Abstract
Land use patterns significantly influence the quantity and composition of litter in the soil humus layers, thereby affecting the dynamics of soil organic carbon. However, the differences in labile organic carbon fractions and the carbon sequestration index under different land use patterns, as well as their impact on soil carbon storage in the humus layers of mollisols—without migration loss and soil erosion—remain unclear. Labile organic carbon is classified into fractions such as dissolved organic carbon, easily oxidized carbon, particulate organic carbon, and microbial biomass carbon, which are identified through different chemical extraction methods. This study investigates the impact of long-term land use patterns on organic carbon dynamics, organic carbon pools, KOS, and CPMI in mollisols across five treatments: SC (continuous soybean cultivation), MC (continuous maize cultivation), MSR (maize–soybean rotation), GB (grass belt), and FB (forest belt). It also selects three soil depths (0–20 cm, 20–40 cm, and 40–60 cm) over an 11-year period for analysis. The results indicate that soil organic carbon, labile organic carbon fractions (EOC, POC, DOC, and MBC), and CPMI decrease with soil depth, while KOS increases. Non-tillage treatments enhance SOC accumulation in the humus layers, with FB exhibiting the highest organic carbon content, surpassing GB, MC, SC, and MSR by 22.88%, 52.35%, 60.64%, and 80.12%, respectively. Non-tillage treatments can enhance the accumulation of labile organic carbon fractions, aligning with the observed trends in soil organic carbon, with the FB treatment identified as optimal. Additionally, these treatments can increase labile organic carbon fractions and CPMI, thereby improving soil stability. To minimize SOC loss, land use patterns should encourage the conversion of farmland to grassland and forest, with the FB treatment recommended as the optimal strategy for the protection of mollisols and the sustainable development of these soils over the long term. This approach is significant for understanding the soil carbon cycle, rationally planning land use strategies, and providing a reference for enhancing soil quality and ecosystem carbon sinks.
1. Introduction
Soil organic carbon (SOC) is a vital component of the soil carbon pool, and the stability and decomposability of SOC play a crucial role in modulating both regional and local carbon cycles, thereby regulating the exchange of CO2 between the atmosphere and the soil [1]. The estimated global stocks of SOC, extending to a depth of 2 m, are approximately 2400 Gt C [2], which is three times the amount of carbon present in the atmosphere [3]. The global carbon cycle was influenced by the interactions among SOC, the biosphere, and the atmosphere; SOC frequently exchanges carbon dioxide with the atmosphere, with approximately two-thirds of the carbon in terrestrial ecosystems being actively exchanged through SOC [4]. Consequently, changes in SOC can influence atmospheric CO2 concentrations, thereby impacting the global carbon cycle [5]. This indicates that even minor fluctuations in SOC stocks can significantly affect atmospheric CO2 levels and contribute to climate change [6,7]. The primary factors influencing changes in SOC levels include land management practices, land use changes, and climate change [8]. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize land use strategies that enhance organic carbon levels and contribute to climate change mitigation.
The stability and decomposability of SOC are influenced by a multitude of factors. The rate of decomposition of soil organic matter is contingent upon the chemical composition of the input materials, including plant litter and exogenous organic matter [9]. Variations in land use patterns lead to differences in litter types, which directly affect the quantity, quality, and rate of carbon input, thereby significantly impacting biomass and organic carbon reserves. Consequently, the chemical properties and recalcitrance of substances introduced into the soil play a critical role in their sequestration, influencing the accumulation of SOC, its composition, structure, and its vital role in nutrient cycling and carbon emissions to the atmosphere [10]. Additionally, the conversion and accumulation of plant biomass into SOC are markedly affected by factors such as crop types and land use. The intricate interactions among plant biomass, soil microorganisms, soil organic matter, and mineral matrices, along with their dependence on land use and vegetation types, render it exceedingly challenging to elucidate the processes and mechanisms underlying the formation and stabilization of soil organic matter [11].
Soil labile organic carbon (LOC) serves as the principal energy source for plants and soil microorganisms and is directly correlated with nutrient cycling and bioavailability. It is utilized as a sensitive indicator of variations in soil quality. Labile organic carbon fractions, such as dissolved organic carbon (DOC), easily oxidizable organic carbon (EOC), particulate organic carbon (POC), and microbial biomass carbon (MBC), are highly susceptible to the influences of planting patterns, land use practices, and agricultural management measures [12,13,14]. In contrast to maize–soybean rotation, continuous maize cultivation inputs more biomass carbon into the soil, resulting in a higher content of soil particulate organic matter (POM) [15]. Studies examining land use patterns on the Loess Plateau indicate that the response rates of EOC, light fraction organic carbon (LFOC), DOC, and POC to different land use patterns are more rapid than those of SOC. Furthermore, the total amounts of SOC and EOC in grassland and forestland exceed those in farmland [16]. The transformation of evergreen broadleaf forests into tea and bamboo plantations reduces the concentrations of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC), light/heavy-fraction organic carbon (LFOC, HFOC), and humic carbon (HC) [13]. Soil microbial biomass, primarily composed of bacteria and fungi, features a short turnover time and rapid rate, responding promptly to alterations in land use patterns and management. MBC and nitrogen regulate the C and N cycles in terrestrial ecosystems and play a crucial role in nutrient transformation and supply. This not only reflects soil microbial activity but also characterizes the available LOC fractions in the soil [17]. Wang et al. [18] confirmed that shrubs and forestland can enhance SOC storage more effectively than farmland. However, Pathak’s study indicated that the contents of MBC and microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) in farmland are higher than those found in grassland and forestland. In the wheat–pearl millet farmland, the MBC and MBN contents in the 0–10 cm soil layer were measured at 418.2 µg/g and 52.9 µg/g, respectively; in contrast, the lowest values were observed in teak forestland, with measurements of 281.2 µg/g for carbon and 36.02 µg/g for nitrogen, while grassland exhibited slightly higher values than teak forestland, at 298.3 µg/g and 37.28 µg/g, respectively [19]. It suggests that soil LOC fractions are highly sensitive to land use patterns, and this sensitivity is not dependent on the soil’s inherent organic carbon reserves [20].
The spatial heterogeneity of SOC content leads to a slow response to subtle variations in the soil environment [21]. Measuring SOC and LOC content does not provide a comprehensive or real-time assessment of changes in soil quality [22]. This limitation highlights the necessity for more holistic approaches that capture the complexity of soil health and its evolution. In this context, CPMI, CPI, and CAI have emerged as innovative tools that address these challenges. By integrating these indices, the CPMI enables dynamic and continuous monitoring of the soil carbon pool, which is essential for understanding the various factors that influence soil health. Furthermore, the CPMI facilitates a detailed examination of how different elements, such as climate change and land use patterns, affect soil carbon dynamics [23]. This capability is particularly important as it allows researchers and land managers to effectively quantify and analyze fluctuations in soil organic carbon across diverse soil environments. By employing the CPMI, stakeholders can achieve a more timely and accurate characterization of the changes occurring within the soil carbon pool, ensuring that their strategies for soil management and conservation are informed by robust data and insights [24]. Additionally, the oxidation stability coefficient (KOS) serves as an effective parameter for measuring changes in the LOC fractions of soil and its fertility. KOS gauges soil oxidation stability and is related to different factors, such as the difficulty of soil organic carbon decomposition and nutrient release [25]. A larger KOS value indicates greater oxidation stability, signifying that the decomposition of soil organic carbon is more challenging and nutrient release is relatively slow, which positively contributes to maintaining soil fertility [26]; conversely, a smaller KOS value reflects lower oxidation stability, suggesting that the decomposition of soil organic carbon is easier and nutrient release is faster, potentially jeopardizing the long-term maintenance of soil fertility [27].
This study utilized mollisols from Northeast China as the test soil and, based on long-term positioning experiments, analyzed and compared the effects of five different land use methods on the organic carbon and labile organic carbon components of soil humus layers at depths of 0–20 cm, 20–40 cm, and 40–60 cm. This study conducted an in-depth examination of soil organic carbon and its active components, as well as the distribution characteristics of CPMI and KOS within the black soil humus layer, under different land use patterns. The findings aim to enhance the organic carbon sequestration capacity of mollisols and estimate the potential for soil carbon sequestration in this region, which holds significant importance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The research was conducted at the experimental base of Jilin Agricultural University, located in Changchun City, Jilin Province, China. The geographical coordinates of this location are 43.82° N latitude and 125.40° E longitude, as depicted in Figure 1. The study site is situated within the Songliao Plain, characterized by its flat terrain and an elevation ranging from 250 to 350 m above sea level. The region exhibits a typical north temperate continental monsoon climate, placing it in a transitional zone between humid and semi-arid climates. Climatically, the area has an annual average temperature of approximately 4.6 °C. It also benefits from an average of 2700 h of sunshine annually, which significantly enhances agricultural productivity. The frost-free period extends for 140 to 150 days, providing a favorable timeframe for farming activities. Additionally, the average annual precipitation ranges from 600 to 700 mm, with the majority occurring during the summer months (June to September). This precipitation pattern is critical for assessing water availability for crops and overall agricultural practices in the region.
Figure 1.
Study site.
The soil in the area was classified as mollisols (according to the soil taxonomy of the USA) [28]. Its basic properties are as follows (Table 1).

Table 1.
Basic properties of the soil at the beginning of the experiment.
2.2. In Situ Experiment
The experiment commenced in 2010 and constitutes a long-term positioning test covering an area of 84 m × 160 m (Figure 2). A plot with adjacent level terrain and relatively homogeneous basic soil fertility was chosen, and five treatments were configured, respectively: (1) continuous soybean cultivation (SC); fertilizer application: diammonium phosphate 120 kg·ha−1, potassium oxide 90 kg·ha−1; (2) continuous maize cultivation (MC); only compound fertilizer was applied, N-P2O5-K2O (26-10-12), with an application rate of 260 kg·ha−1; (3) maize–soybean rotation (MSR); single application of compound fertilizer, N-P2O5-K2O (26-10-12), with an application amount of 260 kg·ha−1; (4) Recreational Grass Belt, referred to as grass belt (GB): no crops were planted, no fertilization was conducted, and vegetation grew naturally; (5) Fallow Forest Belt, referred to as forest belt (FB): poplar trees (Populus L.) were planted and grew naturally, without tillage and any fertilizer application. Each treatment was replicated three times. The soybean variety used was Jinong 40, while the maize variety was Xianyu 335. The planting of crops was undertaken in May, with harvesting occurring in October. Prior to the spring planting, both maize and soybean fields required fertilization. All the fertilizers required in this experiment were from Liaoning Feichi Fertilizer Industry Co., Ltd. (Dandong, China). It was essential to fertilize the base of the field trench before sowing at the end of April, after which it was covered with a thin layer of soil. The crops were subsequently planted in May and were maintained through weeding with tools throughout the growing season. Following the harvest in October, all maize and soybean straw was mechanically crushed and returned to the soil. Additionally, grass in the GB treatment and trees in the FB treatment grew naturally without artificial interference or fertilization.
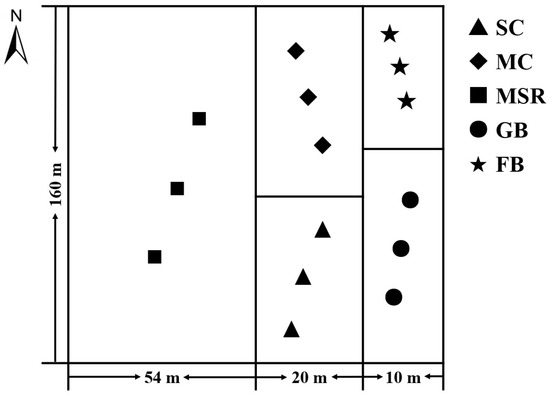
Figure 2.
Distribution of soil humus layers under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB).
2.3. Soil Sampling
The work of this experiment was initiated in the spring of 2020, with seeding conducted in late April and harvest accomplished in early October. MSR was sown with maize this year, and the growth of field crops was investigated throughout the growing season. Soil samples were systematically collected following the autumn harvest, adhering to a structured methodological framework. Each treatment district was randomly divided into three distinct areas, enabling a comprehensive assessment across varied sections, from which soil samples were carefully gathered. Prior to sample collection, the vegetation covering the soil surface was methodically removed to ensure that the samples accurately reflected the soil composition. Soil samples were extracted from three specified depth intervals: 0 to 20 cm, 20 to 40 cm, and 40 to 60 cm. To preserve their integrity, freshly collected soil samples, processed through a 2 mm soil sieve, were promptly placed into ziplock bags. These bags were then transported to the laboratory without delay, utilizing an ice pack to maintain the necessary temperature. During sample preparation, any visible animal and plant residues, as well as stones, were meticulously removed to ensure that only the soil was analyzed for its properties. A portion of the soil samples was air-dried at room temperature, specifically for the analysis of SOC, EOC, and POC. Meanwhile, another section of the samples was kept moist at a temperature of 4 °C, which was essential for conducting analyses related to MBC and DOC. This dual approach in sample processing facilitated a thorough investigation of the soil’s properties, thereby enhancing our understanding of its ecological status and functionality.
2.4. Analysis Methods
The determination of soil organic carbon (SOC) content was conducted using the K2Cr2O7-volumetric method [29], a well-established technique in soil analysis. This method enables accurate quantification of SOC, providing essential insights into soil fertility and health. Additionally, the measurement of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was performed using a 0.5 mol L−1 K2SO4 solution, which effectively extracts and quantifies DOC, crucial for understanding carbon dynamics within the soil [30]. Furthermore, the content of easily oxidized carbon (EOC) was assessed using a 333 mol L−1 KMnO4 solution, allowing researchers to measure the readily available carbon fractions that microorganisms can easily utilize [23]. The evaluation of microbial biomass carbon (MBC) was carried out via chloroform fumigation, a technique that estimates the carbon directly associated with the microbial community in the soil [31]. Finally, the measurement of particulate organic carbon (POC) was achieved using (NaPO3)6, indicating the carbon that remains within the soil matrix in particulate form [32].
To enhance the understanding of soil carbon dynamics, several indices were calculated, namely the carbon pool active degree (CA), carbon pool active index (CAI), carbon pool index (CPI), and carbon pool management index (CPMI). These calculations followed established protocols based on previous research, providing a framework for assessing the active capacity of soil carbon and its management [23]. In this paper, we selected a soil sample collected from bare land in the same area, and in close proximity to each other, as the reference point for calculating the CAI, CPI, and CPMI. The choice of bare land as the reference is justified, as the levels of SOC in crop land are generally among the lowest observed in this study; this comparative analysis is crucial for understanding how land management practices impact soil carbon pools.
CA = Sample EOC/Sample (SOC − EOC),
CAI = CA in sample soil/CA in reference soil,
CPI = Sample SOC/Reference SOC,
CPMI = CPI × CAI × 100%.
The difference between total and labile organic C is termed as the non-labile organic C, and the oxidation stability coefficient (Kos) is calculated by dividing the non-labile organic C content by the labile organic C content [23]:
Oxidation stability coefficient (Kos) = Sample (SOC − EOC)/Sample (EOC).
2.5. Statistical Analyses
The experimental data exhibited a normal distribution, indicating that the underlying assumptions for statistical analysis were satisfied. To assess the differences among the various treatments applied during the study, a one-way ANOVA was utilized, which allowed for the identification of statistically significant differences between the means of the groups. Following this analysis, multiple comparisons of the means were conducted using Fisher’s protected least significant difference (LSD) test, specifically ensuring that the significance level was set at p < 0.05. This comprehensive statistical analysis was carried out employing SPSS software version 26 (IBM Statistics 26.0, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). In addition to these analyses, Pearson correlation analysis was implemented to explore the relationships among different soil carbon fractions, providing insights into the interactions and dependencies within the soil carbon dynamics. The visual representation of the data was achieved through the creation of graphics, which were generated using Origin 2021 software (OriginPro 2021, OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA). Furthermore, to enhance the geographical aspect of the study, maps were drawn using ArcMap 10.8 (Esri Corporation, Redlands, CA, USA), ensuring accurate spatial representation of the experimental findings.
3. Results
3.1. SOC Content
SOC content is illustrated in Figure 3. As the soil profile deepens, the SOC content for each treatment exhibits a consistent pattern of gradual decrease from the surface layer to the bottom layer. Throughout the research process, the SOC content across the 0–60 cm range was highest in the FB treatment and lowest in the MSR treatment. In the 0–20 cm soil layer, the variation in SOC content among all treatments was most pronounced, with the order of abundance being FB > GB > MC ≈ SC > MSR. Notably, the FB treatment was significantly higher than the others, with increases of 22.88%, 52.35%, 60.64%, and 80.12% compared to GB, MC, SC, and MSR, respectively. Each treatment experienced a substantial decrease in SOC content in the 20–40 cm and 40–60 cm soil layers, with trends mirroring those observed in the surface layer. These results indicate that the forest belt has a more pronounced effect on enhancing soil organic carbon levels compared to other land use patterns.
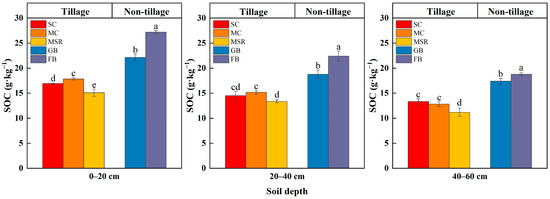
Figure 3.
Soil organic carbon (SOC) concentration in soil humus layers of mollisols under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB). Different letters mean significant differences among different land use patterns in the same soil layer at 0.05 level. n = 3. The same is below.
3.2. LOC Fractions
3.2.1. Changes in DOC
The impacts of diverse land use patterns on the content of DOC in each soil layer are illustrated in Figure 4. This study indicates that land use patterns significantly influence soil DOC levels. In terms of vertical distribution, the DOC content in each treatment decreases with increasing soil depth. The FB treatment exhibited the most substantial decrease at 30.94%, whereas the SC treatment demonstrated the smallest decrease at 20.03%. Notably, there are marked differences among the same treatments at equivalent depths. The DOC content in the 0–20 cm soil layer of each treatment follows the following order: FB > GB > MC > SC > MSR. Compared to GB, FB significantly enhanced the DOC content by 22.88%, while MC, SC, and MSR significantly reduced the soil DOC content, with decreases of 20.46%, 24.65%, and 31.78%, respectively. SC shows no significant difference when compared to MC and MSR; however, the DOC content of MSR is significantly lower than that of MC. Notably, the MSR treatment ranks the lowest among all treatments and also among the three treatments in the field. Considerable decreases are also observed in the 20–40 cm and 40–60 cm soil layers, with trends similar to those observed at the surface.
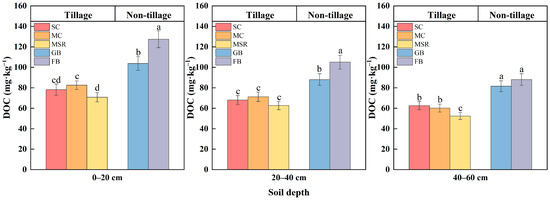
Figure 4.
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration in soil humus layers of mollisols under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB). Different letters mean significant differences among different land use patterns in the same soil layer at 0.05 level. n = 3. The same is below.
3.2.2. Changes in EOC
The effects of different land use patterns on the concentrations of EOC across different soil layers are illustrated in Figure 5. This study demonstrates that land use patterns significantly influence EOC levels in the soil. In terms of vertical distribution, EOC concentrations in all treatment soil layers decreased with increasing depth, with the most pronounced decrease observed in the SC treatment (60.48%) and the least in the FB treatment (43.81%). Notable differences were evident between treatments at the same soil depth. The concentrations of easily oxidizable organic carbon in the 0–20 cm soil layer, ranked by treatment, are as follows: FB > GB > SC ≈ MC > MSR, with no significant differences among these treatments. Compared to GB, FB exhibited an increase of 3.47%, while SC, MC, and MSR showed reductions in EOC content of 10.7%, 11.76%, and 21.93%, respectively. Notably, the MSR treatment not only recorded the lowest EOC levels among all treatments but also ranked lowest among the three treatments conducted in the field. Furthermore, the reductions observed in the 20–40 cm and 40–60 cm soil layers were greater than those in the surface layers, displaying a similar trend.
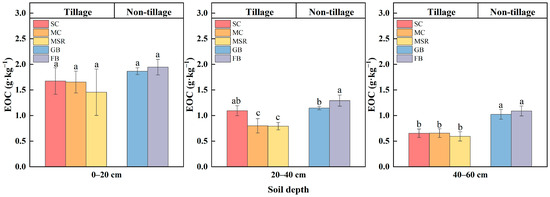
Figure 5.
Easily oxidized carbon (EOC) concentration in soil humus layers of mollisols under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB). Different letters mean significant differences among different land use patterns in the same soil layer at 0.05 level. n = 3. The same is below.
3.2.3. Changes in POC
The effects of different land use patterns on the POC content in different soil layers are illustrated in Figure 6. Land use patterns exhibit distinct responses regarding soil POC. In terms of vertical distribution, POC in each treatment decreased with increasing soil depth, with the most significant decrease observed in the MSR treatment (31.91%) and the least in the SC treatment (16.67%). Notable differences exist among the treatments at the same soil depth. The POC content in the 0–20 cm soil layer for each treatment is ranked as FB > GB > MSR > MC ≈ SC. Significant differences were found between treatments, with FB exhibiting a 3.58% higher POC content than GB. While no significant differences were noted between SC and MC, both treatments had POC content that was significantly higher than the other three treatments. SC, MC, and MSR treatments resulted in reductions in soil POC content of 60.14%, 56.73%, and 32.2%, respectively. The POC content in the MSR treatment was significantly higher than that in the two consecutive cultivation treatments, SC and MC, which did not show significant differences between them. SC demonstrated the lowest POC content among all treatments and was also the lowest in the field across the three treatments. All treatments exhibited substantial decreases in the 20–40 cm soil layer, with a trend similar to that observed in the surface layers; however, MC showed slightly lower POC content than SC in the 40–60 cm soil layer.
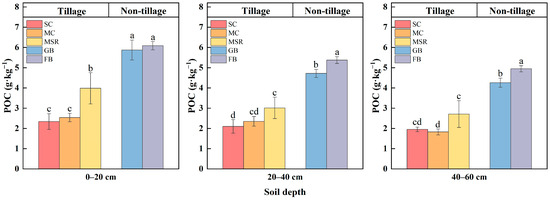
Figure 6.
Particulate organic carbon (POC) concentration in soil humus layers of mollisols under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB). Different letters mean significant differences among different land use patterns in the same soil layer at 0.05 level. n = 3. The same is below.
3.2.4. Changes in MBC
The effects of different land use patterns on the content of MBC across different soil layers are illustrated in Figure 7. These land use patterns exhibit distinct responses in relation to soil MBC. In terms of vertical distribution, the MBC content in each treatment decreases with increasing soil depth, with the most significant reduction observed in the FB treatment at 70.53%, and the smallest reduction in the SC treatment at 21.16%. Notable differences exist between the different treatments within the same soil layer. Specifically, the MBC content in the 0–20 cm depth for each treatment is ranked as FB > GB > MC > MSR > SC, with the FB treatment demonstrating a significantly higher MBC content compared to the other land use patterns. In comparison to GB, the FB treatment shows an increase of 20.25%. Conversely, the SC, MC, and MSR treatments lead to reductions in soil MBC content, with declines of 64.32%, 45.66%, and 48.49%, respectively. There are no significant differences between MC and MSR, both of which are significantly higher than the SC treatment, which has the lowest MBC content among all treatments and within the three farming treatments. However, the MBC content for each treatment in the 20–40 cm and 40–60 cm soil layers differs slightly from that in the 0–20 cm layer, following the trend FB > GB > SC > MC > MSR.
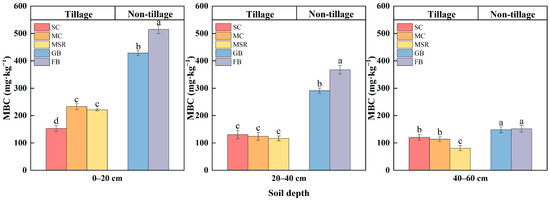
Figure 7.
Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) concentration in soil humus layer of mollisols under different land use patterns. Note: The experiment treatments included continuous soybean cultivation (SC), continuous maize cultivation (MC), maize–soybean rotation (MSR), grass belt (GB), and forest belt (FB). Different letters mean significant differences among different land use patterns in the same soil layer at 0.05 level. n = 3. The same is below.
3.3. Proportions of LOC Fractions Under Different Land Use Patterns
Table 2 illustrates the impacts of different land use patterns on the percentage of labile components of SOC within the humus layers of mollisols, specifically in relation to SOC. The ratios expressed in terms of LOC, which aggregates EOC, DOC, MBC, and POC, are presented below. Generally, the ratios LOC/SOC, EOC/LOC, and MBC/LOC for each treatment predominantly decreased with increasing soil depth, whereas DOC/LOC and POC/LOC exhibited a tendency to increase with soil depth. The ratio of LOC to SOC ranged from 20.71% to 37.76%. The ratios of EOC, DOC, MBC, and POC to LOC were 17.34% to 39.47%, 1.25% to 1.86%, 2.38% to 5.94%, and 55.03% to 78.84%, respectively, indicating that LOC constituted a relatively minor proportion of the soil in this study area. Notably, POC and EOC comprised a larger fraction of LOC compared to DOC and MBC. At different soil depths, the LOC/SOC and POC/LOC ratios within the 0–60 cm range were significantly higher in MSR, GB, and FB compared to SC and MC (EOC/LOC > LOC/SOC > MBC/LOC > DOC/LOC); for MSR, GB, and FB, the order was POC/LOC > LOC/SOC > EOC/LOC > MBC/LOC > DOC/LOC.

Table 2.
Ratios of LOC fractions under different land use patterns.
3.4. Effects of Different Land Use Patterns on CMPI
The effects of different land use patterns on the soil CPMI of the humus layers are presented in Table 3. It is evident that as the depth of the humus layers increases, the CPMI for all treatments exhibits a decreasing trend to varying degrees, with the most significant reduction observed in SC (62.96%) and the least in FB (44.80%). Regarding lateral distribution, notable differences are apparent among the different treatments, with the carbon pool management index for non-cultivated treatments being significantly higher than that for cultivated treatments. In the 0–20 cm soil layer, the order of CPMI was FB > GB > SC > MC > MSR, with FB being 2.85% greater than GB, while SC, MC, and MSR were 8.65%, 10.38%, and 20.49% lower than GB, respectively, although no significant differences were found among these treatments. A similar trend was observed in the 20–40 cm soil layer, where MC and MSR showed no significant differences; FB was 12.26% higher than GB, and SC, MC, and MSR were 2.98%, 30.78%, and 30.88% lower than GB, respectively. FB, GB, and SC did not differ significantly from each other but were significantly higher than the other two treatments. In the 40–60 cm soil layer, FB maintained the highest CPMI, followed closely by GB, with no significant difference between them; both were significantly higher than SC, MC, and MSR. Specifically, SC, MC, and MSR were lower than GB by 36.60%, 36.34%, and 42.29%, respectively, while FB and GB were 67.15% and 57.09% higher than MC.

Table 3.
Effects of different land use patterns on carbon pool management index (CPMI) of soil humus layers.
3.5. Effects of Different Land Use Patterns on KOS
As shown in Table 4, the depth of the humus layers correlated with varying increases in KOS across all treatments, except for the lower layer of the FB treatment. The most significant increase was observed in SC (110.01%), while the smallest increase was noted in FB (25.86%). Tillage treatments generally resulted in a reduction of KOS in the surface layer (0–20 cm) across all treatments, with notable differences among different land use patterns. The non-tillage treatments exhibited significantly higher KOS than the tillage treatments. No significant difference was observed between GB and FB, nor among SC, MC, and MSR. The KOS ranking was as follows: FB > GB > MSR > MC > SC. In the 20–40 cm soil layer, the KOS of the SC was significantly lower than that of the other four treatments, with the order being MC > FB > MSR > GB > SC, showing increases of 49.55%, 33.66%, 29.75%, and 25.35%, respectively, compared to the SC treatment. Furthermore, cultivation also enhanced the KOS in the 40–60 cm soil layer, with the ranking being SC > MC > MSR > FB > GB. Notably, SC was significantly higher than both FB and GB, while no significant differences were found among the other treatments, including between MC and MSR.

Table 4.
Effects of different land use patterns on KOS.
3.6. Correlation Between SOC Fractions and the Soil CPMI
The correlation analysis of various fractions of LOC, the CPMI and the KOS is illustrated in Figure 8. SOC, EOC, MBC, POC, and DOC, under different land use patterns, exhibit extremely significant positive correlations with CPMI (p < 0.01), with correlation coefficients of 0.70, 0.96, 0.73, 0.52, and 0.68, respectively. Conversely, SOC, EOC, MBC, POC, and DOC show negative correlations with KOS, with correlation coefficients of −0.32 (p < 0.05), −0.80 (p < 0.01), −0.38 (p < 0.05), −0.20, and −0.29, respectively. These findings indicated that land use patterns are closely associated with SOC and the fractions of LOC, as well as with the CPMI. Therefore, the CPMI effectively represents variations in soil carbon.
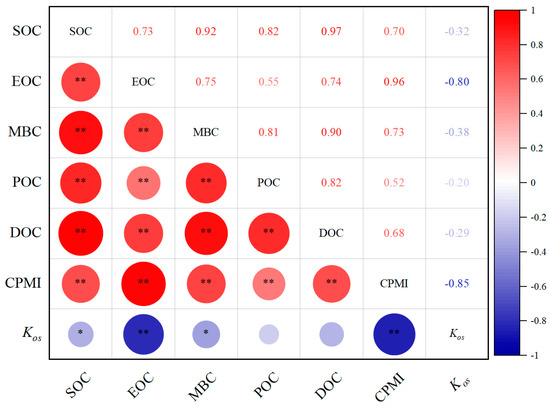
Figure 8.
Correlation coefficients between soil LOC and CPMI. Note: “*” means p < 0.05, “**” means p < 0.01, (SOC, soil organic carbon; EOC, easily oxidizable carbon; MBC, microbial biomass carbon; POC, particulate organic carbon; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; CPMI, carbon pool management index; Kos, oxidation stability coefficients). n = 3.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Different Land Use Patterns on SOC Distribution
Land use patterns are among the primary anthropogenic factors influencing changes in SOC content. Variations in vegetation types resulting from shifts in land use patterns can affect the quantity and quality of plant residues entering the soil ecosystem [33]. Additionally, the amount and nature of organic matter migration from surface soil to underlying layers also change, impacting the distribution of SOC within the humus layers [34,35]. SOC content serves as a crucial indicator for assessing soil quality and fertility [36]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that land use patterns significantly influence SOC storage and accumulation [37,38]. Some research indicates that the effect of ecosystems on SOC in soil humus layers diminishes with increasing depth [39,40]. The results of this experiment revealed that the impacts of different land use patterns on organic carbon in the humus layers of mollisols varied even at a depth of 60 cm, with the organic carbon content in forested and bushy (FB) soils being higher than that in grassland and farmland. This finding underscores the significant influence of land use patterns on SOC in mollisols [41]. In comparison to tillage land, both GB and FB significantly enhanced SOC content in the 0–60 cm layer, with FB demonstrating a particularly positive effect on SOC content increase, aligning with findings from Wang et al.’s study on topsoil in North China. This study reported that plantation soils had the highest SOC content (17.21 g kg−1), followed by grassland (17.07 g kg−1), both exceeding that of cultivated land (14.04 g kg−1). In Northeast China, SOC content is notably elevated (26.55 g kg−1) due to low temperatures [42]. Furthermore, compared to continuous cropping, crop rotation significantly reduced SOC content in soil layers, suggesting that crop rotation, particularly conventional practices, is not conducive to SOC retention in soil humus layers [43].
Tillage disrupts the soil aggregate structure, exposing the organic matter it protects and consequently accelerating the decomposition rate of soil organic matter [44]. Cultivating the same crop in successive years leads to the one-sided consumption of soil nutrients, resulting in an imbalance of soil nutrient levels [45]. Research indicates that reasonable crop rotation can optimize land resource utilization, enhance yield, and promote a balanced use of soil nutrients, although it may also accelerate the decomposition of soil organic matter [46]. Additionally, different vegetation types influence the input of litter and root systems. Compared to fallow grass belts and forest belts, the root systems of farmland are shallower, resulting in lower litter and root biomass input, this limits the capacity to extract nutrients from the soil and import sufficient organic matter, particularly as crop roots are less prevalent in deeper soil layers [47]. In contrast, natural vegetation in fallow grass belts and litter in forest belts provide a more abundant source of organic matter [48]. The accumulation rate of SOC is generally higher in humid areas [49]. Under the climatic conditions of Northeast China, vegetation in grass belts and forest belts is relatively abundant, producing substantial above-ground litter and root exudates annually, which serve as a rich source of SOC [50]. Some studies have confirmed that afforestation significantly increases the surface SOC content of farmland [51], as the sustained generation of above-ground biomass post-afforestation enhances the quantity and quality of organic matter transferred to the soil, while the cessation of tillage effectively mitigates the decomposition of SOC [52]. However, some studies have indicated that SOC content decreases following afforestation. This decline may be associated with various factors, including climate and soil conditions, types of woodlands, the duration since land use change, and the methodologies employed in research [53].
This study indicates that, in contrast to farmland, the forest belt has deeper roots and exhibits more vigorous growth, which can provide a substantial amount of deep soil organic matter through metabolic activities such as shedding, mortality, and secretion [25]. The grass belt, rich in natural vegetation, also contributes significantly to soil organic matter through the accumulation of ground litter and root exudates following the decay of herbaceous plants [54].
4.2. Effect of Different Land Use Patterns on Soil LOC
DOC and EOC are the fractions with the fastest turnover rates in SOC and are vital components of the soil labile organic carbon pool [55]. DOC and EOC are regarded as the primary energy sources for soil microorganisms, which are significantly influenced by factors such as land use practices, vegetation type, temperature, and humidity [56], these fractions can respond rapidly to changes in soil management strategies, making them important indicators for assessing alterations in soil organic carbon, soil fertility, and soil quality. Previous research has shown that converting farmland to grassland and woodland can significantly increase the levels of DOC and EOC in the soil, which aligns with the findings of this study [57,58]. On the one hand, the decomposition of plant residues directly facilitates the formation of the labile organic carbon pool in the soil. On the other hand, plant residues enhance the activity of soil microorganisms, thereby promoting the conversion of plant residue carbon into soil labile organic carbon [59].
As an important fractions of soil labile organic carbon, MBC is sensitive to changes in soil environment and is an important indicator reflecting soil microbial activity and organic carbon quality [60]. In this study, FB significantly increased the content of MBC in soil. This result may be due to the decomposition characteristics of litter in soil. Since plant residues are mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and other fractions, it takes a certain period of time for them to be fully degraded in soil before they can become nutrients directly utilized by soil microorganisms, so the microbial population in the soil also increases significantly [61].
As a constituent of LOC, DOC was significantly influenced by hydrothermal conditions. Favorable hydrothermal conditions during the rainy season enhance the metabolic rates of microorganisms and vegetation, thereby sustaining high levels of DOC in the soil [62]. EOC and MBC were notably affected by land use patterns, soil depth, and their interactions. This may be attributed to the fact that EOC and MBC are components of soil carbon that exhibit rapid turnover rates and respond quickly to changes in soil management practices and surrounding environmental conditions [63]. In this study, the concentrations of EOC and MBC were lowest in cultivated land and highest in the forest belt and grass belt. The increased DOC content in the grass belt (GB) and forest belt (FB) may be due to lower vegetation density, sufficient light and heat conditions, and relatively fast vegetation regeneration, which collectively enhance the litter input both on the surface and underground. Prolonged cultivation in agricultural land leads to significant soil nutrient depletion, which hampers microbial growth, inhibiting both their quantity and activity, and consequently reducing the source of LOC [64]. Furthermore, researchers found that tillage disrupts the aggregate structure, releasing organic carbon previously protected by this structure, which facilitates microbial utilization of organic carbon and accelerates the mineralization and decomposition of organic carbon, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the content of labile organic carbon [65]. As DOC serves as the primary carbon source directly utilized in microbial growth, its concentration reflects the carbon availability for soil microorganisms, which may be a crucial factor in maintaining high EOC and MBC levels in deeper soil layers [66]. Li posited that the soil’s ability to stabilize organic carbon is pivotal for SOC accumulation; if this ability is low, the risk of loss for input organic carbon increases [67].
POC refers to the organic carbon bound to sand particles (53–2000 μm), consisting of incompletely decomposed root systems and plant and animal residues. It plays a crucial role in soil organic carbon turnover and aggregation and can function as a sensitive indicator reflecting the extent of soil disturbance [68]. Li demonstrated that POC primarily originates from decomposing plant residues that are not fully decomposed [69]. This study found that as soil depth increased, the soil POC in each treatment gradually declined. This decline occurs because POC represents coarse organic matter that supplies available carbon to soil microorganisms, which diminishes as it is utilized [70]. This indicates that in the northeast mollisols region, FB may be more advantageous for enhancing the stability of organic carbon, thereby reducing the risk of carbon loss. Furthermore, FB possesses considerable carbon sequestration potential, particularly when it is the primary land use pattern, and can serve as a predominant measure for soil fertility restoration in the area.
4.3. Effects of Agricultural Land Use Change on SOC Stability and Soil Fertility
Some studies have suggested that the labile carbon content proportion within SOC may provide a more accurate reflection of the current state of the soil carbon pool than merely assessing the absolute amount of active carbon [71]. This observation is significant for understanding the dynamics of soil carbon, as it emphasizes the importance of labile carbon in characterizing soil health [72]. Moreover, the ratio of labile carbon to SOC can effectively diminish the effects of SOC content on the measurements of active carbon [73]. Thus, a focus on LOC is critical since its high content is generally beneficial for soil quality due to its rapid decomposition rate, while a lower content promotes carbon sequestration [74]. This highlights a nuanced balance between soil health and its capacity to store carbon, suggesting that both high and low LOC levels play vital roles, depending on the context [72]. The LOC/SOC ratio is recognized as an important measure of organic carbon stability in soil; it was noted that the LOC/SOC ratio was greater in the upper soil layer compared to the deeper layers. These findings align with earlier research [75]. Interestingly, the results of this study indicated that, although no significant difference was observed in the LOC/SOC ratio between tillage and non-tillage treatments, notable variations in both SOC and LOC contents were evident across different land use types, this finding challenges the reliance on the LOC/SOC ratio as the sole indicator for assessing soil organic carbon stability and quality, suggesting that additional factors should be considered. Furthermore, POC constituted the largest share of LOC, indicating its significance in the overall carbon stability within the soil. The distribution ratio of soil POC proved to be an effective measure for reflecting the intensity of organic carbon stability across different land use patterns while minimizing the impact of organic carbon variance [76]. Notably, the observed increase in SOC is primarily linked to the rise in soil POC, which is known to range from 30% to 85% [77]. The findings of this study, which ranged from 55.03% to 78.84%, align closely with the existing literature, thereby reinforcing the importance of POC in understanding soil carbon dynamics.
However, the components of LOC are significantly influenced by agricultural land conversion, particularly the MBC/LOC ratio. MBC/SOC, also referred to as microbial entropy, effectively characterizes microbial carbon conversion efficiency and soil carbon loss, and can be utilized to infer the availability and stability of carbon [78]. A larger MBC/SOC indicates a higher utilization rate of organic carbon. Due to the lower MBC/LOC ratio, which does not provide sufficient nutrients to crops from organic carbon decomposition, additional fertilizers are required to enhance the supply of available nutrients to crops. This reliance on fertilizers may further exacerbate soil quality degradation and negatively impact the sustainability of agricultural land. DOC/LOC serves as an indicator of the stability of soil organic carbon; a higher proportion of DOC in organic carbon corresponds to increased activity and stability, facilitating utilization and enhancing soil fertility [79]. In contrast to Luo’s [57] findings on paddy soil, it is evident that the proportion of LOC is influenced by land use patterns, organic matter input, and soil type. EOC/LOC is commonly used to represent the amount of organic carbon in soil that is readily decomposed through microbial oxidation, also known as the organic carbon oxidation rate [79]; therefore, greater attention should be directed towards changes in soil carbon in the deeper layers below the humus layer, as influenced by land use patterns [80].
4.4. Characterization of Soil Quality by CMPI and Kos Under Different Land Use Patterns
Soil CPMI serves as an effective indicator of alterations in soil carbon dynamics, providing a substantial basis for enhancing soil fertility and increasing soil carbon content. It reflects the differences in soil quality under various land use patterns, particularly regarding the organic carbon pool [81]. The KOS metric can demonstrate the extent of organic carbon decomposition and nutrient release. A higher KOS value indicates lower soil organic matter activity and reduced soil fertility, while a lower value suggests more fertile soil [25]. This research reveals that the non-tillage treatment significantly enhances soil labile organic carbon, stable carbon, CPI, and CPMI, all of which are markedly higher than those observed in the tillage treatment. This indicates that non-tillage not only increases soil labile organic carbon but also boosts the activity of the carbon pool, elucidating the reasons for the elevated levels of labile organic carbon under non-tillage conditions [82]. Among the treatments, FB exhibits the highest CPMI, followed by GB, while MSR has the lowest CPMI. These differences may be attributed to variations in the chemical composition of litter, leading to distinct decomposition rates. The KOS findings in this study further support this notion, suggesting that non-tillage treatment enhances the activity of soil organic carbon and improves soil fertility [83]. Additionally, SOC, DOC, EOC, and MBC, in this study, show significant or extremely significant correlations with the soil carbon pool management index, indicating that the components of labile organic carbon are interdependent, mutually influential, and collectively inclusive [84].
5. Conclusions
The contents of SOC and LOC fractions (EOC, POC, DOC, and MBC) decreased with increasing soil depth. After a long-term positioning test, SOC content exhibited notable differences across various treatments. Non-tillage treatments significantly increased the contents of soil organic carbon and labile organic carbon fractions in the 0–60 cm soil layer compared to tillage treatments, with FB performing the best, followed by GB. Conversely, tillage treatments notably reduced the contents of these carbon fractions, with MSR showing the lowest levels. Continuous cropping resulted in higher SOC levels than rotation cropping. Furthermore, FB processing improved the CPMI value. Under traditional tillage practices, the SOC content across all layers in the humus layers of mollisols in farmland was lower than that in GB and FB. This observation suggests that farmland conditions are not conducive to the fixation of organic carbon in mollisols, while also indicating that mollisols in farmland possess a greater carbon sequestration potential. A significant amount of organic carbon is returned to the grass and forest belts, leading to higher organic carbon storage in these areas compared to farmland. In conclusion, in the mollisols region of Northeast China, non-tillage treatments may be more effective in enhancing the stability of organic carbon and reducing the risk of carbon loss. The findings indicate that vegetation restoration in this region has substantial carbon sink potential, and that improving soil fertility—particularly through restoration models centered on FB as the primary land use pattern—can serve as a crucial strategy for enhancing soil fertility in this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, J.W. and X.D; software, X.D. and W.C.; validation, J.W. and W.C.; formal analysis, X.D.; investigation, X.D. and W.C.; resources, J.W.; data curation, X.D. and W.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.D.; writing—review and editing, J.W.; visualization, X.D. and W.C.; supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Plan Project: Regulation Mechanism of Key Process of Agricultural Soil Organic Matter Transformation-Soil Structure Transformation in Black Land (No: 2022YFD1500103).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the first author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lal, R. Global potential of soil carbon sequestration to mitigate the greenhouse effect. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2003, 22, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S. Global carbon budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsch, W.L.; Bahn, M.; Heinemeyer, A. Soil carbon relations: An overview. In Soil Carbon Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Beillouin, D.; Corbeels, M.; Demenois, J.; Berre, D.; Boyer, A.; Fallot, A.; Feder, F.; Cardinael, R. A global meta-analysis of soil organic carbon in the Anthropocene. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C.; Amiraslani, F.; Chenu, C.; Garcia Cardenas, M.; Kaonga, M.; Koutika, L.-S.; Ladha, J.; Madari, B.; Shirato, Y.; Smith, P. The 4p1000 initiative: Opportunities, limitations and challenges for implementing soil organic carbon sequestration as a sustainable development strategy. Ambio 2020, 49, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Bossio, D.; de Vries, W.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Amundson, R.; Bol, R.; Collins, C.; Lal, R.; Leifeld, J. Towards a global-scale soil climate mitigation strategy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beillouin, D.; Cardinael, R.; Berre, D.; Boyer, A.; Corbeels, M.; Fallot, A.; Feder, F.; Demenois, J. A global overview of studies about land management, land-use change, and climate change effects on soil organic carbon. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Smith, A.R.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Jones, D.L. Microbial uptake and utilization of low molecular weight organic substrates in soil depend on carbon oxidation state. Biogeochemistry 2017, 133, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.V.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; da Silva, T.O.; da Silva, T.L.; da Silva Dias, N.; Matias, M.I.S. Soil organic matter pools and carbon fractions in soil under different land uses. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.A. The nature and dynamics of soil organic matter: Plant inputs, microbial transformations, and organic matter stabilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z. Distribution of microbial biomass and activity within soil aggregates as affected by tea plantation age. Catena 2017, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Gongadze, K.; Wu, L. Soil nutrients of different land-use types and topographic positions in the water-wind erosion crisscross region of China’s Loess Plateau. Catena 2020, 184, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Hu, Q. Effects of tillage years on soil organic carbon fractions in the Poyang Lake reclaimed paddy fields. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- Coulter, J.A.; Nafziger, E.D.; Wander, M.M. Soil organic matter response to cropping system and nitrogen fertilization. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Chang, Q.-R.; Qi, Y.-B.; Liu, J.; Chen, T. Aggregation and soil organic carbon fractions under different land uses on the tableland of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2014, 115, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ussiri, D.A.; Lal, R. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions under different land uses and tillage practices. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Kang, F.; Cheng, X.; Han, H.; Ji, W. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks under different land uses in a hilly ecological restoration area of North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Reddy, A. Vertical distribution analysis of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in different land use patterns of an agro-organic farm. Trop. Ecol. 2021, 62, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Tang, W. Characteristics of soil organic carbon fractions under different land use patterns in a tropical area. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yu, X. Spatial variability in soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in a hilly watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 137, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z. Distinct controls over the temporal dynamics of soil carbon fractions after land use change. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4614–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y. Effects of land-use type on soil organic carbon and carbon pool management index through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi pathways. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, e02432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W. Effects of tillage and residue managements on organic C accumulation and soil aggregation in a sandy loam soil of the North China Plain. Catena 2017, 156, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzinger, F.; Schädler, M.; Reitz, T.; Yin, R.; Auge, H.; Merbach, I.; Roscher, C.; Harpole, W.S.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Siebert, J. Sustainable land management enhances ecological and economic multifunctionality under ambient and future climate. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Qu, X. Effects of organic wastes on labile organic carbon in semiarid soil under plastic mulched drip irrigation. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, A.; Wu, J.; Fan, W.; Hu, J.; Opoku-Kwanowaa, Y.; Abd El-Rahim, M.; Moussa, A.A. Changes in Soil Humic Acid Composition after Nine Years of Repeated Application of Organic Wastes in Black Soil: A Study Using Solid-State FT-IR and (13C-NMR) Analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 5211–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.K.; Xu, Q.F.; Xu, Z.H.; Cao, Z.H. Seasonal changes in soil labile organic carbon pools within a Phyllostachys praecox stand under high rate fertilization and winter mulch in subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 236, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Particulate Soil Organic-Matter Changes across a Grassland Cultivation Sequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Change 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramesh, V.; Singh, S.K.; Mohekar, D.S.; Arunachalam, V.; Misra, S.D.; Jat, S.L.; Kumar, P.; Nath, A.J.; Kumar, N.; Mahajan, G.R. Impact of sustainable land-use management practices on soil carbon storage and soil quality in Goa State, India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooch, Y.; Ghorbanzadeh, N.; Francaviglia, R. Soil carbon stocks can be negatively affected by land use and climate change in natural ecosystems of semi-arid environment of Iran. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 31, e00591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T.; Bolan, N.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Wijesekara, H.; Kanchikerimath, M.; Rao, C.S.; Sandeep, S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Choudhury, B.U. Soil organic carbon dynamics: Impact of land use changes and management practices: A review. Adv. Agron. 2019, 156, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yu, K.; Ren, Z.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. Distribution of soil organic carbon impacted by land-use changes in a hilly watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J. Soil aggregates stability and storage of soil organic carbon respond to cropping systems on Black Soils of Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, J.; Liu, Q.; Lv, D.-a. Land use effects on soil quality along a native wetland to cropland chronosequence. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 53, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pei, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Soil organic carbon depletion in global Mollisols regions and restoration by management practices: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Kooch, Y.; Song, K.; Zheng, S.; Wu, D. Remote estimation of soil organic carbon under different land use types in agroecosystems of Eastern China. Catena 2023, 231, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cai, X.; Bo, Y.; Guan, C.; Cai, L.; Haider, F.U.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Response of soil organic carbon and soil aggregate stability to changes in land use patterns on the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K. Aggregate-associated soil organic matter as an ecosystem property and a measurement tool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, A4–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mng’ong’o, M.; Munishi, L.K.; Blake, W.; Comber, S.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Soil fertility and land sustainability in Usangu Basin-Tanzania. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.S. Resource management, soil fertility and sustainable crop production: Experiences of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; McConkey, B.; Wang, H.; Janzen, H. Root distribution by depth for temperate agricultural crops. Field Crops Res. 2016, 189, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, A.; Liang, Y.; Cornell, C.R.; Guo, X.; Bai, E.; Hou, H.; Wang, D. Differential contribution of microbial and plant-derived organic matter to soil organic carbon sequestration over two decades of natural revegetation and cropping. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.-H.; Jia, B.; Niu, Z.-q.; Mou, X.-M.; Chen, J.; Li, F.-C.; Wu, Y.-N.; Ning, S.; Yakov, K.; Li, X.G. Humidity controls soil organic carbon accrual in grassland on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; You, M.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Zou, W.; Xing, B. Redistribution of Different Organic Carbon Fractions in the Soil Profile of a Typical Chinese Mollisol with Land-Use Change. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.; Peressotti, A.; Galdo, I.D.; Six, J. Assessing the Impact of Land-use on Soil C Sequestration by Means of Soil Organic Matter Fractionation and Stable C Isotopes. Glob. Change Biol. 2001, 9, 0106. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Xu, Z.; Yang, W. Carbon and nutrient transfer via above-and below-ground litter in forests. Forests 2022, 13, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Gifford, R.M. Soil carbon stocks and land use change: A meta analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 8, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, C. Root exudates mediate the processes of soil organic carbon input and efflux. Plants 2023, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, L.J.L.; Shotbolt, L.; Ashmore, M.R. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations in UK soils and the influence of soil, vegetation type and seasonality. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Smreczak, B.; Cai, A. Dissolved organic carbon in cropland soils: A global meta-analysis of management effects. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 371, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; et al. Effects of agricultural land use change on organic carbon and its labile fractions in the soil profile in an urban agricultural area. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xue, S.; Liu, G. Effects of the interaction between temperature and revegetation on the microbial degradation of soil dissolved organic matter (DOM)—A DOM incubation experiment. Geoderma 2019, 337, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lv, X.; Cao, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Alterations of soil labile organic carbon fractions and biological properties under different residue-management methods with equivalent carbon input. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 161, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bending, G.D.; Turner, M.K.; Rayns, F.; Marx, M.C.; Wood, M. Microbial and biochemical soil quality indicators and their potential for differentiating areas under contrasting agricultural management regimes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mondéjar, R.; Zühlke, D.; Becher, D.; Riedel, K.; Baldrian, P. Cellulose and hemicellulose decomposition by forest soil bacteria proceeds by the action of structurally variable enzymatic systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowerby, A.; Emmett, B.A.; Williams, D.; Beier, C.; Evans, C.D. The response of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and the ecosystem carbon balance to experimental drought in a temperate shrubland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, G.; Bünemann, E.K.; Oguejiofor, C.U.; Meier, J.; Gort, G.; Comans, R.; MäDer, P.; Brussaard, L.; Goede, R.D. Sensitivity of labile carbon fractions to tillage and organic matter management and their potential as comprehensive soil quality indicators across pedoclimatic conditions in Europe. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, K.; He, X.; Su, Y. Assessing Nutrient Elements as Indicators for Soil Active Organic Carbon in Topsoil of Karst Areas. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Aggregate and soil organic matter dynamics under conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, G.; Kaiser, K. Dissolved organic matter in soil: Challenging the paradigm of sorptive preservation. Geoderma 2003, 113, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wen, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, K. Afforestation effects on soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools modulated by lithology. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 400, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, G. Particulate organic carbon is more sensitive to nitrogen addition than mineral-associated organic carbon: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 232, 105770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of residue incorporation and plant growth on soil labile organic carbon and microbial function and community composition under two soil moisture levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18849–18859. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, R.; Liu, J.; Lichtfouse, E.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L. Soil microbial carbon use efficiency and the constraints. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifeld, J.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Soil organic matter fractions as early indicators for carbon stock changes under different land-use? Geoderma 2005, 124, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, M.; Ye, X.; Gao, H.; Chu, W.; Mao, J.; Thompson, M.L. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activities after 10 years of continuous fertilization and wheat residue incorporation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Lin, X.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: Microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Pu, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Jia, Y.; Deng, O.; Gong, G. Dynamics of soil labile organic carbon fractions and C-cycle enzyme activities under straw mulch in Chengdu Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Mustafa, A.; Huang, Q.; Liu, K.; Sun, N.; Xu, M. Differences of SOC storage and stability between soil layers influenced by long-term fertilization in a typical paddy soil of Southern China. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Du, F.; Zhu, B. Soil organic carbon fractions in China: Spatial distribution, drivers, and future changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ao, G.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, B. The patterns of forest soil particulate and mineral associated organic carbon characteristics with latitude and soil depth across eastern China. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 12, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, N.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Xin, X. Response of soil microbial biomass C, N, and P and microbial quotient to agriculture and agricultural abandonment in a meadow steppe of northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lan, T.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Ling, J.; Deng, O.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Tang, X. Soil labile organic carbon impacts C: N: P stoichiometry in urban park green spaces depending on vegetation types and time after planting. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasenev, V.; Kuzyakov, Y. Urban soils as hot spots of anthropogenic carbon accumulation: Review of stocks, mechanisms and driving factors. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1607–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Stratification of Carbon Fractions and Carbon Management Index in Deep Soil Affected by the Grain-to-Green Program in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Ren, C.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Pang, G.; Bai, H.; Wang], J. Effect of Soil C, N and P Stoichiometry on Soil Organic C Fractions After Afforestation. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 705–713. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Z.; De Clerck, C.; Meersmans, J.; Colinet, G.; Zhang, W. No-tillage facilitates soil organic carbon sequestration by enhancing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-related soil proteins accumulation and aggregation. Catena 2024, 245, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Lan, Y.; Meng, J.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Q.; Cao, D.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W. Labile organic carbon fractions and carbon pool management index in a 3-year field study with biochar amendment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).