Leveraging Industrial Jarosite Waste for Arsenic(V) and Chromium(III) Adsorption from Water: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
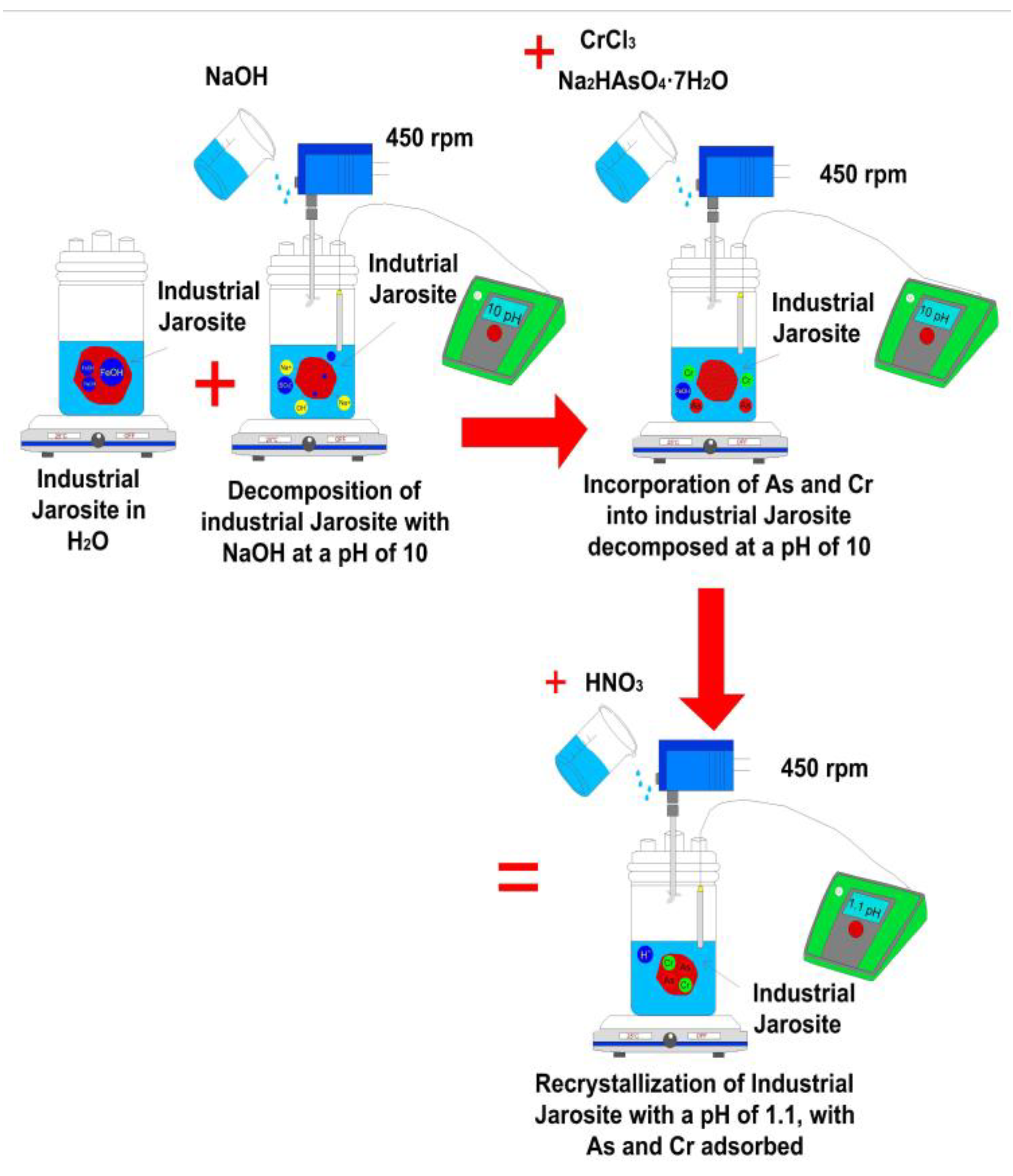
2.1. Sampling of Industrial Jarosite (IJ)
2.2. Adsorption of As(V) and Cr(III) in IJ
2.3. Characterization of Materials
3. Results and Discussion
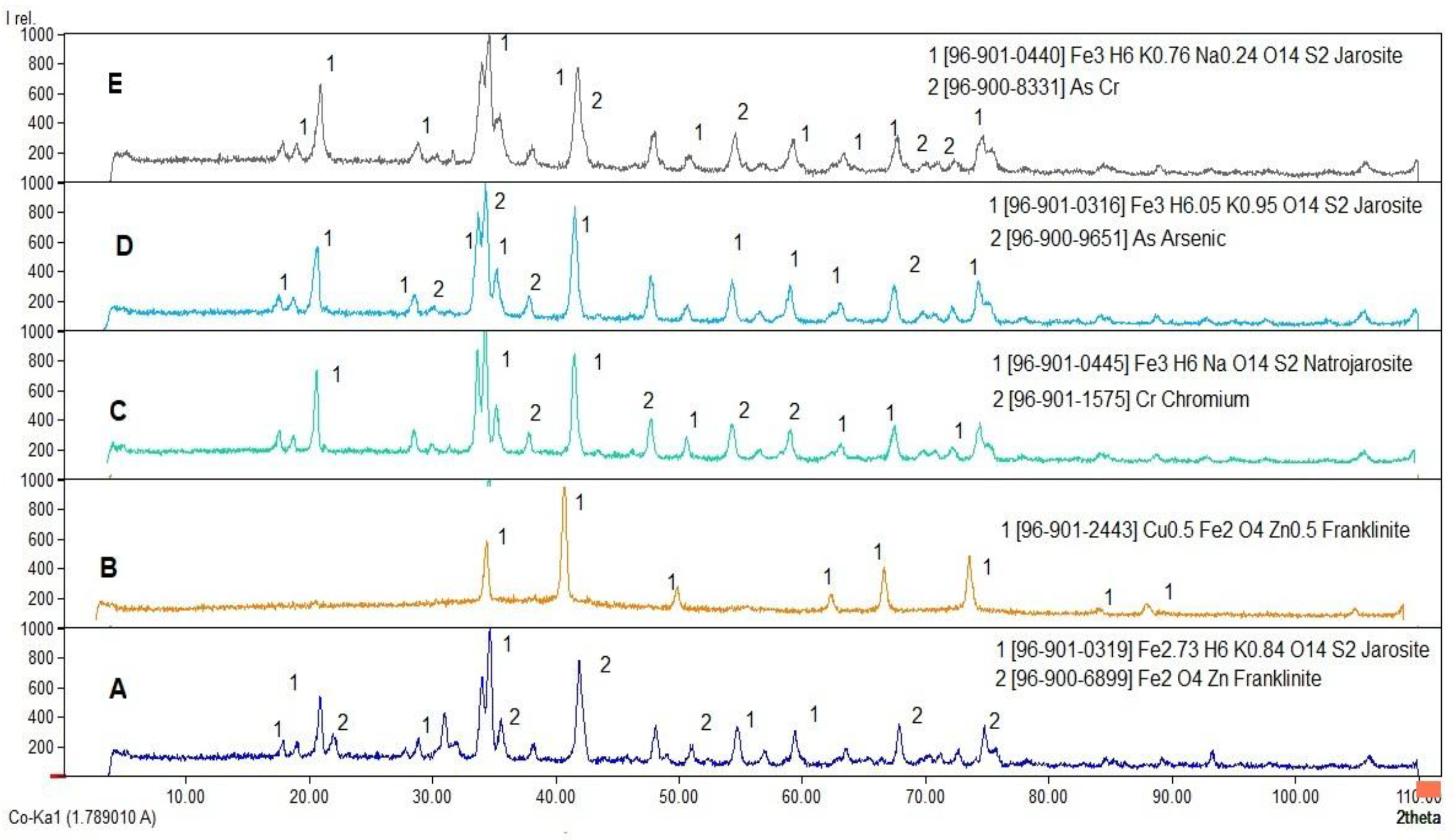
3.1. XRD Analysis
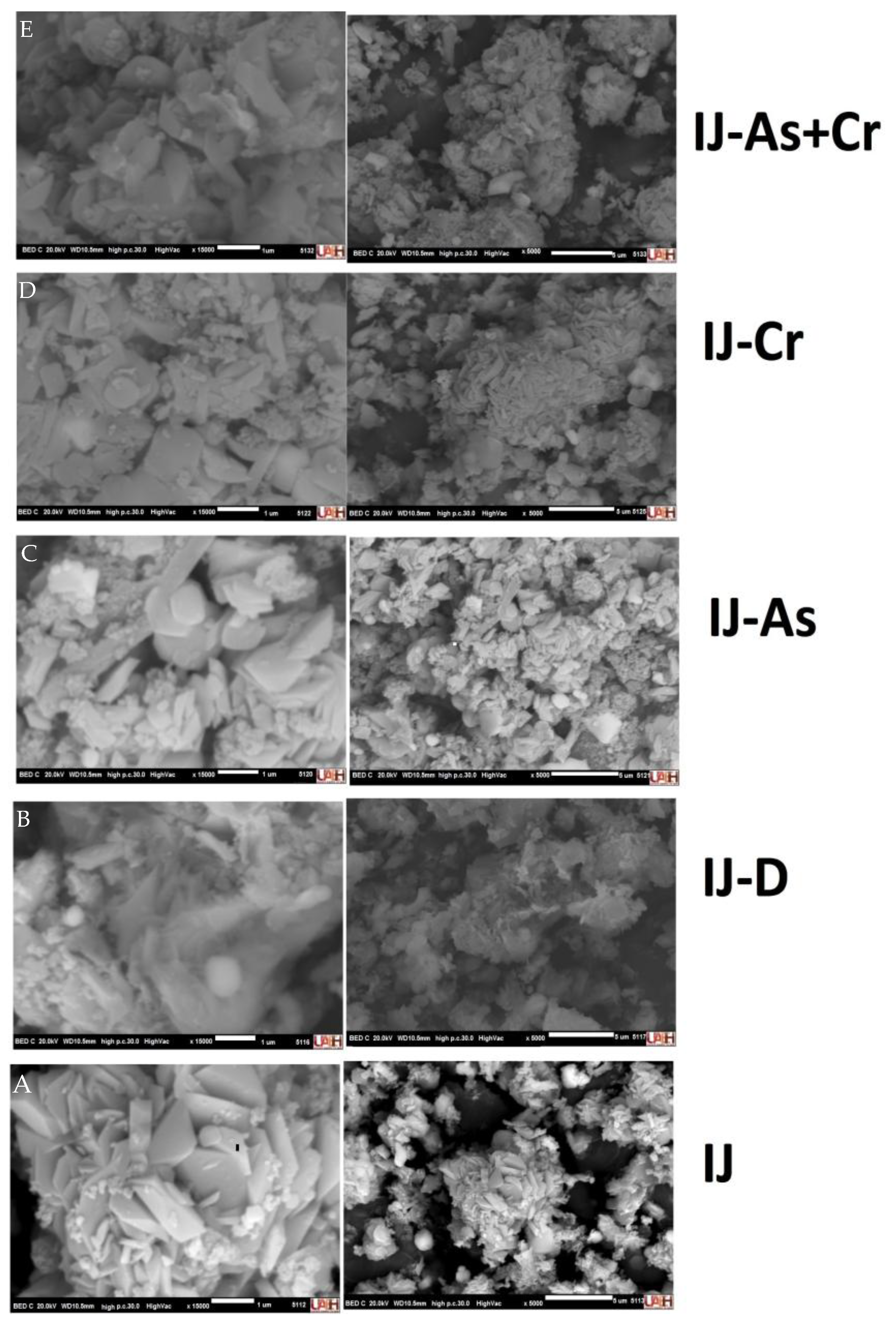
3.2. SEM-EDS Analysis
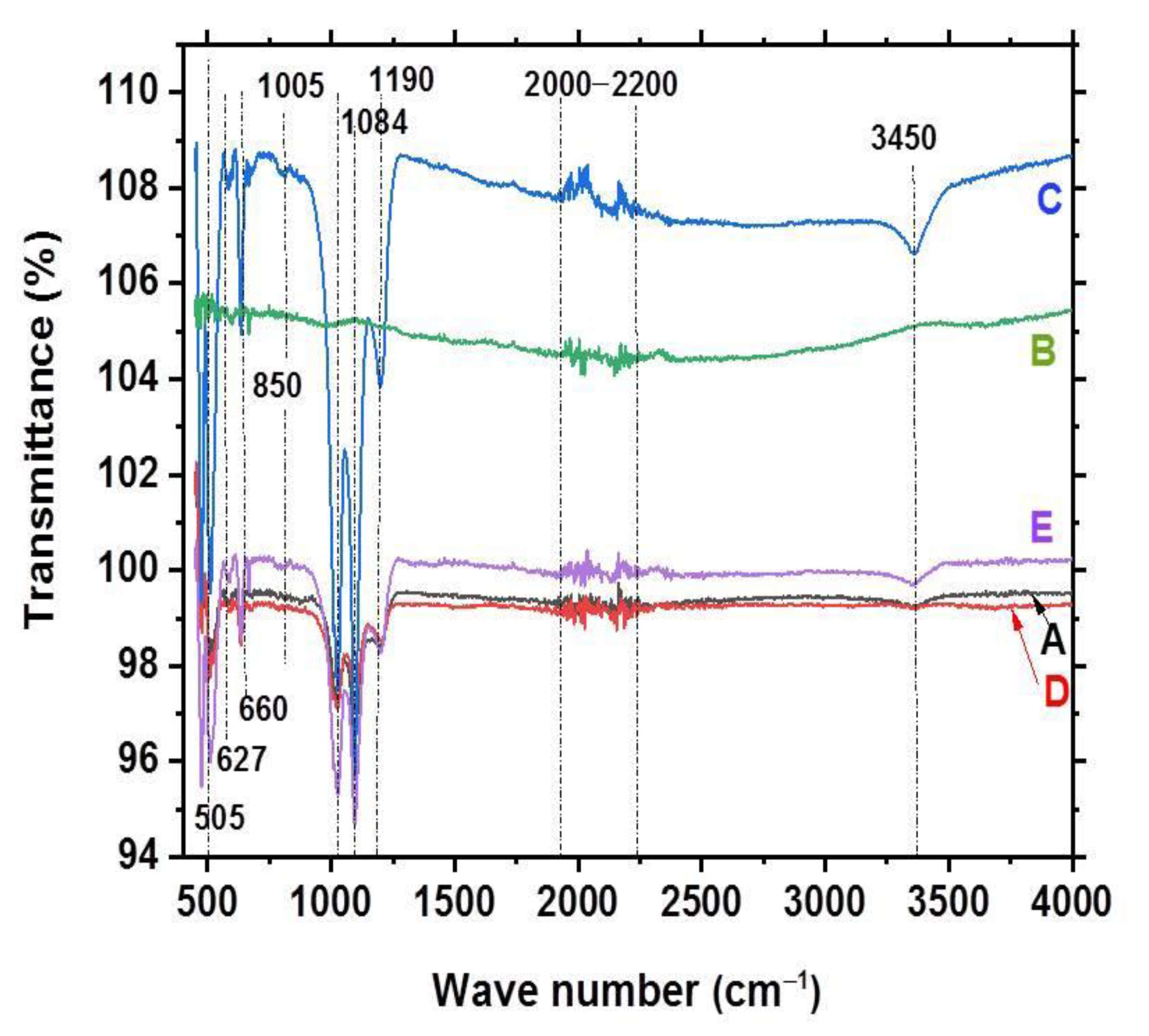
3.3. FTIR Analysis
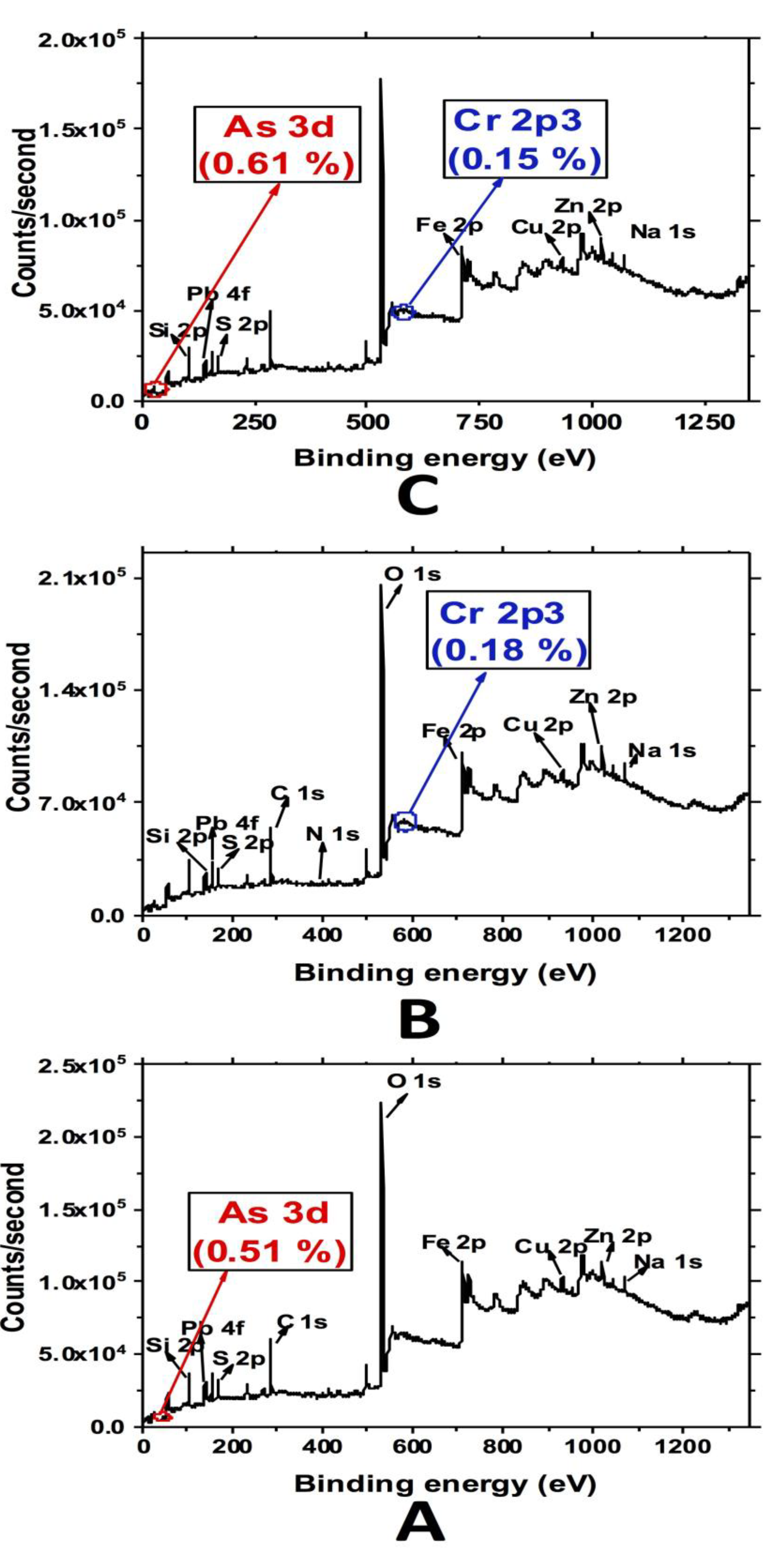
3.4. XPS Analysis
3.5. ICP Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Burgess, J.C. Economics of Water Scarcity and Efficiency. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, J.; Mclntosh, A. Chapter: Water Scarcity. In Environmental Problem Solving in an Age of Climate Change, Voleme One: Basic Tools and Techniques, 1st ed.; Sringer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water Supply and Water Scarcity. Water 2020, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrat, É.; Laurent, A.; Dorber, M.; Rygaard, M.; Verones, F.; Hauschild, M. Advancing water footprint assessments: Combining the impacts of water pollution and scarcity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, R.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, L. Characteristics of Soil Arsenic Contamination and the Potential of Pioneer Plants for Arsenic Remediation in Gold Mine Tailings. Toxics 2023, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endara, A.D.L.M.G.; Heinert, M.E.; Solórzano, H.X.P. Contaminación del agua y aire por agentes químicos. Recimundo 2020, 4, 79–93. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Yadav, P.; Pal, A.K.; Mishra, V. Water Pollutants: Origin and Status. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Materials, 1st ed.; Pooja, D., Kumar, P., Singh, P., Patil, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kushawaha, J.; Chauhan, J.S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Water Pollutants: Sources and Impact on the Environment and Human Health. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Materials, 1st ed.; Pooja, D., Kumar, P., Singh, P., Patil, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nti, E.K.; Cobbina, S.J.; Attafuah, E.E.; Senanu, L.D.; Amenyeku, G.; Gyan, M.A.; Forson, D.; Safo, A. Water pollution control and revitalization using advanced technologies: Uncovering artificial intelligence options towards environmental health protection, sustainability and water security. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Schutte, B.J.; Ulery, A.; Deyholos, M.K.; Sanogo, S.; Lehnhoff, E.A.; Beck, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, M.; Lan, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ru, J. Water Quality Degradation Due to Heavy Metal Contamination: Health Impacts and Eco-Friendly Approaches for Heave Metal Remediation. Toxics 2023, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.W.; Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. A state-of-the-art of phytoremediation approach for sustainable management of heavy metals recovery. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, A.M.; Gamero-Melo, P. Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic (V) and Water. Minerals 2023, 13, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Hernández-Lazcano, E.; Gonzalez-Bedolla, M.J.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Roisales-Ibáñez, R.; Gutiérrez-Amador, M.P.; Sánchez-Castillo, A.; Arenas-Flores, A.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E. Synthesis, Characterization and Decomposition of Potassium Jarosite for Adsorptive As(V) Removal in Contaminated Water: Preliminary Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 15912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; He, B.; Wang, H.; Jin, R.; Tian, T. Remediation of arsenic-and nitrate-contaminated groundwater through iron-dependent autotrophic denitrifying culture. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Shaikh, W.A.; Biswas, J.K. Valorization of invasive plant and leaf litter wastes into biochar: Production, properties and potential for arsenic removal. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 24, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, S. Electrolytic manganese residue-biochar composite for simultaneous removal of antimony and arsenic from water: Adsorption performance and mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Wang, M.H.S.; Shammas, N.K.; Hahn, H.H. Physicochemical Treatment Consisting of Chemical Coagulation, Precipitation, Sedimentation, and Flotation. In Integrated Natural Resources Research. Handbook of Environmental Engineering, 1st ed.; Wang, L.K., Wang, M.H.S., Hung, Y.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 22, pp. 265–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tao, L.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Qiu, S. Arsenic removal from coal by ferric chloride enhanced leaching under ultraviolet irradiation during flue gas desulphuration with coal slurry. Environ. Technol. 2023, 45, 5004–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarhy, G.S.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Omer, A.M.; Eltaweil, A.S. 2D/3D MXene/NiFeMn-layered double hydroxide decorated gelatin for removal of Cr(VI) and Congo red: Performance and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 396, 123889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-Quiñonez, J.L.; Cancino-Gordillo, F.E.; Pal, U. Removal of Cr(III) Ions from Water Using Magnetically Separable Graphene-Oxide-Decorated Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 18491–18507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylyeva, H.; Mironyuk, I.; Strilchuk, M.; Maliuk, I.; Savka, K.; Vasyliev, O. Adsorption and possibility of separation of heavy metal cations by strong cation exchange resin. Chem. Phys. Impacts 2021, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmer, M.F.; Uddin, M.K. Structure properties and industrial applications of anion exchange resins for the removal of electroactive nitrate ions from contaminated water. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33629–33648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Ismail, A.F.; Khongnakorn, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Advances in adsortive membrane technology for water treatment and resource recovery applications: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoti, I.K.; Ogunah, J.; M’Thiruaine, C.M.; Marangu, J.M. Adsorption of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Water Using Zeolite Derived from Agro-Wastes and Clays: A Review. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 4250299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Huang, Z.J.; Wuang, A.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, Z.J.; Cui, X.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Yin, N.Y.; Cui, Y.S. Immobilisation remediation of arsenic-contaminated soils with promising CaAl-layered double hydroxide and bioavailability, bioaccessibility, and speciation-based health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Abdelraheem, W.H.M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Dionysiou, D.D. AsIII-enhanced oxidation by coexisting MnIII-phenolic complexes during arsenic contaminated groundwater treatment by MnO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C.; Lin, Y.; Lee, J.F.; Yi, X.; Dang, Z. Efficient removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by ε-MnO2 adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 141936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, N.; Chang, Y.; Yue, L.; An, L. Natural hydroxyapatite powder from pig-bone waste (pHAP) for the rapid adsorption of heavy metals (Cu) in aqueous solution. Adsorption 2024, 30, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, K.; Sultana, M.; Abid, M.Z.; Quyyum, U.; AlMasoud, N.; Alomar, T.S.; El-Bahy, A.M.; Nasir, M.H.; Hussain, E. Unveiling the impact and selectivity of BiVO4/rGO-SiO2 adsorbents for arsenic in ground water: An effective approach for the public safety. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 139, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnala, S.; Bhushan, B.; Nayak, A. Hydroxyapatite@cellulose@nZVI composite: Fabrication and adsorptive removal of doxycycline, Cr(VI) and As(III) from wastewater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 288, 119796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheverin, V.N.; Diaz, E.M.; Horst, M.F.; Lassalle, V.L. Synthesis of novel magnetic hydroxyapatite-biomass nanocomposite for arsenic and fluoride adsorption. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W. Remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil using nanoscale schwertmannite synthesized by persulfate oxidation with carboxymethyl cellulose stabilization. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Enhancing Coimmobilisation Capacity of Schwertmannite for Arsenic and Cadmium through pH Elevation after Chemical Oxidation. ACS ES&T Eng. 2024, 4, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, D. Sulfidation of nano-Fe/Pd bimetal for highly efficient remediation of Cr(VI) from water: Enhanced reactivity and applicability. Inor. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, K.; Yin, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Cao, Q.; Dang, Z.; Guo, C. Surface properties of schwertmannite with different sulfate contents and its effect on Cr(VI) adsorption. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 373, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Rojo, L.; Marti, V.; Jubany, I.; Bahí, N.; Janer, M.; Martínez-Llladó, X.; Rovira, M. Improvement in Arsenic Adsorption and Calcite Dissolution Kinetics through Size Reduction of a Ferric Hydroxyde-Calcite Adsorbent. Water 2023, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, T.; Campisi, S.; Polito, L.; Arici, S.; Ferruti, L.; Gervasini, A. Adressing the issue of surface mechanisms and competitive effects in Cr (VI) reductive-adsorption on tin-hydroxyapatite in the presence of co-ions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joya-Cárdenas, D.R.; Rodríguez-Caicedo, J.P.; Corona-Rivera, M.A.; Saldaña-Robles, N.; Damián-Ascencio, C.E.; Saldaña-Robles, A. Removal of As(V) in the presence of Cr(VI) in contaminated water from the Bajio region of Mexico using ferrihydrite-functionalized graphene oxide (GOFH): A case study. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Uptake and release of arsenic and antimony in alunite-jarosite and beudantite group minerals. Am. Mineral. 2019, 104, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.F.; Choppola, G.; Lamb, D.; Hamilton, J.L.; Sathish, C.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Naudi, R.; Aughterson, R.; Burton, E.D. Is beudantite a stable host phase of arsenic and lead? New insights from molecular-scale kinetic analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Tang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, H. Mechanism and thermodynamics of scorodite formation by oxidative precipitation from arsenic-bearing solution. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Su, X.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Ou, X.; Cui, Y.; Lin, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S. Cotreatment strategy for hazardous arsenic-calcium residue and siderite tailings via arsenic fixation as scorodite. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 153, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñals, J.; Sunyer, A.; Molera, P.; Cruells, M.; Llorca, N. Arsenic stabilization of calcium arsenate waste by hydrothermal precipitation of arsenical natroalunite. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyer, A.; Viñals, J. Arsenate substitution in natroalunite. A potential medium for arsenic immobilization. Part 1. Synthesis and compositions. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyer, A.; Viñals, J. Arsenate substitution in natroalunite. A potential medium for arsenic immobilization. Part 2. Cell parameters and stability tests. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xue, J.; Cheng, Y.; Nie, Y.; Pi, K.; Du, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, J.; Wuang, Y. Unravelling the impacts of soluble Mn(II)-NOM on arsenic immobilization by ferrihydrite or goethite under aquifer conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Guo, C.; Wuang, C.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, B.; Lu, G.; Reinfelder, J.R.; Dang, Z. Prediction of Cr(VI) and As(V) adsorption on goethite using hybrid surface complexation-machine learning model. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolasco, M.C.; Flores, L.F.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Aguilar, J.; Palacios, E.G.; Flores, M.U.; Rodríguez, I.; Reyes, I.A. Acid dissolution of jarosite-type compounds: Effect of the incorporation of divalent cations into the structure on the reaction rate. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 212, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo-Rodríguez, N.G.; Soria-Aguilar, M.D.J.; Chaidez, J.; Flores, M.; Almaguer-Guzmán, I.; Carrillo-Pedroza, F.R. Analysis of the Behavior of As and Pb during the Pretreatments Applied to a Jarosite Residue for the Recovery of Gold and Silver. Metals 2023, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, A.M.; Khamkure, S.; Gamero-Melo, P. Bifunctional Adsorbents Based on Jarosites for Removal of Inorganic Micropollutants from Water. Separations 2023, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, T.D.; Blackmon, M.D.; Betts, A.R.; Jerden, M.L.; Scheckel, K.G.; Bradham, K.D. Potassium jarosite seeding of soils decreases lead and arsenic bioaccessibility: A path toward concominant remediation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2311564120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, J.; Liu, C.; Ke, P.; Zhao, B.; Hu, Z. Effect of preparation methods on the morphology of jarosite and its adsorption performance for U(VI). J. Ranioanal Nucl. Chem. 2024, 333, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, C.; Huang, Q.; Tao, X.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Dang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, G. Arsenic redistribution associated with Fe(II)-induced jarosite transformation in the presence of polygalacturonic acid. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 935, 173444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhariya, U.; Chien, M.F.; Umetsu, M.; Kamitakahara, M. Effective selenate removal using pH modulated synthesis of biogenic jarosite: Comparative insight with non-biogenic jarosite and biogenic schwertmannite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C. Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, W. Application of fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in sample preparation: Material characterization and mechanism investigation. Adv. Sample Prep. 2024, 11, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassier, C. Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. J. Chem. Educ. 1962, 39, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zou, C.; Mastalerz, M.; Hu, S.; Gasaway, C.; Tao, X. Applications of Micro-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) in the Geological Sciences—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30223–30250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruells, M.; Roca, A. Jarosites: Formation, Structure, Reactivity and Environmental. Metals 2022, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, E.; Roca, A.; Cruells, M.; Patiño, C.; Córdoba, D.A. Characterization and alkaline decomposition-cyanidation kinetics of industrial ammonium jarosite in NaOH media. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Long, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Bai, Z.; Liu, X. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by layered double hydroxide and its composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 1200999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedunkova, O.; Kuznietsov, P.; Gandziura, V. Behaviour of dissolved inorganic salts in the cooling water of a nuclear power plant open recirculation system and formation of water discharge. R. Soc. Open. Sci. 2024, 11, 240492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.J.; Kurniawan, A.; Christidis, G.E.; He, J.Y.; Zhuo, C.H. Interfacial interactions controlling adsorption of metal cations on montmorillonite. Am. Min. 2024, 109, 633–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiar, N.; Suri, R.; McKenzie, E.R. Competitive sorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from stormwater runoff by five low-cost sorbents; Effects of co-contaminants, humic acid, salinity and pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, P. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy: Principles and Spectral Interpretation, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–276. ISBN 978-0-12-804162-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bullen, J.C.; Lapinee, C.; Miller, L.A.; Bullough, F.; Berry, A.J.; Najorka, J.; Cibin, G.; Vilar, R.; Weiss, D.J. Spectroscopic (XAS, FTIR) investigations into arsenic adsorption onto TiO2/Fe2O3 composites: Evaluation of the surface complexes, speciation and precipitation predicted by modelling. Results Surf. Interfaces 2022, 9, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heide, P. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: An Introduction to Principles and Practices, 1st ed.; John Willey & Sons: Hoboke, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–256. ISBN 978-1-118-06253-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Instrumental Methods in Metal Ion Speciation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 1–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, K.; Asghar, S.; Abid, M.Z.; Sultana, M.; Waleed, M.Z.; Hashem, A.; Avila-Quezada, G.D.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Hussain, E. Unveiling the potential of Fe2O3/TiO2 system to produce clean water: An effective and low-cost approach for arsenic removal from ground water. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 52, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, M.L.; Lv, H.G.; He, Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Xue, S.G. Dual-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for As(III) contaminated groundwater remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Xie, X.; Pi, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Spectroscopic and modeling approaches of arsenic (III/V) adsorption onto Illite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 447, 135284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, K.G. Diversity of Iron Oxides: Mechanisms of Formation, Physical Properties and Applications. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, J.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, M.; Thakur, R.R.; Chand, S.; Rout, P.R.; Shaid, M.K. Advances in Nanocomposites for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Water 2024, 16, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element (% wt.) | IJ | IJ-D | IJ-As | IJ-Cr | IJ-As + Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 46.42 | 47.83 | 46.87 | 47.32 | 45.76 |
| Fe | 25.47 | 31.25 | 26.58 | 27.85 | 27.52 |
| S | 12.12 | 4.58 | 12.39 | 11.39 | 10.62 |
| Na | 3.79 | 1.39 | 3.88 | 5.23 | 4.25 |
| Al | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 1.17 | 2.35 |
| Zn | 3.12 | 11.34 | 2.45 | 3.96 | 1.89 |
| Si | 1.02 | 1.09 | 1.59 | 1.22 | 3.94 |
| K | 1.16 | 1.01 | --- | 0.29 | --- |
| As | 0.44 | --- | 1.01 | --- | 1.04 |
| Cr | --- | --- | --- | 0.08 | 0.28 |
| Cu | 1.78 | 0.65 | 1.54 | 1.49 | 2.35 |
| Pb | 3.69 | --- | 2.85 | --- | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Hernández, M.; García-Cerón, A.; Maldonado, R.G.S.; Corro-Escorcia, I.A.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Flores-Badillo, J.; Toro, N.; Saldana, M.; Gutiérrez-Amador, M.P.; et al. Leveraging Industrial Jarosite Waste for Arsenic(V) and Chromium(III) Adsorption from Water: A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031469
Cruz-Hernández M, García-Cerón A, Maldonado RGS, Corro-Escorcia IA, Hernández-Ávila J, Cerecedo-Sáenz E, Flores-Badillo J, Toro N, Saldana M, Gutiérrez-Amador MP, et al. Leveraging Industrial Jarosite Waste for Arsenic(V) and Chromium(III) Adsorption from Water: A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(3):1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031469
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Hernández, Montserrat, Alondra García-Cerón, Ramón G. Salinas Maldonado, Irma A. Corro-Escorcia, Juan Hernández-Ávila, Eduardo Cerecedo-Sáenz, Javier Flores-Badillo, Norman Toro, Manuel Saldana, M. P. Gutiérrez-Amador, and et al. 2025. "Leveraging Industrial Jarosite Waste for Arsenic(V) and Chromium(III) Adsorption from Water: A Preliminary Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 3: 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031469
APA StyleCruz-Hernández, M., García-Cerón, A., Maldonado, R. G. S., Corro-Escorcia, I. A., Hernández-Ávila, J., Cerecedo-Sáenz, E., Flores-Badillo, J., Toro, N., Saldana, M., Gutiérrez-Amador, M. P., Barrientos-Hernández, F. R., & Salinas-Rodríguez, E. (2025). Leveraging Industrial Jarosite Waste for Arsenic(V) and Chromium(III) Adsorption from Water: A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences, 15(3), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031469









