Ultrasonic Dispersion of Pyrolytic Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Stable Colloidal Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
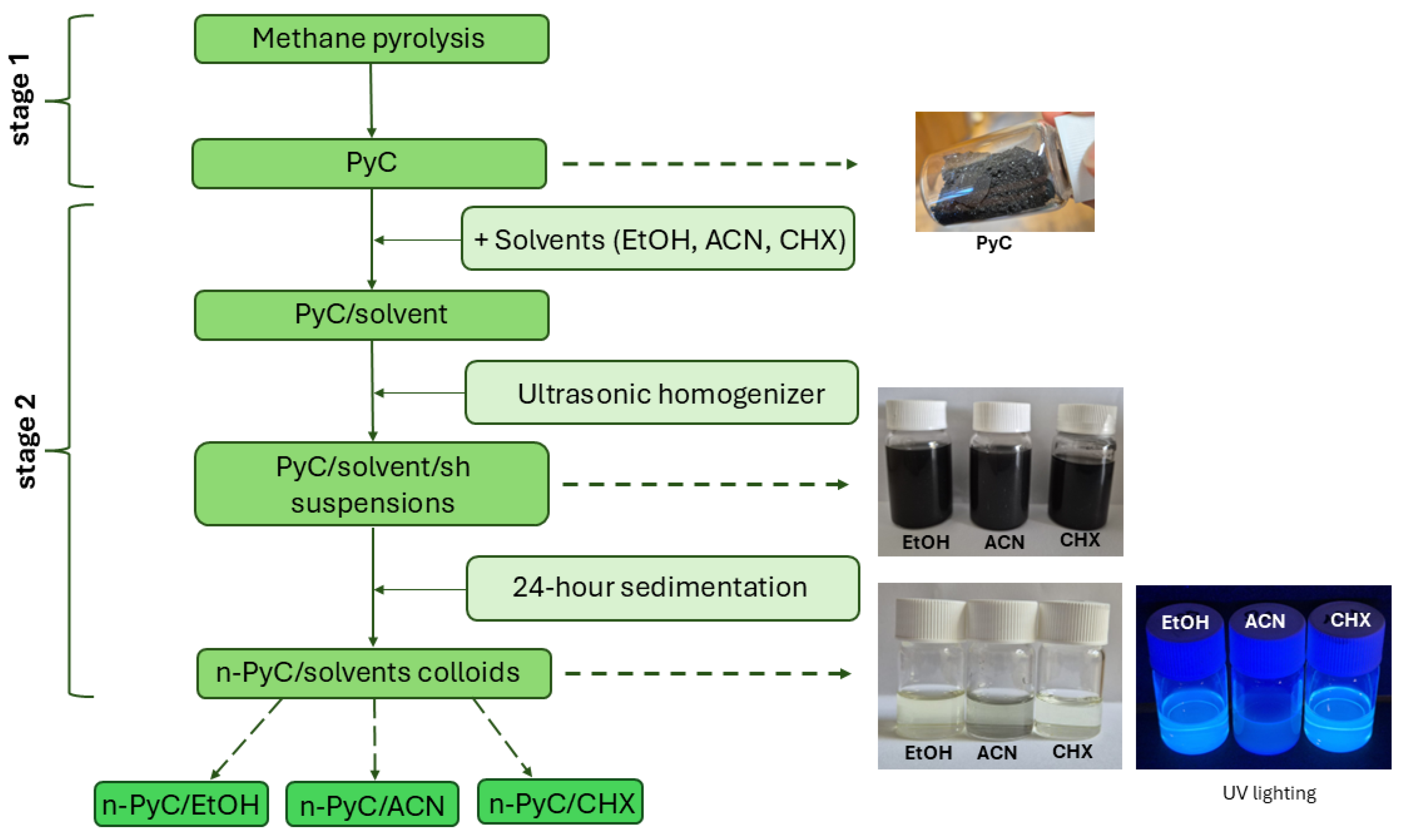
Colloidal Solutions of Pyrolytic Carbon (PyC)
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results
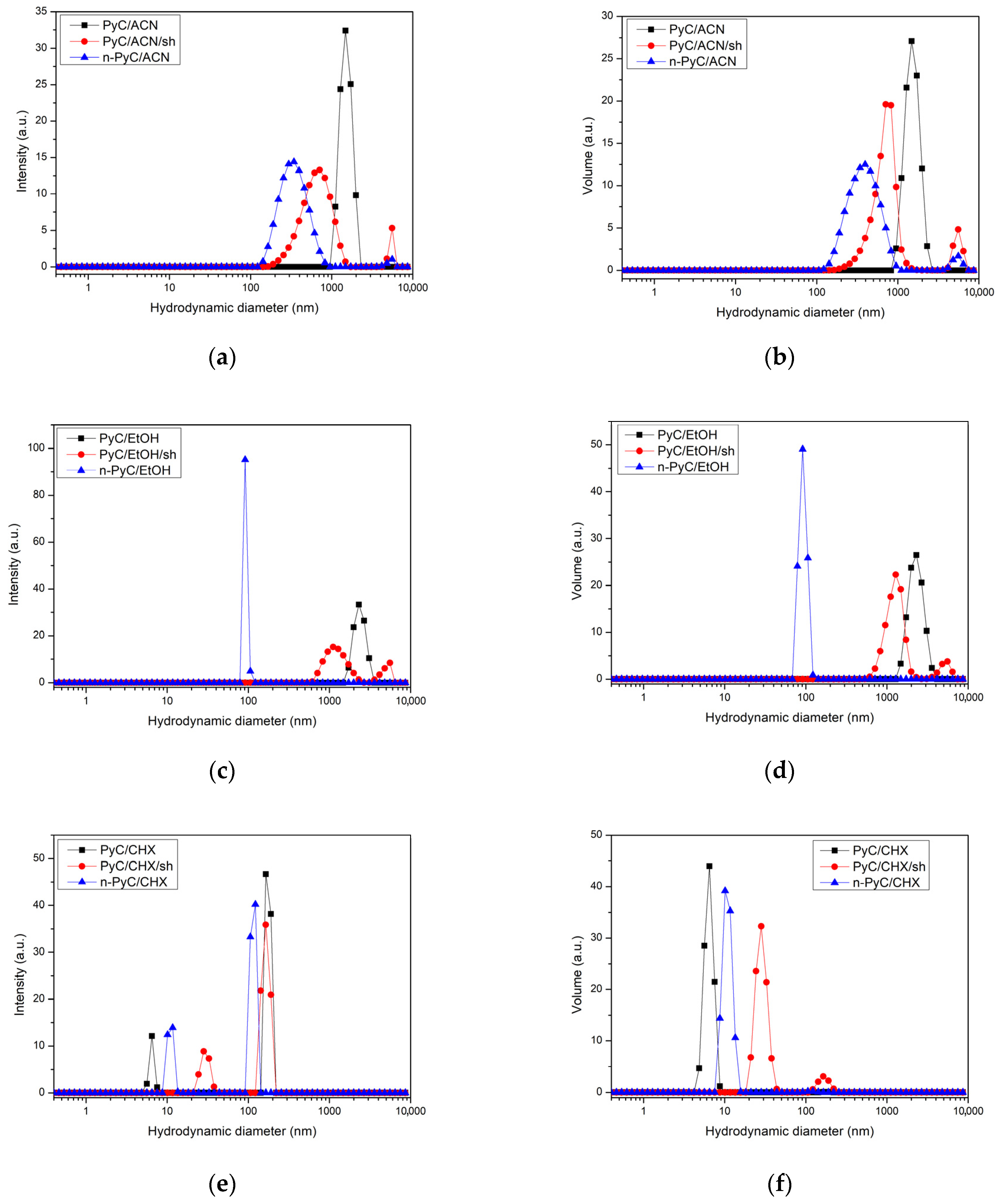
3.1. DLS
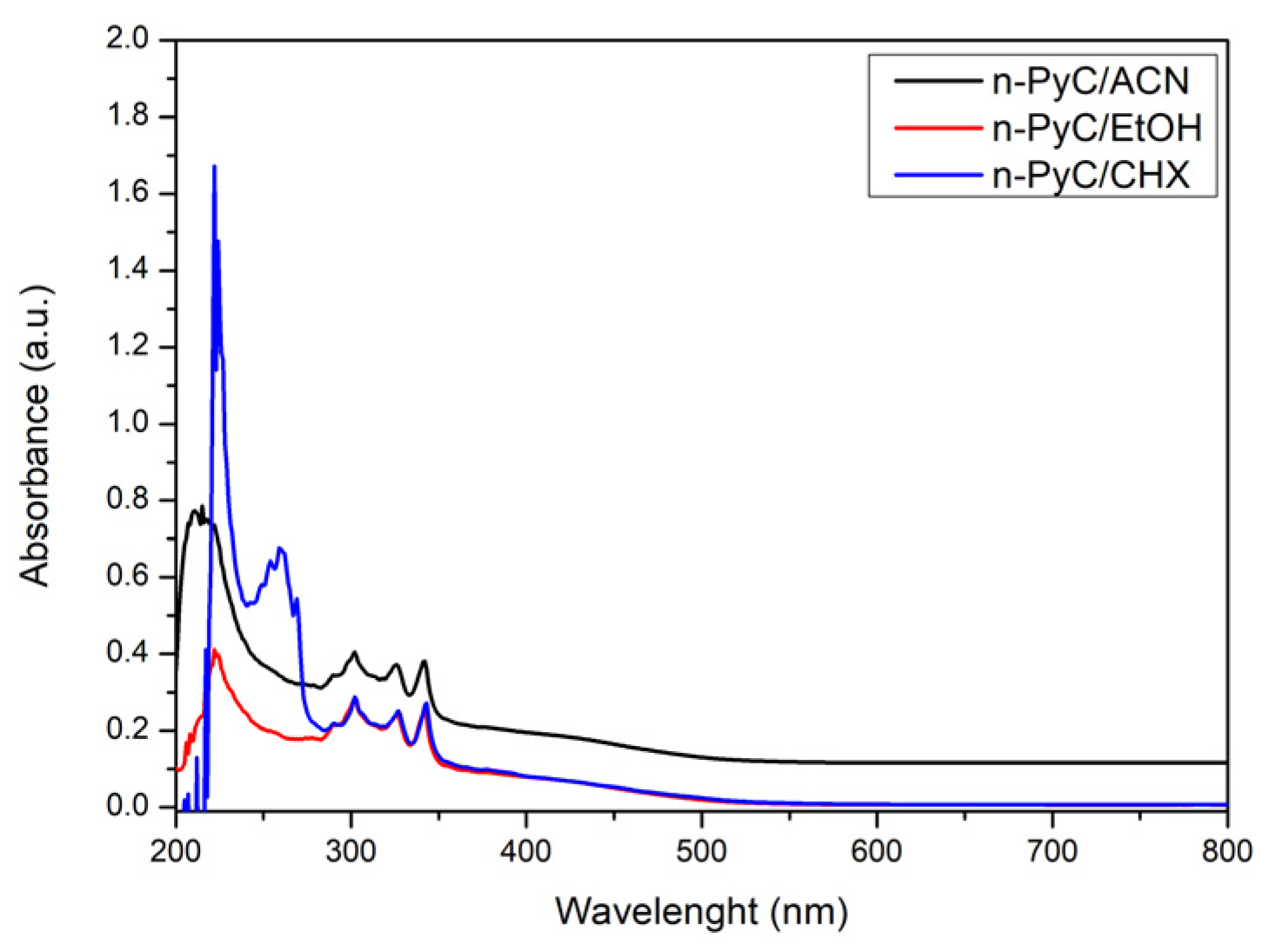
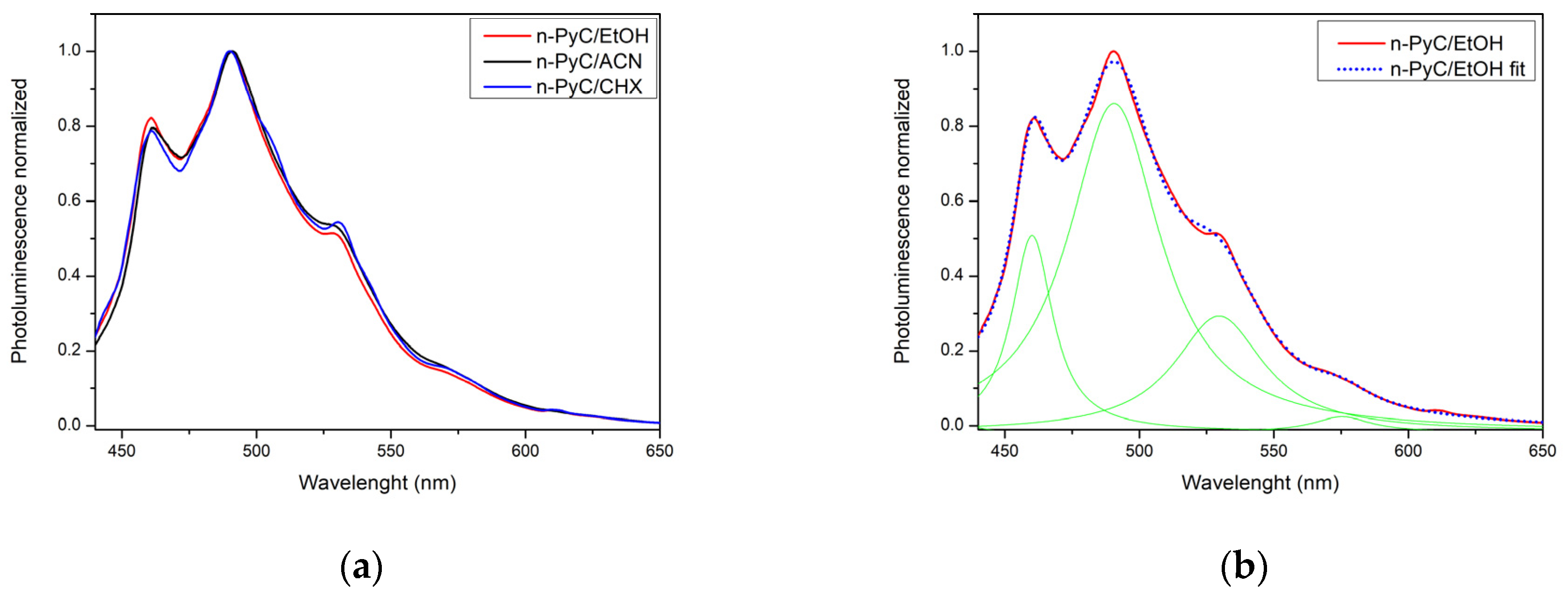
3.2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry and Photoluminescence
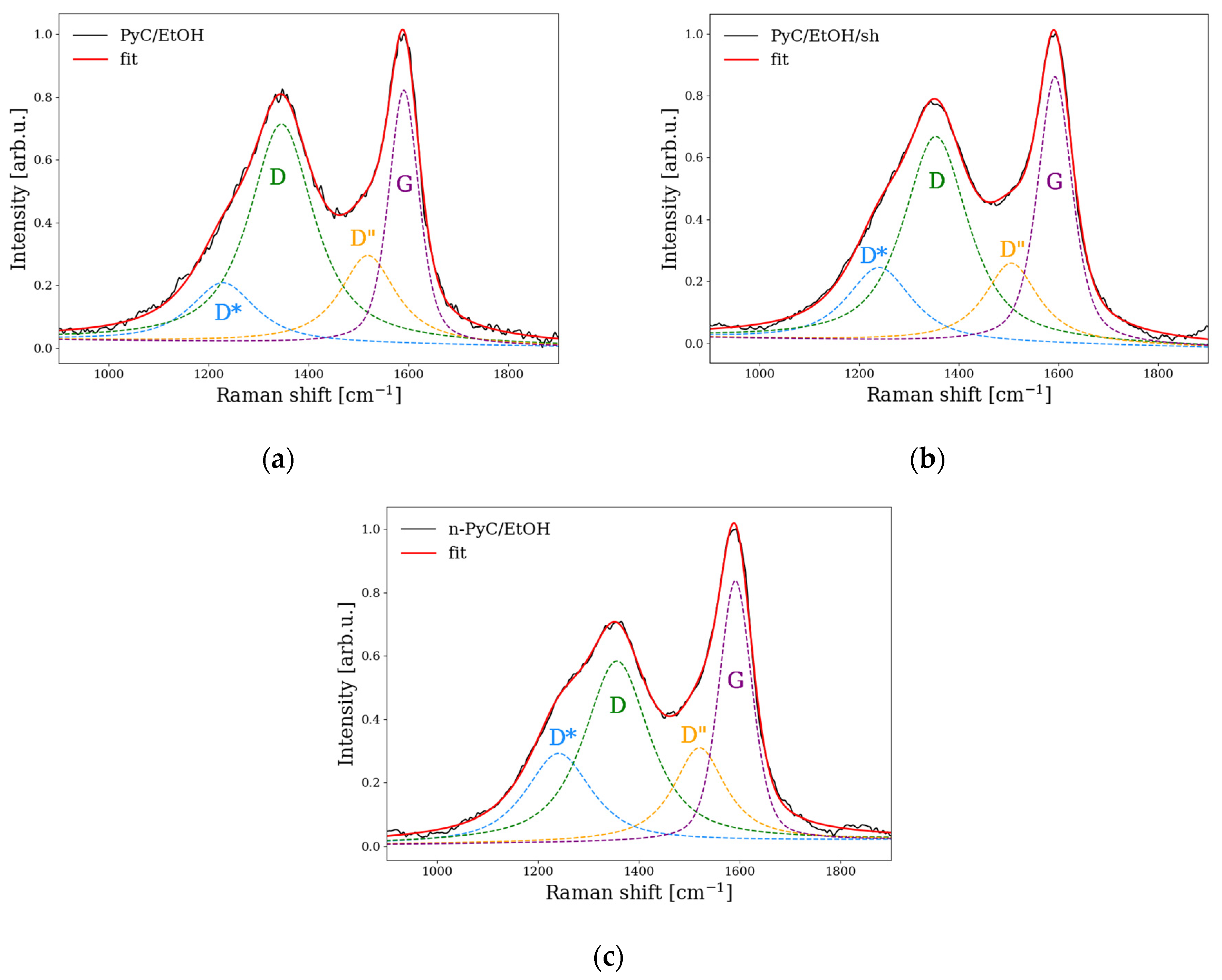
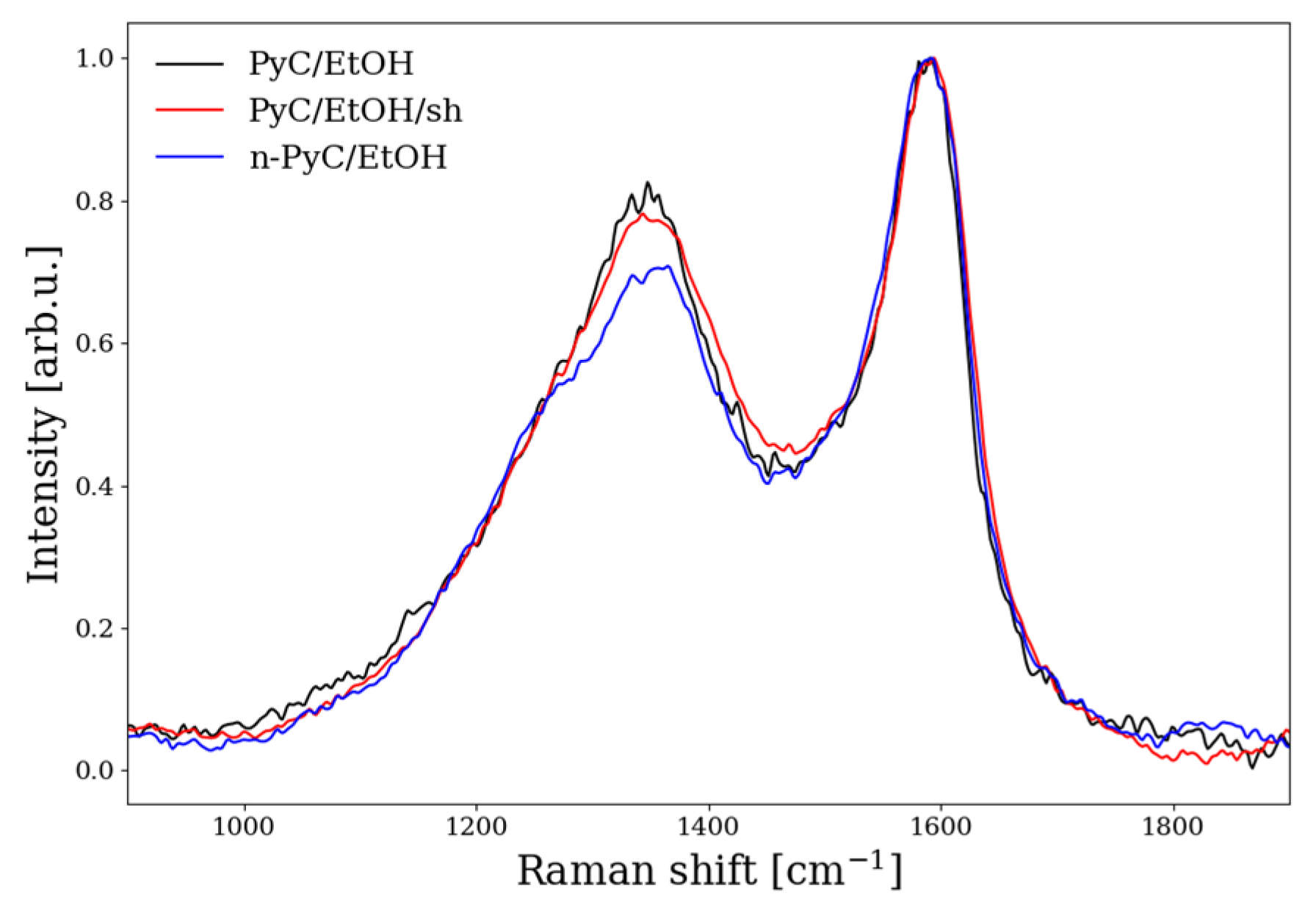
3.3. Raman Spectroscopy
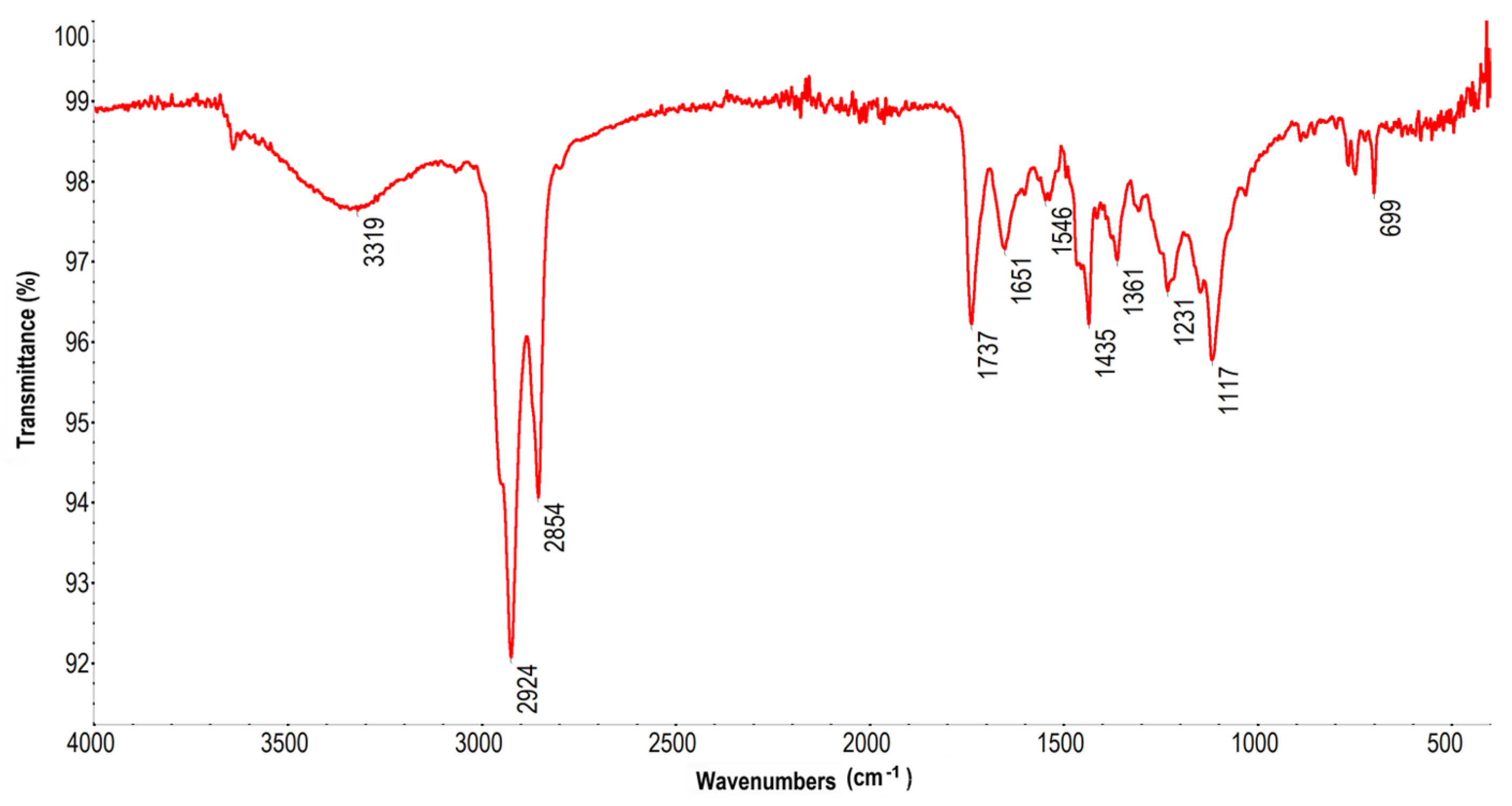
3.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.5. Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Speranza, G. Carbon Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Functionalization and Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzer, E.; Köchling, K.H.; Boehm, H.P.; Marsh, H. Recommended terminology for the description of carbon as a solid. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 473–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.; Rawat, S. A comprehensive review of the pyrolysis process: From carbon nanomaterial synthesis to waste treatment. Oxf. Open Mater. Sci. 2020, 1, itab014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecińska, B.K.; Pusz, S. Pyrolytic carbon—Definition, classification and occurrence. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 163, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, J. Siliconization elimination for SiC coated C/C composites by a pyrolytic carbon coating and the consequent improvement of the mechanical property and oxidation resistances. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 5046–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, J.; Vine, D. Methane Pyrolysis for Hydrogen Production; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lucian, M.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass: Process design, modeling, energy efficiency and cost analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zhao, F.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q.; Shen, Q. Simultaneous Enhancement of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Isotropic Pyrolytic Carbon by Graded Retention Chemical Vapor Deposition Method. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, J.; Wojtasik, M. Piroliza metanu na tle wybranych metod otrzymywania wodoru Methane pyrolysis against the background of selected hydrogen production methods. Nafta-Gaz 2023, 79, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasik, M.; Burnus, Z.; Markowski, J.; Żak, G.; Lubowicz, J. Piroliza metanu-wpływ wybranych parametrów na przebieg procesu Methane pyrolysis-influence of selected parameters on the course of the process. Nafta-Gaz 2023, 79, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghfeli, A.; Xu, H.; Heronimus, B.T.; Jeevaretanam, B.; Spearrin, R.M.; Fisher, T.S. Methane pyrolysis by Joule heating for graphitic carbon and hydrogen production. iScience 2025, 28, 113546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, K.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Hu, B.; Li, K. Characteristics of chemical vapour deposition in micro pore structure in char layer of polymer composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 178, 109222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zou, Y.; Bourbigot, S.; Ji, J.; Chen, X. Pressure effects on morphology of isotropic char layer, shrinkage, cracking and reduced heat transfer of wooden material. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 5063–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.Q.; Larsen, P.E.; Larsen, T.; Goswami, S.B.; Villanueva, L.G.; Boisen, A.; Keller, S.S. Pyrolytic carbon resonators for micromechanical thermal analysis. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Ushakova, E.V.; He, B.; Xing, G.; Tang, Z.; Rogach, A.L.; Qu, S. Assignment of Core and Surface States in Multicolor-Emissive Carbon Dots. Small 2023, 19, 2204158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanta, M.; Filho, W.d.S.; Souza, M.; de Assunção, R.; Champi, A.; Cuevas, R. Deconvolution of photoluminescence spectra and electronic transition in carbon dots nanoparticles from microcrystalline cellulose. J. Lumin. 2023, 255, 119607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Manelski, R.; Vasilas, B.; Jin, Y. Mobile colloidal organic carbon: An underestimated carbon pool in global carbon cycles? Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 405429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, R.; Hashmet, M.R.; Pourafshary, P. Fine Migration Control in Sandstones: Surface Force Analysis and Application of DLVO Theory. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31624–31639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balda, M.; Mackenzie, K.; Woszidlo, S.; Uhlig, H.; Möllmer, J.; Kopinke, F.-D.; Schüürmann, G.; Georgi, A. Bottom-Up Synthesis of De-Functionalized and Dispersible Carbon Spheres as Colloidal Adsorbent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, J. 3. Preparation and Purification of Colloids. Available online: https://www.kdpublications.in (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Skrabalak, S.E. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of carbon materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4930–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, Z. Sonochemical catalysis as a unique strategy for the fabrication of nano-/micro-structured inorganics. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sao, D.; Mandal, R.; Mahato, S.; Das, P.S.; Roy, G.; Panda, B.; Dhak, D.; Kuiri, P.K.; Mukherjee, B.; Nath, R. Sonochemically synthesized integrated silver-tin oxide nanostructure for enhanced photocatalytic applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2025, 715, 417548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Zakri, C.; Maugey, M.; Pasquali, M.; Van Der Schoot, P.; Poulin, P. Kinetics of nanotube and microfiber scission under sonication. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20599–20605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Terentjev, E.M. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes: Mixing, Sonication, Stabilization, and Composite Properties. Polymers 2012, 4, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.M.; Chong, T.H.; Khaleduzzaman, S.S.; Shahrul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Long, B.D.; Amalina, M.A. Effect of ultrasonication duration on colloidal structure and viscosity of alumina-water nanofluid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6677–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasik, K.; Wojtasik, M.; Suchanek, K.; Zięba, M.; Karasiński, P.; Pakieła, W.; Żak, G.; Krasodomski, W. Effect of pyrolytic carbon addition on the structural and optical properties of TiO2 composite thin films. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enríquez-Sánchez, N.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Camacho-López, S.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Camacho-López, M. Photoluminescent carbon colloids prepared by laser fragmentation of carbon from waste coffee grounds. Superf. Vacío 2024, 37, 240901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzetti, S.; Gabriel, J.-C.P. Methods for dispersing carbon nanotubes for nanotechnology applications: Liquid nanocrystals, suspensions, polyelectrolytes, colloids and organization control. Int. Nano Lett. 2018, 9, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Pang, S.; Zhong, M.; Sun, Y.; Qayum, A.; Liu, Y.; Rashid, A.; Xu, B.; Liang, Q.; Ma, H.; et al. A comprehensive review of ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) for bioactive components: Principles, advantages, equipment, and combined technologies. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 101, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, D.; Ramalingame, R.; Adiraju, A.; Nouri, H.; Kanoun, O. Role of Solvent Polarity on Dispersion Quality and Stability of Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustahija, L.; Kern, W. Surface Functionalization of (Pyrolytic) Carbon—An Overview. C 2023, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekumjorn, S.; Gullapalli, S.; Wong, M.S. Understanding the solvent polarity effects on surfactant-capped nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 13063–13070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, A.L.; Kerker, M. Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves from Two Concentric Spheres. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hurley, D.H.; Luther, E.P.; Beaux, M.F.; Vodnik, D.R.; Peterson, R.J.; Bennett, B.L.; Usov, I.O.; Yuan, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Characterization of ultralow thermal conductivity in anisotropic pyrolytic carbon coating for thermal management applications. Carbon 2018, 129, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ren, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Lei, J.; He, M.; Xie, H.; Deng, L.; Yu, F.; et al. Order-in-disordered ultrathin carbon nanostructure with nitrogen-rich defects bridged by pseudographitic domains for high-performance ion capture. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleimeier, N.F.; Liu, Y.; Turner, A.M.; Young, L.A.; Chin, C.-H.; Yang, T.; He, X.; Lo, J.-I.; Cheng, B.-M.; Kaiser, R.I. Excited state photochemically driven surface formation of benzene from acetylene ices on Pluto and in the outer solar system. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 24, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elugoke, S.E.; Uwaya, G.E.; Quadri, T.W.; Ebenso, E.E. Carbon Quantum Dots: Basics, Properties, and Fundamentals. ACS Symp. Ser. 2024, 1465, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.A.; Abdelrahman, H.H.; Fahmy, M.A.; Ebrahim, D.G.; Moustafa, A.H.E. Pure and doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for the detection of phenol compounds and antibiotics in aquariums. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Bohidar, H.B. Observation of fluorescence from non-functionalized carbon nanoparticles and its solvent dependent spectroscopy. J. Lumin. 2013, 141, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Wu, Z.L.; Gao, M.X.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots with aggregation induced emission enhancement for visual permittivity detection. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2063–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond–like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 2477–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claramunt, S.; Varea, A.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M.M.; Cornet, A.; Cirera, A. The importance of interbands on the interpretation of the raman spectrum of graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10123–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollebregt, S.; Ishihara, R.; Tichelaar, F.D.; Hou, Y.; Beenakker, C.I.M. Influence of the growth temperature on the first and second-order Raman band ratios and widths of carbon nanotubes and fibers. Carbon 2012, 50, 3542–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasik, M.; Krasodomski, W.; Żak, G.; Wojtasik, K.; Pakieła, W. Morphological and Structural Analysis of Pyrolytic Carbon from Simple Thermal Methane Pyrolysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Weber, F.; Weigert, F.; Wang, Y.; Choudhury, S.; Xiao, J.; Lauermann, I.; Resch-Genger, U.; Bande, A.; Petit, T. Influence of surface chemistry on optical, chemical and electronic properties of blue luminescent carbon dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.J.; Omer, K.M.; Hawaiz, F.E. Deep insights to explain the mechanism of carbon dot formation at various reaction times using the hydrothermal technique: FT-IR, 13C-NMR, 1H-NMR, and UV-visible spectroscopic approaches. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 14340–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilov, A.S. Solvent Effect on Structural Elucidation of Photoluminescent Graphitic Carbon Nanodots. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20409–20416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; González, L.T.; Madou, M.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Mendoza, A. Synthesis, Purification, and Characterization of Carbon Dots from Non-Activated and Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Eddingsaas, N.C.; Flannigan, D.J.; Hopkins, S.D.; Xu, H. The Chemical History of a Bubble. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Suo, H.; Peng, H.; Xu, P.; Gao, X.; Du, S. Simulation and exploration of cavitation process during microalgae oil extracting with ultrasonic-assisted for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanzai, B.; Mochizuki, A.; Wakikawa, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Oshio, T.; Yagishita, K. Sonoluminescence intensity and ultrasonic cavitation temperature in organic solvents: Effects of generated radicals. Ultrason Sonochem 2023, 95, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
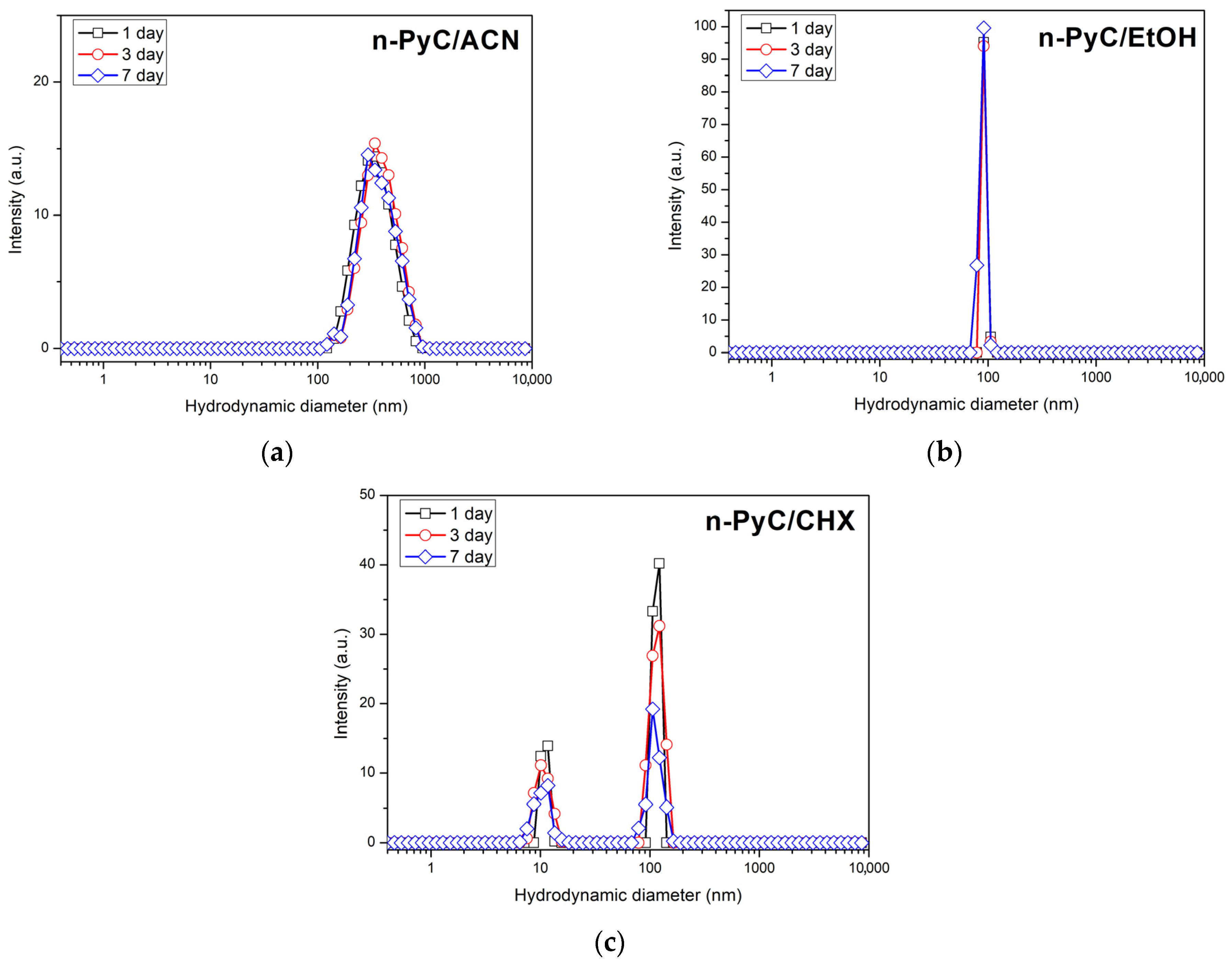
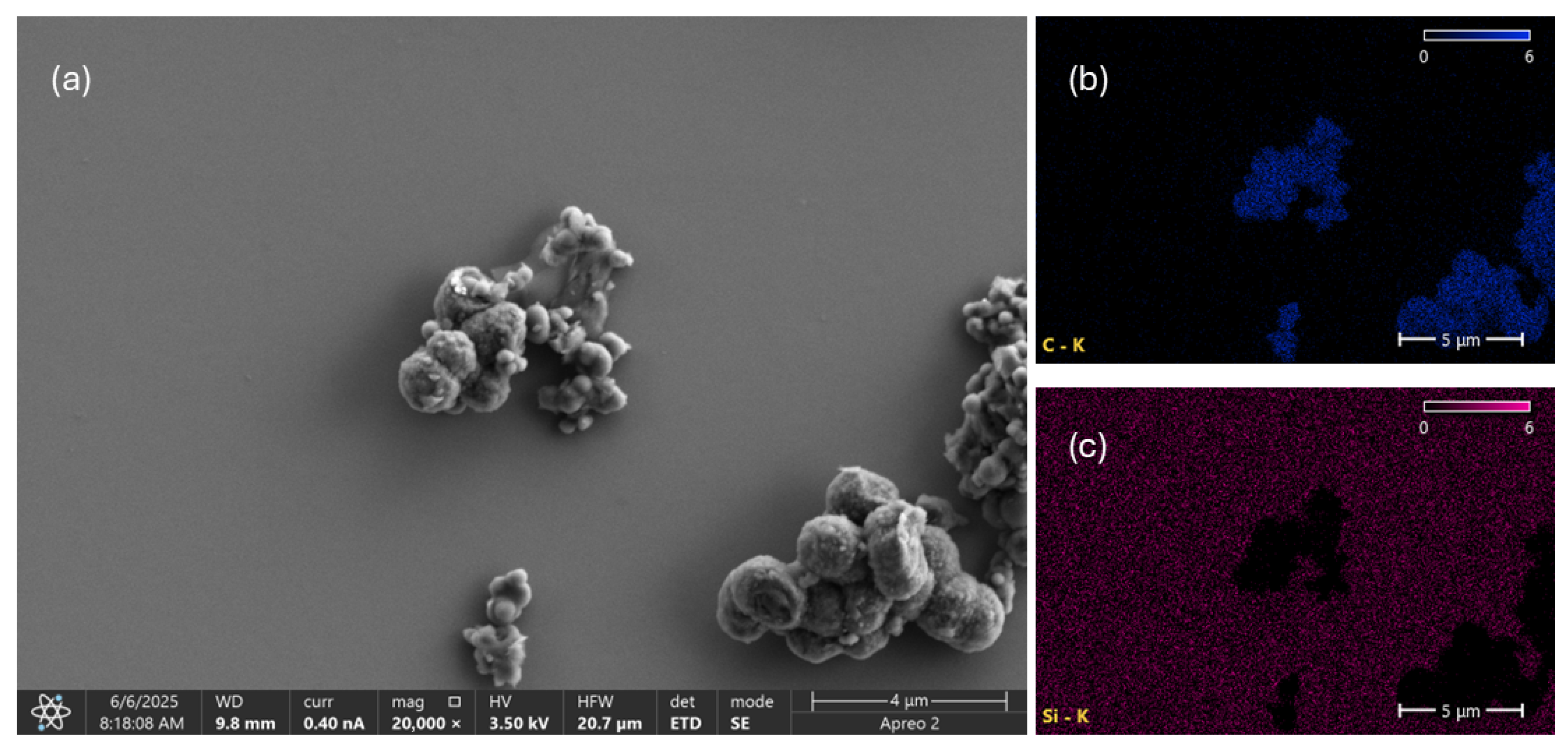
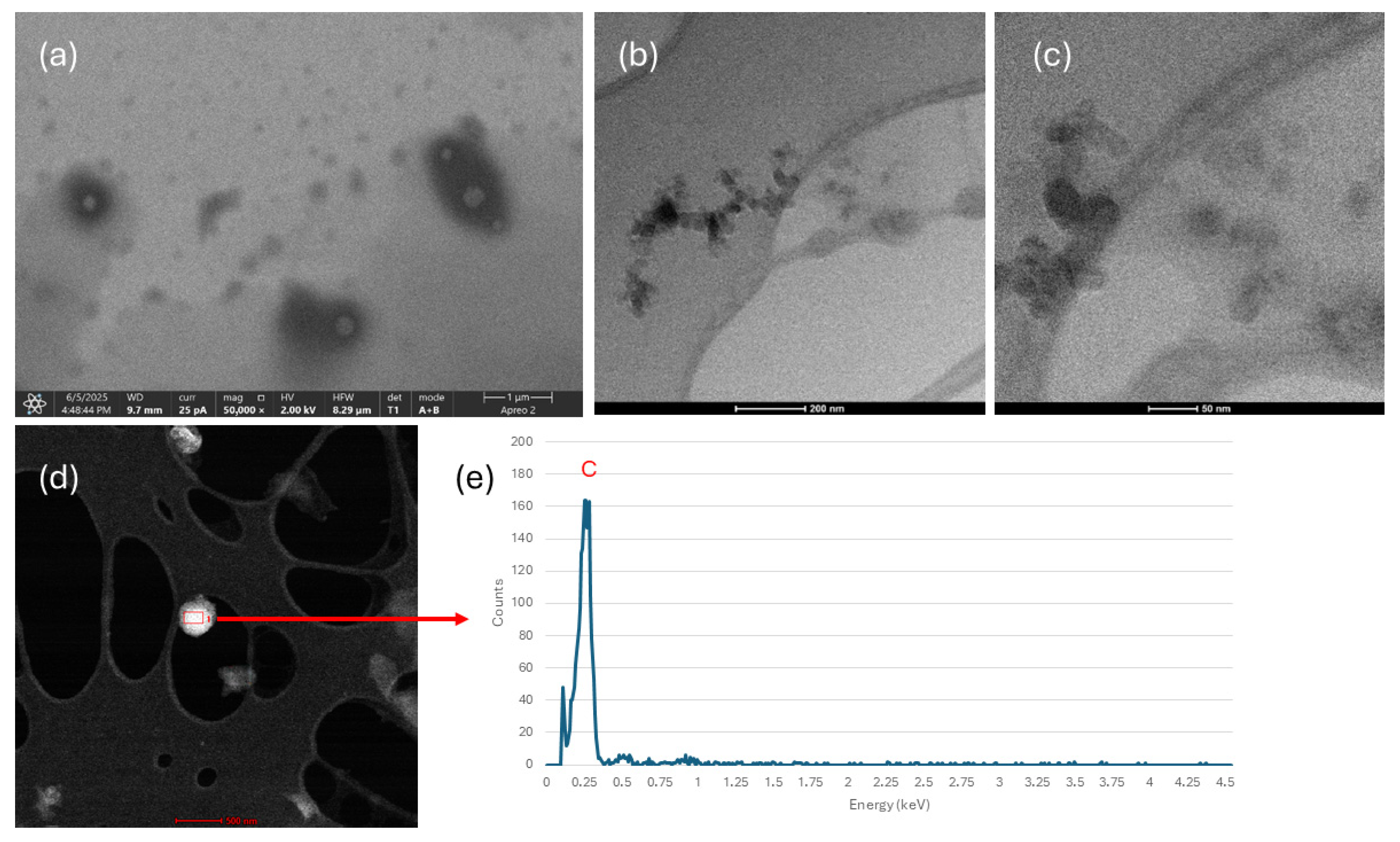
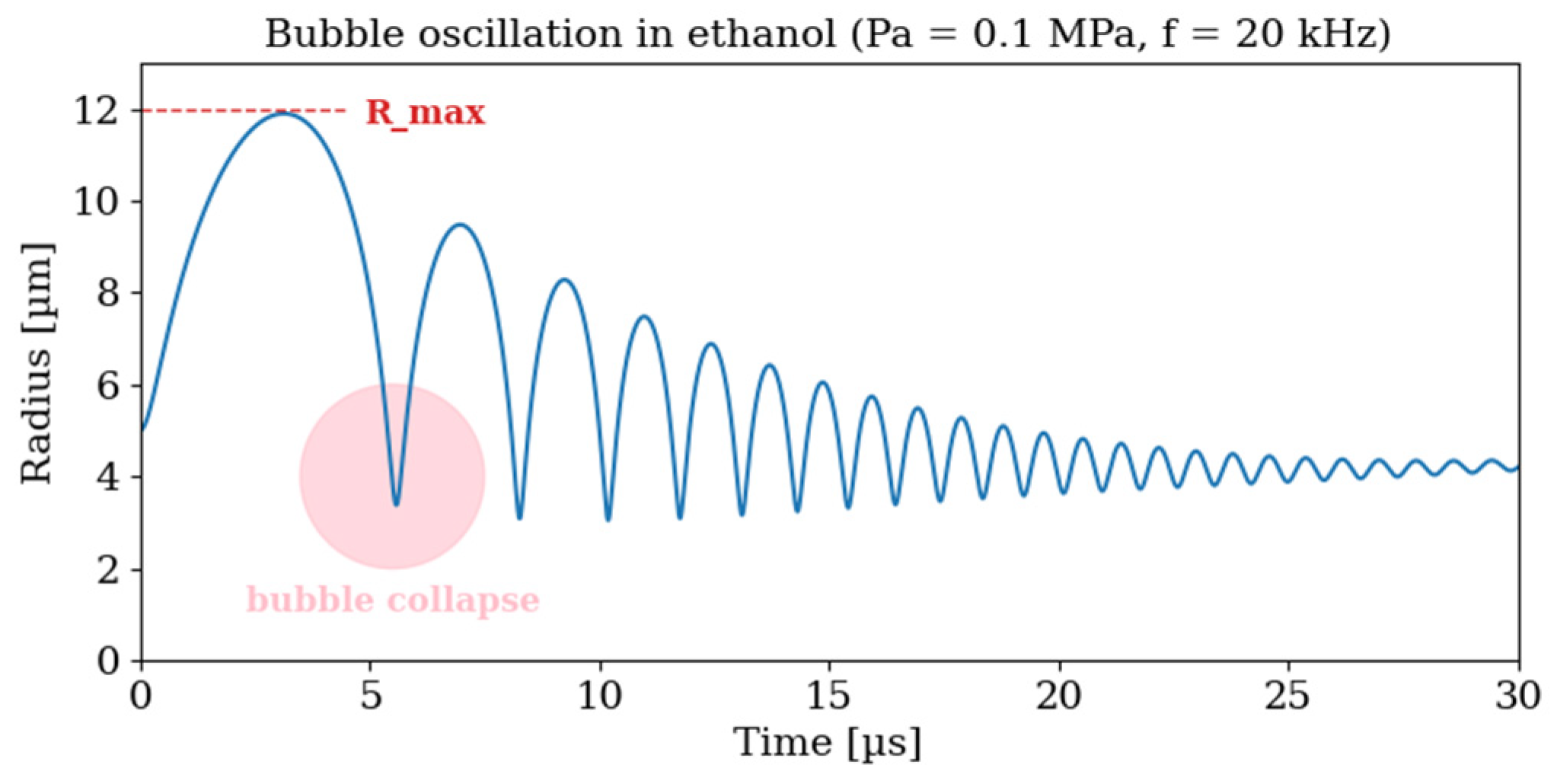
| Colloid | Parameter | 1 Day | 3 Day | 7 Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-PyC/ACN | Z-Average, nm | 163.2 | 163.2 | 157.3 |
| Count Rate, kb/s | 305.5 | 298.7 | 290 | |
| Pdl | 0.146 | 0.146 | 0.148 | |
| n-PyC/EtOH | Z-Average, nm | 141.2 | 139.8 | 139.9 |
| Count Rate, kb/s | 423.9 | 416.8 | 416.1 | |
| Pdl | 0.098 | 0.101 | 0.098 | |
| n-PyC/CHX | Z-Average, nm | 144.6 | 211.8 | 287.7 |
| Count Rate, kb/s | 257.9 | 304.2 | 198.1 | |
| Pdl | 0.479 | 0.516 | 0.299 |
| Band Assignment | PyC/EtOH | PyC/EtOH/sh | n-PyC/EtOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| D* band position [cm–1] | 1231 | 1240 | 1241 |
| D* band integrated peak area | 41.5 | 52.9 | 62.9 |
| D* intensity | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.28 |
| D band position [cm–1] | 1346 | 1354 | 1356 |
| D band integrated peak area | 166.9 | 149.1 | 127.8 |
| D intensity | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.57 |
| D” band position (around 1500 cm−1) [cm–1] | 1514 | 1506 | 1520 |
| D” band integrated peak area | 49.4 | 51.6 | 55.0 |
| D” intensity | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.30 |
| G band position [cm–1] | 1590 | 1593 | 1592 |
| G band integrated peak area | 80.6 | 94.8 | 79.9 |
| G intensity | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtasik, K.; Suchanek, K.; Wojtasik, M.; Dulian, P.; Matus, K.; Mitura-Nowak, M. Ultrasonic Dispersion of Pyrolytic Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Stable Colloidal Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312655
Wojtasik K, Suchanek K, Wojtasik M, Dulian P, Matus K, Mitura-Nowak M. Ultrasonic Dispersion of Pyrolytic Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Stable Colloidal Solutions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312655
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtasik, Katarzyna, Katarzyna Suchanek, Michał Wojtasik, Piotr Dulian, Krzysztof Matus, and Marzena Mitura-Nowak. 2025. "Ultrasonic Dispersion of Pyrolytic Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Stable Colloidal Solutions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312655
APA StyleWojtasik, K., Suchanek, K., Wojtasik, M., Dulian, P., Matus, K., & Mitura-Nowak, M. (2025). Ultrasonic Dispersion of Pyrolytic Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photoluminescence Properties of Stable Colloidal Solutions. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312655






