Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Tensegrity
- T—the structure is a truss,
- S—there is a self-stress state,
- M—there is an infinitesimal mechanism stiffened by the self-stress state,
- D—the extremities of compressed components (struts) do not touch each other and struts constitute a discontinuous set,
- I—the set of compressed components is included inside the set of tensile components,
- C—tensile elements have no rigidity in compression—these are cables.
3. Mathematical Description
4. Results
- —eigenvalues of matrix ,
- —eigenvectors (if any) of corresponding to the zero eigenvalues in responsible for the existence of the mechanism (M),
- —eigenvalues of matrix ,
- —eigenvectors of corresponding to the zero eigenvalues (if any) in responsible for the existence of the self-stress state (S),
- —eigenvalues of matrix with the self-stress taken from the singular value decomposition (SVD).
- truss (T) with five elements and four d.o.f. 5) (Figure 12b).
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuller, R.B. Tensile-Integrity Structures. U.S. Patent 3,063,521, 13 November 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Snelson, K. Continuous Tension, Discontinuous Compression Structures. U.S. Patent 3,169,611, 16 February 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich, D.G. Construction de Reseaux Autotendants. French Patent 1,377,290, 28 September 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, A. An Introduction to Tensegrity; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Motro, R. Tensegrity systems: The state of the art. Int. J. Space Struct. 1992, 7, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motro, R. Tensegrity. Structural Systems for the Future; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hanaor, A. Geometrically rigid double-layer tensegrity grids. Int. J. Space Struct. 1994, 9, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tibert, G. Deployable Tensegrity Structures for Space Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tibert, A.G.; Pellegrino, S. Deployable Tensegrity Masts. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference and Exhibit, Norfolk, VA, USA, 7–10 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.B. Cable-strut systems: Part I—Tensegrity. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1998, 45, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ohsaki, M. Tensegrity Structures. Form, Stability, and Symmetry; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; ISBN 978-4-431-54812-6. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; de Oliveira, M.C. Tensegrity Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; Helton, J.W.; Adhikari, R.; Pinaud, J.P.; Chan, W. An introduction to the mechanics of tensegrity structures. In Handbook of Mechanical Systems Design (Chapter 17); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; Adhikari, R.; Pinaud, J.P.; Chan, W.; Helton, J.W. An Introduction to the Mechanics of Tensegrity Structures. In Proceedings of the 40th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Orlando, FL USA, 4–7 December 2001; pp. 4254–4258. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; Pinaud, J.P.; Mingori, D.L. Dynamics of the shell class of tensegrity structures. J. Franklin Inst. 2001, 338, 255–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E. Deployable Plates Made from Stable-element Class 1 Tensegrity. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2002: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2002; pp. 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; Williamson, D.; Han, J.H. Equilibrium conditions of a class 1 tensegrity structures. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. Spacefl. Mech. 2002, 112, 927–950. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, D.; Skelton, R.E.; Han, J.H. Equilibrium conditions of class 1 tensegrity structures. Revue Francaise de Genie Civil 2003, 7, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilewski, W.; Kłosowska, J.; Obara, P. Applications of tensegrity structures in civil engineering. Procedia Eng. 2015, 111, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, A. Evaluation of Possibilities of Applications of Tensegrity Structures in Bridge Engineering. Ph.D. Thesis, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Tatemichi, I.; Chen, P.S. Optimum shapes of a cable dome structure. Eng. Struct. 1999, 21, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E. Optimization of Class 2 Tensegrity Towers. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s 11th Annual International Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tibert, A.G.; Pellegrino, S. Deployable tensegrity reflectors for small satellites. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2002, 39, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilewski, W.; Al Sabouni-Zawadzka, A. On possible applications of smart structures controlled by self-stress. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2015, 15, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Ni, R.; Marwaha, A. A review of metamaterials and its applications. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2015, 19, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Liu, X.N.; Zhu, R.; Hu, G.K. Wave propagation in tunable lightweight tensegrity metastructure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraddosio, A.; Marzano, S.; Pavone, G.; Piccioni, M.D. Morphology and self-stress design of V-Expander tensegrity cells. Compos. Part B 2017, 115, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Senatore, L.; Daraio, C. Solitary waves on tensegrity lattices. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2012, 60, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Dobah, Y.; Scarpa, F.; Fernando Fraternali, F.; Skelton, R. Tensegrity cell mechanical metamaterial with metal rubber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 031906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilewski, W.; Al Sabouni-Zawadzka, A. Smart metamaterial based on the simplex tensegrity pattern. Materials 2018, 11, 673. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Nashimura, Y. Initial shape finding and modal analyses of cyclic right-cylindrical tensegrity modules. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 891–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E.; Gill, P.E. Algebraic tensegrity form-finding. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 4833–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Lipson, H.; Cuevas, F.V. Evolutionary Form-Finding of Tensegrity Structures. In Proceedings of the 2005 Conference: Genetic & Evolutionary Computation, Washington, DC, USA, 25–29 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ohsaki, M. Adaptive force density method for form-finding problem of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 5658–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Estrada, G.; Bungartz, H.J.; Mohrdieck, C. Numerical form-finding of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 6855–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, A.; Williams, W.O. A marching procedure for form-finding for tensegrity structures. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2007, 2, 857–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Advanced form-finding of tensegrity structures. Comput. Struct. 2010, 88, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Form-finding of tensegrity structures using double singular value decomposition. Eng. Comput. 2011, 29, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Form-finding of tensegrity structures with multiple states of self-stress. Acta Mech. 2011, 222, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, K. Form-finding of tensegrity structures via genetic algorithm. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 49, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J. A form-finding of planar tensegrity structures. Archit. Res. 2012, 14, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibert, A.G.; Pellegrino, S. Review of form-finding methods for tensegrity structures. Int. J. Space Struct. 2003, 18, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, S.H.; Tur, J.M.M. Tensegrity frameworks. Static analysis review. Mech. Mach. Theory 2008, 43, 859–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenendaal, D.; Block, P. An overview and comparison of structural form finding methods for general networks. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 3741–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harichandran, A.; Yamini SreevalIndian, I. Form-finding of tensegrity structures based on force density method. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanga, L.-Y.; Zhua, S.-X.; Lia, S.-X.; Xub, G.-K. Analytical form-finding of tensegrities using determinant of force-density matrix. Compos. Struct. 2018, 189, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caia, J.; Wanga, X.; Dengb, X.; Fenga, J. Form-finding method for multi-mode tensegrity structures using extended force density method by grouping elements. Compos. Struct. 2018, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xua, X.; Wangb, Y.; Luoc, Y. Finding member connectivities and nodal positions of tensegrity structures based on force density method and mixed integer nonlinear programming. Eng. Struct. 2018, 166, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, K.J. Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method. Vol. 1. The Basis; Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gilewski, W.; Kasprzak, A. Introduction to mechanics of tensegrity modules. In Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering. Mechanics of Structures and Materials; Jemioło, S., Lutomirski, S., Eds.; OWPW: Warsaw, Poland, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Calladine, C.R. Buckminster Fuller’s “tensegrity” structures and clerk Maxwell’s rules for the construction of stiff frames. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1978, 14, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calladine, C.R. Modal stiffnesses of a pretensioned cable net. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1982, 18, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, S.; Calladine, C.R. Matrix analysis of statically and kinematically indeterminate frameworks. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1986, 22, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, S. Analysis of prestressed mechanisms. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1990, 26, 1329–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calladine, C.R.; Pellegrino, S. First order infinitesimal mechanisms. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1991, 27, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.; Kahan, W. Calculating the singular values and pseudo-inverse of a matrix. J. SIAM Numer. Anal. Ser. B 1965, 2, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klema, V.C. The singular value decomposition: It’s computation and some applications. IEEE Trans. Automatic Control 1980, 25, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.J. Linear Algebra with Applications; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Long, C. Visualization of matrix singular value decomposition. Math. Mag. 1983, 56, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Guire, W.; Gallagher, R.H. Matrix Structural Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.W. Matrix Algorithms: Basic Decompositions; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Strang, G. Introduction to Linear Algebra; Wellesley-Cambridge Press: Wellesley, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gilewski, W.; Kłosowska, J.; Obara, P. Application of singular value decomposition for qualitative analysis of truss and tensegrity structures. ACTA Sci. Polon. Ser. Archit. 2015, 14, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, S. Structural computations with the singular value decomposition of the equilibrium matrix. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1993, 30, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahami, H.; Kaveh, A.; Ardalan Asl, M.; Mirghaderi, S.R. Analysis of near-regular structures with node irregularity using SVD of equilibrium matrix. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 11, 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Motro, R. Structural morphology of tensegrity systems. Build. Hous. 2009, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwear, N.; Eriksson, A. Natural frequencies describe the pre-stress in tensegrity structures. Comput. Struct. 2014, 138, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwear, N.; Eriksson, A. Influence of temperature on the vibration properties of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 99, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, R.; Back, A. Mathematics and tensegrity. Am. Sci. 1998, 86, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moored, K.W.; Bart-Smith, H. Investigation of clustered actuation in tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 3272–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moored, K.W.; Kemp, T.H.; Bart-Smith, H. Analytical prediction, optimization, and design of a tensegrity-based artificial pectoral fin. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 48, 3142–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.E.; de Oliveira, M.C. Optimal complexity of deployable compressive structures. J. Franklin Inst. 2010, 347, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Initial self-stress design of tensegrity grid structures. Comput. Struct. 2010, 88, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Self-stress design of tensegrity gird structures with exostresses. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; Skelton, R.E.; Han, J. Equilibrium conditions of a tensegrity structure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 6347–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Structural Morphology and Stability of Tensegrity Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ohsaki, M. Stability conditions for tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 3875–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.L.; Skelton, R.E. Equilibria and Stiffness of Planar Tensegrity Structures. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 27–30 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsaki, M.; Zhang, J. Stability conditions of prestressed pin-joint structures. Int. J. Nonline Mech. 2006, 41, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, B.; Skelton, R.E. Stiffness of planar tensegrity truss topologies. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 1308–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E. Selection of prestress for optimal dynamic/control performance of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 2110–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E.; de Oliveira, M.C. Integrated Structure and Control Design of Modular Tensegrities. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference, Seville, Spain, 12–15 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Masic, M.; Skelton, R.E.; Gill, P.E. Optimization of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 42, 4687–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ohsaki, M.; Kanno, Y. A direct approach to design of geometry and forces of tensegrity systems. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 2260–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, A. On generalized reciprocal diagrams for self-stressed frameworks. Int. J. Space Struct. 2008, 23, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deifeld, T.E.C.; de Oliveria Pauletti, R.M. Numerical Simulation of the Assembling of Tensegrity Domes. In Proceedings of the XXVI Iberian Latin-American Congress on Computational Methods in Engineering—CILAMCE 2005, Guarapari, Espirito Santo, Brasil, 19–21 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Determination of a unique configuration of free-form tensegrity structures. Acta Mech. 2011, 220, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, A.; Cadoni, D. Design of Single-Layer Floating-Compression Tensegrities. In Proceedings of the Colloque National en Calcul des Structures, CSMA 2011, Giens, France, 9–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Guest, S.D.; Connelly, R.; Ohsaki, M. Dihedral ‘star’ tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, R.; Fowler, P.W.; Guest, S.D.; Schulze, B.; Whiteley, W.J. When is a symmetric pin-jointed framework isostatic? Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


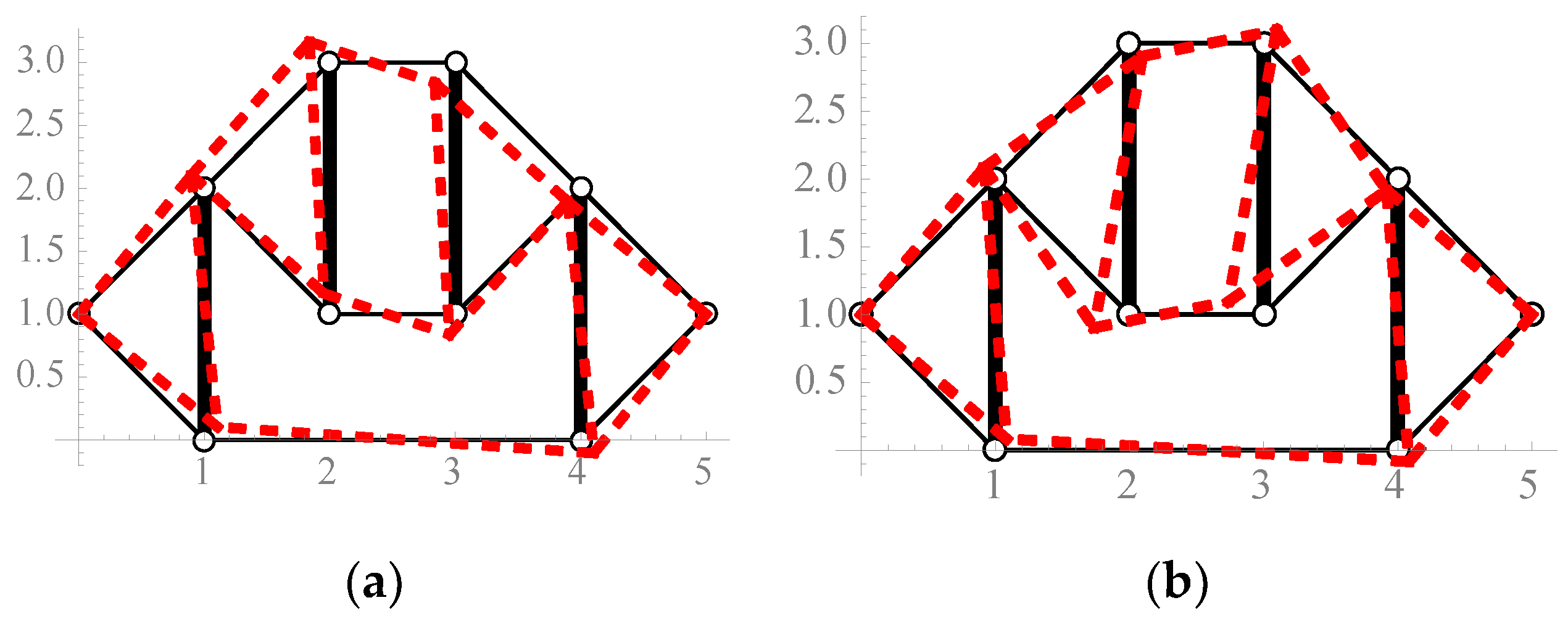

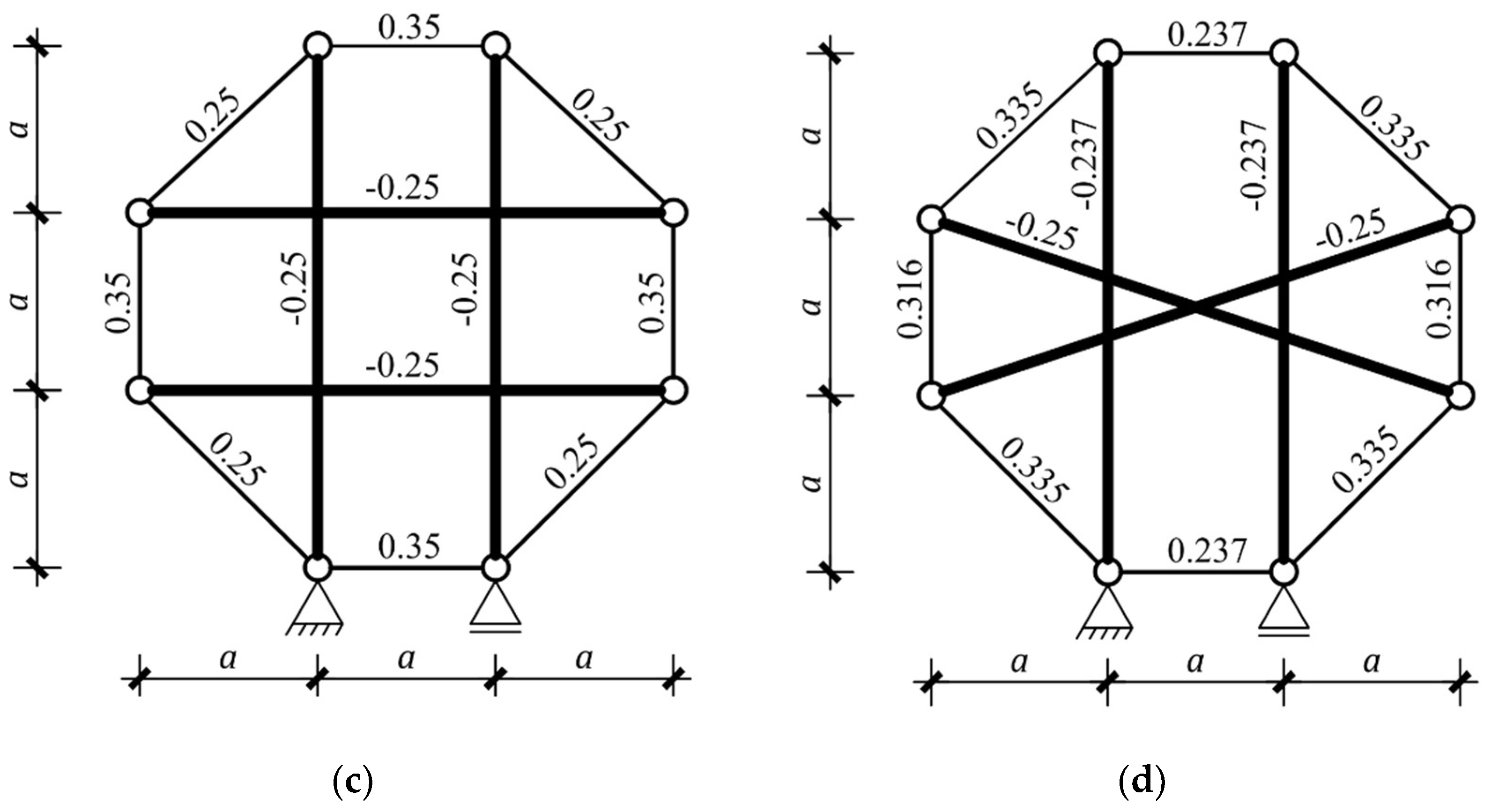
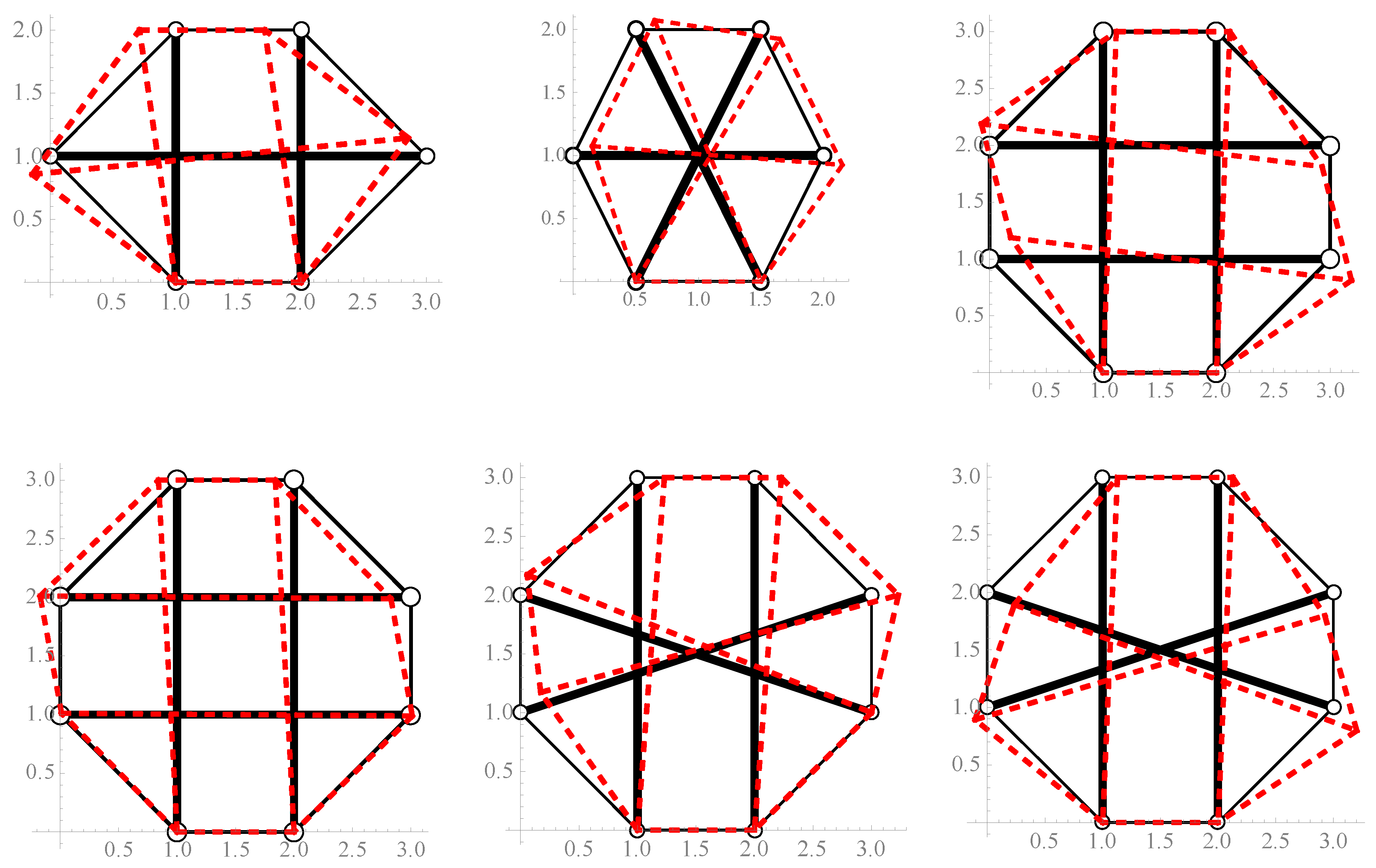
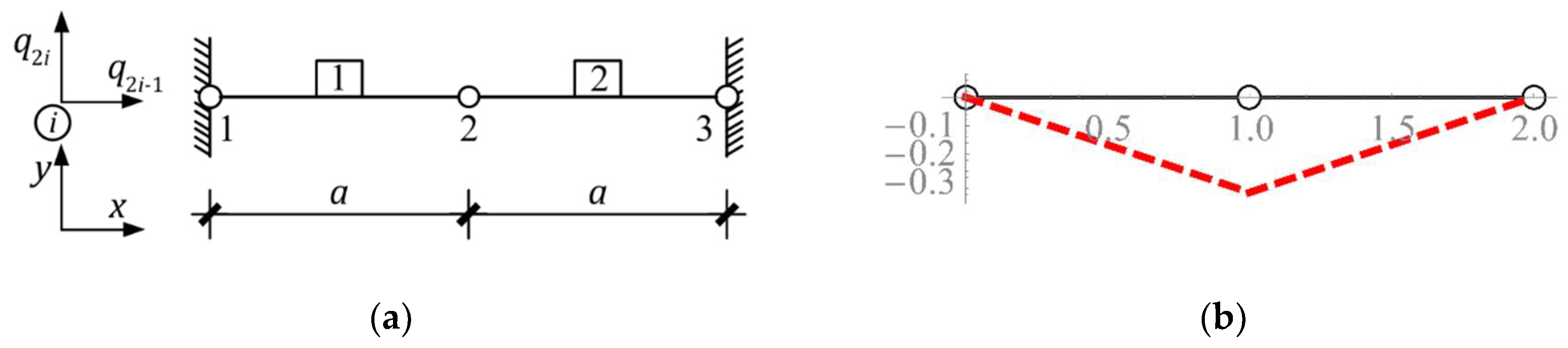
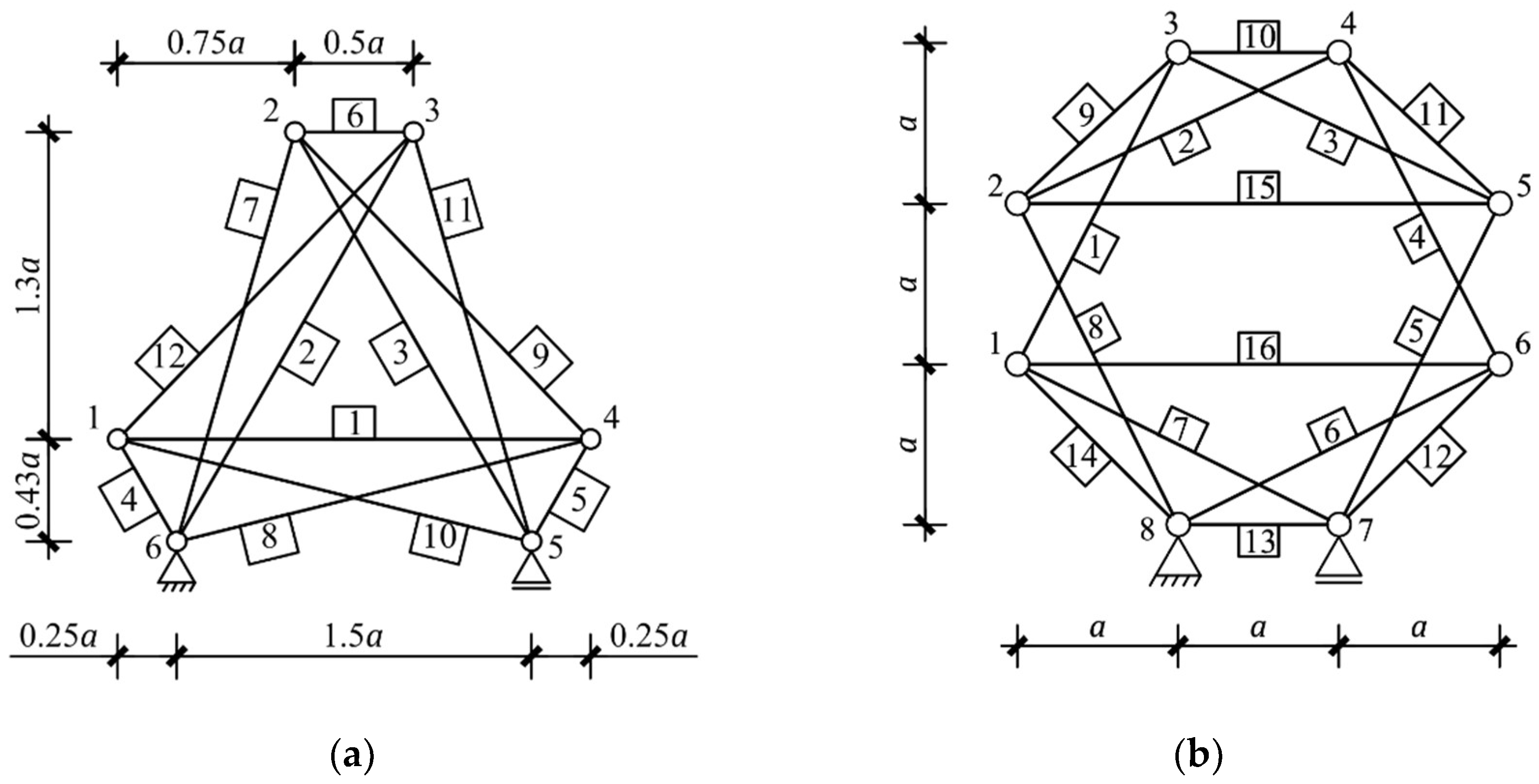
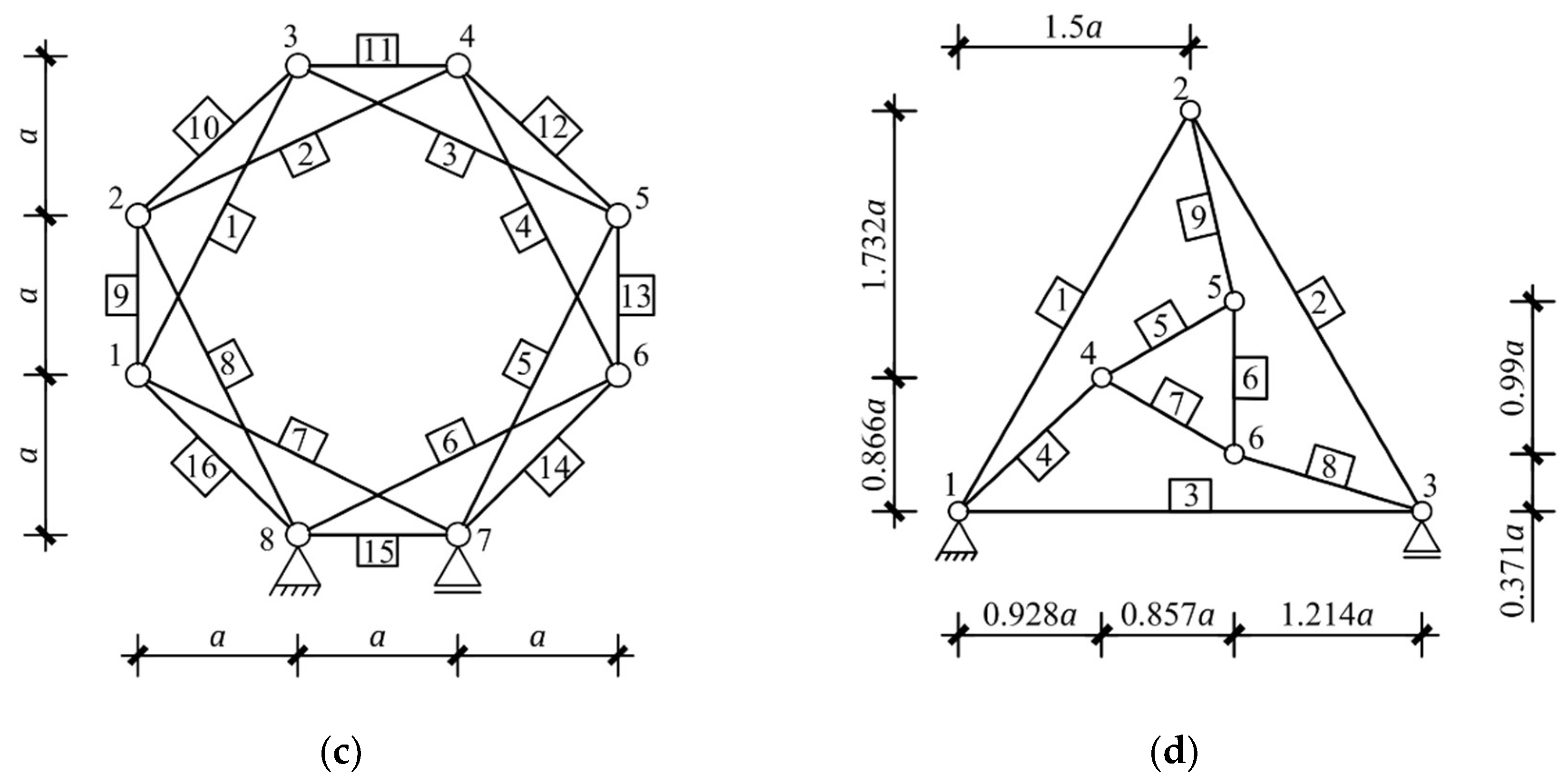
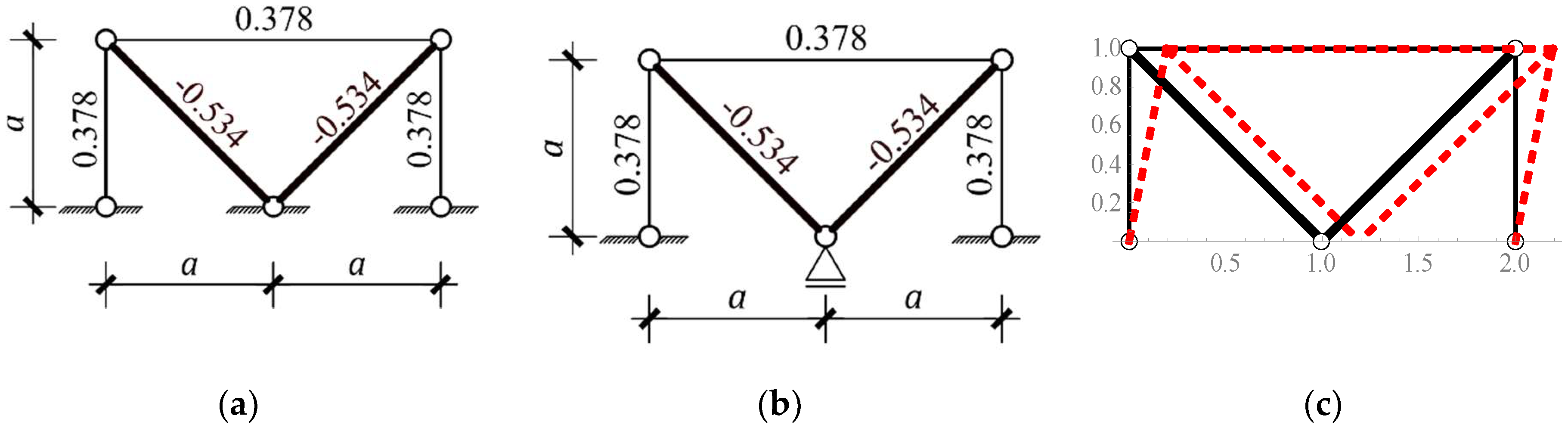
| Example | T | S | C | M | D | I | Classification of the Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obligatory Features | Min. One of {M, D, I} | ||||||
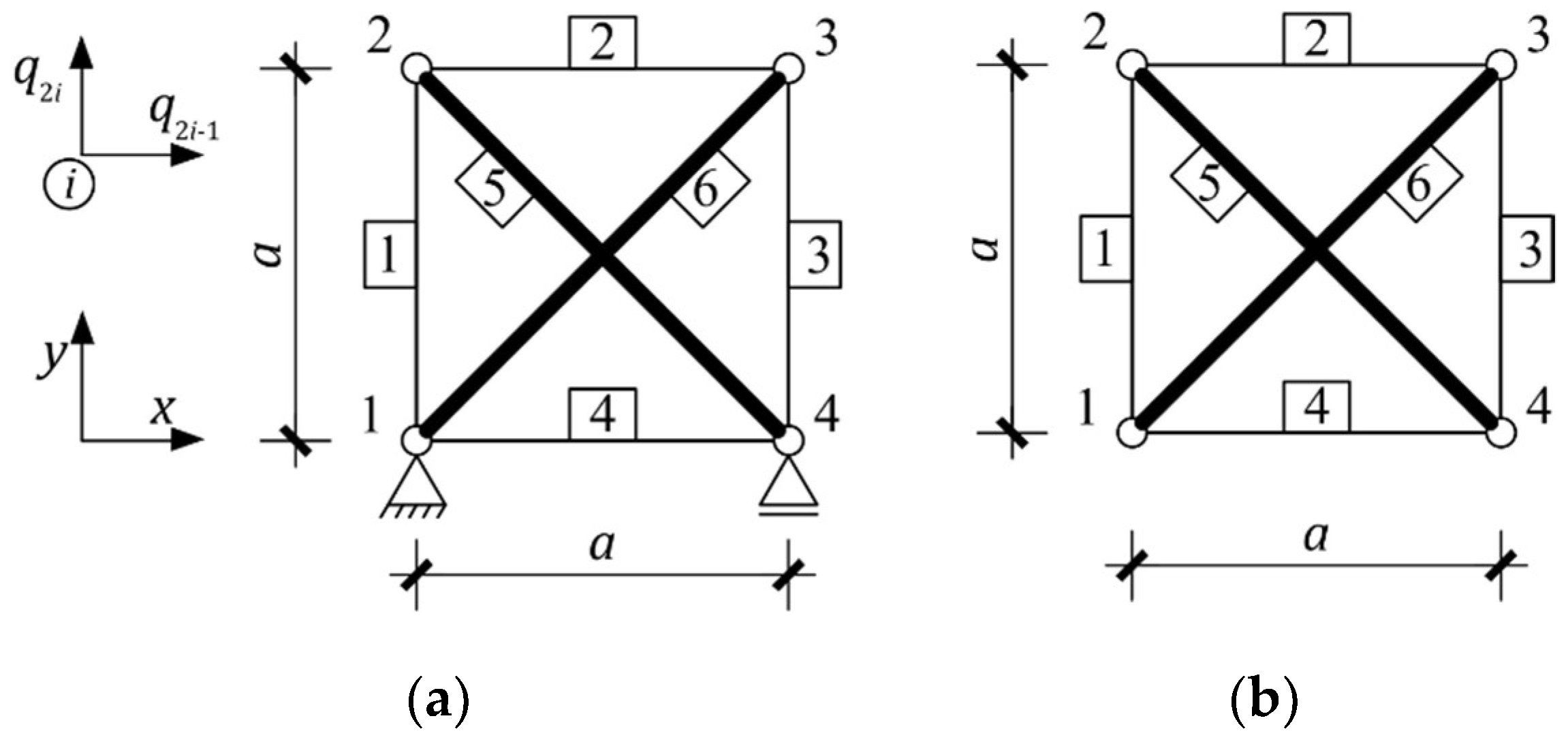
| Figure 2a | + | 1 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
| Figure 2b | + | 1 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
| Figure 4a | + | 1 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
| Figure 4b | + | 1 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
| Figure 4c | + | 1 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
| Figure 4d | + | 3 | + | - | + | + | tensegrity features |
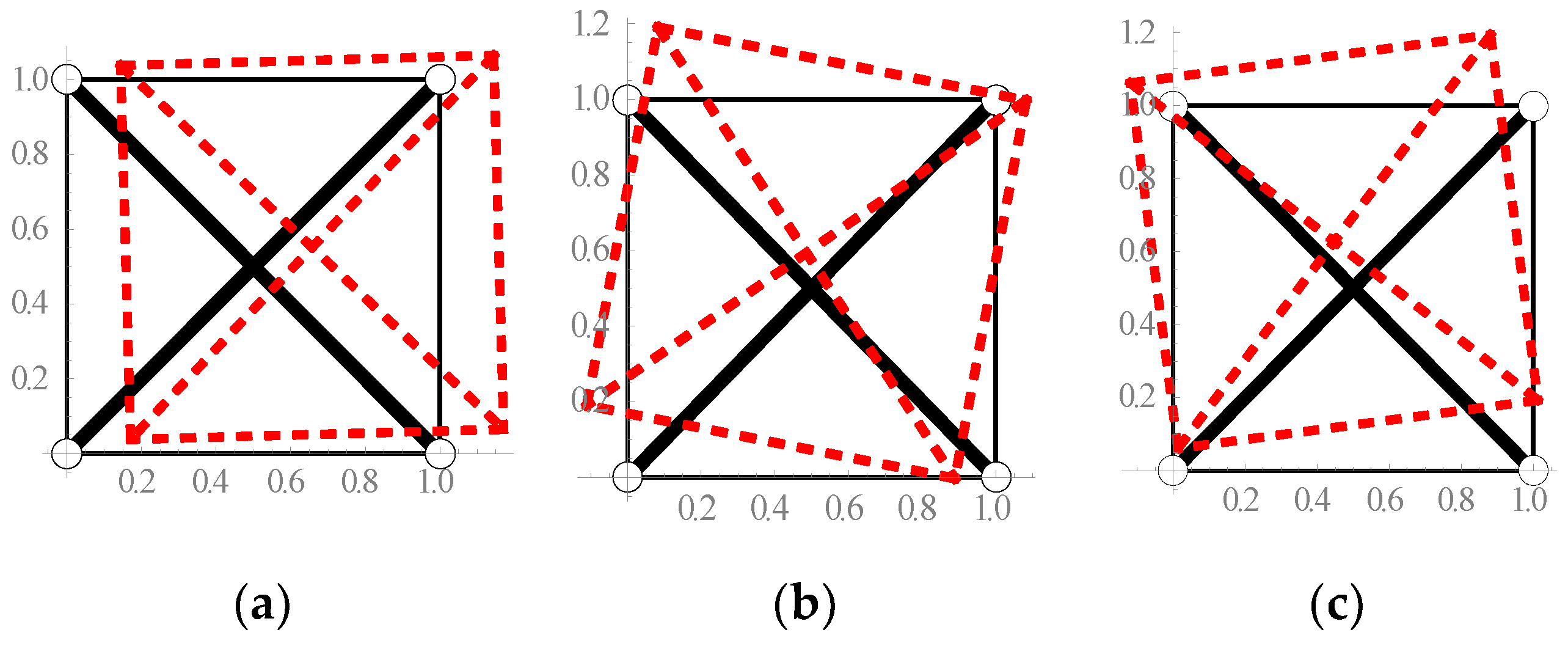
| Figure 5a | + | 1 | + | 1 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
| Figure 6 | + | 1 | + | 2 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
| Figure 8a | + | 1 | + | 1 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
| Figure 8b | + | 1 | + | 1 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
| Figure 8c | + | 1 | + | 2 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
| Figure 8d | + | 1 | + | 2 | + | + | pure tensegrity |
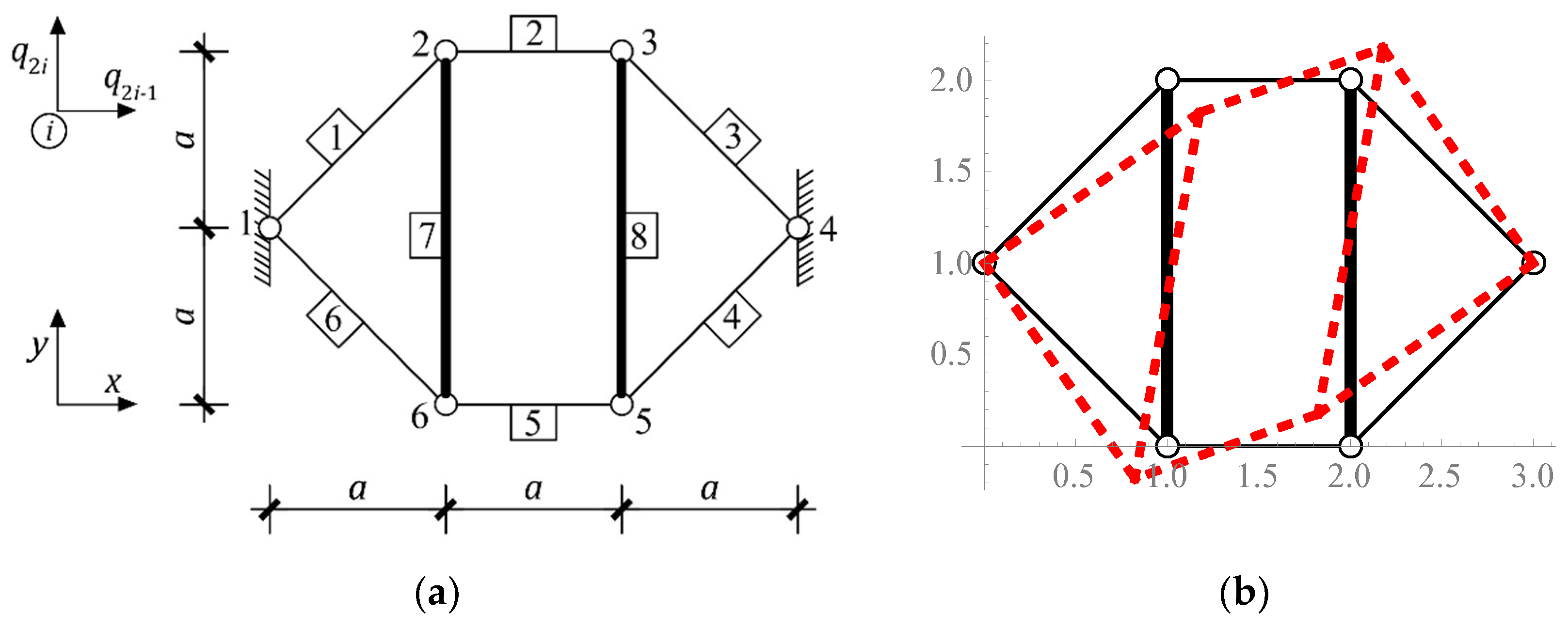
| Figure 10a | + | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | non tensegrity |
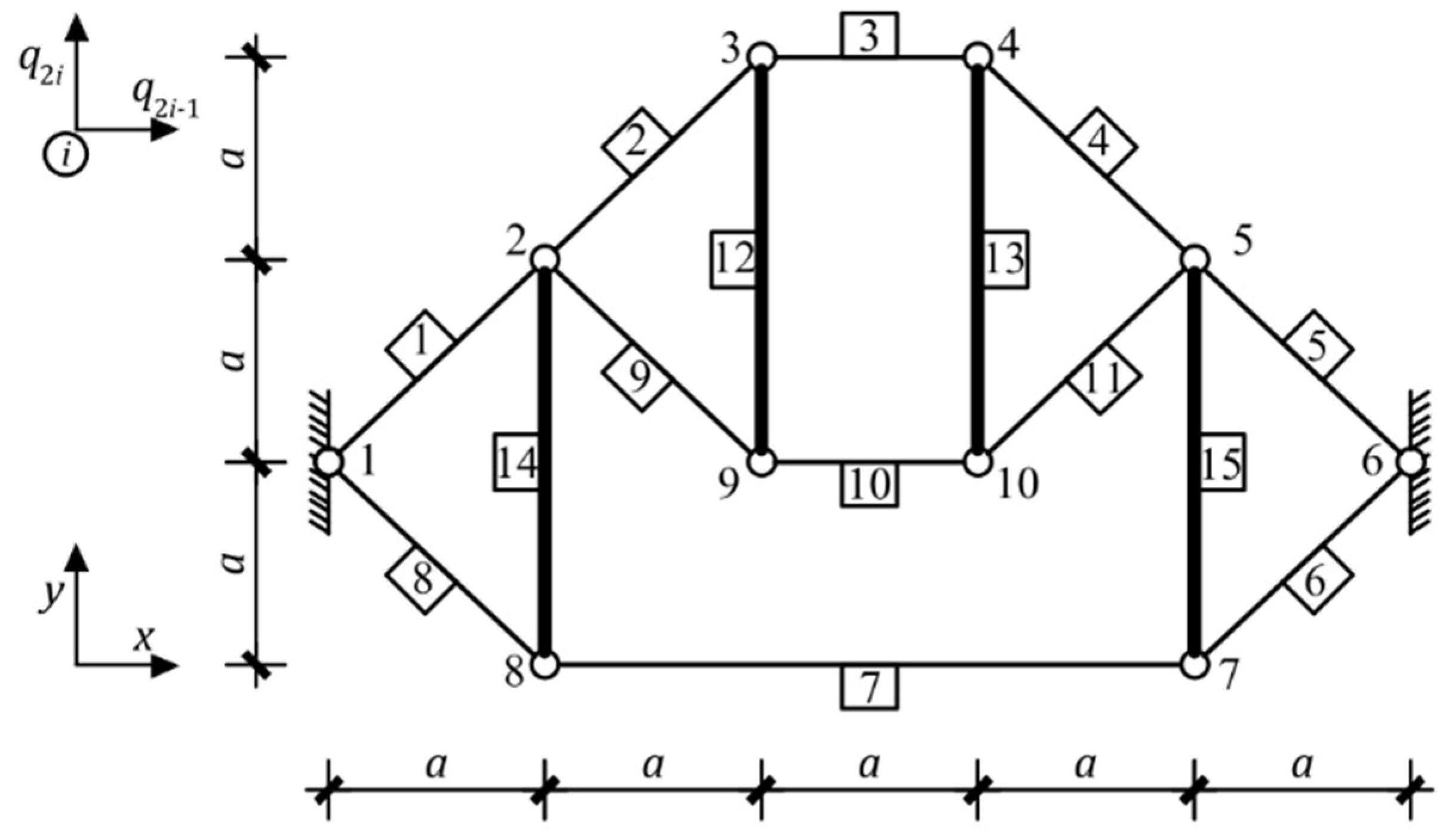
| Figure 11a | + | 3 | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
| Figure 11b | + | 3 | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
| Figure 11c | + | 3 | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
| Figure 11d | + | - | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
| Figure 12a | + | 1 | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
| Figure 12b | + | 1 | - | - | - | - | non tensegrity |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obara, P.; Kłosowska, J.; Gilewski, W. Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010179
Obara P, Kłosowska J, Gilewski W. Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleObara, Paulina, Joanna Kłosowska, and Wojciech Gilewski. 2019. "Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010179
APA StyleObara, P., Kłosowska, J., & Gilewski, W. (2019). Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010179






