The Effect of Rice Straw Gasification Temperature on the Release and Occurrence Modes of Na and K in a Fluidized Bed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Biomass
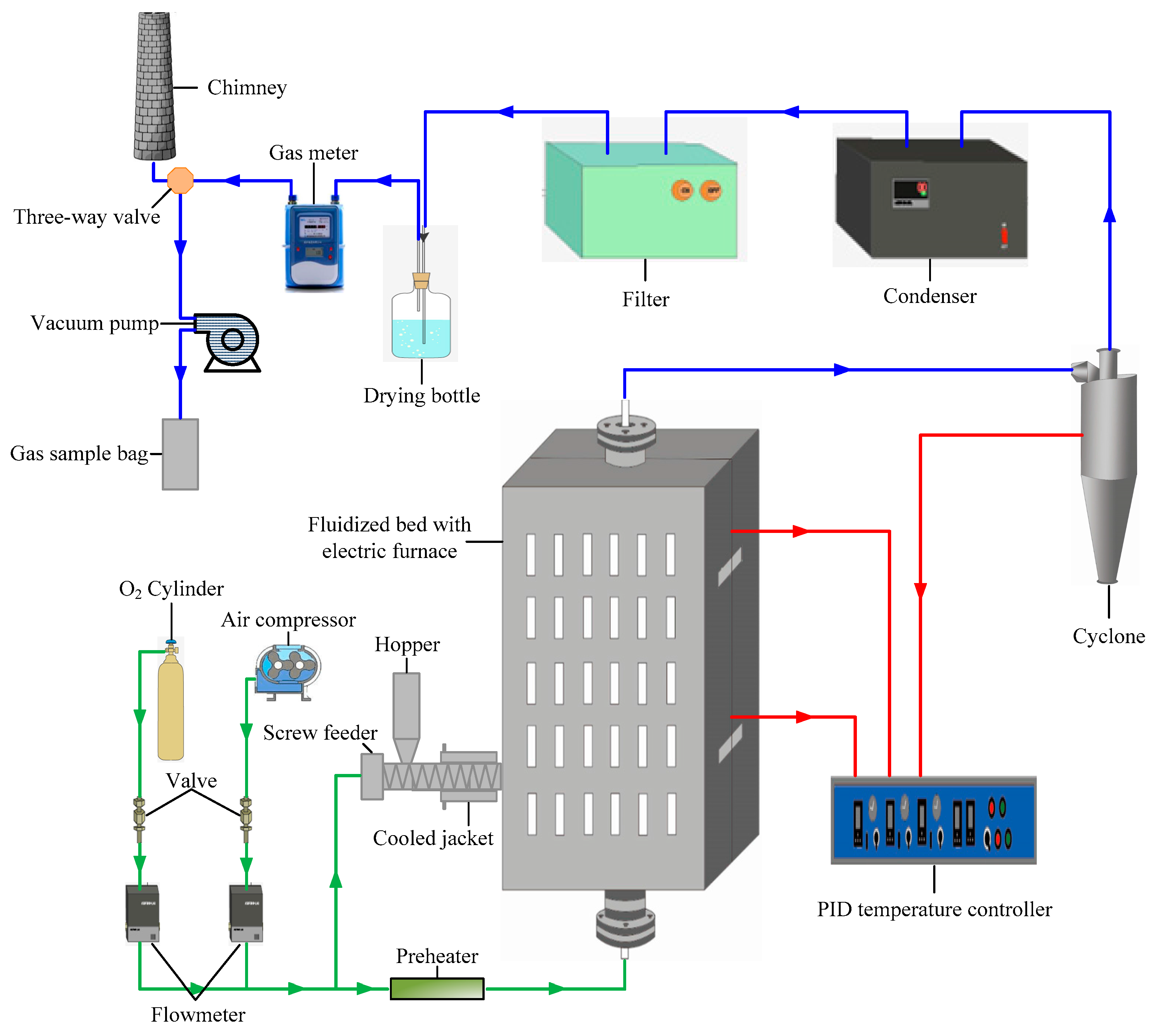
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Alkali Metal Measurement
- 1
- An accurately weighted 1 g of sample was dispersed in 250 mL of ultrapure water at room temperature while being stirred for 10 h. After filtration, leaching (more than three times), and dilution, the dissolved sample was considered to contain the Water-Soluble form of alkali metal (WS), which was then detected by an induced coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-AES) (Perkin Elmer, Boston, MA, USA).
- 2
- The residual solid was dried and further dispersed in ammonium acetate (1 mol/L, 100 mL) under stirring for 5 h, and the mixture was repeatedly filtered and washed.
- 3
- The residual solid was dispersed in hydrochloric acid (1 mol/L, 100 mL) under stirring for 5 h and then repeatedly filtered and washed. The washed solutions from the procedure in steps 2 and 3 were detected by ICP-AES as the Ammonium acetate-Soluble (AA) and Hydrochloric acid-Soluble (HA) forms of alkali metal, respectively.
- 4
- At last, the last residual solid was dried at 105 °C for 24 h. The mixed-acid used for digestion was composed of 1 mL HF, 2.5 mL HCl, 5 mL HNO3, and 0.3 mL H2O2. The residual solid and the reagent were sealed in Teflon ware containing digestion solution for 1 h. Then, 20 mL of saturated boric acid was added to the complex to an excess of F− ion during the following digestion. The digestion solution was detected by ICP-AES to obtain the concentrations of Na and K in their Aluminosilicate Combination-Soluble (AC) forms. Data deviations were considered through five time measurements. All chemical wares made of glass and Teflon for the digestion procedures were immersed in 10% HNO3 solution for at least 24 h and then rinsed with ultrapure water.
2.4. Characteristic Parameters of Gasification and Definition of Alkali Metal Release Rate
2.4.1. Calorific Value of Gas
2.4.2. Gas Production Rate
2.4.3. Gasification Efficiency
2.4.4. Carbon Conversion Rate
2.4.5. Alkali Metal Release Rate
3. Results and Discussion
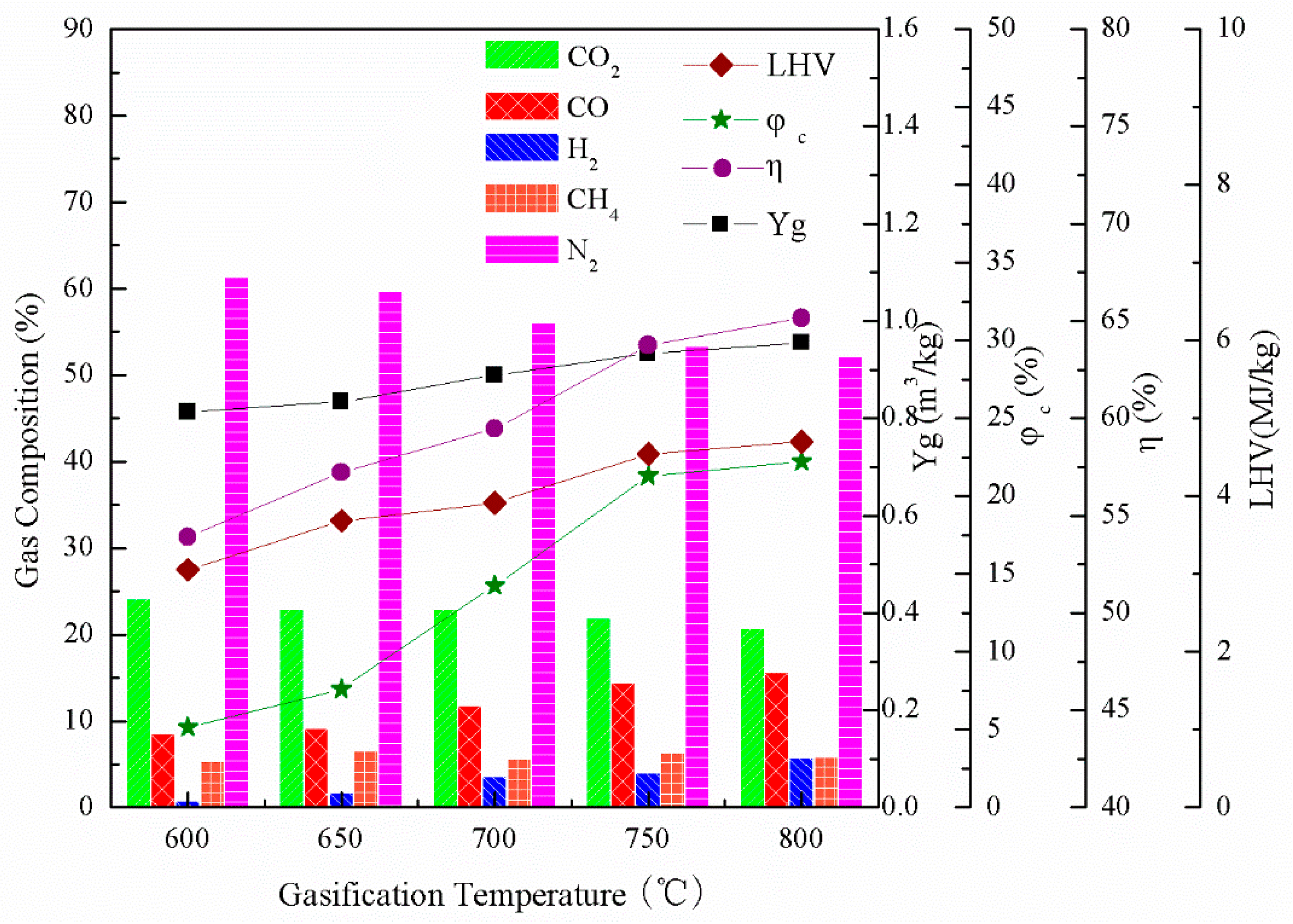
3.1. Effect of Gasification Temperature on Combustible Gas Composition
3.2. Analysis of the Occurrence Forms of Alkali Metals in Rice Straw
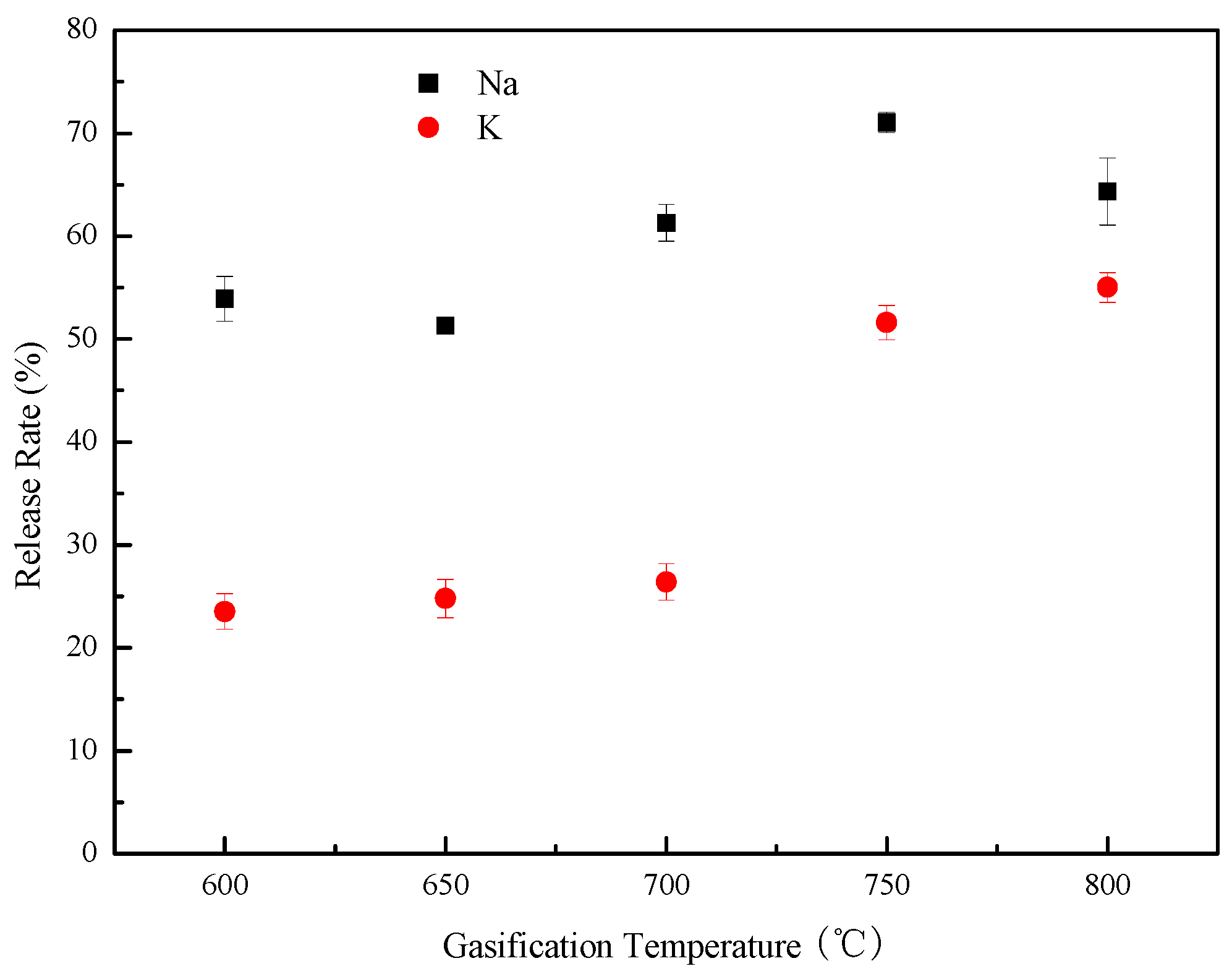
3.3. Influence of Gasification Temperature on the Release Rate of Alkali Metals
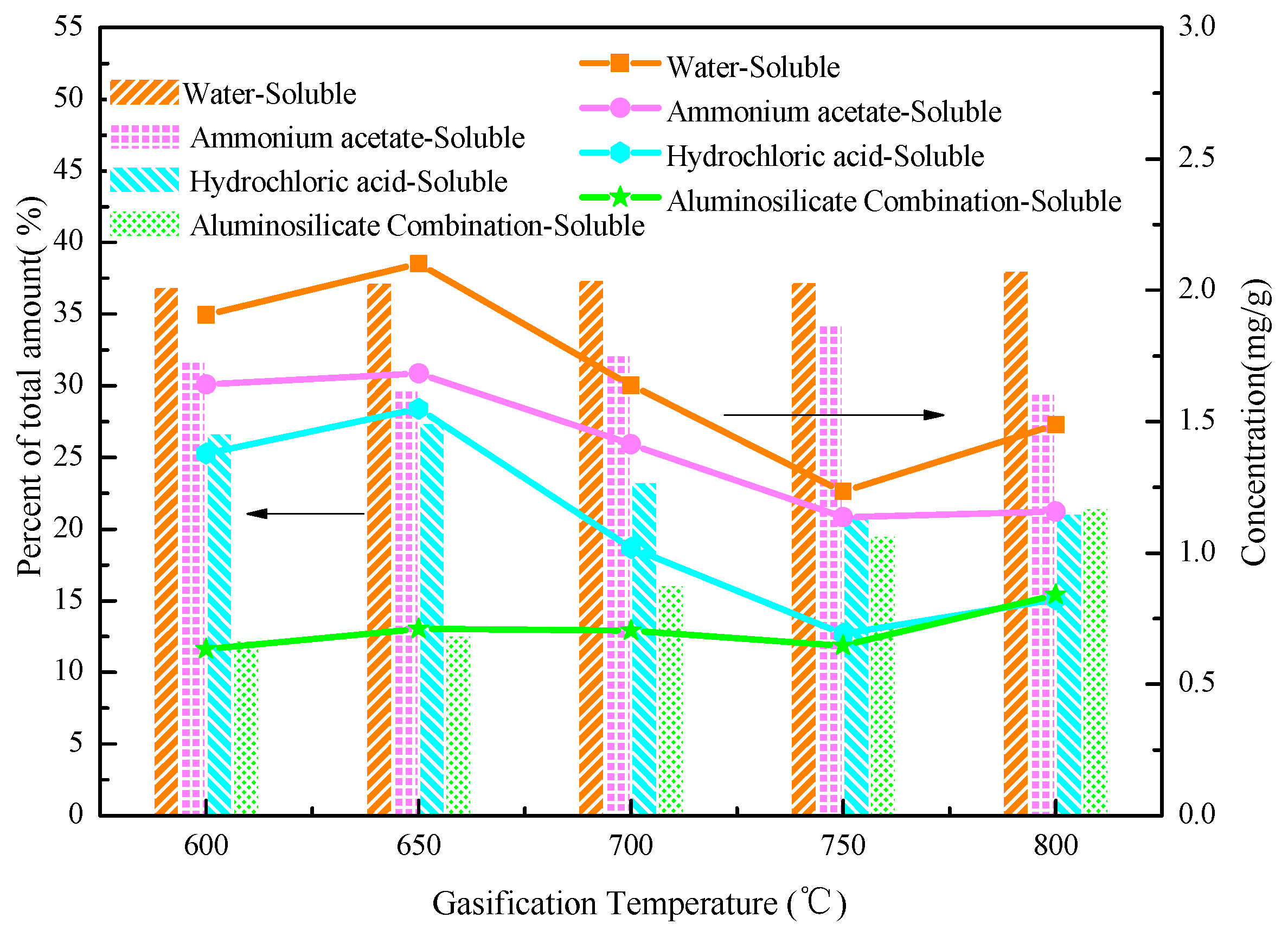
3.4. Influence of Temperature on the Occurrence Form of the Alkali Metal
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidenreich, S.; Foscolo, P.U. New concepts in biomass gasification. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 46, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D. Biomass gasification technology: The state of the art overview. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, S.; Fail, S.; Binder, M.; Rauch, R.; Hofbauer, H.; Molino, A.; Blasi, A.; Musmarra, D. Experimental investigations of hydrogen production from CO catalytic conversion of tar rich syngas by biomass gasification. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, C.J.; Zhang, H.L. Investigation on K and Cl release and migration in micro-spatial distribution during rice straw pyrolysis. Fuel 2016, 167, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Baxter, D.; Andersen, L.K.; Vassileva, C.G. An overview of the chemical composition of biomass. Fuel 2010, 89, 913–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.L.; Miles, T.R.; Miles, T.R., Jr.; Bryers, R.W.; Jenkins, B.M.; Milne, T.; Dayton, D.; Bryers, R.W.; Oden, L.L. The behavior of inorganic material in biomass-fired power boilers: Field and laboratory experiences. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 54, 47–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.A.; Stenholm, M.; Hald, P. Deposition investigation in straw fired boilers. Energy Fuels 1997, 11, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.P.; Larsen, O.H.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K. Deposition and high-temperature corrosion in a 10 MWth strawfired grate. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 54, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbe, C.; Ohman, M.; Lindstrom, E.; Bostrom, D.; Backman, R.; Samuelsson, R.; Burvalll, J. Slagging characteristics during residential combustion of biomass pellets. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3536–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.N.; Jensen, P.A.; Dam-Johansen, K. Transformation and release to the gas phase of Cl, K, and S during combustion of annual biomass. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, M.; Pommer, L.; Nordin, A. Bed agglomeration characteristics and mechanisms during gasification and combustion of biomass fuels. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J. Release characteristics of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during biomass pyrolysis and steam gasification process. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 116, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, P.A.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K. Experimental investigation of the transformation and release to gas phase of potassium and chlorine during straw pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddawi, A.; Jone, J.M.; Williams, A. Influence of alkali metals on the kinetics of the thermal decomposition of biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimple, M.Q.; Wu, H.W.; Hayashi, J. Volatiliation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part IV. Catalytic effects of NaCl and ion-exchangeable Na in coal on char reactivity. Fuel 2003, 82, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Wigmans, T.; Haringa, H. Nature, activity and stability of active sites during alkali metal carbonate-catalysed gasification reaction of coal char. Fuel 1983, 62, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Dai, Z.G.; Yu, G.S.; Gong, X. Effects of alkalimetal and ash on crystallite structure of coal char during pyrolysis and on gasification reactivity. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2010, 24, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraoui, Z.; Dupont, C.; Jeguirim, M.; Limousy, L.; Gadiou, R. CO2 gasification of woody biomass chars: The influence of K and Si on char reactivity. C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraoui, Z.; Jeguirim, M.; Guizani, C.; Limousy, L.; Dupont, C.; Gadiou, R. Thermogravimetric study on the influence of structural, textural and chemical properties of biomass chars on CO2 gasification reactivity. Energy 2015, 88, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joakim, M.; Johansen, M.A.; Kari, P.; Raili, T.; Helge, E.; Jon, G.J.; Flemming, J.F.; Peter, G. Release of K, Cl, and S during combustion and co-combustion with wood of high-chlorine biomass in bench and pilot scale fuel beds. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Keown, D.M.; Favas, G.; Hayashi, J.I.; Li, C.Z. Volatilisation of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis of biomass: Differences between sugar cane bagasse and cane trash. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooya, L.; Zainal, A.Z.; Abdul, R.M.; Maedeh, M. CO2 gasification reactivity of biomass char: Catalytic influence of alkali, alkaline earth and transition metal salts. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Narendra, S.; Sushil, A.; Mario, R.E.; Wang, Z.H.; Ryan, B. Southern pines char gasification with CO2—Kinetics and effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 150, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jeguirim, M.; Elmay, Y.; Limousy, L.; Lajili, M.; Said, R. Devolatilization behavior and pyrolysis kinetics of potential Tunisian biomass fuels. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2014, 33, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.Z.; Xu, M.H.; Liu, X.W.; Zhan, Z.; Li, Z.; Yao, H. Effect of cellulose, lignin, alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on biomass pyrolysis and gasif1cation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musmarra, D. Influence of particle size and density on the jet penetration length in gas fluidized beds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2612–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Xue, L.; Lu, Q.; Dong, C. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth metals on N-containing species release during rice straw pyrolysis. Energies 2015, 8, 13021–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vázquez, M.P.; García, R.; Pevida, C.; Rubiera, F. Optimization of a bubbling fluidized bed plant for low-temperature gasification of biomass. Energies 2017, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James R., A.M.; Yuan, W.; Boyette, M.D. The effect of biomass physical properties on top-lit updraft gasification of woodchips. Energies 2016, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošiūnas, A.; Chouchène, A.; Valatkevičius, P.; Gimžauskaitė, D.; Aikas, M.; Uscila, R.; Ghorbel, M.; Jeguirim, M. The potential of thermal plasma gasification of olive pomace charcoal. Energies 2017, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Niu, W.S.; Zhang, D.L. Biomass Thermochemical Conversion Technology; Chem. Ind. Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Abu El-Rub, Z.; Bramer, E.A.; Brem, G. Experimental comparison of biomass chars with other catalysts for tar reduction. Fuel 2008, 87, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, R.A.; Yusup, S.; Azlina, W.; Nehzati, S.; Tavasoli, A. Investigation on syngas production via biomass conversion through the integration of pyrolysis and air–steam gasification processes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Yang, S.; Song, W.; Qi, X. Release and transformation behaviors of sodium during combustion of high alkali residual carbon. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 122, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, O.; Wakabayashi, T.; Tasska, K.; Fushimi, C.; Furusawa, T.; Kuchonthara, P.; Tsutsumi, A. Release behavior of tar and alkali and alkaline earth metals during biomass steam gasification. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 4235–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.G.; Pettersson, J.B.C.; Padban, N.; Bjerle, I. Alkali metal emission from filter ash and fluidized bed material from PFB gasification of biomass. Energy Fuels 1998, 12, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkelin, J.; Skrifvars, B.J.; Zevenhoven, M.; HolMbom, B.; Hupa, M. Chemical forms of ash-forming elements in woody biomass fuels. Fuel 2010, 89, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K. The Migration Patterns of Chlorine and Alkali Metals (K and Na) in the Biomass Combustion; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yao, D.D.; Qian, K.Z.; Yang, H.P.; Wang, X.H. Releasing behavior of alkali and alkaline earth metals during biomass gasification. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2014, 42, 792–798. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, C.A.; Yan, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Che, D. Release and transformation of sodium during combustion of Zhundong coals. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.L.; Yan, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, C.D.; Pan, W.P. The varying characterization of Alkali Metals (Na, K) from coal during the initial stage of coal combustion. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 2957–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, C.; Pang, Y.Y.; Li, C.Z. Effects of heating rate and ion-exchange cations on the pyrolysis yields from a Victorian brown coal. Energy Fuels 1999, 13, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyn, D.M.; HayashI, J.I.; Li, C. Volatilisation of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the gasification of a Victorian brown coal in CO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.J.; Tang, Y.L.; Feng, M.X.; Luo, Z.Y.; Ceng, K. Experimental study on alkali emission during rice straw pyrolysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2005, 39, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar]

| Proximate Analysis (wt %, daf) | Elemental Analysis (wt %, ad) | Weight Ratios | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Vdaf | FCd | Ad | Cdaf | Hdaf | Ndaf | Odaf | Sd | H/C ratio | O/C ratio |
| 3.58 | 76.28 | 14.8 | 5.34 | 51.67 | 6.21 | 1.44 | 40.45 | 0.2 | 0.120 | 0.783 |
| Content | Na2O | K2O | SO3 | MnO | Al2O3 | P2O5 | CaO | MgO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 2.43 | 7.52 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 1.20 | 4.02 | 2.44 | 3.18 | 73.65 | 0.16 | 4.68 |
| Operating Parameter | Conditions | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding rate of rice straw | 1.11 | kg/h |
| Bed temperature | 600~800 | °C |
| Superficial gas velocity a | 0.7 | m3/h |
| Bed material | alumina | – |
| Particle size of bed material | 0.18~0.25 | mm |
| Apparent density of bed material | 2965 | kg/m3 |
| Bulk density of bed material | 1422 | kg/m3 |
| Minimum fluidization velocity of bed material a | 0.039 | m/s |
| Content | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | P2O5 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 14.18 | 79.41 | 0.32 | 0.02 | 2.41 | 3.29 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Alkali Metals | Water-Soluble | Ammonium Acetate-Soluble | Hydrochloric Acid-Soluble | Aluminosilicate Combination-Soluble | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na (mg/g low-temperature ash) | 6.34 | 3.33 | 1.14 | 0.53 | 11.34 |
| Proportion of total Na (%) | 55.91 | 29.35 | 10.07 | 4.65 | 100 |
| K (mg/g low-temperature ash) | 49.96 | 25.05 | 7.38 | 1.47 | 83.86 |
| Proportion of total K (%) | 69.64 | 20.73 | 7.87 | 1.76 | 100 |
| Gasification Temperature (°C) | WS (mg/g) | AA (mg/g) | HA (mg/g) | AC (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 1.91 | 1.44 | 1.18 | 0.63 |
| 650 | 2.10 | 1.48 | 1.35 | 0.71 |
| 700 | 1.64 | 1.21 | 0.82 | 0.70 |
| 750 | 1.23 | 0.94 | 0.49 | 0.65 |
| 800 | 1.49 | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.84 |
| Gasification Temperature (°C) | WS (mg/g) | AA (mg/g) | HA (mg/g) | AC (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 57.44 | 2.26 | 1.14 | 3.49 |
| 650 | 54.47 | 1.75 | 0.91 | 5.77 |
| 700 | 47.71 | 2.28 | 1.14 | 10.93 |
| 750 | 4.77 | 2.29 | 1.33 | 32.12 |
| 800 | 7.09 | 2.29 | 1.51 | 26.09 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Cao, J.; Jin, B. The Effect of Rice Straw Gasification Temperature on the Release and Occurrence Modes of Na and K in a Fluidized Bed. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121207
Chen T, Cao J, Jin B. The Effect of Rice Straw Gasification Temperature on the Release and Occurrence Modes of Na and K in a Fluidized Bed. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(12):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121207
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tianyu, Jun Cao, and Baosheng Jin. 2017. "The Effect of Rice Straw Gasification Temperature on the Release and Occurrence Modes of Na and K in a Fluidized Bed" Applied Sciences 7, no. 12: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121207
APA StyleChen, T., Cao, J., & Jin, B. (2017). The Effect of Rice Straw Gasification Temperature on the Release and Occurrence Modes of Na and K in a Fluidized Bed. Applied Sciences, 7(12), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121207




