data Applications. Available online: http://jena.apache.org/ (accessed on 26 March 2017).
- Huang, J.; Dang, J.; Vidal, J.M.; Huhns, M.N. Ontology Matching Using an Artificial Neural Network to Learn Weights. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/cd6b/c9913f067968f113762febab025437d8dcaa.pdf (accessed on 03 June 2018).
- Wang, P.; Xu, B. LILY: The Results for the Ontology Alignment Contest OAEI 2007. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Ontology Matching (OM-2007) Collocated with the 6th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC-2007) and the 2nd Asian Semantic Web Conference (ASWC-2007), Busan, Korea, 11 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Unsupervised Feature Learning and Deep Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. Available online: https://docs.huihoo.com/deep-learning/Representation-Learning-A-Review-and-New-Perspectives-v1.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Hinton, G.E.; Zemel, R.S. Autoencoders, Minimum Description Length and Helmholtz Free Energy. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–2 December 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Yang, A. Learning Topic Representation for SMT with Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Apache Jena-Apache Jena Fuseki. Available online: https://jena.apache.org/documentation/fuseki2/ (accessed on 27 February 2018).
- Miranda-Correa, J.A.; Abadi, M.K.; Sebe, N.; Patras, I. AMIGOS: A Dataset for Affect, Personality and Mood Research on Individuals and Groups. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A database for emotion analysis; Using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protégé. A Free, Open-Source Ontology Editor and Framework for Building Intelligent Systems. Available online: https://protege.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- NRC Emotion Lexicon. Available online: https://saifmohammad.com/WebPages/NRC-Emotion-Lexicon.htm (accessed on 4 May 2019).
- Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative: Home. Available online: http://oaei.ontologymatching.org/ (accessed on 17 January 2019).


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Chong, I. Semantic Mediation Model to Promote Improved Data Sharing Using Representation Learning in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194175
Ali S, Chong I. Semantic Mediation Model to Promote Improved Data Sharing Using Representation Learning in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(19):4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194175
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Sajjad, and Ilyoung Chong. 2019. "Semantic Mediation Model to Promote Improved Data Sharing Using Representation Learning in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments" Applied Sciences 9, no. 19: 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194175
APA StyleAli, S., & Chong, I. (2019). Semantic Mediation Model to Promote Improved Data Sharing Using Representation Learning in Heterogeneous Healthcare Service Environments. Applied Sciences, 9(19), 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194175




