Characterisation of the Material and Mechanical Properties of Atomic Force Microscope Cantilevers with a Plan-View Trapezoidal Geometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Euler Beam Equation
1.2. Torque Produced by the Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Tip
1.3. Determination of the Young’s Modulus and Spring Constant of FastScan AFM Cantilevers
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
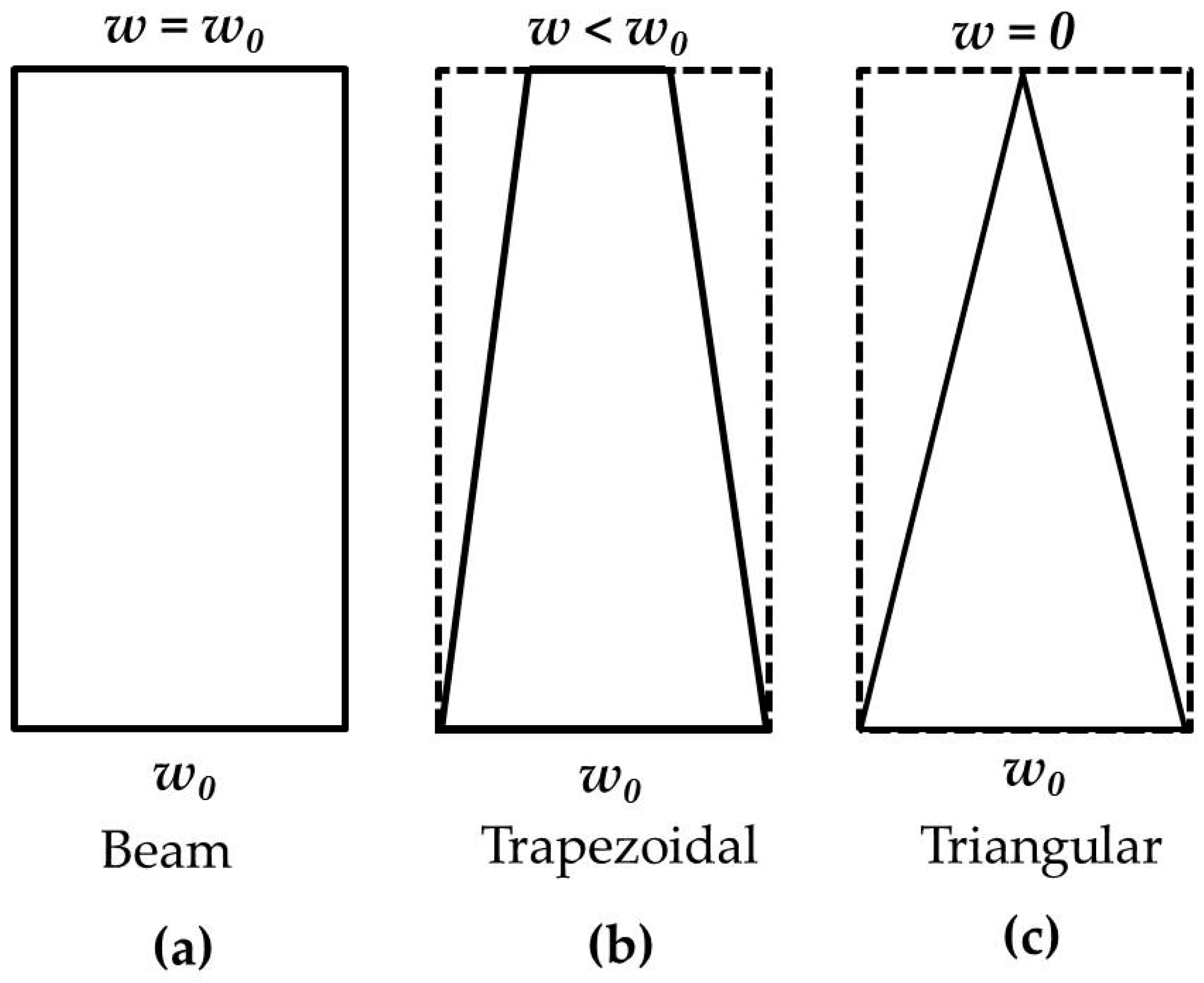
3.1. Correction Factor for Euler Beam Equation for Plan-View Trapezoidal Cantilevers
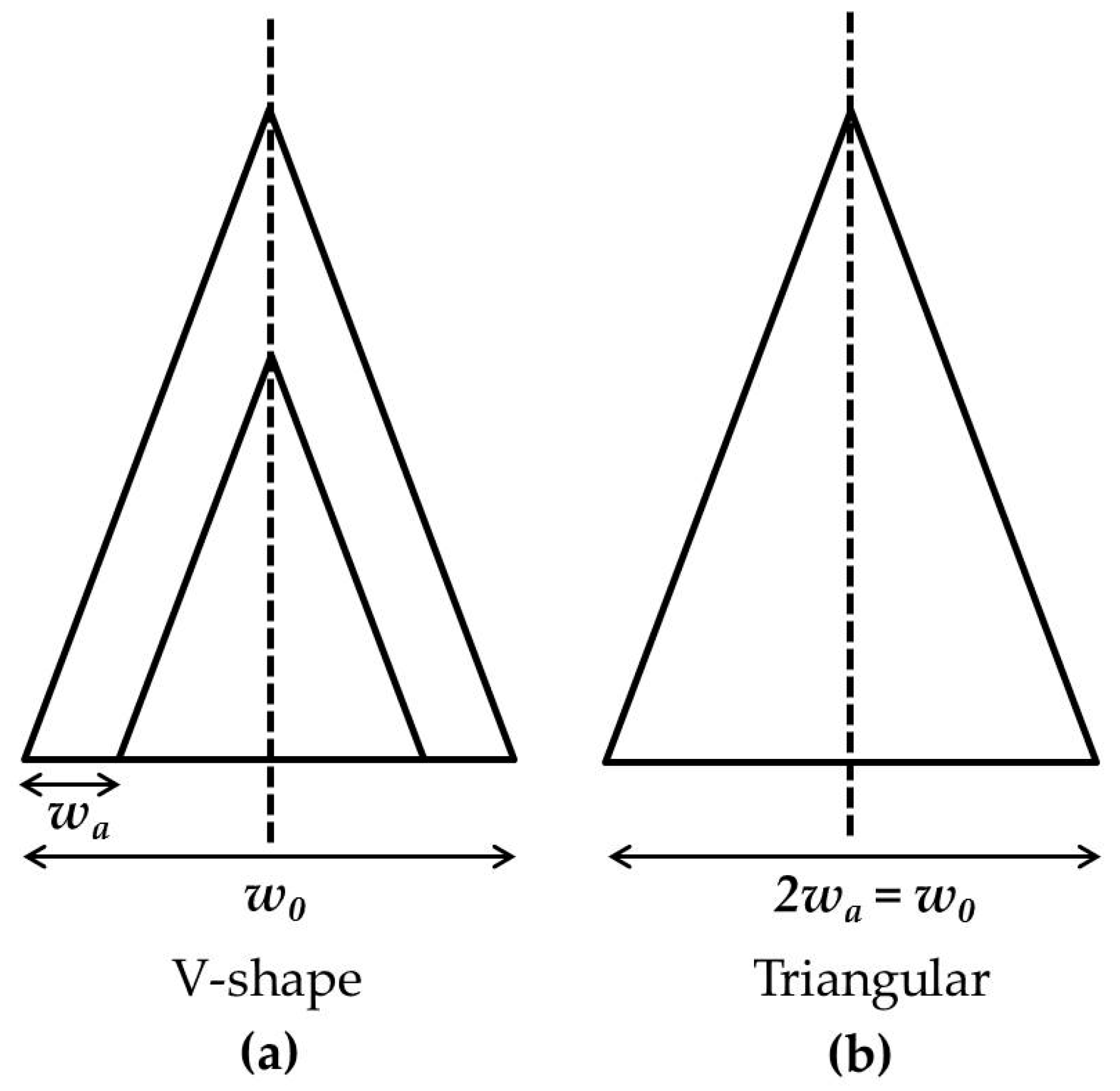
3.2. Deriving Solutions to the Torque Correction Factor for Plan-View Triangular and Trapezoidal Cantilevers
3.3. Application of Derived Expressions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sader, J.E.; White, L. Theoretical analysis of the static deflection of plates for atomic force microscope applications. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steffens, C.; Leite, F.L.; Bueno, C.C.; Manzoli, A.; Herrmann, P.S.D.P. atomic force microscopy as a tool applied to nano/biosensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 8278–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasey, R.; Sharma, S.; Craig, J.E.; Gibson, C.T.; Ebner, A.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Voelcker, N.H. Detecting protein aggregates on untreated human tissue samples by atomic force microscopy recognition imaging. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.C.N.; Deda, D.K.; Da Róz, A.L.; Prado, R.A.; Carvalho, C.C.; Viviani, V.; Leite, F.L. Nanobiosensors based on chemically modified afm probes: a useful tool for metsulfuron-methyl detection. Sensors 2013, 13, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasey, R.; Sharma, S.; Gibson, C.T.; Craig, J.E.; Ebner, A.; Becker, T.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Voelcker, N.H. Atomic force microscopy-based antibody recognition imaging of proteins in the pathological deposits in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdunek, A.; Kurenda, A. Determination of the elastic properties of tomato fruit cells with an atomic force microscope. Sensors 2013, 13, 12175–12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, J.A.A.; Gibson, C.T.; Mapledoram, L.D.; Huson, M.G.; Myhra, S.; Pham, D.K.; Sofield, C.J.; Turner, P.S.; Watson, G.S. Atomic force microscopy analysis of wool fibre surfaces in air and under water. Micron 2000, 31, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goreham, R.V.; Thompson, V.C.; Samura, Y.; Gibson, C.T.; Shapter, J.G.; Köper, I. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with tethered bilayer lipid membranes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 5868–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.R.; Lovitt, R.W.; Wright, C.J. Application of atomic force microscopy to the study of micromechanical properties of biological materials. Biotechnol. Lett. 2000, 22, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.J.; Slattery, A.D.; Stapleton, A.J.; Shapter, J.G.; Gibson, C.T. Accurate thickness measurement of graphene. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrik, N.V.; Sepaniak, M.J.; Datskos, P.G. Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 2229–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, R.; Grattarola, M.; Butt, H.J.; Skladal, P. Micromechanical cantilever-based biosensors. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2001, 79, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, J.P.; Manne, S.; Bocek, D.; Hansma, P.K. A nondestructive method for determining the spring constant of cantilevers for scanning force microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sader, J.E. Parallel beam approximation for V-shaped atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1995, 66, 4583–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, M.A.; McFarland, A.W.; Colton, J.S.; Bottomley, L.A. A method for calculating the spring constant of atomic force microscopy cantilevers with a nonrectangular cross section. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader, J.E.; Chon, J.W.M.; Mulvaney, P. Calibration of rectangular atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1999, 70, 3967–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sader, J.E.; Sanelli, J.A.; Adamson, B.D.; Monty, J.P.; Wei, X.; Crawford, S.A.; Friend, J.R.; Marusic, I.; Mulvaney, P.; Bieske, E.J. Spring constant calibration of atomic force microscope cantilevers of arbitrary shape. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sader, J.E.; Friend, J.R. Calibration of atomic force microscope cantilevers using only their resonant frequency and quality factor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.E.; Borgani, R.; Gibson, C.T.; Haviland, D.B.; Higgins, M.J.; Kilpatrick, J.I.; Lu, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Shearer, C.J.; Slattery, A.D.; et al. A virtual instrument to standardise the calibration of atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 093711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, A.D.; Quinton, J.S.; Gibson, C.T. Atomic force microscope cantilever calibration using a focused ion beam. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 285704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovko, D.S.; Haschke, T.; Wiechert, W.; Bonaccurso, E. Nondestructive and noncontact method for determining the spring constant of rectangular cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 043705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.; Schaffer, T.E.; Chynoweth, K.M.; Wigton, M.; Simmonds, R.W.; Lang, K.M. Practical implementation of dynamic methods for measuring atomic force microscope cantilever spring constants. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lévy, R.; Maaloum, M. Measuring the spring constant of atomic force microscope cantilevers: Thermal fluctuations and other methods. Nanotechnology 2002, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohler, B. Cantilever spring constant calibration using laser Doppler vibrometry. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 063701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, R.S.; Pratt, J.R. Accurate and precise calibration of AFM cantilever spring constants using laser Doppler vibrometry. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 375702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, A.D.; Blanch, A.J.; Quinton, J.S.; Gibson, C.T. Accurate measurement of atomic force microscope cantilever deflection excluding tip-surface contact with application to force calibration. Ultramicroscopy 2013, 131, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, N.A.; Chen, X.; Hodges, C.S.; Matei, G.A.; Thoreson, E.J.; Roberts, C.J.; Davies, M.C.; Tendler, S.J.B. Comparison of calibration methods for atomic-force microscopy cantilevers. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, A.D.; Blanch, A.J.; Quinton, J.S.; Gibson, C.T. Calibration of atomic force microscope cantilevers using standard and inverted static methods assisted by FIB-milled spatial markers. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 015710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, C.A.; Seah, M.P. Improved methods and uncertainty analysis in the calibration of the spring constant of an atomic force microscope cantilever using static experimental methods. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.-K. Accurate determination of spring constant of atomic force microscope cantilevers and comparison with other methods. Measurement 2010, 43, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpson, P.J.; Clifford, C.A.; Hedley, J. Quantitative analytical atomic force microscopy: A cantilever reference device for easy and accurate AFM spring-constant calibration. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, R.S.; Reitsma, M.G. Precise atomic force microscope cantilever spring constant calibration using a reference cantilever array. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 086101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senden, T.; Ducker, W. Experimental determination of spring constants in atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, C.T.; Johnson, D.J.; Anderson, C.; Abell, C.; Rayment, T. Method to determine the spring constant of atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatil, N.R.; Homer, M.E.; Picco, L.; Martin, P.G.; Payton, O.D. A calibration method for the higher modes of a micro-mechanical cantilever. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 223101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payam, A.F.; Trewby, W.; Voitchovsky, K. Determining the spring constant of arbitrarily shaped cantilevers in viscous environments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 083101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cafolla, C.; Payam, A.F.; Voitchovsky, K. A non-destructive method to calibrate the torsional spring constant of atomic force microscope cantilevers in viscous environments. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 154502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labuda, A.; Cao, C.; Walsh, T.; Meinhold, J.; Proksch, R.; Sun, Y.; Filleter, T. Static and dynamic calibration of torsional spring constants of cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 093701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoren, P.-A.; Borgani, R.; Forcheimer, D.; Haviland, D.B. Calibrating torsional eigenmodes of micro-cantilevers for dynamic measurement of frictional forces. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sader, J.E. Susceptibility of atomic force microscope cantilevers to lateral forces. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sader, J.E.; Sader, R.C. Susceptibility of atomic force microscope cantilevers to lateral forces: Experimental verification. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3195–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Kodera, N.; Yamamoto, D.; Miyagi, A.; Taniguchi, M.; Yamashita, H. High-speed AFM and nano-visualization of biomolecular processes. Pflug. Arch. 2008, 456, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, A.D.; Blanch, A.J.; Ejov, V.; Quinton, J.S.; Gibson, C.T. Spring constant calibration techniques for next-generation fast-scanning atomic force microscope cantilevers. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 335705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.; Prorok, B.C. Tailoring beam mechanics towards enhancing detection of hazardous biological species. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, S. A new sensitivity improving approach for mass sensors through integrated optimization of both cantilever profile and cross-section. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longqi, X.; Guiming, Z.; Libo, Z.; Yulong, Z.; Zhuangde, J.; Rahman, H.; Hongyan, W.; Zhigang, L. A fluid viscosity sensor with resonant trapezoidal micro cantilever. IEEE Int. Symp. Assem. Manuf. (ISAM) 2013, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.-B.; Xu, L.-Q.; Zhang, G.-M.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-P.; Liu, Z.-G.; Jiang, Z.-D. A trapezoidal cantilever density sensor based on MEMS technology. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2013, 14, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kwon, S.-R.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, F.-G.; Jiang, X. A trapezoidal flexoelectric accelerometer. J. Intell Mater. Syst Struct. 2014, 25, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-P.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.-Y.; Zhang, J.-M.; Dorantes-Gonzalez, D.J.; Fu, X.; Hu, X.-D. Calibration of the effective spring constant of ultra-short cantilevers for a high-speed atomic force microscope. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, C.J.; Senden, T.J. Characterisation of the mechanical properties of thin film cantilevers with the atomic force microscope. Mater Sci. Forum 1995, 189, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, K.E.; Gleim, P.S.; Yeakley, R.L.; Runyan, W.R. Some properties of vapor deposited silicon nitride films using the SiH4-NH3-H2 system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1967, 114, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.C.; Muller, R.S. Measurement of Young’s modulus on microfabricated structures using a surface profiler. Proc. IEEE Micro. Electro. Mechanical Syst. 1990, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Sader, J.E.; Larson, I.; Mulvaney, P.; White, L.R. Method for the calibration of atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1995, 66, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Akamine, S.; Carver, T.E.; Quate, C.F. Microfabrication of cantilever styli for the atomic force microscope. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 1990, 8, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.A.; Ducker, W.A.; Sader, J.E. Influence of atomic force microscope cantilever tilt and induced torque on force measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 064513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumpson, P.J.; Hedley, J. Accurate analytical measurements in the atomic force microscope: A microfabricated spring constant standard potentially traceable to the SI. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerres, R.E. Machine elements that absorb and store energy. In Standard Handbook of Machine Design; Shigley, J., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, C.T.; Myhra, S.; Watson, G.S.; Huson, M.G.; Pham, D.K.; Turner, P.S. Effects of aqueous exposure on the mechanical properties of wool fibers—Analysis by atomic force microscopy. Text. Res. J. 2001, 71, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alici, G.; Higgins, M. Normal stiffness calibration of microfabricated tri-layer conducting polymer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 065013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, S. Characterization of silicon nitride micromechanical cantilevers and bridges. J. Micro/Nano Process. Technol. 2013, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]

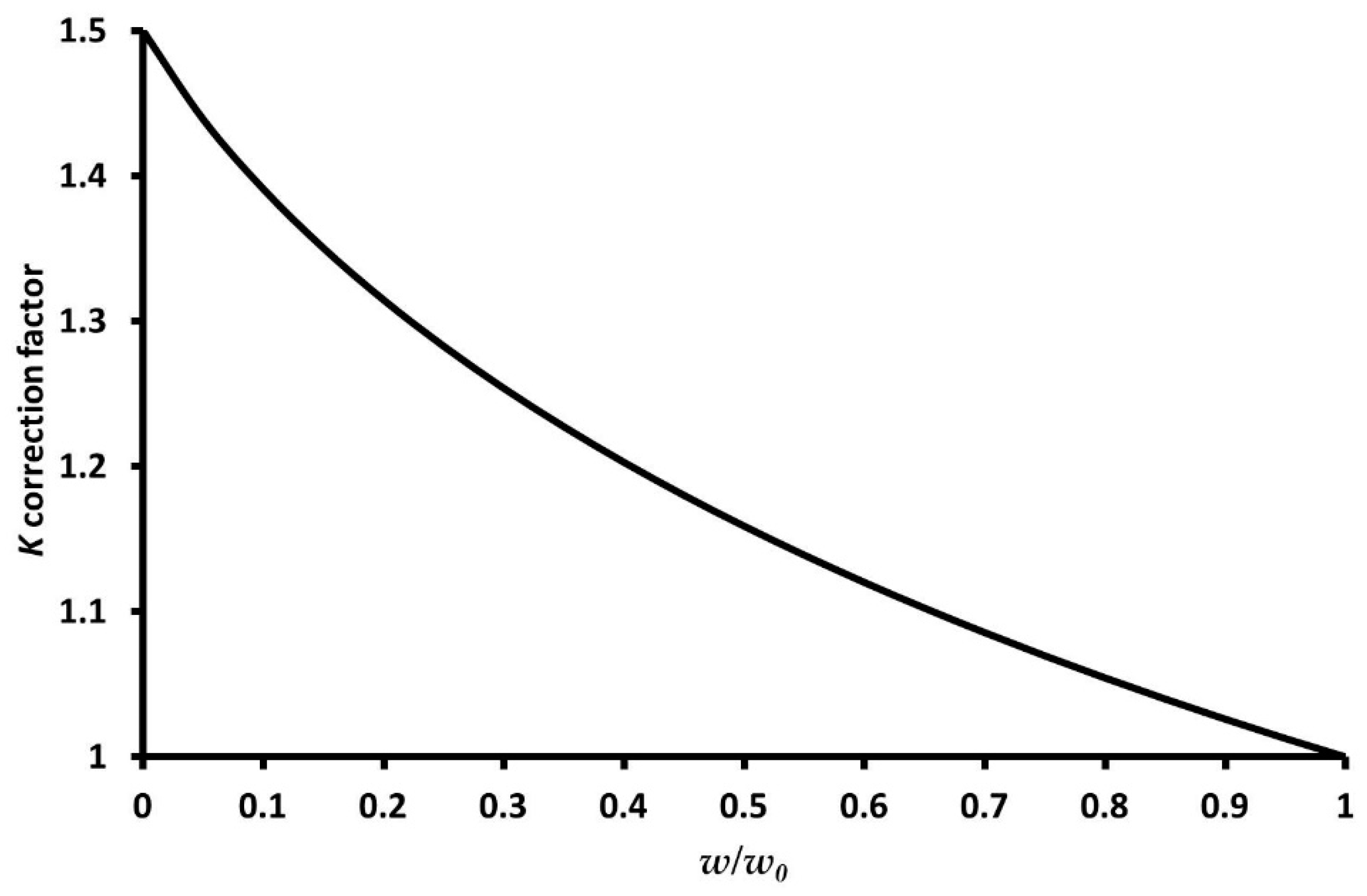
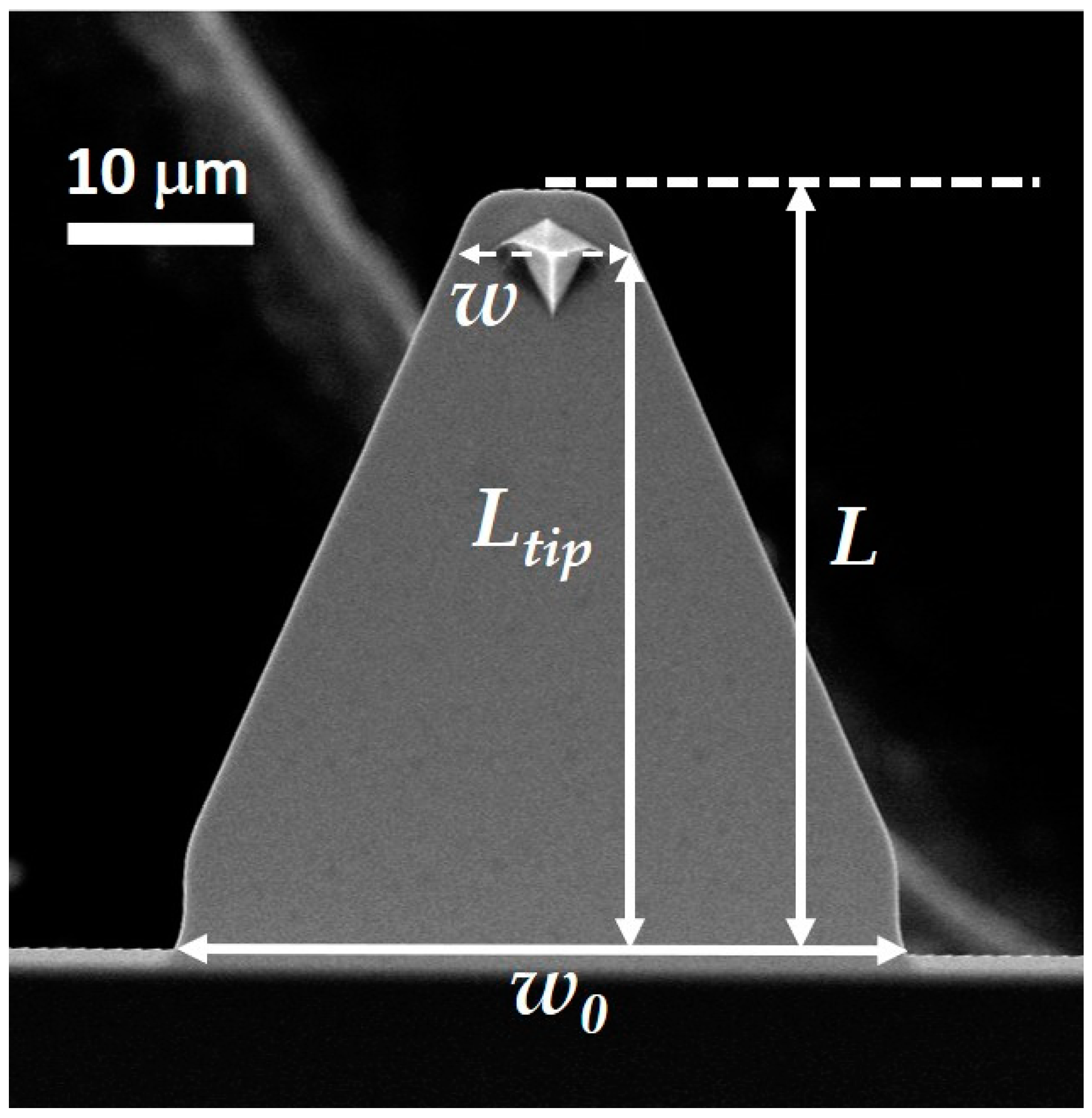
| AFM Probe | Spring Constant, ktip (N/m) | w0 (μm) | w (μm) | w/w0 | Ltip (μm) | L (μm) | t (μm) | D (μm) | D/Ltip | Tbeam | Ttri | Ttrap. | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSA1 | 15.81 * | 30.53 | 10.7 # | 0.35 | 24.46 | 26.61 | 0.57 | 4.55 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.23 |
| FSA2 | 14.24 | 31.86 | 10.7 | 0.34 | 25.60 | 28.46 | 0.56 | 5.03 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.23 |
| FSA3 | 17.05 | 31.36 | 10.7 | 0.34 | 23.06 | 25.82 | 0.60 | 7.03 | 0.30 | 0.9 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 1.23 |
| FSA4 | 11.89 | 30.86 | 10.7 | 0.35 | 24.83 | 26.81 | 0.52 | 6.11 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 1.23 |
| FSA5 | 21.4 | 32.1 | 11.4 | 0.36 | 23.2 | 26.7 | 0.64 | 3.87 | 0.17 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.22 |
| FSA6 | 32.3 | 31.6 | 13.0 | 0.41 | 20.5 | 26.6 | 0.64 | 4.72 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.91 | 1.20 |
| FSA7 | 18.5 | 31.8 | 10.6 | 0.33 | 22.9 | 27.0 | 0.64 | 3.30 | 0.14 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 1.24 |
| FSB1 | 2.24 | 33.6 | 8.80 | 0.26 | 28.8 | 30.9 | 0.37 | 5.60 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.28 |
| FSB2 | 2.05 | 33.9 | 8.81 | 0.26 | 29.1 | 31.1 | 0.36 | 4.82 | 0.17 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.28 |
| FSC1 | 0.938 | 43.5 | 9.10 | 0.21 | 42.6 | 44.9 | 0.35 | 6.79 | 0.16 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.31 |
| FSC2 | 0.916 | 43.9 | 9.14 | 0.21 | 42.4 | 44.7 | 0.34 | 6.75 | 0.16 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 1.31 |
| AFM Probe | Spring Constant (N/m) | Effective Young’s Modulus of Cantilever (GPa) | Silicon Nitride Young’s Modulus of Cantilever (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FSA1 | 15.81 | 201.3 | 229.2 |
| FSA2 | 14.24 | 210.1 | 240.6 |
| FSA3 | 17.05 | 151.9 | 168.3 |
| FSA4 | 11.89 | 216.4 | 238.9 |
| FSA5 | 21.4 | 155 | 171 |
| FSA6 | 32.3 | 161 | 178 |
| FSA7 | 18.5 | 132 | 143 |
| FSB1 | 2.24 | 161 | 177 |
| FSB2 | 2.05 | 164 | 181 |
| FSC1 | 0.938 | 204 | 230 |
| FSC2 | 0.916 | 212 | 241 |
| AFM Probe | Spring Constant (N/m) | Sader Indirect Method (N/m) |
|---|---|---|
| FSA1 | 15.81 | 15.5 |
| FSA2 | 14.24 | 14.1 |
| FSA3 | 17.05 | 19.0 |
| FSA4 | 11.89 | 11.9 |
| FSA5 | 21.4 | 19.1 |
| FSA6 | 32.3 | 27.3 |
| FSA7 | 18.5 | 19.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slattery, A.D.; Blanch, A.J.; Shearer, C.J.; Stapleton, A.J.; Goreham, R.V.; Harmer, S.L.; Quinton, J.S.; Gibson, C.T. Characterisation of the Material and Mechanical Properties of Atomic Force Microscope Cantilevers with a Plan-View Trapezoidal Geometry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132604
Slattery AD, Blanch AJ, Shearer CJ, Stapleton AJ, Goreham RV, Harmer SL, Quinton JS, Gibson CT. Characterisation of the Material and Mechanical Properties of Atomic Force Microscope Cantilevers with a Plan-View Trapezoidal Geometry. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132604
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlattery, Ashley D., Adam J. Blanch, Cameron J. Shearer, Andrew J. Stapleton, Renee V. Goreham, Sarah L. Harmer, Jamie S. Quinton, and Christopher T. Gibson. 2019. "Characterisation of the Material and Mechanical Properties of Atomic Force Microscope Cantilevers with a Plan-View Trapezoidal Geometry" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132604
APA StyleSlattery, A. D., Blanch, A. J., Shearer, C. J., Stapleton, A. J., Goreham, R. V., Harmer, S. L., Quinton, J. S., & Gibson, C. T. (2019). Characterisation of the Material and Mechanical Properties of Atomic Force Microscope Cantilevers with a Plan-View Trapezoidal Geometry. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132604






