Robust Positioning Scheme Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Context-Aware Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposed DRL-based context-aware framework is designed to manage updates to the IAKF by adaptively adjusting noise covariances that adjust for measurement and model uncertainties rather than directly correcting the position. Unlike conventional methods, time-varying uncertainties are addressed through a learning process without reliance on ground-truth data for supervision. By adaptively regulating these uncertainties, the proposed positioning system can mitigate error accumulation, thereby improving positioning accuracy and error drift.
- A two-stage outlier-aware gating scheme is developed to address channel-specific outliers and global inconsistencies, considering both short- and long-term gating. Through the integration of a short-term adaptive measurement noise scaling gate with a long-term NIS-based update gate, error drifts can be effectively suppressed.
- An integrated SH-CAIPS architecture that couples DRL-based IAKF with outlier mitigation, achieving robust and accurate positioning using cost-effective sensors such as GPS, IMU, and wheel odometry without environment-specific prior knowledge.
2. System Model
2.1. Positioning System Operation
2.2. IAKF Formulation
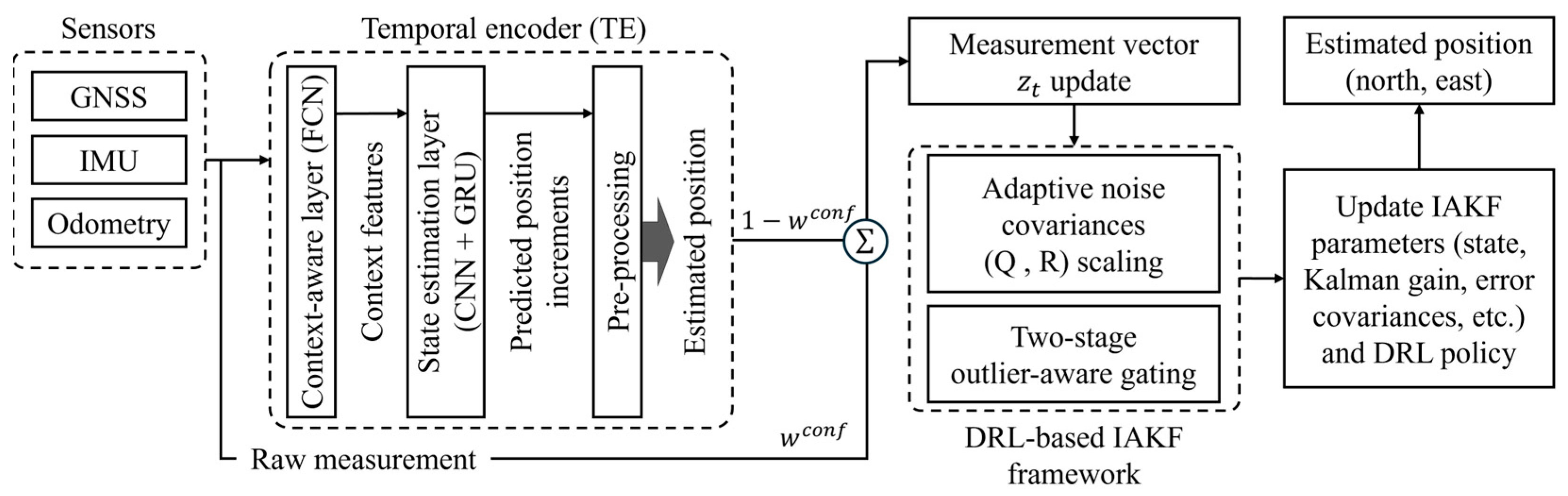
3. SH-CAIPS Architecture and Operation
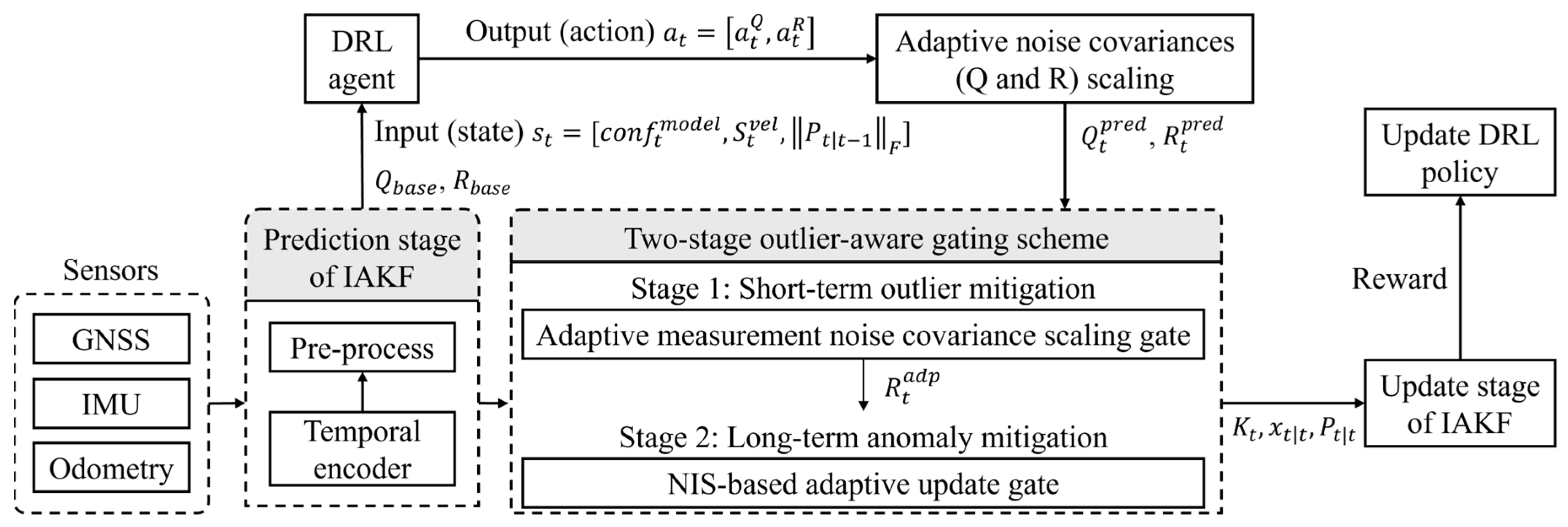
3.1. DRL-Based Adaptive Noise Covariances Scaling
3.2. Adaptive Measurement Noise Covariance Scaling Gate for Short-Term Outlier Mitigation
3.3. NIS-Based Adaptive Update Gate for Long-Term Outlier Mitigation
| Algorithm 1: Training process of the proposed SH-CAIPS |
| 1: Input: Sensor streams (GNSS, IMU, Odometry), measurement vector, pre-traine parameters and model |
| 2: Initialize filter, gate, and PPO parameters |
| 3: Pre-processing: Sensors synchronized and mapped to a common positioning frame |
| 4: Training Loop: |
| 5: for epoch = 1 to do |
| 6: for time step = 1 to do |
| 7: Context-aware sensor fusion and Prediction stage update by Equations (1)–(7) |
| 8: Update noise covariances , by PPO policy action by Equations (11)–(17) |
| 9: Perform adaptive measurement noise covariance scaling by Equations (18)–(21) |
| 10: Perform NIS-based adaptive update gating by Equations (22) and (23) |
| 11: Perform update stage of IAKF by Equations (8)–(10) |
| 12: Update PPO reward |
| 13: end for |
| 14: Update PPO policy |
| 15: end for |
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Simulation Settings
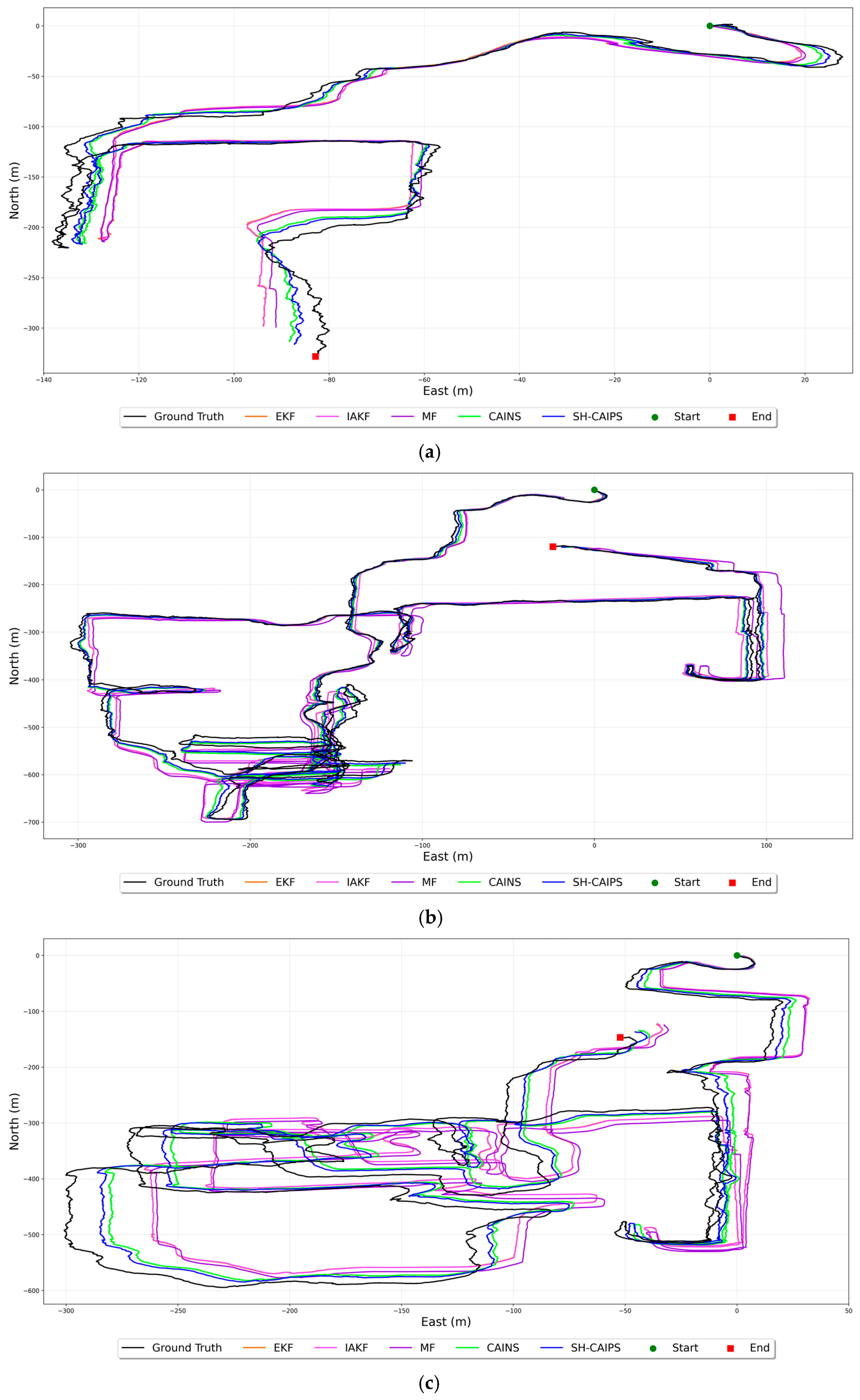
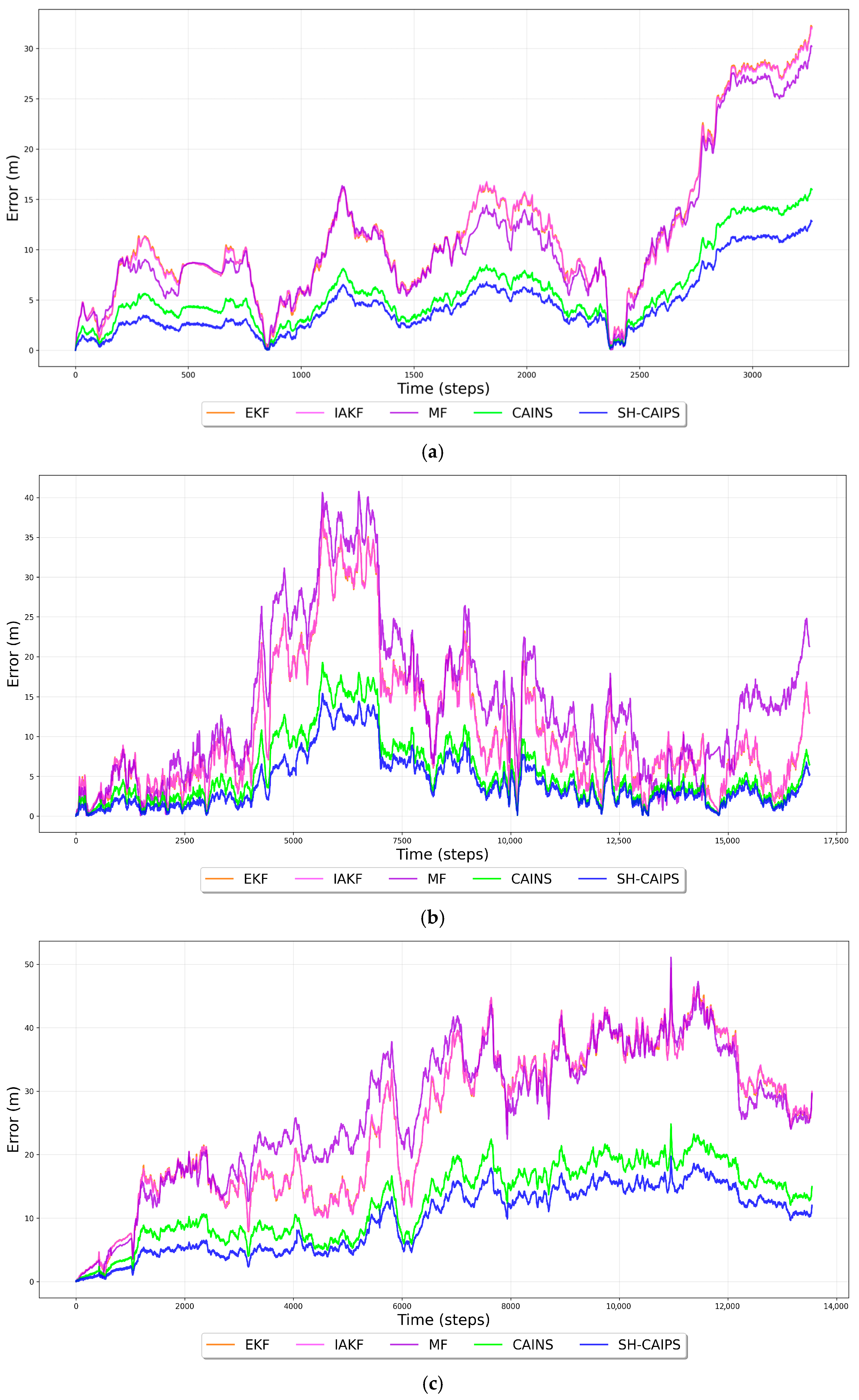
4.2. Performance Evaluations
4.3. Discussions on Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKF | Adaptive Kalman filter |
| DRL | Deep reinforcement learning |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filter |
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite system |
| IAKF | Innovation-based adaptive Kalman filter |
| IMU | Inertial measurement unit |
| KF | Kalman filter |
| LOS | Line-of-sight |
| MF | Median filter |
| NIS | Normalized innovation squared |
| NLOS | Non-line-of-sight |
| PPO | Proximal policy optimization |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| SH-CAIPS | Seamless hierarchical context-aware intelligent positioning system |
References
- Nnodim, T.C.; Arowolo, M.O.; Agboola, B.D.; Ogundokun, R.O.; Abiodun, M.K. Future trends in mechatronics. IAES Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2021, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitceva, I.; Andrievsky, B. Methods of intelligent control in mechatronics and robotic engineering: A survey. Electronics 2022, 11, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia-Salgueiro, A.d.J. Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous mobile robot navigation. In Artificial Intelligence for Robotics and Autonomous Systems Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 195–237. [Google Scholar]
- Asaad, S.M.; Maghdid, H.S. A comprehensive review of indoor/outdoor localization solutions in IoT era: Research challenges and future perspectives. Comput. Netw. 2022, 212, 109041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, F.; Hilairet, M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Monmasson, E.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Katsura, S. Industrial applications of the Kalman filter: A review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5458–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitrapani, A.; Ceccarelli, N.; Scortecci, F.; Garulli, A. Comparison of EKF and UKF for spacecraft localization via angle measurements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R.; Kirubarajan, T. Estimation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation: Theory Algorithms and Software; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Hwang, B.; Kim, J.; Seon, J.; Kim, S.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Enhanced 3D outdoor positioning method based on adaptive Kalman filter and kernel density estimation for 6G wireless system. Electronics 2024, 13, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pan, X. Deep learning for inertial positioning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 10506–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, D.J.; Biswal, A.; Mir, I.A. Artificial neural networks for navigation systems: A review of recent research. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Aggarwal, P.; Taha, T.M.; Chodavarapu, V.P. Improving inertial sensor by reducing errors using deep learning methodology. In Proceedings of the IEEE National Aerospace & Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 23–25 July 2018; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wei, X.; Perusquía-Hernández, M.; Isoyama, N.; Uchiyama, H.; Kiyokawa, K. DUET: Improving inertial-based odometry via deep IMU online calibration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinyalamdary, S. Deep Kalman filter: Simultaneous multi-sensor integration and modelling; a GNSS/IMU case study. Sensors 2018, 18, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, H.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Seamless GPS/Inertial navigation system based on self-learning square-root cubature Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Seon, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Context-aware integrated navigation system based on deep learning for seamless localization. Sensors 2024, 24, 7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, T. Deep reinforcement learning based mobile robot navigation: A review. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2021, 26, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, F.; Heckman, C. Learning to calibrate: Reinforcement learning for guided calibration of visual–inertial rigs. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2019, 38, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvereng, S.S.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hamre, G. Dynamic positioning using deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Eng. 2021, 235, 109433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.Y. Area-selective deep reinforcement learning scheme for wireless localization. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2025; early publication (accepted). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Lu, M. Deep-reinforcement-learning-based autonomous establishment of local positioning systems in unknown indoor environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 13626–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Luo, H.; Ning, B.; Zhao, F.; Bao, L.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, J. RL-AKF: An Adaptive Kalman Filter Navigation Algorithm Based on Reinforcement Learning for Ground Vehicles. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhu, X. A Kalman Filter-Based Localization Calibration Method Optimized by Reinforcement Learning and Information Matrix Fusion. Entropy 2025, 27, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rio, A.; Jimenez, D.; Serrano, J. Comparative analysis of A3C and PPO algorithms in reinforcement learning: A survey on general environments. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 146795–146806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlevaris-Bianco, N.; Ushani, A.K.; Eustice, R.M. University of Michigan north campus long-term vision and LiDAR dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | RMSE (m) | Max Error (m) | Standard Deviation ) | Average Drift Rate (m/min) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EKF | 13.88 | 32.06 | 7.44 | 2.01 | 0.02 |
| IAKF | 13.92 | 32.13 | 7.44 | 2.02 | 0.09 |
| MF | 13.92 | 32.18 | 7.44 | 2.02 | 0.03 |
| CAINS | 6.96 | 16.11 | 3.72 | 1.01 | 0.03 |
| SH-CAIPS (without two-stage outlier gating) | 6.95 | 16.05 | 3.72 | 1.01 | 0.44 |
| SH-CAIPS (with two-stage outlier gating) | 5.47 | 12.87 | 3.10 | 0.76 | 0.44 |
| Method | RMSE (m) | Max Error (m) | Standard Deviation ) | Average Drift Rate (m/min) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EKF | 13.75 | 37.92 | 8.47 | 2.16 | 0.02 |
| IAKF | 13.76 | 38.48 | 8.47 | 2.16 | 0.09 |
| MF | 13.76 | 38.48 | 8.47 | 2.16 | 0.03 |
| CAINS | 6.88 | 19.23 | 4.23 | 1.08 | 0.03 |
| SH-CAIPS (without two-stage outlier gating) | 6.88 | 19.24 | 4.24 | 1.08 | 0.44 |
| SH-CAIPS (with two-stage outlier gating) | 5.34 | 15.46 | 3.39 | 0.82 | 0.44 |
| Method | RMSE (m) | Max Error (m) | Standard Deviation | Average Drift Rate (m/min) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EKF | 27.94 | 49.64 | 11.77 | 5.04 | 0.02 |
| IAKF | 27.96 | 49.40 | 11.79 | 5.04 | 0.09 |
| MF | 27.97 | 49.40 | 11.79 | 5.04 | 0.03 |
| CAINS | 13.98 | 24.71 | 5.89 | 2.52 | 0.03 |
| SH-CAIPS (without two-stage outlier gating) | 13.98 | 24.70 | 5.89 | 2.52 | 0.44 |
| SH-CAIPS (with two-stage outlier gating) | 11.00 | 19.80 | 5.07 | 1.93 | 0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Hwang, B.; Seon, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Robust Positioning Scheme Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Context-Aware Intelligence. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312785
Lee S, Hwang B, Seon J, Kim J, Kim K, Kim J, Lee M, Kim S, Sun Y, Kim J. Robust Positioning Scheme Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Context-Aware Intelligence. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312785
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seongwoo, Byungsun Hwang, Joonho Seon, Jinwook Kim, Kyounghun Kim, Jeongho Kim, Mingyu Lee, Soohyun Kim, Youngghyu Sun, and Jinyoung Kim. 2025. "Robust Positioning Scheme Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Context-Aware Intelligence" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312785
APA StyleLee, S., Hwang, B., Seon, J., Kim, J., Kim, K., Kim, J., Lee, M., Kim, S., Sun, Y., & Kim, J. (2025). Robust Positioning Scheme Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Context-Aware Intelligence. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312785





