Quantitative Flow Cytometry to Measure Viral Production Using Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus as a Model: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus and Cell Line Employed
2.2. Titration by Plaque and Endpoint Dilution Assays
2.3. MARIS Staining and Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.4. Quantitative Flow Cytometry (qFCM) Assessment
2.5. RNA Isolation
2.6. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.7. Preliminary Optimization of the Assay and Evaluation of qFCM Reliability
2.8. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Quantitative Flow Cytometry Measurements
2.9. Comparative Evaluation of Correlation between qFCM and Traditional Titration Methods
2.10. Assessment of VP2 Protein Expression during the IPNV Time Course Infection
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Procedure and Assessment of the Reliability of the Data
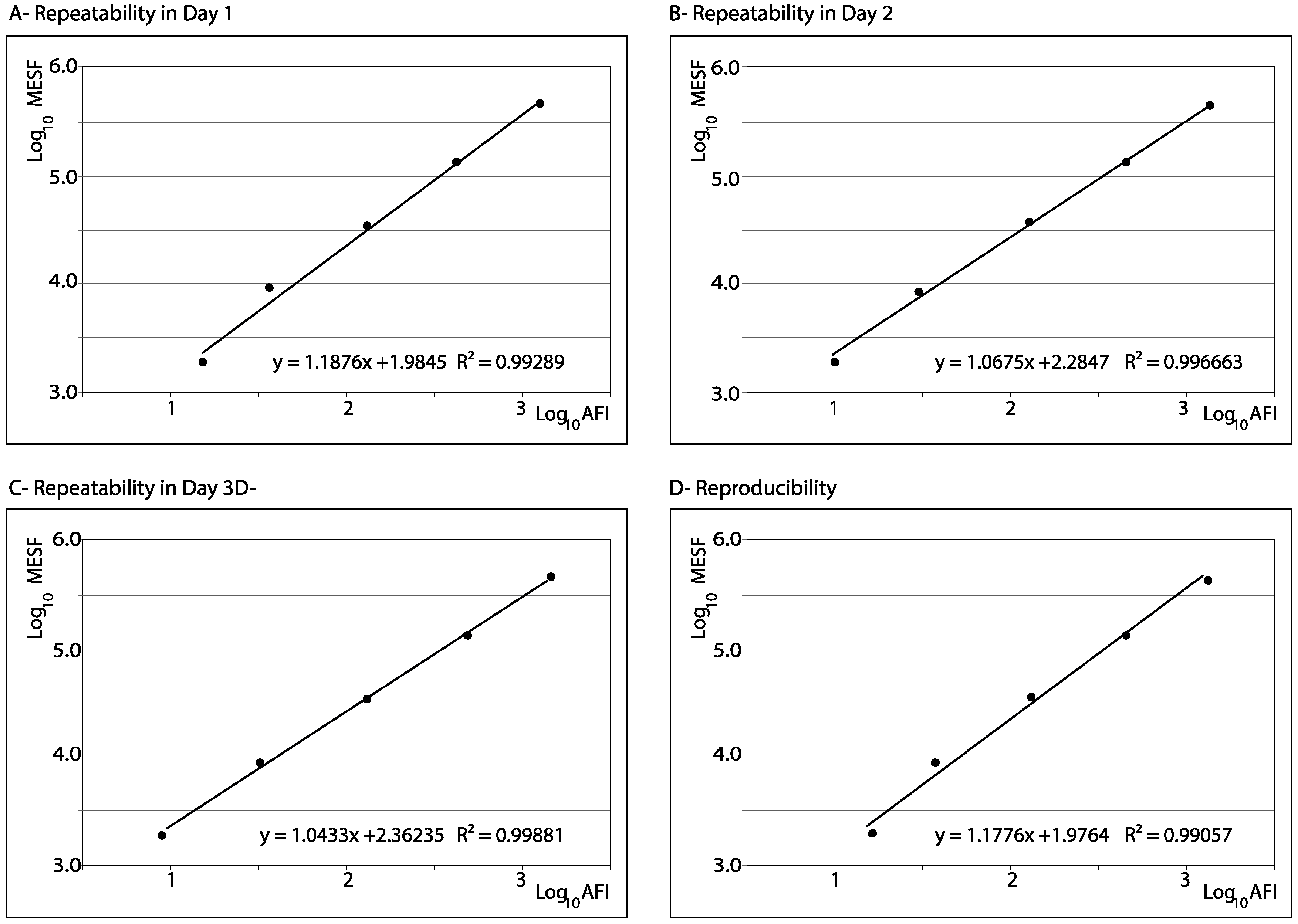
3.2. Repeatability and Reproducibility
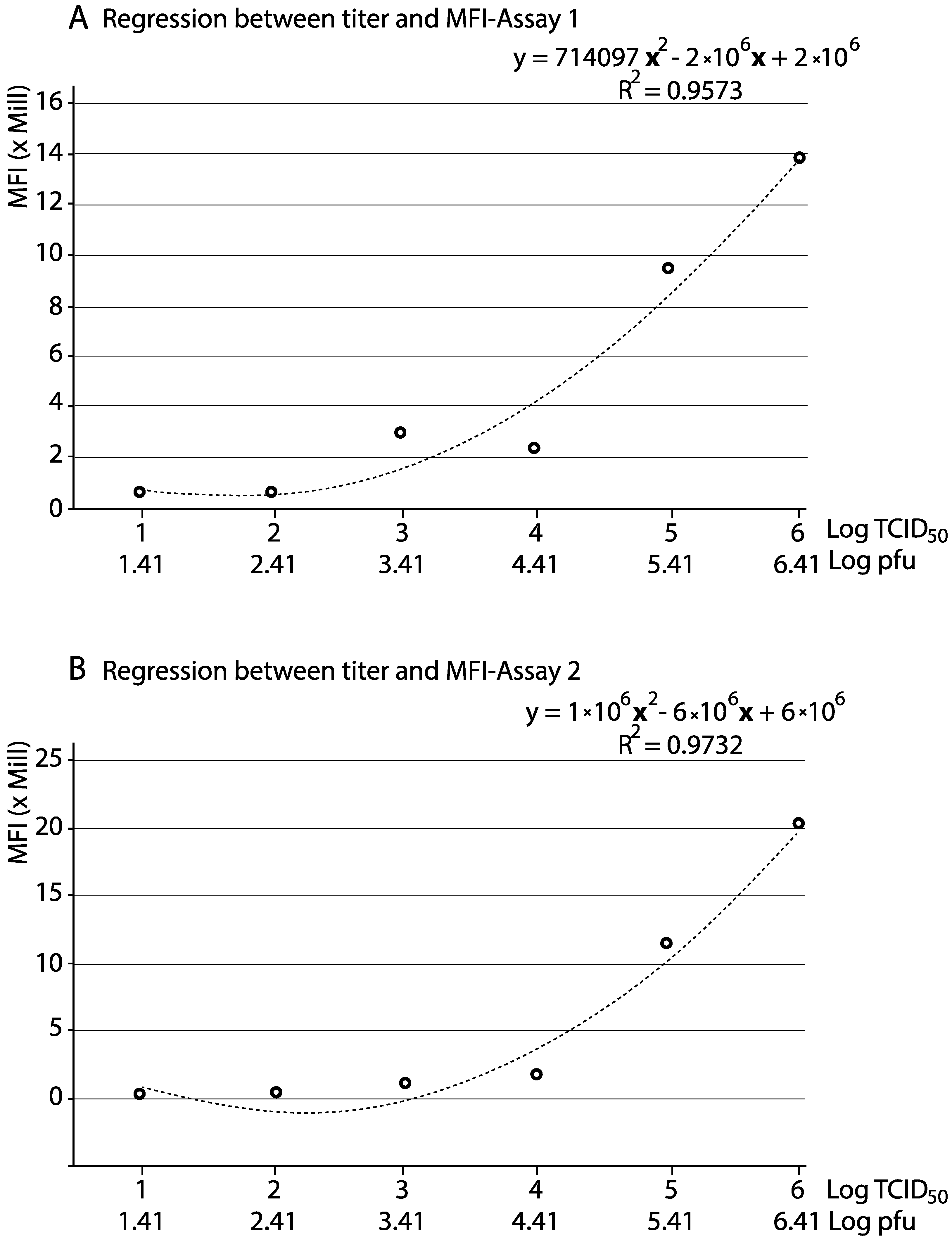
3.3. Reliability of the qFCM for Viral Titration
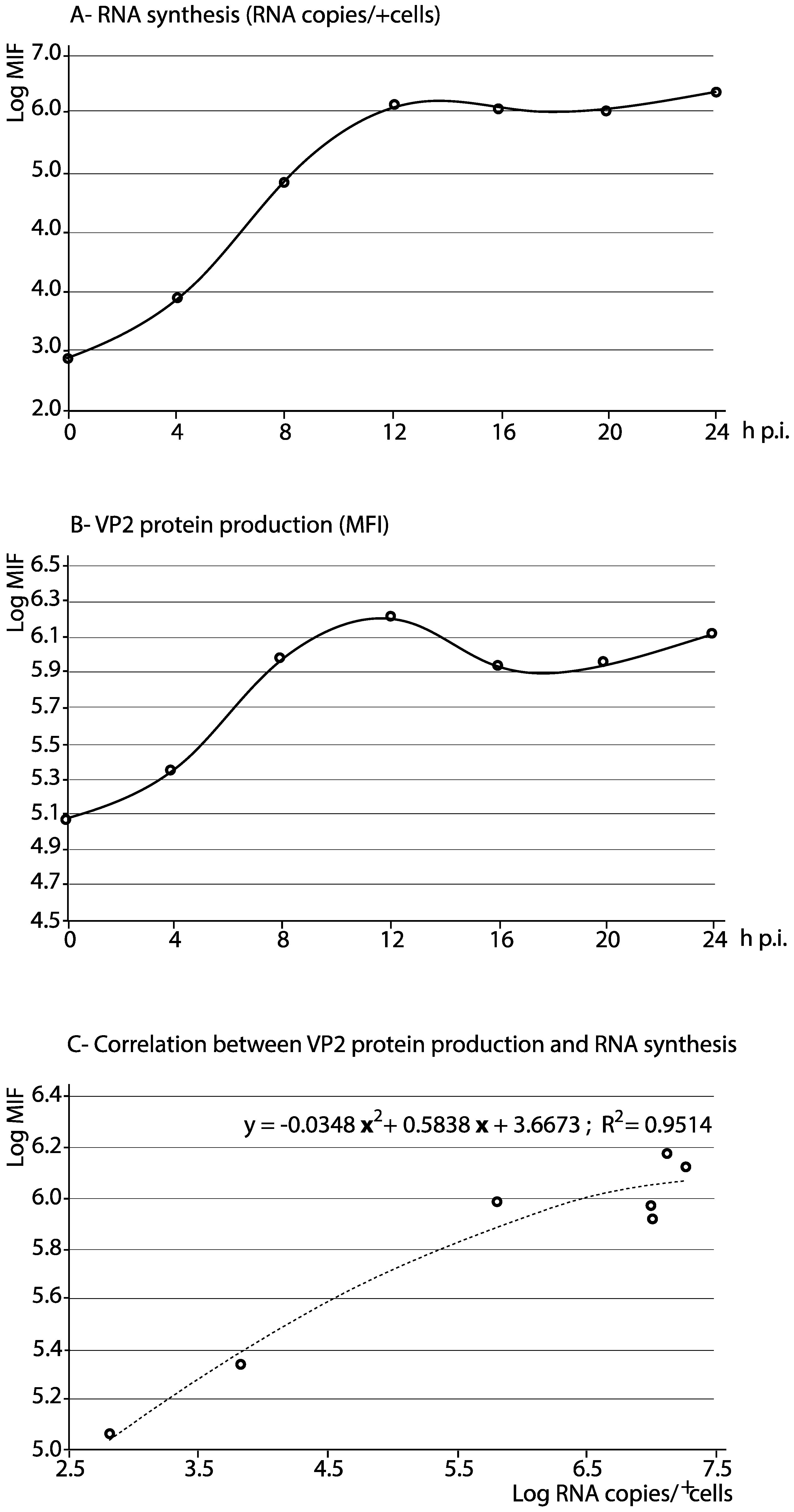
3.4. Quantification of the VP2 Protein Production and RNA Synthesis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kürzinger, K.; Reynolds, T.; Germain, R.N.; Davignon, D.; Martz, E.; Springer, T.A. A novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): Cellular distribution, quantitative expression, and structure. J. Immunol. 1981, 127, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poncelet, P.; Carayon, P. Cytofluorometric quantification of cell-surface antigens by indirect immunofluorescence using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. Methods 1985, 85, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.O.; Marti, G.E.; Gaigalas, A.; Hannon, W.H.; Vogt, R.F. Terminology and nomenclature for standardization in quantitative fluorescence cytometry. Cytometry 1998, 33, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, K.J.; Fletcher, M.A. Quantitative flow cytometry in the clinical laboratory. Clin. Appl. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 5, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, N.; Duron, J.; Gingras, D.; Lippe, R. Quantitative Evaluation of Protein Heterogeneity within Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Particles. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, M.A.; Liu, A.H.; Calatroni, A.; Krouse, R.Z.; Shao, B.; Schiltz, A.; Gern, J.E.; Togias, A.; Busse, W.W. Enhanced plasmacytoid dendritic cell antiviral responses after omalizumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Horsel, J.; Genzel, Y.; Reichl, U. Flow cytometric monitoring of influenza A virus infection in MDCK cells during vaccine production. BMC Biotechnol. 2008, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z.-G. High throughput screening of scFv antibodies against viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus by flow cytometry. J. Virol. Method 2015, 219, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, S.; Alonso, M.; Perez-Prieto, S.I. Detection of infections pancreatic necrosis virus (ipnv) from leukocytes of carrier rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Pathol. 2001, 36, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Saint-Jean, S.; Vilas, P.; Palacios, M.; Pérez, S. Detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis in a carrier population of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Richardson), by flow cytometry. J. Fish Dis. 1991, 14, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Saint-Jean, S.; Borrego, J.J.; Pérez-Prieto, S.I. Comparative evaluation of five serological methods and RT-PCR assay for the detection of IPNV in fish. J. Virol. Method 2001, 97, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønneseth, A.; Pettersen, E.F.; Wergeland, H.I. Flow cytometry assay for intracellular detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1292e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rønneseth, A.; Haugland, G.T.; Wergeland, H.I. Flow cytometry detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) within subpopulations of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) leucocytes after vaccination and during the time course of experimental infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rosado, E.; Castro, D.; Cano, I.; Perez-Prieto, S.I.; Borrego, J.J. Serological techniques for detection of lymphocystis virus in fish. Aquat. Living Resour. 2002, 15, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Stein, D.A.; Thomann, E.; Moulton, H.M.; Leong, J.C.; Iversen, P.; Mourich, D.V. Inhibition of infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus in cell cultures with peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.W.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Lee, L.Y.; Gedaria, A.I.; Sheng Zhang, S. Development of a flow cytometry based method for rapid and sensitive detection of a novel marine fish iridovirus in cell culture. J. Virol. Method 2002, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Perez-Prieto, S.I. Viral coinfection in salmonids: Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus interferes with infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.S.; Chi, S.C. GHSC70 Is Involved in the Cellular Entry of Nervous Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finstad, Ø.W.; Dahle, M.K.; Lindholm, T.H.; Nyman, I.B.; Løvoll, M.; Wallace, C.; Olsen, C.M.; Storset, A.K.; Rimstad, E. Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) infects Atlantic salmon erythrocytes. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.; Alonso, M.; Perez-Prieto, S.I. Comparison of two birnavirus–rhabdovirus coinfections in fish cell lines. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 67, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, Ø.; Olsen, C.M.; Rimstad, E.; Dahle, M.K. Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) replicates in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) erythrocytes ex vivo. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, T.; Skjesol, A.; Jørgensen, J.B. VP3, a structural protein of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus, interacts with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase VP1 and with double-stranded RNA. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6652–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julin, K. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV)—Persistent Infections, Virulence and Antiviral Defence. Ph.D. Thesis, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, R.; Mason, C.L.; Nagy, E.; Leong, J.A.; Dobos, P. Sequence analysis of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus genome segment B and its encoded VP1 protein: A putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase lacking the Gly-Asp-Asp motif. Virology 1991, 181, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønneseth, A.; Pettersen, E.F.; Wergeland, H.I. Neutrophils and B-cells in blood and head kidney of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) challenged with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Saint-Jean, S.; de Las Heras, A.I.; Pérez-Prieto, S.I. The persistence of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and its influence on the early immune response. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 136, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrvatin, S.; Deng, F.; O’Donnell, C.W.; Gifford, D.K.; Melton, D.A. MARIS: Method for analyzing RNA following intracellular sorting. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.; Marti, G.E.; Poon, R.; Gratama, J.W.; Fernández-Repollet, E. Standardizing flow cytometry: A classification system of fluorescence standards used for flow cytometry. Cytometry 1998, 33, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.F.; Russell, D.W. (Eds.) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-87969-309-6. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, D.; Cutrín, J.M.; Olveira, J.G.; Dopazo, C.P. Design and validation of a RT-qPCR procedure for diagnosis and quantification of most types of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus using a single pair of degenerated primers. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 40, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarlund, E.; Amanna, I.J.; Dubois, M.E.; Barron, A.; Engelmann, F.; Messaoudi, I.; Slifka, M.K. A Flow Cytometry-Based Assay for Quantifying Non-Plaque Forming Strains of Yellow Fever Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, J.C.; Hjalmarsson, A.; Everitt, E.; Kuznar, J. Temporal and subcellular localization of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus structural proteins. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
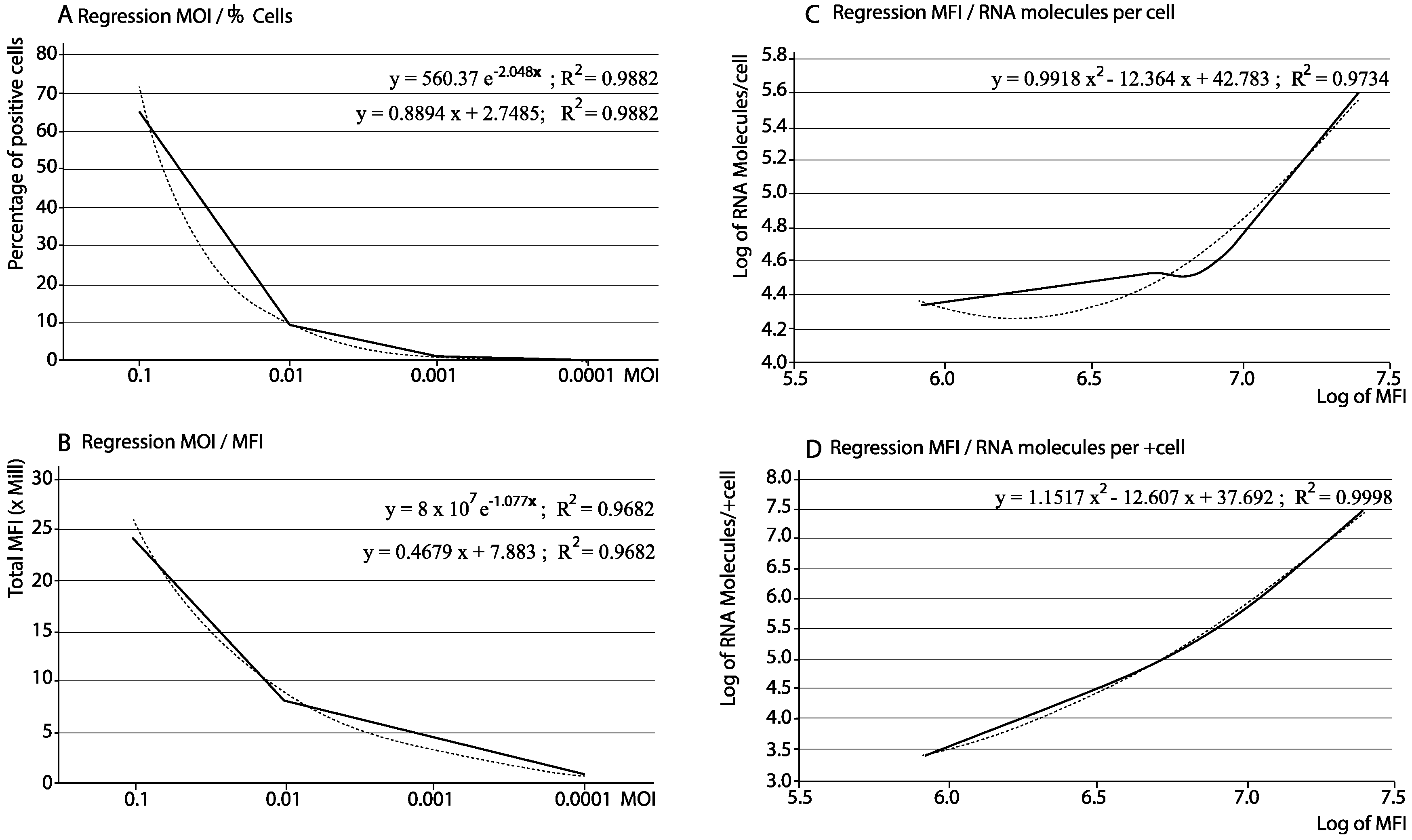
| Fluorescence Parameters | Viral RNA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | % +Cells 1 | AFI 2 | MESF 3 | MFI 4 | Per Cell 5 | Per All +Cells 6 |
| FITC+ | ||||||
| MOI 0.1 | 65.40 | 1025 | 373,696 | 24,439,718.4 | 402,807 | 26,343,577.8 |
| MOI 0.01 | 8.81 | 34,962 | 919,698 | 8,102,539.4 | 38,615 | 340,198.2 |
| MOI 0.001 | 1.82 | 4537 | 2,386,761 | 4,343,905.0 | 33,104 | 60,249.3 |
| MOI 0.0001 | 0.12 | 211,266 | 6,912,796 | 829,535.5 | 21,675 | 2601.0 |
| Repeatability Day 1 | ||||||||||||||
| AFI | MESF | |||||||||||||
| Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | |||
| Beads | ||||||||||||||
| B1 | 15.07 | 15.14 | 15.39 | 15.20 | 0.17 | 1.1 | 1929 | 1929 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B2 | 36.10 | 36.30 | 37.39 | 36.60 | 0.70 | 1.9 | 8750 | 8750 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B3 | 127.85 | 127.91 | 134.23 | 130.00 | 3.67 | 2.8 | 34,864 | 34,864 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B4 | 406.90 | 425.17 | 463.92 | 432.00 | 29.12 | 6.7 | 127,311 | 127,311 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B5 | 1197.54 | 1219.18 | 1325.49 | 1247.40 | 68.49 | 5.5 | 421,992 | 421,992 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Samples | ||||||||||||||
| Blank | 102.50 | 105.80 | 112.70 | 107.00 | 5.20 | 4.9 | 23,579.62 | 24,483.96 | 26,391.86 | 24,818.48 | 1435.66 | 5.8 | ||
| C-MOCK | 140.20 | 131.50 | 145.40 | 139.03 | 7.02 | 5.1 | 34,205.24 | 31,699.19 | 35,717.23 | 33,873.88 | 2029.41 | 6.0 | ||
| FITC + | 1647.40 | 1656.80 | 1795.20 | 1699.80 | 82.75 | 4.9 | 638,252.09 | 642,579.82 | 706,821.61 | 662,551.17 | 38,400.90 | 5.8 | ||
| Repeatability Day 2 | ||||||||||||||
| AFI | MESF | |||||||||||||
| Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | |||
| Beads | ||||||||||||||
| B1 | 18.41 | 17.05 | 17.64 | 17.70 | 0.68 | 3.9 | 1929 | 1929 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B2 | 38.67 | 36.72 | 38.01 | 37.80 | 0.99 | 2.6 | 8750 | 8750 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B3 | 152.00 | 129.09 | 117.91 | 335.00 | 7.91 | 5.9 | 34,864 | 34,864 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B4 | 457.93 | 487.65 | 449.49 | 465.02 | 20.04 | 4.3 | 127,311 | 127,311 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B5 | 1495.67 | 1410.55 | 1263.89 | 1390.04 | 117.24 | 8.4 | 421,992 | 421,992 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Samples | ||||||||||||||
| Blank | 96.51 | 95.59 | 90.93 | 94.30 | 2.99 | 3.2 | 20,011.7 | 19,785.44 | 18,645.63 | 19,480.93 | 732.18 | 3.8 | ||
| C-MOCK | 178.71 | 145.90 | 130.96 | 151.90 | 24.43 | 16.1 | 41,586.38 | 32,686.35 | 28,751.93 | 34,341.55 | 6575.37 | 19.1 | ||
| FITC + | 1847.76 | 1949.35 | 1761.12 | 1852.70 | 133.10 | 7.2 | 665,827.32 | 709,507.84 | 628,507.58 | 668,087.58 | 40,337.94 | 6.0 | ||
| Repeatability Day 3 | ||||||||||||||
| AFI | MESF | |||||||||||||
| Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | Replica 1 | Replica 2 | Replica 3 | Mean | SD | CV | |||
| Beads | ||||||||||||||
| B1 | 16.69 | 16.28 | 15.34 | 16.10 | 0.69 | 4.3 | 1929 | 1929 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B2 | 41.19 | 38.93 | 37.48 | 39.20 | 1.87 | 4.8 | 8750 | 8750 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B3 | 145.51 | 130.46 | 128.15 | 135.04 | 10.00 | 7.4 | 34,864 | 34,864 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B4 | 490.08 | 543.75 | 434.09 | 489.31 | 44.84 | 9.2 | 127,311 | 127,311 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| B5 | 1560.61 | 1544.34 | 1314.78 | 1473.24 | 137.47 | 9.3 | 421,992 | 421,992 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Samples | ||||||||||||||
| Blank | 135.17 | 135.82 | 128.07 | 133.00 | 4.3 | 3.2 | 29,451.79 | 29,615.92 | 27,667.32 | 28,911.68 | 1080.77 | 3.7 | ||
| C-MOCK | 184.52 | 186.45 | 169.11 | 180.01 | 9.50 | 5.3 | 42,236.19 | 42,748.36 | 38,177.84 | 46.032.39 | 2504.07 | 6.1 | ||
| FITC + | 1980.12 | 1906.03 | 1818.85 | 1901.70 | 80.72 | 4.2 | 660,066.13 | 631,542.06 | 598,203.17 | 629,937.12 | 30,962.69 | 4.9 | ||
| Reproducibility | ||||||||||||||
| Day 1 | AFI | MESF | ||||||||||||
| Beads | AFI | MESF | AFI | MESF | AFI | MESF | Mean | SD | CV | Mean | SD | CV | ||
| B1 | 15.2 | 1929.0 | 17.7 | 1929.0 | 16.1 | 1929.0 | 16.33 | 1.3 | 7.8 | 1929.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| B2 | 36.6 | 8750.0 | 37.8 | 8750.0 | 39.2 | 8750.0 | 37.87 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 8750.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| B3 | 130.0 | 34,864.0 | 133.0 | 34,864.0 | 135.0 | 34,864.0 | 132.67 | 2.5 | 1.9 | 34,864.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| B4 | 432.0 | 127,311.0 | 465.0 | 127,311.0 | 489.0 | 127,311.0 | 462.00 | 28.8 | 6.2 | 127,311.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| B5 | 1247.4 | 421,992.0 | 1390.0 | 421,992.0 | 1473.0 | 421,992.0 | 1370.23 | 114.2 | 8.3 | 421,992.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| Blank | 107.00 | 24,818.48 | 94.34 | 19,480.93 | 133.02 | 28,911.68 | 111.45 | 19.7 | 17.7 | 24,403.69 | 4729.0 | 19.4 | ||
| C-MOCK | 139.03 | 33,818.88 | 151.86 | 34,341.55 | 180.03 | 41,054.13 | 156.97 | 21.0 | 13.4 | 34,215.67 | 4017.3 | 11.7 | ||
| FITC+ | 1699.80 | 662,551.17 | 1852.74 | 668,087.58 | 1901.67 | 629,937.12 | 1818.07 | 105.3 | 5.8 | 635,525.29 | 20,614.7 | 3.2 | ||
| (MFI) | (24,050,607.6) | (25,387,328.0) | (29,859,019.5) | (26,432,318.4) | (3,041,943) | (11.5) | ||||||||
| Inoculated Virus 1 | Assay 1 | Assay 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOI | TCID50/mL | pfu/mL | % +Cells 2 | AFI 3 | MESF 4 | MFI 5 | % +Cells 2 | AFI | MESF | MFI |
| 0.1 | 1 × 106 | 2.6 × 106 | 66.4 | 7901 | 206,112 | 13,685,836.8 | 82.6 | 5761 | 241,276 | 19,929,423.9 |
| 0.01 | 1 × 105 | 2.6 × 105 | 54.1 | 6641 | 173,314 | 9,376,287.4 | 67.8 | 4154 | 166,502 | 11,288,862.9 |
| 0.001 | 1 × 104 | 2.6 × 104 | 13.3 | 6967 | 181,801 | 2,417,953.3 | 23.7 | 1655 | 58,628.7 | 1,389,500.3 |
| 0.0001 | 1 × 103 | 2.6 × 103 | 17.6 | 6344 | 165,581 | 2,914,225.6 | 18.6 | 1395 | 48,297.5 | 898,333.3 |
| 0.00001 | 1 × 102 | 2.6 × 102 | 1.87 | 13,615 | 324,712 | 607,211.4 | 2.63 | 874 | 28,418.9 | 74,741.8 |
| 0.000001 | 1 × 101 | 2.6 × 101 | 1.97 | 11,188 | 291,618 | 574,487.5 | 2.76 | 963 | 31,723 | 87,555.6 |
| Time p.i. 1 | % +Cells 2 | MESF 3 | MFI 4 | RNA/Cell 5 | RNA/+Cells 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 6.3 | 18,179 | 115,073.1 | 103.3 | 653.9 |
| 4 h | 11.0 | 19,647 | 216,117.0 | 615.5 | 6770.6 |
| 8 h | 26.8 | 34,673 | 929,236.4 | 24,000.5 | 643,213.7 |
| 12 h | 43.7 | 34,206 | 1,494,802.2 | 297,121.5 | 12,984,209.8 |
| 16 h | 32.6 | 25,698 | 837,754.8 | 319,035.6 | 10,400,561.0 |
| 20 h | 38.5 | 23,221 | 894,008.5 | 250,950.8 | 9,661,604.2 |
| 24 h | 51.9 | 25,471 | 1,321,944.9 | 370,657.1 | 19,237,102.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, D.; López-Vázquez, C.; Olveira, J.G.; Bandín, I.; Dopazo, C.P. Quantitative Flow Cytometry to Measure Viral Production Using Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus as a Model: A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101734
Vázquez D, López-Vázquez C, Olveira JG, Bandín I, Dopazo CP. Quantitative Flow Cytometry to Measure Viral Production Using Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus as a Model: A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101734
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Diego, Carmen López-Vázquez, José G. Olveira, Isabel Bandín, and Carlos P. Dopazo. 2018. "Quantitative Flow Cytometry to Measure Viral Production Using Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus as a Model: A Preliminary Study" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101734
APA StyleVázquez, D., López-Vázquez, C., Olveira, J. G., Bandín, I., & Dopazo, C. P. (2018). Quantitative Flow Cytometry to Measure Viral Production Using Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus as a Model: A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101734






