Abstract
This study presents an integrated framework that combines Geographic Information System (GIS)-based spatial analysis with the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to quantitatively evaluate the tourism and educational reuse potential of abandoned mines. Five spatial indicators—population density, slope, urban ratio, road accessibility, and proximity to tourist attractions—were normalized using logarithmic transformation and cumulative distribution functions and weighted through expert-based AHP evaluation. The framework was applied to large-scale mine datasets in the United States and South Korea, followed by in-depth case validation in the Gangwon region. The results indicate that successfully redeveloped mines consistently exhibited higher composite scores than the national averages in both countries, confirming the framework’s explanatory power. The Gangwon analysis further demonstrated that mine reuse potential extends beyond tourism to include smart mining education and environmental testbed applications. Overall, this study provides a transferable GIS–AHP model for assessing post-mining utilization and supports evidence-based, region-specific policy design for sustainable mine redevelopment.
1. Introduction
South Korea’s mining sector has been declining due to resource depletion and deteriorating profitability, leading to a steady increase in the number of abandoned mines. According to the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy, the number of operating mines fell from 322 in 2023 to 305 in 2024, while employment in the mining industry decreased from 5529 to 5243 over the same period [1]. In contrast, statistics from the Korea Mine Rehabilitation and Mineral Resources Corporation (KOMIR) indicate that, as of 2025, the number of abandoned mines reached 5147 and continues to rise annually [2]. Abandoned mines are associated with environmental impacts, including acid mine drainage (AMD), soil and water contamination, tailings loss, deforestation, ground subsidence, noise, and dust. These issues have prompted governments and public agencies to implement continuous remediation programs, such as water treatment, land restoration, and tailings management [3].
However, environmental remediation alone has limited capacity to reverse regional economic decline and population outflow in mining-dependent areas. To address this, the government enacted the Special Act on the Assistance to the Development of Abandoned Mine Areas, promoting alternative industrial strategies for former mining regions. A representative case is Kangwon Land (High1 Resort), which catalyzed local economic recovery by developing a tourism complex incorporating a casino, a ski resort, and hotels. Other strategies have included repurposing industrial mines into cultural and experiential attractions [4,5,6]. Nevertheless, these initiatives have not produced uniform economic outcomes across all regions, underscoring the need for more granular, place-sensitive analyses.
Internationally, the reuse of abandoned mines is expanding beyond tourism to include education, research, and technology demonstrations. In Finland, the Pyhäsalmi mine, supported by the EU’s “Callio Future-MINE” project, has been transformed into a testbed for validating electrified equipment and digital technologies in real underground environments [7]. Sweden’s Kankberg mine has established a private 5G network to pilot remote operation and automation, while the Boulby mine in the United Kingdom hosts an ultra-low-background underground laboratory at a depth of approximately 1.1 km [8,9]. These cases illustrate that mines can evolve from mere remediation targets into platforms that integrate advanced technologies and knowledge-based industries. In South Korea, similar discussions have emerged under the Fourth Basic Plan for the Mining Industry, which highlights the potential of transforming both active and abandoned mines into spaces for smart mining education, research, and demonstration [10]. These facilities could serve as living laboratories connecting education, research, and industrial collaboration. Given these trends, a systematic evaluation of site conditions, including accessibility, infrastructure, and environmental constraints, is required to identify locations with high potential for sustainable and diversified utilization.
Despite extensive Geographic Information System (GIS)-based research on mine-related environmental and safety management, comprehensive evaluations of reuse potential remain limited. Earlier studies have mainly focused on quantifying subsidence risks, assessing environmental contamination, or developing hazard indices through the frequency ratio (FR), influence-radius models, and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [11,12,13,14]. Other research has examined broader environmental and health concerns, including health risk assessments near asbestos mines, GIS-based decision support for coalfield revitalization, and the development of an integrated total mine health index (TMHI) to prioritize environmental risks [15,16,17,18]. However, relatively little attention has been paid to the spatial and socio-economic conditions that determine whether abandoned or active mines can be transformed into tourism, education, or smart mining hubs.
To evaluate post-mining reuse potential, five spatial indicators used in site suitability studies were selected, with detailed definitions provided in Section 2.2. The study focuses on representative mining sites in the United States and South Korea to test the framework’s transferability and identify both general and location-specific determinants of successful reuse. Although social, cultural, and environmental determinants, such as community acceptance, cultural heritage value, ecological sensitivity, and governance capacity, may influence post-mining reuse, globally standardized datasets are not consistently available for the United States or South Korea. Therefore, this study focuses on five spatial indicators that can be objectively derived from nationwide public datasets. By bridging spatial analysis with expert judgment, this approach establishes a transparent and replicable method for evaluating post-mining potential. The findings are expected to support data-driven decision making in mine transition planning and contribute to developing an internationally comparable foundation for regional development and heritage management strategies.
2. Methods
This study integrates GIS–based spatial analysis with multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) to evaluate the potential of mining sites for tourism and educational reuse. The suitability of mines for post-mining utilization cannot be explained by a single indicator, as multiple factors, such as accessibility, demand, topography, infrastructure, and links to nearby tourist attractions, interact. Therefore, a framework capable of quantifying and integrating these diverse factors is required.
Previous GIS-based studies on abandoned mines have primarily focused on environmental and safety aspects, including mine hazard prediction, subsidence vulnerability assessment, and forest restoration planning. However, comprehensive spatial suitability analyses that address tourism and educational repurposing remain limited. To fill this gap, the spatial characteristics of each factor were quantified using GIS, combined with AHP-derived weights, and used to produce an integrated suitability map.
First, key factors related to tourism development potential were defined, and the corresponding spatial datasets were collected. Second, spatial analyses, including buffer generation, distance calculation, spatial joining, and zonal statistics, were conducted to derive the values of each factor. Third, because the units and statistical distributions of the variables differ, logarithmic transformation, cumulative distribution function (CDF)-based scoring, and min–max normalization were applied to standardize the indicators on a 0–1 scale. Finally, AHP was used to derive the relative importance of each factor from expert surveys, and these weights were combined with the GIS-based scores to calculate the final composite suitability index.
This procedure captures the spatial distribution of each factor while incorporating expert knowledge that is difficult to quantify through data alone. Given the large number of mines and the difficulty of obtaining consistent site-level data, it is challenging to produce reliable results using only regression or purely statistical estimation. Accordingly, the integrated GIS–AHP methodology employed in this study enables a spatially informed yet quantitatively rigorous assessment, enhancing credibility.
2.1. Data Composition and Sources
A unified spatial dataset was constructed for the United States and South Korea to comparatively evaluate the potential of mining sites for tourism and educational utilization. Although the two countries differ significantly in geography and industrial structure, the contrasting spatial distribution of their mines and their different regional redevelopment strategies provide a meaningful basis for comparative analysis. To this end, five key spatial factors—population density, topography, accessibility, urbanization, tourism resources, and mine locations—were defined using consistent criteria and extracted from national public datasets for spatial analysis.
All data were obtained from open-access sources and standardized to a common coordinate system and spatial resolution to ensure cross-country comparability. Population and urbanization indicators represent the potential demand for tourism and education; road networks reflect accessibility and infrastructure levels; the distribution of tourism-related facilities and attractions (hereafter referred to as points of interest (POIs)) captures local connectivity; slope indicates physical constraints on development; and mine locations delineate the spatial extent of the study areas. The analysis encompassed approximately 250,000 operating and inactive mines in the United States and more than 5000 operating and inactive mines in South Korea. The tourism-related POI dataset was processed through deduplication, removal of non-tourism facilities, and consolidation of overlapping categories. After refinement, approximately 9500 POIs were retained for the United States and approximately 750 for South Korea, which were used to represent tourism resources in the spatial analysis.
2.1.1. The United States
Population density data (Figure 1a) for the United States were obtained from DIVA-GIS. Road network data (Figure 1b) were sourced from the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Tourism-related POI data (Figure 1c) were extracted from OpenStreetMap (OSM). Figure 1d presents urban areas derived from the Global Land Cover by National Mapping Organizations (GLCNMO) dataset. Figure 1e displays slope values calculated from the DIVA-GIS Digital Elevation Model (DEM). Finally, Figure 1f shows mine locations provided by the USGS mineral resources database.
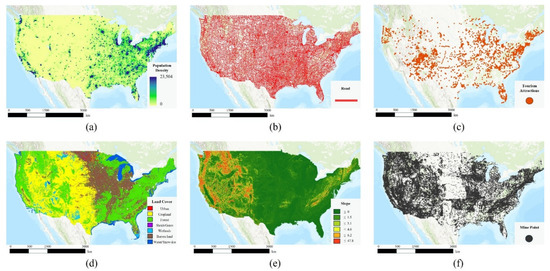
Figure 1.
Input datasets for the United States. (a) Population density, (b) road network, (c) tourism attraction, (d) land cover, (e) slope, and (f) mine locations.
2.1.2. South Korea
Population density data (Figure 2a) for South Korea were obtained from the National Geographic Information Institute (NGII). Road network data (Figure 2b) were sourced from OSM, and tourism-related POI data (Figure 2c) were collected from the National Open Data Portal. Urban areas were extracted from the GLCNMO land cover dataset (Figure 2d). Figure 2e shows slope data derived from the DIVA-GIS DEM, and Figure 2f presents mine locations provided by KOMIR, showing a strong concentration of mining sites in the eastern region, encompassing Yeongwol, Jeongseon, Taebaek, and Samcheok.
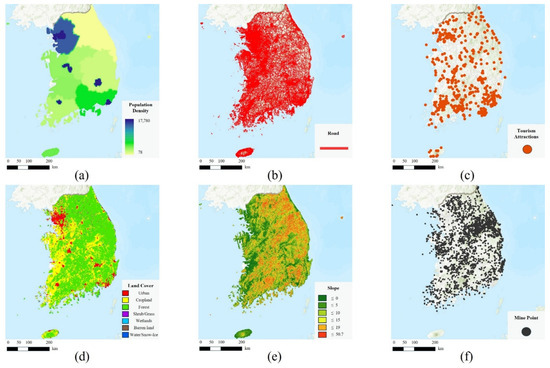
Figure 2.
Input datasets for South Korea. (a) Population density, (b) road network, (c) tourism attraction, (d) land cover, (e) slope, and (f) mine locations.
2.2. GIS-Based Factor Analysis
To quantitatively evaluate mining sites’ potential for tourism and educational utilization, five spatial factors were selected: population density, urbanization, road accessibility, proximity to tourism-related facilities, and slope. These variables represent, respectively, the potential demand, infrastructure level, accessibility, spatial linkage, and physical constraints associated with post-mining development. Each factor is a meaningful indicator of suitability for tourism and educational reuse, and their inclusion is supported by previous studies on site suitability assessment. This reflects a logical progression from demand and infrastructure to accessibility, spatial synergy, and physical feasibility, supporting a comprehensive framework for spatial evaluation of mining site utilization.
2.2.1. Population Density
Population density is a key indicator of potential demand and plays a critical role in assessing mining sites’ suitability for tourism and educational development. Regions with low population bases often face difficulties in generating initial visitor demand and sustaining long-term operations. Moghaddam et al. [19] identified population density as one of the most influential variables in evaluating urban tourism potential, while Zikirya and Zhou [20] employed population distribution as a primary explanatory factor in their spatial analysis of 9296 tourist destinations across China. These studies highlight the importance of population distribution as a determinant of tourism and educational site suitability. In this study, buffer zones were generated around the centroid of each mining site—100 km for the United States and 10 km for South Korea—to account for the approximately 100-fold difference in land area between the two countries. In addition to differences in national land area, the buffer radii also reflect distinct mobility patterns and settlement structures in each country. Long-distance intercity travel (often exceeding 80–120 km) is common in the United States due to low-density spatial distribution, whereas tourism and educational visits in South Korea generally occur within a 10–20 km catchment because of its compact geography and urban concentration. The selected radii therefore represent realistic service areas for capturing population-based demand around each mining site. The mean population density within each buffer zone was calculated using the Zonal Statistics as Table tool in ArcGIS Pro 3.4.0 (Esri, The Redlands, CA, USA), providing a standardized representation of local population potential across both national contexts. The population density index (PD) was defined as follows:
Here, represents each mining site, denotes the total number of population density raster cells within the buffer zone centered on , and is the population density value of cell . Accordingly, indicates the mean population density within the buffer area, providing a quantitative measure of the local population base surrounding each mine.
2.2.2. Urban Ratio
Urban ratio (UR) is an indirect indicator of access to tourism-related infrastructure, including accommodation, transportation, and commercial facilities. A higher level of urbanization generally facilitates the inflow of tourism demand and the provision of related services, thereby acting as a key determinant of a site’s potential for tourism and educational utilization. Withanage et al. [21] employed the urban ratio as a major variable in evaluating urban tourism suitability, while Uyan [22] used it as a proxy indicator of regional accessibility in land use suitability analysis. In this study, pixels classified as urban areas were extracted from the land cover dataset, and the proportion of urbanized land within each mine-centered buffer was calculated. The urban ratio is defined as follows:
Here, denotes each mining site, represents the total area classified as urban within the buffer zone centered on , and indicates the total valid area excluding water surfaces and missing data. The value ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values signifying greater access to tourism-related infrastructure.
2.2.3. Road Accessibility
Road accessibility is a critical determinant of potential visitor inflow and operating costs. Şener et al. [23] identified road accessibility as the most influential siting factor in landfill location analysis, and Yasin and Woldemariam [24] found that areas with higher road accessibility exhibit substantially greater tourism suitability. In this study, road accessibility was operationalized as the shortest straight-line distance from each mine to the nearest road, computed in GIS using the Euclidean Distance function (units in meters under the working coordinate reference system); smaller values indicate greater accessibility.
2.2.4. Tourist Attraction
Tourist attraction (TA) enhances mines’ tourism-oriented redevelopment. A greater density of nearby tourist attractions increases visitor retention and the likelihood of integrated tourism activities. Acharya et al. [25] reported that areas with a greater concentration of tourist sites in West Bengal, India, exhibited higher tourism. In this study, a buffer zone with a 10 km radius was created around each mine, and the number of tourist attractions within this area was counted using the Spatial Join function. The tourist attraction linkage index is defined as follows:
Here, denotes each mining site, and represents the total number of tourist attractions located within 10 km of the site. A higher value indicates a denser distribution of surrounding tourist attractions, reflecting greater potential for integrated tourism development.
2.2.5. Slope
Slope reflects terrain constraints, accessibility, and construction feasibility. Areas with steep slopes generally face greater challenges in developing transportation and tourism infrastructure, as well as limitations in safety. Luan et al. [26] incorporated slope as a major evaluation factor in assessing land suitability for urban development, while Pradhan [27] identified slope as a decisive topographic determinant in landslide susceptibility analysis. Building on these studies, the present study includes slope as one of the primary variables for evaluating the suitability of mine site utilization. Slope values were derived from the DEM using the Slope function in ArcGIS, which calculates the maximum rate of elevation change between adjacent cells and expresses the result in degrees or percentages. Because slope is a physical variable, the mean slope within a 1 km radius around each mining site was computed and used for both the United States and South Korea.
2.3. Statistical Standardization and Normalization
Because each factor encompasses different units and statistical distributions, direct comparison or aggregation is difficult. In particular, population density and the number of tourist attractions exhibit non-normal distributions concentrated in small values, with a few extreme outliers. This asymmetry may distort statistical interpretation; therefore, following Kim et al. [18], the data were log-transformed to approximate a normal distribution. Subsequently, the standard normal CDF was applied to convert each variable into a relative score ranging from 0 to 1. This procedure minimizes the influence of extreme values and ensures comparability among variables. The log transformation and CDF-based scoring are defined as follows:
Here, denotes the standardized score (ranging from 0 to 1) of object for indicator , denotes the raw value of object , represents the log-transformed value of the variable, is the mean of the log-transformed variable, is the standard deviation of the log-transformed variable, and denotes the CDF of the standard normal distribution. Assuming that the log-transformed variable follows a normal distribution, the standardized score represents the cumulative probability of that value within the overall distribution. This method reduces skewness and enables consistent comparison across variables. For variables with relatively uniform distributions, or where log transformation was unnecessary, linear min–max normalization was applied.
2.4. AHP-Based Weight Derivation and Composite Scoring
The AHP is an MCDA method that hierarchically structures multiple decision criteria and quantifies expert judgments through pairwise comparisons to derive the relative importance of each factor [28]. Previous studies [24,25,29,30] have demonstrated that AHP is one of the most widely used and reliable techniques when integrated with GIS-based spatial analysis. The pairwise comparison matrix is constructed as follows:
Because AHP relies on expert judgment, a certain degree of subjectivity cannot be avoided. To reduce individual bias, experts were selected from multiple fields, including mine reclamation, tourism development, and regional planning, and their pairwise comparison matrices were aggregated using the geometric mean, which is widely recognized as an effective way to stabilize AHP weights. The final composite score was calculated using the Weighted Linear Combination (WLC) method [31].

Table 1.
Results of weight calculation using the AHP.
3. Results
3.1. Results of the United States Case Analysis
Approximately 250,000 mining sites across the United States were evaluated by combining the standardized scores of five spatial factors with the AHP-derived weights to calculate a composite score (Figure 3). The national average score was approximately 47, with high-suitability zones clearly concentrated along major metropolitan areas in the eastern United States and transportation corridors (Figure 4). This spatial pattern indicates that population density, urban ratio, accessibility, and proximity to tourist attractions jointly contribute to favorable conditions for tourism- and education-oriented reuse.
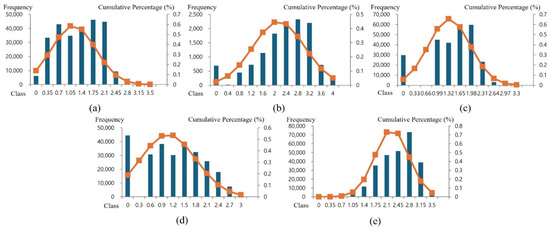
Figure 3.
Frequency distributions of log-transformed variables and fitted normal probability curves for the United States. (a) Population density, (b) urban ratio, (c) road accessibility, (d) tourist attractions, and (e) slope.
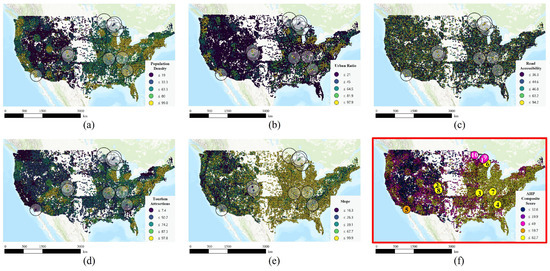
Figure 4.
Normalized indicator scores and overall composite score for the United States. (a) Population density, (b) urban ratio, (c) road accessibility, (d) tourist attractions, (e) slope, and (f) overall composite score map and locations of the ten selected restored mine sites (1–10).
Table 2 summarizes ten representative mines that have been successfully redeveloped into tourist destinations. Their identification numbers are included in Figure 4f. These cases encompass diverse utilization types, such as scuba diving, underground guided tours, mining museums, and adventure facilities. Despite their different regional contexts and operational models, most are located in or near urban areas with accessible transportation. This is consistent with the suitability analysis.

Table 2.
Representative abandoned mine reuse cases in the United States.
The average composite score of the ten successful cases was approximately 63, exceeding the overall national mean of 47. Among them, the Louisville limestone mine (78.9), Bonne Terre mine (77.0), and Argo gold mine (76.7) had the highest values (Table 2). Quincy mine exhibited a relatively lower score of 41.0, which reflects differences in population and accessibility conditions rather than poor tourism performance.
Figure 5 depicts the factor-specific scores of each mine as pentagon radar charts. Most successful cases show generally high values for population density, tourist attraction, and road accessibility. In particular, the Louisville limestone mine and the Bonne Terre mine display balanced high scores across all indicators, resulting in the highest composite suitability values. These patterns indicate that the combined influence of population-based demand, transportation infrastructure, and spatial linkage enhances the reuse potential of abandoned mines.
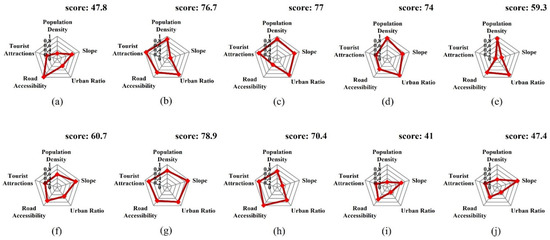
Figure 5.
Indicator score radar charts for representative reclaimed mines in the United States. (a) Adventure, (b) Argo, (c) Bonne Terre, (d) Consolidated, (e) Eagle, (f) Iron Mountain, (g) Louisville, (h) Mollie Kathleen, (i) Quincy, and (j) Soudan.
Beyond their spatial characteristics, successful U.S. redevelopment cases have faced challenges including extensive environmental remediation requirements, limited funding for initial stabilization, and the need to establish new governance partnerships. Many sites have addressed these issues through phased redevelopment strategies, public–private collaboration, and integration with existing regional tourism clusters. These qualitative aspects help explain why certain locations have been successful despite moderate spatial suitability scores.
The U.S. case analysis shows that the GIS–AHP framework can sensitively reflect real-world reuse outcomes at a national scale. These results provide a basis for applying the same framework to South Korea, where distinct geographical and socio-spatial conditions—such as mountainous terrain and lower population density—are expected to yield different suitability patterns.
3.2. Results of the South Korea Case Study
For mines across South Korea, the overall composite scores were calculated by combining the standardized values of five spatial factors with the AHP-derived weights (Figure 6). The national average score was approximately 38.8, lower than that of the United States (47.0). Spatially, low-grade zones were widely distributed across the mountainous interior of the Gangwon region, while higher-grade areas appeared near the Seoul Metropolitan Area, parts of Gyeongsang Province, and the eastern coastal region (Figure 7). These high-ranking areas generally exhibit higher population density, better road access, and stronger links to nearby tourist attractions, whereas abandoned mines located in the inland mountains of Gangwon tended to be less suitable due to steep slopes and limited accessibility. This pattern highlights the inherent geographical and infrastructural constraints of abandoned mines in South Korea.
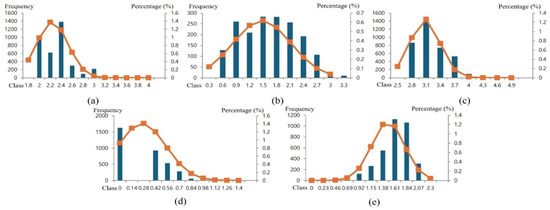
Figure 6.
Frequency distributions of log-transformed variables and fitted normal probability curves for South Korea. (a) Population density, (b) urban ratio, (c) road accessibility, (d) tourist attractions, and (e) slope.
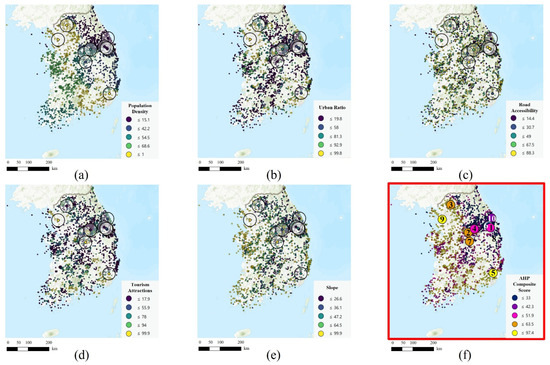
Figure 7.
Normalized indicator scores and overall composite score for South Korea. (a) Population density, (b) urban ratio, (c) road accessibility, (d) tourist attractions, (e) slope, and (f) overall composite score map and locations of the ten selected restored mine sites (1–10).
Table 3 summarizes ten representative abandoned mines that have been successfully converted into tourism resources. These include Gwangmyeong cave, Samtan art mine, Hwaam cave, and Pocheon art valley, which have been redeveloped into museums, experiential facilities, and cultural spaces. Although their regional contexts vary, most are situated in locations with favorable transportation access or strong connections to existing tourist destinations, which is consistent with the spatial suitability results.

Table 3.
Representative abandoned mine reuse cases in South Korea.
The average overall composite score for the ten successful cases was 53.0, which is notably higher than the national average (38.8). In particular, Siheung mine recorded the highest score nationwide, reflecting a combination of a dense metropolitan population, gentle topography, excellent road network, and strong synergy with nearby attractions. Most sites had scores exceeding the national average, indicating generally higher performance levels (Table 3, Figure 7f).
Figure 8 illustrates the factor-based profiles of the successful cases as pentagon radar charts. Siheung mine and Pocheon Art Valley achieved balanced high scores across all factors, while Jeil mine and Eunsung colliery exhibited particularly strong values for the tourist attraction factor, underscoring the importance of cluster effects in regional tourism development.
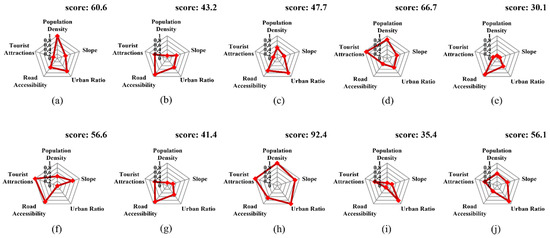
Figure 8.
Indicator score radar charts for representative reclaimed mines in South Korea. (a) Pocheon art valley, (b) Hamtae anthracite mine, (c) Danyang limestone mine, (d) Jeil mine, (e) Samtan art mine, (f) Eunsung colliery, (g) Jangseong colliery, (h) Siheung mine, (i) Ssangyong Mukho district 3, and (j) Hwalok cave.
In Korea, many redevelopment projects have faced constraints related to land use regulations, conservation of industrial heritage structures, and accessibility challenges due to mountainous terrain. Successful cases were able to overcome these limitations through targeted infrastructure improvements, heritage-oriented design approaches, and close coordination with local governments. These qualitative aspects complement the GIS–AHP findings by showing that practical implementation depends not only on spatial suitability but also institutional and contextual conditions beyond the measured indicators.
In South Korea, the nationwide average suitability of abandoned mines is generally lower than that of the United States, the successfully redeveloped cases have substantially higher scores than the mean, and the combined influence of the population base, accessibility, and tourist linkage plays a decisive role in maximizing abandoned mines’ reuse potential.
3.3. Comparison Between the United States and South Korea: Key Insights
Applying the same GIS–AHP framework to both the United States and South Korea revealed a clear disparity in the reuse potential of abandoned mines, primarily stemming from differences in population base and accessibility. In the United States, many mines are located near industrial and metropolitan areas in the eastern and central regions, resulting in an average composite score of 47.3. In contrast, South Korea’s mines are largely concentrated in low-density, mountainous, inland regions, yielding a lower average of 38.8. Population density and road accessibility contributed most significantly to the inter-country score gap, while the spatial distribution of tourist attractions formed a nationwide cluster pattern in the United States and a localized pattern in South Korea. These results indicate that abandoned mines in the United States, embedded within established urban–industrial corridors, possess inherent advantages for conversion into tourism and educational resources, whereas Korean mines face much higher initial barriers due to geographic constraints. Despite these differences, the successful U.S. and Korean cases demonstrated substantially higher suitability values than their national averages, confirming the framework’s predictive validity.
South Korea’s lower national average should not be interpreted as an indicator of limited reuse potential. Rather, these low-scoring areas often coincide with regions that lack tourism infrastructure and have experienced industrial decline, areas where new transformation initiatives are most needed. In this context, lower scores signal the limitations of market-driven development while simultaneously emphasizing the need for public sector intervention. Therefore, redevelopment strategies for South Korea’s abandoned mines should be differentiated; sites with favorable geographic conditions may benefit from private investment and intensive development, whereas remote and low-density areas require gradual revitalization supported by public infrastructure and long-term policy assistance.
Overall, this cross-country comparison demonstrates that the proposed GIS–AHP analytical framework possesses both benchmark validity and practical applicability. It quantitatively reflects national contextual differences while identifying the necessity of targeted social and policy intervention. These insights provide a foundation for the in-depth analysis of the Gangwon region presented in the next section.
3.4. In-Depth Analysis and On-Site Verification in Gangwon Region
The nationwide analysis confirmed that mines’ potential utilization is determined by a combination of spatial factors, including population density, accessibility, and proximity to tourist attractions. However, locational analyses alone cannot sufficiently explain mine utilization in the Gangwon region. Gangwon is not only the region with the highest concentration of abandoned mines in South Korea but also a focal area for financial and policy resources related to mine rehabilitation, making it a practical base for large-scale mine redevelopment initiatives. Historically, Gangwon served as the center of South Korea’s coal industry, and after the Coal Industry Rationalization Policy of the 1990s, extensive mine closures occurred. Today, the region faces structural challenges, including industrial decline and population outflow.
In response, the Special Act on Assistance to Abandoned Mine Areas was enacted, establishing a development fund that has been used for various projects, such as community welfare, environmental improvement, tourism development, and start-up support. More recently, this fund has expanded to include programs related to mining education and advanced technology demonstration, providing Gangwon region with a unique financial foundation that enables practical implementation of this study’s findings. Because locational analysis alone cannot fully capture the physical and social characteristics of individual sites, on-site verification was conducted for selected mines within the Gangwon region.
The first case, the Dogye mine in Samcheok (Figure 9a), had relatively low population density and slope indicators, resulting in a composite score of 35.2, which is slightly below the national average. However, the mine recorded relatively high scores in road accessibility and urban proximity. As the last operating coal mine of the Korea Coal Corporation, it is scheduled for closure in June 2025, and the preservation of surface facilities is excellent. Field investigations confirmed its strong spatial linkage with the Dogye-eup urban area and easy accessibility, with visible remnants of aboveground mining structures. These characteristics suggest that a low-impact transformation focused on interpretation, exhibition, and experiential tourism could be achieved without the need for major new construction.
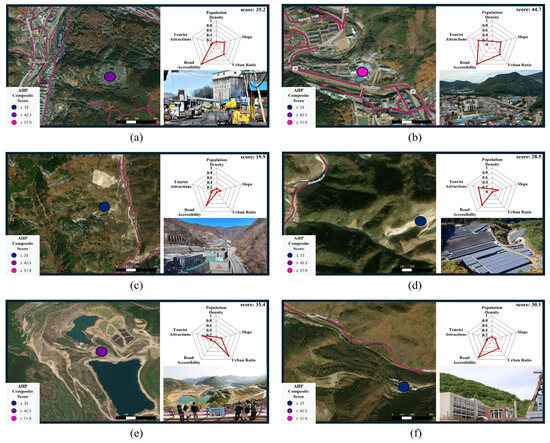
Figure 9.
AHP-based suitability and site imagery for four selected mines: (a) Dogye mine [32], (b) Jangseong mine [33], (c) Sangdong mine [34], (d) open-pit mine in hajeon-myeon [35], (e) Mureung Byeolyucheonji [36], and (f) Samtan Art Mine [37].
The second case, the Jangseong mine in Taebaek (Figure 9b), had a composite score of 44.7, exceeding the national average, with high values for urban ratio, tourism linkage, and road accessibility. The mine ceased operation in 2024, and its surface area remains well-integrated with the surrounding urban environment. Taebaek-si is currently considering utilizing the site as an underground research facility for high-level radioactive waste studies, reflecting the potential for linking industrial transition with urban regeneration. Its proximity to KOMIR’s facilities further enhances its future development potential.
The third case, the Sangdong mine in Yeongwol (Figure 9c), had lower scores for most indicators, except for road accessibility, suggesting limited potential for tourism development. However, Sangdong mine is a symbolic metallic mine that is currently being redeveloped following the recent rise in tungsten prices. Field investigations confirmed convenient vehicular access and the presence of functioning communication and monitoring infrastructure. Given this, the site is better suited to smart mining demonstrations and training rather than tourism.
The fourth case, an open-pit mine in Hajeon-myeon, Samcheok (Figure 9d), scored low across most indicators, except for road accessibility and proximity to tourist sites, resulting in a composite score of 28.5. Field observations revealed that the site has been rehabilitated and is currently operating as a solar power generation facility, with almost no remaining traces of the original mining topography or structures. Although unsuitable for tourism or educational purposes, this case illustrates the potential for repurposing abandoned mines as energy transition sites.
Lastly, Mureung Byeolyucheonji in Donghae (Figure 9e) and Samtan Art Mine in Jeongseon (Figure 9f) were examined. Mureung Byeolyucheonji is a complex experiential tourism site developed on a former open-pit limestone quarry that operated for approximately 40–50 years beginning in the late 1970s. The site preserves the deep quarry pit and the artificial lake created by past extraction activities and combines them with observation decks, sculptural installations, and rest areas to create a distinctive landscape. Samtan Art Mine is a cultural and artistic regeneration project. The abandoned mining area was redeveloped as “a mine that excavates art instead of coal,” and existing structures, such as tunnels, coal preparation facilities, and conveyor systems, were retained as much as possible and adapted into galleries, museums, and experiential spaces. This approach allows visitors to engage with both the historical legacy and the industrial landscape of the region’s former coal industry.
Although the spatial scores for Mureung Byeolyucheonji and Samtan Art Mine were lower than those of sites near the metropolitan area, both have achieved successful redevelopment through diverse cultural programming, community-driven initiatives, and supportive local policies. These observations suggest that spatial disadvantages do not necessarily constrain redevelopment outcomes, as cultural capital, historical identity, and community engagement can compensate for physical limitations. More broadly, the field verification results confirm the general consistency of the GIS–AHP framework with real-world conditions while underscoring the importance of local rehabilitation status and administrative support—factors that are difficult to capture through spatial indicators alone. Accordingly, site-specific strategies tailored to regional characteristics are essential for effective post-mining revitalization.
4. Discussion
This study combined GIS-based spatial analysis with AHP to quantitatively evaluate the tourism and educational reuse potential of abandoned mines and applied the framework to cases in the United States, South Korea, and, specifically, the Gangwon region. The results revealed national and regional variations and consistently showed that successfully redeveloped mines achieved higher composite scores, indicating that the proposed analytical framework can partially explain actual performance outcomes.
Previous research has largely relied on case-specific qualitative approaches focusing on the sociocultural context or symbolic meaning of individual mine sites. In contrast, this study established a quantitative and scalable evaluation framework using nationwide spatial datasets, enabling objective comparison and policy-level applicability. The integration of quantified expert judgment through AHP and the use of statistical normalization helped mitigate variable imbalance issues, providing a robust basis for comparing mine reuse potential. Although AHP offers a structured and transparent method for deriving factor weights, its reliance on expert pairwise comparison introduces a degree of subjectivity. Future research may strengthen the robustness of weighting by applying data-driven approaches, such as entropy weighting, principal-component-based weighting, or machine-learning-assisted MCDM techniques. These complementary methods could facilitate sensitivity testing of AHP-derived weights and enhance the framework’s reliability. A supplementary equal-weight scenario was compared with the AHP-derived weighting scheme for representative cases in both countries. Only one site in the United States and two sites in South Korea exhibited minor shifts in ranking, and the magnitude of these changes was small. The overall ordering of high-scoring sites remained stable across both weighting approaches, indicating that the suitability outcomes are not highly sensitive to moderate variations in factor weights. This suggests that the framework maintains internal consistency while still reflecting expert judgment. Moreover, although all pairwise comparison matrices satisfied the commonly accepted threshold of CR < 0.1, employing a more stringent criterion may further improve robustness.
However, quantitative analysis alone cannot fully capture the complex realities underlying mine reuse. In addition to spatial and infrastructural attributes, successful redevelopment often depends on qualitative factors, such as local community support, historical and cultural significance, environmental vulnerability, and institutional readiness. These aspects were not included due to the lack of internationally comparable datasets, but they represent essential complementary factors that future research should incorporate through survey-based indicators, community-level socioeconomic data, or participatory GIS approaches. Furthermore, substantial geographical and socioeconomic differences between the United States and South Korea suggest that the framework should be used as a cross-regional analytical tool rather than a universally generalizable model.
This study focused on five factors due to data availability. Future analyses should consider incorporating additional variables, such as environmental stability, geological structure, and institutional constraints, and improve spatial precision using high-resolution datasets, such as LiDAR or drone imagery.
Ultimately, the GIS–AHP framework developed in this study serves as a first-stage quantitative screening tool for evaluating abandoned mines’ reuse potential. Building on these results, subsequent research should conduct detailed qualitative assessments of high-potential sites to verify their feasibility. By emphasizing the need for a stepwise approach, this study provides a foundational reference for future policymaking in mine rehabilitation and regional regeneration.
5. Conclusions
This study integrated GIS-based spatial analysis with AHP to evaluate the tourism and educational reuse potential of abandoned mines, applying the proposed framework to cases in the United States, South Korea, and the Gangwon region. The main findings can be summarized as follows.
First, the analysis of the United States demonstrated that the proposed methodology aligns well with actual performance outcomes. Mines that were successfully transformed into tourist destinations consistently exhibited high overall composite scores, indicating that population base, accessibility, and proximity to existing tourist attractions are key determinants of success.
Second, although South Korea’s overall score was relatively lower, several successful cases had exceptionally high suitability values. This suggests that while Korean mines may face structural disadvantages in average locations, those with specific geographic advantages still hold considerable potential for redevelopment.
Third, the cross-national comparison between the United States and Korea verified both the universality and regional specificity of the proposed framework. In the United States, higher population density and well-developed transportation infrastructure enabled a broad distribution of high-potential sites, whereas in Korea only a limited number of sites had comparable conditions. This implies that a selective and concentrated development strategy is more appropriate for Korea, rather than a uniform nationwide policy.
Fourth, the detailed analysis of the Gangwon region revealed that some mines have potential for tourism-oriented reuse, while others could be transformed into smart mining education and demonstration hubs. The existence of an independent financial foundation, such as the Mine Area Development Fund, enhances the practical feasibility of translating these analytical results into actionable policy initiatives.
From an academic perspective, this study (1) introduced a logarithmic transformation and cumulative-distribution-based scoring method to correct data skewness, (2) quantified expert judgment through AHP to reduce subjectivity, and (3) presented a new analytical framework for quantitatively evaluating the reuse potential of abandoned mines. This framework complements previous qualitative, case-oriented studies by providing comparable and scalable results at both national and regional levels.
From a policy standpoint, the findings indicate that Korea’s mine reuse strategy should be site-specific. The Gangwon region in particular represents an optimal pilot area where tourism, smart mining, and environmental restoration initiatives can be jointly tested and implemented.
Future research should incorporate additional social and environmental factors, such as community acceptance, safety, and ecological resilience, into the GIS–MCDA framework. Expanding the dataset and conducting scenario-based simulations could further quantify the impacts of infrastructure expansion and tourism development on mine reuse potential.
In conclusion, this study provides one of the first systematic frameworks for quantitatively assessing the reuse potential of abandoned mines. It serves as a bridge between academic analysis and policy implementation, and future work combining quantitative evaluation with qualitative and field-based validation can contribute to establishing a multi-layered decision making system for sustainable mine regeneration. The qualitative findings suggest that institutional conditions, community support, and environmental constraints are essential determinants of successful mine reuse and should be incorporated into future evaluation frameworks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-M.K.; formal analysis, D.-H.L.; methodology, S.-M.K.; software, D.-H.L. and H.K.; writing—original draft, D.-H.L. and H.K.; writing—review and editing, S.-M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by (1) the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00213956), and (2) the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (No. RS-2022-KP002711).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| AMD | Acid Mine Drainage |
| CDF | Cumulative Distribution Function |
| CI | Consistency Index |
| CR | Consistency Ratio |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GLCNMO | Global Land Cover by National Mapping Organizations |
| KOMIR | Korea Mine Rehabilitation and Mineral Resources Corporation |
| MCDA | Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis |
| MCDM | Multi-Criteria Decision Making |
| NGII | National Geographic Information Institute |
| OSM | OpenStreetMap |
| PD | Population Density |
| POI | Points of Interest |
| TA | Tourist Attraction |
| TMHI | Total Mine Health Index |
| UR | Urban Ratio |
| USGS | United States Geological Survey |
| WLC | Weighted Linear Combination |
References
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE). National Mine Status. Available online: https://www.motie.go.kr/mine/emine/mineIntroduction/generalMine/generalMineStatus.jsp (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Korea Mine Rehabilitation and Mineral Resources Corporation (KOMIR). MiRe-GIS—Mine Status. Available online: https://miregis.komir.or.kr (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE). The Fourth Basic Plan for Prevention of Mining Damage (2022–2026); MOTIE: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://www.motir.go.kr/kor/article/ATCL3f49a5a8c/165286/view (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Korea Tourism Organization (KTO). Gwangmyeong Cave. Available online: https://english.visitkorea.or.kr/svc/contents/contentsView.do?vcontsId=194429 (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- KOCIS Webzine. Mureung Byeolyucheonji Turns Abandoned Limestone Mine into a Natural Spectacle. Available online: https://www.kocis.go.kr/eng/webzine/202209/sub02.html (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Korea Tourism Organization (KTO). Samtan Art Mine (Jeongseon). Available online: https://english.visitkorea.or.kr/svc/contents/contentsView.do?vcontsId=66073 (accessed on 22 September 2025).
- Callio. FutureMINE—Digital Test Mine at Pyhäsalmi. Available online: https://callio.info/invest-opportunities/futuremine/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Boliden, A.B. 5G Kankberg—World’s First Underground 5G NR Network. Available online: https://www.boliden.com/news/5g-kankberg/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- UK Research and Innovation (UKRI). Boulby Underground Laboratory. Available online: https://www.ukri.org/who-we-are/stfc/facilities/boulby-underground-laboratory/ (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE). The Fourth Basic Plan for Mining (2025–2034) Announced; MOTIE: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2024. Available online: https://www.motir.go.kr/kor/article/ATCL3f49a5a8c/169988/view (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Suh, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Kwon, H.-H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Go, W.-R. Application of Frequency Ratio and Analytic Hierarchy Process to Subsidence Hazard Assessment Around Abandoned Coal Mine. J. Korean Soc. Geosystem Eng. 2010, 47, 690–704. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.; Suh, J.; Yi, H.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, S. GIS-Based Subsidence Hazard Analysis on Abandoned Coal Mine Sites Combining the Frequency Ratio and Radius of Influence. J. Korean Soc. Miner. Energy Resour. Eng. 2015, 52, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, S. Development of a Software for Assessing Mining Subsidence Susceptibility Using GIS Combined with Frequency Ratio, Fuzzy Membership Functions and Analytic Hierarchy Process. J. Korean Soc. Miner. Energy Resour. Eng. 2015, 52, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, H. Development of Ground Subsidence Risk Assessment Model Using Analytic Hierarchy Process Method. J. Korean Geotech. Soc. 2024, 40, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-B.; Son, I.; Noh, J.-H. Health Risk Assessments Using GIS Method for the Abandoned Asbestos Mines. J. Mineral. Soc. Korea 2011, 24, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Oh, S.; Park, H.-D.; Kwon, H.-H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Go, W.-R. Development of a GIS Based Decision Support System for Planning the Reforestation at Abandoned Coal Mines. J. Korean Soc. Geosyst. Eng. 2009, 46, 691–702. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-K.; Kim, K.-D.; Lee, S.; Kim, I.-S.; Won, J.-S. Prediction of Ground Subsidence Hazard Area Using GIS and Probability Model Near Abandoned Underground Coal Mine. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2007, 40, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-M.; Suh, J.; Oh, S.; Son, J.; Hyun, C.-U.; Park, H.-D.; Shin, S.-H.; Choi, Y. Assessing and prioritizing environmental hazards associated with abandoned mines in Gangwon-do, South Korea: The Total Mine Hazards Index. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.D.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Valizadeh, R. A GIS-Based Assessment of Urban Tourism Potential with a Branding Approach Utilizing Hybrid Modeling. Spat. Inf. Res. 2022, 30, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikirya, B.; Zhou, C. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanage, N.C.; Wijesinghe, D.C.; Mishra, P.K.; Abdelrahman, K.; Mishra, V.; Fnais, M.S. An ecotourism suitability index for a world heritage city using GIS-multi criteria decision analysis techniques. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, M. GIS-based solar farms site selection using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in Karapinar region, Konya/Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Nas, B.; Karagüzel, R. Combining AHP with GIS for landfill site selection: A case study in the Lake Beyşehir catchment area (Konya, Turkey). Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, K.H.; Woldemariam, G.W. GIS-based ecotourism potentiality mapping in the East Hararghe Zone, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.; Mondal, B.K.; Bhadra, T.; Abdelrahman, K.; Mishra, P.K.; Tiwari, A.; Das, R. Geospatial Analysis of Geo-Ecotourism Site Suitability Using AHP and GIS for Sustainable and Resilient Tourism Planning in West Bengal, India. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Peng, S. Land-use suitability assessment for urban development using a GIS-based soft computing approach: A case study of Ili Valley, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B. Landslide susceptibility mapping of a catchment area using frequency ratio, fuzzy logic and multivariate logistic regression approaches. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: A survey of the literature. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, E.H.; Gass, S.I. The analytic hierarchy process—An exposition. Oper. Res. 2001, 49, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. On the use of weighted linear combination method in GIS: Common and best practice approaches. Trans. GIS 2000, 4, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonhap News Agency. Available online: https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20241224114800062 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Yonhap News Agency. Available online: https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20240625141800062 (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Business Post. Available online: https://www.businesspost.co.kr/BP?command=article_view&num=380903 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Gangwon Jibang Sinmun. Available online: https://www.gwunion.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=7257 (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- The Chosun Daily. Available online: https://www.chosun.com/national/regional/2021/11/15/NYKTQAKNBRDLNPXJMUVDMUPAGY/ (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Today Energy. Available online: https://www.todayenergy.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=83109 (accessed on 14 November 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).