Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
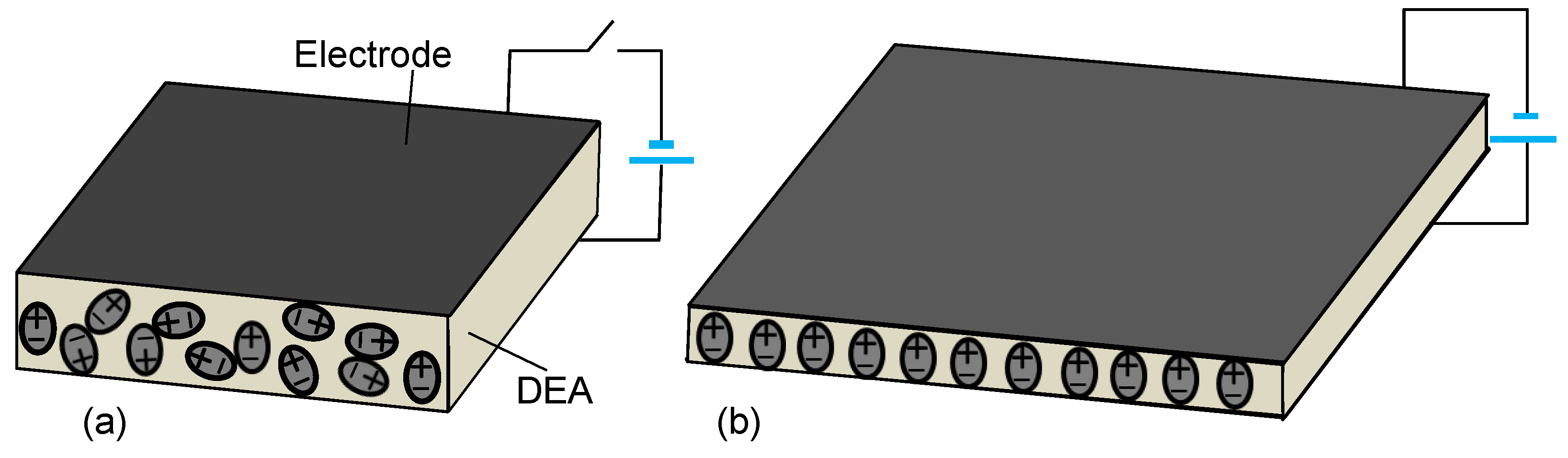
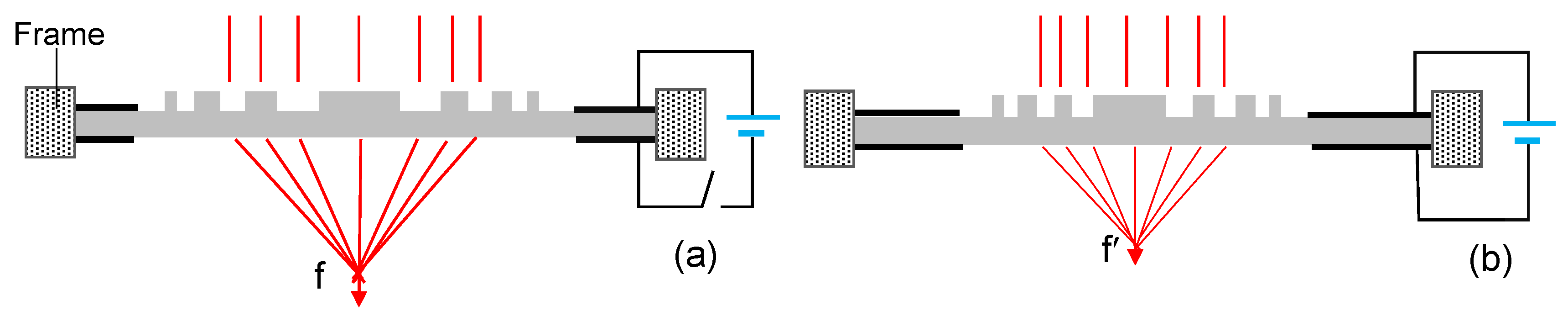
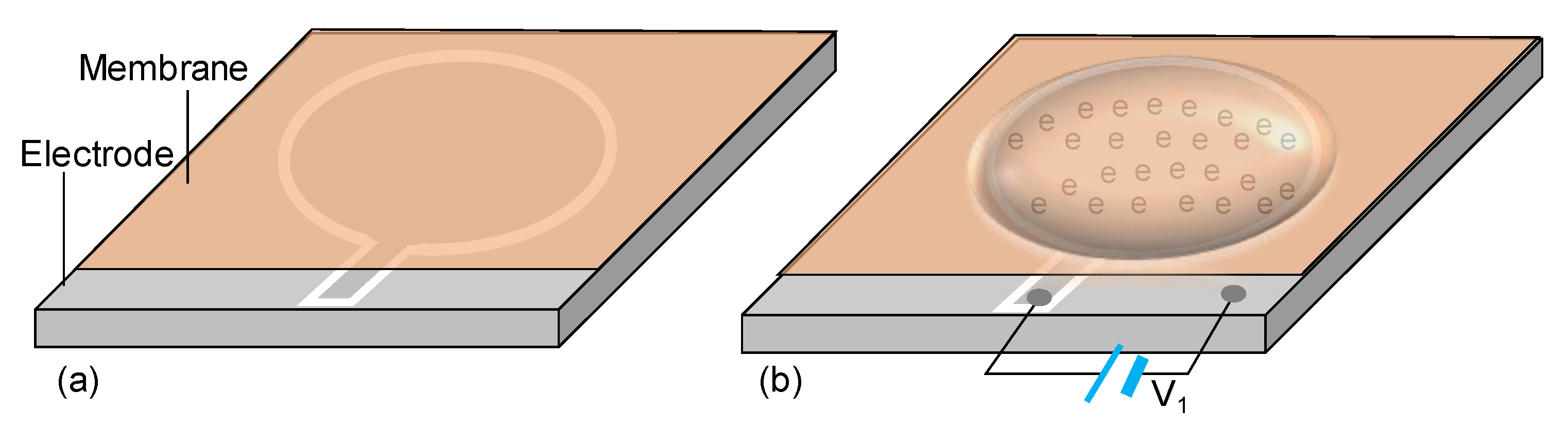
2. DEA Lens
2.1. Working Principle
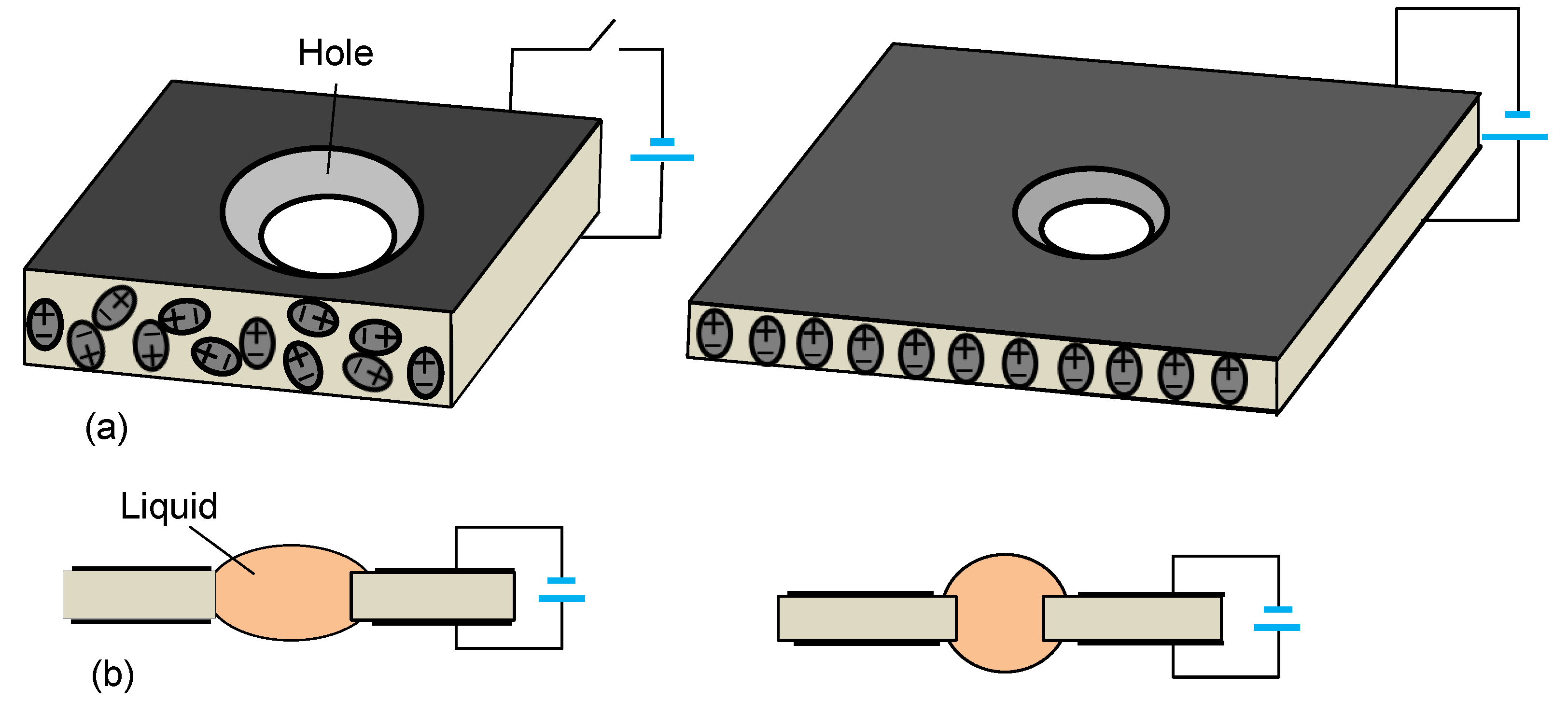
2.2. Liquid Encapsulation
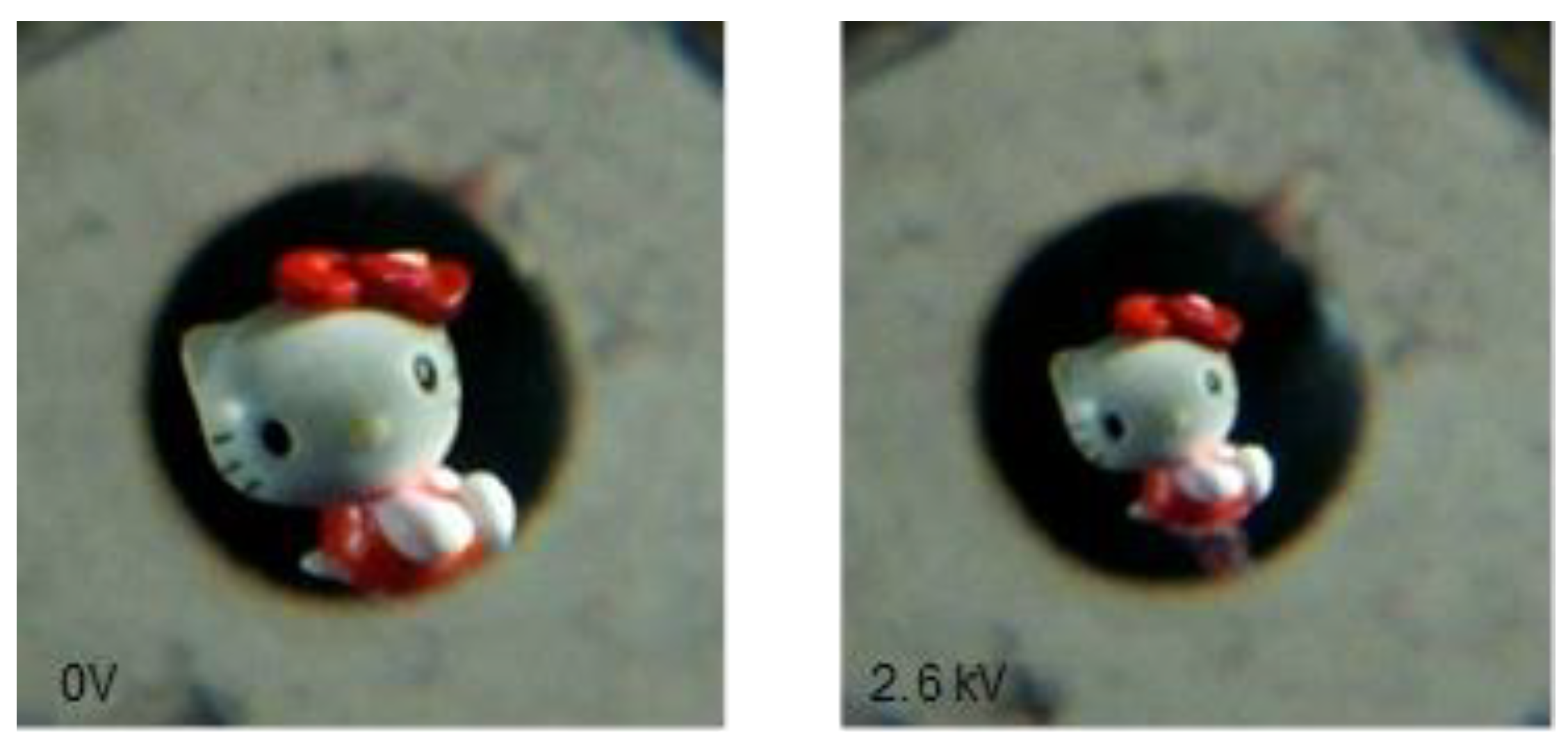
2.3. Free Constrained Boundary
2.4. Fresnel Zone Plate Lens
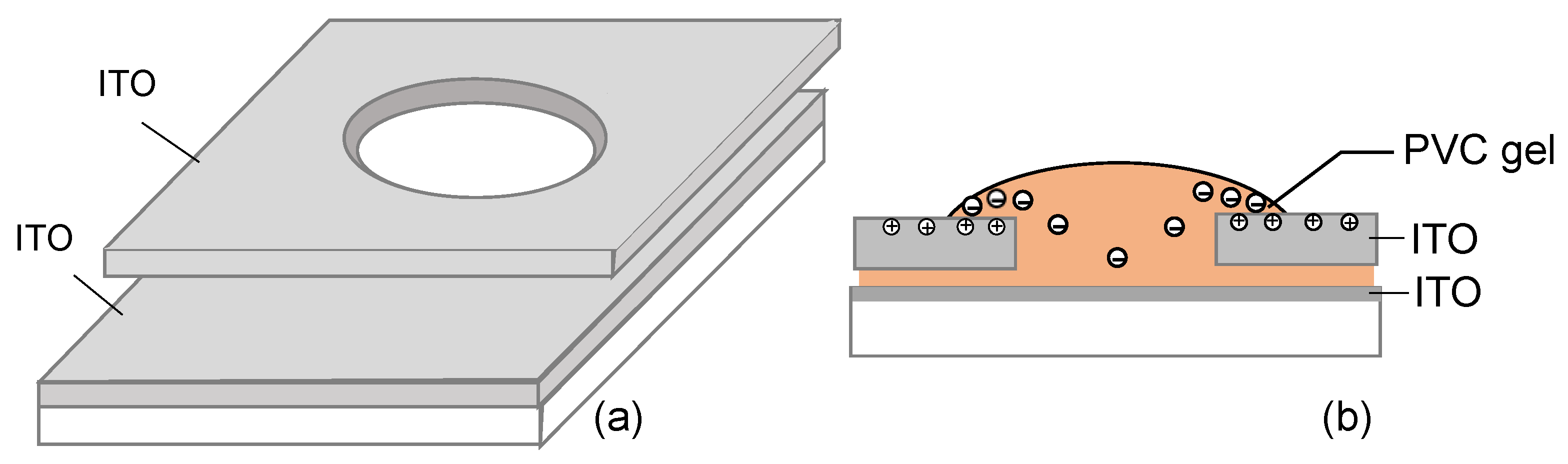
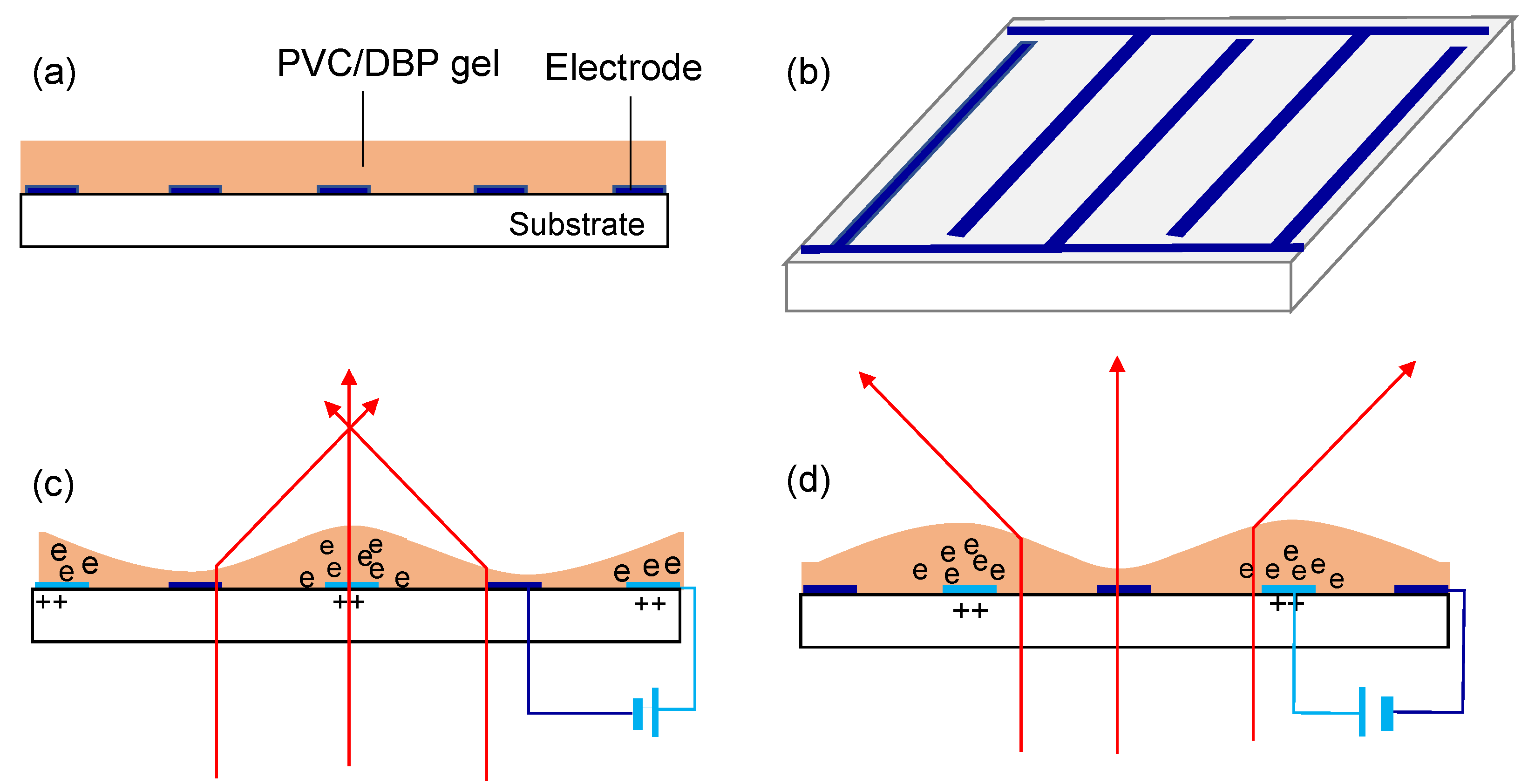
3. PVC Gel Lens
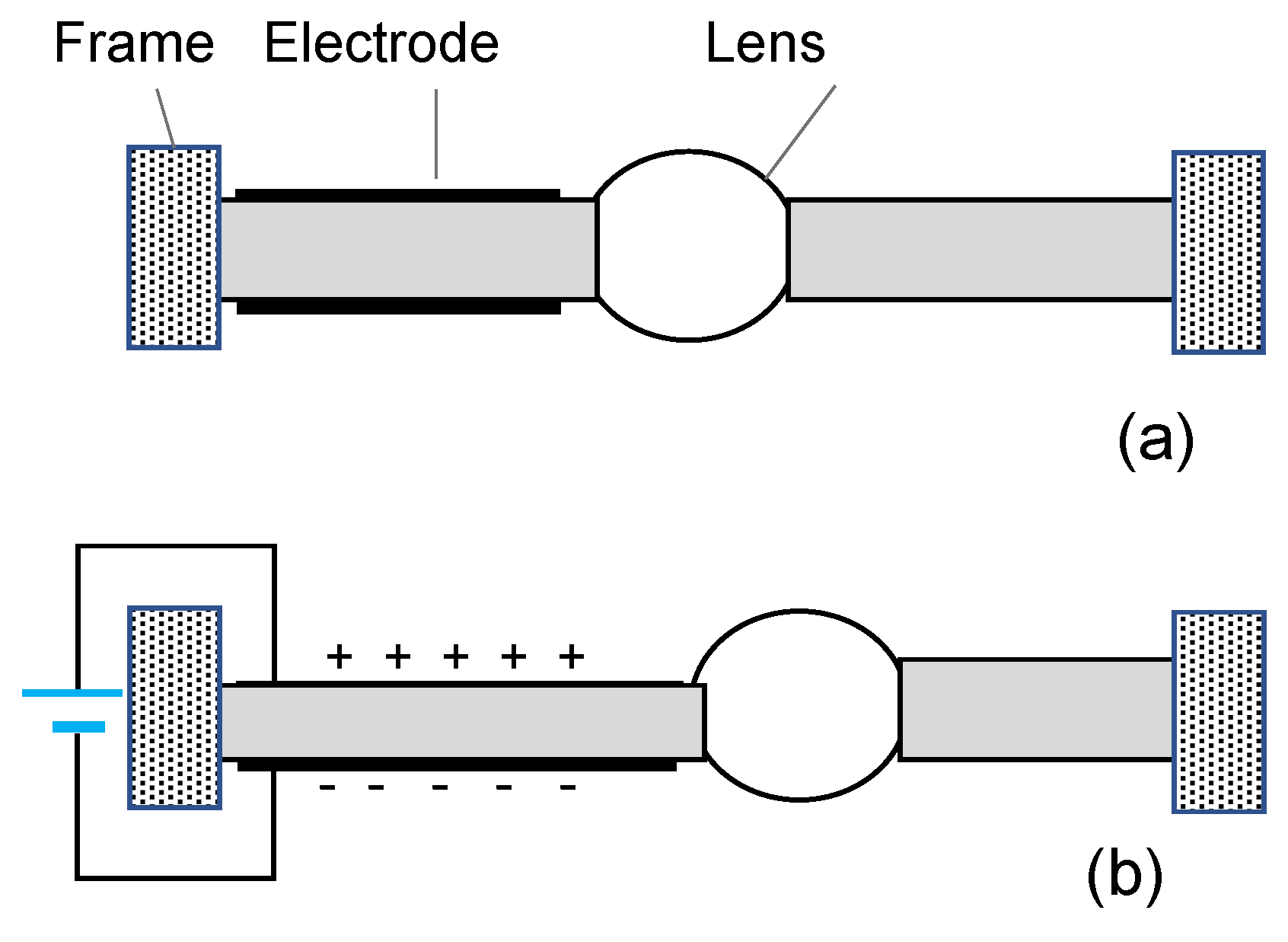
3.1. Working Principle
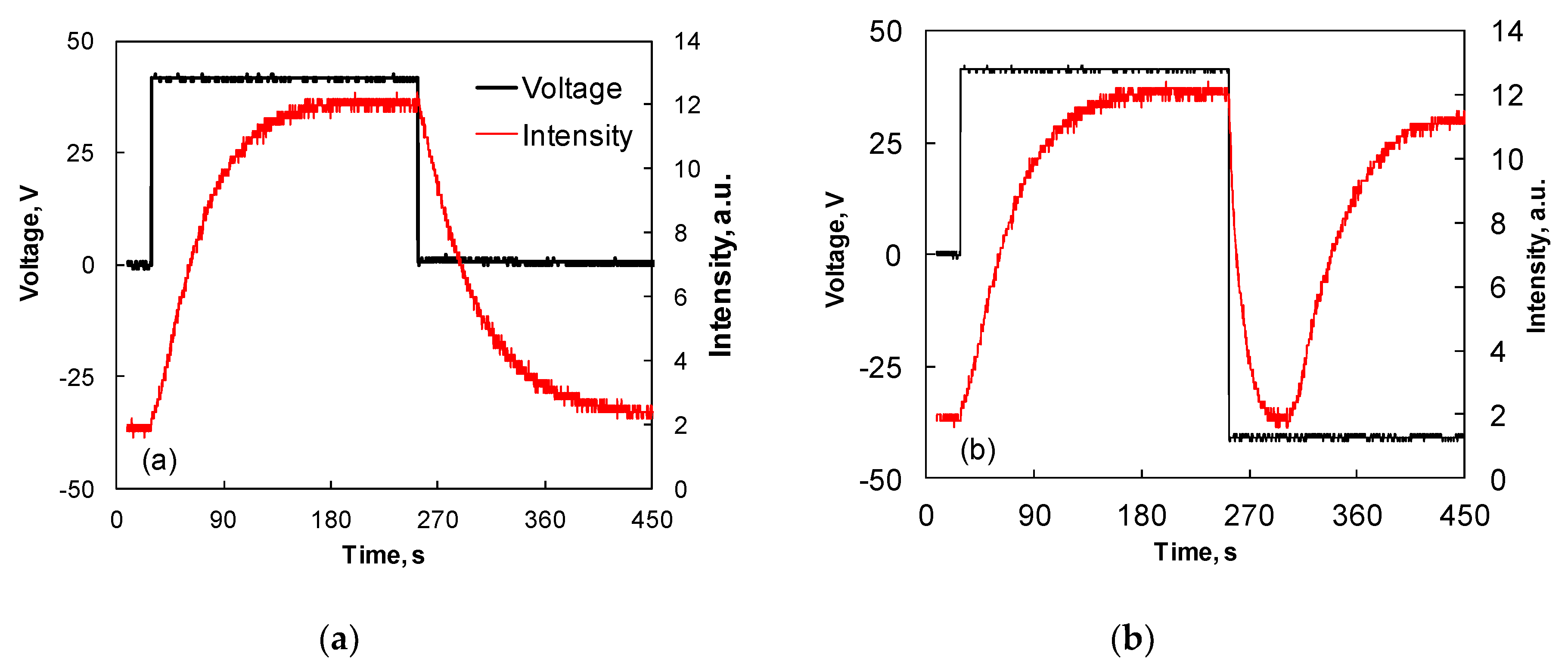
3.2. Macro-Sized Circular Lens
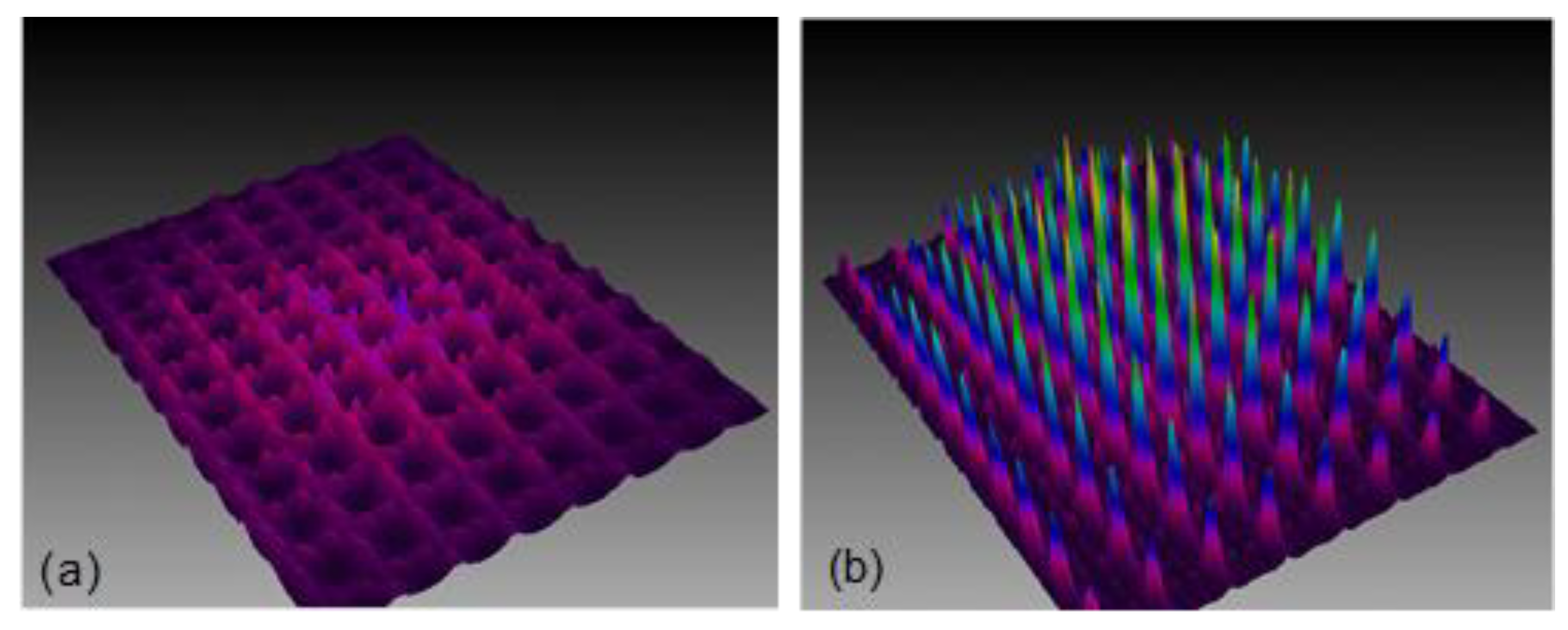
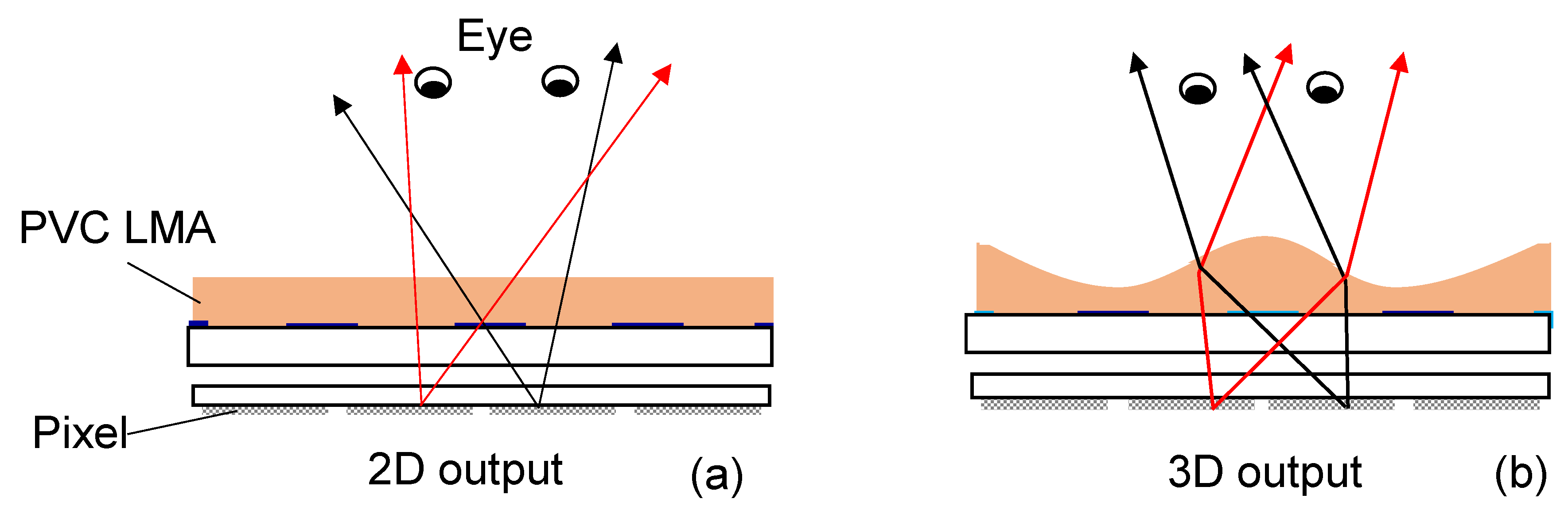
3.3. Lenticular Microlens Array
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEAs | Dielectric Elastomer Actuators |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| LC | Liquid Crystal |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| MLAs | Microlens Arrays |
| DC | Direct Current |
| FZP | Fresnel zone plate |
| ITO | Indium Tin Ixide |
| DBP | Dibutyl Phthalate |
| DBA | Dibutyl-Adipate |
| 2D | Two-Dimension |
| 3D | Three-Dimension |
References
- Sato, S. Liquid-crystal lens-cells with variable focal length. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1979, 18, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Sato, S. Optical properties of liquid crystal lens of any size. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, L571–L573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fan, Y.H.; Gauza, S.; Wu, S.T. Tunable flat liquid crystal spherical lens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4789–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sergan, V.; Heugten, T.V.; Duston, D.; Bhowmik, A.; Bos, P.J. Surface localized polymer aligned liquid crystal lens. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7133–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xu, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, S.-T. Reconfigurable fabrication of scattering-free polymer network liquid crystal prism/grating/lens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 161106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanfiroozi, A.; Huang, Y.-P.; Javidi, B.; Shien, H.-P.D. Dual layer electrode liquid crystal lens for 2D/3D tunable endoscopy imaging system. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 8527–8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Fan, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Wu, S.-T. Tunable-focus microlens arrays using nanosized polymer-dispersed liquid crystal droplets. Opt. Commun. 2005, 247, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-S.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsou, Y.-S.; Hsu, H.-K.; Li, W.-Y. Polarizer-free and fast response microlens arrays using polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.T. Polarization independent adaptive microlens with a blue-phase liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8045–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Lien, V.; Berdichevsky, Y.; Choi, J.; Lo, Y.H. Fluidic adaptive lens with high focal length tunability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3171–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fox, D.; Anderson, A.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.-T. Tunable-focus liquid lens controlled using a servo motor. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 8031–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, F.; Draheim, J.; Kamberger, R.; Waibel, P.; Wallrabe, U. Optical characterization of adaptive fluidic silicone-membrane lenses. Opt. Express 2009, 14, 11813–11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, S.; Hendriks, B.H.W. Variable-focus liquid lens for miniature cameras. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.R.; Hou, L.; Zhang, J.; Heikenfeld, J. Fabrication and demonstration of electrowetting liquid lens arrays. J. Disp. Technol. 2009, 5, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, S.; Miccio, L.; Vespini, V.; Finizio, A.; De Nicola, S.; Ferraro, P. Liquid micro-lens array activated by selective electrowetting on lithium niobate substrates. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 8084–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.C.; Yeh, J.A. Dielectrically actuated liquid lens. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7140–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Xianyu, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.-T. Adaptive dielectric liquid lens. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 14954–14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, S.-T. Dielectric liquid microlens with well-shaped electrode. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 10499–10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Hardt, S. An adaptive liquid microlens driven by a ferrofluidic transducer. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 055032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Levi, S.; Wu, S.T. Adaptive mechanical-wetting lens actuated by ferrofluids. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2118–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malouin, B.; Vogel, M., Jr.; Olles, J.; Chen, L.; Hirsa, A. Electromagnetic liquid pistons for capillarity-based pumping. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Agarwal, A.K.; Beebe, D.J.; Jiang, H. Adaptive liquid microlenses activated by stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Nature 2006, 442, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrick, J.D.; Stokes, S.; Bachas-Daunert, S.; Moschou, E.A.; Deo, S.K.; Bachas, L.G.; Daunert, S. Chemically tunable lensing of stimuli-responsive hydrogel microdomes. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4024–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ren, H.; Lin, Y.J.; Moharam, M.G.J.; Wu, S.T.; Tabiryan, N. Adaptive liquid lens actuated by photo-polymer. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 17590–17595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, T.; Ogiwara, T.; Fujii, K.; Ueki, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Takasaki, M. Electrically active artificial pupil showing amoeba-like pseudopodial deformation. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2886–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; Turco, S.; De Rossi, D. Bioinspired tunable lens with muscle-like electroactive elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shian, S.; Diebold, R.M.; Clarke, D.R. Tunable lenses using transparent dielectric elastomer actuators. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8669–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.W.; Yeo, M.; Shin, E.-J.; Park, W.-H.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, B.-U.; Kim, S.-Y. Eco-friendly plasticized poly (vinyl chloride)–acetyl tributyl citrate gels for varifocal lens. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 94919–94925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jin, B.; He, R.; Ren, H. Adaptive lenticular microlens array based on voltage-induced waves at the surface of polyvinyl chloride/dibutyl phthalate gels. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 8142–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, H. Dynamic response of a lenticular microlens array using a polyvinyl chloride gel. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 127103. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, N.; Morita, S. Variable-focus liquid-filled optics lens. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 4181–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Wu, S.T. Variable-focus liquid lens with changing aperture. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 211107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, M.; Berge, B.; Vovelle, L. Electrowetting of water and aqueous solutions on poly (ethylene terephthalate) insulating films. Polymer 1996, 37, 2465–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, B.; Peseux, J. Variable focal lens controlled by an external voltage: An application of electrowetting. Eur. Phys. J. E 2000, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Francl, J.; Taheri, B.; West, J.L. A method for the formation of polymer walls in liquid crystal/polymer mixtures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2253–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Photomechanics: Directed bending of a polymer film by light. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabiryan, N.; Serak, S.; Dai, X.M.; Bunning, T. Polymer film with optically controlled form and actuation. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 7442–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.K.; Prusty, S. Review on conducting polymers and their applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat-Nasser, S.; Wu, Y. Comparative experimental study of ionic polymer-metal composites with different backbone ionomers and in various cation forms. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 5255–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Cui, C.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Barisci, J.N.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Mazzoldi, A.; De Rossi, D.; Rinzler, A.G.; et al. Carbon nanotube actuators. Science 1999, 284, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Takasaki, M.; Hirai, T. Actuation mechanism of plasticized PVC by electric field. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 157, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ueki, T.; Tsurumi, D.; Hirai, T. Influence of plasticizer content on the transition of electromechanical behavior of PVC gel actuator. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7902–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keplinger, C.; Li, T.; Baumgartner, R.; Suo, Z.; Bauer, S. Harnessing snap-through instability in soft dielectrics to achieve giant voltage-triggered deformation. Soft Matter. 2012, 8, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffli, L.; Rosset, S.; Ghilardi, M.; Carpi, F.; Shea, H. Ultrafast all-polymer electrically tunable silicone lenses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudykh, S.; Bhattachary, K.; deBotton, G. Snap-through actuation of thick-wall electroactive balloons. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 2012, 47, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lee, G.-B.; Ren, H.; Nah, C. Adaptive liquid lens driven by elastomer actuator. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Ren, H. Position-movable lens driven by dielectric elastomer actuator. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 075101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, B.; Nam, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.K.; Mun, S.; Lim, J.M.; Ryu, Y.; Song, S.H.; Kyung, K.-U. Electrically tunable binary phase Fresnel lens based on a dielectric elastomer actuator. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 23801–23808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md Uddin, Z.; Yamaguchi, W.M.; Shirai, H.H. Electrically induced creeping and bending deformation of plasticized poly (vinyl chloride). Chem. Lett. 2001, 4, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, T.; Ueki, T.; Takasaki, M. Electrical actuation of textile polymer materials. J. Fiber Bioeng. Inform. 2008, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Yeo, M.; Shin, E.-J.; Park, W.-H.; Jang, J.-S.; Nam, B.-U.; Bae, J.W. Fabrication and evaluation of variable focus and large deformation plano-convex microlens based on non-ionic poly (vinyl chloride)/dibutyl adipate gels. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ren, H. Adaptive microlens array based on electrically charged polyvinyl chloride/dibutyl phthalate gel. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 095104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijn, M.P.C.M.; de Boer, S.T.; Willemsen, O.H.; Sluijter, M. 2D-3D displays based on switchable lenticulars. J. SID 2008, 16, 847–854. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.T. Switchable focus using a polymeric lenticular microlens array and a polarization rotator. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7916–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| PVC/DBA | 1:1 | 1:5 | 1:9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ||||
| Charge density near the anode (C/cm3) | ~60 | ~365 | ~85 | |
| Stress induced 200% strain (kPa) | ~3100 | ~250 | ~5 | |
| Young’s modulus (kPa) | ~495 | ~30 | ~5 | |
| Electrostatiic adhesive force with 500 V on the anode (g/cm2) | ~25 | ~185 | 115 | |
| Transmittance (%) | Very low | ~82 | ~88 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Wu, S.-T. Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071085
Ren H, Wu S-T. Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071085
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hongwen, and Shin-Tson Wu. 2018. "Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071085
APA StyleRen, H., & Wu, S.-T. (2018). Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071085






