Improved Diagnostic Process of Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated Detection and Selection Process in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
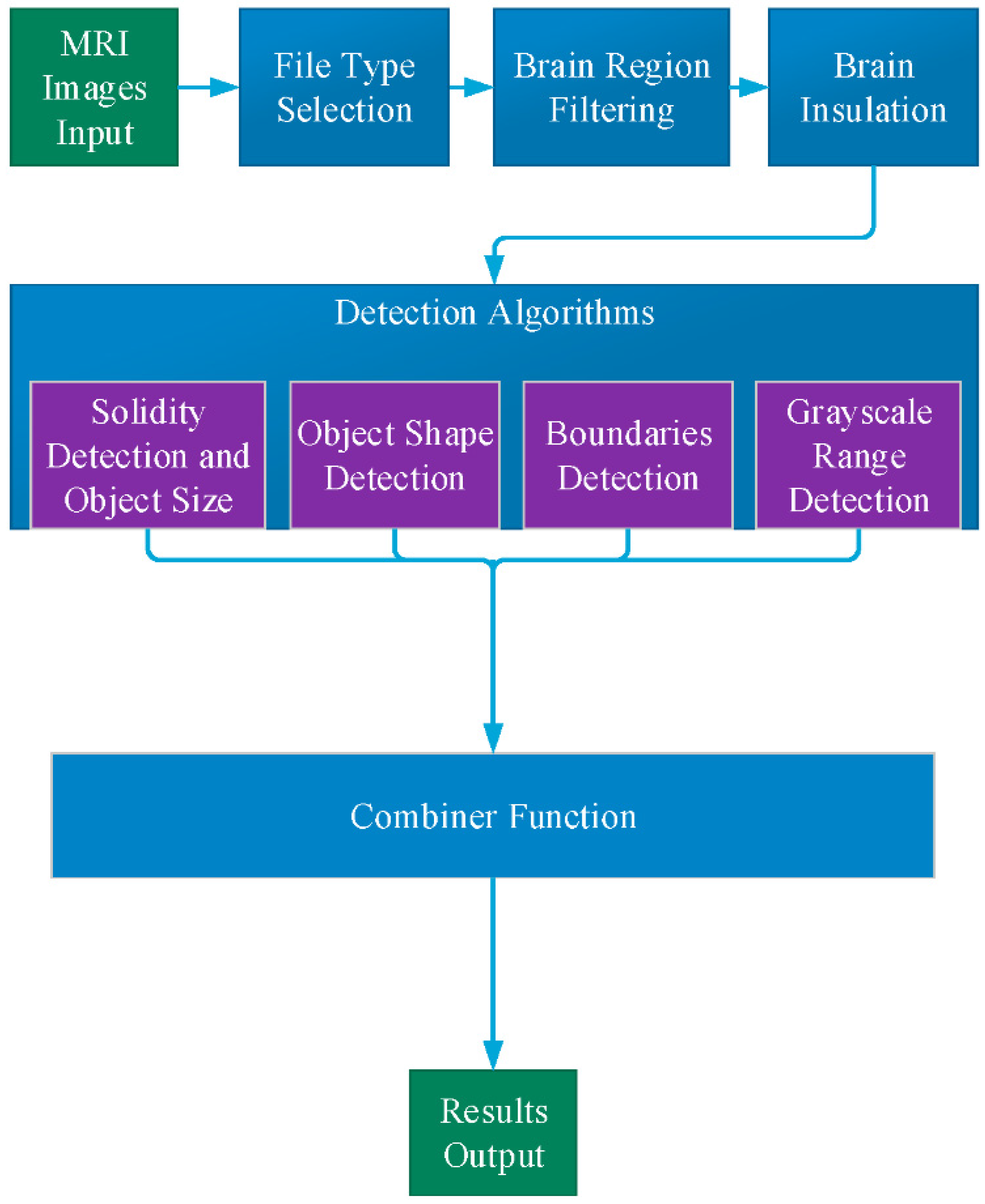
2. Methods
- File type selection filter which removes all images of irrelevant MRI types
- Range filter and image alignment which removes images with irrelevant brain regions
2.1. File Type Selection
2.2. Brain Region Filtering
2.3. Brain Isolation
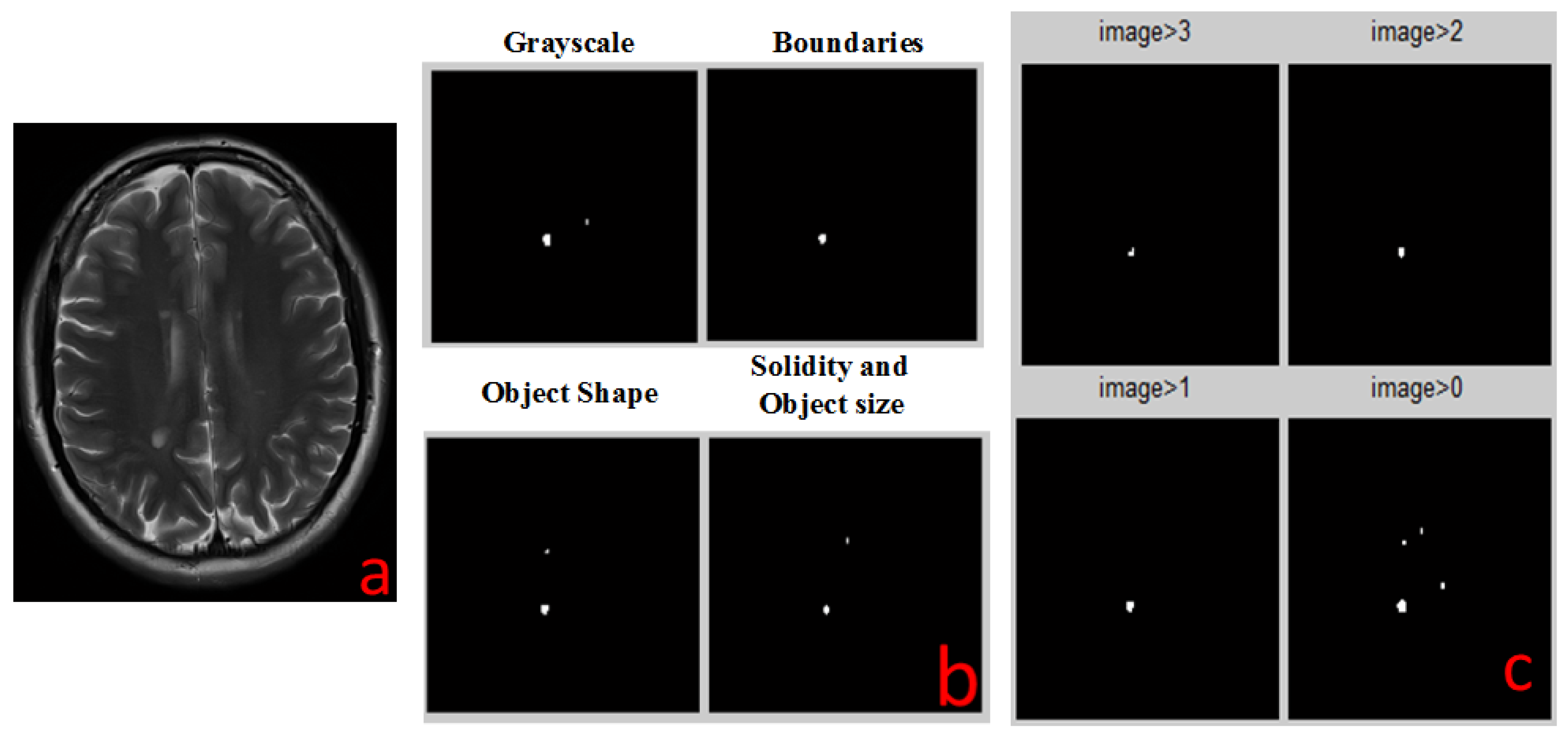
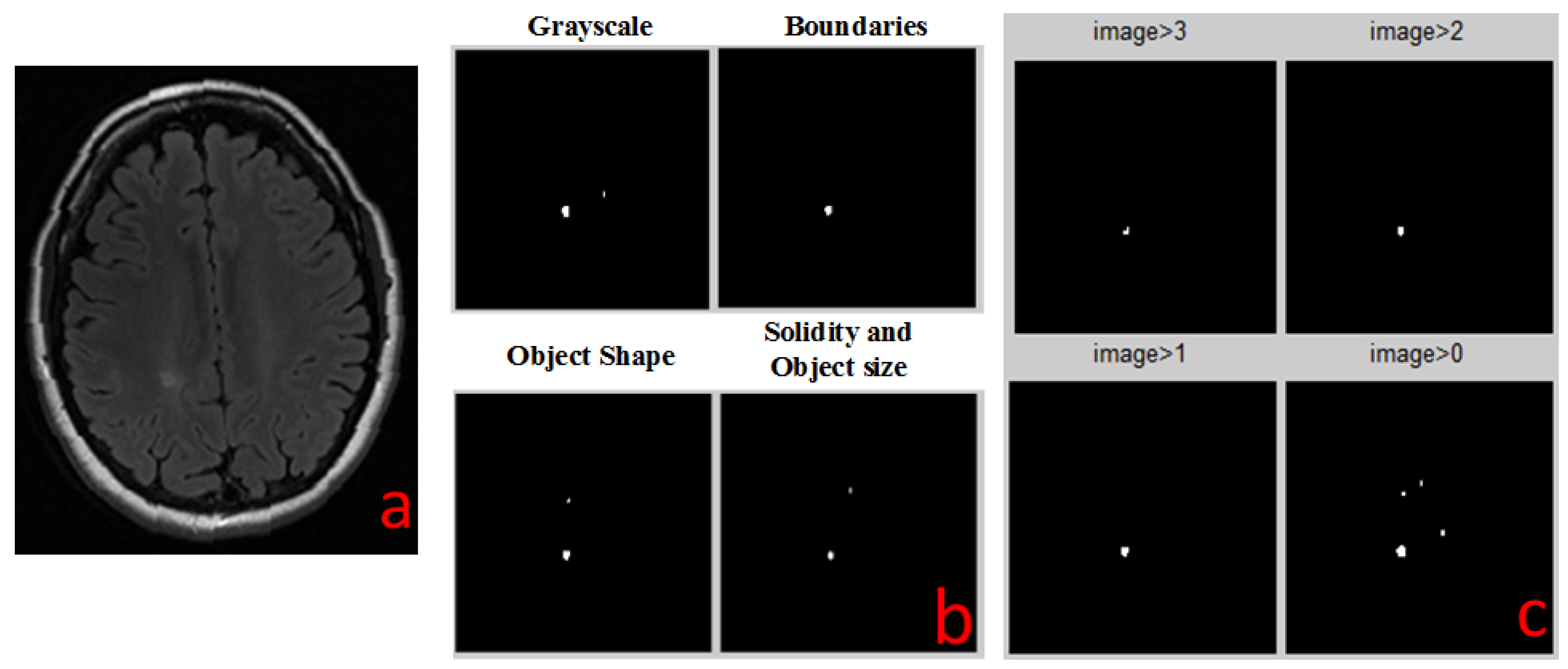
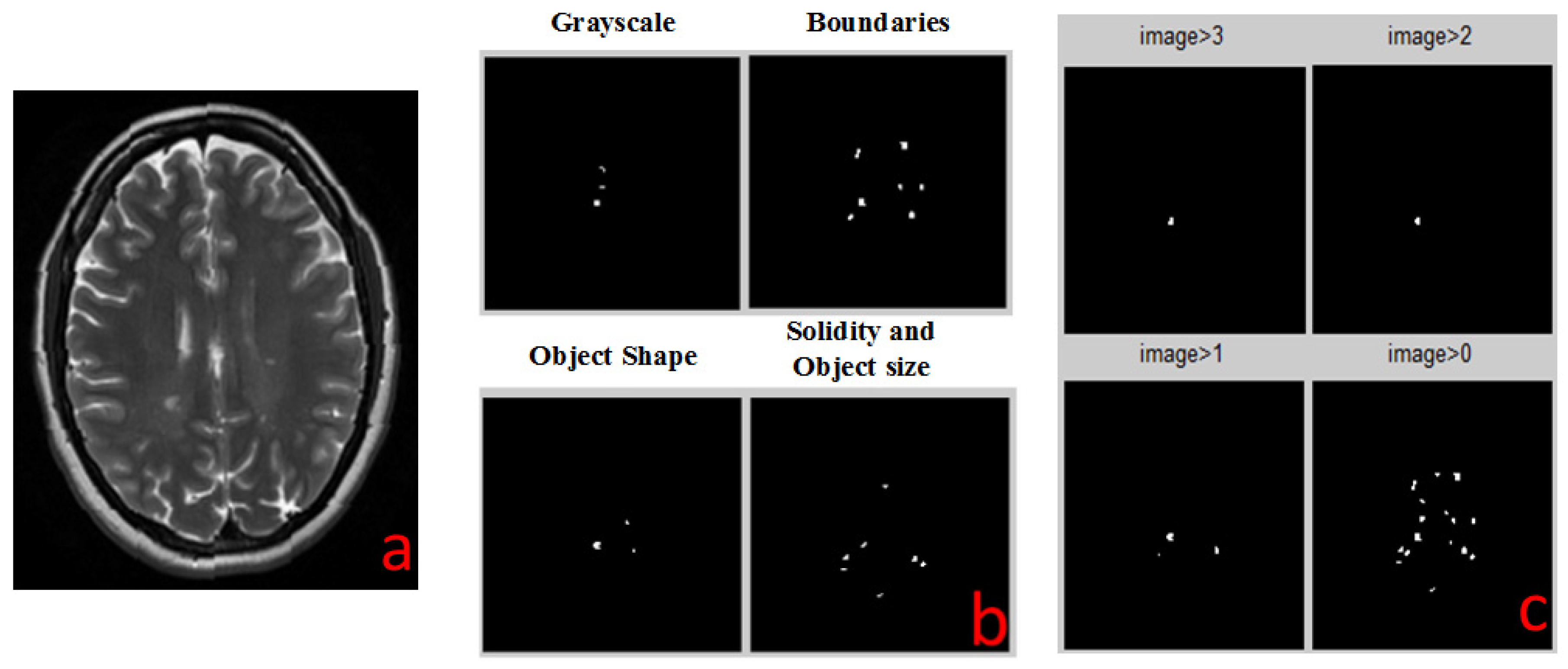
2.4. Detection Algorithms
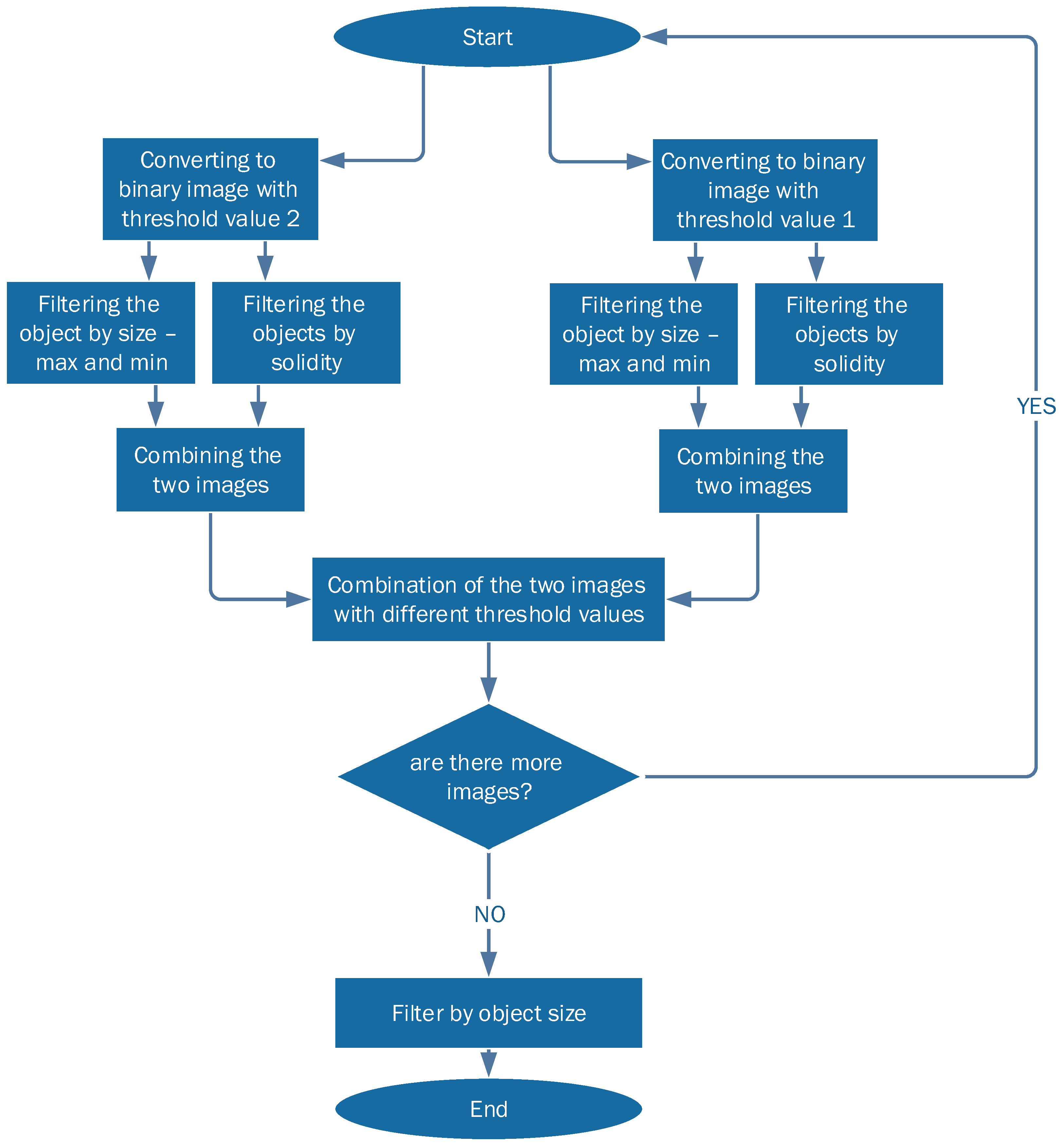
2.4.1. Solidity Detection and Object Size Filtering
- The images are converted into two binary images with different thresholds. This is done in order to collect all the relevant objects by simplifying the identification process.
- Each threshold image goes through two additional levels of filtration:
- (a)
- Filtering objects by size: objects that are either too small or too large are discarded.
- (b)
- Filtering out all objects with curvature that does not match MS lesions statistics.
- The two resulting filtered images are combined into one: candidate MS lesions are positive in both images.
- The two combined images (each with different initial threshold) are combined into one, resulting in a full picture, with enhancement of lesion-suspected objects and reduction of the irrelevant objects.
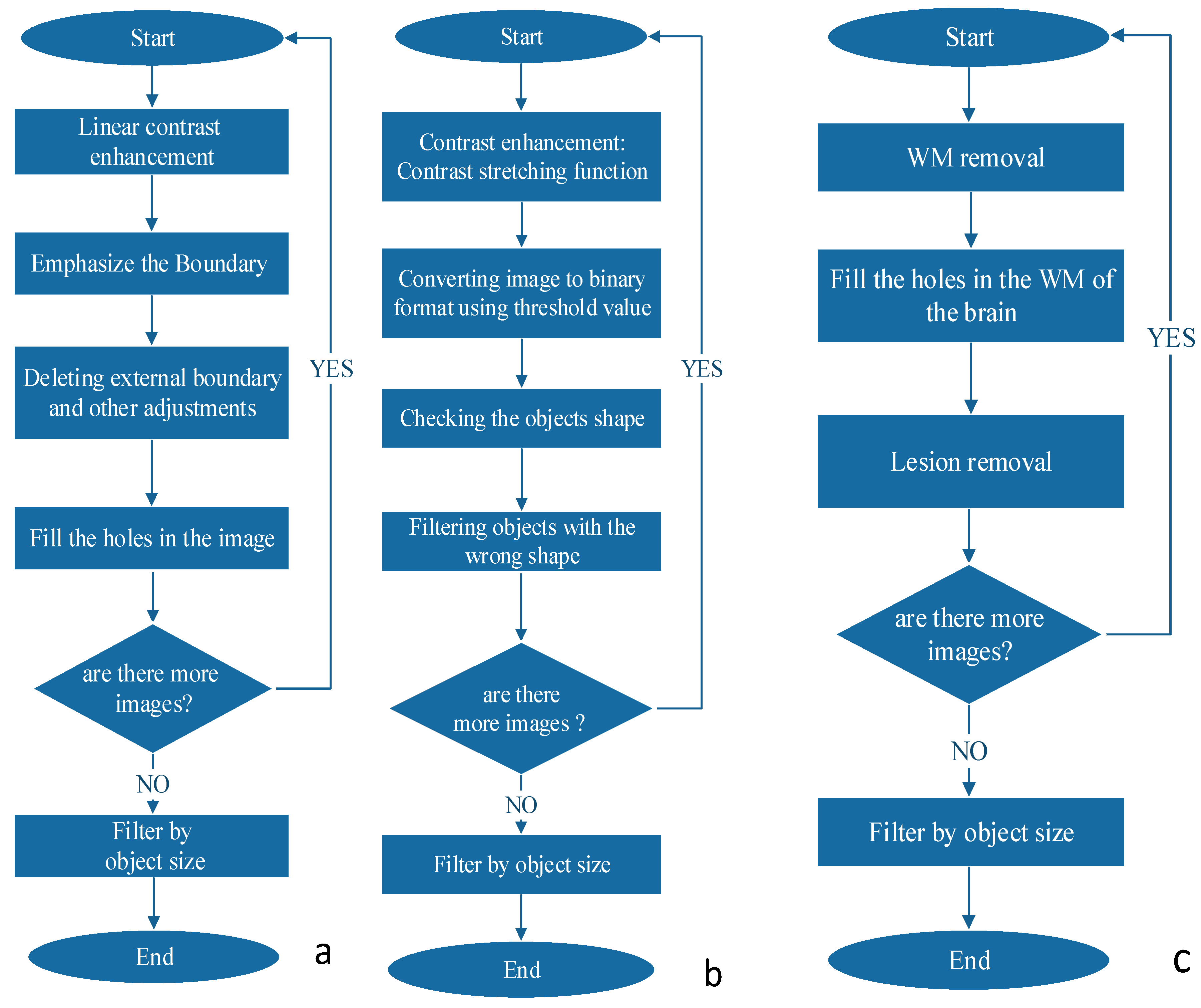
2.4.2. Boundaries Detection
2.4.3. Object Shape Detection
2.4.4. Grayscale Range Detection
2.5. Combiner Function
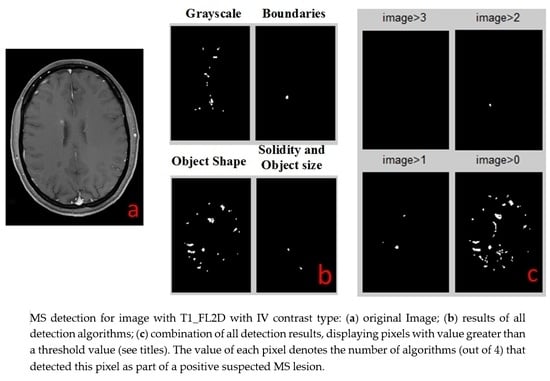
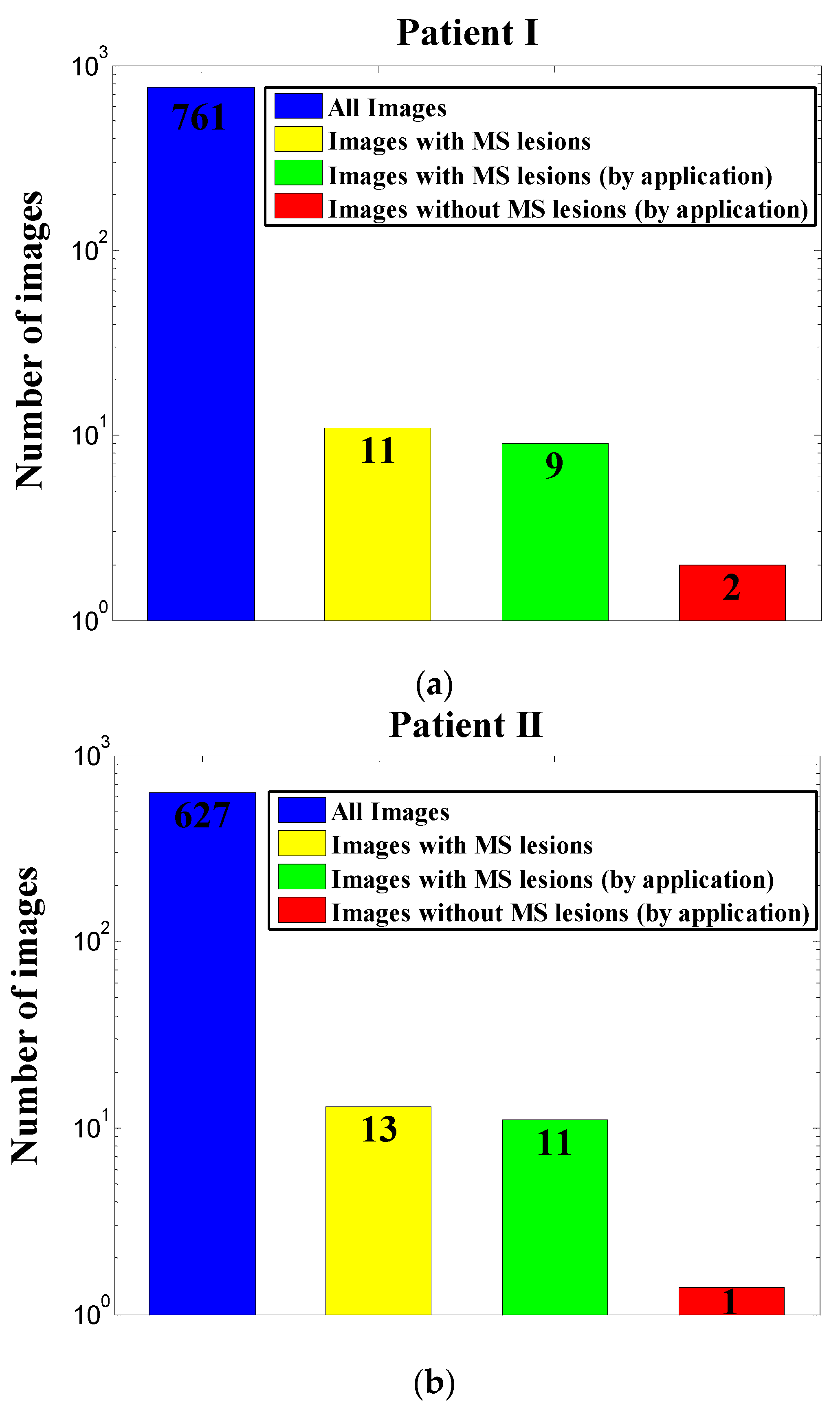
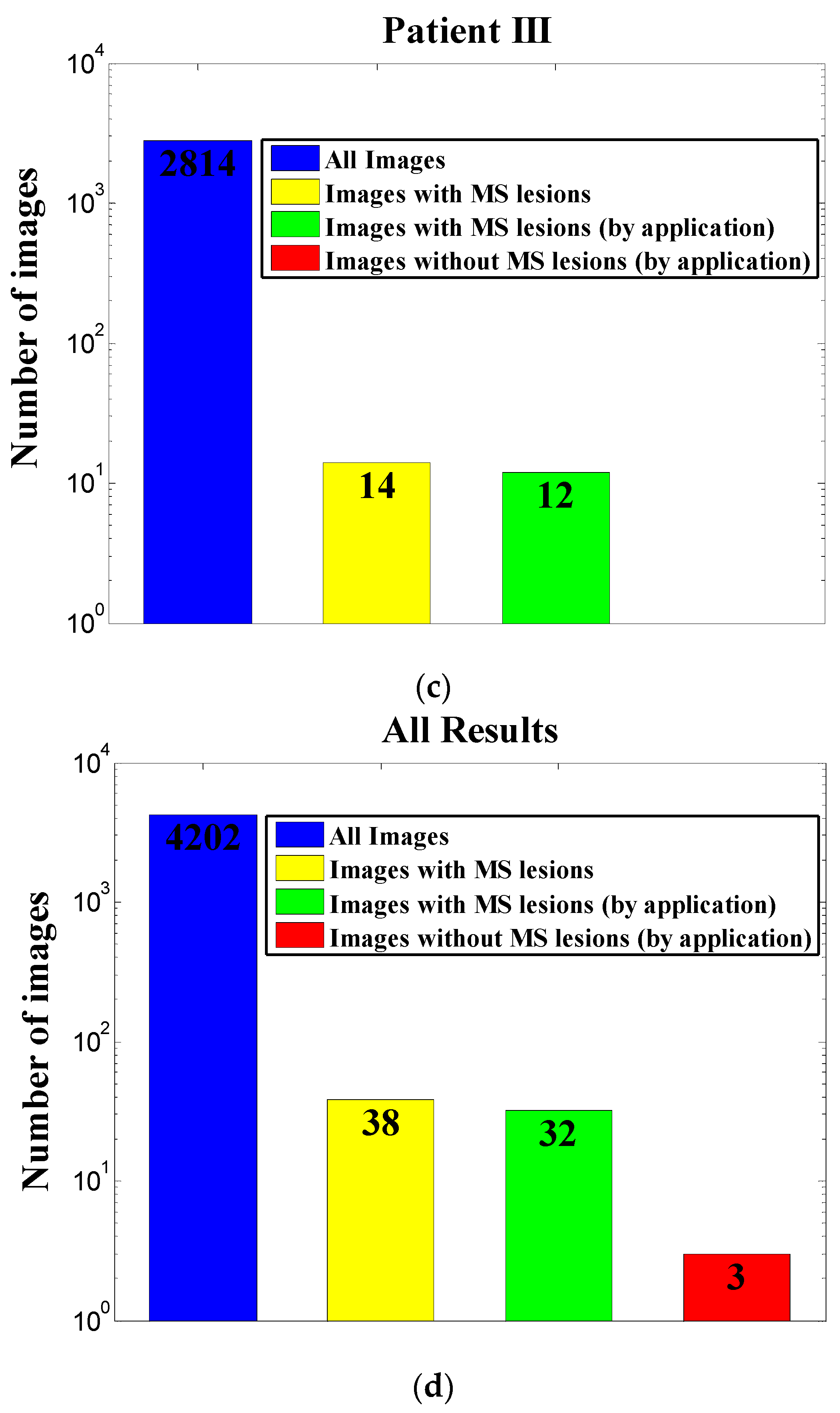
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H.D.; Wang, P.P. Medical image processing. Inf. Sci. 2005, 175, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajn, L.; Kukar, M. Image processing and machine learning for fully automated probabilistic evaluation of medical images. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2011, 104, e75–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confavreux, C.; Vukusic, S. The Clinical Epidemiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 18, 589–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, H.L. The Challenge of Multiple Sclerosis: How Do We Cure A Chronic Heterogeneous Disease? Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminoff, M.J.; Boller, F.; Swaab, D.F. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders: Handbook of Clnical Neurology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y. Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of MR Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McFarland, H.F.; Stone, L.A.; Calabresi, P.A.; Malonil, H.; Bash, C.N.; Frank, J.A. MRI studies of multiple sclerosis: Implications for the natural history of the disease and for monitoring efectiveness of experimental therapies. Mult. Scler. 1996, 2, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodneland, E.; Ystad, M.; Haasz, J.; Munthe-Kaas, A.; Lundervold, A. Automated approaches for analysis of multimodal MRI acquisitions in a study of cognitive aging. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2012, 106, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, F.; Oubel, E.; Pontabry, J.; Schweitzer, M.; Studholme, C.; Koob, M.; Dietemann, J.L. BTK: An open-source toolkit for fetal brain MR image processing. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2013, 109, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, C.J.; Kao, H.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Lo, C.P.; Hsu, C.C.; Liu, D.W.; Hsu, W.L. Comparison of the 2010 and 2005 versions of the McDonald MRI criteria for dissemination-in-time in Taiwanese patients with classic multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 329, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, A.; Auger, C.; Alonso, J. Magnetic resonance monitoring of lesion evolution in multiple sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2013, 6, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousry, T.A.; Filippi, M.; Becker, C.; Horsfield, M.A.; Voltz, R. Comparison of MR Pulse Sequences in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1997, 18, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rovaris, M.; Iannucci, G.; Pereira, C.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Detection of multiple sclerosis lesions using EPI-FLAIR images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 18, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayati, R.; Vafadust, M.; Towhidkhah, F.; Nabavi, S.M. Fully automatic segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MR T2FLAIR images using adaptive mixtures method and markov random field model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2008, 38, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, P.; Gaser, C.; Arsic, M.; Buck, D.; Förschler, A.; Berthele, A.; Hoshi, M.; Ilg, R.; Schmid, V.J.; Zimmer, C.; et al. An automated tool for detection of FLAIR-hyperintense white-matter lesions in Multiple Sclerosis. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3774–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Sima, D.M.; Ribbens, A.; Cambron, M.; Maertens, A.; Van Hecke, W.; De Mey, J.; Barkhof, F.; Steenwijk, M.D.; Daams, M.; et al. Automatic segmentation and volumetry of multiple sclerosis brain lesions from MR images. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 8, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rey, D.; Subsol, G.; Delingette, H.; Ayache, N. Automatic detection and segmentation of evolving processes in 3D medical images: Application to multiple sclerosis. Med. Image Anal. 2002, 6, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lorenzo, D.; Francis, S.; Narayanan, S.; Arnold, D.L.; Collins, D.L. Review of automatic segmentation methods of multiple sclerosis white matter lesions on conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, R.; Mörschner, D.; Pöppl, S.J.; Moser, A. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2009, 10, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimura, H.; Magome, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Yamamoto, D. Computer-Aided Diagnosis Systems for Brain Diseases in Magnetic Resonance Images. Algorithms 2009, 2, 925–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malka, D.; Vegerhof, A.; Cohen, E.; Rayhshtat, M.; Libenson, A.; Aviv Shalev, M.; Zalevsky, Z. Improved Diagnostic Process of Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated Detection and Selection Process in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080831
Malka D, Vegerhof A, Cohen E, Rayhshtat M, Libenson A, Aviv Shalev M, Zalevsky Z. Improved Diagnostic Process of Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated Detection and Selection Process in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(8):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080831
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalka, Dror, Adi Vegerhof, Eyal Cohen, Mark Rayhshtat, Alex Libenson, Maya Aviv Shalev, and Zeev Zalevsky. 2017. "Improved Diagnostic Process of Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated Detection and Selection Process in Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Applied Sciences 7, no. 8: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080831
APA StyleMalka, D., Vegerhof, A., Cohen, E., Rayhshtat, M., Libenson, A., Aviv Shalev, M., & Zalevsky, Z. (2017). Improved Diagnostic Process of Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated Detection and Selection Process in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences, 7(8), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080831