The Suppression Characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud Composite Powders on Methane Explosion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
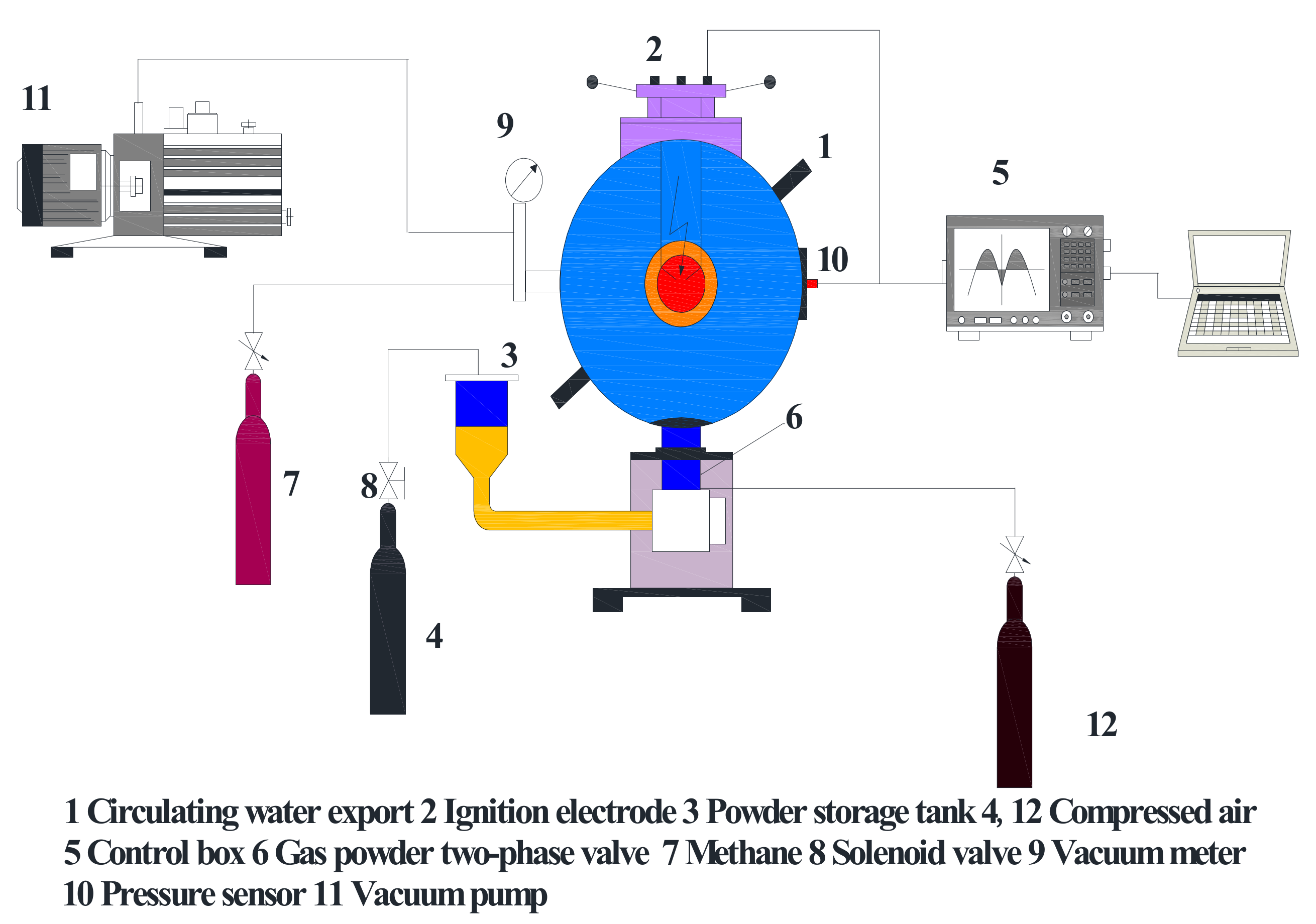
2.3. Explosion Experiment Device and Test Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Characterization
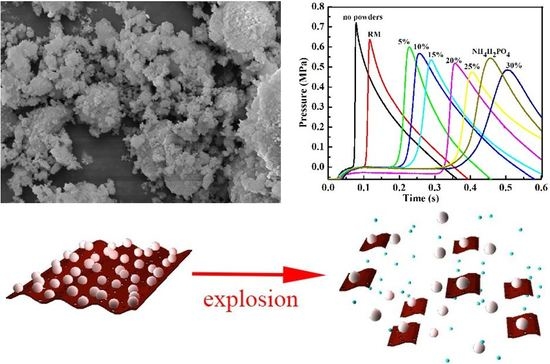
3.2. Suppression Properties of the NH4H2PO4/RM Composite Powders
3.3. Suppression Mechanism of the NH4H2PO4/RM Composite Powders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.M. The construction and development of the emergency refuge system in coal mine. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.D. Analysis of Underground Coal Mine Refuge Shelters. Ph.D. Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA, 20 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.P. The function and configuration scheme in coal mine. Ind. Mine Autom. 2010, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.J.; Qian, X.M.; Li, J. Simulation analysis on structure safety of coal mine mobile refuge chamber under explosion load. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.W.; Jin, L.Z.; Zhan, Z.N. Numerical simulation study of air distribution law of air pressure system in the mine refuge chamber. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2012, 45, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.H. Pressure characteristics and dynamic respond of coal mine refuge chamber with underground gas explosion. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 30, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.W.; Jing, G.X.; Cheng, L. Study on propagation regulation about shock wave of gas explosion at laneway area break. China Saf. Sci. J. 2007, 17, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhai, D.X.; Wang, W. Failure mode analysis and dynamic response of a coal mine refuge chamber with a gas explosion. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.G.; Wan, S.J.; Xu, Y.L.; Zheng, K.; Liang, D.L. The influence of the charge-to-mass ratio of the charged water mist on a methane explosion. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 41, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Ren, J.J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, Q.J. Suppression of methane explosion by ultrafine water mist containing sodium chloride additive. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.Y.; Ren, J.J.; Bi, M.S.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, Y.M. Experimental research on the characteristics of methane explosion affected by ultrafine water mist. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Yu, M.G.; Wan, S.J. Study on the characteristics of gas explosion affected by induction charged water mist in confined space. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 40, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitu, M.; Giurcan, V.; Razus, D.; Oancea, D. Inert gas influence on the laminar burning velocity of methane-air mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitu, M.; Giurcan, V.; Razus, D.; Oancea, D. Influence of inert gas addition on propagation indices of methane–air deflagrations. Process. Saf. Environ. 2016, 102, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Ni, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.C.; Wang, R. Effects of N2/CO2 on explosion characteristics of methane and air mixture. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 31, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Tang, M.Y.; Yang, K.; Lv, P.; Lin, B.Q. Active suppression of premixed methaneair explosion propagation by non-premixed suppressant with nitrogen and ABC powder in a semiconfined duct. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 29, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.M.; Wang, T.; Tian, Z.H.; Cheng, F.M.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.T. Experimental study on the suppression of gas explosion using the gas-solid suppressant of CO2/ABC powder. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 30, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.G.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhu, X.C.; Pan, R.K.; Wang, Y. Effect of blockage ratios on the characteristics of methane/air explosion suppressed by BC powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 355, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, B.S.; Yang, L.L.; Ge, B.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Li, X.C. Chemical kinetic characteristics of methane mixture explosion and its affecting factors. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2017, 49, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.M.; Hu, X.M.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.Y. An intelligent gel designed to control the spontaneous combustion of coal: Fire prevention and extinguishing properties. Fuel 2017, 210, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.P.; Bi, M.S.; Gao, W.; Gan, B.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, Q. Inhibition of aluminum dust explosion by NaHCO3 with different particle size distributions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.L.; Sapko, M.J.; Zlochower, I.A.; Perera, I.E.; Weiss, E.S. Particle size and surface area effects on explosibility using a 20-L chamber. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 37, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.M.; Kuang, K.Q.; Yang, D.L.; Jin, X.; Liao, G.X. A new type of fire suppressant powder of NaHCO3/zeolite nanocomposites with core–shell structure. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G. Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.L.; Zheng, L.G.; Yi, H.W. Methane explosion suppression characteristics based on the NaHCO3/red-mud composite powders with core-shell structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 335, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachel, A.P.; Sara, J.C.; Graeme, J.M. Value adding red mud waste: Impact of red mud composition upon fluoride removal performance of synthesised akaganeite sorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Min, X.B.; Ke, Y.; Chai, L.Y.; Shi, M.Q.; Tang, C.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Liang, Y.J.; Lei, J.; Liu, D.G. Utilization of red mud and Pb/Zn smelter waste for the synthesis of a red mud-based cementitious material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Aswath, M.U.; Ranganath, R.V. Effect of mechanical activation of red mud on the strength of geopolymer binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, N.; Rincón, A.; Avadhut, Y.S.; Hartmann, M.; Bernardo, E.; Boccaccini, A.R. Novel geopolymers incorporating red mud and waste glass cullet. Mater. Lett. 2018, 219, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.L.; Yan, Z.L.; Deng, Q.F.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.D.; Hari, B.; Zhang, Z.Y. Homogeneous precipitation method preparation of modified red mud supported Ni mesoporous catalysts for ammonia decomposition. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.G.; Kong, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zheng, L.G. Experimental research on gas explosion suppression by modified red mud. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Kordylewski, W.; Amrogowicz, J. Comparison of NaHCO3 and NH4H2PO4 Effectiveness as Dust Explosion Suppressants. Combust. Flame 1992, 90, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenklach, M.; Wang, H.; Rabinowitz, M.J. Optimization and analysis of large chemical kinetic mechanisms using the solution mapping method-combustion of methane. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1992, 18, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Samples | Max Pressure (MPa) | The Rate of Max-Pressure Rise (MPa·s−1) | Time of Pressure Peak Arriving (s) | Decline Rate of Max Pressure (%) | Decline Rate of Max Pressure Rise (%) | Delay Time of Pressure Peak Arriving (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No powders | 0.749 | 41.16 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| RM | 0.651 | 21.48 | 0.11 | 13.1 | 47.8 | 0.04 |
| 5%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.607 | 8.79 | 0.23 | 19.9 | 78.6 | 0.16 |
| 10%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.571 | 6.16 | 0.26 | 23.8 | 85.1 | 0.19 |
| 15%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.562 | 5.17 | 0.29 | 24.9 | 87.4 | 0.22 |
| 20%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.519 | 4.32 | 0.36 | 30.7 | 89.5 | 0.29 |
| 25%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.497 | 2.54 | 0.40 | 33.6 | 93.8 | 0.33 |
| 30%-NH4H2PO4/RM | 0.486 | 1.72 | 0.50 | 35.1 | 95.8 | 0.43 |
| NH4H2PO4 | 0.545 | 2.99 | 0.45 | 27.2 | 92.8 | 0.38 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zheng, L.; Gao, J. The Suppression Characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud Composite Powders on Methane Explosion. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091433
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Meng X, Zheng L, Gao J. The Suppression Characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud Composite Powders on Methane Explosion. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(9):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091433
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yimin, Yan Wang, Xiangqing Meng, Ligang Zheng, and Jianliang Gao. 2018. "The Suppression Characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud Composite Powders on Methane Explosion" Applied Sciences 8, no. 9: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091433
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Y., Meng, X., Zheng, L., & Gao, J. (2018). The Suppression Characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud Composite Powders on Methane Explosion. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091433