Abstract
The paper presents complex analyses of geophysical site investigation results. The electrical resistivity method was used to investigate the potential pollutant migration pathways within areas of existing and former landfill sites. For the purpose of the present study, there were four municipal waste landfills and one industrial landfill chosen for further comprehensive analyses. The landfill bottom was isolated using geomembrane liner. However, ground water monitoring results revealed that the base was not leakage-free. Another two landfills were established in the past, when no containment systems were legally required. The geoelectrical investigation was the final part of an overall analytical assessment of the contaminated sites. The study was aimed at pollution spatial migration analyses and the interpretation of results, for further design of the reclamation and restoration plans. A clear correlation between pollution indicators such as salt compounds and electrical resistivity, allow aerial analyses and the precise determination of contaminated zones. The research results presented in the paper have been recently obtained and concern a period from 2010 to 2015.
1. Introduction
There are several thousands of closed landfills in Poland that have not been investigated for an Environmental Risk Assessment or reclamation plans [1]. From a practical point of view, contaminated site investigations are usually based on geological and geotechnical techniques. These methods allow soil and water sampling for analytical tests and permit direct measurements of the contamination level of the study site [2,3,4]. However, such methods result in sampling bias, as the material is usually collected locally, from particular boreholes or piezometers. For the spatial assessment of contaminated soil layers within landfill subsoil, direct methods should be accompanied and extended by using geophysical investigations, such as an electrical resistivity method or another similar technique [5,6,7,8,9].
The results of soil resistivity tests for contaminated sites generally reveal a close relationship between free electrolytes, oils, and salt solutions [10,11,12,13,14,15], which are also the main components of leachate infiltrating from landfills. On the basis of the research results and gained experiences, the method for an assessment of environmental contamination for four independent landfills, was established and then verified. Three of these sites are municipal landfills (one with leakage detected at the base, another without any signs of soil-water environmental contamination, and the other with no containment system installed) and one is a former industrial landfill, located near an environmentally precious area without a sealing liner at the bottom. Two of the study sites are located in the central part of Poland, one is in the east, and the other is in the northern region. All of the sites are provided with a monitoring program, extended to electro resistivity tests, where the capability of using geophysical methods on such sites, was analysed. The proposed investigation helped to decide upon the methodology for testing, but more importantly, allowed the precise detection of a contaminant’s leakage location and the final reclamation plans for landfills.
The geophysical testing of the study sites confirmed that the methodology was appropriate for the geological and environmental surveying purposes. However, it is important to bear in mind that a comprehensive interpretation of the results is only possible when reliable geological and geochemical data are available [7,11,16,17,18].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology Used in the Study
Due to economic factors and efficiency, the recommended method for the environmental investigation of a landfill site is the electrical resistivity test. The advantages of this technique are: (1) the precision in measuring the electromagnetic excitation and neutral field, including the continuous monitoring of such parameters; (2) close relationships between the parameter magnitude, chemical composition, and mechanical properties; (3) the established and verified methods of complex electrical resistivity and geochemical testing; (4) allowing a physical transformation of the investigated material, into chemical characteristics; (5) the capability of geochemical and hydro-geochemical change monitoring, as well as a stress determination of the soil layer; and (6) the non-invasive character of the tests, free of an environmental impact and causing no changes in the soil hydrology and structure.
Furthermore, the method allows: (1) the identification of the lithology of a landfill subsoil; (2) the determination of the groundwater table depth; (3) the determination of the distribution of the contamination zones and the direction of the pollutant migration; and (4) the evaluation of waste thickness disposed at a landfill site.
The resistivity method has been of great use over the last 50 years [7,11,19,20,21,22]. In practice, the electrical resistivity of the soil is measured using a four-electrode configuration. In this method, an electrical current is injected into the soil using two electrodes (A and B), whereas M and N electrodes measure its potential. The apparent resistivity of the soil can be determined, based on the known difference between the electric field potential (ΔV) and the current (I), and the distance between the electrodes [11]. The resistivity is given by the equation:
where:
- ρa—resistivity of a bedrock,
- I—intensity of current applied to the soil by electrodes AB (mA),
- ΔV—differential potential between electrodes MN (mV),
- k—geometrical coefficient of electrode positioning (m).
The geometrical factor k is dependent on the distribution geometry of the electrodes, as follows:
where:
- , , , —distance between electrodes (m).
The resistivity does not reflect the properties of one particular soil type; however, it presents the capability of electrical conductivity measurements for the investigated subsoil. Such resistivity is called apparent resistivity, and depends on the resistivity of a particular soil type, its deposition, and the distance and distribution between the electrodes. The geoelectrical investigation is based on the measurement of apparent resistivity, accompanied by a symmetrical increase of distance between charged electrodes A and B. The width of the distance dipper for the electric field penetration of the subsoil, significantly influences the investigation depth.
For the purpose of the present study, the Wenner and Schlumberger survey was used. Resistivity imaging was carried out as a number of 1D (1st and 4th case study—Vertical Electrical Sounding) and 2D sections (2nd and 3rd site—Electrical Resistivity Tomography). Each single Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) test was based on a Wenner array measurement of the electrical potential between two inner electrodes (M and N), resulting from a constant current injected through two outer electrodes (A and B). Each VES test were performed using the Schlumberger method. In both cases, the apparent electrical conductivity was calculated as the ratio of the injected current to the measured potential, with a correction applied for the geometrical effects of the electrode spacing which were appropriate for each method. A detailed description of the proposed method, like most efficient electrode configurations, has been published by Keller et al. [19], Zahody et al. [20], Stummer et al. [23], and Loke et al. [24].
All of the data was collected using a Chauvin Arnoux Earth Resistivity Tester, and a Res2Dinv program was used for inverse modelling, to interpret the data as cross-sections and profiles of subsoil resistivity [24]. Based on these results, the inverted sections were further processed in Surfer software.
2.2. Contamination Influencing the Resistivity of a Soil
It is always a challenge to establish a relationship for soil parameters versus electrical resistivity. The common assumption is that the soil skeleton plays the role of an isolator (in sandy soils), while the electric current flows through the soil voids filled with water. The results of the resistivity test could be significantly affected due to the mineralisation of water (or leachate from a landfill, in this case) [15,17]. If the water content is constant, the resistivity of the soil becomes a function of salts dissolved in a soil water solution. The principal empirical equations concerning the relationships between soil resistivity and its physical parameters, have been presented by Archie [25] and others [26,27,28,29,30].
There is a direct correlation between the electrical conductivity (EC) and the amount of elements dissolved in water, and a similar correlation can be seen for the content of other elements and the water quality (chlorides, sulphates, and petroleum). Practically, even small, dissolved elemental changes in water affect the conductivity [31,32]. Thus, it can be used as a way of recording the changes in water composition, which is also influenced by contamination of the groundwater. This feature, when properly calibrated and based on analytical assessment, could be used as valuable information for a soil-water environment quality assessment [24,33].
Water is not an efficient electrical conductor; it’s electrical conductivity is 5 × 10−8 μS/cm (at temperature 25 °C). In dissolved suspensions, the EC is proportional to the concentration. The higher the concentration of a suspension is, the better the electrical conductivity will be. This is because there is a better dissociation of the elements into ions, in dissolved suspensions. In particular ranges, the relationships between the conductivity and electrolyte concentration are linear functions. Figure 1 presents the collection of data concerning the relationship of electrical conductivity and selected chemical solutions. During a number of investigations, it was also noticed that the conductivity of the electrolytes increases with a temperature rise of about 2%/1 °C. It is mainly caused by a decrease in the suspension viscosity and an increase in the mobility at higher temperatures. The EC of natural water falls in a range of 50 to 1000 μS/cm, but leachate conductivity can exceed 10,000 μS/cm. It is assumed that, for shallow groundwater, potentially affected by anthropogenic activity, values of EC above 1000 μS/cm indicate water contamination.
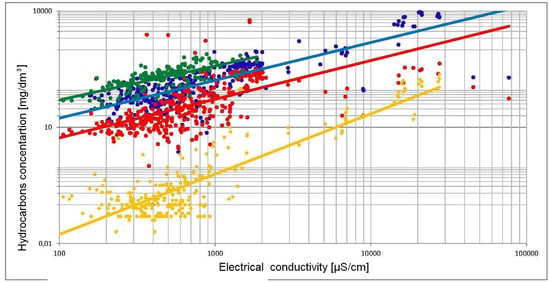
Figure 1.
Correlation between EC and hydrocarbons (● set of 194 data points), sulfate (● set of 380 data points), chlorate (● set of 392 data points), ammonium (● set of 248 data points).
The organic compounds present in water either dissociate insignificantly or not at all. That is why the conductivity of water influenced by organic pollutants is usually very low.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Municpal Landfill with Liners Installed-Leakage Investigation
The first case study—municipal solid waste (MSW) disposal—is located in the central part of Poland. The thickness of the quaternary deposits varies from 11 to 60 m. The deposits consist of glacial tills, river sand, and gravels of the Mazovian interglacial.
The investigation was performed due to the EC and TOC (total organic carbon) present in groundwater samples, collected from a selected piezometer. The piezometer was located where groundwater was discharged from the landfill (south western part). The changes of EC and TOC with ground water table fluctuations over time, are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3. From the monitoring results, it was determined that the leakage had appeared in 2005 and had been most intensive in the following three years. The later drop in EC and TOC values was achieved by applying remediation solutions at the site (purifying pumping). The results of selected indicators of a groundwater quality assessment, are presented in Table 1. According to Polish standards, the salinity parameters indicate a IV and V quality class [34].
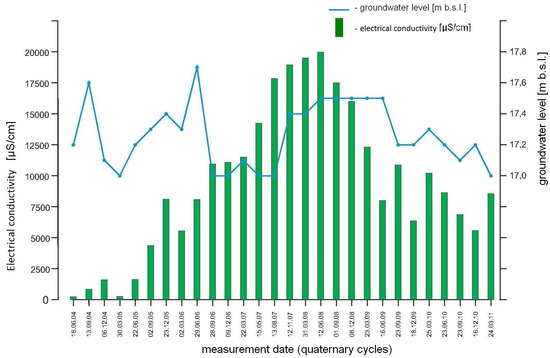
Figure 2.
Electrical conductivity (EC) and ground water table changes over time.
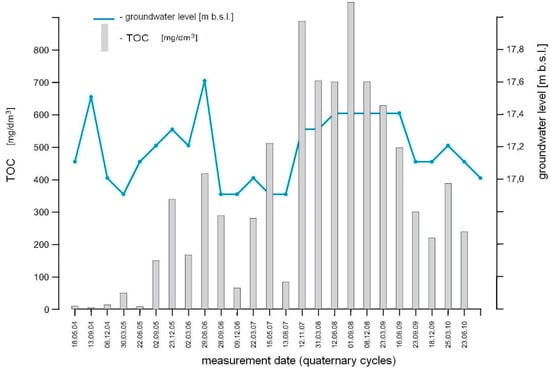
Figure 3.
Total organic carbon (TOC) and ground water table changes over time.

Table 1.
The results of a groundwater quality assessment for a selected piezometer.
For the site investigation purposes, geophysical investigation was performed to identify the leakage zones. The electrical resistivity method was used to distinguish the top of the less permeable layers of clay in the landfill’s subsoil. The purpose of the tests was also to investigate the depth of the groundwater table and to confirm the direction of the groundwater flow in the south eastern part, where the leakage had occurred. The distance between testing points allowed an investigation of the subsoil as deep as 35 m below the ground level. The quantity interpretation gave a full picture of the resistivity characteristics, which are listed in Table 2. The interpretation and testing results are presented in Figure 4.

Table 2.
Soil resistivity characteristics.
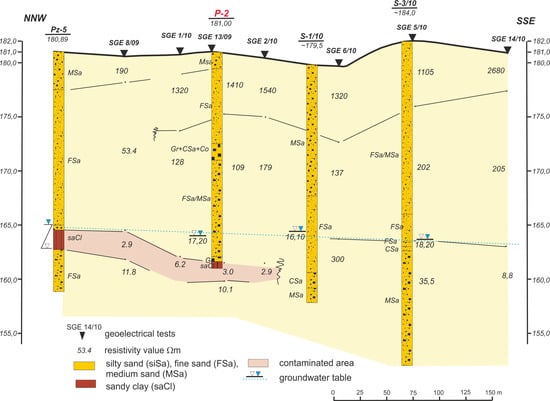
Figure 4.
Geoelectrical cross-section of the landfill subsoil.
The proposed solutions for remedial works at the landfill site consisted of:
- The pumping of contaminated water from piezometer P-2 and the redirecting to the pumping station on the landfill;
- A depression well construction of enough discharge to transmit the leachate from the landfill, to a sewage treatment plant;
- A landfill bottom sealing in the area where leakage was detected, with the use of injecting methods.
The changes of EC, the mass of sewage sludge, and the amount of pumped water, is present in Figure 5.
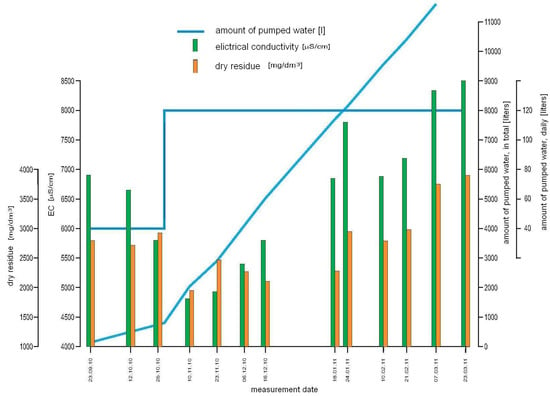
Figure 5.
Changes of EC, dry residues, and the amount of pumped water at the landfill site (daily and in total).
Due to the high values of EC, tests of the residual dry mass were also performed for collected water samples. This is a water class indicator that is used in hydrogeology and is determined in the laboratory. It is expressed as a mass of sediment left after evaporating 1 dm3 of water at a temperature of 105 °C, and drying the residue in a temperature which does not exceed 105 °C. The dry residue, which is also an indicator of water mineralization, is expressed in mg/dm3. The mineral matter content, which is the dry residue, is a principal classification of highly mineralized water, with the content exceeding 1500 mg/dm3.
Pumping out 12,930 dm3 of water did not result in a significant increase in the water quality in piezometer P-2. At the beginning, pumping was carried out at a capacity of 40 L per day (blue line at Figure 5). The values of EC within this time decreased from 6961 to 4752 μS/cm, and the mass of dry residue (dried sewage sludge) decreased from 2804 to 1944 mg/dm3. Following this, the pumping capacity was tripled to 120 L per day. As a result, the EC increased to 8589 μS/cm, and the mass of the dry residue increased to 3916 mg/dm3. The increase of EC after the intensification of pumping could be a result of:
- too much water being pumped, causing the chloride concentration to increase (lower dissolution);
- seasonal changes of the groundwater table and a wash out of the soil elements.
There is a possibility that both of these reasons resulted in an increased contamination. The position of the groundwater levels at that time fluctuated by about 1 m.
The lack of treatment effects during the pumping from the piezometer forced the landfill’s owner to apply further reclamation solutions, which involved the construction of another depression well to catch all of the stream of leachate from the landfill. Moreover, by using an injection method, we were able to isolate the landfill’s base, remove some of the waste from the landfill body, and repair the isolation layer in place.
The main factors affecting the soil resistivity, apart from the factors specified above, are the soil’s water content and the concentration of salts dissolved in the water. The effect of groundwater salinity significantly affects the resistivity of soil and ground water. It could cause the differences in the resistivity of soils contaminated with the landfill leachates. The use of electrical resistivity tests for monitoring the mechanical condition of a landfill containment system, contouring the zone of soil contamination, and determining migration routes for the contaminants, is fully justified. The test also allows a determination of the specific test locations, including boreholes, standpipe piezometer installation points, and chemical analysis sampling points.
The second case study is an active MSW landfill located in the eastern part of Poland, in a post-mining sand and gravel pit. It is a sub-horizon landfill of a depth up to 12 m below the ground level. The landfill base and slopes are sealed with a 1.5 mm thick HDPE geomembrane, laid down on the 0.5 m thick clay layer. The geomembrane is covered with the protective layer, and subsoil drainage is made of perforated vitrified clay pipes. The liner was installed at the bottom of the landfill.
An occurrence of the glacial clay and sandy clay loam deposits of a thickness of approximately 4 m, lined with sands and gravel with an unknown floor depth was determined, based on the data from the boreholes. A free water table was observed at 16.3 and 17.5 m below the ground level. The electrical resistivity tomography (Figure 6) was performed by using electrodes spaced 4.8 m apart and a total measured length of 72 m.
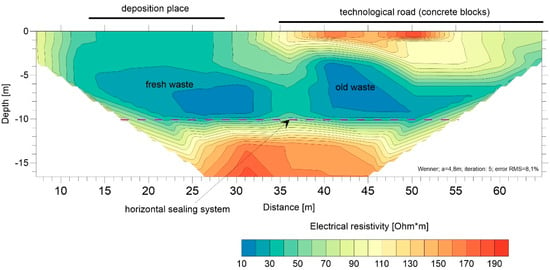
Figure 6.
The electrical resistivity cross-section of waste disposal with a bottom sealing system.
In the middle and right side of the profile, the electrical resistivity was 150–200 Ωm, mainly due to the location of an access road to the landfill facilities. An old waste layer with an electrical resistivity of approximately 30–40 Ωm is located just below the road. The facilities, where the deposited municipal wastes are mixed, featured an electrical resistivity of less than 50 Ωm, on the left side of the profile.
The other distinguished part of the profile is its middle section and the boundary between the landfill body and the soil below the liner. The section, of a depth between 12 and 16 m below the ground level, has an electrical resistivity of more than 160 Ωm, which indicates the occurrence of sand deposits. The layer was also observed in the geological profile investigated before the construction of the landfill. The electrical resistivity tests did not indicate leakage at the bottom or slopes of the landfill, since no areas of low electrical resistivity were detected in the sand layer below the landfill. The ground water monitoring and water sample chemical analysis from the standpipe piezometers also did not show any leakage from inside the landfill sealing.
Another example is the way in which the electrical resistivity test results were used to determine the integrity of a cut-off wall constructed around the MSW disposal, near a large metropolitan area. A vertical cut-off wall in the form of a slurry wall was constructed around the landfill at the end of the 1990s. The field tests included electrical resistivity tomography (Figure 7), to indicate any possible cut-off wall leakage, as well as points of the material permeability tests. The electrical resistivity tomography was used along the sealing at a distance of approximately 5 m from the cut-off wall, on the outside and on the inside of the separated area. Areas with reduced electrical resistivity were observed (less than 1 Ωm) in the profile, on the inside of the cut-off wall (Figure 7). It confirms the occurrence of soils contaminated with the landfill leachate. The electrical resistivity outside the cut-off wall (second profile, Figure 7) is between 20 and 70 Ωm for the entire profile. The test results did not show any contamination from the landfill and prove that the cut-off wall material has maintained its properties and is impermeable.
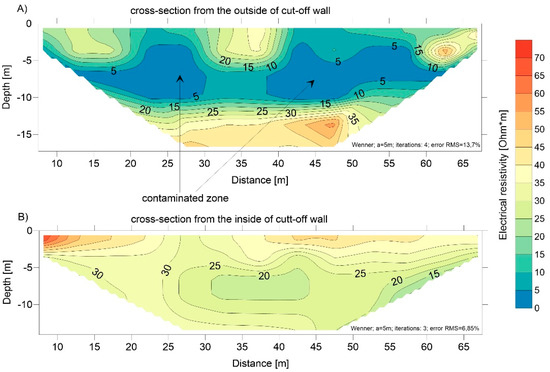
Figure 7.
The electrical resistivity cross-section inside (A) and outside (B) the cut-off wall.
3.2. Municipal Landfill with No Liner
The remediated municipal landfill site is located in northern part of Poland, in the Kaszuby Lakeland mesoregion. The geological structure of the site consists of quaternary glaciation deposits. Morphologically, it is morainic plateau created during Pomeranian Vistula glaciation. The area of plateau is folded with depressions of gully-shaped lakes.
The study site was closed in 1998/1999 and located at the area where a new development plan for a road construction was established. The cubic capacity of the landfill exceeds 0.6 mln m3 (municipal waste, debris, and soil), and the thickness reaches 10 m. During reclamation works, the landfill body was capped with a 0.7–1.5 m clay layer. The site investigation comprised geotechnical tests, to determine the soil and waste mechanical parameters for future construction plans, and an environmental survey, aimed at a soil-water quality assessment. The geotechnical investigation included electric-resistivity tests to investigate the thickness of waste disposed on the landfill and to determine the depth of the impermeable soil layers within the subsoil.
Based on geophysical tests, the geological structure (from the top) consists of a sandy layer with a thickness from 8.3 to 19.7 m, layered with clayey deposits. The hydraulic conductivity of the sand layers falls in a range of 1.7 × 10−5 to 5.5 × 10−3 m/s.
The quantity interpretation of the results allowed the precise determination of the resistivity characteristics, which are presented in Table 3 and Table 4. The graphical presentation of the results is provided in Figure 8.

Table 3.
Subsoil resistivity characteristics.

Table 4.
Geoelectrical investigation results.
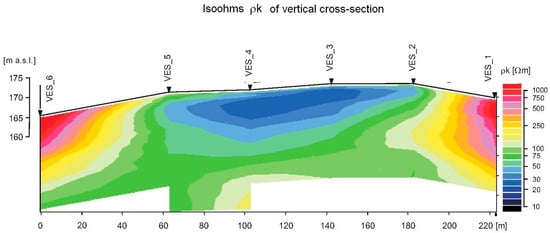
Figure 8.
Results of the quantity interpretation of the geophysical investigation.
The thickness of the waste investigated by geoelectrical tests could be biased due to an error, caused by the fact that, below the anthropogenic material, there is also a highly contaminated deposit of sand. It is worth highlighting that the geophysical tests were also compared and correlated with geological boreholes (10 drillings down to 12 m) and geotechnical static cone penetration tests (seven CPT tests down to 12 m). The CPT tests confirmed the presence of sandy soils with a friction ratio (Rf) of less than 2.2%, whereas the waste body Rf was between 3.2% and 4.8%.
3.3. Closed Industrial Waste Landfill with No Liner Installed
The landfill is located in the central part of Poland, within the Warsaw plateau mesoregion, consisting of tills, glacial sands, silts, and clay deposits. In the close vicinity of the landfill, there is a number of environmentally valuable protected areas, and this is why there are plans to restore it. The entire site is going to be adapted for recreational and commercial purposes, after the reclamation works are accomplished.
Beyond the ordinary geological survey, the site investigation also included 32 geoelectrical tests. The purpose of the geophysical investigation was to determine the thickness of the industrial waste (part of the landfill is located on former sand pits), investigate the potential contamination of the transport paths, and to determine a depth of impermeable layers (Pliocene clays) within the subsoil. The geophysical test allowed an investigation down to 25 m below the surface level. Based on a quantity interpretation of the tests, the resistivity of each soil layer was evaluated. The results are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Resistivity characteristics of the soil layers.
The measured resistivity distribution indicated a long-term emission of contaminants from the landfill, within the first aquifer layer (the groundwater table at 6 m b.s.l). The results of the geoelectrical tests are presented in Figure 9 and Figure 10, as subsoil cross-sections.
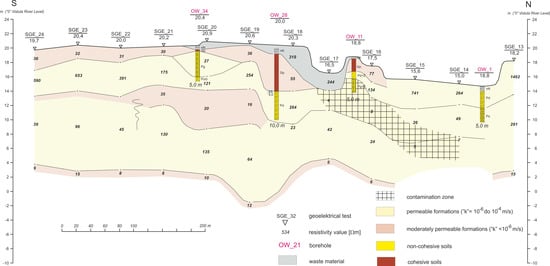
Figure 9.
Geophysical cross-section of the landfill subsoil—Section I.
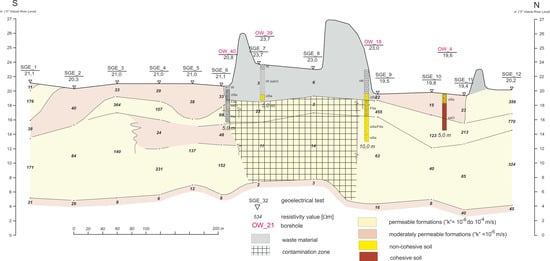
Figure 10.
Geophysical cross-section of the landfill subsoil—Section II.
The migration in the upper part of the zone is vertically directed; however, within the saturation zone, the contaminants flow in the direction of the groundwater stream.
The zones of the cross-sections where the resistivity is low are hatched. The contaminated zones are mainly located in former sand pits where the cohesive top soil was removed, and which initially created weak liners of the landfill bottom. From Figure 10, it can be seen that the pattern of the contamination zone overlies the direction of groundwater flow and moves towards the top of the lower permeability soil layer.
The geophysical investigation also allowed a detailed determination of the landfill base’s precise location and verification of the cubic capacity of the waste disposed on the landfill (255,000 m3), permitting an evaluation of the amount of contaminated soil to be removed (110,000 m3) during reclamation works.
4. Conclusions
The geophysical investigations performed on selected landfills confirmed the usefulness of contaminated sites when analyzing geological, hydrogeological, and environmental conditions.
The migration of pollutants emitted from the landfill to the soil-water environment, mainly depend on the mineralogical composition, moisture content, porosity, temperature, grain size distribution, or the chemical solution. These features significantly influence the resistivity of soil. However, it needs to be emphasized that a comprehensive interpretation of the geophysical test can only be conducted when reliable geological survey (boreholes) and geochemical data sets are available. A complex interpretation of these types of data allows the appropriate design of reclamation and restoration works; also from an economical point of view.
The application of geophisical investigation gives the opportunity to evaluate the scale and the spread of contamination into the soil-water environment from the landfill, especially when the compounds of the pollutants are mainly salts and bicarbonates.
Author Contributions
Eugeniusz Koda and Andrzej Tkaczyk conceived and designed the experiments; Andrzej Tkaczyk and Mariusz Lech performed the experiments; Andrzej Tkaczyk, Eugeniusz Koda, Mariusz Lech, and Piotr Osiński analyzed the data; Eugeniusz Koda, Piotr Osiński, and Mariusz Lech wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koda, E. Landfill Stability under Reclamation and Pollutant Transport Using the Observational Method; Warsaw University of Life Sciences Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vaverková, M.; Toman, F.; Adamcová, D.; Kotovicová, J. Verifying Research of Waste Landfill Environmental Impact Using Bioindicators. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Gozdowski, D.; Koda, E.; Osiecka, R.; Borzyszkowski, J. Influence of a Municipal Waste Landfill on the Spatial Distribution of Mercury in the Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamcová, D.; Vaverková, M.D.; Bartoň, S.; Havlíček, Z.; Břoušková, E. Soil Contamination in Landfills: A Case Study of a Landfill in Czech Republic. Sol. Earth 2016, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elis, V.R.; Mondelli, G.; Giacheti, H.L.; Peixoto, A.S.P.; Hamada, J. The Use of Electrical Resistivity for Detection of Leachate Plumes in Waste Disposal Sites. In Proceedings of the ISC-2 on Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization, Porto, Portugal, 19–22 September 2004; pp. 467–474.
- Batayneh, A.T. 2D Electrical Imaging of an LNAPL Contamination, Al Amiriya Fuel Station, Jordan. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koda, E.; Kołanka, T.; Osiński, P. Investigation of Soil Contamination Level beneath the Metallurgical Waste Landfill for the Purpose of Future Reclamation Works. Land Reclam. 2013, 45, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Osiński, P. Site Investigation of an Industrial Landfill for the Purpose of a Remedial Works Project. In Proceedings of the Geo-Chicago 2016: Sustainable Waste Management and Remediation 2016, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 August 2016; pp. 750–757.
- Friedman, S.P. Soil Properties Influencing Apparent Electrical Conductivity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrie, W. Fundamentals of Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli, G.; Giacheti, H.L.; Elis, V.R. The use of resistivity for detecting MSW contamination plumes in a tropical soil site. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics, New Delhi, India, 8–12 November 2010; Hill, M.G., Ed.; Volume II, pp. 1544–1549.
- Giang, N.V.; Marquis, G.; Minh, L.H. EM and GPR Investigations of Contaminant Spread Around the Hoc Mon Waste Site, Vietnam. Acta Geophys. 2010, 58, 1040–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, N.V.; Duan, N.B.; Thanh, L.N.; Hida, N. Geophysical Techniques to Aquifer Locating and Monitoring for Industrial Zones in North Hanoi, Vietnam. Acta Geophys. 2013, 61, 1573–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.-M.; Cho, G.-C.; Lee, C. Effect of Soil Mineralogy and Pore-Water Chemistry on the Electrical Resistivity of Saturated Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfahani, J.; Zakhem, B.A. Geoelectrical and Hydrochemical Investigations for Characterizing the Salt Water Intrusion in the Khanasser Valley, Northern Syria. Acta Geophys. 2013, 61, 422–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carlo, L.; Perri, M.T.; Caputo, M.C.; Deiana, R.; Vurro, M.; Cassiani, G. Characterization of a Dismissed Landfill via Electrical Resistivity Tomography and Mise-à-la-Masse Method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 98, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, W.; Głuchowski, A.; Radziemska, M.; Dzięcioł, J.; Szymański, A. Environmental and Geotechnical Assessment of the Steel Slags as a Material for Road Structure. Materials 2015, 8, 4857–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, G.V.; Frischknecht, F.C. Electrical Methods in Geophysical Prospecting; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Zahody, A.A.P.; Eaton, G.P.; Mabey, D.R. Electrical Methods in US Geological Survey. Ch. 2: Application of Surface Geophysics to Ground—Water Investigations; USGS Publications: Denver, CO, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Wisen, R.; Dahlin, T.; Auken, E. Resistivity Imaging as a Tool in Shallow Site Investigation—A Case Study. In Proceedings of the ISC-2 on Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization, Porto, Portugal, 19–22 September 2004; pp. 607–613.
- Samouelian, A.; Cousin, I.; Tabbagh, A.; Bruand, A.; Richard, G. Electrical Resistivity Survey in Soil Science. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 83, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, P.; Maurer, H.; Green, A. Experimental design: Electrical Resistivity Data Sets that Provide Optimum Subsurface Information. Geophysics 2004, 69, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Chambers, J.E.; Rucker, D.F.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P.B. Recent Developments in the Direct-Current Geoelectrical Imaging Method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1942, 146, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, E.R.; Smith, G.H. The Significance of Particle Shape in Formation Resistivity Factor–Porosity Relationships. J. Petrol. Technol. 1961, 13, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.D.; Taylor Smith, D.; Stanford, P.N. Resistivity–Porosity–Particle Shape Relationships for Marine Sands. Geophysics 1978, 43, 1250–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang, D. Environmental Geophysics. A Practical Guide; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Donohue, S.; L’Heureux, J.-S.; Solberg, I.-L.; Rønning, J.S.; Limacher, R.; O’Connor, P.; Sauvin, G.; Rømoen, M.; Lecomte, I. Relationship between Electrical Resistivity and Basic Geotechnical Parameters for Marine Clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, B.S. Impacts of the Pore- and Petro-fabrics on Porosity Exponent and Lithology Factor of Archie’s Equation for Carbonate Rocks. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 108, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleńska, M.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, A.; Kądziałko-Hofmokl, M.; Kopcewicz, B.; Sukhorada, A.; Bondar, K.; Matviishina, Z. Magnetic Structure of Polluted Soil Profiles from Eastern Ukraine. Acta Geophys. 2008, 56, 1043–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knődel, K.; Krummel, H.; Lange, G. Handbuch zur Erkundung des Untergrundes von Deponien und Altlasten; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koda, E. Influence of Vertical Barrier Surrounding Old Sanitary Landfill on Eliminating Transport of Pollutants on the Basis of Numerical Modelling and Monitoring Results. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 929–935. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of The Minister of Environment Dated 21 December 2015 on The Criteria and Method of Evaluating The Underground Water Condition. Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/DetailsServlet?id=WDU20160000085 (accessed on 22 June 2016).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).