A New Method for Haul Road Design in Open-Pit Mines to Support Efficient Truck Haulage Operations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
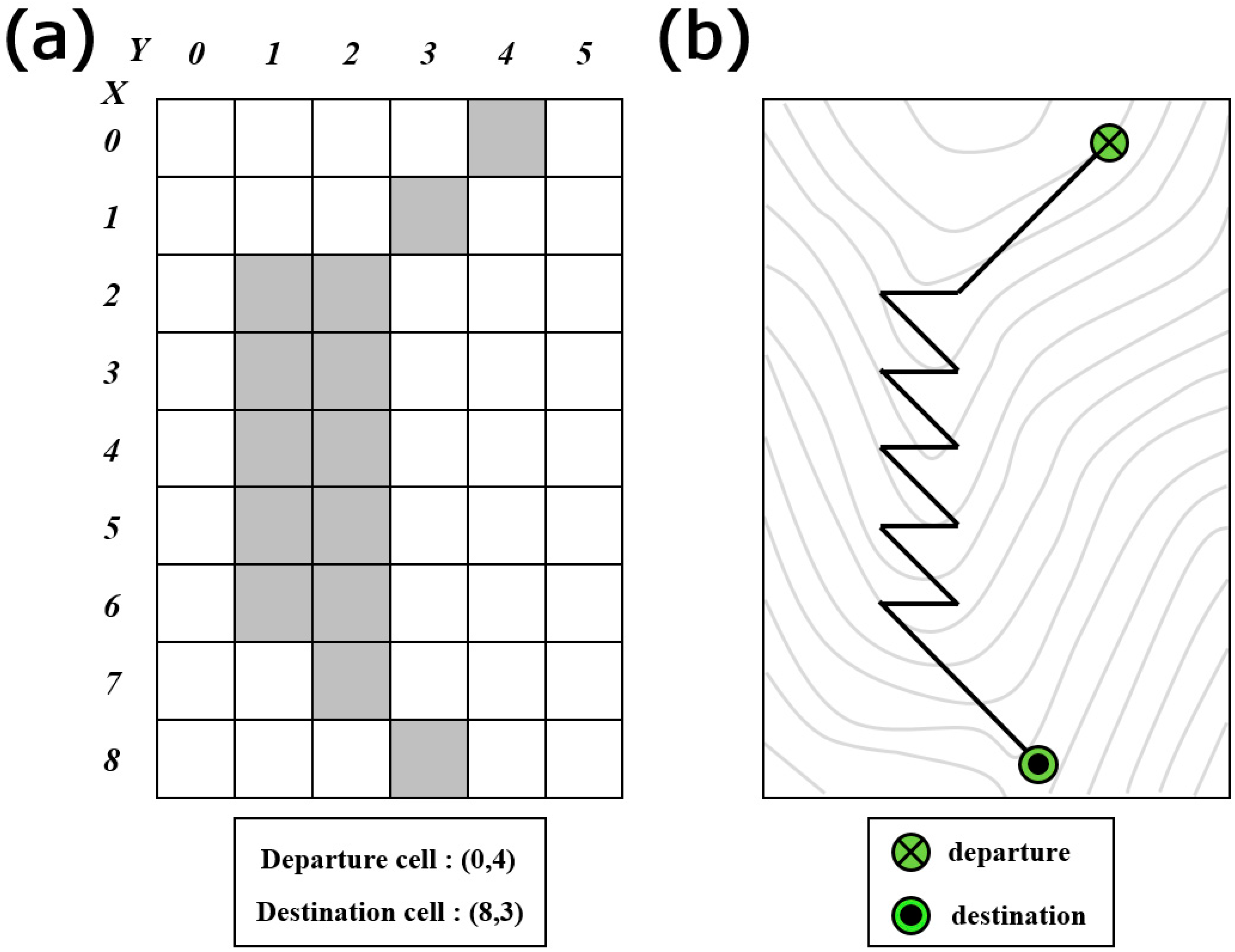
2. Problems with the Determination of Road Layout by Raster-based Least-Cost Path Analysis
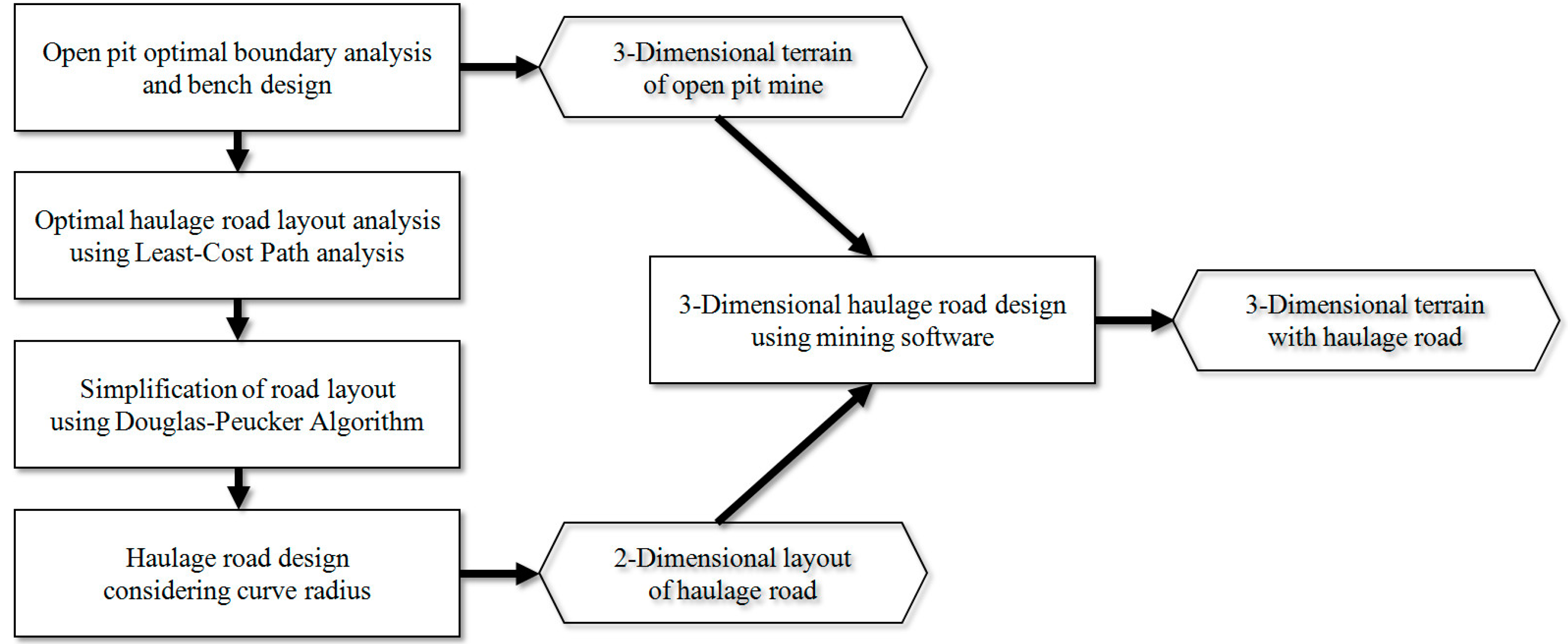
3. Methods
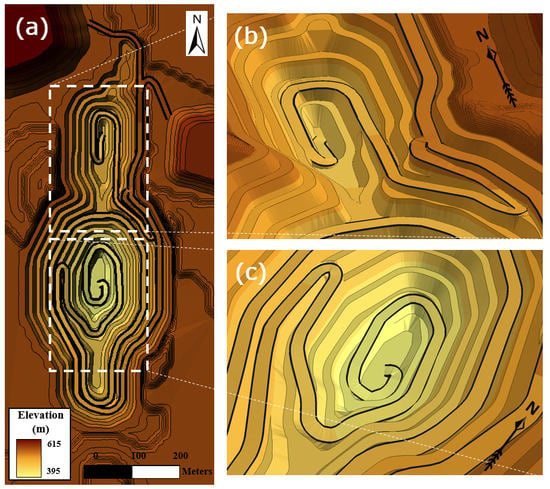
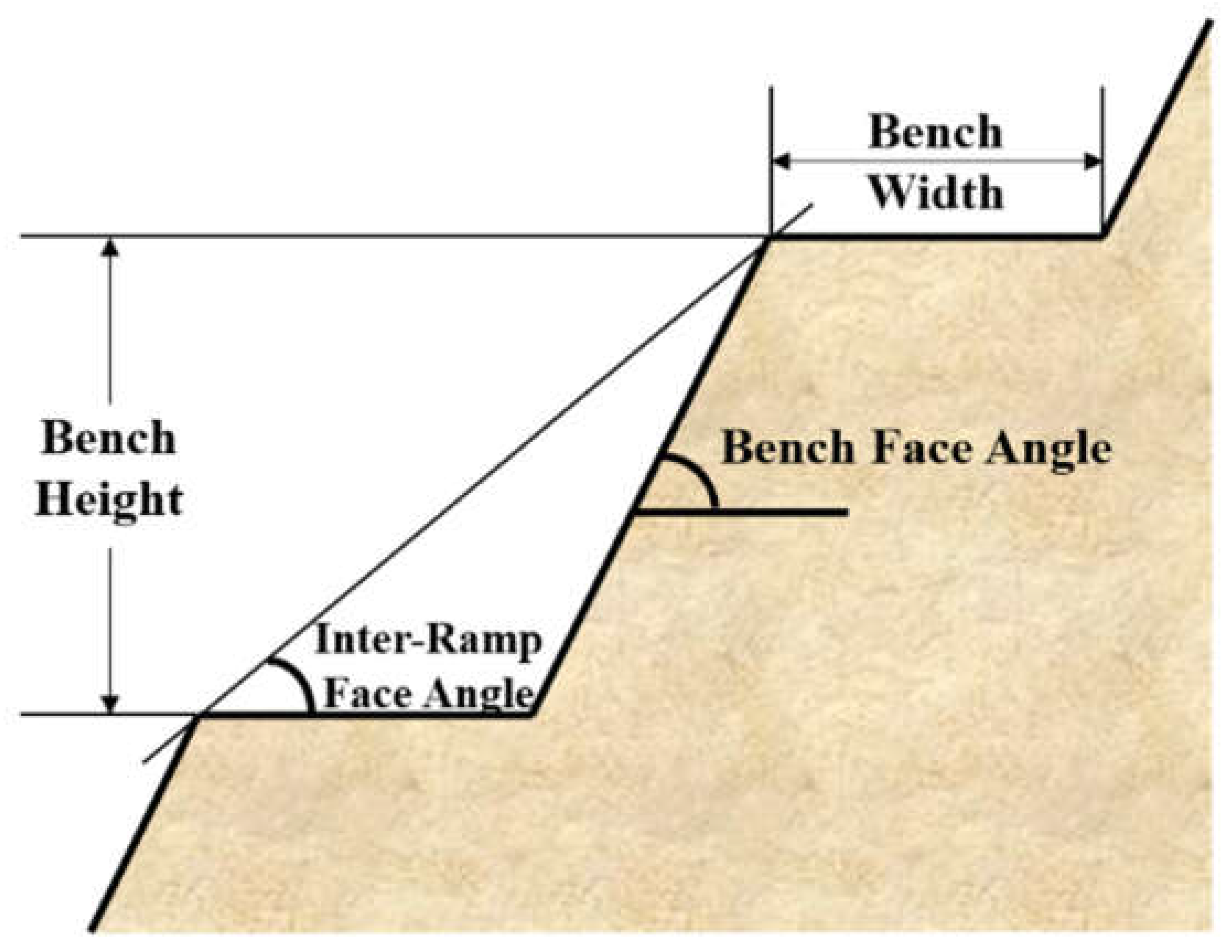
3.1. Optimal Boundary Analysis and Bench Design in Open-Pit Mines
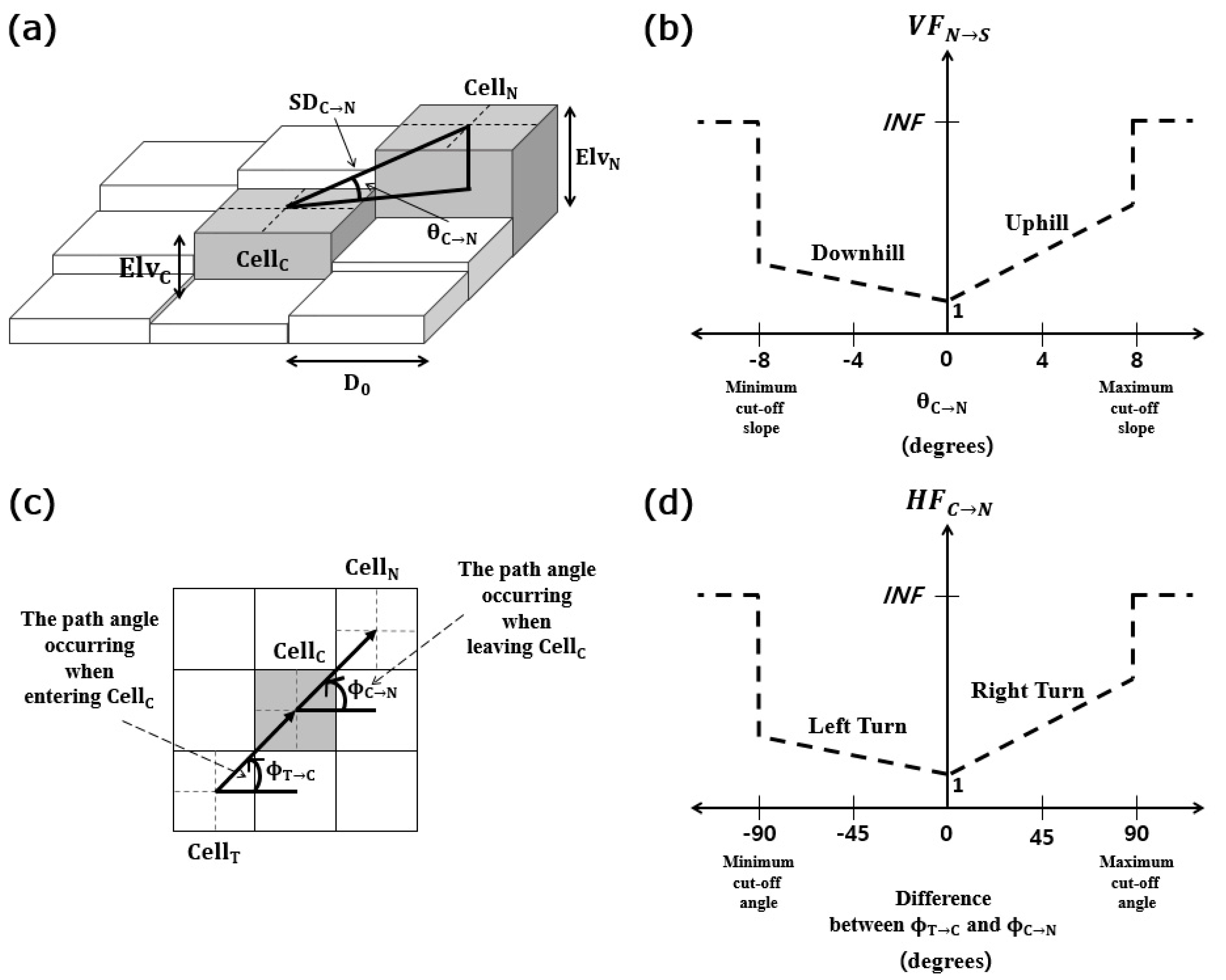
3.2. Road Layout Analysis Using LCPA
3.3. Simplification of Road Layout Using the Douglas-Peucker Algorithm
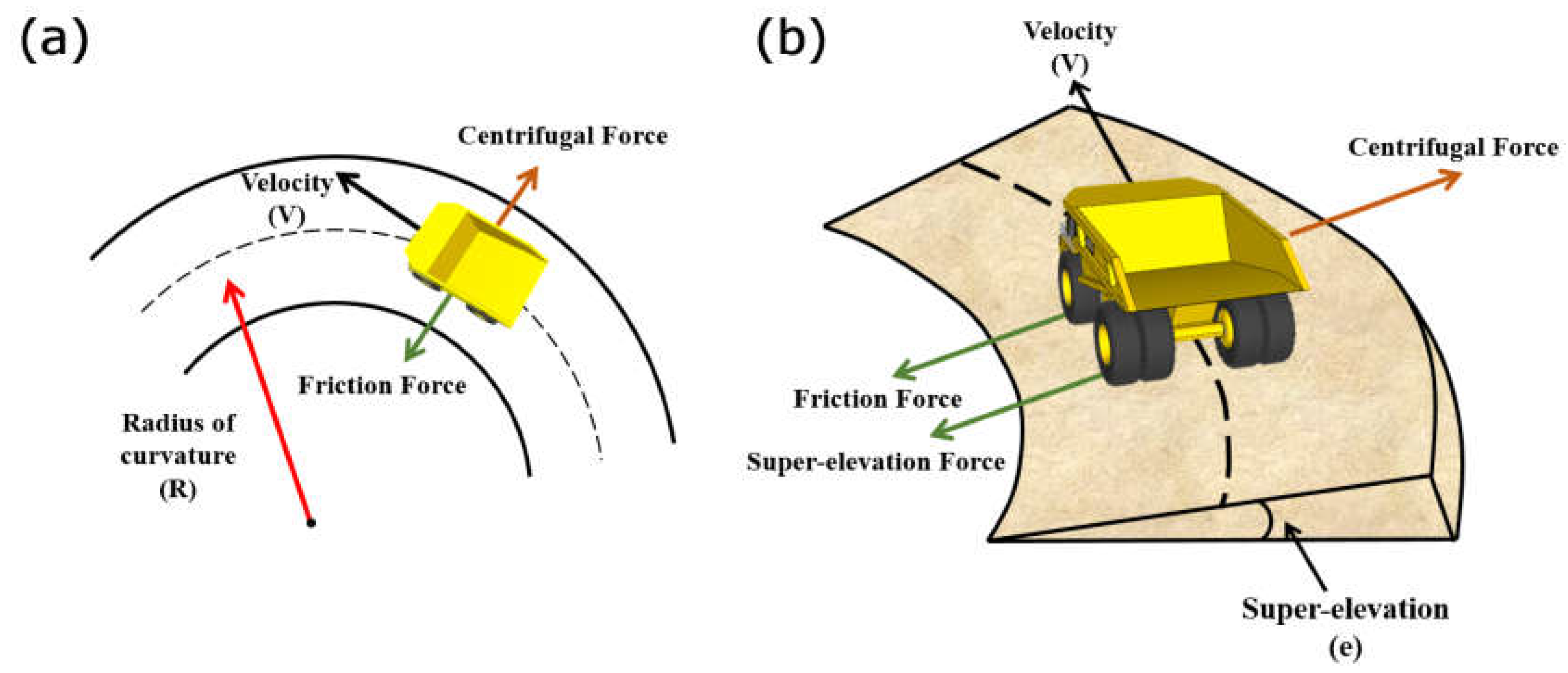
3.4. Modification of Road Layout Considering the Radius of Curvature Constraints
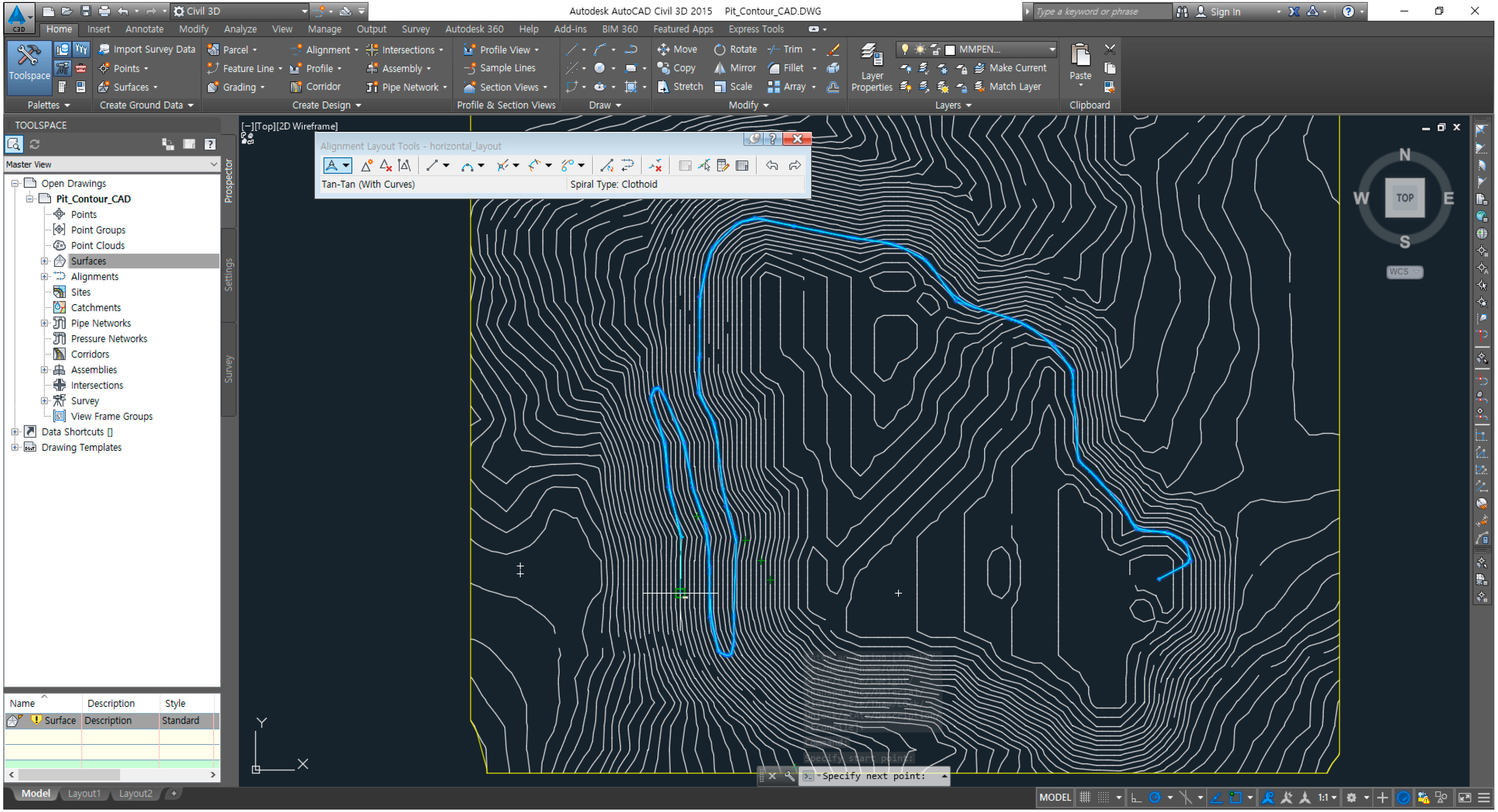
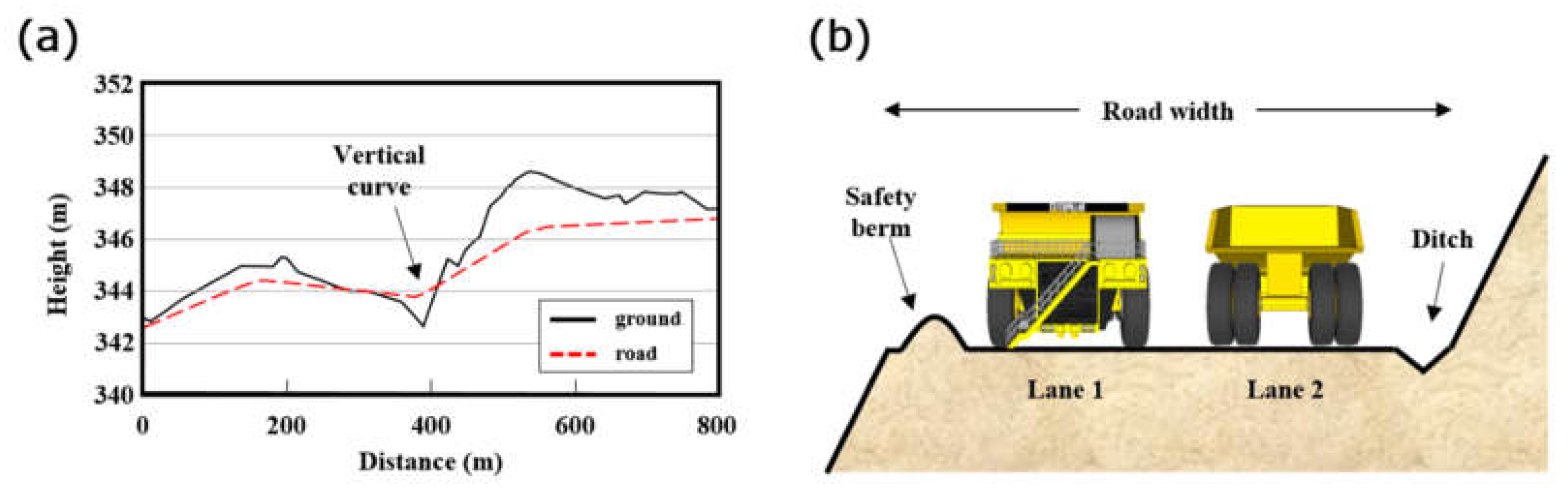
3.5. Three-Dimensional Haul Road Design Using Mine Design Software
4. Case Study
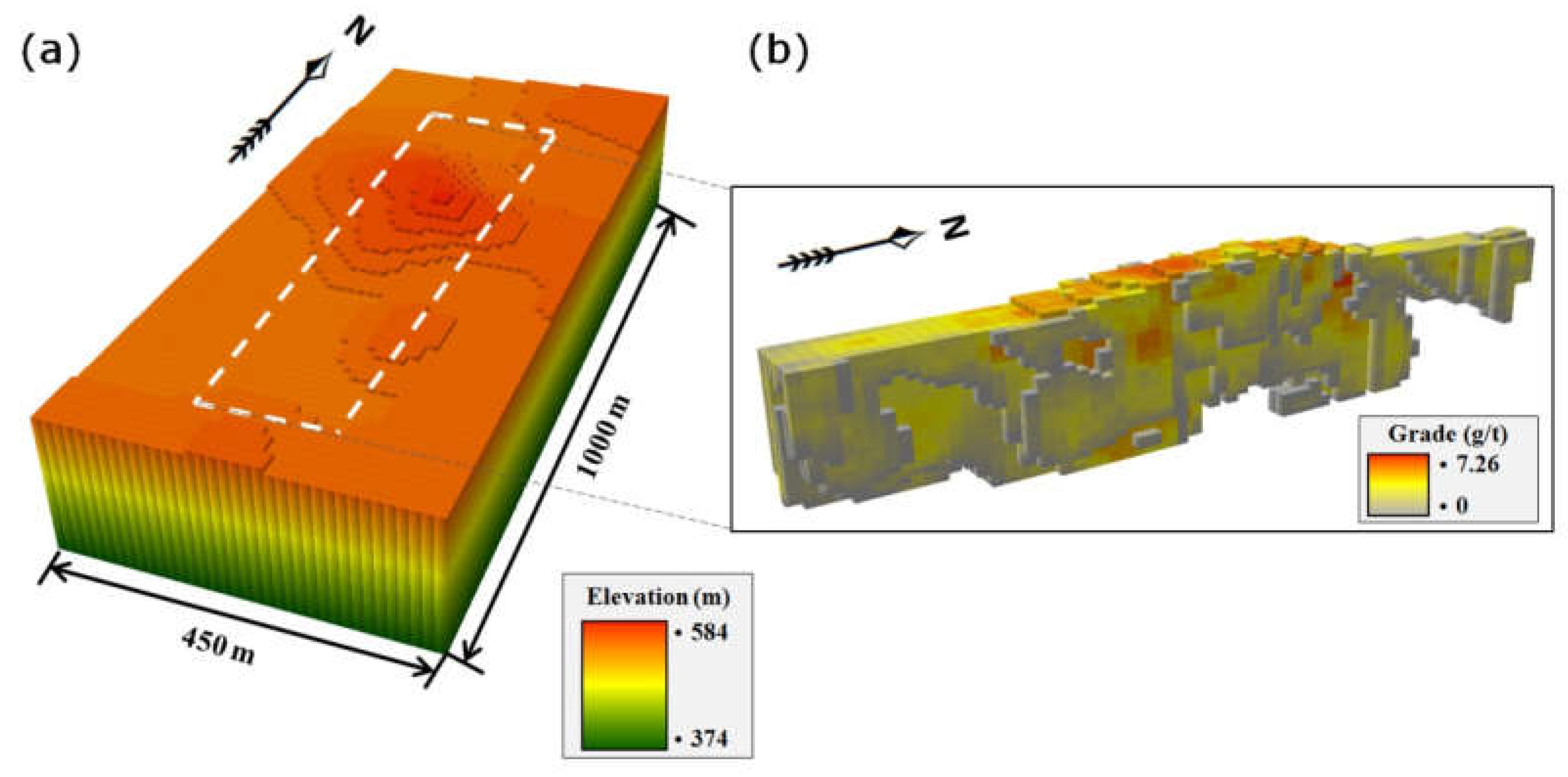
4.1. Study Area and Data
4.2. Creation of Input Data
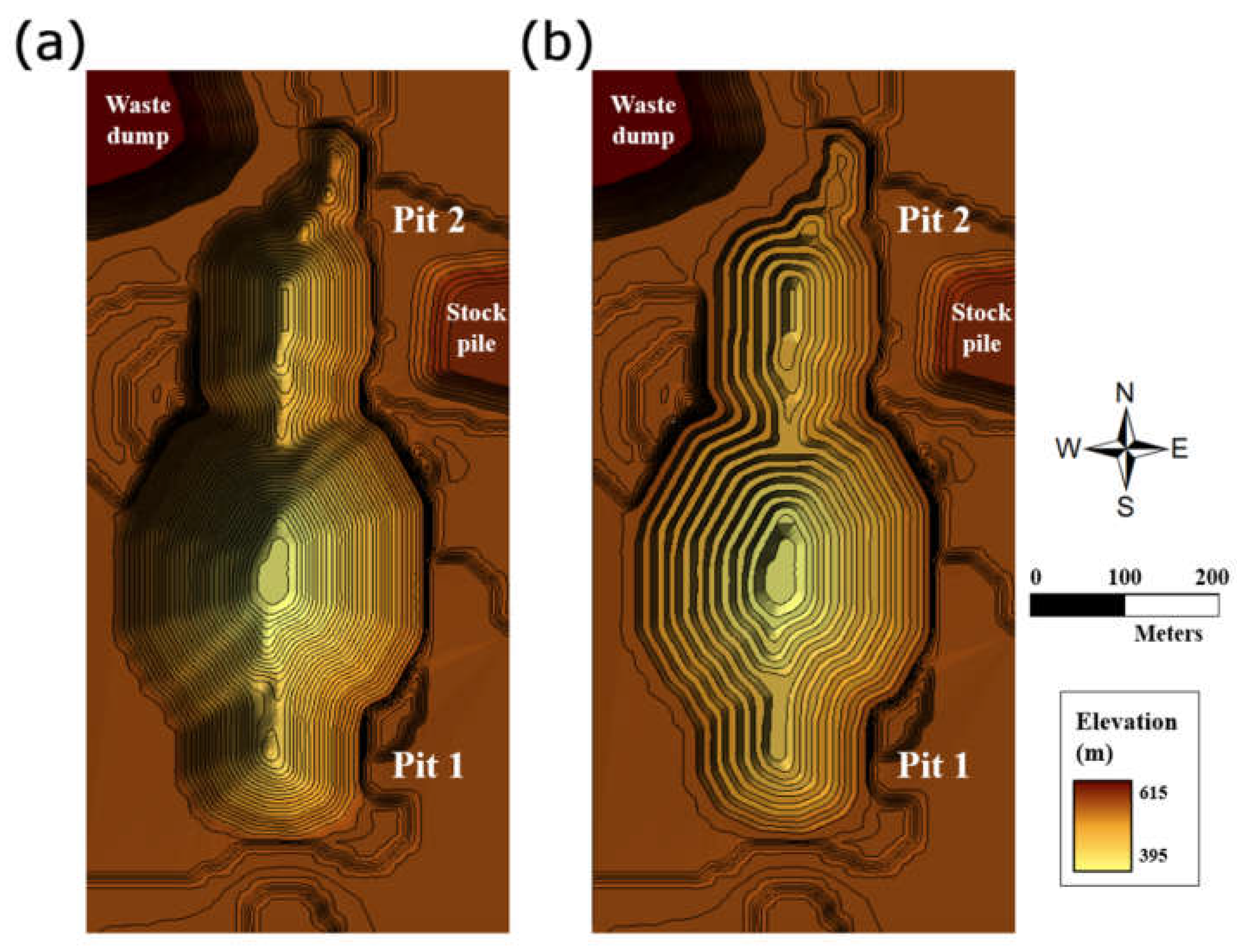
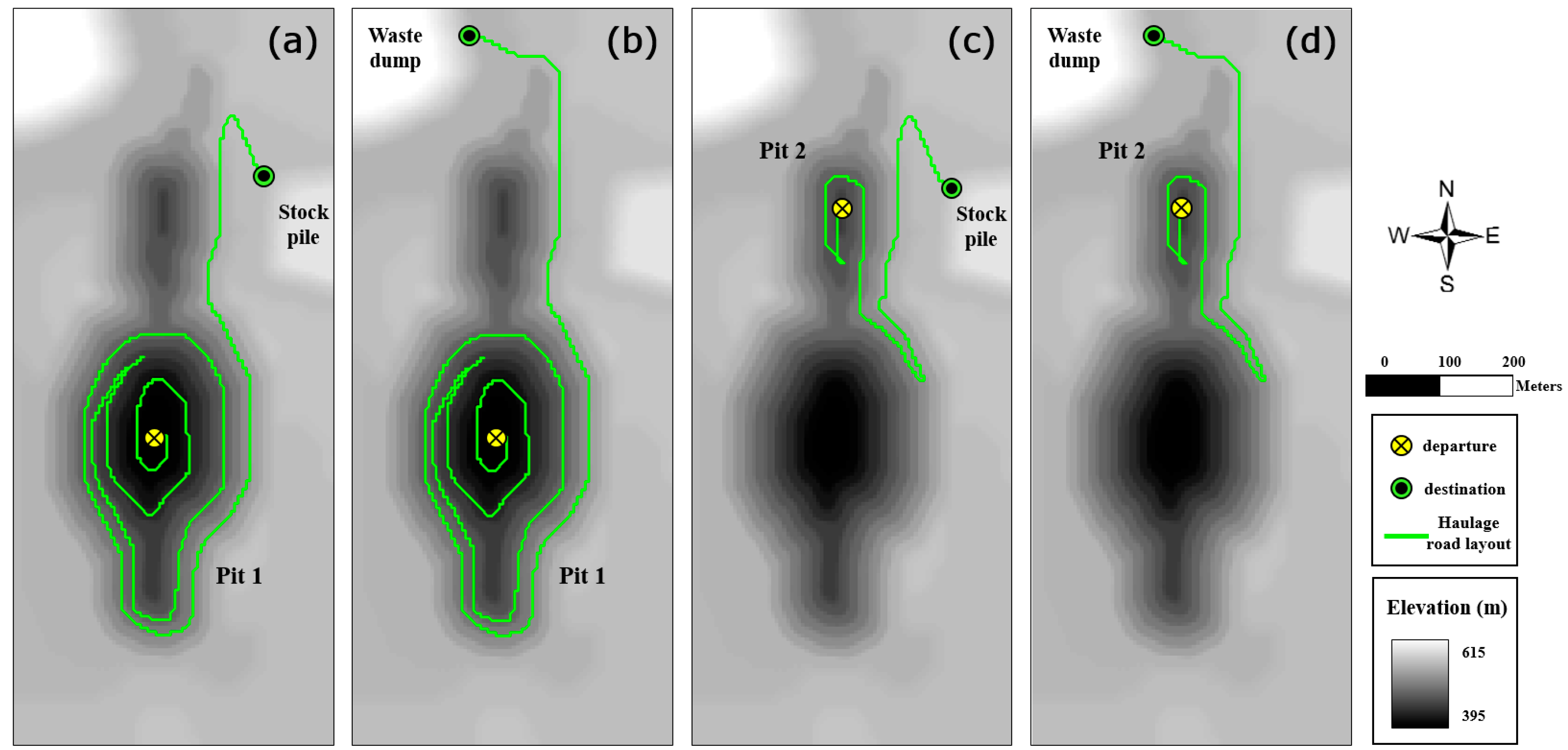
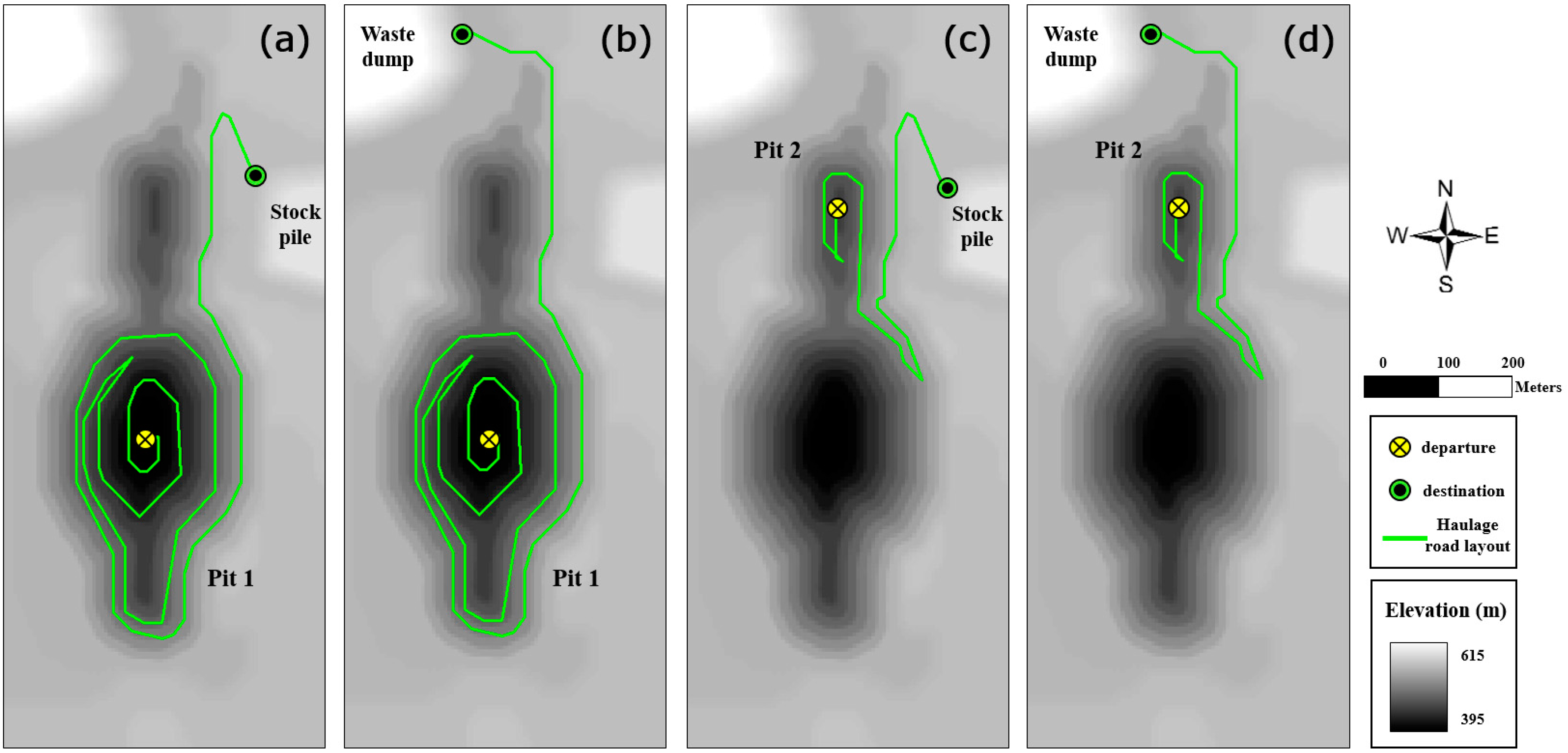
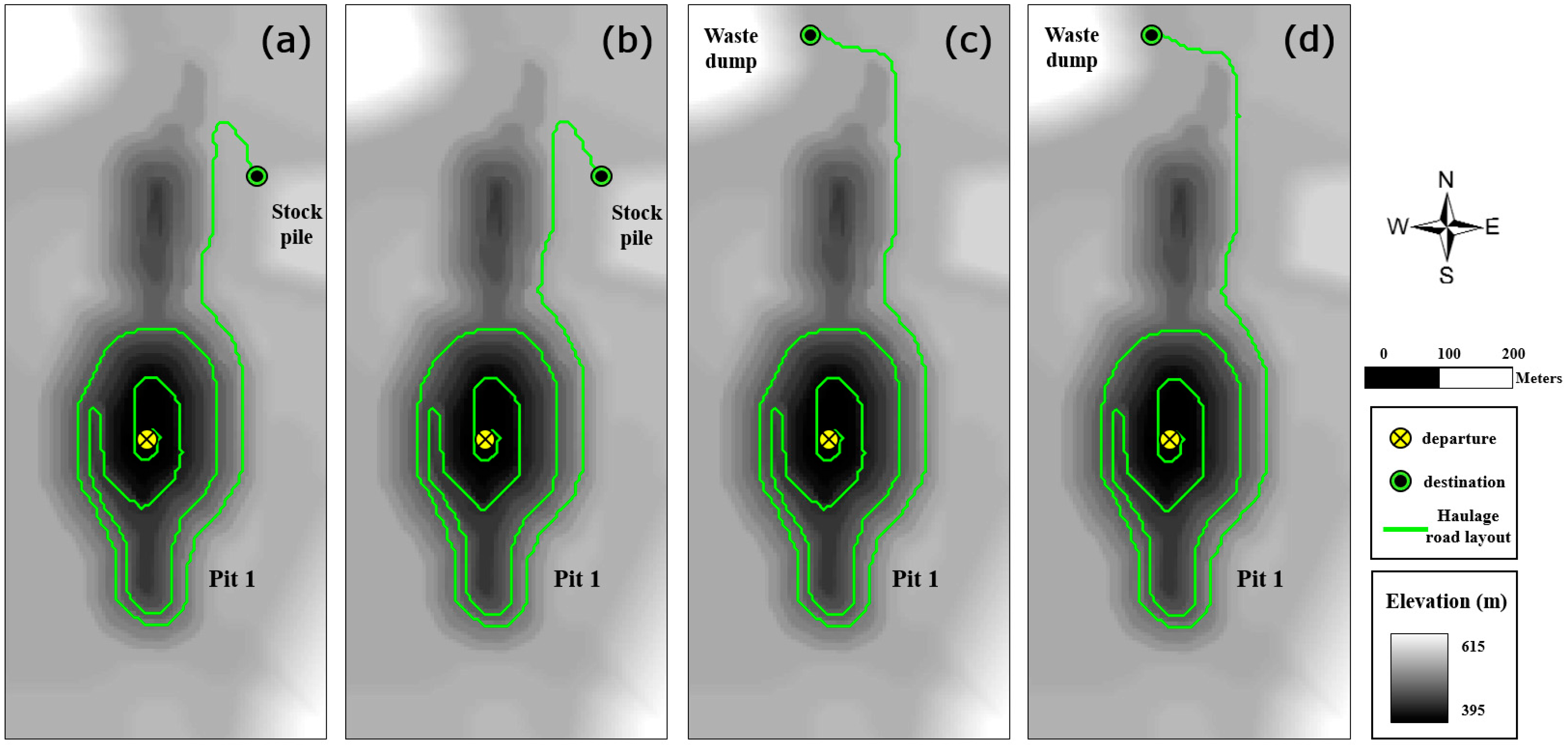
4.3. Optimization and Modification of Road Layout
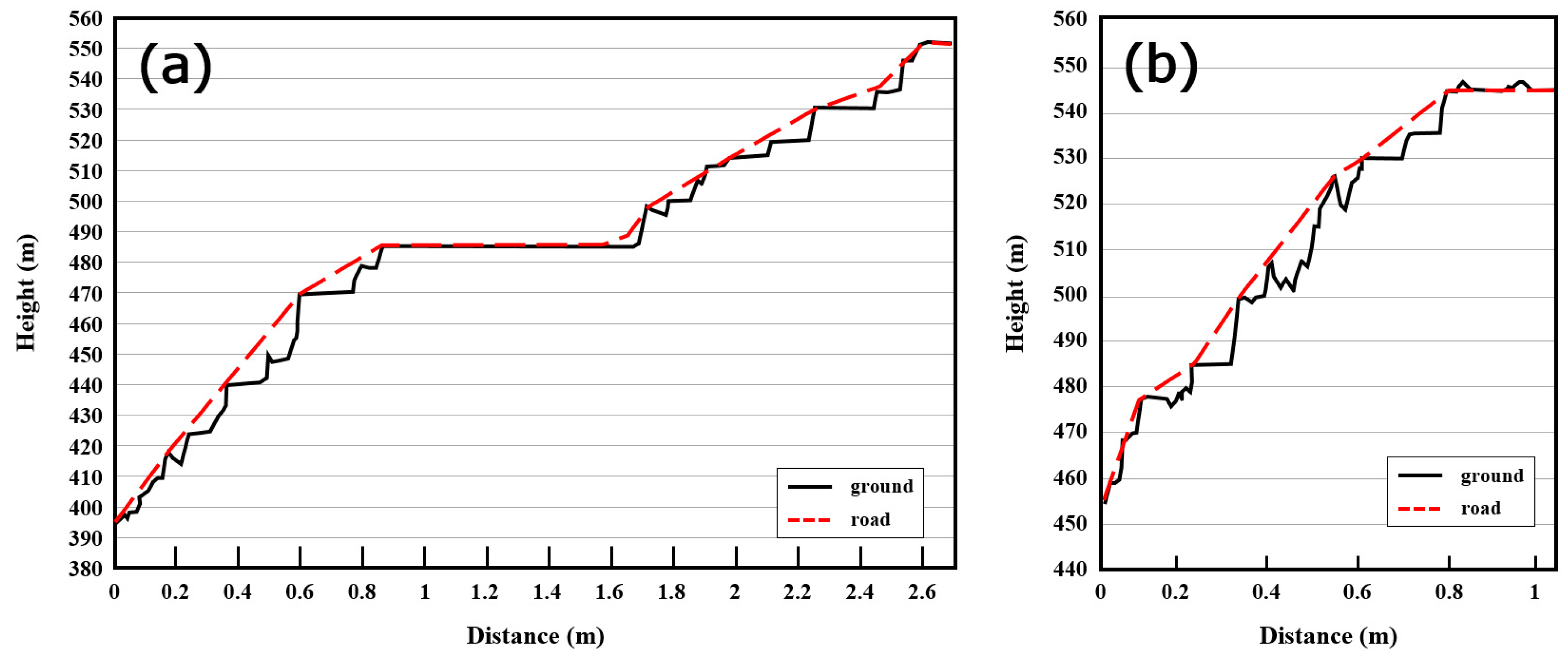
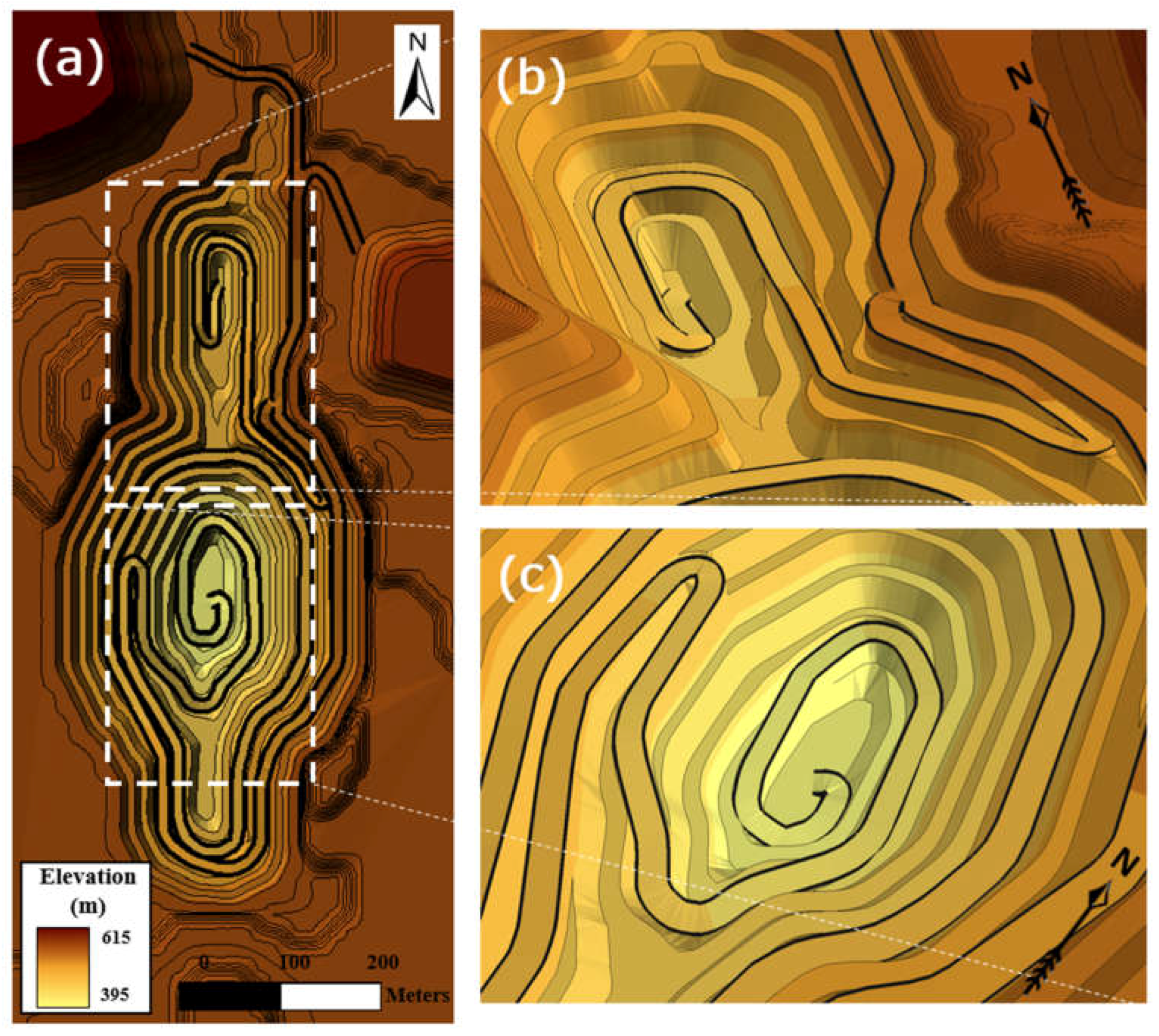
4.4. Three-Dimensional Modeling and Visualization of Road Design Result
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R. Mine Haul Road Design and Management Best Practices for Safe and Cost-Efficient Truck Haulage. In Proceedings of the Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration Annual Meeting & Exhibit, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 28 February–3 March 2010; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration (SME): Littleton, CO, USA, 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, W.W.; Ault, J.C. Design of Surface Mine Haulage Roads-A Manual; United States Bureau of Mines (USBM), United States Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; pp. 1–49.
- Tannant, D.; Regensburg, B. Guidelines for Mine Haul Road Design; University of British Columbia Library: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2010; pp. 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hustrulid, W.A.; Kuchta, M.; Martin, R.K. Open Pit Mine Planning and Design, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Leiden, Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, P. SME Mining Engineering Handbook, 3rd ed.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration (SME): Littleton, CO, USA, 2011; pp. 1–1837. [Google Scholar]
- AutoCAD Civil 3D. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/autocad-civil-3d/overview (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- GEOVIA GEMS. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/geovia/products/gems/ (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- Carlson Surface Mining. Available online: http://www.carlsonsw.com/solutions/mining-solutions/surface-mining/ (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- 3D Mine Planning, Mine Design, Geology & Scheduling in Vulcan. Available online: http://www.maptek.com/products/vulcan/ (accessed on 29 June 2017).
- Autodesk, Inc. AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 User’s Guide; Autodesk, Inc.: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Gemcom Software International Inc. Gemcom for Windows User Manual; Gemcom Software International Inc.: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1998; pp. 1–4103. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Park, H.D.; Sunwoo, C.; Clarke, K.C. Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Least-Cost Path Analysis for Optimal Haulage Routing of Dump Trucks in Large Scale Open-Pit Mines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 23, 1541–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lee, J.; Munro-Stasiuk, M.J. Extensions to least-cost path algorithms for roadway planning. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2003, 17, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collischonn, W.; Pilar, J.V. A Direction Dependent Least-Cost-Path Algorithm for Roads and Canals. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2000, 14, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Um, J.G.; Park, M.H. Cartography and Geographic Information Science Finding least-cost paths across a continuous raster surface with discrete vector networks. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 41, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H. Least-cost path in GIS using an accumulated cost surface and slopelines. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovis. 1994, 31, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lathrop, R.G. Improving Cost-Path Tracing in a Raster Data Format. Comput. Geosci. 1994, 20, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etherington, T.R. Least-Cost Modelling and Landscape Ecology: Concepts, Applicatons, and Opportunities. Curr. Landsc. Ecol. Rep. 2016, 1, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, S.C.; Pelletier, R.E.; Waker, E.; Smoot, J.C.; Ahl, D. A Prototype for Pipeline Routing Using Remotely Sensed Data and Geographic Information System Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 53, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.G. Least-Cost Paths in Mountainous Terrain. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D.M.; Deadman, P.; Dudycha, D.; Traynor, S. Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Least Cost Path Analysis for an Arctic All-Weather Road. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagli, S.; Geneletti, D.; Orsi, F. Routeing of Power Lines Through Least-Cost Path Analysis and Multicriteria Evaluation to Minimise Environmental Impacts. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2011, 31, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Seo, J. GIS Method for Haul Road Layout Planning in Large Earthmoving Projects: Framework and Case Study. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effat, H.A.; Hassan, O.A. Designing and Evaluation of Three Alternatives Highway Routes Using The Analytical Hierarchy Process and The Least-Cost Path Analysis, application in Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2013, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Nieto, A. Optimal Haulage Routing of Off-road Dump Trucks in Construction and Mining Sites Using Google Earth and a Modified Least-Cost Path Algorithm. Autom. Constr. 2011, 20, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the Reduction of the Number of Points Required to Represent a Digitized Line or Its Caricature. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovis. 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlin, D. Propagating Radial Waves of Travel Cost in a Grid. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 1391–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerchs, H.; Grossmann, L. Optimum Design of Open-Pit Mines. Trans. CIM. 1965, 58, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- David, M.; Dowd, P.A.; Korobov, S. Forecasting Departure from Planning in Open Pit Design and Grade Control. In Proceedings of the 12th International APCOM Symposium, Golden, CO, USA, 8–12 April 1974; pp. F131–F142. [Google Scholar]
- Berlanga, J.M.; Cardona, R.; Ibarra, M.A. Recursive Formulae for Floating Cone Algorithm. Int. J. Surf. Mining, Reclam. Environ. 1989, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, H. Uncertainty Representation Method for Open Pit Optimization Results Due to Variation in Mineral Prices. Minerals 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Peter, S. Guidelines for Open Pit Slope Design; Csiro Publishing: Collingwood, VIC, Australia, 2009; pp. 1–496. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.K.; Miles, R.D. The GCARS System: A Computer-Assisted Method of Regional Route Location; Highway Research Record: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bemmelen, J.; Quak, W.; van Hekken, M.; van Oosterom, P. Vector vs. Raster-based Algorithms for Cross Country Movement Planning. In Proceedings of the Auto Carto 11, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 30 October–1 November 1993; American Congress on Surveying and Mapping and the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1993; pp. 304–317. Available online: http://www.gdmc.nl/oosterom/autoca11.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2017).
- Xu, J.; Lathrop, R.G. Improving Simulation Accuracy of Spread Phenomena in a Raster-Based Geographic Information System. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Menon, S.; Gao, P. A Directional Path Distance Model for Raster Distance Mapping. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Spatial Information Theory (COSIT’93), Marciana Marina, Elba Islance, Italy, 19–22 September 1993; Frank, A.U., Campari, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; pp. 434–443. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.K.; Arora, M.K.; Gupta, R.P.; Virdi, M.L.; Csaplovics, E. GIS-Based Route Planning in Landslide-Prone Areas. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 1149–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T. Rules for Robot Draughtsmen. Geogr. Mag. 1969, 42, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Reumann, K.; Witkam, A.P.M. Optimizing Curve Segmentation in Computer Graphics. In Proceedings of the International Computing Symposium, Davos, Switzerland, 4–7 September 1973; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1974; pp. 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Opheim, H. Smoothing a Digitized Curve by Data Reduction Methods. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition, Eurographics, Darmstadt University of Technology, Darmstadt, Germany, 9–11 September 1981; Encarnacao, J.L., Ed.; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, 1981; pp. 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Visvalingam, M.; Whyatt, J.D. Line Generalisation by Repeated Elimination of Points. Cartogr. J. 1993, 30, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Saalfeld, A. Linear-Time Sleeve-Fitting Polyline Simplification Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Auto-Carto 13, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–10 April 1997; American Congress on Surveying and Mapping and the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Cheung, C. Performance Evaluation of Line Simplification Algorithms for Vector Generalization. Cartogr. J. 2006, 43, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.J.; Visser, A.T. Designing and Managing Unpaved Opencast Mine Haul Roads for Optimum Performance. In Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 1–3 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.J.; Visser, A.T. The Functional Design of Surface Mine Haul Roads. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2000, 100, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.J.; Visser, A.T. Mine Haul Road Maintenance Management Systems. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2003, 103, 303–312. [Google Scholar]




| Radius of Curvature (m) | Speed (km/h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 32 | 40 | 48 | >56 | |
| 15 | 4% (≈2°) | ||||
| 30 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | |||
| 45 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 5% (≈2°) | ||
| 75 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 6% (≈3°) | |
| 90 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 5% (≈3°) | 6% (≈3°) |
| 180 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 5% (≈3°) |
| 300 | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) | 4% (≈2°) |
| Economic Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Price of gold ($/ounce) | 1300 |
| Recovery (%) | 90 |
| Mining cost ($/tonne) | 2.5 |
| Selling cost ($/ounce) | 35 |
| Processing cost ($/ounce) | 18 |
| Revenue factor | 1 |
| Haul Type | Grade (%) | Approximate Speed (km/h) |
|---|---|---|
| Full haul moving uphill | 0–4 (≈0°–2°) | 25 |
| 4–8 (≈2°–5°) | 20 | |
| 8–12 (≈5°–7°) | 15 | |
| over 12 (≈over 7°) | 10 | |
| Empty haul moving downhill | 0–4 (≈0°–2°) | 25 |
| over 4 (≈over 2°) | 40 |
| Haulage route From To | Slope condition | Haulage time (min) | Haulage distance (km) | Average speed (km/h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pit 1 | Stockpile | uphill | 17.6 | 2.8 | 9.4 |
| downhill | 11.7 | 2.8 | 14.1 | ||
| Waste dump | uphill | 18.1 | 2.9 | 9.5 | |
| downhill | 12.4 | 2.9 | 13.8 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, J.; Choi, Y. A New Method for Haul Road Design in Open-Pit Mines to Support Efficient Truck Haulage Operations. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070747
Baek J, Choi Y. A New Method for Haul Road Design in Open-Pit Mines to Support Efficient Truck Haulage Operations. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(7):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070747
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Jieun, and Yosoon Choi. 2017. "A New Method for Haul Road Design in Open-Pit Mines to Support Efficient Truck Haulage Operations" Applied Sciences 7, no. 7: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070747
APA StyleBaek, J., & Choi, Y. (2017). A New Method for Haul Road Design in Open-Pit Mines to Support Efficient Truck Haulage Operations. Applied Sciences, 7(7), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070747