A High Resolution Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter Implemented with 65 nm FPGA
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Operation Principle of the Proposed DTC
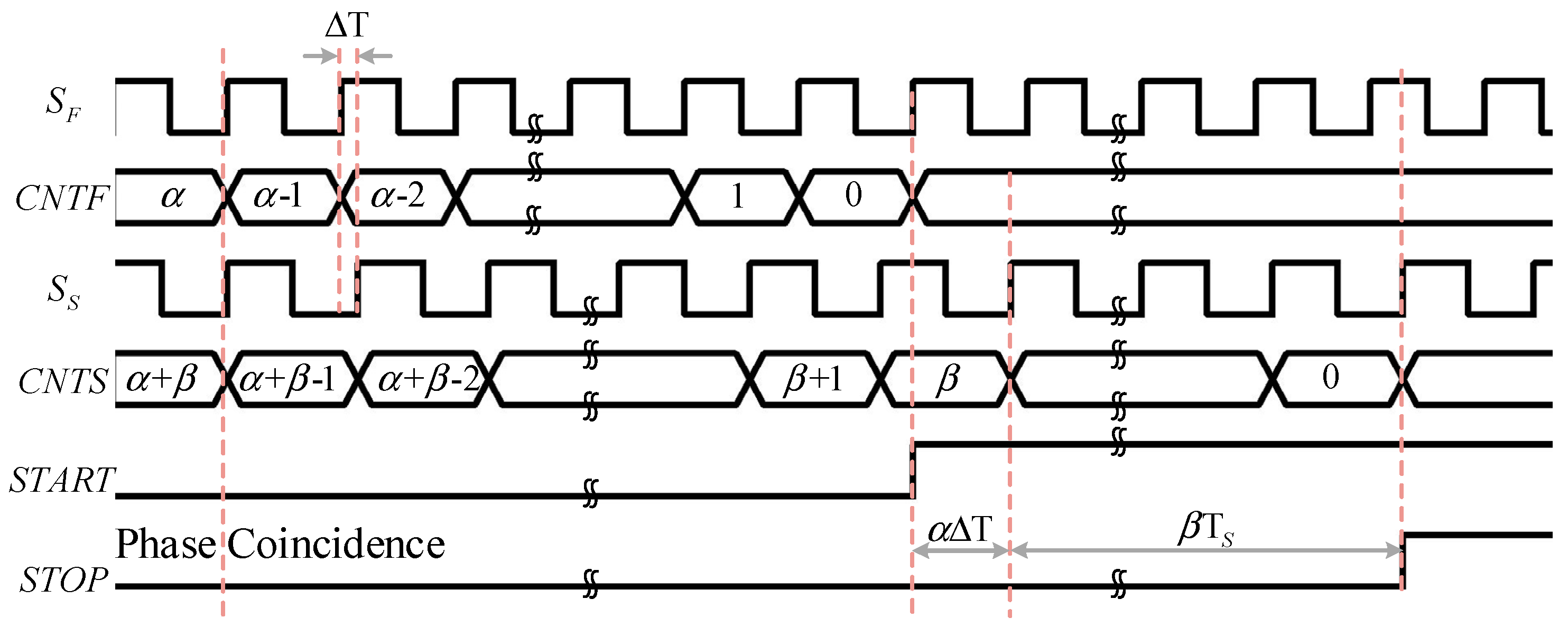
2.1. Principle of Vernier DTC
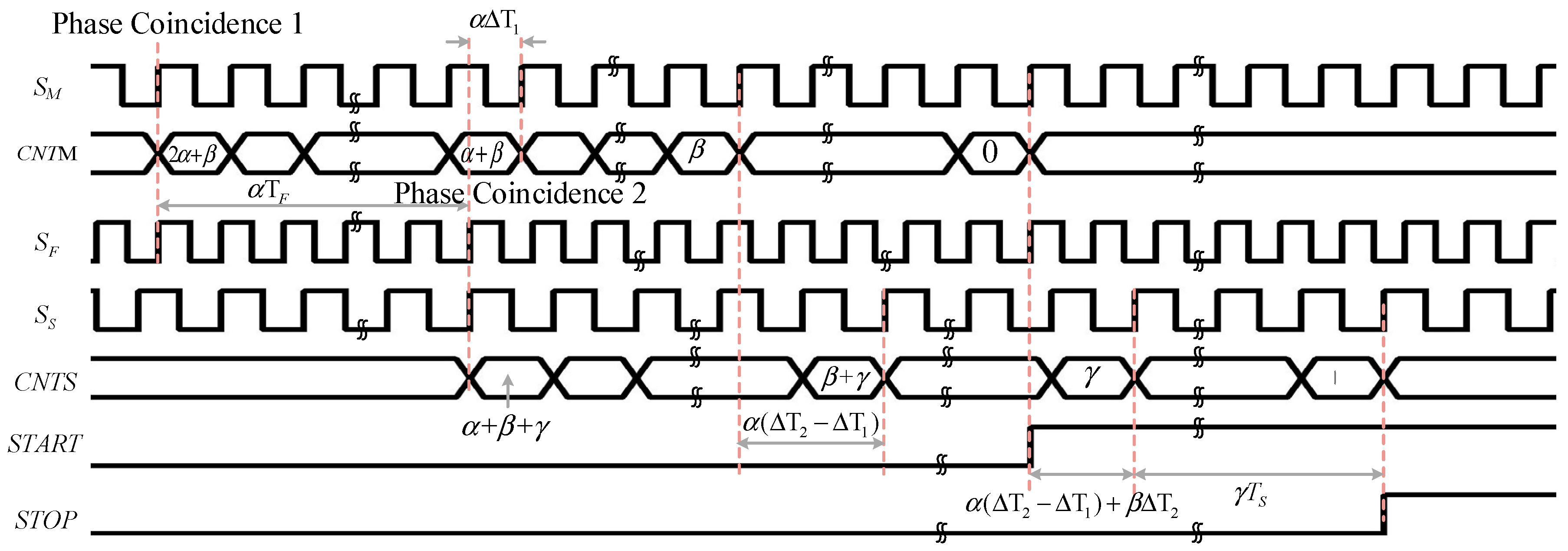
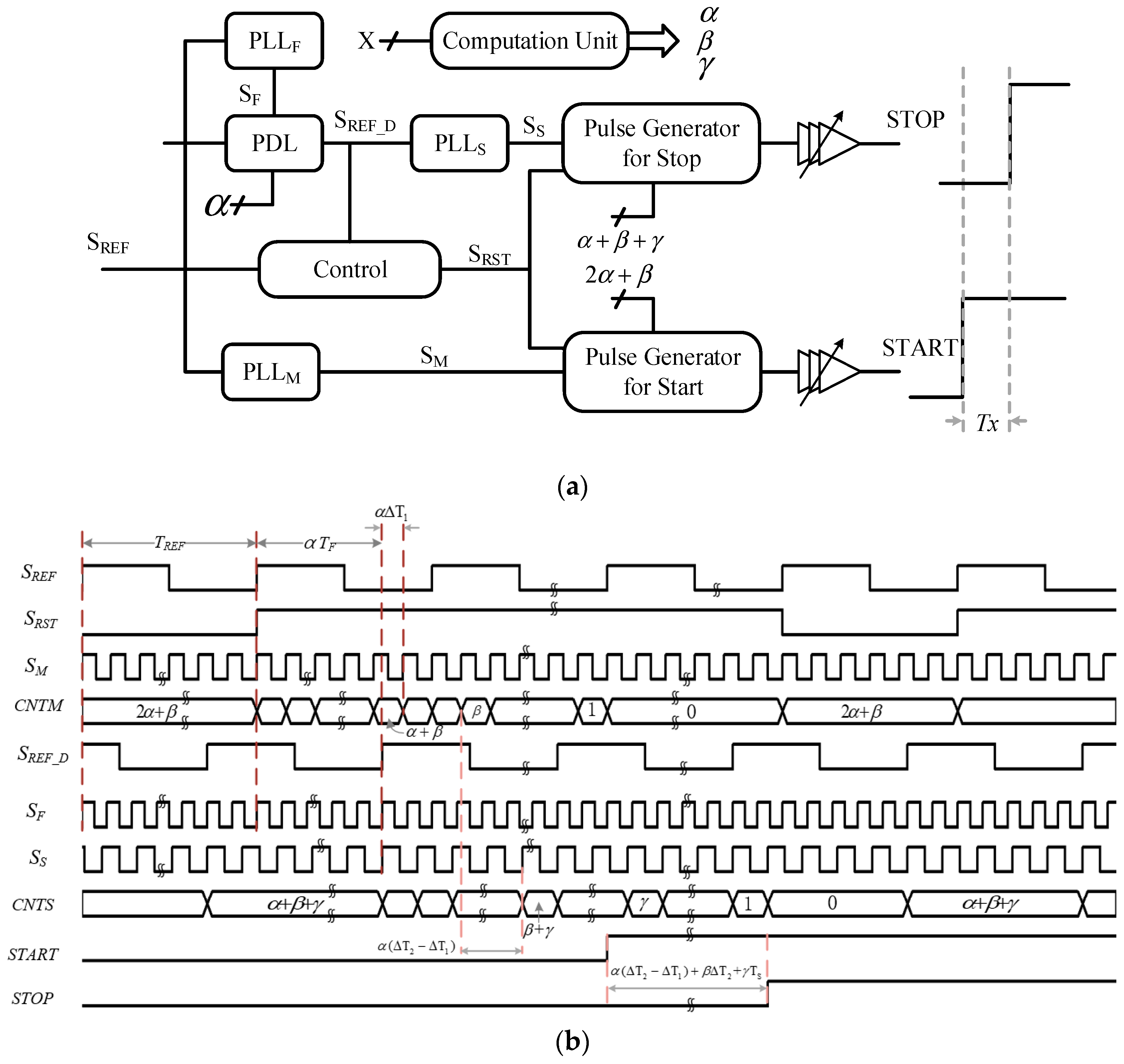
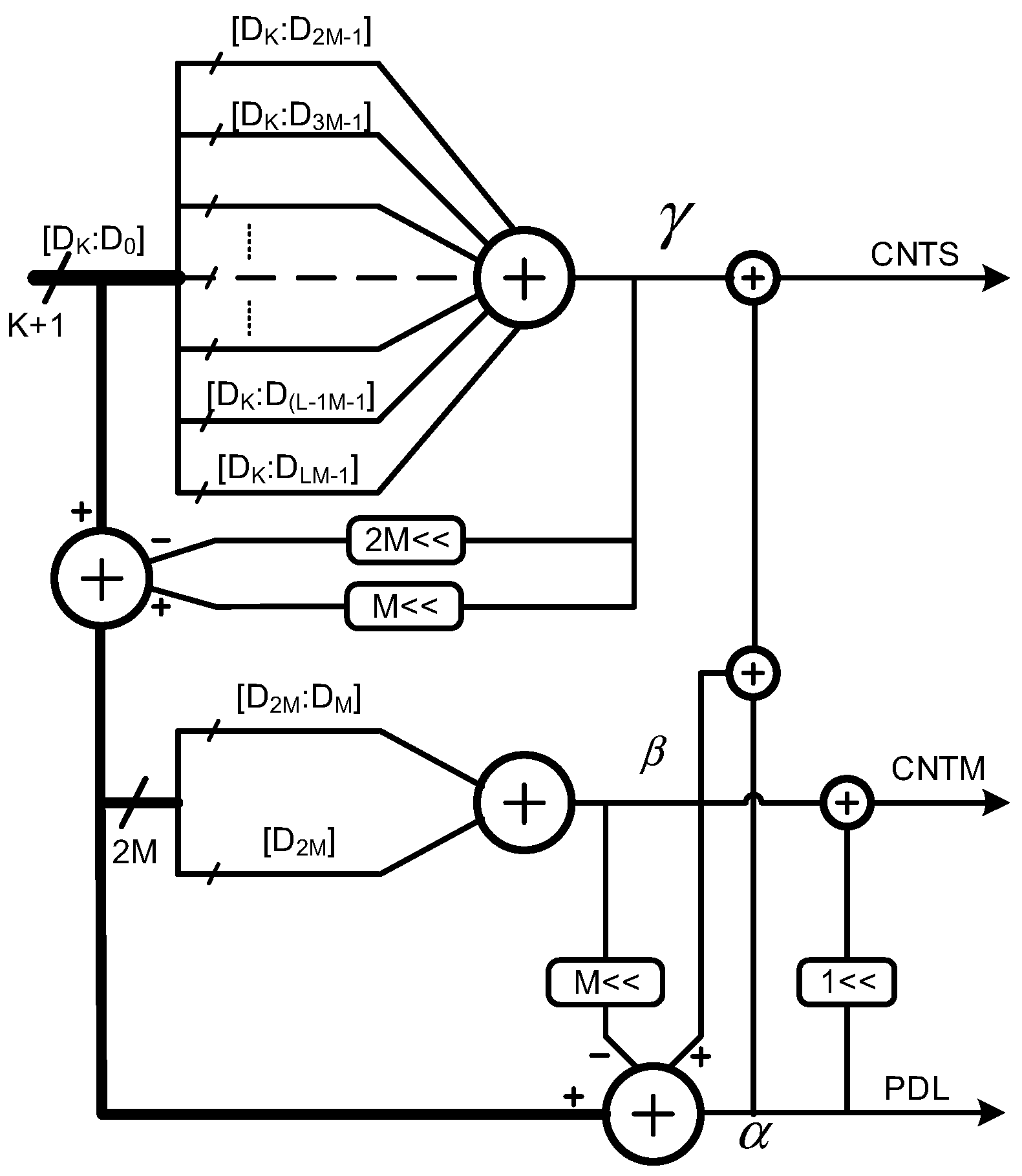
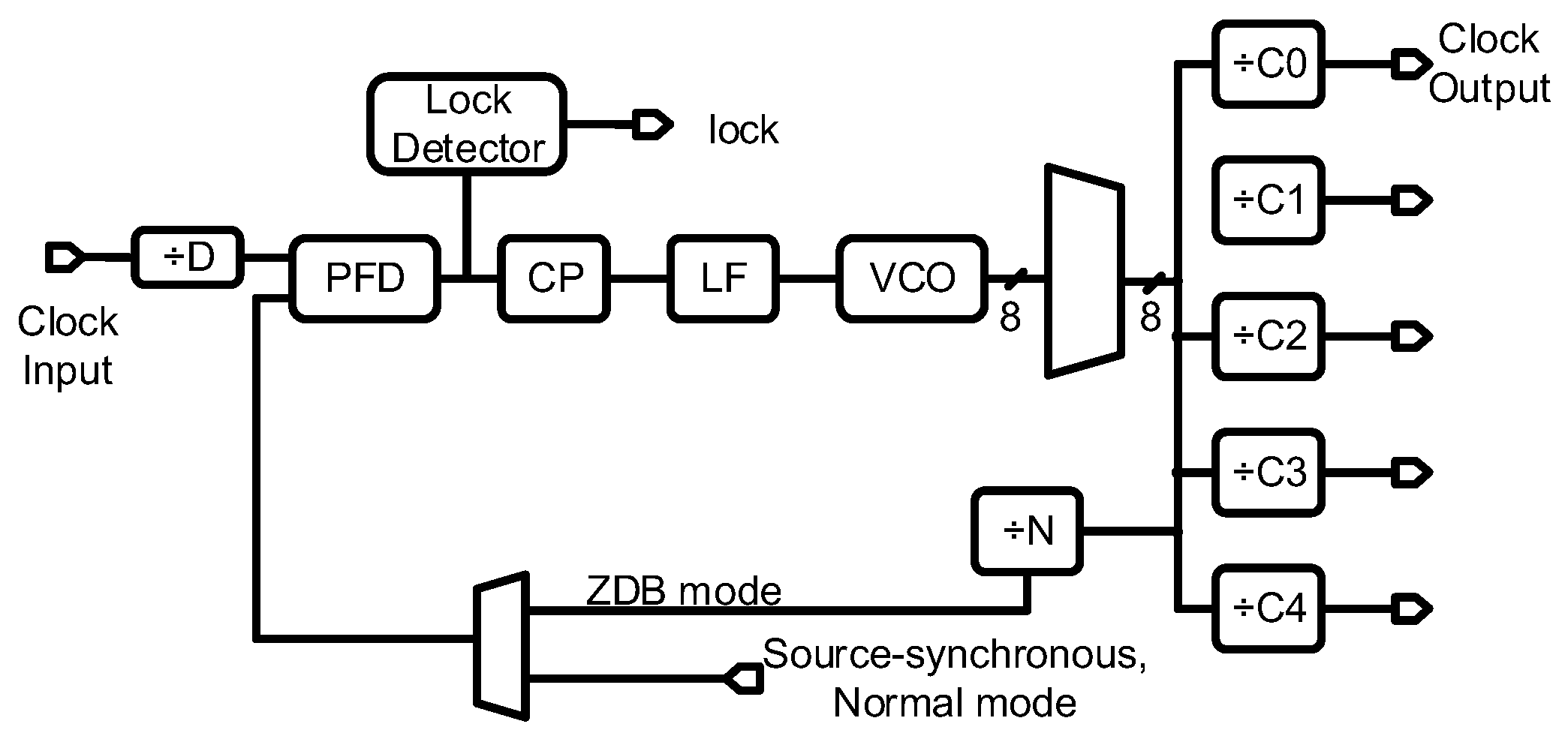
2.2. Circuit Description of 3D Vernier DTC
3. Experimental Results
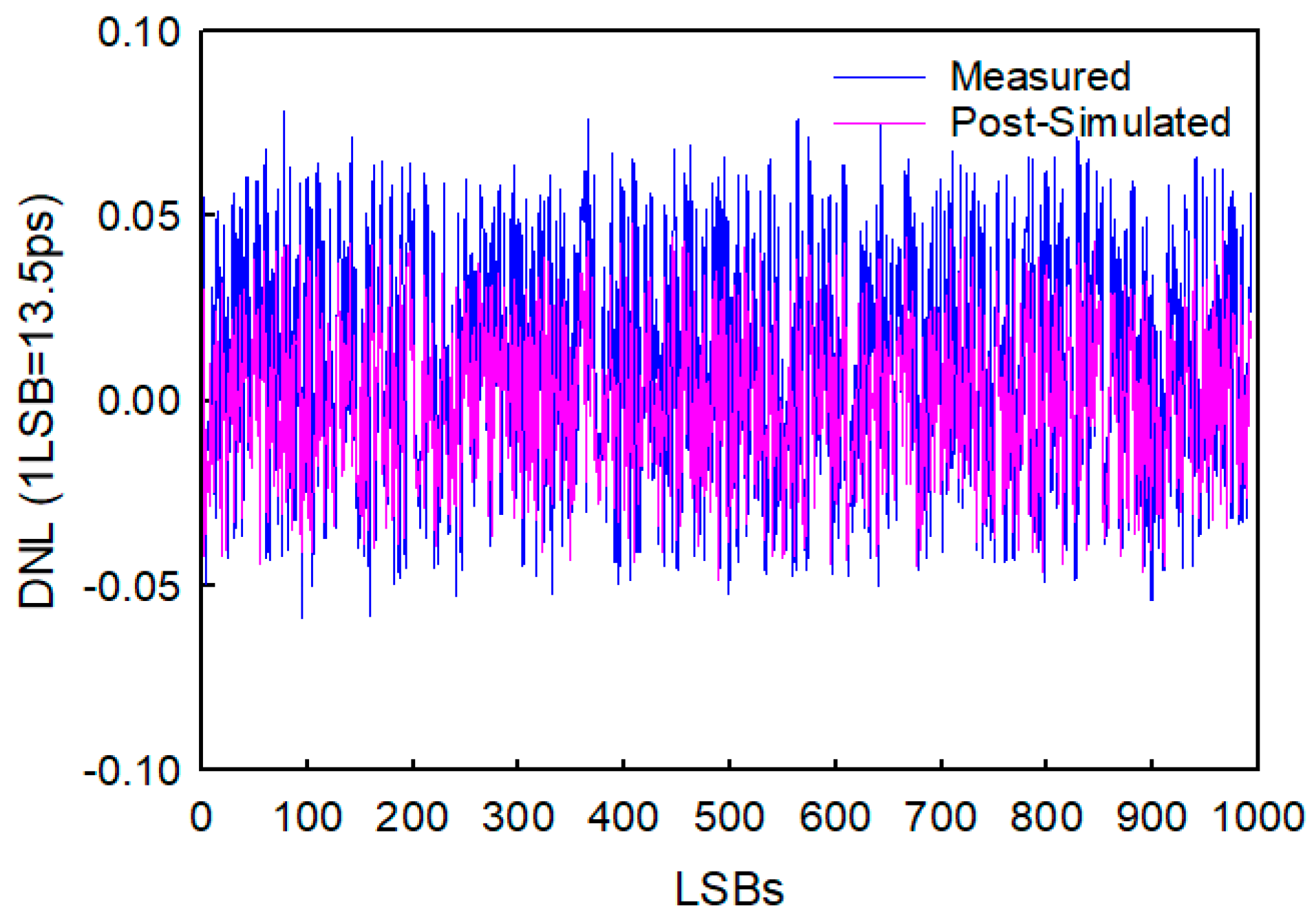
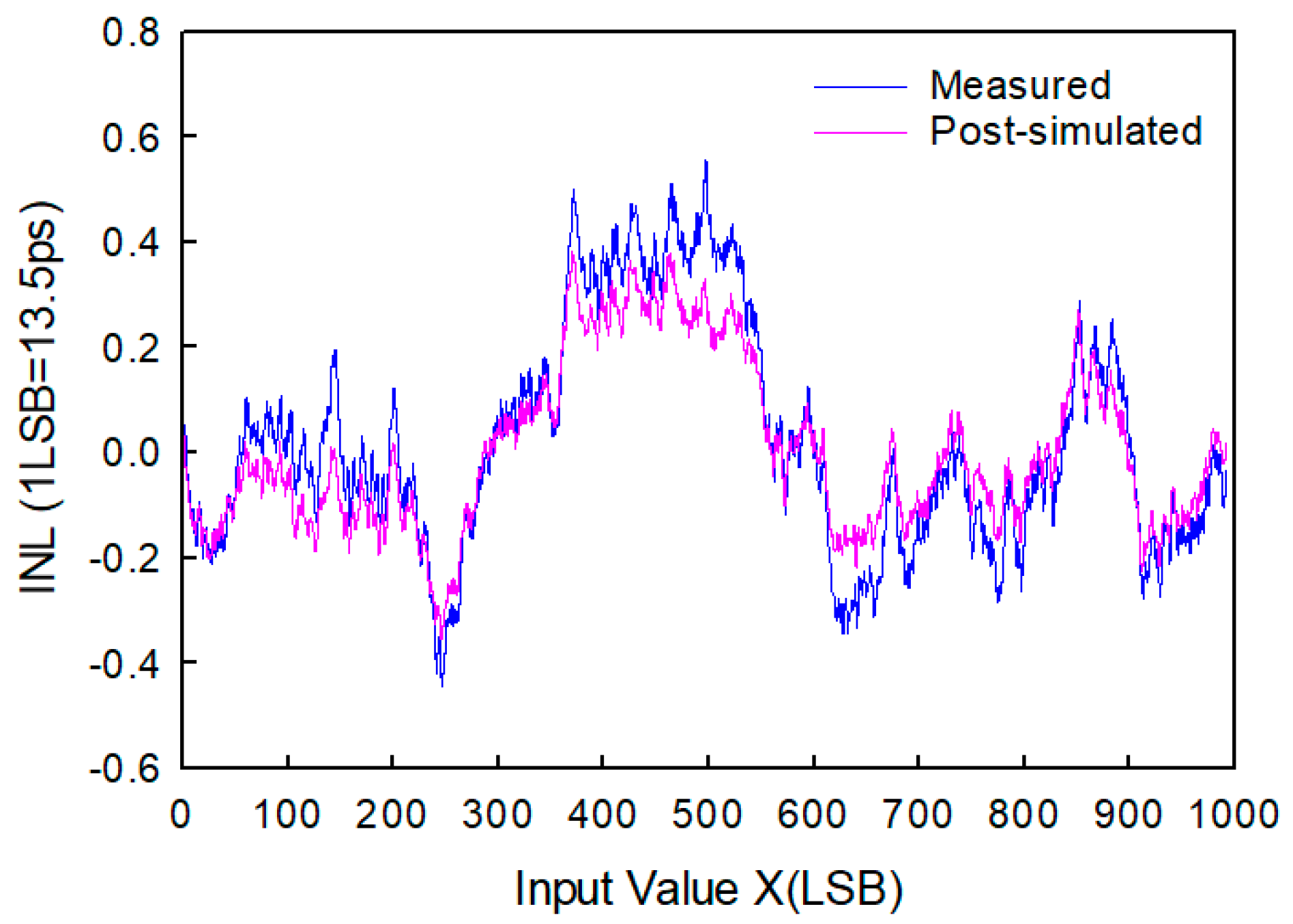
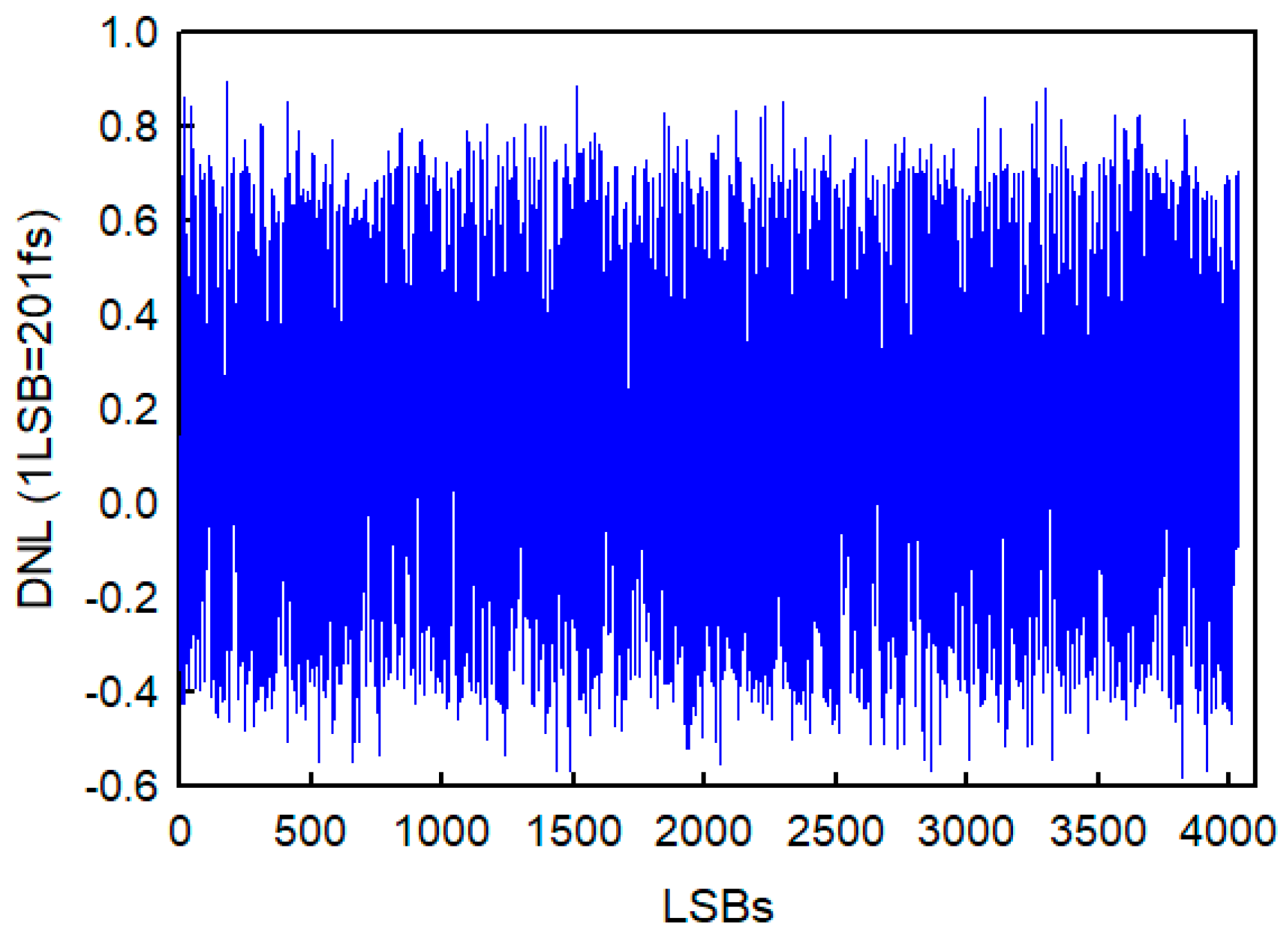
3.1. Implementation with Cyclone IV E FPGA
3.2. Implementation with Stratix III FPGA
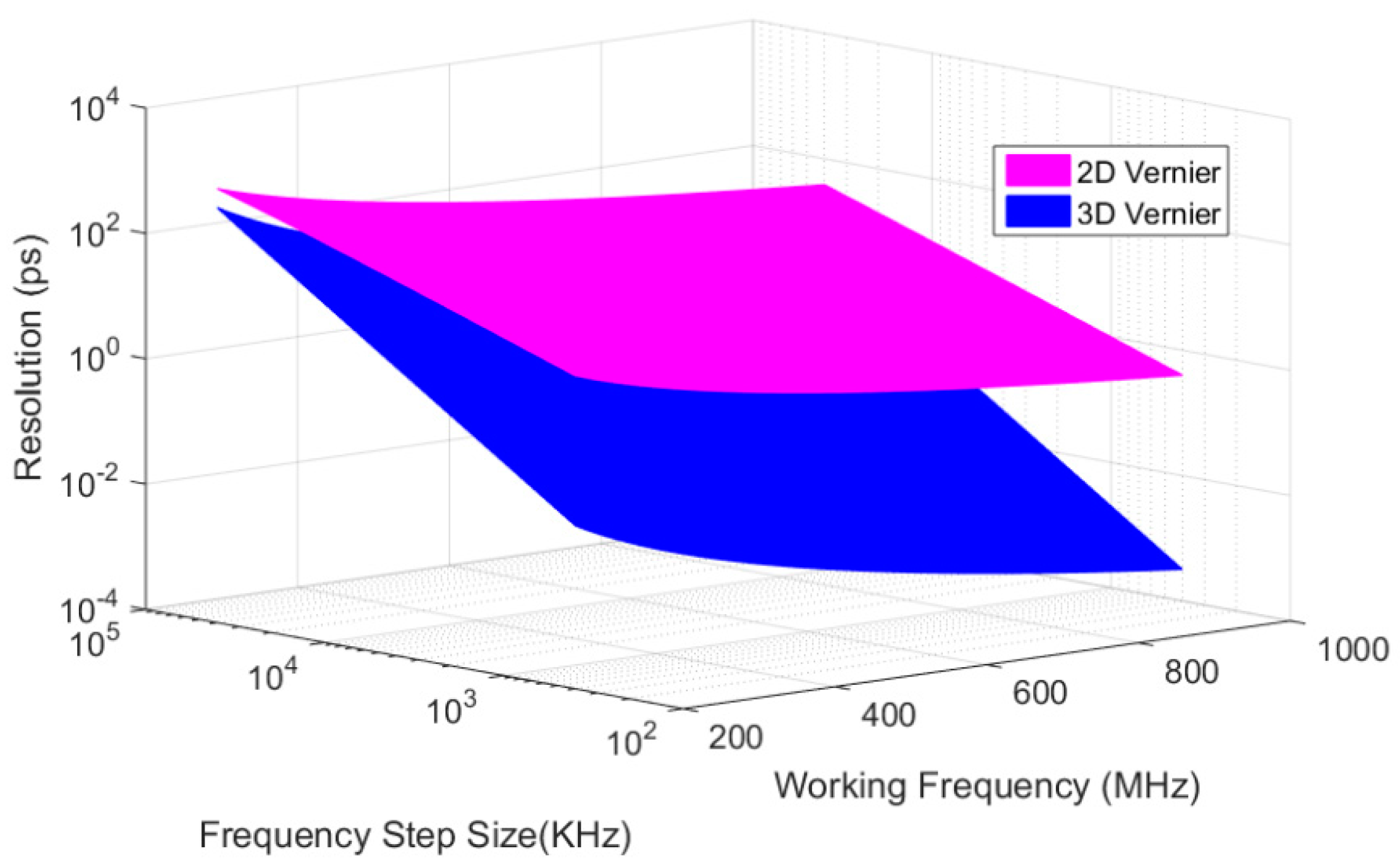
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adabi, E.; Niknejad, A.M. Broadband variable passive delay elements based on an inductance multiplication technique. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 June 2008; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.Y.; Lin, S.M.; Tsao, H.W. Multiple channel programmable timing generators with single cyclic delay line. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004, 53, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, G.; Miller, S.; Stengel, B.; Cafaro, G.; Gradishar, T.; Olson, S.; Hekmann, R. A self-calibrating sub-picosecond resolution digital-totime converter. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–8 June 2007; pp. 2201–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Palattella, C.; Klumperink, E.A.; Ru, J.Z.; Nauta, B. A sensitive method to measure the integral nonlinearity of a digital-to-time converter based on phase modulation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2015, 62, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mourabit, A.; Lu, G.N.; Pittet, P.; Birjali, Y.; Lahjomri, F. Low power, high resolution CMOS variable-delay element. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2012, 66, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vornicu, I.; Carmona-Galán, R.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, Á. Time interval generator with 8 ps resolution and wide range for large TDC array characterization. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2016, 87, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Chen, L.; Jin, G. Design of time interval generator based on hybrid counting method. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2016, 832, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Digital-to-Time Converter with 3.93 ps Resolution Implemented on FPGA Chips. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6842–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuji, T.I.; Narumi, N. A 3-ns range, 8-ps resolution, timing generator LSI utilizing Si bipolar gate array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1991, 26, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, B. Realizing a production ATE custom processor and timing IC containing 400 independent low-power and high-linearity timing verniers. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37519), San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–19 February 2004; pp. 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Chen, P.Y.; Lai, J.S.; Chen, Y.J. FPGA vernier digital-to-time converter with 1.58 ps resolution and 59.3 minutes operation range. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Reg. Papers 2010, 57, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepacki, K.; Pawłowski, M.; Szplet, R. Low-jitter wide-range integrated time interval/delay generator based on combination of period counting and capacitor charging. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 025111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahkonen, T.E.; Kostamovaara, J.T. The use of stabilized CMOS delay line for the digitization of short time intervals. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1993, 28, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartus II Version 8.0 Handbook, Volume 2. Design Implementation and Optimization: Section II. Area, Timing, and Power Optimization. Altera Corp. Available online: www.altera.com (accessed on 30 June 2008).
- Quartus II Version 8.0 Handbook, Volume 3. Verification: Section II. Timing Analysis, Altera Corp. Available online: www.altera.com (accessed on 30 June 2008).
- Clock Networks and PLLs in Cyclone IV Devices Altera Corp. Available online: www.altera.com (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- Clock Networks and PLLs in Stratix III Devices. Altera Corp. Available online: www.altera.com (accessed on 31 July 2009).
- Lai, C.M.; Wu, J.M.; Huang, P.C.; Chu, T.S. A scalable direct sampling broadband radar receiver supporting simultaneous digital multi beam array in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2013; pp. 242–243. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. High-resolution digital-to-time converter implemented in an FPGA chip. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cyclone IV E | Stratix III | |
|---|---|---|
| Fabrication Process | 90 nm | 65 nm |
| Input frequency | 5–474 MHz | 5–717 MHz |
| Output frequency | 600–1300 MHz | 600–1600 MHz |
| Input Divisor (D) | 1–512 | 1–512 |
| Feedback Divisor (N) | 1–512 | 1–512 |
| Post scale counter (C) | 1–512 | 1–512 |
| Cyclone IV E DTC | Stratix III | |
|---|---|---|
| Process | 90 nm | 65 nm |
| Input Frequency | 50 MHz | 50 MHz |
| Output Fast Frequency | 160 MHz | 640 MHz |
| Output Medium Frequency | 155 MHz | 635 MHz |
| Output Slow Frequency | 150 MHz | 630 MHz |
| Input Bits | 32 | 48 |
| Theoretical Resolution | 13.44ps | 195fs |
| PLLs | 3 | 3 |
| ALUTs | 344 | 448 |
| Dedicated Logic Registers | 201 | 237 |
| Power Consumption | 160 mW | 210 mW |
| [7] | [8] | [11] | [18] | [19] | This Work | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | 28 nm FPGA | 40 nm FPGA | 65 nm FPGA | 40 nm FPGA | 65 nm ASIC | 90 nm FPGA | 65 nm FPGA |
| Power | - | 196 mW | 681 mW* | 165 mW | 72 mW | 160 mW | 210 mW |
| Principle | VPDL | Dual PLLs | Dual PLLs | VPDL | Dual PLLs | Three PLLs | |
| Working Frequency | 500 MHz | 100.04 MHz | 1025 MHz | 200 MHz | >1 GHz | 160 MHz | 640 MHz |
| Resolution | 10ps | 3.93ps | 1.58ps | 1.02ps | 6.25ps | 13.5ps | 203.3fs |
| Dynamic range | 8 s | 43 s | 59.3 min | 590 ns | 100 ns | 58 ms | 54 s |
| Integrated Linearity (LSB) | −1.09–4.73 | −2.6–2.5 | −0.93–0.75 | −0.35–0.62 | <15 | −0.43–0.58 | −3.8–4.4 ** |
| Integrated Linearity (ps) | −10.9–47.3 | −10.2–9.8 | −1.47–1.19 | −0.36–0.63 | <93.8 | −5.8–7.83 | −0.76–0.88 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, C.; Hu, C.; Wu, J. A High Resolution Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter Implemented with 65 nm FPGA. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132705
Yan C, Hu C, Wu J. A High Resolution Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter Implemented with 65 nm FPGA. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132705
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Chenggang, Chen Hu, and Jianhui Wu. 2019. "A High Resolution Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter Implemented with 65 nm FPGA" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132705
APA StyleYan, C., Hu, C., & Wu, J. (2019). A High Resolution Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter Implemented with 65 nm FPGA. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132705




