Abstract
A new series of benzylaminochalcone derivatives with different substituents on ring B were synthesized and evaluated as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. The study is aimed at identification of novel benzylaminochalcones capable of blocking acetylcholinesterase activity for further development of an approach to Alzheimer’s disease treatment. These compounds were produced in moderate to good yields via Claisen-Schmidt condensation and subjected to an in vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibition assay, using Ellman’s method. The in silico docking procedure was also employed to identify molecular interactions between the chalcone compounds and the enzyme. Compounds with ring B bearing pyridin-4-yl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl and 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl moieties were discovered to exhibit significant inhibitory activities against acetylcholinesterase, with IC50 values ranging from 23 to 39 µM. The molecular modeling studies are consistent with the hypothesis that benzylaminochalcones could exert their effects as dual-binding-site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which might simultaneously enhance cholinergic neurotransmission and inhibit β-amyloid aggregation through binding to both catalytic and peripheral sites of the enzyme. These derivatives could be further developed to provide novel leads for the discovery of new anti-Alzheimer drugs in the future.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common cause of dementia in the elderly, is affecting millions of people worldwide. The ailment is characterized by a complex neurodegenerative process occurring in the central nervous system which leads to progressive cognitive decline and memory loss [1,2]. The etiology of AD is not fully known, although factors including the low levels of acetylcholine (ACh), accumulation of abnormal proteins namely β-amyloid (βA) and τ-protein, homeostasis irregularity of biometals, and oxidative stress are considered to play significant roles in the pathophysiology of AD [3,4].
At the present, clinical therapy for AD patients is primarily established upon the cholinergic hypothesis which suggests that the decline of the ACh level might lead to cognitive and memory deficits, and drugs with the ability of inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (AChE) would control symptoms of the disease [5,6]. AChE inhibitors including rivastigmine, donepezil and galantamine are given top priorities in the therapeutic treatment of AD. Mediated through the same mechanism, i.e., elevating the levels and duration of action of acetylcholine at synaptic clefts, these agents, however, only allow for the alleviation of the symptomatology in most patients and differ greatly in pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles as well as result in adverse effects [7]. According to the crystallographic structural studies, AChE has a narrow 20 Å gorge with two binding sites: the catalytic active site (CAS) at the bottom of the structure and the peripheral anionic site (PAS) near the entrance of the gorge [8,9,10]. Consequently, inhibitors that bind to either one or two of the sites could inhibit the AChE. In addition, recent studies have revealed that AChE could increase the formation of amyloid fibrils by interacting with the residues in the PAS of AChE, generating a more stable and toxic AChE-βA complex than single βA peptides alone [11]. Moreover, the dual binding inhibitors, which might simultaneously elevate the level of ACh and inhibit β-amyloid aggregation via binding to both the catalytic and peripheral sites of the enzyme, have become more promising in AD treatment [12,13,14].
Flavonoids, a group of naturalcompounds with low molecular weight and low toxicity have increasingly attracted the interest of medicinal chemists due to their diversebioactivities. They express a variety of pharmacological properties, such as AchE-inhibitory [15,16], antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, vasodilator activities, as well as the inhibition of βA fibril formation [17,18,19]. Flavonoids also exhibit especially low toxicity, so they have been considered as promising anti-AD compounds. Of the synthetic flavonoids, chalcone derivatives with either sulfonamide or amino moieties at position 4’, represent AchE-inhibitory and βA anti-aggregating effects at the nanomolar concentrations [20].
In this paper we describe the synthesis, pharmacological evaluation and molecular modeling of a series of new benzylaminochalcone derivatives as AChE inhibitors. The moiety of 2-hydroxybenzylamino was integrated into chalcone structures in the hope of enhancing hydrophobicity and promoting interactions with the active site of AChE via hydrogen bonds generated by hydroxyl groups. Phenyls in ring B are modified and replaced by substituted pyridinyl, furanyl and thiophenyl (Figure 1) with the aim of providing the molecules with the ability to bind at the AChE peripheral site and resulting in stronger AChE inhibition. Finally, molecular interactions between inhibitors and AChE revealed by molecular modeling studies would explain the results of an in vitro bioassay and help gain insight into the binding mode and structure-activity relationships of the novel compounds.
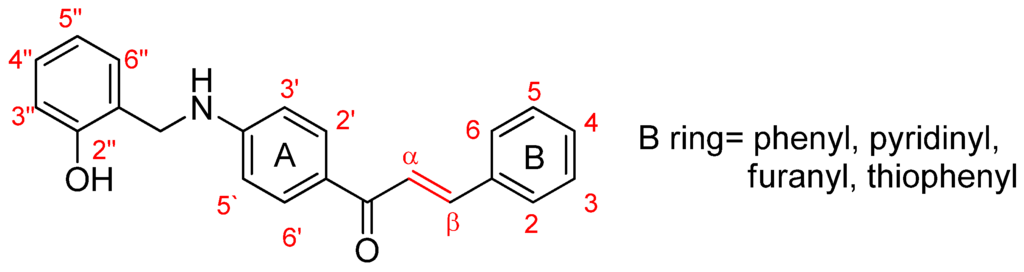
Figure 1.
The general structure of benzylaminochalcones.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
All starting materials such as benzaldehyde, 2-chlorobenzaldehyde, 4-chlorobenzaldehyde, 4-nitrobenzaldehyde were purchased from Acros Organics BVBA—Thermo Fisher Scientific, Geel Belgium (Geel, Antwerp, Belgium); 2,3-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, 2,4-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde, 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, furfural and galantamine were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich Fine Chemicals (St. Louis, MO, USA). The chemicals were used without further purification. The other starting material named 1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)ethanone was obtained from Pharmaceutical Chemistry’s Laboratory, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam.
2.2. Instrumentation
Melting points were determined on open capillary tubes and are uncorrected using Gallenkamp melting point apparatus (Sanyo Gallenkamp, Southborough, UK). UV spectra were measured on a Hitachi U-2010 instrument (Hitachi High-Technologies, Tokyo, Japan). 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance II spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) at 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively. Chemical shifts are reported in parts per million (ppm) downfield relative to tetramethylsilane as an internal standard. Peak splitting patterns are abbreviated as m (multiplet), s (singlet), bs (broad singlet), d (doublet), bd (broad doublet), t (triplet) and dd (doublet of doublets). MS spectra were recorded on an Agilent LC-MS 1200 Series instrument with MS detector of micrOTOF-QII Bruker (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.3. General Procedures for the Preparation of Compounds A1–A10
Ten benzylaminochalcones derivatives (A1–A10) with different substituents on ring B were prepared as shown in Scheme 1 [21,22,23,24,25]. The 1-(4-((2-Hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)-ethanone 1 and benzaldehyde derivatives (in proportion of 1:1) were dissolved in methanol with stirring. Potassium hydroxide was then added in portion that is twice as much as that of compound 1. Resulting solution was stirred at the ambient temperature or cooled with ice as needed. Subsequently, the chemical reaction was monitored by a thin layer chromatography. Final mixture was cooled and neutralized using concentrated HCl to pH ≈ 4–6. The resulting yellow solid was filtered, washed with cold water, and recrystallized from methanol or mixture of methanol and dichloromethane (1:1) to form the product.
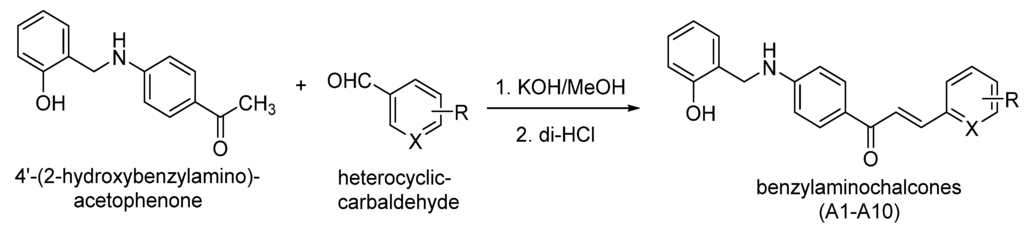
Scheme 1.
The synthesis of benzylaminochalcones.
2.4. In Vitro Inhibition Assay on AChE
AChE-inhibitory activities of benzylaminochalcones derivatives A1–A10 were determined by the Ellman’s method [26], using galantamine as a reference compound. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE, E.C. 3.1.1.7, from electric eel), 5,5‘-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB), acetyl-thiocholine iodide (ATCI), galantamine were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Tested compounds were dissolved in a minimum volume of 10% methanol in Tris buffer pH 8 to provide a final concentration range: 120 μM; 60 μM; 30 μM; 15 μM; 7.5 μM.
All the assays were performed in 96-well microtiter plates in the same condition for benzylaminochalcone and galantamine. Briefly, 30 µL of 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer pH 8, 30 µL of sample (several quantities of samples, all dissolved in methanol, in order to calculate IC50 values) and 30 µL acetylcholinesterase solution containing 0.54 U/mL were mixed in a well of 96 plate and allowed to incubate for 15 min at 25 °C. Subsequently, 30 µL of a solution of ATCI (15 mM, dissolved in water) and 150 µL of 3 mM Ellmen's reagent (DTNB) were added. The absorbance at 405 nm was read during the first 5 min of the reaction. A control reaction which was considered to have 100% activity was carried out using the same volume of methanol/water instead of tested solutions. All samples were assayed in triplicate.
Percentage (%) of AChE inhibition is calculated based on the absorbance value as following:
where A0E is the absorbance value of the control blank sample plus enzyme; A0 is the absorbance value of the blank sample; At is the absorbance value of the test (chalcone) sample and A0t is the absorbance value of the blank test sample. The compositions of sample solutions were prepared as follows (Table 1).

Table 1.
Compositions of sample solutions.
Linear equation indicating the correlation between the common logarithm of the compound concentration (µM) and the percentage of AChE inhibition (%) was built, and from which the IC50 values (concentration that inhibits 50% AChE activity) of studied benzylaminochalcones were extrapolated.
2.5. Molecular Modeling Study
In an attempt to propose a binding mode for benzylaminochalcones to their target enzyme, molecular modeling was carried out by software packages including Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) [27], BiosolveIT LeadIT 2.1.1 [28] and Sybyl X-2.0 [29].
The Protein Data Bank crystallographic structure of TcAChE (−)-Galanthamine complex (PDB code ID: 1DX6) [30,31] was used as a receptor model in this study. The 3D structure of the crystallographic complex was rendered by BioSolveIT LeadIT. The active site was defined as all the important amino acid residues enclosed within 6.5 Å radius sphere centered by the bound ligand, Galanthamine. All unbound water molecules were eliminated and the structures of amino acid residues were checked before re-establishing the active site of the enzyme.
The 2D and 3D chemical structures of 10 benzylaminochalcones were built by ChemBioOffice 2008 [32]. The structures of molecules were optimized using the energy minimization and molecular dynamic modules in SYBYL-X 2.0. In the energy minimization process, Conj Grad method was chosen and the structures of molecules were optimized until converged to a minimum energy change of 0.001 kcal.mol−1. Gasteiger-Huckel charges were assigned to the structure atoms and the maximum number of iterations to perform during minimization was set to 10,000. Molecular dynamic process was proceeded to obtain conformations with the minimum global energy. The method used in this process was Simulated Annealing. In this method, the molecules were heated at 700 K in a period of 1000 femtoseconds, then they were cooled down to 200 K in another period of 1000 femtoseconds to come to the stable states from which their final conformations were obtained. The process was run in five cycles to figure out different necessary structures. Finally, the energy minimization process was performed one more time and the steric energy of final conformations was specified [33,34].
Initially, docking was performed with the co-crystallized AChE: (−)-Galanthamine.which was re-prepared in SYBYL-X 2.0. The RMSD value between re-docked conformation and the original structure, which was ≤ 1.5Å, indicated the reliability of the binding ability prediction of new ligands. Docking process was utilized BioSolveIT LeadIT with the following options: The method in which base fragment placed in binding pocket was Triangle Matching; the maximum number of solutions per iteration was set to 1000; the maximum number of solutions per fragmentation was set to 200; the number of poses to keep for further analysis of interaction was set to 10. The best conformation is the one that has the most minus docking score [33,34,35].
The interactions between chalcone molecules and their target were rendered and analyzed in MOE 2008.10 such as hydrogen bonds, π-π interaction, cation-π interaction, ionic interaction. Van der Waals surface interactions were detected by the contact of hydrophilic and lipophilic surfaces of the ligands with those of binding points.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
All synthesized chalcone analogues were obtained via Claisen Schmidt condensation reactions. Briefly, 1-(4-((2-Hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)ethanone 1 (5 mM) and aromatic aldehyde (5 mM) were dissolved in methanol (15 mL) and cooled to 5–10 °C in an ice bath. The cooled solution was treated with a small portion of pulverized KOH (10 mM) before stirring for 60 min. The reaction mixture was then left overnight or longer, and was monitored by thin-layer chromatography using n-hexane–acetone (5:1) as a developing solvent. Ice water was used to dilute the resulting dark solution before it was carefully acidified using dilute hydrochloric acid. The chalcones, which separated as a yellow solid, were collected by filtration after washing with water and further purified by crystallization from methanol, followed by further purification by silica gel column chromatography.
3.1.1. (E)-3-(phenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A1)
Yellow crystals, very soluble in acetone, methanol and ethanol, poorly soluble in water, mp: 183–184 °C; EIMS (m/z): 328.1359 [M − H]− (MW: 329.14); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 275, 338, 390; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.3 (d, 1H, J = 9 Hz, CH2), 6.66 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (dd, 1H, J = 1 Hz, 8 Hz, H3”), 7.08 (m, 2H, H4”, 5”), 7.16 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz, H6”), 7.40–7.43 (m, 3H, H2, H4, H6); 7.6 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H, Hα), 7.80 (dd, 2H, J = 1.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz, H3 and H5); 7.85 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H, Hβ), 7.94 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H2’, H6’), 9.61 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56.0 (CH2), 114.9 (C3”), 118.86 (C6”), 124.4 (C5”), 124.7 (Cα), 125.3 (C1”), 125.3 (C1’), 127.8 (C1), 128.2 (C4’), 128.4 (C4), 128.8 (C2, C6), 129.9 (C3, C5), 130.9 (C2’, C6’), 141.3 (C1’), 151.5 (Cβ), 153.1 (C4), 155 (C2”), 185.9 (C=O).
3.1.2. (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A2)
Dark yellow crystals, very soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, poorly soluble in water; mp: 204–206 °C; EIMS (m/z): 362.0930 [M − H]− (MW: 363.10); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 309, 383; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δppm: 4.30 (d, 1H, CH2), 6.66 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3”), 7.08 (t, 1H, J = 7 Hz, H5”), 7.14 (d, 1H, J = 15 Hz, Ha), 7.16 (t, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H4”), 7.40–7.43 (m, 3H, H4, H5, H6); 7.54 (d, 1H, J = 2 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, H6”), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 7.91 (d, 1H, J = 5 Hz, H6), 7.95 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, H2’, H6’), 8.14 (dd, J = 1.5 Hz, J = 8 Hz, H3), 9.61 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56.03 (CH2), 114.9 (C3’, C5’), 118.8 (C3”), 124.6 (C6”), 125.0 (Cα), 125.26 (C5”), 127.6 (C1”), 127.8 (C1’), 128.3 (C6), 128.3 (C4”), 129.9 (C4), 131.1 (C3), 131.3 (C2’, C6’), 132.8 (C1), 133.9 (C2), 136 (Cβ), 153.3 (C4’), 155.3 (C2”), 185.5 (C=O).
3.1.3. (E)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A3)
Pale yellow solid, very soluble in acetone, slightly solube in ethanol and methanol, poorly soluble in water; mp: 198–200 °C; EIMS (m/z): 362.0930 [M − H]− (MW = 363.10); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 280, 297, 354; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.30 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, CH2), 6.66 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (6, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3”), 7.08–7.10 (m, 2H, H4”, H5”), 7.16 (d, 1H, J = 7 Hz, H6”), 7.49 (d, 2H, J = 8 Hz, H2, H6), 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.85 (d, 2H, J = 8 Hz, H3 and H5), 7.88 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 7.94 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H2’ and H6’), 9.61 (s, 1H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56.0 (CH2), 111.2 (C3’, C5’), 115.0 (C6”), 118.8 (C5”), 123.2 (Cα), 124.7 (C1”), 125.2 (C1’), 127.8 (C1”), 128.3 (C1’), 128.8 (C4”), 130.2 (C3’,C5’), 131.0 (C2’,6’), 134.16 (C2”), 134.4 (C1), 139.9 (Cβ), 153.24 (C4’), 155.0 (C2”), 185.7 (C=O).
3.1.4. (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxy-benzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A4)
Red solid, very soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, in soluble in water; mp: 202–203 °C; EIMS (m/z): 373.1234 [M − H]−, (MW: 374.13); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 262, 386; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.31 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, CH2), 6.68 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3”), 7.07-7.18 (m, 3H, H4”, H5”, H6”), 7.68 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.97 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H2’, H6’), 8.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 8.11 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, H2, H6), 8.26 (d, 2H, J = 9Hz, H3, H5), 9.62 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56.0 (CH2), 114.9 (C3’, C5’), 118.8 (C6”), 123.8 (C5”), 124.6 (Cα), 125.0 (C1”), 126.7 (C3, C5), 127.8 (C1’), 128.3 (C4”), 129.4 (C2, C6), 131.2 (C2’, C6’), 138.6 (C1), 141.8 (Cβ), 147.7 (C4), 153.4 (C4’), 155.0 (C2”), 185.4 (C=O).
3.1.5. (E)-3-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A5)
Yellow solid, very soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, poorly solube in water; mp: 186–188 °C; EIMS (m/z): 373.1245 [M − CH3]− (MW: 389.16); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 359; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 3.77 (s, 3H, OMe), 3.83 (s, 3H, OMe), 4.3 (d, 2H, J = 5.5 Hz, CH2), 6.66 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, H6”), 7.05–7.16 (m, 5H, H3”, H4”, H5”, H4, H5), 7.55 (dd, 1H, J = 2Hz, J = 7Hz, H6), 7.80 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H, Hα), 7.87 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H, Hβ), 7.92 (d, 2H, J = 8.5Hz, H2’, H6’), 9.61 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 55.79 (CH2), 56.05 (OCH3), 60.87 (OCH3), 111.2 (C3’, C5’), 114.4 (C4), 118.8 (C3”), 119 (C6”), 123.3 (C6), 124.2 (Cα), 124.7 (C5), 125.38 (C1”), 127.8 (C1’), 128.3 (C4”), 128.7 (C1), 130.9 (C2’, C6’), 135.4 (Cβ), 147.98 (C2), 152.7 (C3), 153.1 (C4’), 155 (C2”), 186 (C=O).
3.1.6. (E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A6)
Yellow solid, very soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, poorly soluble in water; mp: 179–180 °C; EIMS (m/z): 373.1245 [M − CH3]− (MW: 389.16); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 265, 286; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 3.82 (s, 3H, OMe), 3.88 (s, 3H, OMe), 4.29 (d, 2H, J = 5.5 Hz, CH2), 6.65 (d, 2H, J = 8 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.73 (t, 1H, J = 7.Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H3”), 6.99 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H6”), 7.06 (m, 2H, H4”, H5”), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 7 Hz, H6), 7.30 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H5), 7.47 (s, 1H, H2), 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 7.94 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, H2’, H6’), 9.6 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 55.5 (CH3O), 55.6 (CH3O), 56.0 (CH2), 110.5 (C2), 111.5 (C5), 114.9 (C3’, C5’), 118.8 (C3”), 120 (C6”), 123.2 (C5”), 124.7 (Cα), 125.5 (C6), 127.8 (C1”), 128 (C1), 128.2 (C4”), 130.8 (C2’, C6’), 141.8 (Cβ), 149 (C4), 150.7 (C3), 152.9 (C4’), 155 (C2”), 185.9 (C=O).
3.1.7. (E)-3-(2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A7)
Yellow solid, very solube in ethanol and methanol, insoluble in water; mp: 181–182 °C; EIMS (m/z): 373.1245 [M − H]−, (MW: 389.16); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 245, 386; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 3.82 (s, 3H, OMe), 3.88 (s, 3H, OMe), 4.29 (d, 2H, J = 5 Hz, CH2), 6.59–6.75 (m, 3H, H3’, H5’, H5), 6.63–6.84 (m, 2H, H3”, H6”), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, J = 8 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3), 7.01–7.06 (m, 2H, H4”, H5”), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 7 Hz, H6), 7.67 (d, 1H, J =15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.86 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 7.86 (d, 2H, J = 8 Hz, H2’, H6’), 9.59 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 55.2 (CH3O), 55.4 (CH3O), 55.7 (CH2), 98.3 (C3), 106.1 (C5), 111.1 (C3’, C5’), 114.9 (C3”), 116.4 (C1), 118.8 (C6”), 119.5 (C5”), 124.8 (C1”), 125.7 (Cα), 127.8 (C1’), 128.2 (C4”), 129.6 (C6), 130.6 (C2’, C6’), 136.1 (Cβ), 152.8 (C2), 155 (C4’), 159.5 (C2”), 162.4 (C4), 186.1 (C=O).
3.1.8. (E)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxy-benzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A8)
Orange solid, very soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, poorly soluble in water; mp: 196–198 °C; EIMS (m/z): 329.1303 [M − H]−, (MW: 330.14); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 280, 300, 392; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.3 (d, 2H, J = 5.5-Hz, CH2), 6.68 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H3”), 7.07 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H4”), 7.14–7.16 (m, 2H, H5”, H6”), 7.39 (t, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz, J = 5 Hz, H4), 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.84–7.87 (m, 2H, H5, H6), 7.89 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, H2’,H6’), 8.09 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H, Hβ), 8.65 (d, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz, H3), 9.61 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56 (CH2), 114.9 (C3’, C5’), 118.8 (C3”), 124.3 (C6”), 124.6 (C5”), 125.1 (C3, C4), 125.6 (C6), 127.8 (C1’), 127,7 (Cα), 128.2 (C4”), 130.9 (C2’, C6’), 137 (C5), 140.6 (Cβ), 145 (C3), 149.8 (C1), 153.3 (C4’), 155 (C”), 185.8 (C=O).
3.1.9. (E)-3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxy-benzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A9)
Red solid, very soluble in ethanol and methanol, slightly soluble in acetone, poorly soluble in water; bp: 229–230 °C; EIMS (m/z): 329.1303 [M − H]−, (MW = 330.14); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 378, 397; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.31 (d, 2H, J = 6 Hz, CH2), 6.67 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, J = 8 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3”), 7.07 (t, 1H, J = 7 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, H5”), 7.15–7.19 (m, 2H, H4”, H6”), 7.54 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.77 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H, H2, H6), 7.96 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz, H2’, H6’), 8.07 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 8.63 (d, 2H, J = 5.5 Hz, H3, H5), 9.62 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56 (CH2), 114.9 (C3’, C5’), 118.8 (C3”), 122.3 (C5”), 124.6 (C4”), 124.9 (C1”, C2, C6), 126.8 (C1’), 127.9 (Cα), 128.3 (C4’), 131.2 (C2’, C6’), 138.4 (C1), 142.3 (C1, Cβ), 150.2 (C3, C5), 153.4 (C4’), 155 (C2”), 185.5 (C=O).
3.1.10. (E)-3-(furan-2-yl)-1-(4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-ene-1-one (A10)
Yellow crystals, very soluble in ethanol and methanol, insoluble in water; mp: 187–189 °C; EIMS (m/z): 328.1114 [M − H]−, (MW = 319.12); UV (λmax nm, EtOH): 269; 285; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 4.29 (d, 2H, J = 5.5 Hz, CH2), 6.64 (m, 1H, H4), 6.65 (d, J = 7 Hz, H3’, H5’), 6.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 6.84 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H3”), 6.98 (d, J = 1.5 Hz, H6”), 7.06–7.10 (m, 2H, H4”, H5”), 7.14 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H5), 7.43 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hα), 7.49 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, Hβ), 7.84 (d, 1H, J = 9 Hz, H2’, H6’), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H3), 9.6 (s, 1H, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm: 56.1 (CH2), 111.2 (C3’, C5’), 112.8 (C4), 114.9 (C5), 115.3 (C3”), 118.8 (C6”), 119.30 (Cβ), 124.7 (C5”), 125.2 (C1”), 127.8 (C1’), 128.2 (Cα), 128.2 (C4”), 130.7 (C2’, C6’), 145.4 (C3), 151.5 (C1), 153.1 (C4’), 155 (C”), 185.32 (C=O).
3.2. Anti-Acetylcholinesterase Activity
The IC50 values for AChE inhibition are summarized in Table 2. The results showed that most of the studied compounds had weak to moderate AChE-inhibitory activities. Derivatives with ring B of 4-chlorophenyl (A3), 4-nitrophenyl (A4), 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl (A6) and 4-pyridinyl (A9) showed considerable inhibition of AChE in the tested group.

Table 2.
Inhibition of AChE (acetylcholinesterase) activity and docking scores.

The docking results demonstrated that benzylaminochalcones A3, A4, A6 and A9 span along almost the whole length of the catalytic gorge of AChE, in which the benzylamino side-chain points towards the bottom. Moreover, two of the three rings A, B or C manage to generate stacking interactions (π-π type) with the aromatic amino acids making up the gorge surface. More interestingly, there is a hydrogen bond between the OH group of the benzylamino chain of A9 with Ser203, a position near Ser200 of the catalytic triad (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
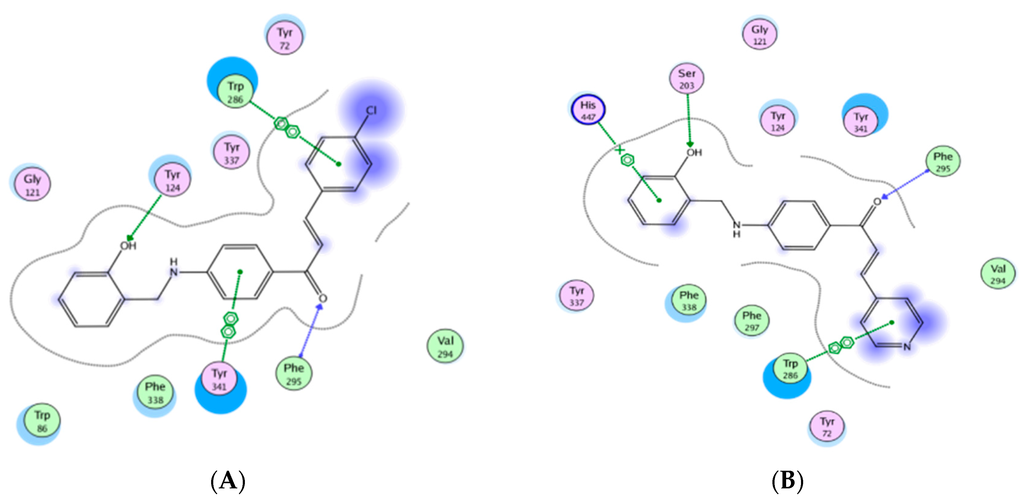
Figure 2.
Interactions between A3 and A9 with AChE (acetylcholinesterase): (A) A3; (B) A9.
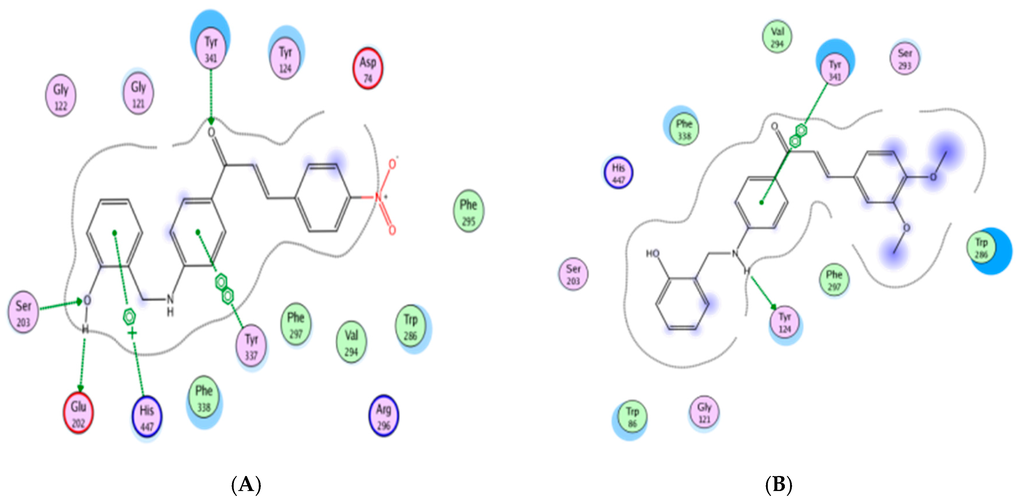
Figure 3.
Interactions between A4 and A6 with AChE: (A) A4; (B) A6.
It is found that AChE could bind to β-amyloid and accelerate its aggregation into amyloid fibrils. The presence of this enzyme also enhanced the toxicity of β-amyloid. The studied structures exhibited interactions of ring B with Trp286 of the peripheral binding site. This could lead to developing benzylaminochalcone analogues with dual effect, which would simulaneously increase acetylcholines and anti-β-amyloid aggregation.
4. Conclusions
A series of 10 novel benzylaminochalcones were synthesized, characterized and evaluated for AchE-inhibitory activity. All synthesized hydroxybenzylaminochalcones have not been published in any scientific journals. The derivatives with ring B of 4-pyridinyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl and 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl demonstrated weak to moderate activities against AChE. Molecular modeling studies confirmed the dual binding effects on active and peripheral anionic binding sites. These derivatives could be further developed to provide novel leads for the discovery of new anti-Alzheimer’s drugs in the future. Cell assays will be performed and the results will be published in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Vietnam’s National Foundation for Science and Technology Development-NAFOSTED (Grant #104.01.2012.78 to Thanh-Dao Tran). Authors would like to thank Pharm. Thuy-Viet-Phuong Nguyen and Pharm. Nguyen-Viet-Khoa Tran for critical reading and format of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
This study was conceived, designed, directed and coordinated by T.-D.T., K.-M.T. and M.-T.L. The chemical synthesis and product characterization was performed and the data was analyzed by T.-C.-V. N., N.-S.N., D.-M.N., T.-T.-H.N., M.-T.L., K.-M.T. and T.-D.T. The in vitro inhibition assay on AchE was planned and performed by T.-C.-V.N., N.-S.N., D.-M.N., K.-M.T. and T.-D.T. The molecular modeling study was planned, performed and analyzed by T.-C.-V.N., N.-S.N., D.-M.N., M.-T.L., K.-M.T. and T.-D.T. The manuscript was written by T.-C.-V.N., N.-S.N., D.-M.N., K.-M.T. and T.-D.T. All authors give final approval of the version to be submitted and the final version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scarpini, E.; Scheltens, P.; Feldman, H. Treatment of Alzheimer's disease: Current status and new perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Rampa, A.; Bisi, A.; Gobbi, S.; Belluti, F.; Cavalli, A.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Valenti, P.; Recanatini, M. 3-(4-{[Benzyl(methyl)amino]methyl}phenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238) Inhibits Both Acetylcholinesterase and Acetylcholinesterase-Induced β-Amyloid Aggregation: A Dual Function Lead for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2279–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer's Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumiatti, V.; Minarini, A.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Milelli, A.; Rosini, M.; Melchiorre, C. Tacrine Derivatives and Alzheimers Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, H.; Xia, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Fu, U.; Tang, Y.; Sheng, W.; Li, W.; et al. Bis-(−)-nor-meptazinols as Novel Nanomolar Cholinesterase Inhibitors with High Inhibitory Potency on Amyloid-β Aggregation. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartus, R.T.; Dean, R.L.; Beer, B.; Lippa, A.S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 1982, 217, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, C.W.; Ames, D.; Clayton, T.; Lai, R. Metaanalysis of Randomized Trials of the Efficacy and Safety of Donepezil, Galantamine, and Rivastigmine for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Geriat. Psychiat. 2004, 4, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, M.; Sonoda, L.K.; Silman, I.; Sussman, I.; Rosenberry, T.L. Crystal Structure of Thioflavin T Bound to the Peripheral Site of Torpedo californica Acetylcholinesterase Reveals How Thioflavin T Acts as a Sensitive Fluorescent Reporter of Ligand Binding to the Acylation Site. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7856–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butini, S.; Campiani, G.; Borriello, M.; Gemma, S.; Panico, A.; Persico, M.; Catalanotti, B.; Ros, S.; Brindisi, M.; Agnusdei, M.; et al. Exploiting Protein Fluctuations at the Active-Site Gorge of Human Cholinesterases: Further Optimization of the Design Strategy to Develop Extremely Potent Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3154–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Taylor, P.; Radic, Z.; Marchot, P. Structural insights into ligand interactions at the acetylcholinesterase peripheral anionic site. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.E.; Chacon, M.A.; Dinamarca, M.C.; Cerpa, W.; Morgan, C.; Inestrosa, N.C. Acetylcholinesterase-Aβ Complexes Are More Toxic than Aβ Fibrils in Rat Hippocampus. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturan, O.E.; Tan, O.U.; Ozadali, K.; Kucukkilinc, T.; Balkan, A.; Ucar, G. Synthesis, molecular modeling and evaluation of novel N′-2-(4-benzylpiperidin-/piperazin-1-yl)acylhydrazone derivatives as dual inhibitors for cholinesterases and Aβ aggregation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ferrari, G.V.; Canales, M.A.; Shin, I.; Weiner, L.M.; Silman, I.; Inestrosa, N.C. A Structural Motif of Acetylcholinesterase that Promotes Amyloid β-Peptide Fibril Formation. Biochem. 2001, 40, 10447–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Ruiz, P.; Rubio, L.; Garcia-Palomero, E.; Dorronsoro, I.; del Monte-Millan, M.; Valenzuela, R.; Usan, P.; de Austria, C.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Dual Binding Site Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: New Disease-Modifying Agents for Alzheimer's Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katalinic, M.; Rusak, G.; Domacinovic, B.J.; Sinko, G.; Jelic, D.; Antolovic, R.; Kovarik, Z. Structural aspects of flavonoids as inhibitors of human butyrylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uriarte-Pueyo, I.; Calvo, M.I. Flavonoids as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 34, 5289–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, B.S.; Lee, K.G.; Choi, C.Y.; Jang, S.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.E. Effects of Naturally Occurring Compounds on Fibril Formation and Oxidative Stress of β-Amyloid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8537–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Fan, P.; Perez, R.G. Neuroprotective effects of linarin through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in amyloid-β-induced neuronal cell death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4021–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Park, H.M.; Hyung, S.J.; DeToma, A.S.; Kim, C.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Lim, M.H. Exploring the reactivity of flavonoid compounds with metal-associated amyloid-β species. Dalton Trans. 2012, 21, 6558–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.E.; Cho, J.K.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Ryu, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yuk, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Park, K.H. Inhibitory Evaluation of Sulfonamide Chalcones on β–Secretase and Acylcholinesterase. Molecules 2012, 18, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.B.; March, J. Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1218–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, T.B.; Kang, S.K. Clean and simple chemoselective reduction of imines to amines using boric acid-activated sodium borohydride under solvent-free conditions. Synlett 2004, 9, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.-H.; Nguyen, D.-M.; Truong, V.-D.; Do, T.-H.-T.; Le, M.-T.; Pham, T.-Q.; Thai, K.-M.; Tran, T.-D. Synthesis and Selective Cytotoxic Activities on Rhabdomyosarcoma and Noncancerous Cells of Some Heterocyclic Chalcones. Molecules 2016, 21, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.-D.; Do, T.-H.; Tran, N.-C.; Ngo, T.-D.; Huynh, T.-N.-P.; Tran, C.-D.; Thai, K.-M. Synthesis and anti Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity of substituted chalcones alone and in combination with non-beta-lactam antibiotics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4555–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.-D.; Nguyen, T.-T.-N.; Do, T.-H.; Huynh, T.-N.-P.; Tran, C.-D.; Thai, K.-M. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Some Heterocyclic Chalcone Analogues Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics. Molecules 2012, 17, 6684–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOE. 2008.10 edition. Chemical Computing Group Inc., 1010 Sherbrooke St. W, Suite 910, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3A 2R7. Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- LeadIT. 2.0.2 edition. BioSolveIT GmbH, An der Ziegelei 79, 53757 St. Augustin, Germany. Available online: http://www.biosolveit.de/ (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- Sybyl. Available online: http://www.tripos.com (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- Dvir, H.; Silman, I.; Harel, M.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: From 3D Structure to Function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 187, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protein Data Bank. Available online: http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1dx6 (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- ChemBioDrawUltra. 12.0 edition. PerkinElmer, CambridgeSoft. Available online: http://www.cambridgesoft.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- Thai, K.-M.; Le, D.-P.; Tran, N.-V.-K.; Nguyen, T.-T.-H.; Tran, T.-D.; Le, M.-T. Computational assay of Zanamivir binding affinity with original and mutant influenza neuraminidase 9 using molecular docking. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 385, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, K.-M.; Ngo, T.-D.; Phan, T.-V.; Tran, T.-D.; Nguyen, N.-V.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Le, M.-T. Virtual screening for novel Staphylococcus Aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors from natural products. Med. Chem. 2015, 11, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, K.-M.; Huynh, N.-T.; Ngo, T.-D.; Mai, T.-T.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Tran, T.-D. Three- and four-class classification models for P-glycoprotein inhibitors using counter-propagation neural networks. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2015, 26, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).