Active Noise Control Using Modified FsLMS and Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Contribution
- The MFsLMS algorithm reduces the computational complexity of the FsLMS algorithm.
- The McLaurin series relaxes the functional expansion of the MFsLMS algorithm.
- The stability of the proposed ANC system is evaluated via HPSOFF, by the stability factor.
3. Related Works
The Recent Works Related to the Proposed Method Are Given Below
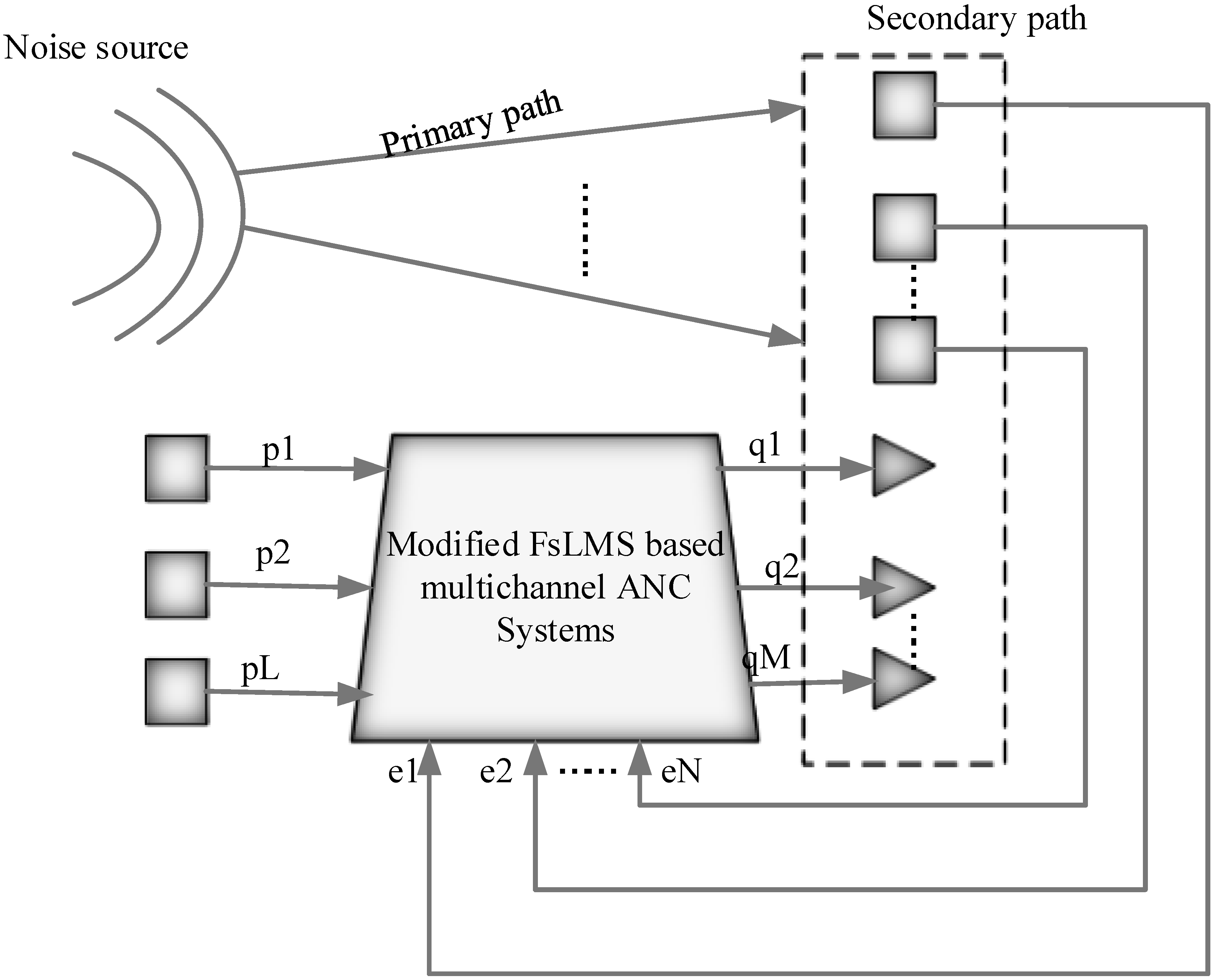
4. Proposed Method
4.1. MFsLMS Algorithm
4.2. Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm
5. Reduction of Computational Difficulty of MFsLMS
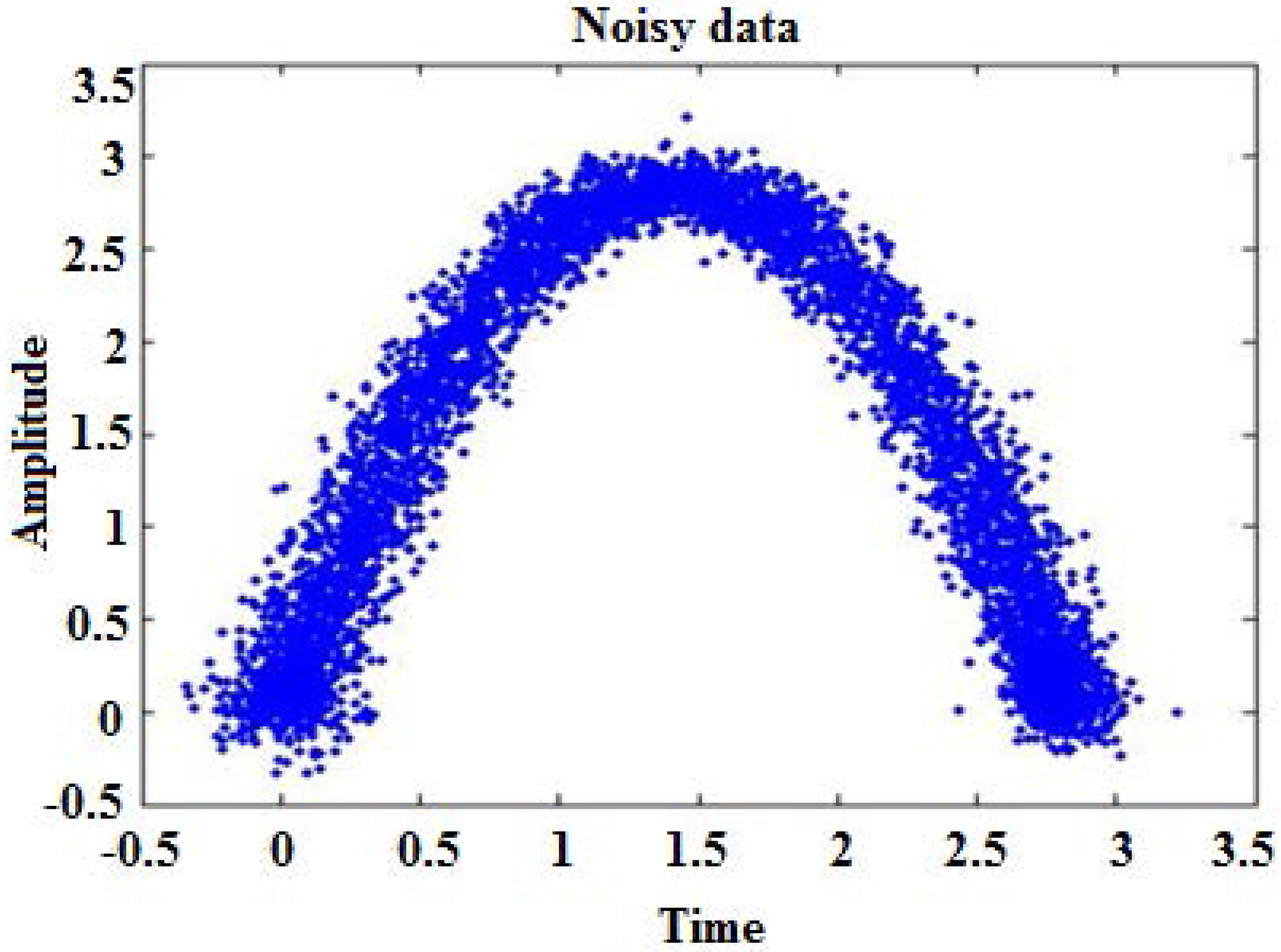
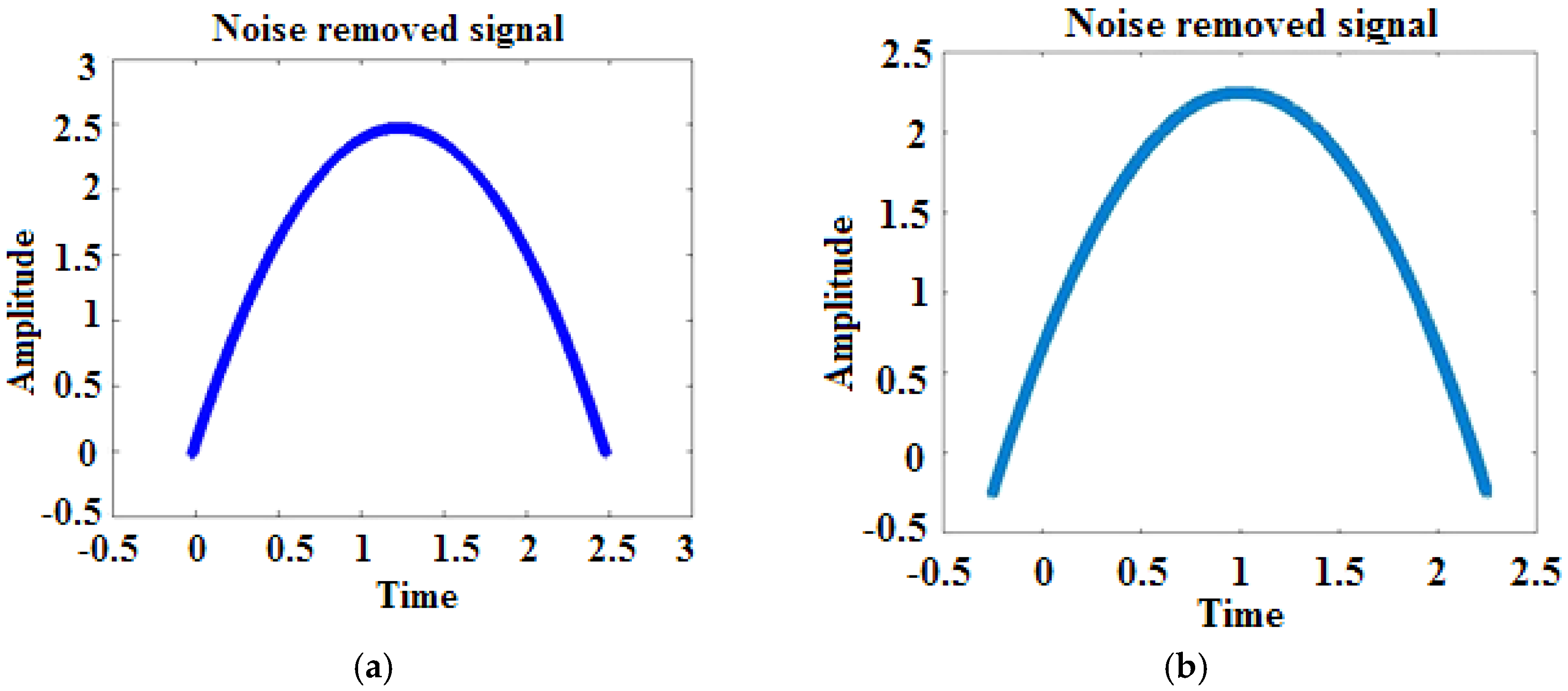
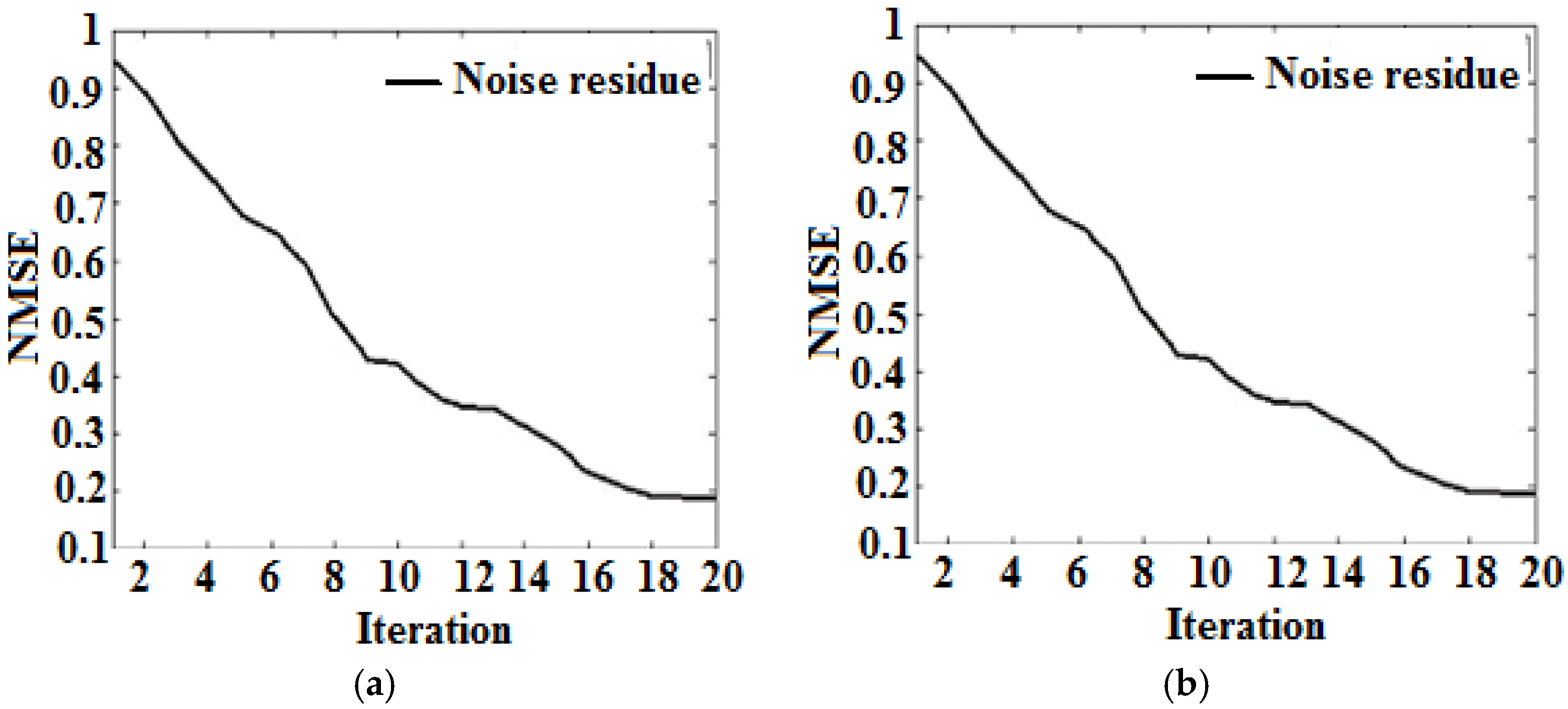
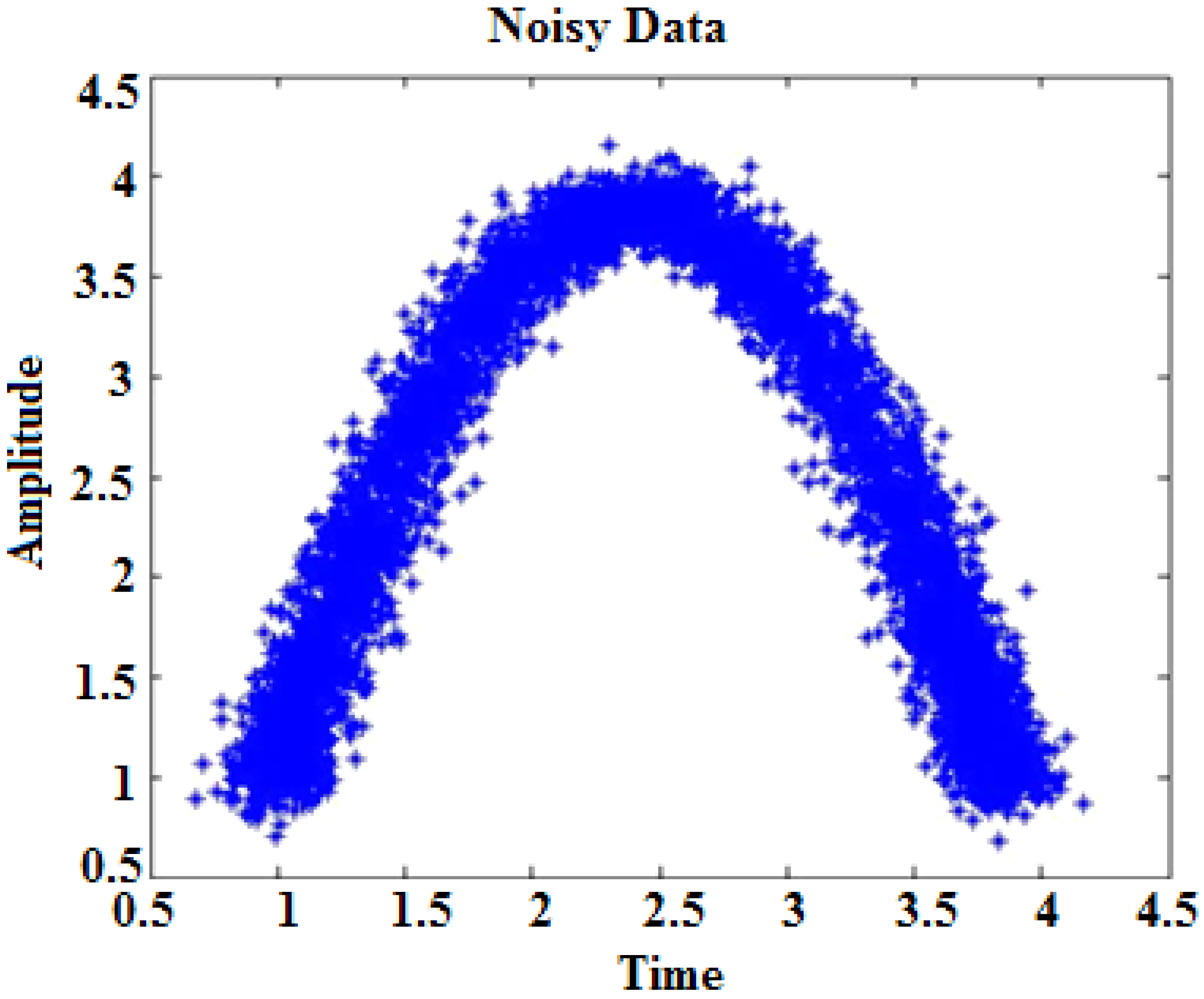
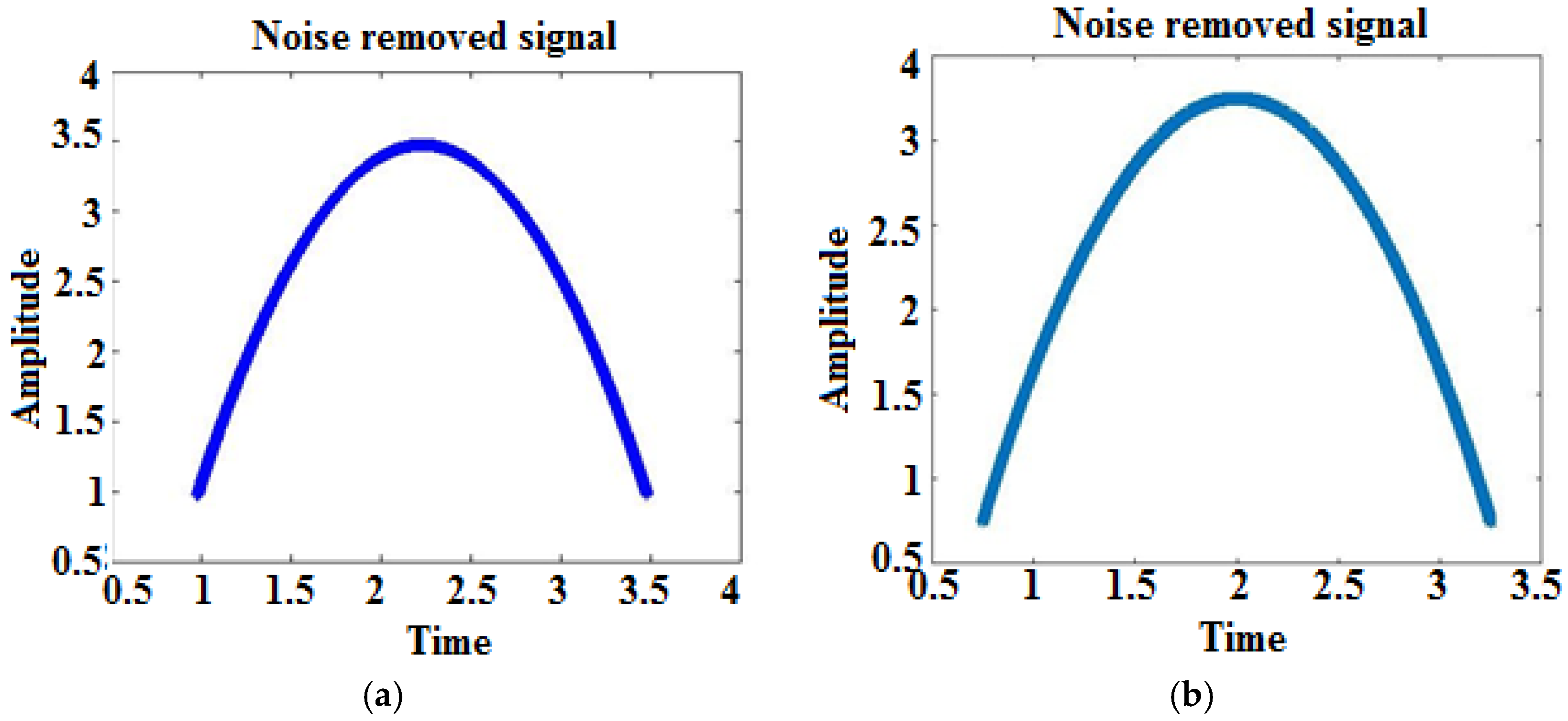
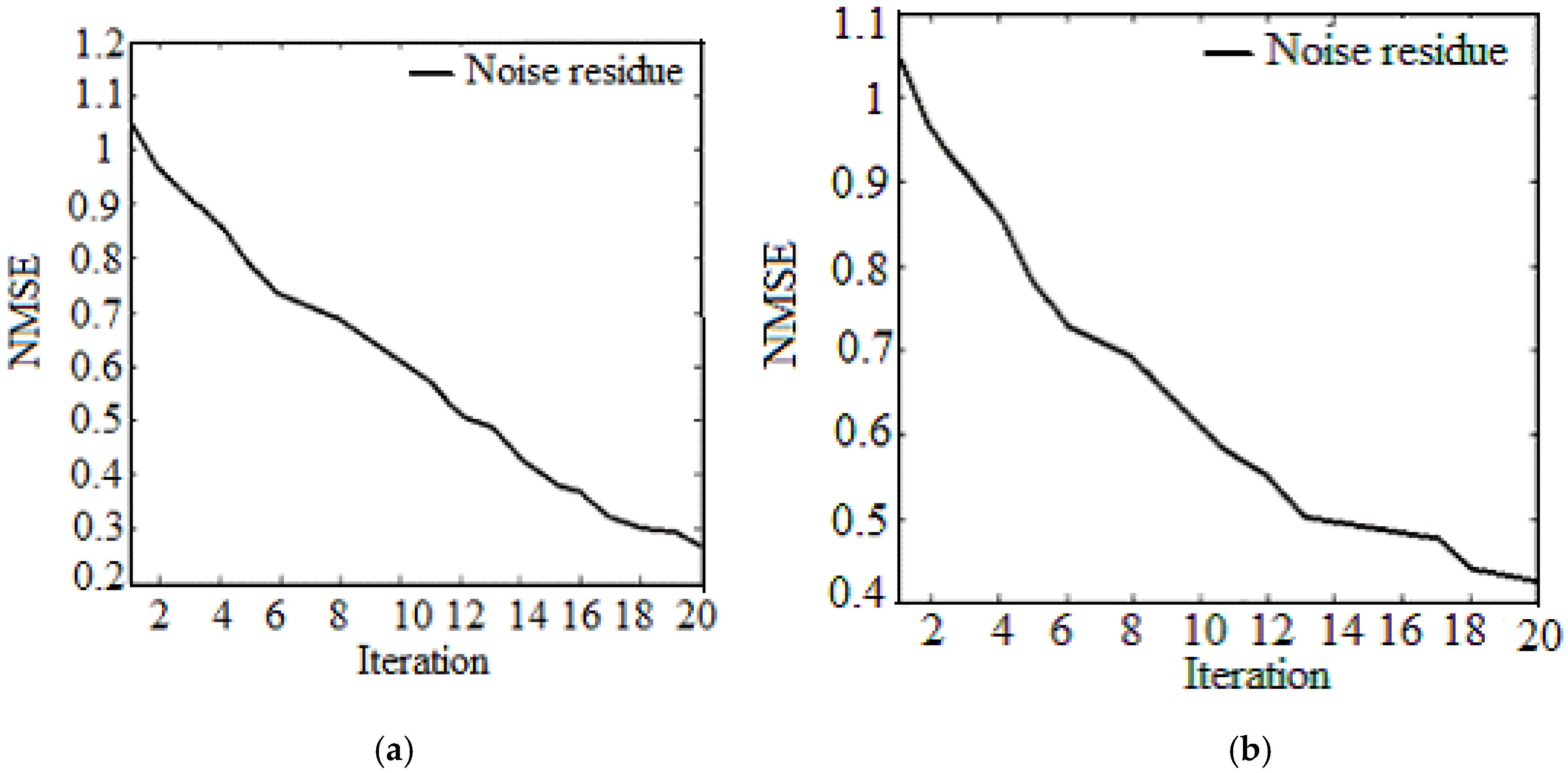
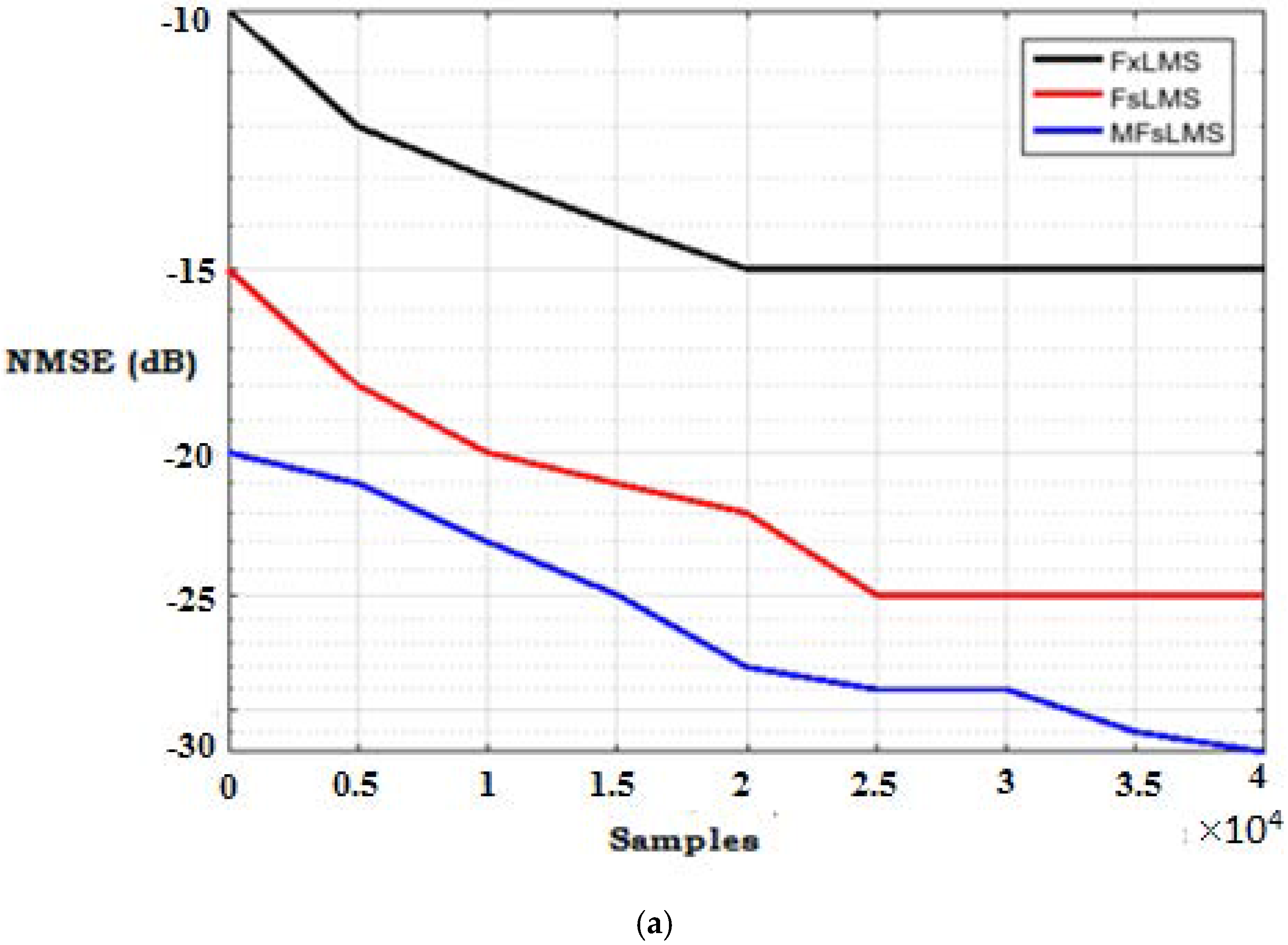
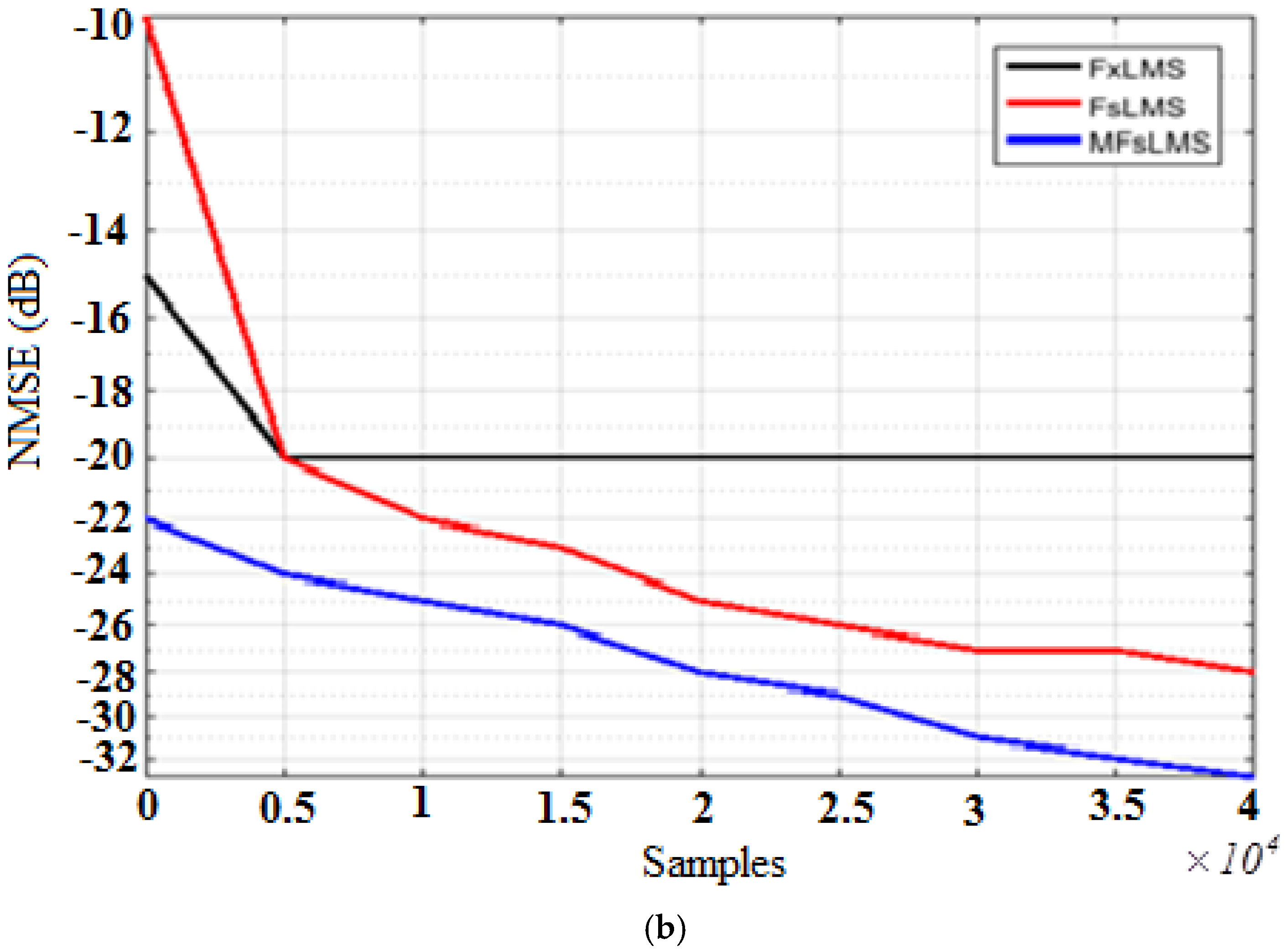
6. Result and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, D.P.; Panda, G. Active mitigation of nonlinear noise processes using a novel filtered-s LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2004, 12, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawełczyk, M. Active noise control—A review of control-related problems. Archit. Acoust. 2008, 33, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, A.; Ferrer, M.; Diego, M.D.; Pinero, G.; Garcia-Bonito, J.J. Sound quality of low-frequency and car engine noises after active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jong, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Kim, J. Enhancement of noise reduction efficiency based on compensation in the ANC headset using fixed-point DSP. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 116, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.D.; Hansen, C.H. Design considerations for active noise control systems implementing the multiple input multiple output LMS algorithm. J. Sound Vib. 1992, 159, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.K.; Lovstedt, S.P.; Blotter, J.D.; Sommerfeldt, S.D. Eigenvalue equalization filtered-x algorithm for the multichannel active noise control of stationary and nonstationary signals. J. Acoust. Am. 2008, 123, 4238–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodson, M.; Jensen, J.S.; Douglas, S.C. Active noise control for periodic disturbances. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2001, 9, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Mitra, S.; Gan, W.S. Active noise control system for headphone applications. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Kong, X.; Gan, W.S. Applications of adaptive feedback active noise control system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 11, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.D.; Bai, M.R. Application of feedforward adaptive active-noise control for reducing blade passing noise in centrifugal fans. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 239, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurers, T.; Veres, M.S.; Elliott, S.J. Frequency selective feedback for active noise control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2002, 22, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.; Quednau, S. Multichannel recursive-least-square algorithms and fast-transversal-filter algorithms for active noise control and sound reproduction systems. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2000, 8, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lan, H.; Ser, W. Cross-updated active noise control system with online secondary path modelling. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2001, 9, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Kar, A.; Chandra, M. A technical review on adaptive algorithms for acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 3–5 April 2014; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, X. Active noise cancellation algorithms for impulsive noise. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 36, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Z.; Gao, S.; Jiang, E. Analysis and implementation of improved multi-input multi-output filtered-X least mean square algorithm for active structural vibration control. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2013, 20, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Lee, C.M.; Xu, Z.H.; Sui, L.N. A multi-resolution filtered-x LMS algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 66, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.K.; Ren, W. Convergence analysis of the multi-variable filtered-X LMS algorithm with application to active noise control. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H. Current and future industrial applications of active noise control. Noise Control Eng. J. 2005, 53, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Jiang, J. Adaptive Volterra filters for active control of nonlinear noise processes. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Gan, W.S.; Kuo, S.M. Recent advances on active noise control: Open issues and innovative applications. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2001, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.P.; Panda, G.; Nayak, D.K. Development of Frequency Domain Block Filtered-s LMS (FBFSLMS) Algorithm for Active Noise Control System. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2006), Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.H.; Stewart, R.W. Adaptive IIR filtered-v algorithms for active noise control. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, N.K.; Das, D.P.; Panda, G. Particle swarm optimization based nonlinear active noise control under saturation nonlinearity. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 41, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Panda, G. A particle-swarm-optimization-based decentralized nonlinear active noise control system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Sicuranza, G.L. Accuracy and performance evaluation in the genetic optimization of nonlinear systems for active noise control. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Diego, M.D.; Pinero, G. Convex combination filtered-x algorithms for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Diego, M.D.; Gonzalez, A.; Pinero, G. Steady-State Mean Square Performance of the Multichannel Filtered-X Affine Projection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 2771–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, G. A variable step-size FXLMS algorithm for narrowband active noise control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Panda, G. On the development of adaptive hybrid active noise control system for effective mitigation of nonlinear noise. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuranza, G.L.; Carini, A. On the BIBO stability condition of adaptive recursive FLANN filters with application to nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Rai, C.S.; Singh, A.P. Comparative study of firefly algorithm and particle swarm optimization for noisy non-linear optimization problems. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2012, 10, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Firefly algorithm. Stochastic test functions and design optimization. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2010, 2, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.P.; Mohapatra, S.R.; Routray, A.; Basu, T.K. Filtered-s LMS algorithm for multichannel active control of nonlinear noise processes. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Algorithm | FsLMS | MFsLMS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of Secondary Path (V) | Multiplication | Addition | Multiplication | Addition | |
| 2 | 852 | 634 | 316 | 154 | |
| 4 | 950 | 781 | 332 | 202 | |
| 6 | 1024 | 948 | 348 | 250 | |
| 8 | 1095 | 1012 | 364 | 298 | |
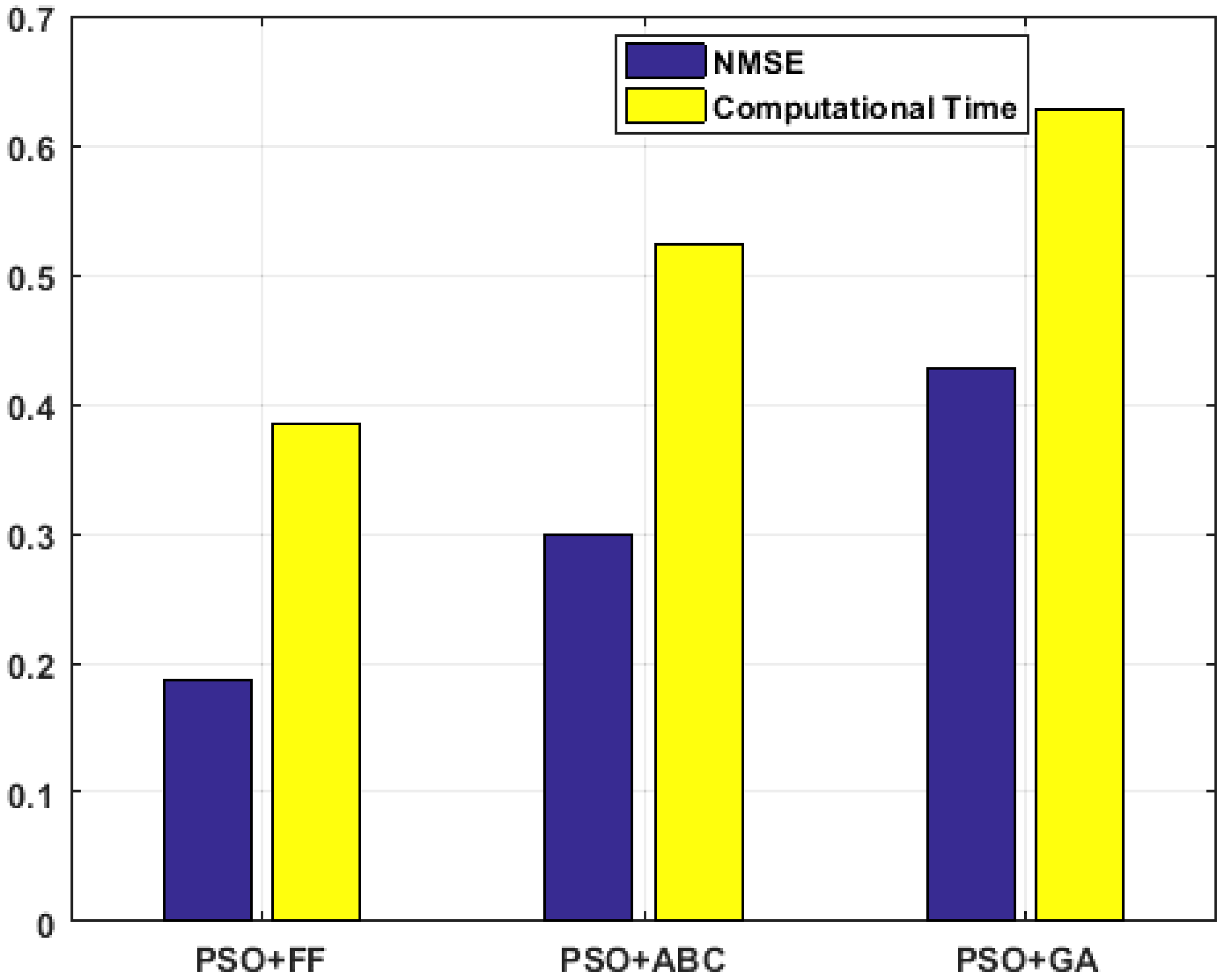
| S.no | Method | NMSE (dB) | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Proposed Method | 0.187 | 0.385 |
| 2 | Hybrid PSO—ABC | 0.300 | 0.524 |
| 3 | Hybrid PSO—GA | 0.428 | 0.628 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walia, R.; Ghosh, S. Active Noise Control Using Modified FsLMS and Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050686
Walia R, Ghosh S. Active Noise Control Using Modified FsLMS and Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(5):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050686
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalia, Ranjan, and Smarajit Ghosh. 2018. "Active Noise Control Using Modified FsLMS and Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm" Applied Sciences 8, no. 5: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050686
APA StyleWalia, R., & Ghosh, S. (2018). Active Noise Control Using Modified FsLMS and Hybrid PSOFF Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 8(5), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050686






