Effect of the Presence of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on the Mobility of Metribuzin in Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Soil Characteristics
| Soil Type | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | pH | Bulk Density (Mg m−3) | Organic Matter (%) | CEC (cmol kg−1) | Hydraulic Conductivity (cm Day−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy | 92.2 | 4.3 | 5.5 | 1.350 | 2.97 | 4.9 | 1.67 (* SD = 0.45) |
2.3. Sorption Study


2.4. Experimental Set Up
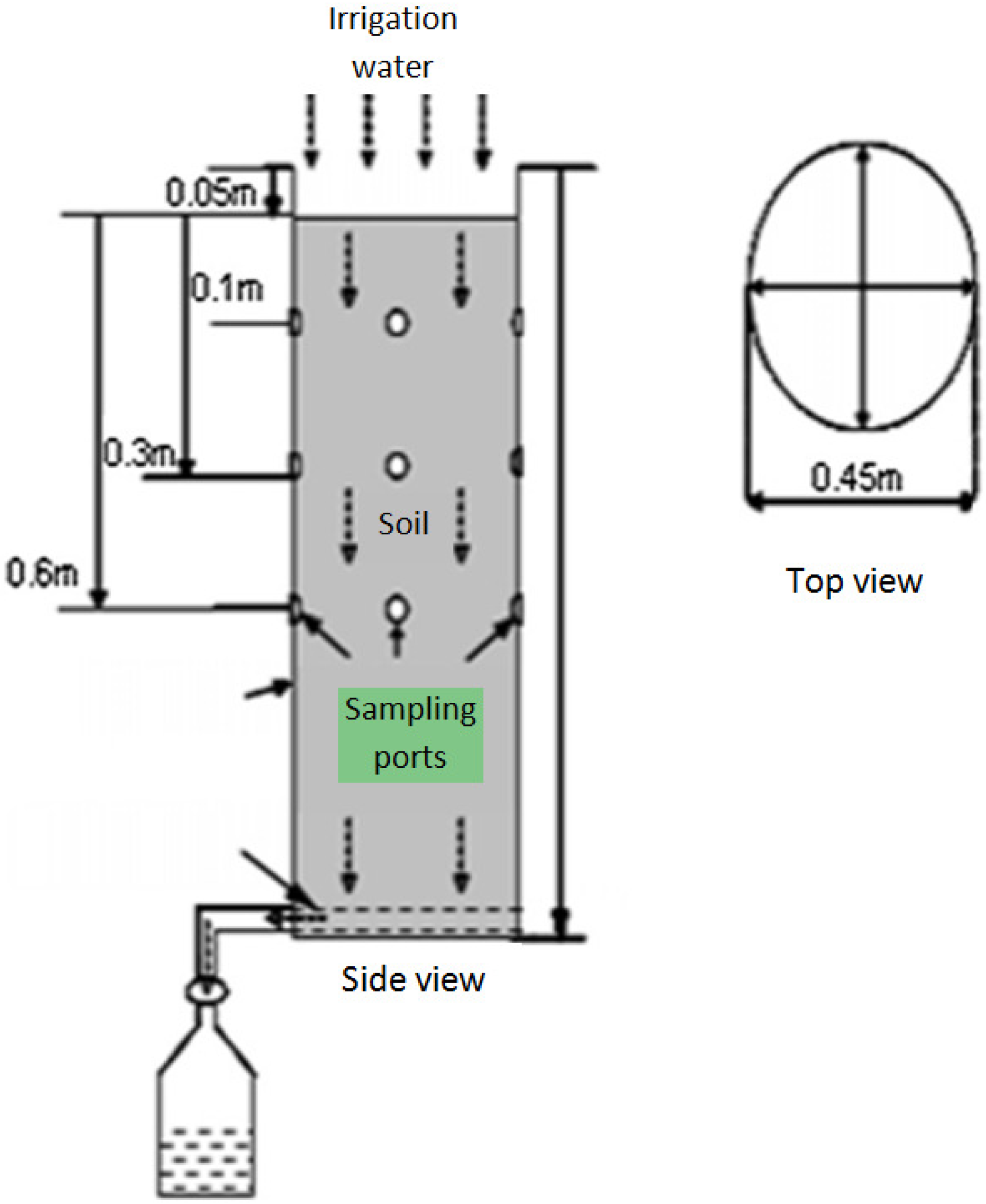
2.4.1. Application of Tested Compounds
2.4.2. Soil and Leachate Sampling
2.5. Mass Balance Calculations

 , where D = 45 cm.
, where D = 45 cm.
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.6.1. Leachate Sample Extraction
2.6.2. Soil Sample Extraction
2.6.3. Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorption

| Concentration of Brij35 (g L−1) | Kd | R2 | Koc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.8 | 0.97 | 60.61 |
| 0.5 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 31.31 |
| 5 | 1.38 | 0.99 | 46.46 |
3.2. Mass Balance
| Day | Irrigation Solution Soil Profile Depth Range (cm)/Leachate/Total | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | Brij35 at 0.5 g L−1 | Brij35 at 5 g L−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–45 | 45–70 | Leach cumul | Total | 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–45 | 45–70 | Leach cumul | Total | 0-5 | 5-15 | 15-45 | 45-70 | Leach cumul | Total | |||
| 0 | 19.25 | —Irrigation I— | 0 | 19.25 | 19.85 | —Irrigation I— | 0 | 19.85 | 20.06 | —Irrigation I— | 0 | 20.06 | ||||||||
| 1 | 9.62 | 8.90 | — | — | 0.09 | 18.61 | 10.30 | 2.13 | 5.72 | — | 0.34 | 18.49 | 8.49 | 2.75 | 6.65 | — | 0.65 | 18.54 | ||
| 5 | 5.05 | 3.08 | 0.94 | — | 0.09 | 9.16 | 4.91 | 1.79 | 2.55 | — | 0.34 | 9.59 | 2.82 | 2.26 | 3.52 | — | 0.65 | 9.25 | ||
| 15 | 2.59 | 1.05 | 1.95 | — | 0.09 | 5.68 | 1.88 | 0.11 | 4.93 | 1.99 | 0.34 | 9.25 | 1.54 | 0.33 | 2.44 | 3.29 | 0.65 | 8.25 | ||
| 21 | ——Irrigation II—— | 0.17 | 5.76 | ——Irrigation II—— | 0.80 | 9.71 | ——Irrigation II—— | 1.27 | 8.87 | |||||||||||
| 22 | 1.32 | 0.21 | 1.36 | — | 0.17 | 3.06 | 0.78 | — | 1.60 | 1.72 | 0.80 | 4.90 | 0.95 | — | 0.91 | 1.09 | 1.27 | 4.22 | ||
| 30 | 0.85 | — | — | — | 0.17 | 1.02 | 0.62 | — | 0.82 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 2.80 | 0.22 | — | 1.20 | 1.08 | 1.27 | 3.77 | ||
| 42 | ——Irrigation III—— | 0.25 | 1.10 | ——Irrigation III—— | 1.33 | 3.33 | ——Irrigation III—— | 1.55 | 4.05 | |||||||||||
| 60 | 0.12 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.09 | — | — | 0.93 | 1.33 | 2.35 | 0.07 | — | — | 0.17 | 1.55 | 1.79 | ||
| 63 | ——Irrigation IV—— | 0.25 | 0.37 | ——Irrigation IV—— | 1.54 | 2.56 | ——Irrigation IV—— | 1.55 | 1.79 | |||||||||||
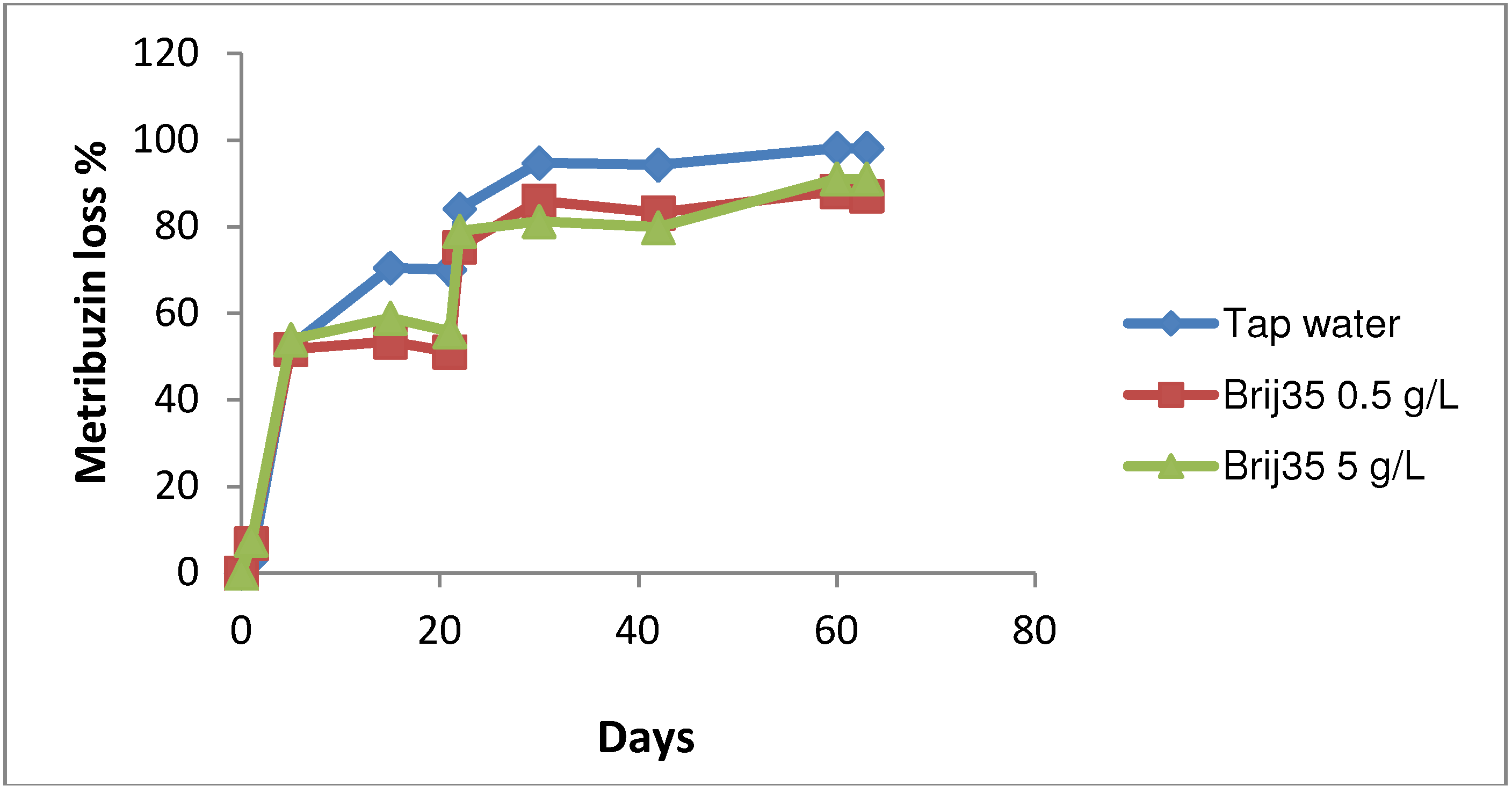
3.3. Effect of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on Metribuzin Residues in Soil

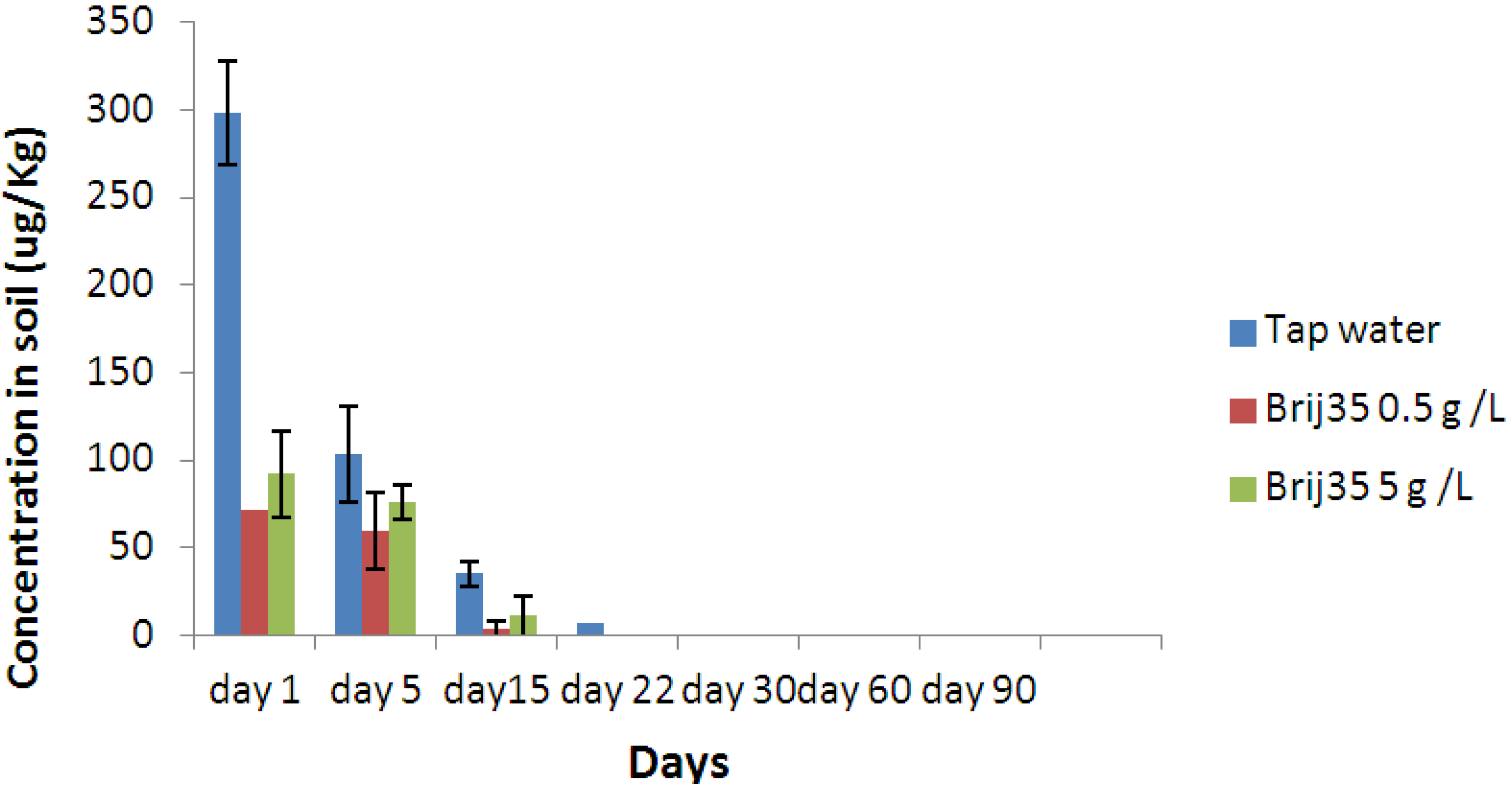
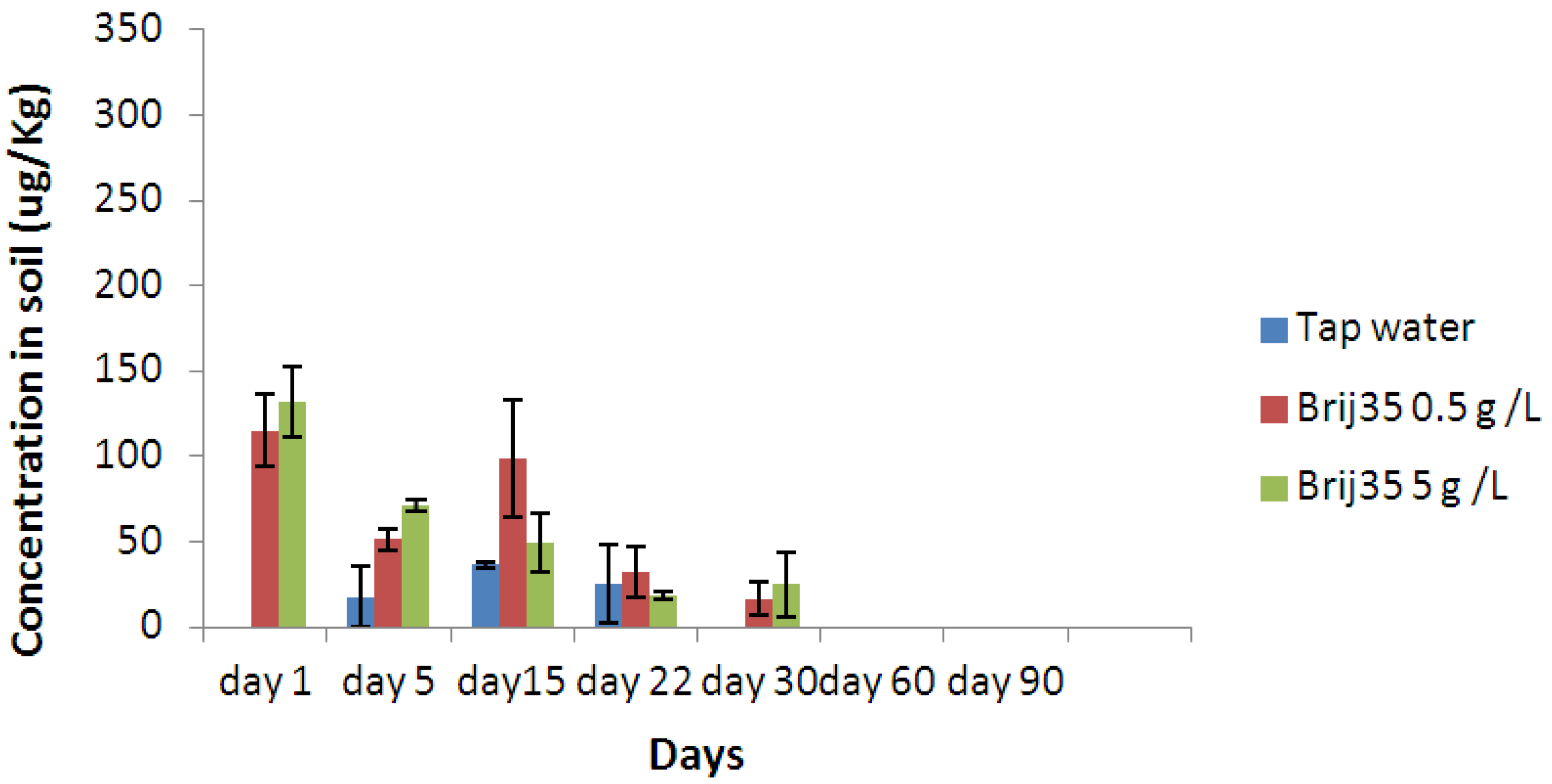
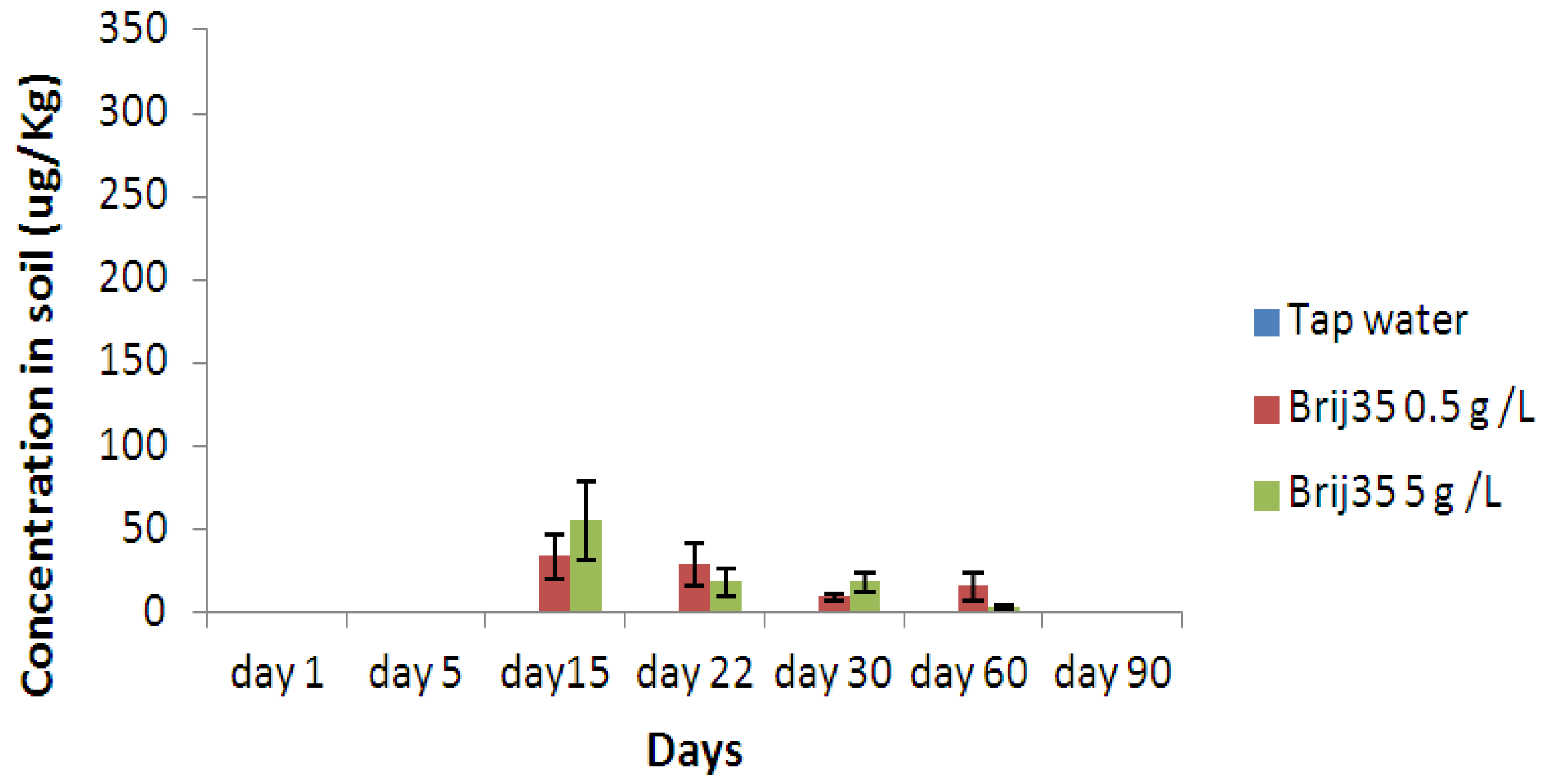
3.4. Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactant Brij35 on Metribuzin in Leachate
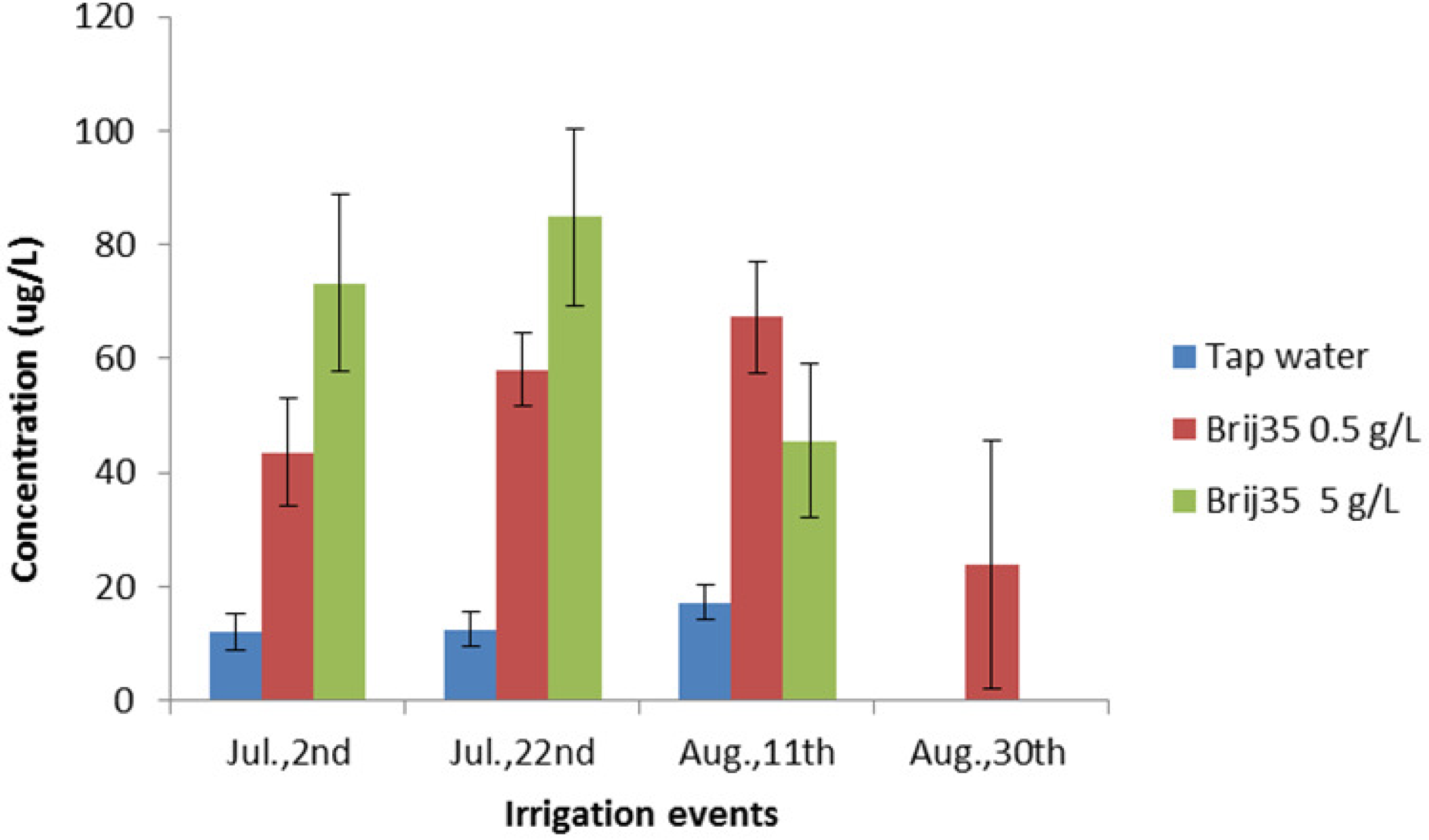
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Comprehensive Assessment of the Freshwater Resources of the World; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, NY, USA, 1997.
- Rahman, S.H.; Khanam, D.; Adyel, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Ahsan, M.A.; Akbor, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil around dhaka export processing zone (DEPZ), bangladesh:Implication of seasonal variation and indices. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.N. Fresh produce from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, C.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Redwood, M.; Bahri, A. Water Irrigation and Health. Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Earthscan/IDRC: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, A.J.; Stagnitti, F.; Xiong, X.; Kreidl, S.L.; Benke, K.K.; Maher, P. Wastewater irrigation: The state of play. Vadose Zone J. 2007, 6, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.H.; Capri, S.; Marcomini, A.; Giger, W. Occurrence and behavior of linear alkylbenzenesulphonates, nonylphenol, nonylphenol mono- and nonylphenol diethoxylates in sewage and sewage sludge treatment. Water Res. 1988, 22, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A.; Leenheer, J.A.; Thorn, K.A.; Barber, L.B.; Rostad, C.; Macalady, D.L.; Daniel, S.R. Identification of persistent anionic surfactant derived chemicals in sewage effluent and ground water. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1992, 9, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.B.; Waterrath, K.S.; Jones, K.F. Organic contaminants in an agricultural soil with a known history of sewage sludge amendments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkis, N.; Ben-David, B. Adsorption of nonionic surfactants on active carbon and mineral clay. Water Res. 1985, 19, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; Alonso, M.C.; Riu, J.; Barcelo, D. Identification of polar, ionic, and highly water soluble organic pollutants in untreated industrial wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitkenhauer, H.; Meyer, U. On-line titration of non-ionic surfactants in wastewater treatment plants using a specific electrode. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zoller, U. Non-ionic surfactants in reused water: Are activated sludge/soil aquifer treatments sufficient? Water Res. 1994, 28, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyo-Rosales, J.E.; Rice, C.P.; Torrents, A. Fate of octyl and nonylphenol ethoxylates and some carboxylated derivatives in three american wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6815–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, A.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Adams, G.D.; Champagne, P.; Ong, S.K.; Tyagi, R.D.; Zhang, T. Contaminats of Emerging Environmental Concern; The American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, K.E.; Barber, L.B.; Brown, G.K.; Siegrist, R.L. Occurrence and fate of organic contaminants during onsite wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7358–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperanza, M.; Suidan, M.T.; Nishimura, F.; Wang, Z.; Sorial, G.A. Determination of sex hormones and nonylphenol ethoxylates in the aqueous matrixes of two pilot-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3028–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Keefe, S.H.; Leblanc, D.R.; Bradley, P.M.; Chapelle, F.H.; Meyer, M.T.; Loftin, K.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Rubio, F. Fate of sulfamethoxazole, 4-Nonylphenol, and 17-Estradiol in groundwater contaminated by wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4843–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggenberger, F.H.; Letey, J.; Farmer, W.J. Effect of two nonionic surfactants on adsorption and mobility of selected pesticides in a soil-system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1973, 37, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, T.A.; Tomson, M.B. Ground water transport of hydrophobic organic compounds in the presence of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronstein, B.N.; Calvillo, Y.M.; Alexander, M. Effect of surfactants at low concentrations on the desorption and biodegradation of sorbed aromatic compounds in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cruz, M.S.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.; Sanchez-Camazano, M. Enhanced desorption of herbicides sorbed on soils by addition of Triton X-100. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagi, T. Surfactant effects on environmental behavior of pesticides. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 194, 71–177. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Q.; Dong, S.; Hong, X.; Wang, T. Effect of surfactants at low concentrations on the sorption of atrazine by natural sediment. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Camazano, M.; Arienzo, M.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.; Crisanto, T. Effect of different surfactants on the mobility of selected non-ionic pesticides in soil. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 3793–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilufar, F. Fate and Transport of Herbicides in Soil in the Presence of Surfactants in the Irrigation Water. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.P.; Baker, D.B. Pesticide concentration patterns in agricultural drainage networks in the Lake Erie basin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores, E.F.G.C.; Navickiene, S.; Cunha, M.L.F.; Carbo, L.; Ribeiro, M.L.; de-Lamonica-Freire, E.M. Multiresidue determination of herbicides in environmental waters from Primavera do Leste region (Middle West of Brazil) by SPE-GC-NPD. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2006, 17, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.R.B.; Reimer, G.J. Field degradation of the herbicide metribuzin and its degradation products in a Manitoba sandy loam soil. Weed Res. 1976, 16, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, J.F.; Ruessler, D.S.; Carlson, A.R. Comparative sensitivity of five species of macrophytes and six species of algae to atrazine, metribuzin, alachlor, and metolachlor. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, J.F.; Sappington, L.C. Fate and effects of the triazinone herbicide metribuzin in experimental pond mesocosms. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Plhalova, L.; Stepanova, S.; Praskova, E.; Chromcova, L.; Zelnickova, L.; Divisova, L.; Skoric, M.; Pistekova, V.; Bedanova, I.; Svobodova, Z. The effects of subchronic exposure to metribuzin on Danio rerio. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladlie, J.S.; Meggitt, W.F.; Penner, D. Effect of soil pH on microbial degradation, adsorption, and mobility of metribuzin. Weed Sci. 1976, 24, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sharom, M.S.; Stephenson, G.C. Behaviour and fate of metribuzin in eight Ontario soils. Weed Sci. 1976, 24, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Khoury, R.; Geahchan, A.; Coste, C.M.; Antoun, M.A. The Behavior of Pesticide in Soil: The Influence of Various Environmental Factors on the Degradation of Metribuzin. In Proceedings of 2000 Mediterranean Conference for Environment and Solar, Beirut, Lebanon, 16–17 November 2000; pp. 34–39.
- Ramsey, R.J.L.; Stephenson, G.R.; Hall, J.C. A review of the effects of humidity, humectants, and surfactant composition on the absorption and efficacy of highly water—Soluble herbicides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 82, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, D.T.; Mertens, J.; Spanoghe, P.; Ryckeboer, J.; Jaeken, P.; Springael, D. Sorption kinetics and its effects on retention and leaching. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, M.; Thapa, U. Integrated nutrient management with farm yard manure on potatos (Solanum tuberosum) under gangetic plains of west Bengal. Environ. Ecol. 2004, 22, 766–769. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Zreig, M.; Rudra, R.P.; Dickinson, W.T.; Evans, L.J. Effect of surfactants on sorption of atrazine by soil. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1999, 36, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, E.M.; Prasher, S.O.; Patel, R.M. Effect of nonionic surfactant Brij35 on the fate and transport of oxytetracycline antibiotic in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 116, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS/GRAPH, 2nd, SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2010.
- Sun, S.; Inskeep, W.P.; Boyd, S. Sorption of nonionic compounds in soil-water systems containing a micelle-forming surfactant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.A.; Laird, D.A.; Thompson, M.L.; Evangelou, V.P. Cosorption of atrazine and a lauryl polyoxyethylene oxide nonionic surfactant on smectite. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 10127–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; He, F.; Zhao, D.; Hao, X. Degradation of soil-sorbed trichloroethylene by stabilizedzero valent iron nanoparticles: Effects of sorption, surfactants, and natural organic matter. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Edwards, D.; Luthy, R. Sorption of non-ionic surfactants onto soils. Water Res. 1992, 26, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Sandoval, J.C.; Karns, J.; Torrents, A. Effects of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 on the solubilization of pesticides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Keller, A.A. Partitioning of hydrophobic organic compounds within soil–water–surfactant systems. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, M.; Messina, C.; Abbate, C.; Baglieri, A.; Boursier, C. Solubility and adsorption behaviors of chlorpyriphos-methyl in the presence of surfactants. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part B 2009, 44, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Southwick, L.M.; Willis, G.H.; Johnson, D.C.; Selim, H.M. Leaching of nitrate, atrazine and metribuzin from sugarcane in southern Louisiana. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 684–690. [Google Scholar]
- Comfort, S.D.; Shea, P.J.; Roeth, F.W. Understanding Pesticides and Water Quality in Nebraska; Nebraska Cooperative Extension EC, University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Nebraska, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.B.; Keller, K.E. Mobility of Pesticides in Field Lysimeters. In Mechanisms of Pesticide Movement into Ground Water; Honeycutt, R.C., Schabacker, D.J., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bedmar, F.; Costa, J.L.; Suero, E.; Gimenez, D. Transport of atrazine and metribuzin in three soils of the humid pampas of Argentina. Weed Technol. 2004, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M. Fate and Transport of Herbicides in a Sandy Soil in the Presence of Antibiotics in Poultry Manure. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pandiselvi, V.; Sathiyanarayanan, S.; Ayyappan, S.; Ramesh, A. Photolysis of metribuzin in water under direct sunlight—Identification of phototransformation products by LC-MS-MS electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and impact on aquatic species (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata). Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2012, 2, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sabadie, J. Degradation of bensulfuron-methyl on various minerals and humic acids. Weed Res. 1997, 37, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Jurado-Exposito, M.; Walker, A. Degradation of isoproturon, propyzamide and alachlor in soil with constant and variable incubation conditions. Weed Res. 1998, 38, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, J.; Olsen, P.; Henriksen, T.; Ullum, M. Leaching of metribuzin metabolites and the associated contamination of a sandy danish aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8374–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N. Nonylphenol in the environment: A critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.; Luthy, R.G. Effects of nonionic surfactants on the solubilization and mineralization of phenanthrene in soil-water systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 40, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, S.; Jaffe, P.R. Bioavailability of hydrophobic compounds partitioned into the micellar phase of nonionic surfactants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.C.R.; Boyd, D.R.; Hempenstall, F.; Larkin, M.J.; Sharm, N.D. Contrasting effects of a nonionic surfactant on the biotransformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to cis-dihydrodiols by soil bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, K.E. Adsorption and mobility of metribuzin in soil. Weed Sci. 1976, 24, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, D.C.; Lavy, T.L.; Marx, D.B. Fate of metribuzin, metolachlor, and fluometuron in soil. Weed Sci. 1982, 30, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Fuscaldo, F.; Bedmar, F.; Monterubbianse, G. Perseistance of atrazin, metribuzin and simazine herbicides in soils. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 1999, 34, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, H.M. Retention and runoff losses of atrazine and metribuzin in soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, T.; Svensmark, B.; Juhler, R.K. Degradation and sorption of metribuzin and primary metabolites in a sandy soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, J.; Kah, M.; Brown, C.D. Adsorption and degradation of four acidic pesticides in soils from southern Spain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, C.; Villaverde, J.; Sopena, F.; Undabeytia, T.; Morillo, E. Effects of soil characteristics on metribuzin dissipation using clay-gel-based formulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3273–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, B.T. Mobility and dissipation studies of metribuzin, atrazine and their metabolities in plainfield sand using field lysimeters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1991, 10, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Aylmore, L.A.G.; Kookana, R.S. Degradation rates of eight pesticides in surface and subsurface soils under laboratory and field conditions. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 404–411. [Google Scholar]
- Denial, P.E.; Bedmar, F.; Costa, L.J.; Aparicio, V.C. Atrazine and metribuzin sorption in soils of the Argentinean humid pampas. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebellie, J.; Prasher, S.O. Role of water table management in reducing metribuzin pollution. Trans. ASAE 1998, 41, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Olness, A.; Basta, N.T.; Rinke, J. Redox effects on resin extraction of herbicides from soil. Talanta 2002, 57, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, K.; Magesan, G.N.; Bolan, N.S. A critical review of the influence of effluent irrigation on the fate of pesticides in soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 120, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiarchos, I.; Doulia, D. Effect of nonionic surfactants on the solubilization of alachlor. J. Hazard. Mater 2006, B136, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafverti, C.T.; Vanhoof, P.L.; Heath, J. Solubilization of non polar compounds by non ionic surfactant micelles. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Li, H.; Laird, D.A.; Boyd, S.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Teppen, B.J. Sorption of Triazines and Trichloroethene to Homoionic Smectites. In Proceedings of the 18th World Congress of Soil Science, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 9–15 July 2006.
- Health Canada. 2010. Available online: http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/ewh-semt/pubs/water-eau/2010-sum_guide-res_recom/index-eng.php (accessed on 24 August 2011).
- Cheah, P.S.; Reible, D.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Constant, D.; Walsh, W.; Thibodeaux, L.J. Simulation of soil washing with surfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 59, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.B.; Kibbey, T.C.G.; Cowell, M.A.; Hayes, K.F. Partitioning of ethoxylated nonionic surfactants into nonaqueous-phase organic liquids: Influence on solubilization behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, D.E.; Chiou, C.T. Water solubility enhancement of DDT and Trichlorobenzene by some surfactants below and above the critical micelle concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.A.; Koskinen, W.C. Triazine Soil Interactions. In The Triazine Herbicides,50 years Revolutionizing Agriculture; Lebaron, H.M., Macfarland, J.E., Burnside, O.C., Eds.; Elsevier: San Deigo, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 275–299. [Google Scholar]
- Undabeytia, T.; Recio, E.; Maqueda, C.; Morillo, E.; Gomez-Pantoja, E.; Sanchez-Verdejo, T. Reduced metribuzin pollution with phosphatidylcholine-clay formulations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
ElSayed, E.M.; Prasher, S.O. Effect of the Presence of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on the Mobility of Metribuzin in Soil. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 469-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3020469
ElSayed EM, Prasher SO. Effect of the Presence of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on the Mobility of Metribuzin in Soil. Applied Sciences. 2013; 3(2):469-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3020469
Chicago/Turabian StyleElSayed, Eman M., and Shiv O. Prasher. 2013. "Effect of the Presence of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on the Mobility of Metribuzin in Soil" Applied Sciences 3, no. 2: 469-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3020469
APA StyleElSayed, E. M., & Prasher, S. O. (2013). Effect of the Presence of Nonionic Surfactant Brij35 on the Mobility of Metribuzin in Soil. Applied Sciences, 3(2), 469-489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app3020469




