Heat Flow Characteristics of a Newly-Designed Cooling System with Multi-Fans and Thermal Baffle in the Wheel Loader
Abstract
:1. Introduction
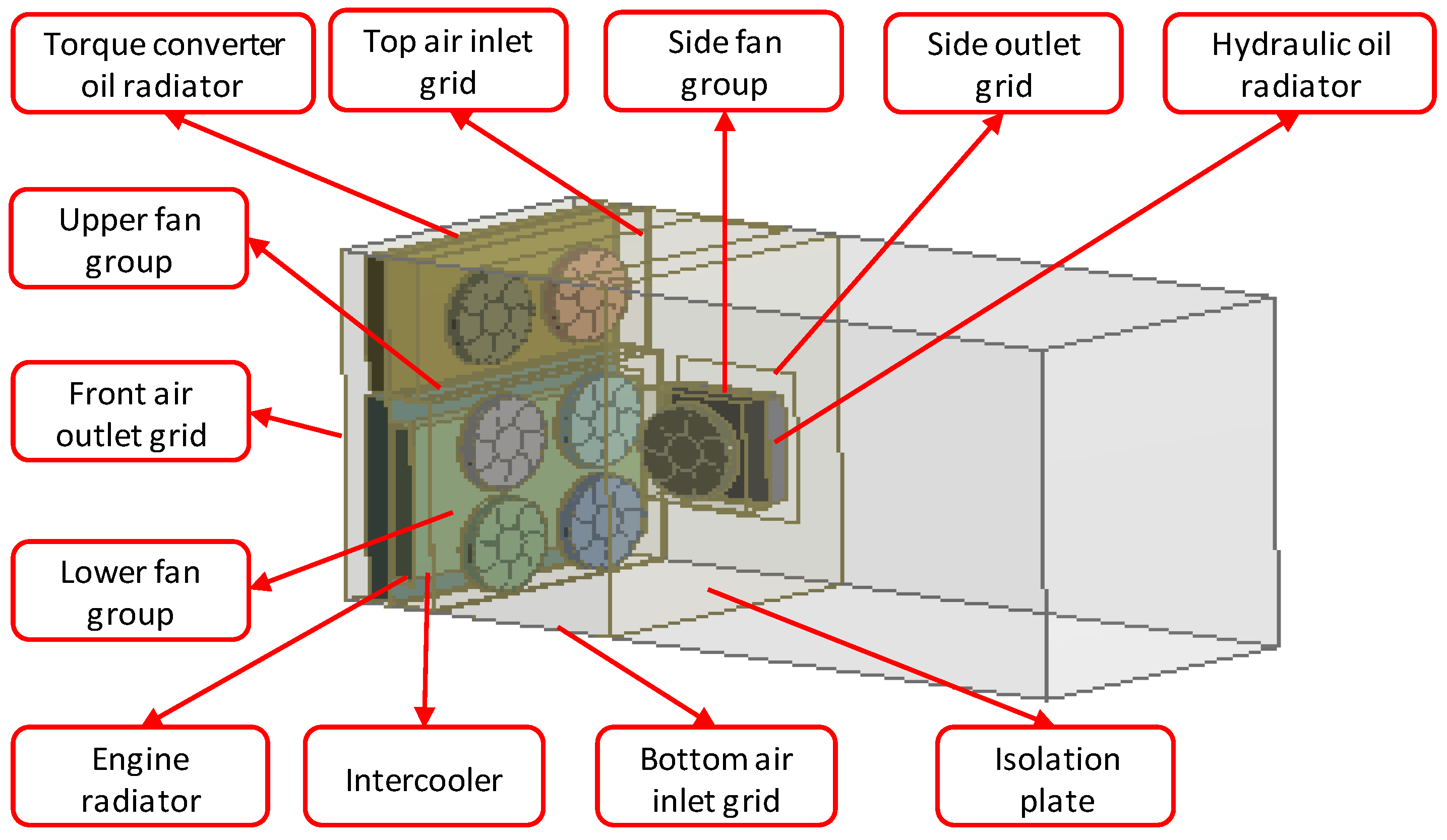
2. New-Design Engine Compartment
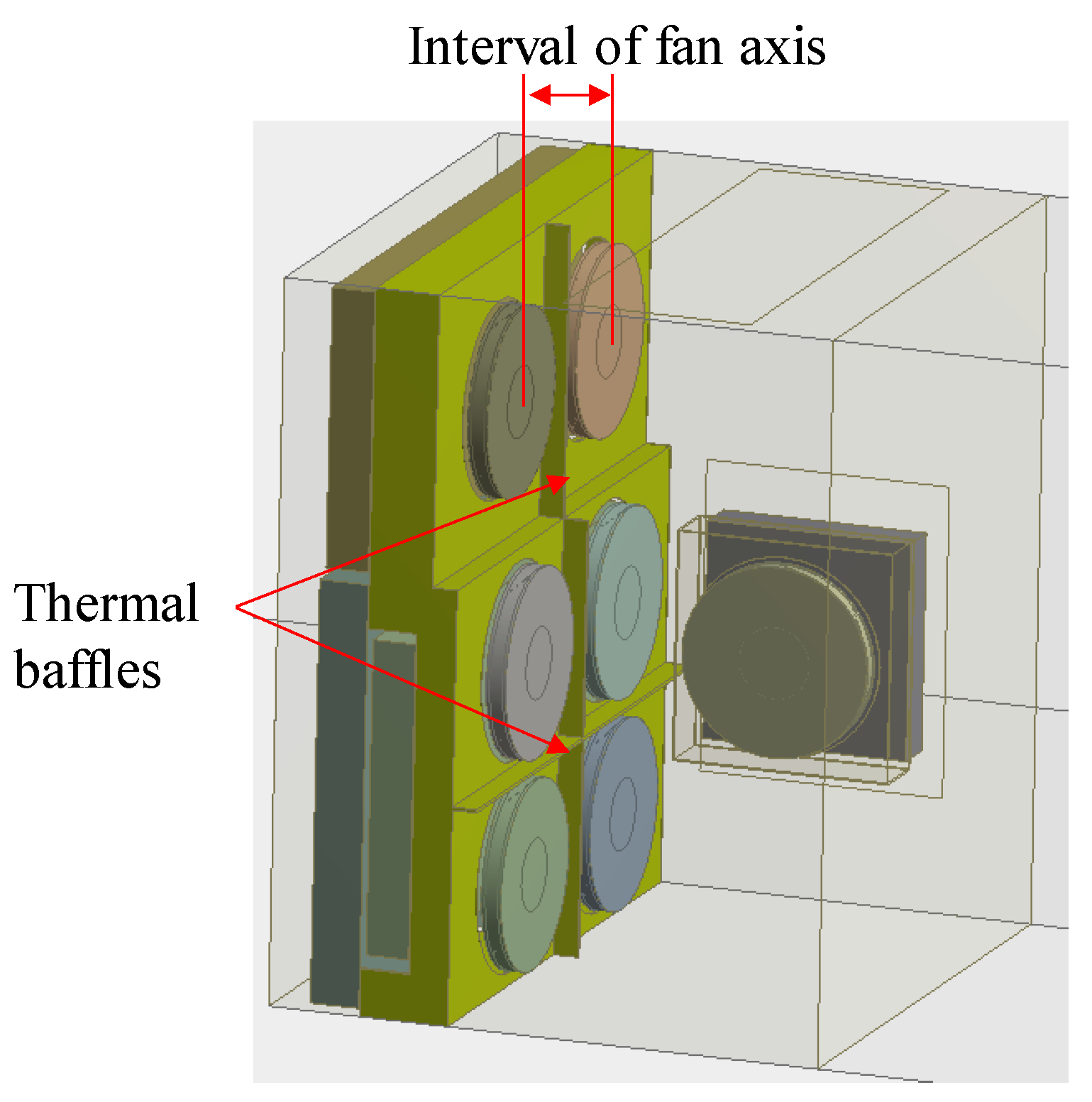
2.1. Fan Design and Matching
2.2. Flowing Channel Design
3. Simulation of the Engine Compartment
3.1. Model Building
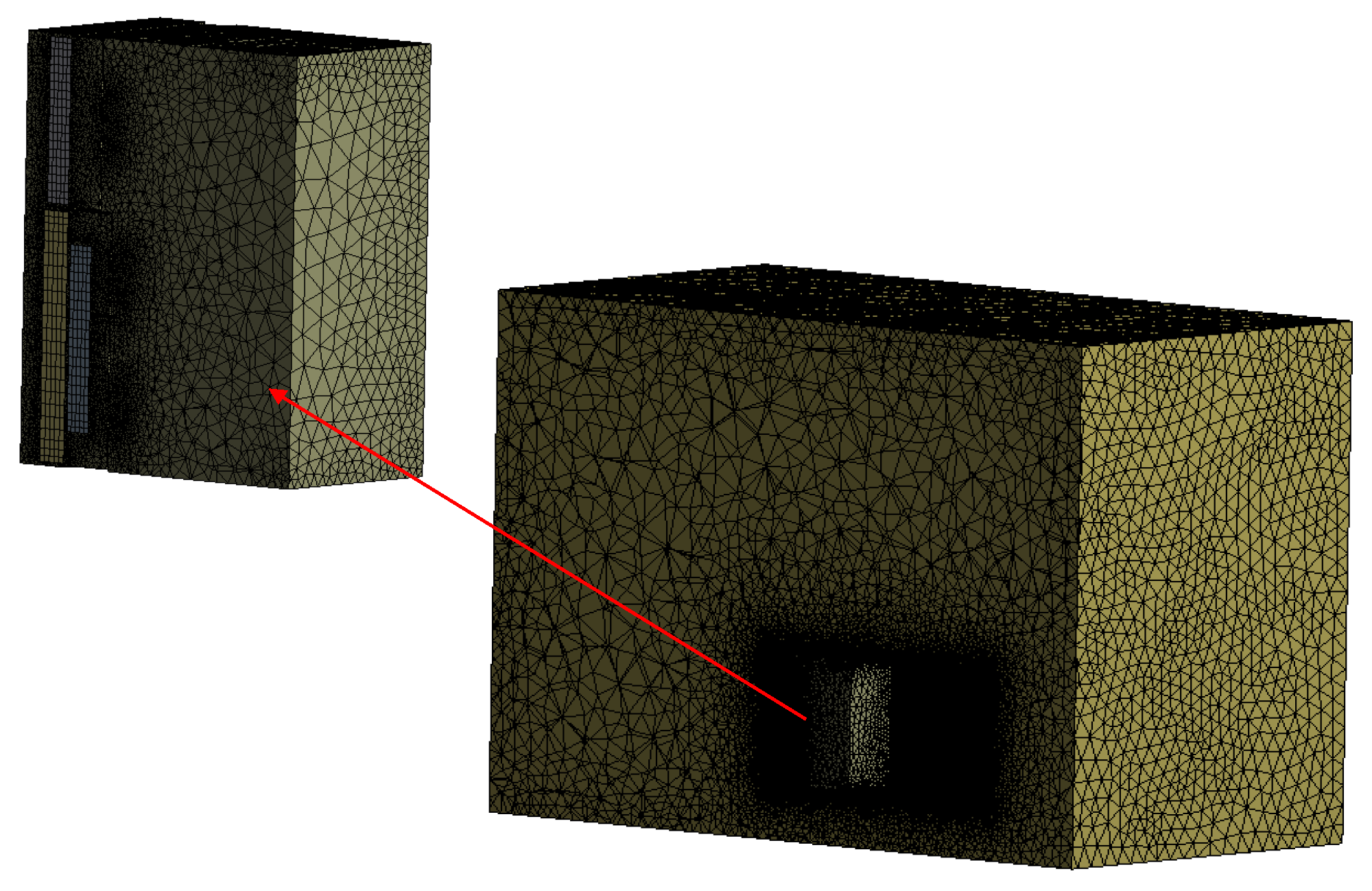
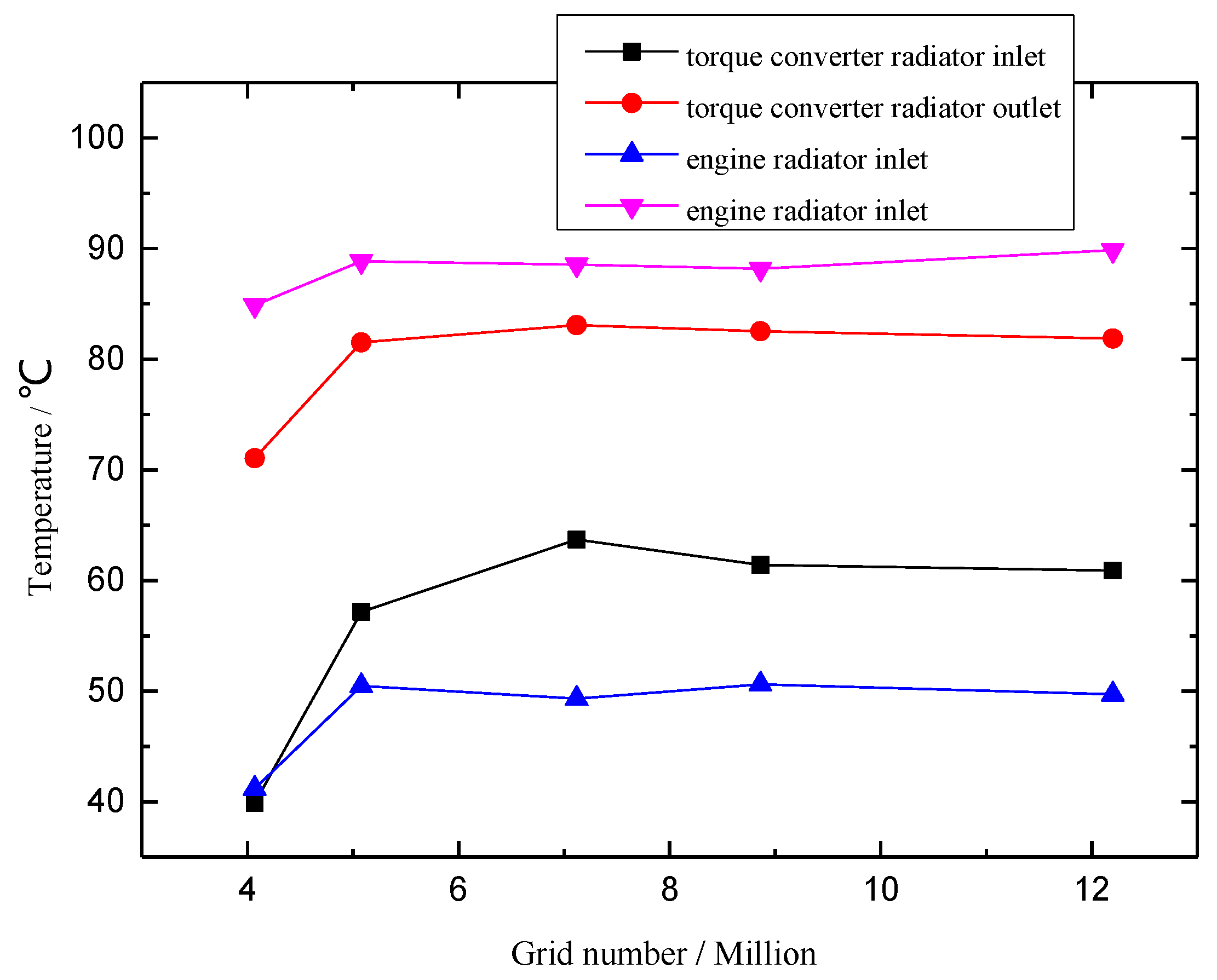
3.2. Mesh Generation
3.3. Boundary Conditions Settlement
4. Experimental Comparison
5. Discussions of Simulation Analyses
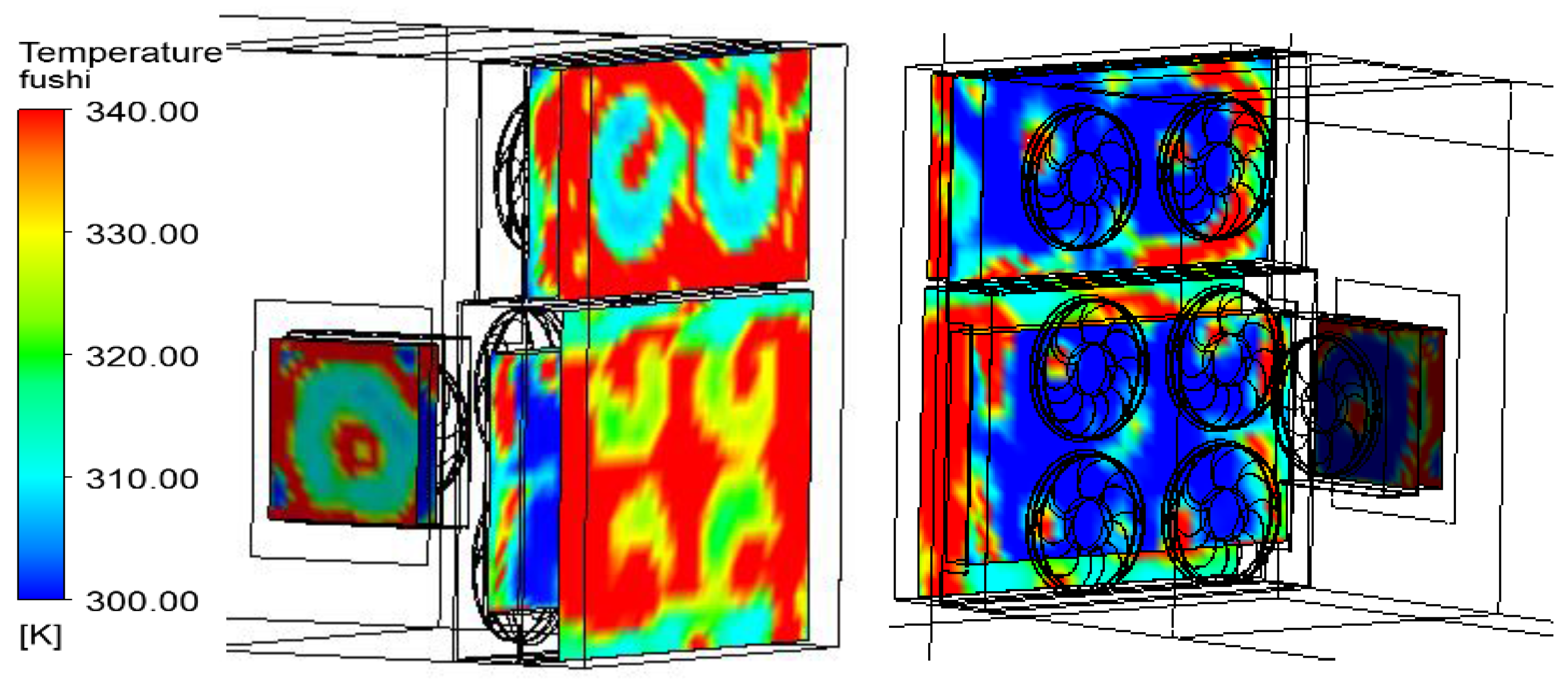
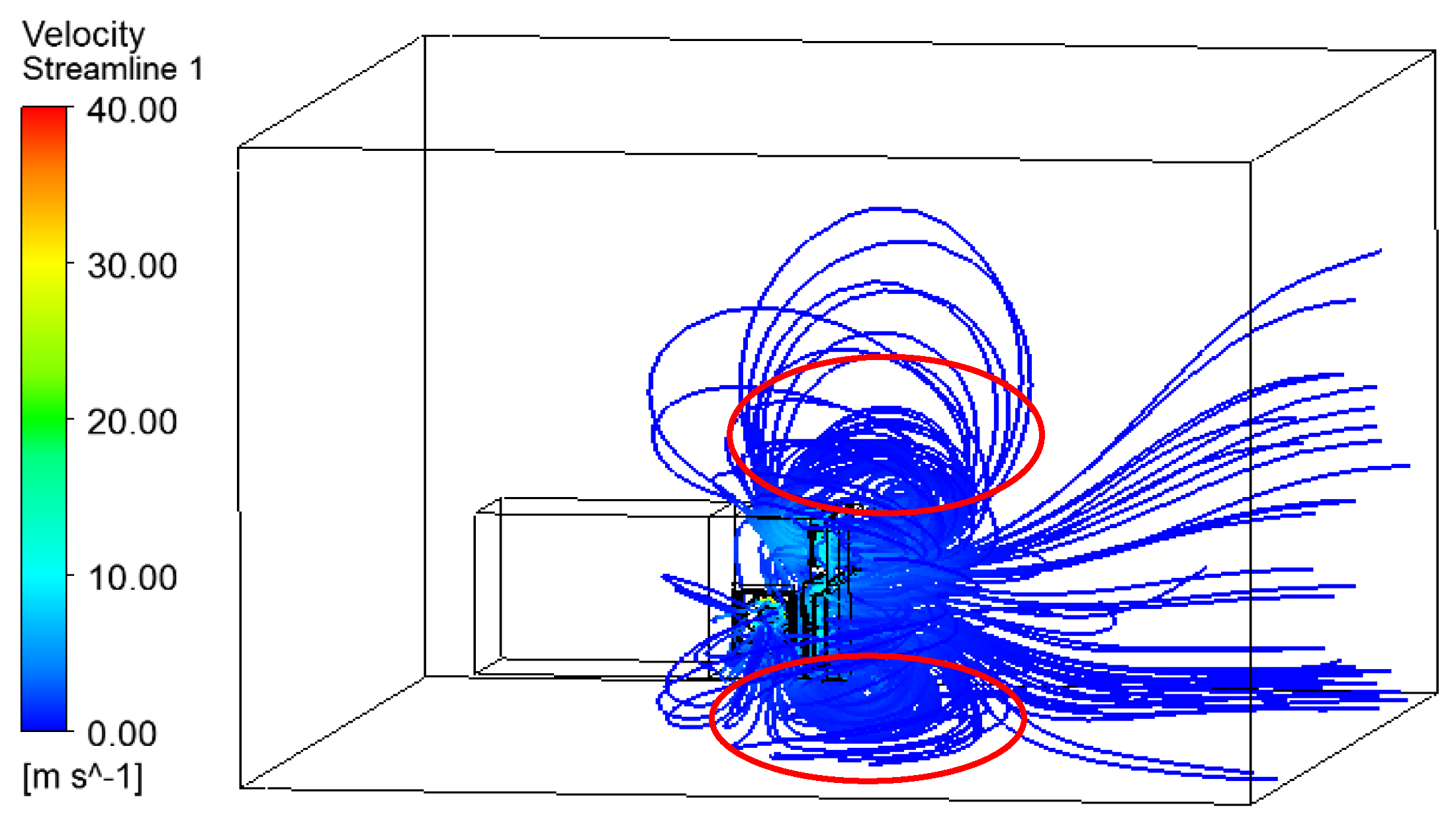
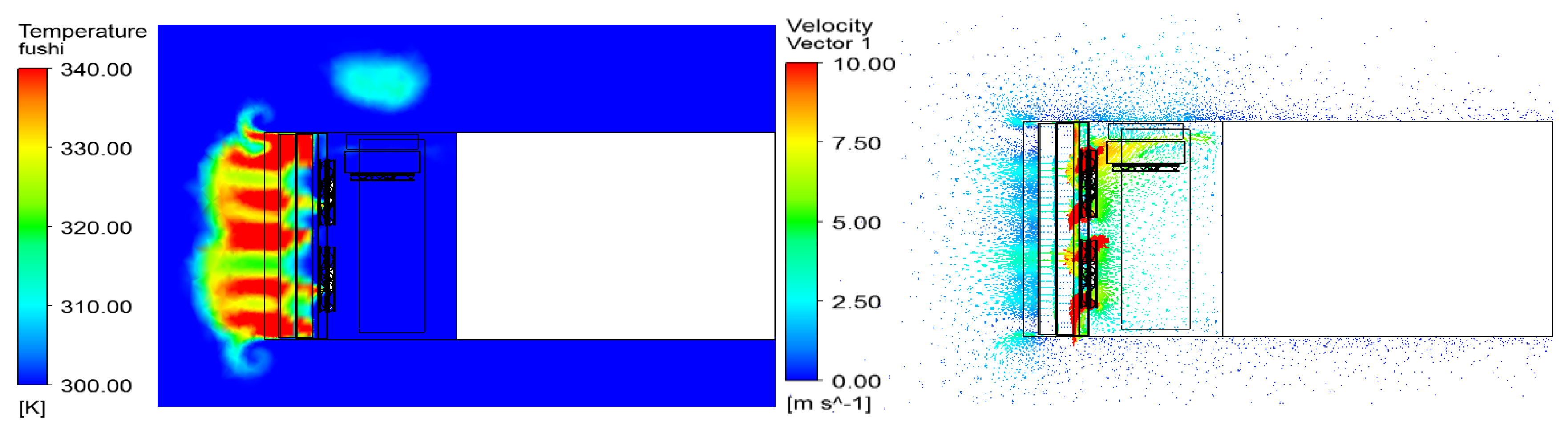
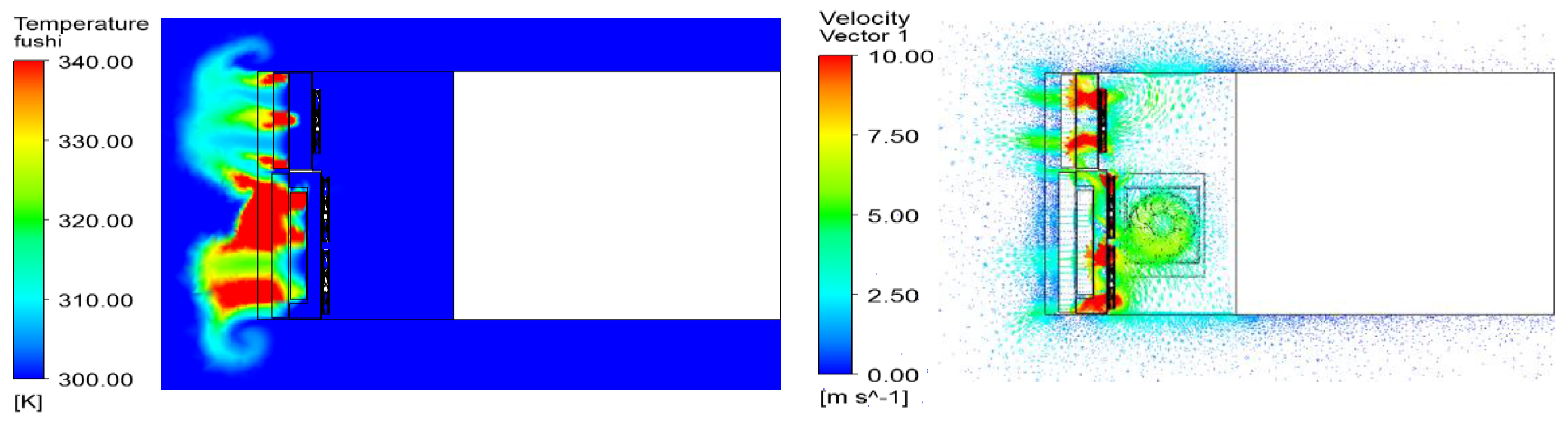
5.1. Temperature and Flow Distributions of the Cooling Regions
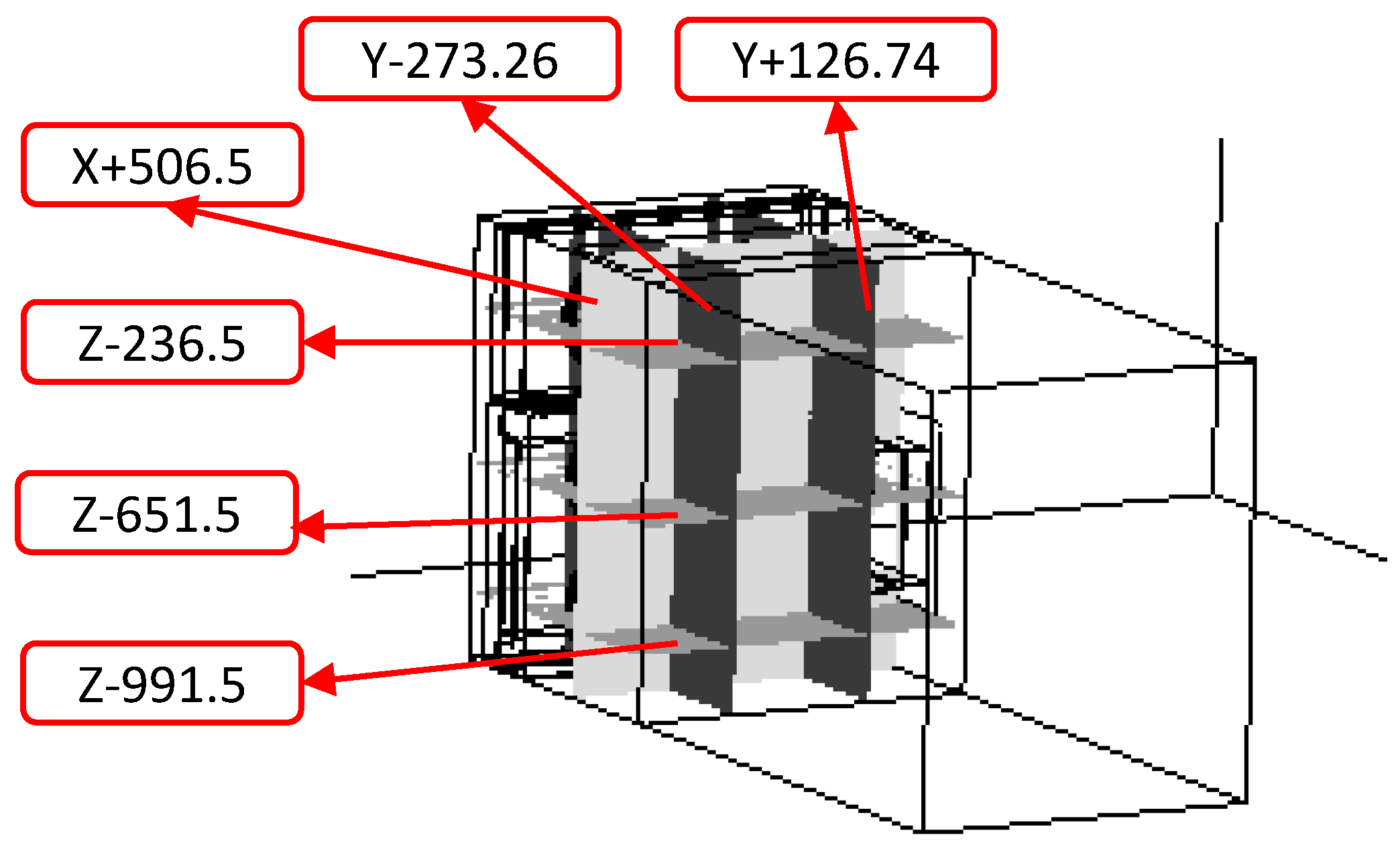
5.2. Thermal Analyses of Six Cross-Sections
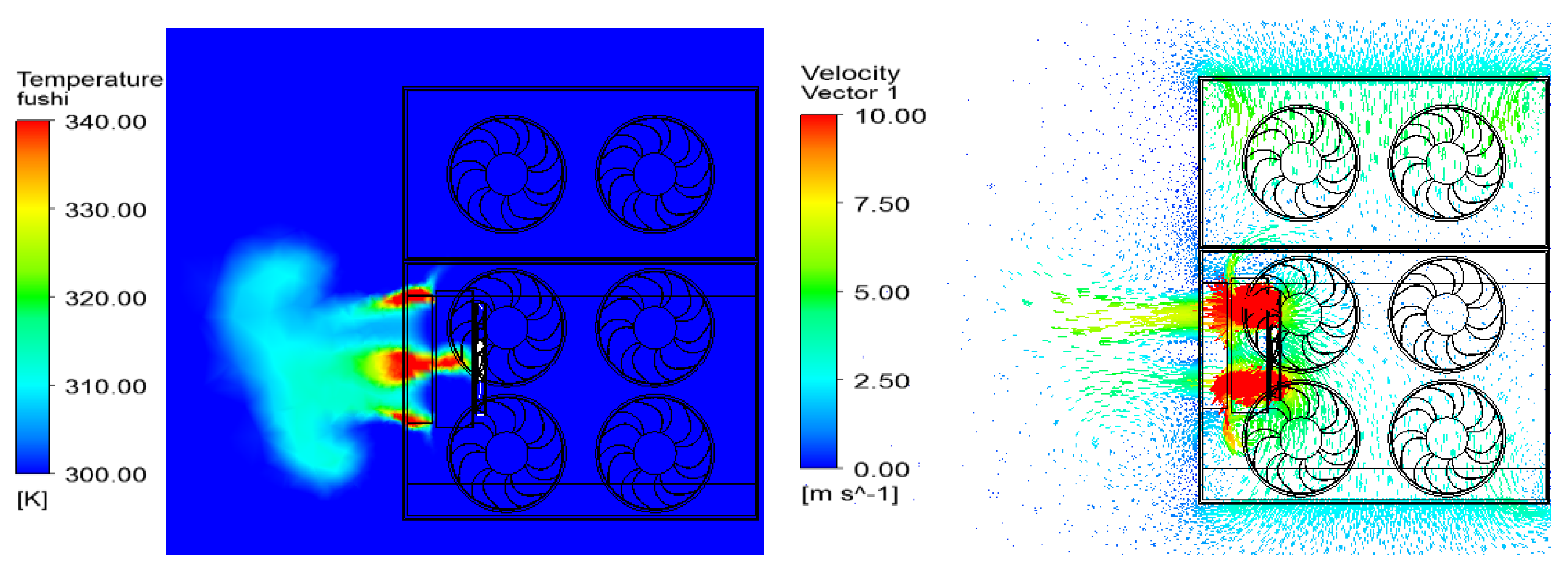
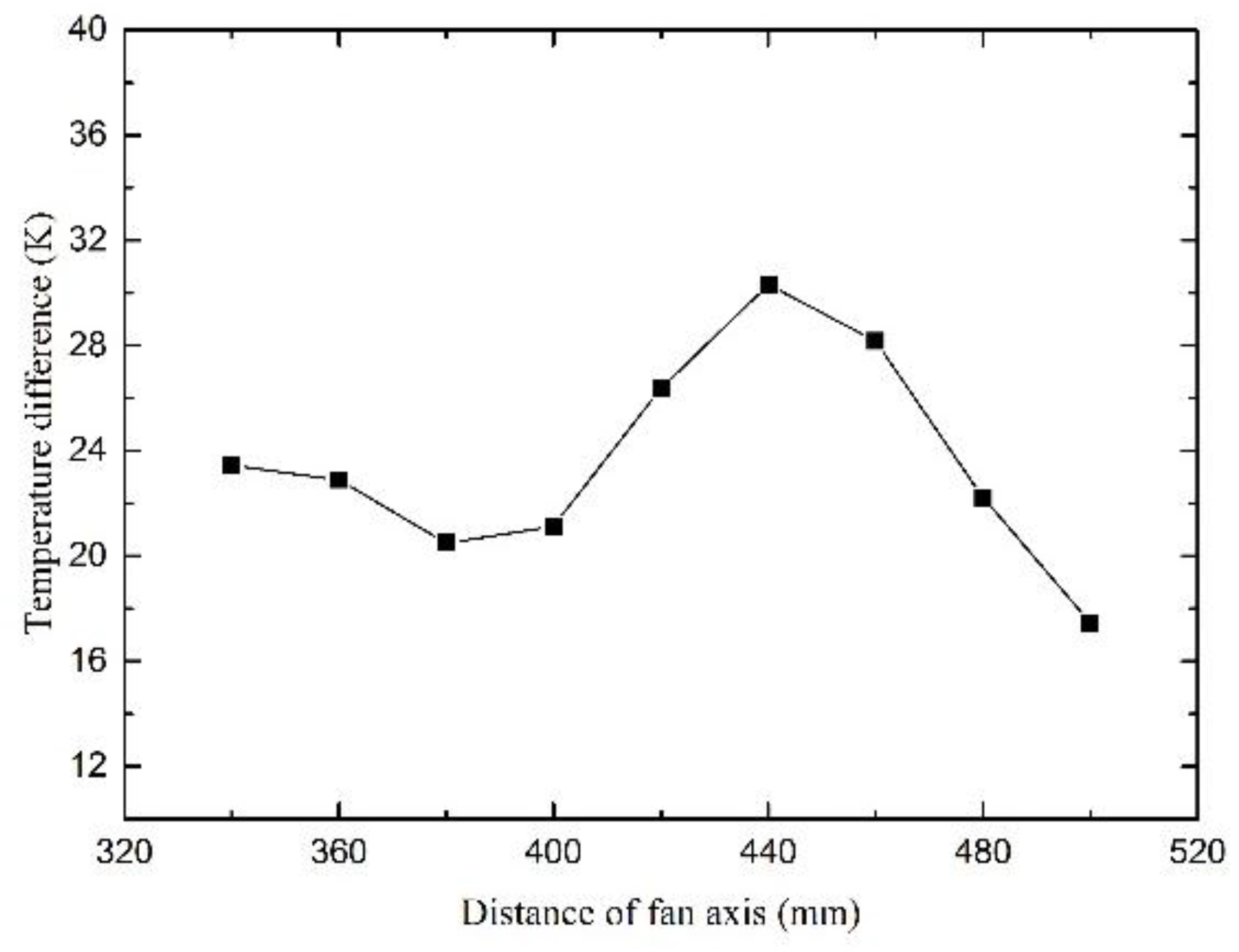
5.3. The Effect of Different Axes Distances on Temperature Distribution
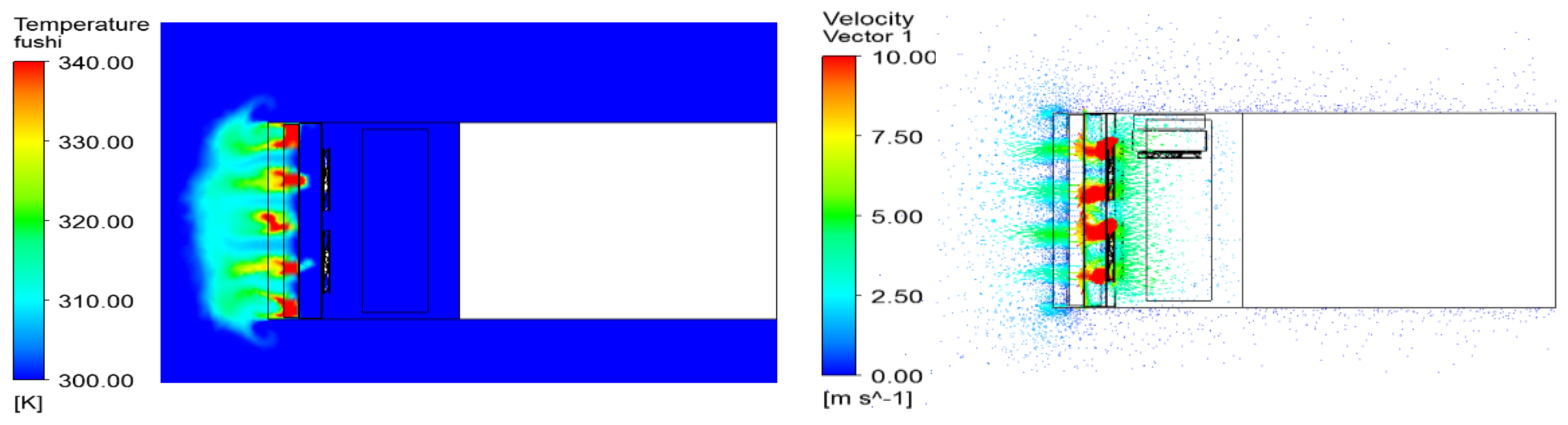
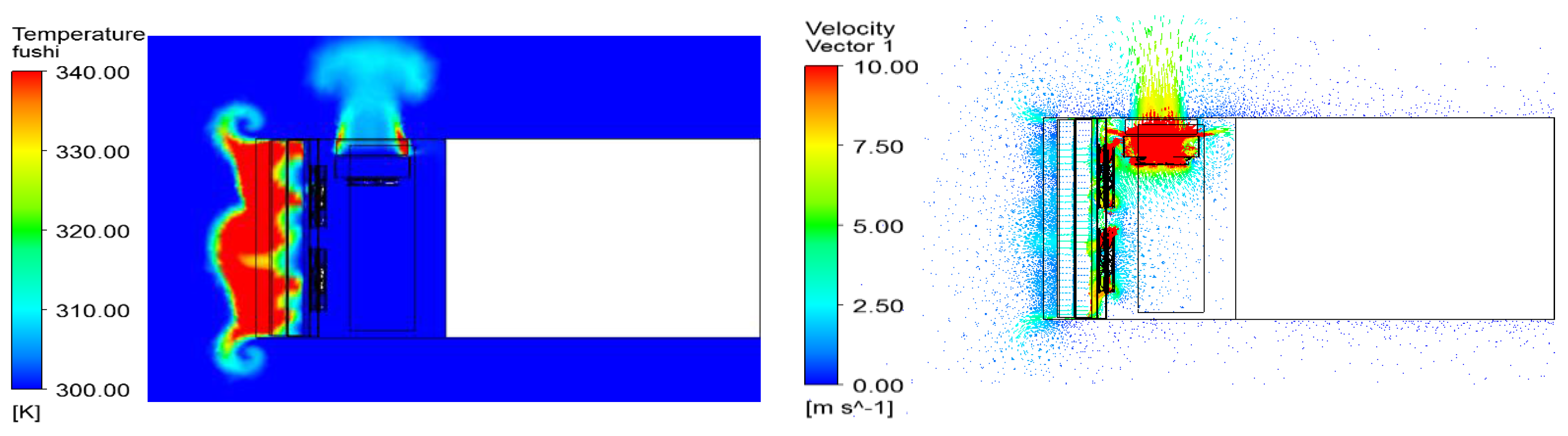
5.4. The Effect of Thermal Baffles on Temperature Distribution
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Li, J. Design Handle Book of Vehicle Cooling System; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1984. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X. Hydraulic excavator of LZ600-1 load type in Komatsu. Constr. Mach. 2014, 11, 73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Caterpillar. Smart steel era, innovation construction productivity, efficiency and security. Constr. Mach. 2016, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mahmound, K.G.; Loibner, E.; Wiesler, B. Simulation-based vehicle thermal management system concept and methodology. SAE Tech. Paper 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.N.; Zhou, W.; Guo, C. Experiment and simulation of the performance of automotive radiator. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2014, 33, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Torregrosa, A. Assessment of the influence of different cooling system configurations on engine warm-up, emissions and fuel consumption. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2008, 9, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, D. Research on the structure optimization of automobile radiators. Energy Res. Inf. 2014, 30, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; He, S. Overview of cooling fan research in construction machinery. Constr. Mach. 2007, 38, 33–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Allen, D.J.; Lasecki, M.P. Thermal management evolution and controlled coolant flow. SAE Tech. Paper 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoung, S.P.; Jong, P.W.; Hyung, S.H. Thermal flow analysis of vehicle engine cooling system. KSME Int. J. 2002, 16, 975–985. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, W.P.; Wsewolod, J.H.; Jeffrey, K. Thermal management for the 21st century—Improved thermal control and fuel economy in an army medium tactical vehicle. SAE Tech. Paper 2005. [CrossRef]
- Tannoury, E.; Khelladi, S.; Demory, B.; Henner, M.; Bakir, F. Influence of blade compactness and segmentation strategy on tonal noise prediction of an automotive engine cooling fan. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Jung, D.; Assanis, D.N. Control strategy of electric coolant pumps for fuel economy improvement. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2005, 6, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.; Kim, H.; Ko, K.; Kim, P.; Yi, K. Integrated wheel loader simulation model for improving performance and energy flow. Autom. Constr. 2015, 58, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, T.; Cross, T. Fan and Heat Exchanger Flow Interactions. SAE Paper 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Double fans with each speed regulation used in tracked vehicle. Veh. Power Technol. 2007, 3, 11–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, T. Energy saving application of electronic fan on Higer Bus. Bus Coach Technol. Res. 2011, 6, 36–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, Y. Research and design of fan driven system in meter combustion motor rail unit. Railw. Haul. Mot. Car 2013, 9, 25–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, G.; Yu, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, W.; Xia, L. A study on the matching of multi-fan cooling module for commercial vehicles. Automot. Eng. 2014, 36, 552–556. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Qian, Y.; Hou, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, E.; Yang, W. Virtual design and analysis with multi-dimension coupling for construction machinery cooling system. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Simulation Analysis and Experiment Research on Heat and Flow of Vehicle Radiator. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Missirlis, D.; Donnerhack, S.; Seite, O.; Albanakis, C.; Sideridis, A. Numerical development of a heat transfer and pressure drop porosity model for a heat exchanger for aero engine applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Numerical analysis for inner flow field in a centrifugal pump under maximum operating conditions. J. Mech. Electr. Eng. 2014, 31, 974–979. [Google Scholar]



| Engine Radiator | Intercooler | Torque Converter Radiator | Hydraulic Oil Radiator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat dissipating capacity (kW) | 75 | 26 | 50 | 26 |
| Cooling medium | Engine coolant | cooling air | oil | Hydraulic oil |
| size | 320 mm diameter, 400 m axis distance, 300 W power | |||
| Volume (m3) | 0.0430 | 0.0278 | 0.0296 | 0.00905 |
| Heat source (kW/m3) | 1745.16 | 897.98 | 1688.62 | 2874.52 |
| porosity | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Resistance coefficient KQ | 35 | 30 | 30 | 25 |
| Re number | 1.38 × 105 | 1.38 × 105 | 1.38 × 105 | 1.84 × 105 |
| Experimental Value | Simulation Value | Relative Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature of torque converter radiator (K) | inlet | 321 | 330 | 2.8% |
| outlet | 356 | 360 | 1.1% | |
| Temperature of engine radiator (K) | inlet | 323 | 318 | −1.5% |
| outlet | 348 | 349 | 0.28% | |
| Relative error = (simulation value − experimental value)/experimental value | ||||
| Temperature Difference of Outlet and Inlet (K) | Performance Improvement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Without baffle (A) | With baffle (B) | ||
| Torque converter radiator | 21.12 | 31.83 | 50.71% |
| Engine radiator | 37.59 | 51.02 | 35.73% |
| Hydraulic oil radiator | 18.71 | 22.5 | 20.26% |
| Performance improvement = (B − A)/A | |||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H.; Huang, H.; Cai, H. Heat Flow Characteristics of a Newly-Designed Cooling System with Multi-Fans and Thermal Baffle in the Wheel Loader. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030231
Liao Y, Zhuo J, Zhang Y, Guan H, Huang H, Cai H. Heat Flow Characteristics of a Newly-Designed Cooling System with Multi-Fans and Thermal Baffle in the Wheel Loader. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(3):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030231
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yidai, Jiwen Zhuo, Yinliang Zhang, Honger Guan, Heting Huang, and Huikun Cai. 2017. "Heat Flow Characteristics of a Newly-Designed Cooling System with Multi-Fans and Thermal Baffle in the Wheel Loader" Applied Sciences 7, no. 3: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030231
APA StyleLiao, Y., Zhuo, J., Zhang, Y., Guan, H., Huang, H., & Cai, H. (2017). Heat Flow Characteristics of a Newly-Designed Cooling System with Multi-Fans and Thermal Baffle in the Wheel Loader. Applied Sciences, 7(3), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030231





