Abstract
Extracting cybersecurity entities and the relationships between them from online textual resources such as articles, bulletins, and blogs and converting these resources into more structured and formal representations has important applications in cybersecurity research and is valuable for professional practitioners. Previous works to accomplish this task were mainly based on utilizing feature-based models. Feature-based models are time-consuming and need labor-intensive feature engineering to describe the properties of entities, domain knowledge, entity context, and linguistic characteristics. Therefore, to alleviate the need for feature engineering, we propose the usage of neural network models, specifically the long short-term memory (LSTM) models to accomplish the tasks of Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Relation Extraction (RE). We evaluated the proposed models on two tasks. The first task is performing NER and evaluating the results against the state-of-the-art Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) method. The second task is performing RE using three LSTM models and comparing their results to assess which model is more suitable for the domain of cybersecurity. The proposed models achieved competitive performance with less feature-engineering work. We demonstrate that exploiting neural network models in cybersecurity text mining is effective and practical.
1. Introduction
Information systems are increasingly exposed to a variety of security threats that need constant attention from corporate decision makers. Despite being an effective approach to measure security risks, current risk management approaches lack in some areas such as the need for very detailed knowledge about the company environment and the cybersecurity body of knowledge [1]. To stay current with the latest security knowledge, a security professional has to stay abreast with the latest information about security aspects such as vulnerabilities, attacks, etc., which is a challenging task as information is updated on a daily basis.
The public disclosure of important security information often first occurs in different online resources like blogs, vendor bulletins, and online databases [2]. The information is then collected and stored in semi-structured vulnerability databases such as the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) [3]. The timely analysis of cyber-security information necessitates automated information extraction from web sources. This is particularly difficult because the information is unstructured and dispersed over the web, which is the first source of information and not present in one location. It is useful and more practical for the cybersecurity community if the relevant information is recognized, extracted, and represented as an integrated, shared, and structured form like databases or ontologies. A potential immediate benefit is the increase of situation awareness and enabling of intrusion detection systems to detect and prevent potential “zero-day” attacks.
The two main tasks of information extraction are Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Relation Extraction (RE). NER can be generic where the aim is to extract general entities such as the names of places, people, etc., or can be specific to a domain. For instance, products, vendors, vulnerabilities are names of entities in the cybersecurity domain. Nowadays, the mainstream tools used for NER that give the best results rely on feature engineering to describe entities. These tools are usually domain specific, thus, depending on the features that characterize the entities in the domain. For instance, a sequence of entities in the financial domain are likely to be a company name, whereas in cybersecurity, they are more likely to be a software name. Figure 1 highlights some entities from the cybersecurity domain. The aim of relation extraction, on the other hand, is to extract knowledge about related entities from unstructured language sources such as text or speech and represent that knowledge usually as a triplet that has the form (subject, predicate, object). For instance, from the vulnerability description in Figure 1, we can extract the tuple (IBM, is_vendor_of, WebSphere), which is an instance of the relation type: (Software vendor, is_vendor_of, Software product).

Figure 1.
Vulnerability description from the national vulnerability database (NVD).
Previous works have shown that off-the-shelf NLP tools are not capable of extracting security-related entities and their relations [4,5]. Comparatively, traditional statistical-based extraction methods achieve good results; however, they rely heavily on feature engineering, which has some limitations. Firstly, it relies heavily on the experience of the person in the domain and the lengthy trial and error process that accompanies that. Secondly, feature engineering relies on look-ups or dictionaries to identify known entities [6]. These dictionaries are hard to build and harder to maintain especially with highly dynamic fields, such as cybersecurity.
Neural networks-based methods, which became more practical in recent years, can learn non-linear combinations of features, which relieves us from the laborious feature engineering [7]. A category of neural networks called Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are particularly suited for dealing with data that comes in sequences such as natural languages or time series and achieved good results in the NLP field [8,9]. In practice, the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks became the preferred alternative for text processing using deep learning methods. LSTMs are a type of RNN and address the long-term dependency learning of general RNNs.
The objective of this paper is to evaluate the LSTM-based neural network model in performing information extraction tasks for the domain of cybersecurity. To evaluate the performance of LSTMs for the NER tasks, we compare the performance of an LSTM-based model and a CRF-based model that are trained on the same corpus of vulnerability descriptions collected from various online sources. For RE, we compare three recent LSTM architectures in terms of their performance in information extraction. These architectures are “LSTM along shortest dependency paths”, “LSTM on least common ancestor sub tree”, and “LSTM on sequences and tree structures”. To train the models, we auto generate an annotated training corpus using a bootstrapping algorithm [10] and generate a word embeddings model from the NVD. The models are compared in terms of training/testing accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 scores.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 reviews the related work in the field. Section 3 provides an overview of the evaluated LSTM models. Section 4 describes the data used for training. The next section explains the data preprocessing needed for training. Section 6 covers the training methods for the models. The outcomes of the training and the discussion of the results are covered in Section 7 and Section 8. Finally, Section 9 concludes the paper.
2. Related Work
Various methods have been applied to extract cybersecurity entities and their relations in the cybersecurity domain. Joshi et al. [11] developed a framework prototype to spot entities and concepts from heterogeneous data sources. They leveraged the maximum entropy models (MEMs) and trained the CoreNLP off-the-self entity recognition tool on a labeled corpus. With the help of 12 Computer science students who have a good understanding of cybersecurity concepts, the training corpus was painstakingly hand-labeled and contained around 50,000 tokens. The precision and F1 scores of their model are 0.799 and 0.75, respectively.
Bridges et al. [2] used the perceptron algorithm, which has been proven to be better than the maximum likelihood estimation techniques [12], and implemented a custom tool for the task, which provided more flexible feature engineering. To automatically build the training corpus, Bridges et al. leveraged the structure of the data in NVD to create a set of heuristics for labelling the text. This resulted in a corpus containing around 750,000 tokens. Compared to Joshi et al., Bridges et al. achieved a precision of 0.963 and an F1 score of 0.965 because their training corpus was much larger. However, their corpus is not as varied as the corpus of Joshi et al., which affected the results.
An SVM classifier has been used by Mulwad et al. [13] to separate cybersecurity vulnerability descriptions from non-relevant ones. The classifier uses Wikitology and a computer security taxonomy to identify and classify domain entities. They used the average precision as a measure for their model performance and achieved an average precision of 0.8. Jones et al. [10] implemented a bootstrapping algorithm that requires little input data consisting of few relation samples and their patterns to extract security entities and the relationship between them from the text. The test on a small corpus obtained a precision of 0.82.
McNeil et al. [14] implemented a semi-supervised learning algorithm. The bootstrapping algorithm learns heuristics to identify cyber entities and recognize additional entities through iterative cycling on a large unannotated corpus. The algorithm achieved a precision of 0.9 and a recall of 0.12 with a corpus that contained entity types that have few seeds and a recall of 0.39 when omitting these entity types. Bridges el al. [15] compared previous MEM models in the field, showing that the training data for these models were unrepresentative of the data in the wild and hence, these models over-fit to the training data. Therefore, they used documents from more diverse security-related resources and crafted three cyber entity extractors based on their set of collected data, which improved the state-of-the-art cyber entity tagging. Their model obtained a precision of 0.8 and an F1 score of 0.61.
More recently, deep neural networks have been considered as a potential alternative to the traditional statistical methods as they address many of their shortcomings [16]. With neural networks, features can automatically be learned, which considerably decreases the effort needed by human experts in several domains. Moreover, the results achieved in various domains have demonstrated that the features learned by neural networks are better in terms of accuracy than the human-engineered features. RNNs have been studied and proved that they can process input with variable lengths as they have a long-time memory. This property resulted in notable successes with several NLP tasks like speech recognition and machine translation [17]. LSTM further improved the performance of RNNs and allowed the learning between arbitrary long-distance dependencies [18]. With properly annotated large corpus, deep neural networks can provide a viable alternative to the traditional methods, which are labor-intensive and time consuming [16].
The goal of this paper is to leverage the recent neural network techniques to extract information from cyber text as an alternative to the traditional statistical-based methods. The studied LSTM models have been evaluated using general English corpus and in isolation, but as far as we know, they have not been compared against each other and in a specific field such as cybersecurity.
3. Models
To evaluate the performance of LSTMs for the NER tasks, we applied the LSTM-CRF method introduced by Lample et al. [19] to the domain of cybersecurity vulnerability management. This architecture is a combination of LSTMs, CRFs, and word embeddings. Its input is an annotated corpus in a format similar to the format of the CoNLL-2000 dataset [20]. This dataset contains a list of words with a tag denoting the type of the word. There is no description of the features of entities, hence it is domain and entity agnostic. We compared the results we obtained with a notably fast and accurate CRFs implementation called CRFSuite [21]. Annotated corpus is not widely available in the cybersecurity domain as opposed to other domains such as the biomedical domain. To train the models, we used the annotated corpora provided by Bridges et al. [2].
For the RE task, we implemented three models. The “LSTM along Shortest Dependency Paths” (SDP) architecture following the work of Yan Xu et al. [22]. This neural architecture utilizes the shortest dependency path between two entities in a sentence. The shortest dependency paths retain the relevant information needed for relation classification and eliminate insignificant words in the sentence. As for the “LSTM on Sequences and Tree Structures” (STS) model, we implemented an architecture based on the paper [23] by Miwa et al. This neural network jointly models the word sequence in the sentence and its dependency tree structure by stacking two bidirectional LSTM networks, one for the sequence and one for the tree structure. The resulting network jointly represents the entities and their relations in a single unified model with shared parameters between the two tasks. The “LSTM on the Least Common Ancestor Sub Tree” (LCA) model is a variation of the STS model, where the difference is that this model is based on the least common ancestor between two entities in the dependency tree.
3.1. Background
LSTMs are a type of RNNs that have the ability to detect and learn patterns in a sequence of input data. Sequences of data can be stock market time series, natural language text or voice, genomes, etc. RNNs combines the current input (e.g., current word in the text) with the knowledge learned from the previous input (e.g., previous words in the text). While RNNs perform well with short sequence, they suffer from an issue called vanishing or exploding grading issue when the processed sequence becomes too long. When the input becomes long, RNNs become difficult to train especially when the number of model parameters becomes large. In this case, the training is very unlikely to converge.
The LSTM architecture was introduced by Hochreiter et al. [24] in 1997 to address the problem of long-term dependency learning. The model introduced the concept of a memory cell, shown in Figure 2, which preserves long-term dependency state over time in the memory. Since then, several variants have been proposed. LSTMs and RNNs in general have been applied to various NLP tasks including advanced tasks such as recognizing textual entailment (RTE) [25]. An LSTM cell, at each step t, is defined as a collection of vectors (where d is the memory dimension of the LSTM). These vectors are defined as follows: Input gate , forget gate , output gate , memory cell , next memory state , and a hidden state . The entries of the vectors , , and are in the range [0, 1]. The transition from a state to the next is defined by the following equations:
| . |
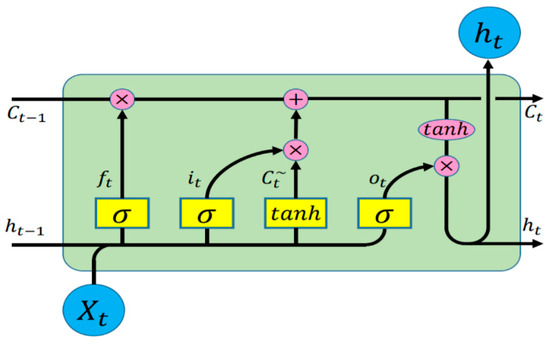
Figure 2.
Long short-term memory (LSTM) cell.
Here, is the input of the current time step, the symbol σ represents the logistic sigmoid function, and ʘ represents element-wise multiplication. The forget gate calculates the amount of the previous cell state that should be forgotten. The input gate calculates the amount of information passed as input to each unit, and the output gate calculates the amount of the exposure of the internal memory state. The hidden state vector is therefore the partial view of the state of the unit’s internal memory cell. The model learns the representation of information over time because the values of the different gating variables vary for each vector element in .
Word embeddings also contributed to the encouraging results of LSTMs in the NLP field [26]. They were introduced by Mikolov et al. [27] and represented a significant improvement over one-hot encoding vectors, the traditional way of representing text [16]. Their first advantage is that they are low-dimensional vectors of usually 200–300 length as opposed to one-hot vectors, which tend to be as long as the number of words in the vocabulary of the text. The second advantage is that they capture the semantic relationship between words that had a big impact on NLP tasks such as NER. For example, when the value of a vector representing the word ‘King’ is subtracted from the ‘Queen’ vector, we get a result that is equal to the difference between the vectors representing the words ‘Man’ and ‘Woman’. Another characteristic of word embedding is word clustering. Words that are from the same family are grouped in separate cluster in the word embeddings space. For instance, the company names ‘Microsoft’ and ‘Oracle’ appear in the same cluster whereas the product names ‘WebLogic’ and ‘Eclipse’ appear in another cluster.
3.2. LSTM-CRF for Named Entity Recognition
In this Section, we will provide an overview of the LSTM-CRF architecture as presented by Lample et al. [19]. Figure 3 shows the architecture of LSTM-CRF. It consists of three layers.
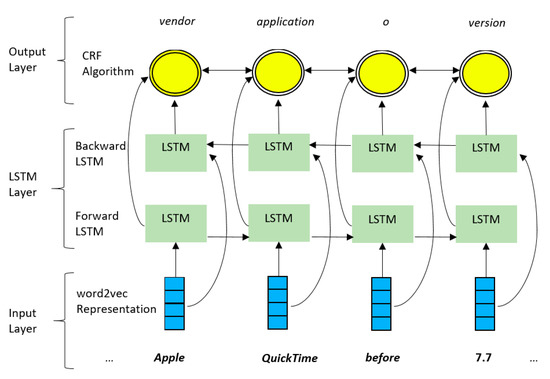
Figure 3.
Bidirectional LSTM-conditional random fields (CRF) architecture.
The first layer in the architecture is the input layer at the bottom. It takes the input sequence of words , , …, and for each of these words, it produces an embedding (dense vector representation) . The resulting embeddings sequence , , …, is fed into the next layer, which is the bi-directional LSTM layer. This layer performs training on the input and passes the output to the last layer, CRF algorithm layer, where the algorithm is applied and produces the final output of the neural network [28]. The output is the prediction of the tag with the highest probability for the word.
The bi-directional LSTM layer of the architecture consists of two parts, a forward LSTM that reads the input from the beginning and moves forward, and a backward LSTM, which starts from the end of the sequence and moves backward. The forward LSTM computes a left context lht and represents the text that precedes the current word t. The backward LSTM calculates the right context rht by reading the text in reverse order and represents the words that follows the word t. The final representation of the word is the combination of the left and right contexts so ht = [lht;rht]. Bi-directional LSTM proved useful in tagging applications such as NER [29].
3.3. Models for Relation Extraction
The state-of-the-art neural models introduced by Miwa et al. [23] and Xu et al. [22] are used to carry out the task of extracting relations between entities in cybersecurity vulnerability descriptions text. The architecture of each model is described in the following sections.
3.3.1. LSTMs on Sequences and Tree Structures (STS)
The design of this model is based on LSTM-RNNs that represent word sequences and dependency tree structures and perform end-to-end extraction of relations between entities on top of these RNNs. Figure 4 provides an overview of the model.
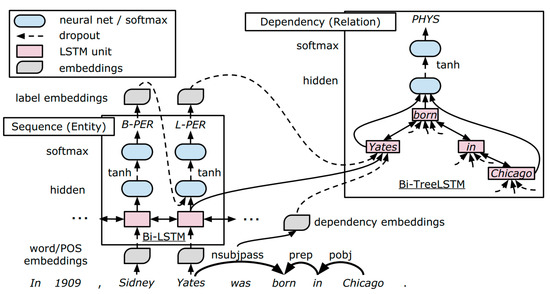
Figure 4.
Sequences and tree structures LSTM architecture. Source [23].
The model consists mainly of three representation layers: Embedding layer (word/POS embeddings), the LSTM sequence layer, which represents the words sequence, and the LSTM dependency layer, which represents the dependency subtree. In the sequence layer, the model performs a greedy left-to-right entity detection. Then, in the dependency layer, the model performs relation classification between detected entities based on the dependency subtrees between entities. Finally, after decoding the model, the parameters of the model are updated simultaneously using backpropagation through time (BPTT) [30]. The parameters of the model are shared between entity and relation classifications since the embedding and sequence layers are shared by both tasks because the dependency layer is stacked on top of the sequence layer.
The embedding representations are handled by the embedding layer. Embeddings are used to represent words, part-of-speech (POS) tags, dependency types, and entity labels. Using the word embeddings, the sequence layer represents the linear sequence of the words. This layer represents the context information of the sentences and its constituent entities (lower left box of Figure 4). Taking two candidate target entities, the dependency layer represents the dependency tree between the two entities and is responsible for representing such relationships (top-right box of Figure 4). The dependency layer is mainly concerned in the shortest path between two entities in the dependency tree as these paths proved to be effective as shown by the SDP model that is covered in the next section.
3.3.2. LSTMs along Shortest Dependency Paths (SDP)
The architecture of the SDP model is depicted in Figure 5. In the first step, the sentence is parsed to generate its dependency tree using the Stanford parser. In the second step, the shortest dependency path is extracted to serve as the input for the network. In addition to the shortest dependency path, four other types of information represented as embeddings are passed to the model, namely words, grammatical relations (GRs), POS tags, and WordNet hypernyms. Embeddings are vectors of real values that represent the semantics of each of these inputs.
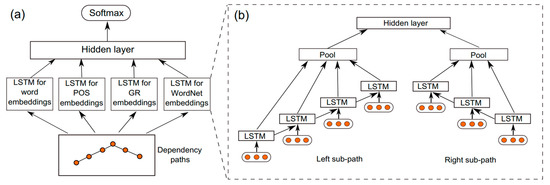
Figure 5.
LSTM networks along shortest dependency paths (SDP) architecture. Source [22].
The common ancestor node of two entities is used to separate the SDP into a left and right sub-path. These two sub-paths are picked up by two RNNs. In each RNN, LSTM units are used for information propagation. The information that propagate from both sub-paths is propagated to the max pooling layer (Figure 5b). The pooling layers from the four channels are then concatenated and fed into a higher hidden layer and, finally, a soft max is applied on its output as the resulting classification (Figure 5a).
3.3.3. LSTMs on the Least Common Ancestor Sub Tree (LCA)
The LCA model is a variant of the STS model. The difference in this model lies in the structure of representing the relation between two target entities in the sentence. Whereas the STS model is implemented by capturing the full dependency tree between two entities in the context of the entire sentence, the LCA model only captures the subtree below the common ancestor of the target entity pair.
4. Data
The corpus used for training the models of this paper is extracted mainly from the NVD. It is a standards-based US government vulnerability management repository. Its role is to enable the vulnerability automation management and consists of data that include security-related information about software flaws, impact metrics, and product names.
4.1. Data for Named Entity Recognition
The corpus used in the training of the NER model is based mainly on the NVD data and contains 40 entity types. The corpus contains descriptions of the cybersecurity vulnerabilities and was generated as part of the Stucco project [31]. It mainly contains the descriptions of entries in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) [32] and NVD databases from 2010. Each word in the corpus is annotated with an entity type. Since not all the entity types are common, we concentrated our analysis of the model performance on the seven most common entities of the domain. The statistics in Table 1 show the number of entities for the most significant entities in the training and test corpora:

Table 1.
Named entity recognition (NER) corpus statistics.
4.2. Data for Relation Extraction
The corpus for RE training was challenging because there was no annotated textual data available for cybersecurity vulnerability descriptions and the manual annotation of the NVD corpus is costly and impractical. This is a common case when applying NLP to specific domains. For this reason, we applied the bootstrapping algorithm developed by Jones et al. [10,33] for the cybersecurity domain that obtained a precision of 82% to generate an automatically annotated corpus. The algorithm follows a semi-supervised approach for extracting relations by querying the users to assist in labelling a seed of few important relations and the algorithm iteratively builds on the seed to generate a bigger corpus.
We applied the bootstrapping algorithm on the NVD corpus using the seed provided by Jones et al. as an input to generate the corpus. We then trained the model on the data for the year 2015. The NVD database for 2015 consisted of 20,125 sentences divided into training and test data. The training data constituted 80% of the corpus with 13,569 sentences and test data consisted of 6556 sentences. The aim of our experiment is to concentrate initially on the most important relations in the domain. The list of studied relations and the statistics of the final data used in our experiments is shown in Table 2:

Table 2.
Relation extraction (RE) corpus statistics.
The word embeddings needed by the models were generated from the text of the whole NVD corpus using the google word2vec tool [34]. The reason for not using general embeddings available online is that these embeddings are based on general English text and having embedding generated from the text of a specific domain improves the quality of the results.
5. Preprocessing
5.1. Named Entity Recognition Preprocessing
In its original form as provided by Bridges et al. [2], all the corpora were stored in a single JSON file with each corpus represented by a high-level JSON element. To facilitate further processing, we converted the file to the CoNLL2000 format as the input for the LSTM-CRF model. In the newly annotated corpus, we removed the separation between each of the three corpora and annotated every word in a separate line. Each line contains the word mentioned in the text and its entity type for example (Apple B-vendor).
As for the CRF model, the CRFSuite requires the training data to be in the CoNLL2003 [33] format that includes the part of speech (POS) and chunking information with the NER tag appearing first (for example: B-vendor Apple NNP O). As the original corpus did not contain the POS and chunking information, the training corpus had to be reprocessed. We started by converting it to its original form (i.e., a set of paragraphs). Then, we used the python NLTK library [35] to extract the necessary information for each word in the corpus. Finally, we converted the text back to the expected CoNLL2003 format.
5.2. Relation Extraction Preprocessing
Given the NVD data, we extracted the vulnerability descriptions from the xml files representing vulnerability reports. Each vulnerability description is considered as the input for the model. Descriptions range from short sentences to long paragraphs consisting of many sentences. Long paragraphs consisting of more than 500 characters were removed because they caused out-of-memory issues further in the processing pipeline. The resulting paragraphs were fed to the bootstrapping algorithm, which using a small seed, detects entities in the paragraph and the relationship between them. The algorithm makes an exhaustive search to find all possible entity combinations in each paragraph. Therefore, we end up with lots of repetitive paragraphs but each instance contained a different entity annotation and relation. In the following description:
“The Windows Error Reporting component in <e1>Microsoft</e1> <e2>Windows 8</e2> and 8.1 allows local users to bypass...”.
SOFTWARE_VENDOR-is_vendor_of-SOFTWARE_PRODUCT (e1, e2).
The algorithm detected that ‘Microsoft’ is a vendor of ‘Windows’ and denotes that with the tuple (e1, e2). Each of the three evaluated models then has its own preprocessing depending on the model architecture and its expected input. The common preprocessing steps such as POS tagging and dependency parsing were carried out using Stanford CoreNLP toolkit version 3.7. The main preprocessing work for all the models is extracting the shortest path for the least common ancestor for candidate entities. Some processing errors occurred when extracting the information needed by corresponding models such as the dependency paths, mapping words to their embeddings id, etc. These errors include unsupported dependency types, unsupported POS types, etc. These errors are not critical, and the models can still be trained but this could impact the performance of the model. Therefore, during preprocessing, input that contained errors has been removed for the SDP and LCA models. However, for the STS model and due to its complexity, that could not be done because most of the input contained errors. By removing all the errors, the remaining data are not sufficient for proper model training.
6. Training
We trained the LSTM-CRF model on the NER task to recognize 40 entity tags in cybersecurity vulnerability descriptions. Then, we trained the CRFSuite on the same corpus and compared the performance of both models. For named entity recognition, CRFSuite uses a generic set of features that were defined by the tool writer to describe entities. We split the corpus into three subsets: training, development (holdout cross-validation), and testing with the following percentages, respectively: 70%, 10%, and 20%. The aim of the relation extraction task is to train the three LSTM models on extracting the relations shown in Table 2. The input for each model is a set of information such as POS tagging, dependency trees, dependency paths, etc. We divided the corpus to 80% training data and 20% for the test data. To ensure the quality of training, this division is performed on the level of each relation type, i.e., for each relation type, its instances are divided as such. To select the appropriate training parameters, we experimented with different batch sizes and number of epochs and chose a batch size of size 10 and 100 epochs as the most appropriate combination. Smaller batch size makes the training faster but lowers the accuracy of the model while larger batch size resulted in a very slow training to the point of being impractical because of memory-related failures. We chose to run the model for 100 epochs as the accuracy of the models stabilized and did not improve afterwards. The training time between the models varied considerably. The SDP model took the least time with an average epoch time of 50 s, followed by the LCA model with epochs taking 150 s, and finally the STS model that took 1300 s on average per epoch.
6.1. Evaluation Metrics
The evaluation metrics used for the NER and RE models’ evaluation are the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. For the NER task, we calculated these metrics for the full set of entity tags as well as for the subset of the seven common entities. The evaluation metrics are calculated as follows:
As for RE, a correctly extracted relation is considered as true positive (TP) if the type of relation is correct and the type of the entities in this relation match the type of entities in the training data. Otherwise, the extracted relation is considered as a false positive (FP). False negative instances were computed as the total number of gold relations that our model did not identify. We evaluated the model using the 20% test data we set aside from the corpus. The resulting evaluation metrics were computed using macro averaged scores. The results of each of the three models were compared in terms of the evaluation metrics above to evaluate the performance of each model.
6.2. Model Parameter Settings
For the parameters set of the LSTM-CRF model, we set the default values used by Lample et al. [8]. For the CRFSuite model, the default settings of the tool were used to train the CRF model. As for the RE models, the hyper-parameters were initially set randomly with a uniform distribution. We then tuned the parameters according to the development set in the NER model while most other parameters in the RE models were selected based on empirical testing based on the previous works [15,16] as a full scan for all parameters is impractical given the lengthy training times. The final values of the models’ parameters are shown in Table 3:

Table 3.
RE models’ parameters.
We set the hidden state size of the LSTM models to 100. The dimensions of embeddings for the words, POS, and dependency trees were set to 100, 25, and 25, respectively.
7. Results
7.1. Named Entity Recognition Model
We performed an evaluation of the LSTM-CRF model and the CRF tool that uses the state of the art CRF method and uses feature engineering that is not domain specific. For evaluation, we used a corpus combined from several sources but mainly from NVD, containing 40 entity types. For evaluation, we will analyze the average performance of both models against the whole set of entity types and then consider only the most frequent entities of the domain and evaluate the models on the prediction of only this set of entities. The entities we considered are application, vendor, version, edition, operating system, file, and hardware.
The global item accuracy of the two models is shown in Figure 6. It shows the trend of accuracy for the development set over the training of 100 epochs. As we can see, the LSTM-CRF model achieved an accuracy of 95.8% from the first epochs and continued to increase to reach a maximum of 98.3% at the 23rd epoch until the end of training. The CRF method on the other hand, started with a low accuracy of 65% but increased quickly over the training epochs to eventually reach an accuracy of 96% and stabilized to the end of the training with an accuracy of 96.35%.
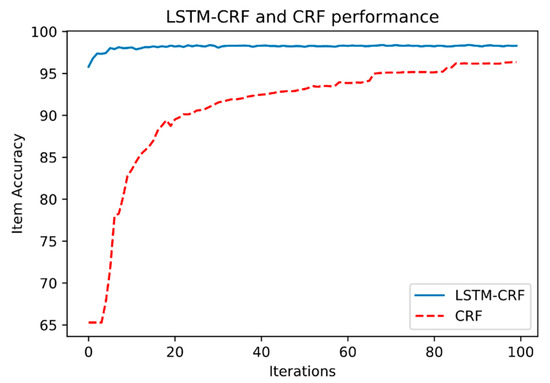
Figure 6.
Item accuracy for LSRM-CRF and CRFSuite.
The average performance of the two models across all the entity types in the training set is shown in Table 4:

Table 4.
Average performance metrics for all entity types.
As we can see, the performance metrics in terms of precision, recall, and F1 score shows that the results for LSTM-CRF are better that their CRF counterparts. The results of each method for the entities subset in terms of F1 score, precision, and recall are shown in the Table 5:

Table 5.
Precision, recall, and F1 scores of CRF and LSTM-CRF for seven entity tags.
7.2. Relation Extraction Models
The results obtained for the three models varied considerably. The average performance of the three RE models is shown in the following Table 6:

Table 6.
Precision, recall, and F1 scores of the RE models.
As we can see, the performance metrics in terms of precision, recall, and F1 score shows that the results of the SDP model are better than the two other models. It performed well both in training and testing accuracy while achieving the best F1 score with 94.3%. The STS model performed well in training but did not achieve a high F1 score in the validation phase. The LCA model score was average in terms of training and testing.
We trained the models for 100 epochs. Figure 7 shows the decrease of the loss for the three models during training. We can see that the STS and SDP models achieved the lowest loss at the end of the training while the LCA model ended the training with a relatively high loss.
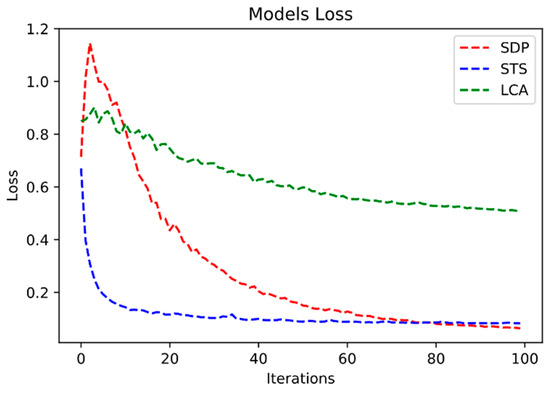
Figure 7.
RE models’ loss per epoch.
8. Discussion
As we can see from the results, The LSTM-CRF model achieved an overall items accuracy for the NER task that is 2% higher than the CRF model. Also, the average precision, recall, and F1 score across all the entities is higher by an average of 6.5%. Regarding the performance of the models for the subset of chosen entities, the LSTM-CRF model performed better for five entity tags and the CRF model performed better for two tags only, which are the ‘hardware’ and the ‘edition’ tags. This result is due to the size of the training data. The neural network models require a large amount of data to be able to learn better and make more predictions that are accurate. In other words, the more times a tag is seen in the training data, the better the model becomes at predicting it. When looking at the training corpus statistics from Table 1, we can see that the number of entities with these two tags are few compared with the other tags. These numbers are comparatively lower than other tags such as ‘application’ and ‘vendor’. For this reason, the five more frequent tags in the corpus overwhelmed the less frequent ones.
The performance of the RE models was not as expected. The STS model took the longest time in training with epoch times of around 21 min on average while the SDP model training was very quick with epoch times of only 50 s. This gave the impression that the STS model will perform better and gives better results. However, the outcome was in the favor of SDP model with an F1 score of 94.3%. The long training times for STS is due to the complexity of the model. Comparing the STS model and its LCA variant, it seems that only capturing the subtree under the least common ancestor improved the performance of the LCA model and increased the speed of its training.
There are threats to validation in this study. The first threat to validity is in the corpus of RE models. The corpus is not manually annotated and, as such, contains some wrongly annotated parts. This could affect the performance of a model more than its effect on another. Evaluation is another major issue; regarding relation extraction, there is a lack of a gold-standard corpus in the domain of cybersecurity vulnerabilities management that enables the comparison of the different algorithms and techniques and provides repeatability. Creating a large hand-annotated corpus for the domain by professionals that is large enough to be suitable for deep learning algorithms is very expensive in terms of time and funding needed. Web-based collaborative tools can reduce the cost, but they are still not popular in the research community. Another issue that affected the models is the errors during preprocessing. As mentioned in the preprocessing section, STS could not be cleaned. This gave advantage to the other models and impacted the results. Nevertheless, this shows that the complexity of the STS model compared to the other two models affected its performance.
9. Conclusions
This paper evaluated the suitability of LSTM-based models in information extraction from cybersecurity corpus and more specifically textual descriptions of cybersecurity vulnerability descriptions. The results are promising. It showed a remarkable improvement in the NER task over the traditional statistical-based CRF model. The LSTM models used for relation extraction showed that there is a variance in their performance in this domain. Despite this, the SDP model achieved a very high accuracy. One of the strengths of the studied LSTM models is being domain agnostic and can be applied to other domains as is. The traditional methods required extensive feature engineering which made them time consuming, labor-intensive, and the resulting model is domain specific and cannot be applied to other domains without modifications. With this approach, the need for domain specific tools is alleviated. The training corpus consequently is much simpler, as shown in this paper, and requires much simple preprocessing.
However, this approach requires a large hand-annotated corpus to achieve the best results. This task does not require experts but the amount of data to be annotated is big and needs time and funding and innovative techniques such as collaborative tools. If this hurdle is overcome and information extraction becomes automated with the improved accuracy of the recent neural network models, there is a pressing need to turn this advancement into applications in the domain of cybersecurity. One such application is the conversion of the textual descriptions of cybersecurity vulnerabilities that are scattered all over the web into a more consolidated, formal representation like ontologies. This gives cybersecurity professionals the necessary tools that grant them rapid access to the information needed for a better understanding of the threats and decision-making. In future, our work will concentrate on building a gold-standard corpus and make it available to researchers in the field. Different approaches of information extraction from cyber text will be analyzed in the context of an automated ontology population system of consolidated online sources.
Author Contributions
H.G. suggested the topic and approach, worked on the technical design and the implementation, and wrote the paper. The co-authors J.L. and A.B. monitored and supervised the research and its progress. They also contributed to the writing and review of the paper. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This publication was made possible by the support of Qatar University and DISP laboratory (Lumière University Lyon 2, France).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Finkel, J.R.; Grenager, T.; Manning, C. Incorporating non-local information into information extraction systems by gibbs sampling. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; pp. 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, R.A.; Jones, C.L.; Iannacone, M.D.; Testa, K.M.; Goodall, J.R. Automatic labeling for entity extraction in cyber security. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1308.4941. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1308.4941 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- National Vulnerability Database. Available online: https://nvd.nist.gov/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Liao, X.; Yuan, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, L.; Beyah, R. Acing the ioc game: Toward automatic discovery and analysis of open-source cyber threat intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- More, S.; Matthews, M.; Joshi, A.; Finin, T. A knowledge-based approach to intrusion detection modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–25 May 2012; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Grishman, R. Event detection and domain adaptation with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; Volume 2, pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TH Pham, P.L.H. End-to-End Recurrent Neural Network Models for Vietnamese Named Entity Recognition: Word-Level vs. Character-Level. In Computational Linguistics, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference of the Pacific Association for Computational Linguistics, PACLING 2017, Yangon, Myanmar, 16–18 August 2017; Revised Selected Papers; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 781, p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Athavale, V.; Bharadwaj, S.; Pamecha, M.; Prabhu, A.; Shrivastava, M. Towards deep learning in hindi ner: An approach to tackle the labelled data scarcity. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.09756. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.09756 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Jones, C.L.; Bridges, R.A.; Huffer, K.M.; Goodall, J.R. Towards a relation extraction framework for cyber-security concepts. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Cyber and Information Security Research Conference, Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 7–9 April 2015; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Lal, R.; Finin, T.; Joshi, A. Extracting cybersecurity related linked data from text. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Seventh International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), Irvine, CA, USA, 16–18 September 2013; pp. 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M. Discriminative training methods for hidden markov models: Theory and experiments with perceptron algorithms. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; Volume 10, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mulwad, V.; Li, W.; Joshi, A.; Finin, T.; Viswanathan, K. Extracting information about security vulnerabilities from web text. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT), Lyon, France, 22–27 August 2011; Volume 3, pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, N.; Bridges, R.A.; Iannacone, M.D.; Czejdo, B.; Perez, N.; Goodall, J.R. Pace: Pattern accurate computationally efficient bootstrapping for timely discovery of cyber-security concepts. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Miami, FL, USA, 4–7 December 2013; Volume 2, pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, R.A.; Huffer, K.M.; Jones, C.L.; Iannacone, M.D.; Goodall, J.R. Cybersecurity Automated Information Extraction Techniques: Drawbacks of Current Methods, and Enhanced Extractors. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, Y. A primer on neural network models for natural language processing. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2016, 57, 345–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Mohamed, A.; Hinton, G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (Icassp), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 6645–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks: ICANN’99, Edinburgh, UK, 7–10 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lample, G.; Ballesteros, M.; Subramanian, S.; Kawakami, K.; Dyer, C. Neural architectures for named entity recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.01360. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.01360 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Tjong Kim Sang, E.F.; Buchholz, S. Introduction to the CoNLL-2000 shared task: Chunking. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Learning Language in Logic and the 4th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–14 September 2000; Volume 7, pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, N. CRFsuite: A fast implementation of Conditional Random Fields (CRFs). 2007. Available online: http://www.chokkan.org/software/crfsuite/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Xu, Y.; Mou, L.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Peng, H.; Jin, Z. Classifying relations via long short term memory networks along shortest dependency paths. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 1785–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Miwa, M.; Bansal, M. End-to-end relation extraction using lstms on sequences and tree structures. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.00770. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1601.00770 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Chang, B.; Sui, Z.; Li, S. Reading and thinking: Re-read lstm unit for textual entailment recognition. In Proceedings of the COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, Osaka, Japan, 11–16 December 2016; pp. 2870–2879. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, M.; Weber, L.; Neves, M.; Wiegandt, D.L.; Leser, U. Deep learning with word embeddings improves biomedical named entity recognition. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, i37–i48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, H.-L. Implementing the Viterbi algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1995, 12, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.01991. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.01991 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Werbos, P.J. Others Backpropagation through time: What it does and how to do it. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucco. Available online: https://www.ornl.gov/division/projects/stucco (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- CVE—Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE). Available online: https://cve.mitre.org/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Tjong Kim Sang, E.F.; De Meulder, F. Introduction to the CoNLL-2003 shared task: Language-independent named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the Seventh Conference on Natural Language Learning at HLT-NAACL 2003, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 31 May–1 June 2003; Volume 4, pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Google Code Archive—Long-term storage for Google Code Project Hosting. Available online: https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Natural Language Toolkit—NLTK 3.4.4 documentation. Available online: https://www.nltk.org/ (accessed on 24 July 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).