Adaptive Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG with Optimal Wavelet Packets and SE-Isomap
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Primary Theory
2.1. Wavelet Packet Decomposition
2.2. SE-Isomap Algorithm
- (1)
- Constructing the intra-class distance matrix: Calculate the k-nearest neighbors for each sample in class to get and regard as . Then, the neighborhood graph is constructed with the sample as the vertex and the Euclidean distance between the sample as the edge. The shortest path distance in the neighbor graph between the two vertexes will be regarded as an approximation of the geodesic distance between two corresponding samples. For convenience of expression, the geodesic distance is simplified to , then the geodesic distance between and is as follows:Then, the intra-class geodesic distance matrix is constructed according to the approximate geodesic distance between two arbitrary points.
- (2)
- Constructing the global discriminative distance matrix: Calculate the inter-class geodetic distance between any two samples when , and the computational equation is as follows:where the sample pairs ; denotes the shortest euclidean distance between class and class ; and denote the intra-class geodesic distance between and , and , respectively. In general, the calculative strategy of inter-class geodesic distance is different when applied to different experimental tasks. Equation (5) is chosen for visualization to ensure the authenticity of the structure of the dataset:When the classify experiment is implemented to enhance the separability, Equation (6) will be taken into consideration:The inter-class distance parameter is used to balance the fidelity of visualization and the separability of data. Then, the inter-class distance matrix can be denoted as . Finally, the global geodesic distance matrix G representing the distance between any individual sample points is constructed as:where and are the intra-class geodesic distance matrices of class and class , respectively, and are the inter-class geodesic distance matrices of the samples belong to different classes and and parameters are used to reduce the intra-class distance properly for the reason that the gather effect will be reinforced.
- (3)
- Utilizing the explicit-MDS algorithm to obtain the low-dimensional embedding expression and the corresponding mapping relation of the dataset: The explicit-MDS algorithm is applied to obtain the low-dimensional expression and explicit mapping matrix .
2.3. Explicit-MDS
- Step 1. Let t = 0, and initialize the weight matrix ;
- Step 2. Let V = ;
- Step 3. Update ; is the solution of minimization problem , and , where:is the Moore–Penrose inverse of A,
- Step 4. Check for convergence. If not, then let t = t + 1, and go to Step 2 to continue the iteration; otherwise, stop.
3. Feature Extraction Method Based on WPD and SE-Isomap
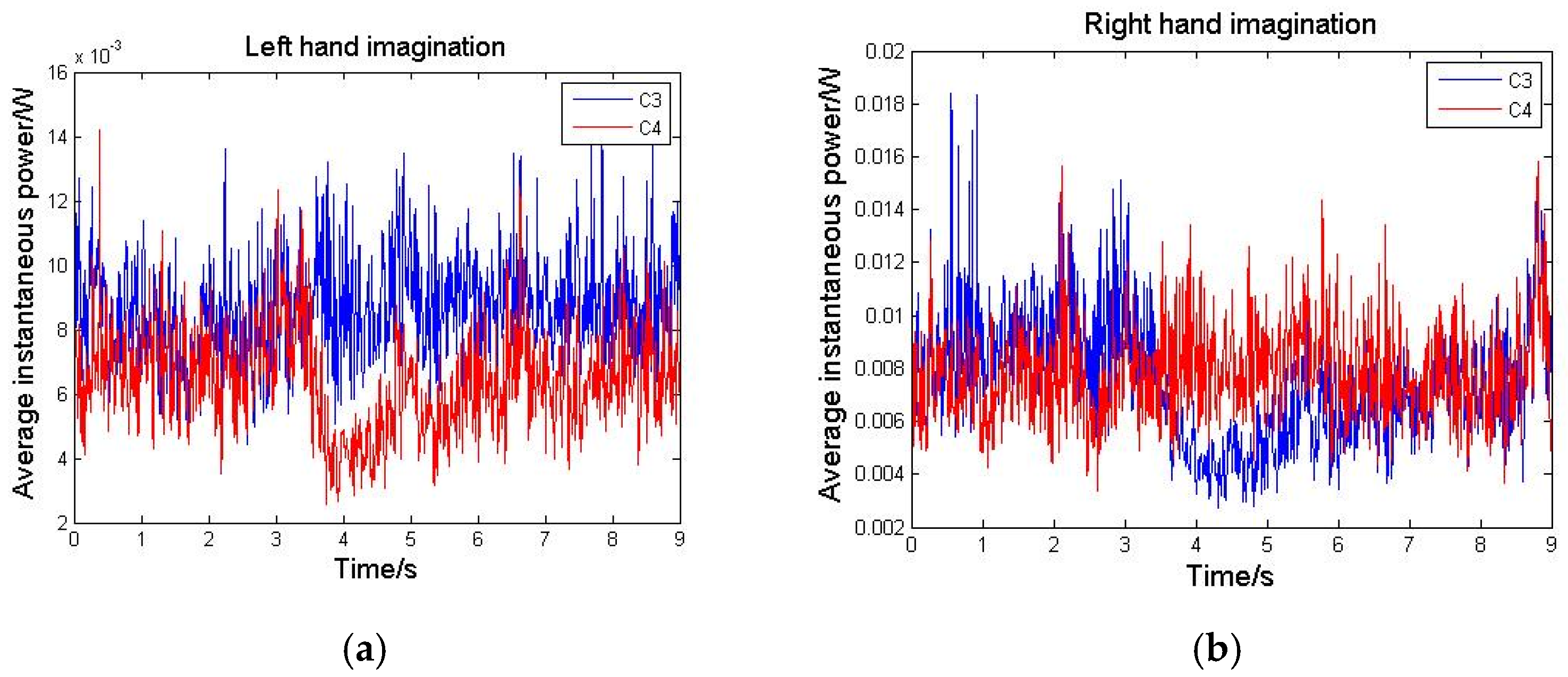
3.1. Instantaneous Power Spectra Analysis
3.2. Selection of Optimal Wavelet Packets
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.3.1. Statistical Features Based on OWP
3.3.2. Non-Liner Structure Feature with SE-Isomap
3.3.3. Feature Fusion
3.4. Feature Evaluation
4. Experimental Research
4.1. Dataset
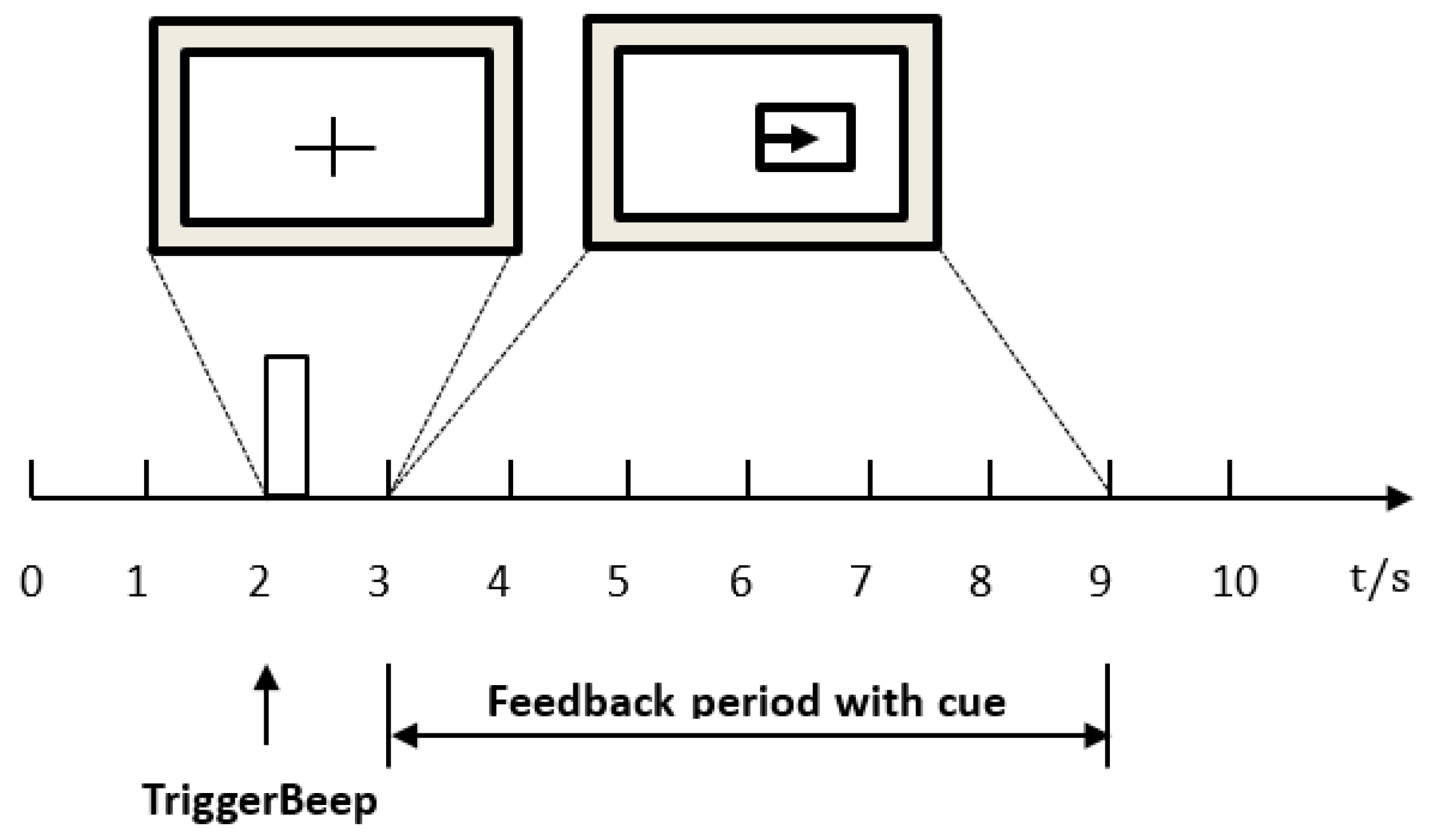
4.2. Data Preprocessing and Determination of the Optimal Time Interval
4.3. Time-Frequency Analysis with WPD
4.3.1. Selection of the Optimal Wavelet Packet Basis Function
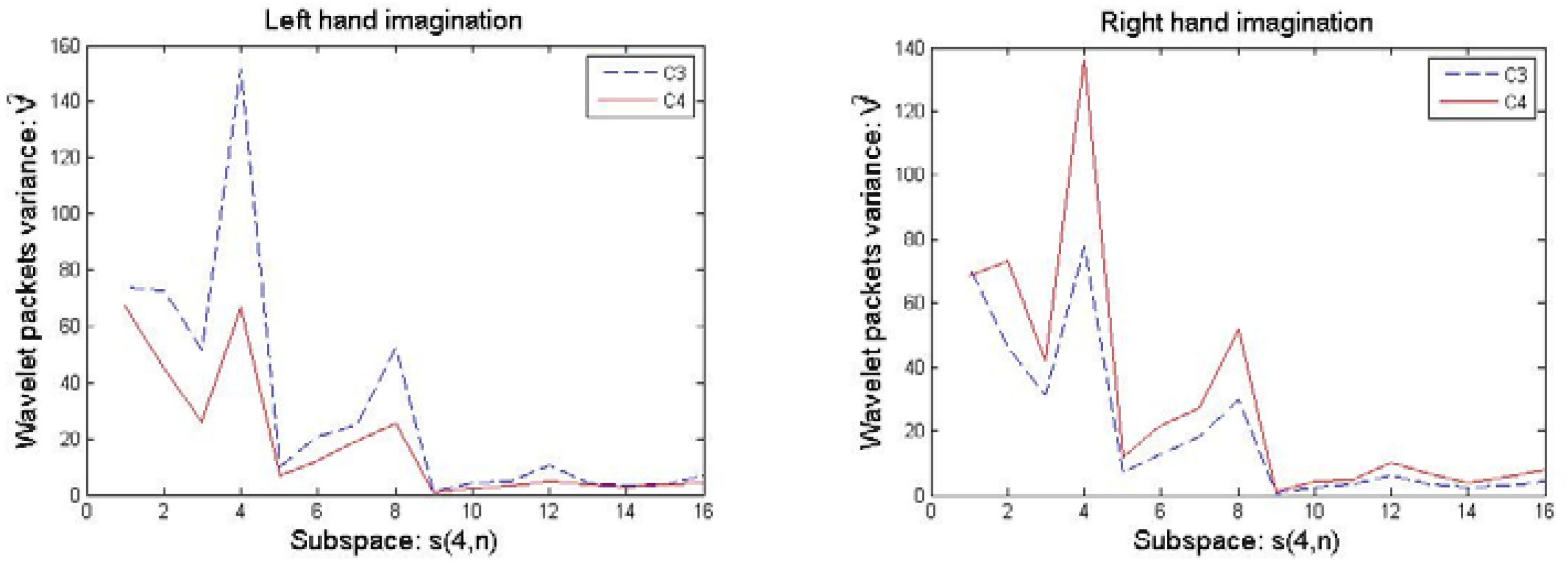
4.3.2. Selection of Optimal Wavelet Packets
4.3.3. Calculation of Time-Frequency Features
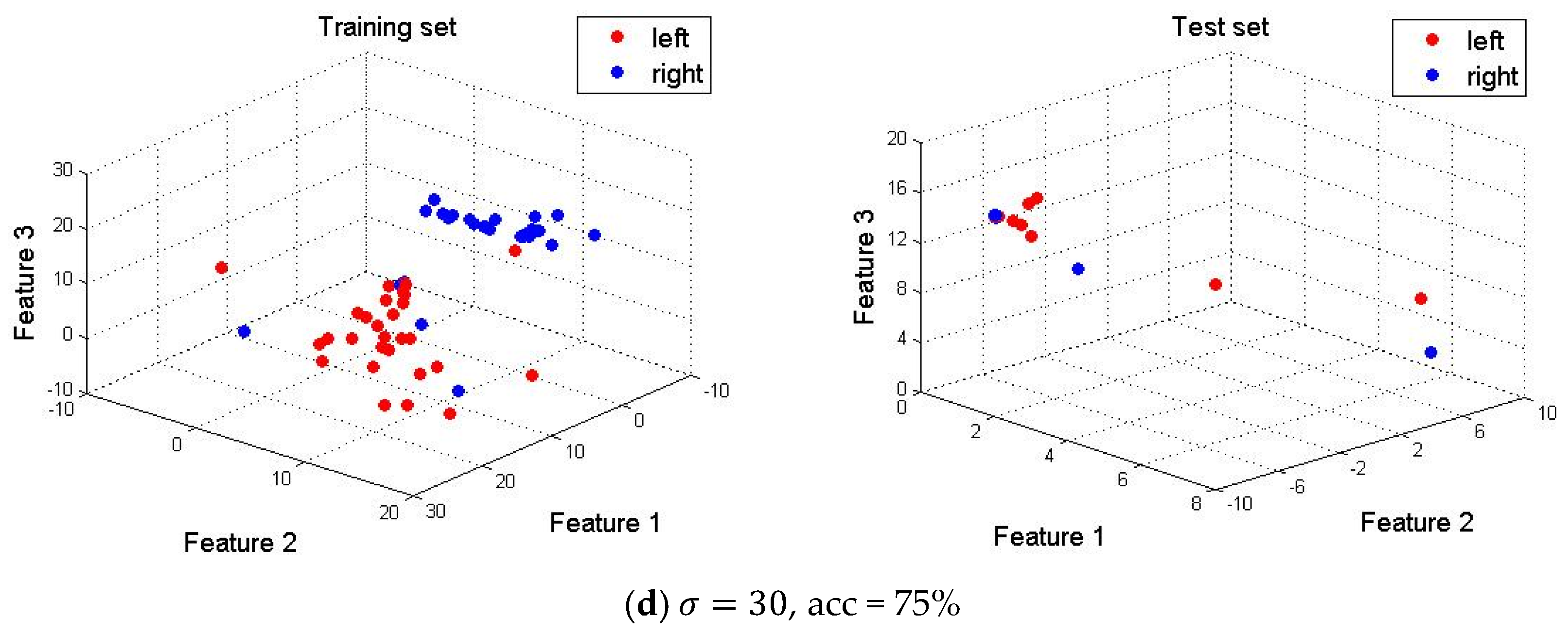
4.4. Dimension Reduction and Feature Visualization
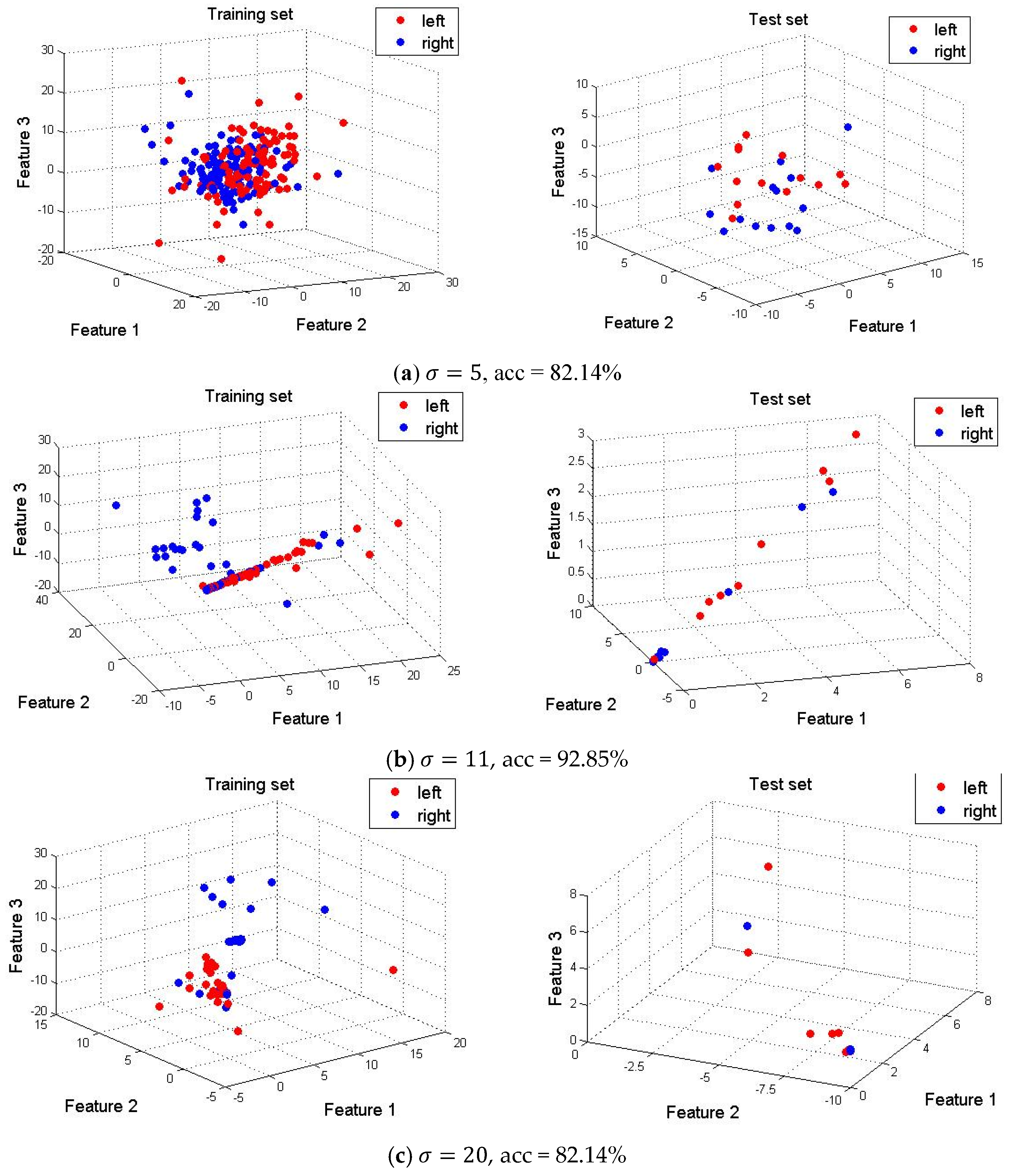
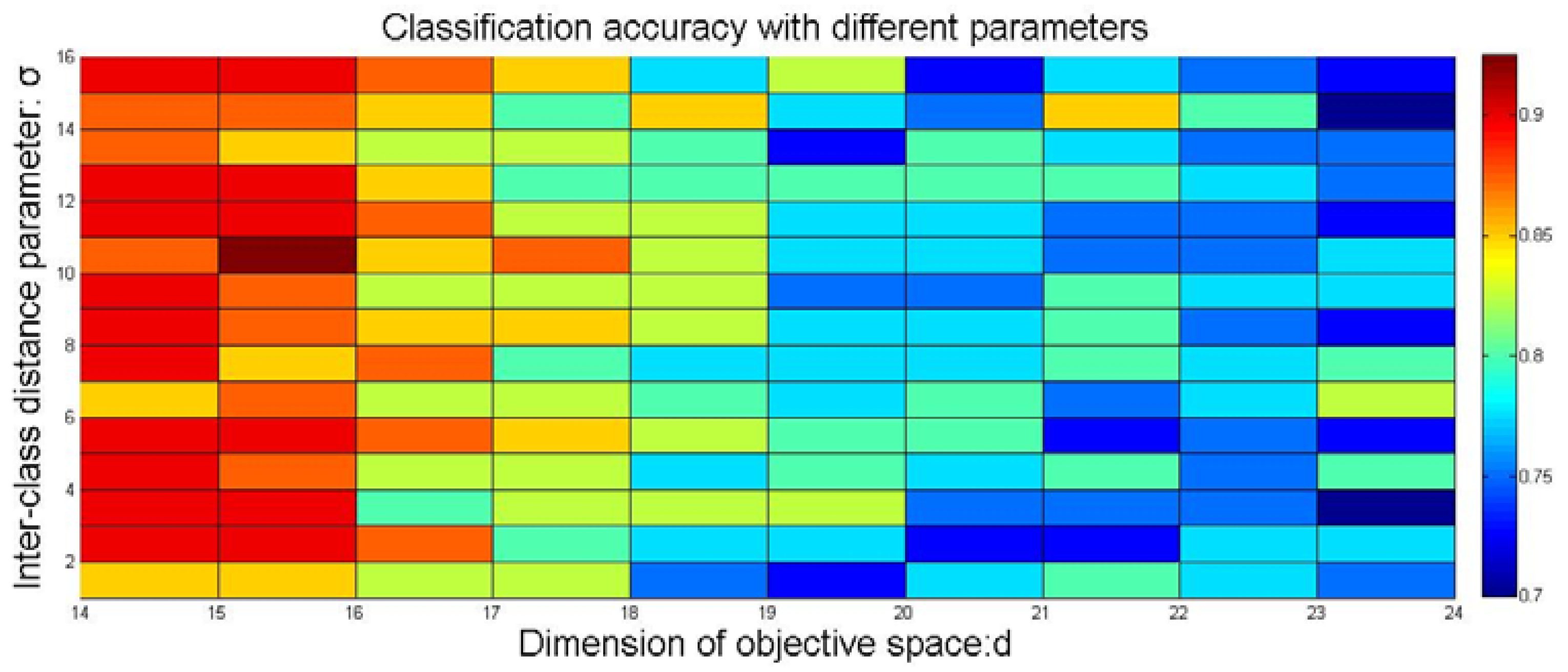
4.5. Optimal Selection of Parameters in SE-Isomap
4.6. Determination of Parameter k in the KNN Classifier
4.7. Comparison of Variety of Feature Extraction Algorithm Combined with WPD
4.8. Comparison of the Computational Cost with Multi-Feature Extraction Methods
4.9. Comparison Study Based on a Multi-Subject MI-EEG Database
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, K.S. Decoding answers to four-choice questions using functional near infrared spectroscopy. J. Infrared Spectrosc. 2015, 23, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.S.; Naseer, N.; Kim, Y.H. Classification of prefrontal and motor cortex signals for three-class fNIRS–BCI. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, K.S. Classification of functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals corresponding to the right-and left-wrist motor imagery for development of a brain–computer interface. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 553, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvaneh, M.; Guan, C.; KengAng, K.; Quek, C. Optimizing spatial filters by minimizing within-class dissimilarities in electroencephalogram-based brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, D.; Meng, J.; Huang, G.; Zhu, X. Unsupervised adaptation of electroencephalogram signal processing based on fuzzy C-means algorithm. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2012, 26, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, J.R. On the need for on-line learning in brain–computer interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; pp. 2877–2882. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Chum, P.; Sim, K.B. Analysis the effect of PCA for feature reduction in non-stationary EEG based motor imagery of BCI system. Optik 2014, 125, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhan, D.C.; Zhou, Z.H. Supervised nonlinear dimensionality reduction for visualization and classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2005, 35, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivov, E.; Belyaev, M. Dimensionality reduction with isomap algorithm for EEG covariance matrices. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Yongpyong, Korea, 22–24 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, H.U.; Malik, A.S.; Ahmad, R.F.; Badruddin, N.; Kamel, N.; Hussain, M.; Chooi, W.-T. Feature extraction and classification for EEG signals using wavelet transform and machine learning techniques. J. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2015, 38, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenenbaum, J.B.; Silva, V.; Langford, J.C. A Global Geometric Framework for Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction. Science 2000, 290, 2319–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roweis, T.; Saul, K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 2000, 29, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.G.; Guo, J.; Chen, G.; Nie, X.F.; Yang, Z. A version of isomap with explicit mapping. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Dalian, China, 13–16 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sadatnejad, K.; Ghidary, S.S. Kernel learning over the manifold of symmetric positive definite matrices for dimensionality reduction in a BCI application. J. Neurocomput. 2016, 179, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsadeghi, M.; Behnam, H.; Shalbaf, R.; Moghadam, H. Characterizing awake and anesthetized states using a dimensionality reduction method. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.G.; Guo, J. Supervised isomap with explicit mapping. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Innovative Computing, Information and Control (ICICIC’2006), Beijing, China, 30 August–1 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Luo, X.; Yang, J. Extracting the nonlinear features of motor imagery EEG using parametric t-SNE. J. Neurocomput. 2016, 218, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Subject-based feature extraction by using fisher WPD-CSP in brain–computer interfaces. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 129, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Yan, G.Z.; Yang, B.H.; Sun, H. EEG feature extraction based on wavelet packet decomposition for brain computer interface. Measurement 2008, 41, 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. Comparison of signal decomposition methods in classification of EEG signals for motor-imagery BCI system. J. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, N. Dynamic frequency feature selection based approach for classification of motor imageries. J. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 75, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonnak, N.; Kamonsantiroj, S. Wavelet Transform Enhancement for Drowsiness Classification in EEG Records Using Energy Coefficient Distribution and Neural Network. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2015, 5, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, H. Brain-Computer Interface Design Based on Wavelet Packet Transform and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI 2012), Yantai, China, 19–20 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.G. Feature extraction and classification of single trial motor imagery EEG. J. Southeast Univ. 2007, 37, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Da Silva, F.H.L. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: Basic principles. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, W.; Chen, X. Feature extraction of motor imagery EEG signals based on wavelet packet decomposition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME), Harbin, China, 22–25 May 2011; pp. 694–697. [Google Scholar]
- Adeli, H.; Zhou, Z.; Dadmehr, N. Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 123, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, R.; Brunner, C.; Müller-Putz, G.; Schlögl, A.; Pfurtscheller, G. BCI Competition 2008—Graz Data Set B; Graz University of Technology: Graz, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Morabito, F.; Labate, D.; Bramanti, A.; La Foresta, F.; Morabito, G.; Palamara, I.; Szu, H.H. Enhanced compressibility of EEG signal in Alzheimer’s disease patients. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Basis Function | sym6 | sym10 | coif4 | coif2 | Haar | db4 | db5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | 81.7 | 82.4 | 87.2 | 88.3 | 90.1 | 92.7 | 89.8 |
| k-Value | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | 82.9 | 83.1 | 86.2 | 87.5 | 88.3 | 90.6 | 92.7 | 89.1 | 91.2 |
| Methods | Feature Dimension | Accuracy | Methods | Feature Dimension | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 317 | 68.1 ± 6.3 | WPD + PCA | 96 | 73.1 ± 10.3 |
| ICA | 78 | 85.9 ± 8.9 | WPD + ICA | 42 | 87.3 ± 6.2 |
| MDS | 112 | 73.6 ± 7.4 | WPD + MDS | 84 | 77.4 ± 12.8 |
| LLE | 24 | 86.3 ± 4.2 | WPD + LLE | 33 | 91.8 ± 3.5 |
| SE-isomap | 16 | 88.5 ± 6.5 | WPD + SE-isomap | 25 | 92.7 ± 3.9 |
| Methods | Training Time (s) | Test Time (s) | Classification Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 152.2 | 1.7 | 68.1 ± 6.3 |
| MDS | 35.3 | 1.5 | 73.6 ± 7.4 |
| LLE | 207.2 | 2.7 | 86.3 ± 4.2 |
| WPD | 99.5 | 2.3 | 82.7 ± 8.8 |
| SE-isomap | 325.7 | 0.61 | 88.5 ± 6.5 |
| WPD + PCA | 258.7 | 7.9 | 73.1 ± 10.3 |
| WPD + ICA | 195.1 | 6.4 | 87.3 ± 6.2 |
| WPD + MDS | 140.5 | 4.3 | 77.4 ± 12.8 |
| WPD + LLE | 312.6 | 5.3 | 91.8 ± 3.5 |
| WPD + SE-isomap | 515.3 | 0.68 | 92.7 ± 3.9 |
| Subject | WPD + DFFS [22] | WPD + SE-Isomap |
|---|---|---|
| B01 | 73.24 | 84.58 |
| B02 | 67.48 | 66.25 |
| B03 | 63.01 | 62.92 |
| B04 | 97.4 | 95.83 |
| B05 | 95.49 | 89.17 |
| B06 | 86.66 | 97.92 |
| B07 | 84.68 | 82.08 |
| B08 | 95.93 | 86.25 |
| B09 | 92.61 | 97.08 |
| Average | 84.06 | 84.68 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.-a.; Zhu, W.; Liu, H.-n.; Yang, J.-f. Adaptive Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG with Optimal Wavelet Packets and SE-Isomap. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040390
Li M-a, Zhu W, Liu H-n, Yang J-f. Adaptive Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG with Optimal Wavelet Packets and SE-Isomap. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(4):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ming-ai, Wei Zhu, Hai-na Liu, and Jin-fu Yang. 2017. "Adaptive Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG with Optimal Wavelet Packets and SE-Isomap" Applied Sciences 7, no. 4: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040390
APA StyleLi, M.-a., Zhu, W., Liu, H.-n., & Yang, J.-f. (2017). Adaptive Feature Extraction of Motor Imagery EEG with Optimal Wavelet Packets and SE-Isomap. Applied Sciences, 7(4), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040390






