Changes in Physicochemical Properties and In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch by Ultrasound and Quercetin Dual Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ultrasound-Assisted Preparation of Modified Starch
2.3. Preparation of Ultrasound-Modified Starch Composites
2.4. Observation of Particle Morphology
2.5. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
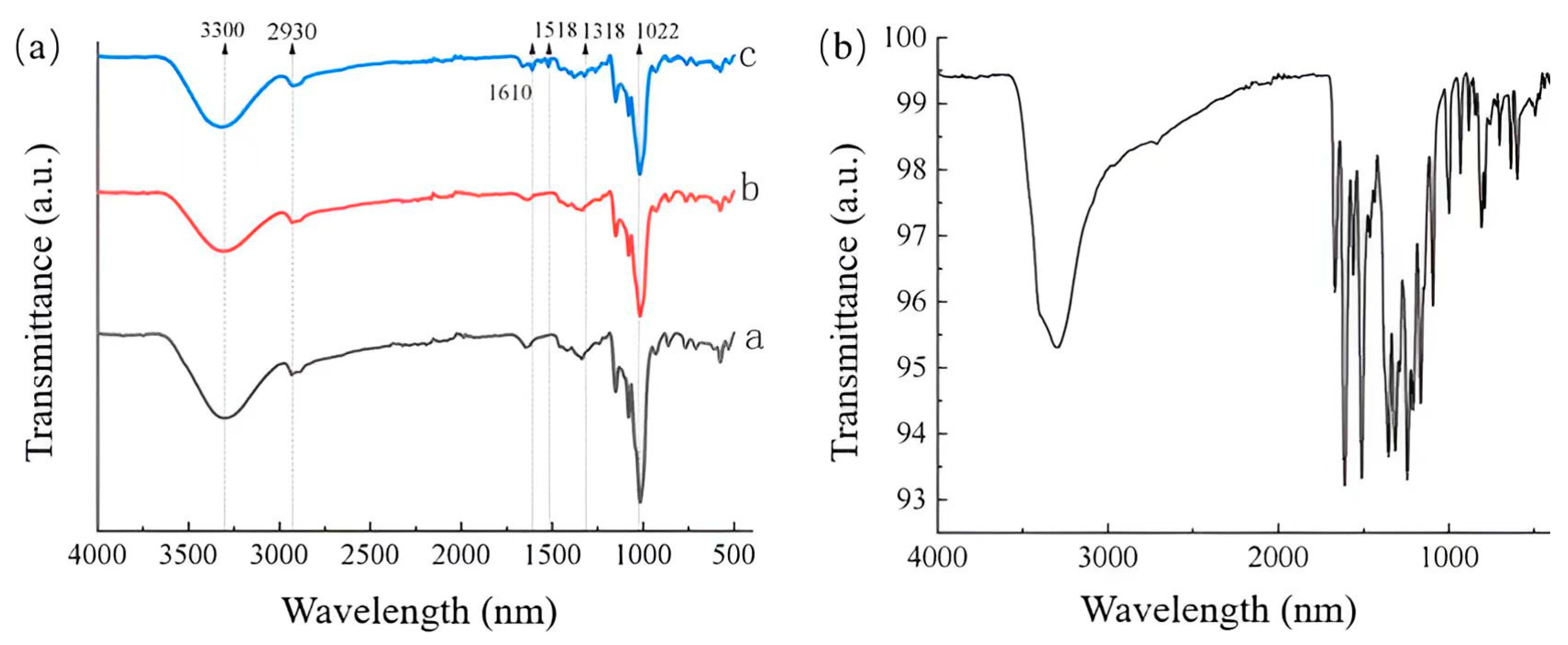
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
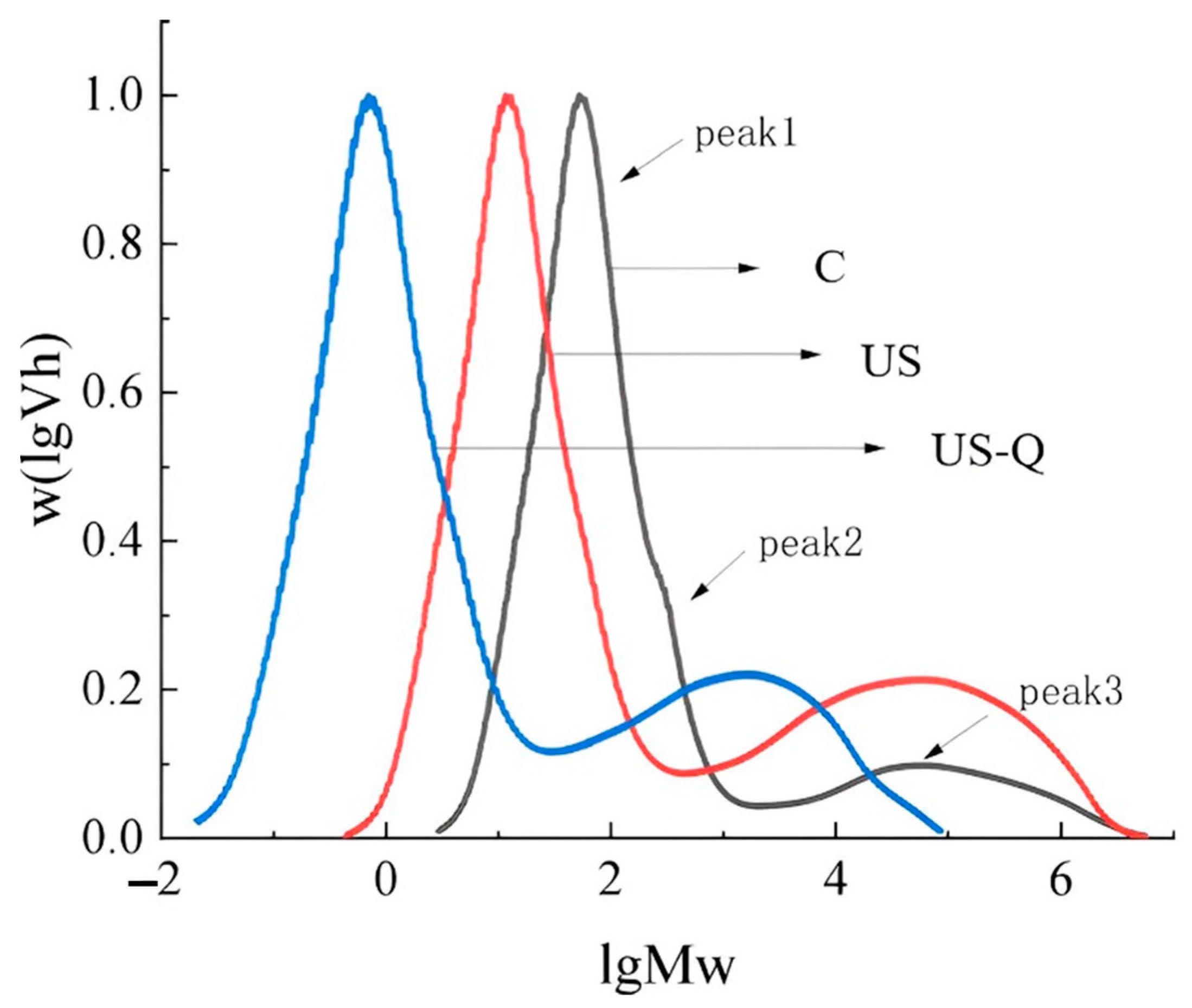
2.7. Determination of Molecular Weight and Chain Length Distribution
2.8. Measurement of Pasting Characteristics
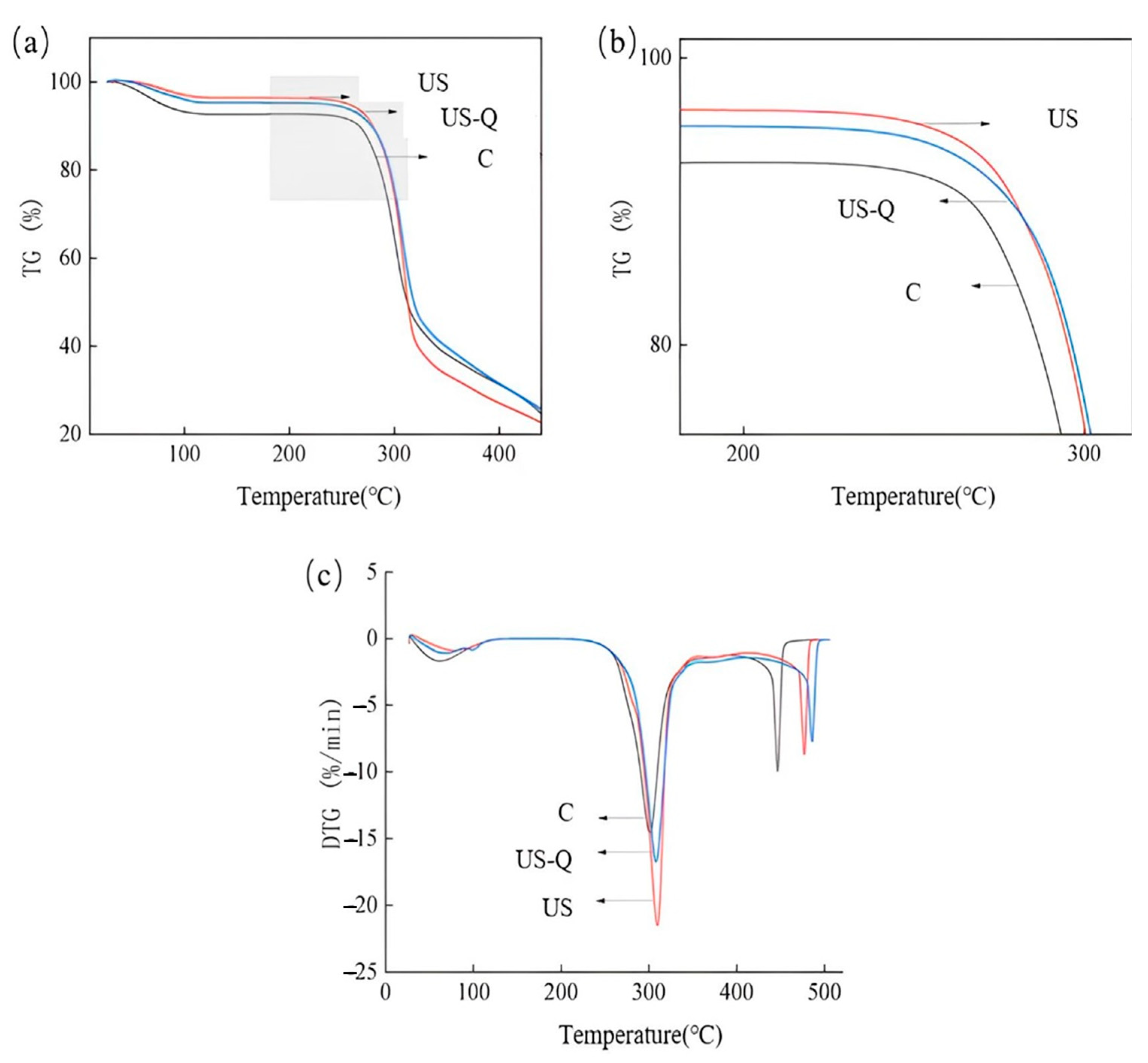
2.9. Thermal Characterization
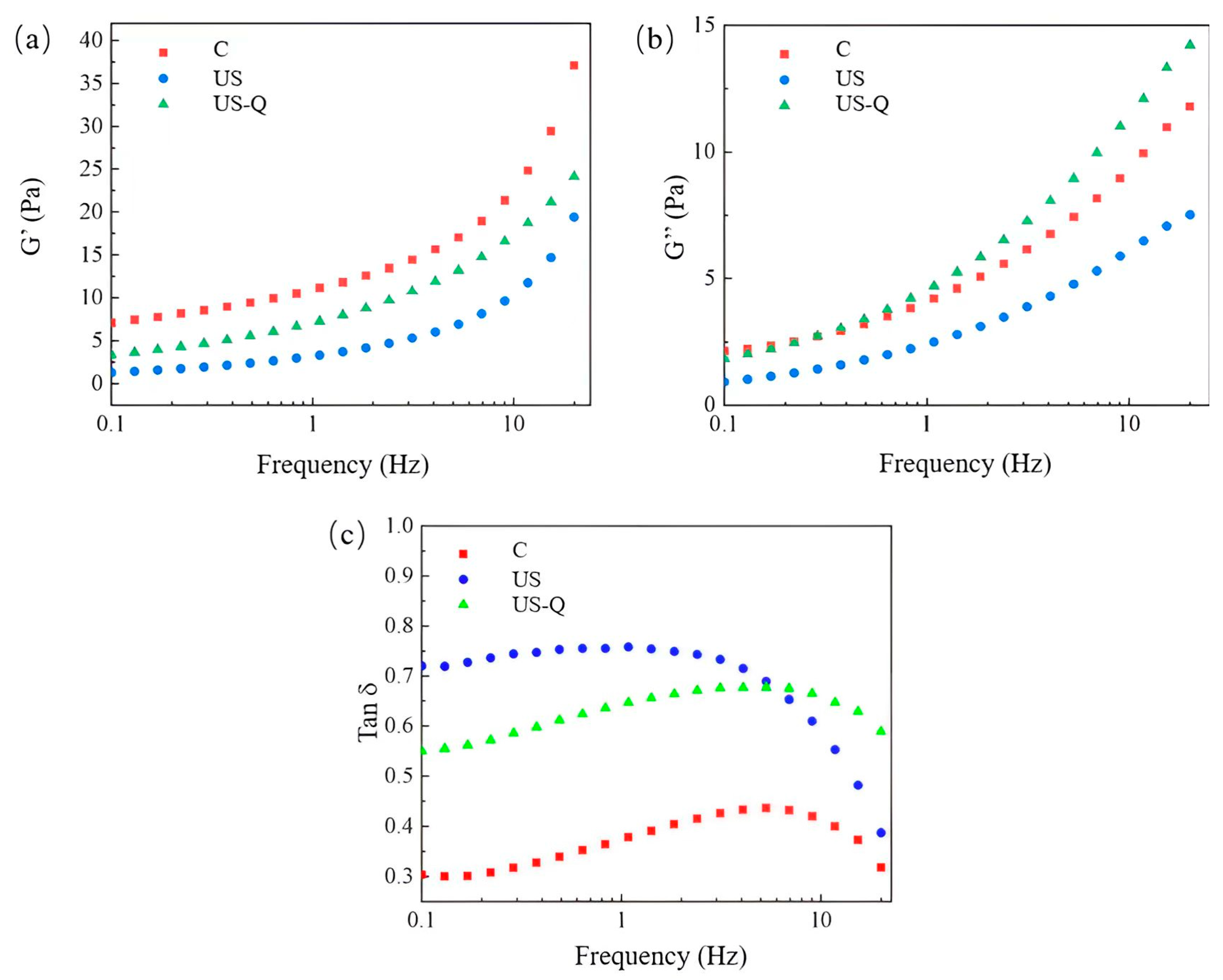
2.10. Dynamic Rheology
2.11. Determination of Solubility and Swelling Power
2.12. Determination of Particle Size of Starch
2.13. In Vitro Digestibility Measurement
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Analysis
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
3.3. FTIR Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Molecular Weight and Chain Length Distribution
3.5. Analysis of Starch Gelatinization Characteristics
3.6. Thermal Performance Analysis
3.7. Analysis of Dynamic Rheology of Starch
3.8. Analysis of Starch Solubility and Swelling Power
3.9. Starch Particle Size Analysis
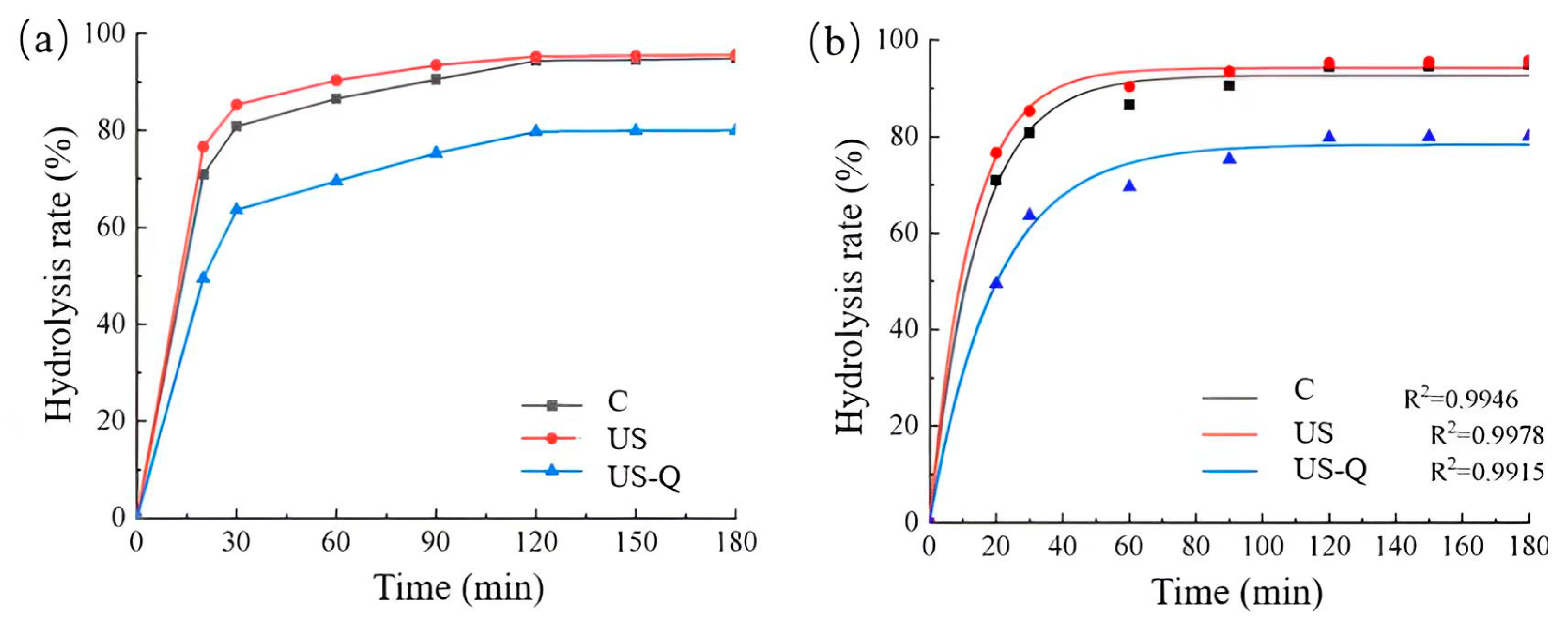
3.10. Effect of Modification on the In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Phillips, J.; Durand-Morat, A.; Nalley, L.L.; Graterol, E.; Bonatti, M.; Loaiza de la Pava, K.; Urioste, S.; Yang, W. Understanding demand for broken rice and its potential food security implications in Colombia. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 15, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Yang, F.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Han, W.; Liu, G.-Q. Preparation and characterization of broken-rice starch nanoparticles with different sizes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apriyanto, A.; Compart, J.; Fettke, J. A review of starch, a unique biopolymer—Structure, metabolism and in planta modifications. Plant Sci. 2022, 318, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korompokis, K.; Verbeke, K.; Delcour, J.A. Structural factors governing starch digestion and glycemic responses and how they can be modified by enzymatic approaches: A review and a guide. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5965–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockyer, S.; Nugent, A.P. Health effects of resistant starch. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 10–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Skąpska, S.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Marszałek, K. Health benefits of resistant starch: A review of the literature. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 93, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masina, N.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Govender, M.; Indermun, S.; Pillay, V. A review of the chemical modification techniques of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, F. Nonthermal physical modification of starch: An overview of recent research into structure and property alterations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniglia, B.C.; Castanha, N.; Le-Bail, P.; Le-Bail, A.; Augusto, P.E.D. Starch modification through environmentally friendly alternatives: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Yu, J. Recent Advances in Physical Processing Techniques to Enhance the Resistant Starch Content in Foods: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Meng, L.; Qiu, L. Recent progress of starch modification assisted by ultrasonic wave. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Effect of a dual modification by hydroxypropylation and acid hydrolysis on the structure and rheological properties of potato starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Gill, B.S. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound treatment on nutritional, rheological and structural properties of starches obtained from different cereals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-H.; Wu, R.-G.; Shao, Y.-Y. The effects of ultrasonic treatment on physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of semigelatinized high amylose maize starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, A.; Nie, M.; Lin, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; et al. New insights into influence of green composite modification on the structure, digestive, and physicochemical properties of rice flour. LWT 2023, 189, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Deng, Z.; Tang, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, T.; Hu, X. Formation, structure and properties of the starch-polyphenol inclusion complex: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Interactions between starch and phenolic compound. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yong, H.; Kan, J.; Zhang, N.; Jin, C. Preparation, characterization, digestibility and antioxidant activity of quercetin grafted Cynanchum auriculatum starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrofi, M.; Abral, H.; Putra, Y.K.; Sapuan, S.M.; Kim, H.-J. Effect of duration of sonication during gelatinization on properties of tapioca starch water hyacinth fiber biocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the cooking and fermentation properties of Shanlan rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zaxilazong; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, W.; Yu, B. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Millet Starch. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, S.M.; Brodusch, N.; Gauvin, R. Investigation of the Effect of Magnification, Accelerating Voltage, and Working Distance on the 3D Digital Reconstruction Techniques. Scanning 2020, 2020, 3743267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Huang, S.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying the formation of starch-lipid complexes during simulated food processing: A dynamic structural analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 244, 116464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, W. The multi-scale structure and physicochemical properties of mung bean starch modified by ultrasound combined with plasma treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H.; Qiu, J.; Cao, R. Enhancement of physicochemical properties and baking quality of broken rice flour through superheated steam. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2024, 7, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Huang, J.; Feng, J.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, R.; Dong, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Luo, Z. Combined ultrasound and germination treatment on the fine structure of highland barley starch. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, I.; Singh, S.; Saxena, D.C. Exploring the influence of heat moisture treatment on physicochemical, pasting, structural and morphological properties of mango kernel starches from Indian cultivars. LWT 2019, 110, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X. Effect of wet media milling on starch-quercetin complex: Enhancement of Pickering emulsifying ability and oxidative resistance. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Li, Y.; Ibáñez, A.M.; Oh, M.H.; McKenzie, K.S.; Shoemaker, C. The effect of rice variety and starch isolation method on the pasting and rheological properties of rice starch pastes. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.; Gunaratne, A.; Ranaweera, K.; Bamunuarachchi, A. Effect of Heat Moisture Treatment Conditions on Swelling Power and Water Soluble Index of Different Cultivars of Sweet Potato (Ipomea batatas (L.) Lam) Starch. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 502457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanta, P.; Kasemwong, K.; Grisdanurak, N. Production and characterization of starch microspheres using supercritical carbon dioxide assisted spray drying. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Luo, F.; Lin, Q.; Ding, Y. Changes in structural, digestive, and rheological properties of corn, potato, and pea starches as influenced by different ultrasonic treatments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujka, M.; Jamroz, J. Ultrasound-treated starch: SEM and TEM imaging, and functional behaviour. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwasra, B.L.; Kaur, M.; Gill, B.S. Impact of ultrasonication on functional and structural properties of Indian wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Xu, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhang, B.; Niu, M.; Zhao, S. Structural changes of rice starch and activity inhibition of starch digestive enzymes by anthocyanins retarded starch digestibility. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, I.; Pooja, N.; Mal, S.S.; Paul, U.C.; Rahman, M.H.; Mazumder, N. An Insight into the Gelatinization Properties Influencing the Modified Starches Used in Food Industry: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 1195–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.K.; Anthero, A.G.d.S.; Emerick, L.B.; Zabot, G.L.; Hubinger, M.D.; Meireles, M.A.A. Low-frequency ultrasound-assisted esterification of Bixa orellana L. seed starch with octenyl succinic anhydride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Fang, H.; Tian, J.; Ye, X. Controlled ultrasound treatments modify the morphology and physical properties of rice starch rather than the fine structure. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonto, A.P.; Tiozon, R.N.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Camacho, D.H. Impact of ultrasonic treatment on rice starch and grain functional properties: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, D.B.; Awika, J.M. Resistant starch formation through intrahelical V-complexes between polymeric proanthocyanidins and amylose. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Cai, S.; Duan, Q.; Huang, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, P.; Xie, F. Combined effect of heat moisture and ultrasound treatment on the physicochemical, thermal and structural properties of new variety of purple rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwar, B.A.; Gani, A.; Shah, A.; Masoodi, F.A. Physicochemical properties, in-vitro digestibility and structural elucidation of RS4 from rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; He, J.; Cheng, K.W.; Dai, S.; Wang, M. Effects of ultrasound-induced V-type rice starch-tannic acid interactions on starch in vitro digestion and multiscale structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidley, M.J.; Hanashiro, I.; Hani, N.M.; Hill, S.E.; Huber, A.; Jane, J.-L.; Liu, Q.; Morris, G.A.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Striegel, A.M.; et al. Reliable measurements of the size distributions of starch molecules in solution: Current dilemmas and recommendations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, R.A.; Seabrook, S.A.; Gidley, M.J.; Gilbert, R.G. Characterization of Starch by Size-Exclusion Chromatography: The Limitations Imposed by Shear Scission. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Feng, C.-H.; Ren, F.; Liu, H. Research progress on the regulation of starch-polyphenol interactions in food processing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J. Dual-frequency ultrasonic effect on the structure and properties of starch with different size. LWT 2019, 106, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhong, F.; Yokoyama, W.; Huang, D.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y. Interactions in starch co-gelatinized with phenolic compound systems: Effect of complexity of phenolic compounds and amylose content of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Gao, W. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro digestibility on solid complex of maize starches with quercetin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Ji, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, N.; Yang, J.; Lu, M.; Han, L.; Wang, M. Evaluation studies on effects of quercetin with different concentrations on the physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Tartary buckwheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Zhou, Q.; Cheng, K.-W.; He, J.; Wang, M. Synergistic impact of ultrasound-high pressure homogenization on the formation, structural properties, and slow digestion of the starch-phenolic acid complex. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsafi, S.R.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Aalami, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Raeisi, M. Physicochemical and morphological properties of resistant starch type 4 prepared under ultrasound and conventional conditions and their in-vitro and in-vivo digestibilities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 53, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, M. Rheological, thermal and in vitro digestibility properties on complex of plasma modified Tartary buckwheat starches with quercetin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on the formation and in vitro digestion of Tartary buckwheat starch/flavonoid complexes. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, A.; Tugrul, N. Effect of ultrasound-microwave and microwave-ultrasound treatment on physicochemical properties of corn starch. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Wang, K.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Ma, X.; Duan, Y.; Xiao, Z. Effects of quercetin on the structure and functional properties of extrusion rice starch. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2024, 40, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufi, S.; Bel Haaj, S.; Magnin, A.; Pignon, F.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Mortha, G. Ultrasonic assisted production of starch nanoparticles: Structural characterization and mechanism of disintegration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, L.; Oliviero, T.; Verkerk, R.; Fogliano, V.; Capuano, E. Interaction of bread and berry polyphenols affects starch digestibility and polyphenols bio-accessibility. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.T.; Kim, H.R.; Moon, T.W.; Choi, S.J. Isothermal and temperature-cycling retrogradation of high-amylose corn starch: Impact of sonication on its structural and retrogradation properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-P.; He, H.; Lu, Y.-H. Four Flavonoid Compounds from Phyllostachys edulis Leaf Extract Retard the Digestion of Starch and Its Working Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7760–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günal-Köroğlu, D.; Catalkaya, G.; Yusufoğlu, B.; Kezer, G.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Capanoglu, E. Quercetin: Potential antidiabetic effects through enzyme inhibition and starch digestibility. Food Saf. Health 2025, 3, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-F.; Xu, H.-X.; Yin, Z.-P.; Chen, J.-G.; Zhang, Q.-F. The combinationeffects of quercetin on starch and digestive enzymes reduce postprandial blood glucose in rats. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, K.; Tomas, M.; McClements, D.J.; Capanoglu, E. Recent advances on the improvement of quercetin bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Peak Viscosity (cp) | Minimum Viscosity (cp) | Attenuation Value (cp) | Final Viscosity (cp) | Return to Life Value (cp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2782 ± 16.34 b | 2782 ± 16.34 a | 2782 ± 16.34 b | 2782 ± 16.34 a | 2782 ± 16.34 b |
| US | 3795 ± 20.32 a | 3795 ± 20.32 b | 3795 ± 20.32 a | 3795 ± 20.32 b | 3795 ± 20.32 a |
| US-Q | 1368 ± 8.95 c | 1368 ± 8.95 c | 1368 ± 8.95 c | 1368 ± 8.95 c | 1368 ± 8.95 c |
| Sample | Solubility (%) | Swelling Power (%) | Average Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 20.33 ± 0.02 a | 10.01 ± 0.05 a | 131.5 ± 10.65 c |
| US | 23.27 ± 0.01 a | 10.26 ± 0.07 a | 314.53 ± 15.21 a |
| US-Q | 12.73 ± 0.03 b | 9.85 ± 0.12 b | 242.53 ± 13.33 b |
| Sample | RDS (%) | SDS (%) | RS (%) | C∞ | k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 70.94 ± 0.53 a | 22.49 ± 0.13 a | 6.57 ± 0.13 a | 92.6 ± 1.30 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a |
| US | 76.63 ± 0.58 c | 18.65 ± 0.16 c | 4.72 ± 0.14 c | 94.21 ± 0.82 c | 0.08 ± 0.01 c |
| US-Q | 49.51 ± 0.42 b | 30.26 ± 0.13 b | 20.23 ± 0.13 b | 78.35 ± 1.47 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, N. Changes in Physicochemical Properties and In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch by Ultrasound and Quercetin Dual Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084203
Yang P, Qiu C, Zhang N. Changes in Physicochemical Properties and In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch by Ultrasound and Quercetin Dual Treatment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084203
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ping, Chenhao Qiu, and Na Zhang. 2025. "Changes in Physicochemical Properties and In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch by Ultrasound and Quercetin Dual Treatment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084203
APA StyleYang, P., Qiu, C., & Zhang, N. (2025). Changes in Physicochemical Properties and In Vitro Digestibility of Broken Rice Starch by Ultrasound and Quercetin Dual Treatment. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084203






