Optimal Location of the Access Points for MIMO-UWB Systems
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
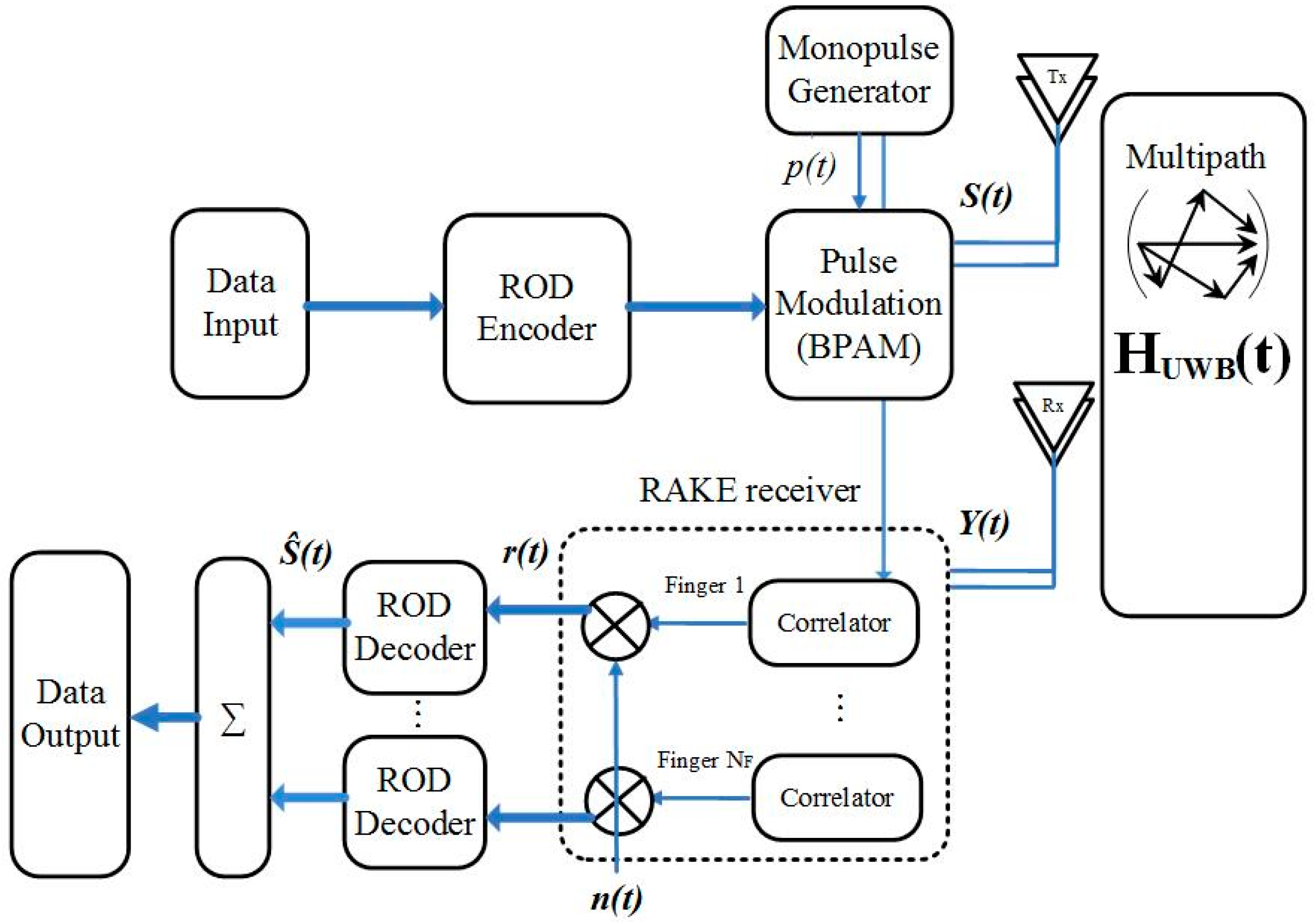
2.1. System Description
2.2. Evolution Algorithms
2.2.1. Self-Adaptive Dynamic Differential Evolution
2.2.2. Asynchronous Particle Swarm Optimization
3. Numerical Results
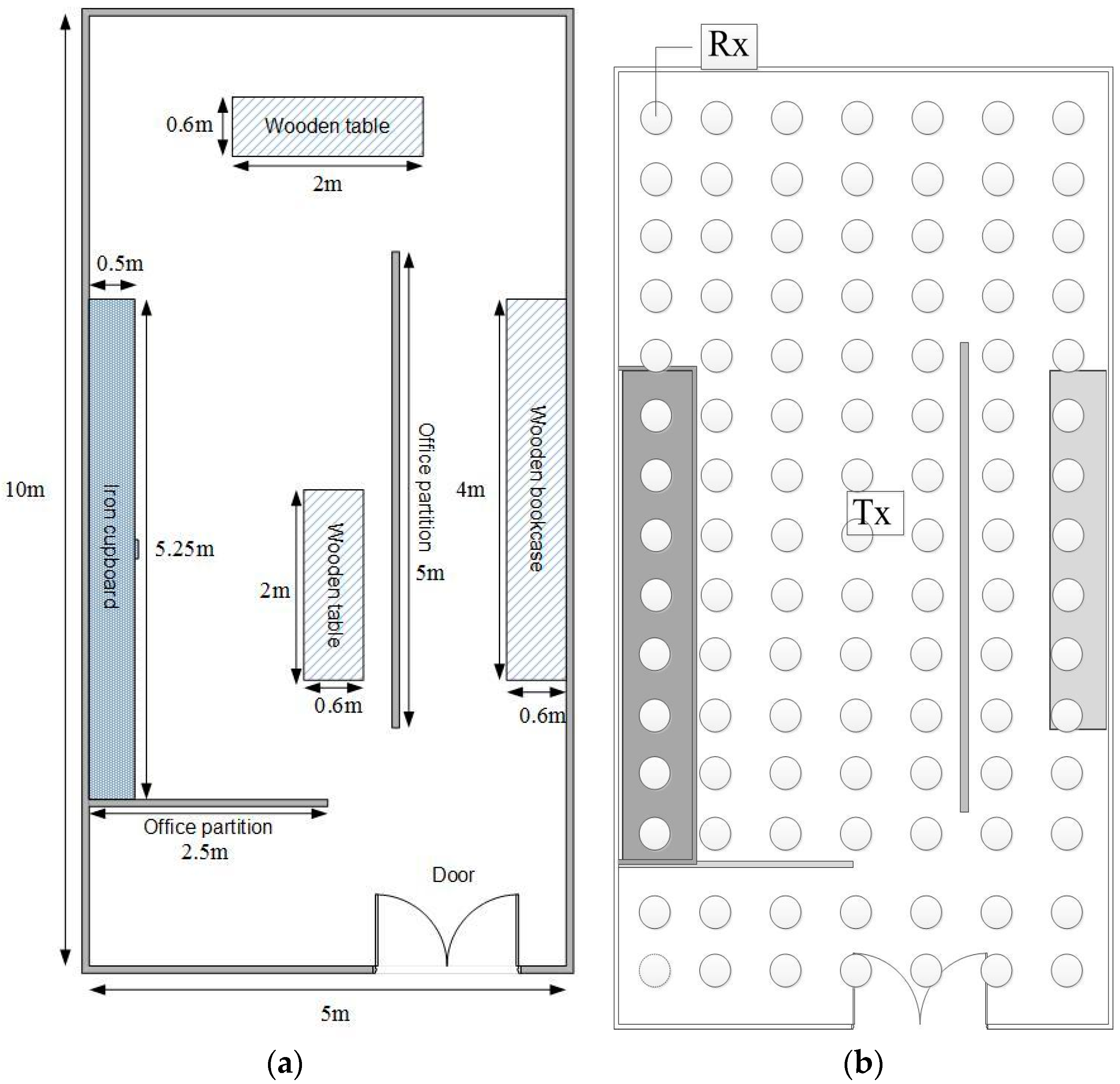
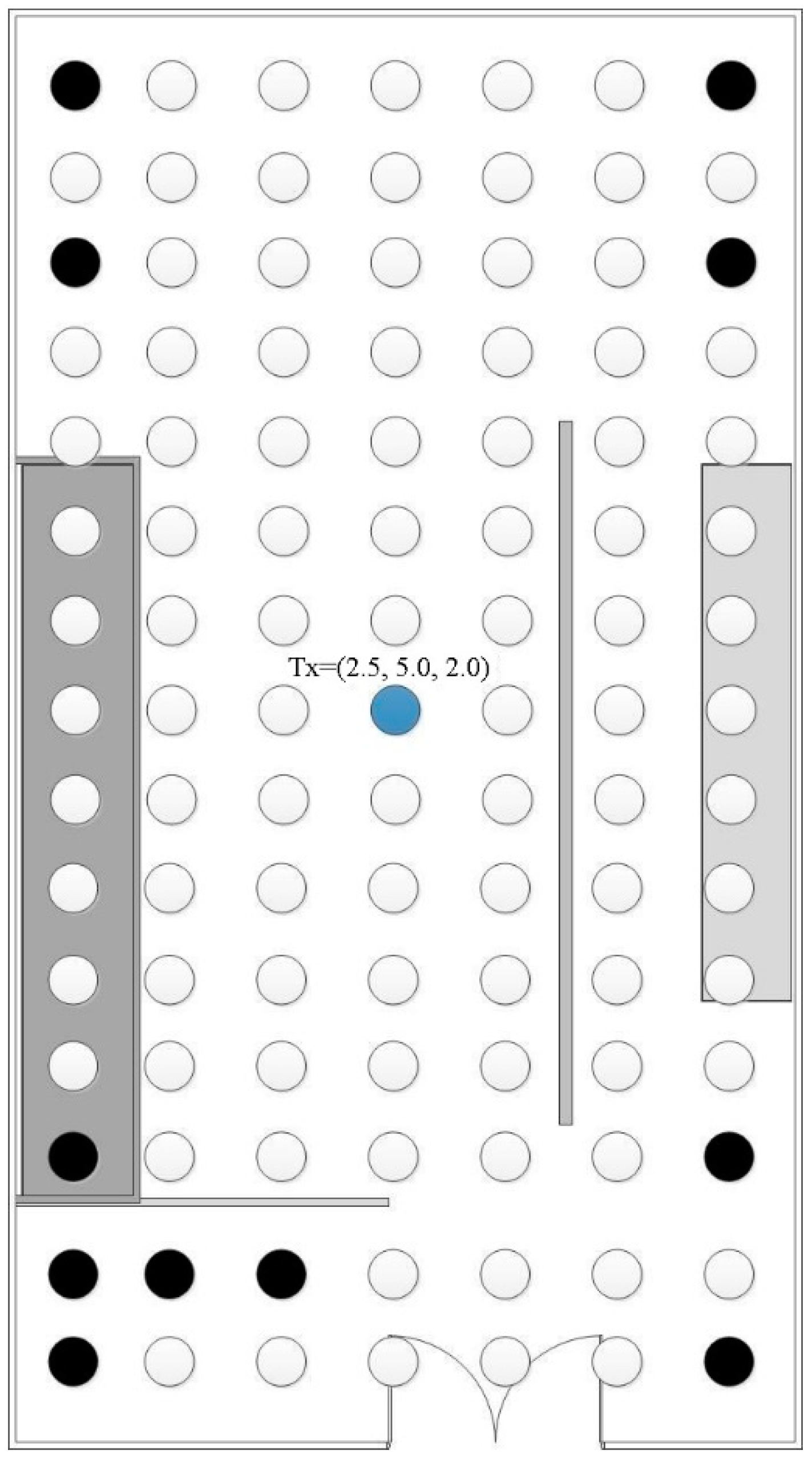
3.1. Case (A): Antenna Array
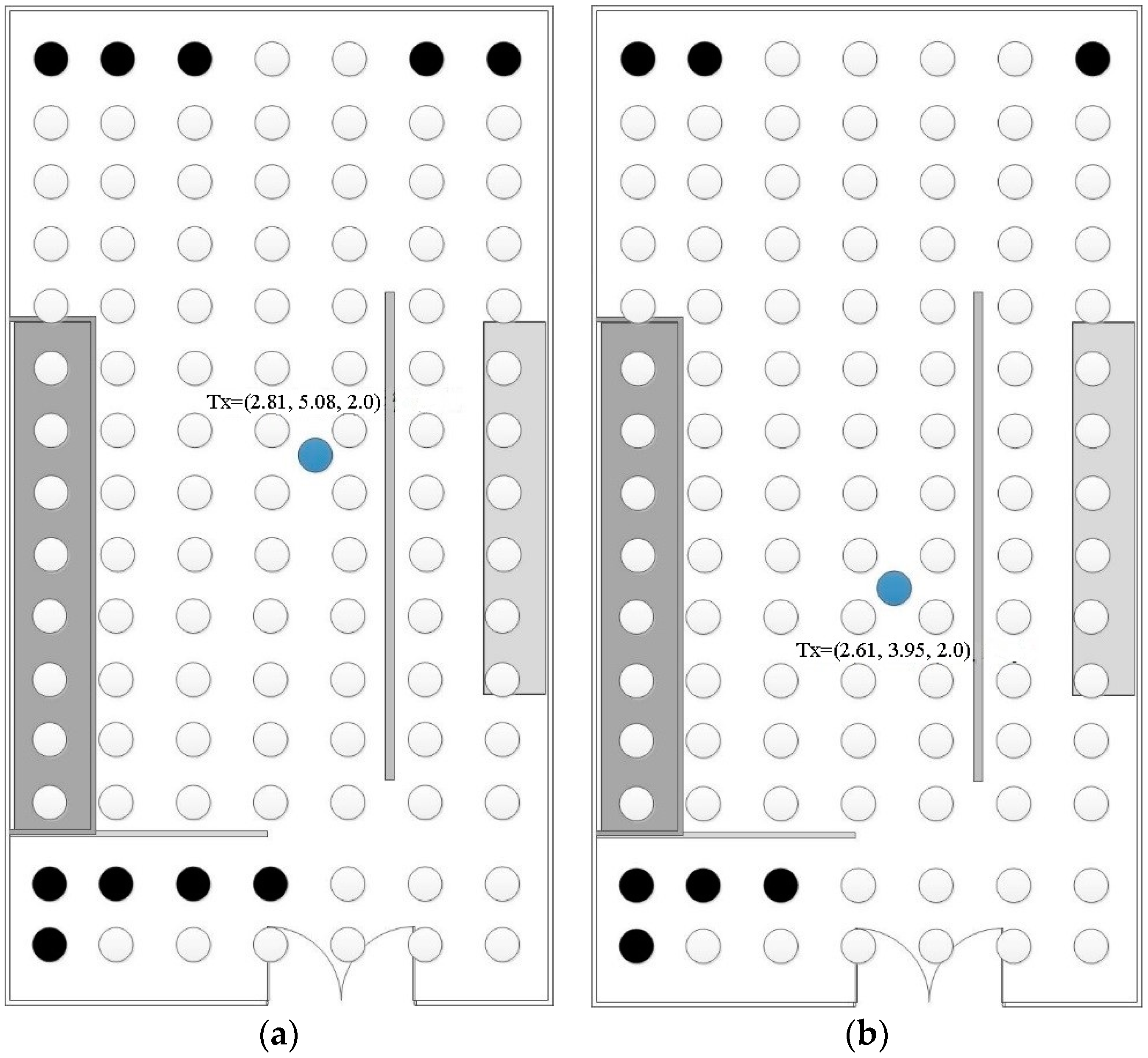
3.2. Case (B): Optimal Location by Evolution Algorithm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Migliore, M.D.; Pinchera, D.; Massa, A.; Azaro, R.; Schettino, F.; Lizzi, L. An Investigation on UWB-MIMO Communication Systems Based on an Experimental Channel Characterization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 3081–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, C.-L.; Chiu, C.-C.; Hu, T.-M. Ultra-wide Band Channel Calculation by SBR/Image Techniques for Indoor Communication. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2006, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, B.; Alsindi, N.; Pahlavan, K. UWB channel measurements for accurate indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Washington, DC, USA, 23–25 October 2006; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, U.; Bas, C.U.; Ergen, S.C. Engine compartment UWB channel model for intra-vehicular wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, C.U.; Ergen, S.C. Ultra-wideband channel model for intra-vehicular wireless sensor networks beneath the chassis: From statistical model to simulations. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadi, Y.; Ergen, S.C. Optimal power control, rate adaptation, and scheduling for UWB-based intravehicular wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Yu, C.Y.; Liao, S.H.; Wu, M.K. Channel capacity of multiple-input multiple-output systems for optimal antenna spacing by particle swarm optimizer. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2013, 69, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, H.M.; Honary, B.; Ahmed, H. Multiple-input multiple-output ultra-wide band channel modelling method based on ray tracing. IET Commun. 2012, 6, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boche, H.; Bourdoux, A.; Fonollosa, J.R.; Kaiser, T.; Molisch, A.; Utschick, W. Antennas: State of the art. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2006, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, A.J.; Gore, D.A.; Nabar, R.U.; Bolcskei, H. An overview of MIMO communications—A key to gigabit wireless. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Ottersten, B.; Hong, W. Energy Efficient Coordinated Beamforming for Multicell System: Duality-Based Algorithm Design and Massive MIMO Transition. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 4920–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Choi, J.; Heath, R.W. Two-dimensional AoD and AoA acquisition for wideband millimeter-wave systems with dual-polarized MIMO. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 7890–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Heath, R.W., Jr.; Daniels, R.C.; Murdock, J.N. Millimeter Wave Wireless Communications, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0132172288. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.-J.; Tarng, J.-H.; Peng, S.-Y. Frequency-Space-Polarization on UWB MIMO Performance for Body Area Network Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, D. The BER Performance of MB-IR-UWB System Based on MIMO. In Proceedings of the 2014 3rd Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Harbin, China, 26–29 July 2014; pp. 1384–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Ko, D.-S.; Park, J.-D. A Compact Multiple Notched Ultra-Wide Band Antenna with an Analysis of the CSRR-TO-CSRR Coupling for Portable UWB Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.A. Code-Multiplexing-Based One-Way Detect-and-Forward Relaying Schemes for Multiuser UWB MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 4859–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Khan, W.T.; Imran, M. Penta-notched UWB antenna with sharp frequency edge selectivity using combination of SRR, CSRR, and DGS. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 93, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, G.H.S. Performance Characterisation of MIMO-UWB Systems for Indoor Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tarokh, V.; Jafarkhani, H.; Calderbank, A.R. Space-time block codes from orthogonal designs. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1999, 45, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamouti, S.M. A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1998, 16, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minoli, D.; Fried, S. Transmission Techniques for Emergent Multicast and Broadcast Systems; Auerbach Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781439840665. [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann, I.; Hamalainen, M.; Iinatti, J. UWB Theory and Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 0470869178. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, T.; Zheng, F. Ultra Wideband Systems with MIMO; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470740002. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, M.-H.; Liao, S.-H.; Chiu, C.-C. UWB Communication Characteristics for Different Distribution of People and Various Materials of Walls. Tamkang J. Sci. Eng. 2010, 13, 315–326. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-C. Inverse scattering of dielectric cylindrical target using dynamic differential evolution and self-adaptive dynamic differential evolution. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2013, 23, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-T.; Sun, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Li, J.-F. Nondestructive Evaluation of Buried Dielectric Cylinders by Asynchronous Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Test. Eval. 2015, 43, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brest, J.; Greiner, S.; Boskovic, B.; Mernik, M.; Zumer, V. Self-adapting control parameters in differential evolution: A comparative study on numerical benchmark problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 10, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Cho, Y.J.; Hur, S.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Molisch, A.F.; Haneda, K.; Peter, M.; Park, D.J.; Cho, D.H. Millimeter-Wave Channel Measurements and Analysis for Statistical Spatial Channel Model in In-Building and Urban Environments at 28 GHz. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 5853–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, B.K.; Suraweera, H.A.; Zheng, G.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Beamforming Optimization for Full-Duplex Wireless-Powered MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 3750–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Shokouh, J.; Tavakoli, S.; Talepour, Z. Optimality of transmitter location in a wireless network with RAKE receivers. IET Commun. 2012, 6, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassioli, D.; Win, M.Z.; Vatalaro, F.; Molisch, A.F. Low complexity Rake receivers in ultra-wideband channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2007, 6, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarek, B.; Wessman, M.O.; Svensson, A. Performance of coherent UWB Rake receivers with channel estimators. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE 58th Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC 2003-Fall (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37484), Orlando, FL, USA, 6–9 October 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1880–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Ho, M.-H.; Lin, C.H. Optimal Relay Antenna Location in Indoor Environment Using Particle Swarm Optimizer and Genetic Algorithm. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2012, 62, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudos, S.K.; Siakavara, K.; Samaras, T.; Vafiadis, E.E.; Sahalos, J.N. Self-adaptive differential evolution applied to real-valued antenna and microwave design problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M. The swarm and the queen: Towards a deterministic and adaptive particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| search target (m) = (x, y, z) | location of the transmitter (x, y, 2.0) |
| fitness function | outage probability of the receivers |
| frequency range | 3.1–10.6 GHz |
| SNR | 40 dB to 80 dB |
| Algorithm | SADDE | APSO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | |||
| SNR = 56 dB | Number of outage points = 10 | Number of outage points = 7 | |
| SNR = 70 dB | Number of outage points = 1 | Number of outage points = 0 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chien, W.; Yu, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Huang, P.-H. Optimal Location of the Access Points for MIMO-UWB Systems. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091509
Chien W, Yu C-Y, Chiu C-C, Huang P-H. Optimal Location of the Access Points for MIMO-UWB Systems. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(9):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091509
Chicago/Turabian StyleChien, Wei, Chia-Ying Yu, Chien-Ching Chiu, and Po-Hsuan Huang. 2018. "Optimal Location of the Access Points for MIMO-UWB Systems" Applied Sciences 8, no. 9: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091509
APA StyleChien, W., Yu, C.-Y., Chiu, C.-C., & Huang, P.-H. (2018). Optimal Location of the Access Points for MIMO-UWB Systems. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091509






