Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Proteins Extracted from Seven Different Snails
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification
2.2. Extraction of Proteins from Seven Snail Species
2.3. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals and Protein Extraction
3.2. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities and MIC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González, Y.; Tanaka, A.S.; Hirata, I.Y.; del Rivero, M.A.; Oliva, M.L.V.; Araujo, M.S.; Chávez, M.A. Purification and partial characterization of human neutrophil elastase inhibitors from the marine snail Cenchritis muricatus (Mollusca). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. Antibiotic-Resistant Bugs in the 21st Century—A Clinical Super-Challenge. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.-P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, T.P.; Edward, J.K.P. Antimicrobial activity in the tissue extracts of five species of cowries cypraea spp. (Mollusca: Gastropoda) and an ascidian didemnum psammathodes (Tunicata: Didemnidae). Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 31, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, H.; Muramoto, K.; Goto, R.; Sakai, M.; Endo, Y.; Yamazaki, M. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial and antineoplastic protein secretion of a sea hare, Aplysia juliana. Toxicon 1989, 27, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Kamano, Y.; Herald, C.L.; Tuinman, A.A.; Boettner, F.E.; Kizu, H.; Schmidt, J.M.; Baczynskyj, L.; Tomer, K.B.; Bontems, R.J. The isolation and structure of a remarkable marine animal antineoplastic constituent: dolastatin 10. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6883–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaganapathi, J.; Thyagarajan, S.P.; Patterson Edward, J.K. Study on cephalopod’s ink for anti-retroviral activity. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 38, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitta, G.; Hubert, F.; Noel, T.; Roch, P. Myticin, a novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from haemocytes and plasma of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Furunaka, H.; Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Muta, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Niwa, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 16709–16713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueguen, Y.; Garnier, J.; Robert, L.; Lefranc, M.P.; Mougenot, I.; de Lorgeril, J.; Janech, M.; Gross, P.S.; Warr, G.W.; Cuthbertson, B.; et al. PenBase, the shrimp antimicrobial peptide penaeidin database: sequence-based classification and recommended nomenclature. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olicard, C.; Renault, T.; Torhy, C.; Benmansour, A.; Bourgougnon, N. Putative antiviral activity in hemolymph from adult Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas {UR} {-://WOS:000229819900008}. Antivir. Res. 2005, 66, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roch, P.; Yang, Y.; Toubiana, M.; Aumelas, A. NMR structure of mussel mytilin, and antiviral-antibacterial activities of derived synthetic peptides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, A.; Ulagesan, S. Antimicrobial activity of protein hydrolysate from marine molluscs babylonia spirata (Linnaeus, 1758). J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mubarak, M.A.S.; Lamari, F.N.; Kontoyannis, C. Simultaneous determination of allantoin and glycolic acid in snail mucus and cosmetic creams with high performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1322, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez Abarrategui, C.; Alba, A.; Lima, L.; Neto, S.; Vasconcelos, I.; Oliveira, J.; Dias, S.; Otero, A.; Franco, O. Screening of Antimicrobials from Caribbean Sea Animals and Isolation of Bactericidal Proteins from the Littoral Mollusk Cenchritis muricatus. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAEMMLI, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauth, X.; Shike, H.; Burns, J.C.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Nizet, V.; Taylor, S.W.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugesh, S.; Mayavu, P.; Ezhilarasan, P.; Sivashankar, P.; Arivuselvan, N. Screening of Antibacterial Activities of Marine Gastropod Hemifusus Pugilinus. Curr. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 5, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dolashka, P.; Dolashki, A.; Voelter, W.; Van Beeumen, J.; Stevanovic, S. Antimicrobial activity of peptides from the hemolymph of Helix lucorum snails. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantara Santana, W.; Melo, C.; Cardoso, J.; Nely Pereira-Filho, R.; Rabelo, A.; Reis, F.; de Albuquerque, R.L.C. Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity and Healing Potential of Mucous Secretion of Achatina fulica. Int. J. Morphol. 2012, 30, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gayathri, M.; Sanjeevi, S.B. Antipathogenic activity of freshwater Gastropod Pila virens (Lamarck, 1822) from Lower Grand Anaicut Reservoir, Tamilnadu. Int. J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2014, 5, 3894–3898. [Google Scholar]



| Snails | Micro-Organisms | Zone of Inhibition in mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL | 100 µg/mL | N.C | Chloramphenicol 100 µg/mL | ||
| A. fulica | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 27.5 ± 0.5 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 22.6 ± 1.5 | |
| H. alvei | 6.33 ± 1.1 | 8 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | - | 22.6 ± 0.4 | |
| S. marcescens | 9.33 ± 1.1 | 11 ± 1 | 14 ± 2 | - | 21.33 ± 1.5 | |
| S. aureus | 9 ± 1 | 11.5 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | - | 24.33 ± 0.5 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 24.66 ± 0.5 | |
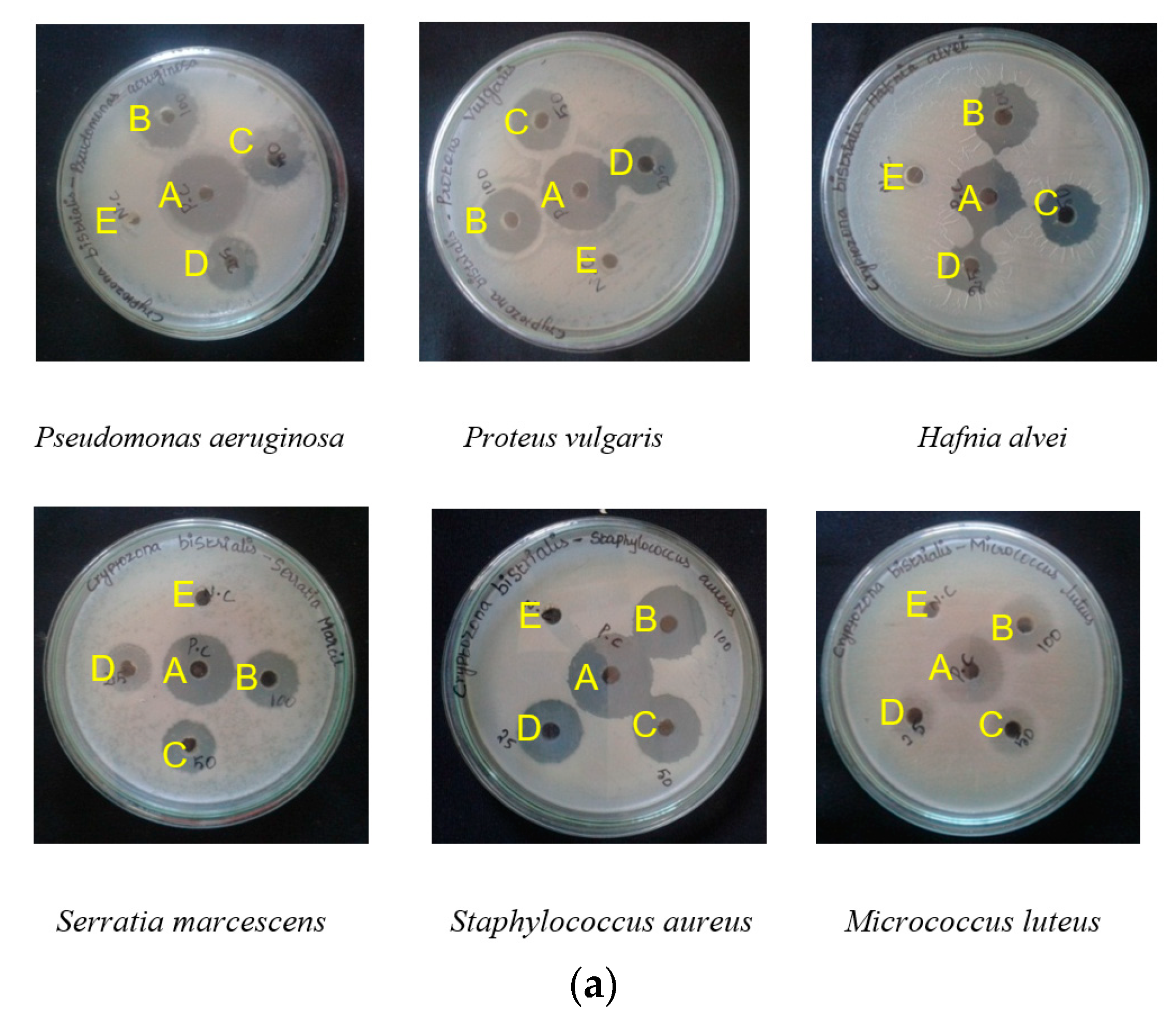
| C. bistrialis | P. aeruginosa | 11 ± 1 | 13.33 ± 1.5 | 21.66 ± 1.15 | - | 25 ± 1 |
| P. vulgaris | 11.33 ± 0.4 | 15.33 ± 0.5 | 19 ± 1 | - | 25.3 ± 0.5 | |
| H. alvei | 11.6 ± 0.5 | 15 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | - | 22.3 ± 0.5 | |
| S. marcescens | 10 ± 1 | 14.33 ± 1.52 | 19 ± 1 | - | 24.33 ± 0.57 | |
| S. aureus | 10 ± 1 | 11.3 ± 0.76 | 14.6 ± 1.1 | - | 25 ± 1 | |
| M. luteus | 9.5 ± 1.3 | 11.5 ± 1.3 | 20.6 ± 1.5 | - | 25.5 ± 0.5 | |
| P. globosa | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 23.6 ± 0.57 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 24 ± 1 | |
| H. alvei | - | - | - | - | 21.3 ± 0.5 | |
| S. marcescens | - | - | - | - | 19 ± 1 | |
| S. aureus | 8.16 ± 0.28 | 10.3 ± 0.5 | 15.83 ± 0.76 | - | 24 ± 1 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 17.6 ± 0.5 | |
| P. virens | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 25.6 ± 0.5 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 22.5 ± 0.5 | |
| H. alvei | - | - | - | - | 24.66 ± 0.57 | |
| S. marcescens | - | - | - | - | 22.5 ± 0.5 | |
| S. aureus | - | - | - | - | 24.3 ± 0.5 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 24 ± 1 | |
| B. dissimilis | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 25.6 ± 0.57 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 20.66 ± 1.15 | |
| H. alvei | - | - | - | - | 20.66 ± 0.57 | |
| S. marcescens | - | - | - | - | 20 ± 1 | |
| S. aureus | - | - | - | - | 24.6 ± 0.57 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 23 ± 0.5 | |
| B. pulchella | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 24.5 ± 0.76 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 20.3 ± 0.57 | |
| H. alvei | - | - | - | - | 19.5 ± 0.5 | |
| S. marcescens | - | - | - | - | 19.3 ± 0.57 | |
| S. aureus | - | - | - | - | 23.6 ± 0.5 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 23.6 ± 0.6 | |
| M. tuberculata | P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | - | 25.5 ± 0.5 |
| P. vulgaris | - | - | - | - | 23 ± 1 | |
| H. alvei | - | - | - | - | 20.5 ± 0.5 | |
| S. marcescens | - | - | - | - | 22 ± 1 | |
| S. aureus | - | - | - | - | 23.3 ± 0.5 | |
| M. luteus | - | - | - | - | 24.76 ± 0.6 | |
| Organisms | P. aeruginosa | P. vulgaris | H. alvei | S. marcescens | S. aureus | M. luteus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fulica | 100 1 (16.4 2) | ND. | 100 1 (9.2 2) | 100 1 (16.5 2) | 100 1 (12.8 2) | ND. |
| C. bistrialis | 12.5 1 (86.6 2) | 12.5 1 (88.2 2) | 25 1 (86.5 2) | 25 1 (86.8 2) | 12.5 1 (90.9 2) | 25 1 (70.82 2) |
| P. globosa | 50 1 (14.8 2) | ND. | ND. | ND. | 100 1 (10.02 2) | ND. |
| P. virens | 100 1 (11.38 2) | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| B. dissimilis | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| B. pulchella | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| M. tuberculata | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| Snails | Micro-Organisms | Zone of Inhibition in mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL | 100 µg/mL | N.C | Amphotericin-B (100 µg/mL) | ||
| A. fulica | C.albicans | 8.6 ± 0.57 | 11.16 ± 0.76 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | - | 19.6 ± 0.57 |
| P.chrysogenum | - | 8 ± 1 | 11.83 ± 0.76 | - | 15.93 ± 0.1 | |
| A. fumigatus | - | - | 12.3 ± 0.5 | - | 21 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | - | - | - | - | 11 ± 0.76 | |
| C. bistrialis | C. albicans | 8.5 ± 0.5 | 13.3 ± 0.5 | 15.83 ± 0.2 | - | 20 ± 1 |
| P. chrysogenum | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 18 ± 1 | 19.83 ± 0.2 | - | 20.83 ± 0.76 | |
| A. fumigatus | 18.6 ± 1.1 | 22 ± 1 | 24.6 ± 0.5 | 25.6 ± 0.57 | ||
| M.racemosus | 11 ± 0.1 | 16 ± 0.7 | 21 ± 0.2 | - | 22 ± 0.5 | |
| P. globosa | C. albicans | - | - | - | - | 15.3 ± 0.57 |
| P. chrysogenum | - | - | - | - | 10.83 ± 1.04 | |
| A.fumigatus | 7.43 ± 0.60 | 8 ± 1 | 11.6 ± 0.57 | - | 21 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | - | 16 ± 0.5 | 20 ± 0.1 | - | 22 ± 0.2 | |
| P. virens | C. albicans | 7 ± 1 | 7.6 ± 0.5 | 9 ± 1 | - | 14.6 ± 1.1 |
| P. chrysogenum | - | 8 ± 1 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | - | 15.58 ± 0.5 | |
| A.fumigatus | - | 7.33 ± 1.52 | 11 ± 1 | - | 23 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | 6 ± 1 | 8 ± 0.56 | 10 ± 1 | - | 13 ± 0.8 | |
| B. dissimilis | C. albicans | - | - | - | - | 14.5 ± 0.5 |
| P.chrysogenum | - | - | - | - | 13 ± 1 | |
| A. fumigatus | - | - | - | - | 15 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | - | - | 20 ± 0.2 | - | 22 ± 0.76 | |
| B. pulchella | C. albicans | - | - | - | - | 11.5 ± 1.1 |
| P. chrysogenum | - | - | 9 ± 1 | - | 12.1 ± 0.1 | |
| A. fumigatus | - | - | - | - | 15 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | - | - | - | - | 22 ± 0.5 | |
| M. tuberculata | C. albicans | - | - | - | - | 11 ± 1 |
| P. chrysogenum | - | - | - | - | 13.3 ± 0.57 | |
| A. fumigatus | - | - | - | - | 13 ± 1 | |
| M.racemosus | - | - | - | - | 16 ± 0.1 | |
| Organisms | C. albicans | P. chrysogenum | A. fumigatus | M. racemosus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fulica | 100 1 (10.4 2) | 100 1 (12.8 2) | ND. | ND. |
| C. bistrialis | 50 1 (74.6 2) | 50 1 (80.1 2) | 25 1 (66.82 2) | 25 1 (70.8 2) |
| P. globosa | 100 1 (11.3 2) | 100 1 (15.12 2) | ND. | ND. |
| P. virens | 100 1 (17.18 2) | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| B. dissimilis | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| B. pulchella | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
| M. tuberculata | ND. | ND. | ND. | ND. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulagesan, S.; Kim, H.J. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Proteins Extracted from Seven Different Snails. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081362
Ulagesan S, Kim HJ. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Proteins Extracted from Seven Different Snails. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(8):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081362
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlagesan, Selvakumari, and Hak Jun Kim. 2018. "Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Proteins Extracted from Seven Different Snails" Applied Sciences 8, no. 8: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081362
APA StyleUlagesan, S., & Kim, H. J. (2018). Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Proteins Extracted from Seven Different Snails. Applied Sciences, 8(8), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081362