Stability Analysis of Surface Facilities in Underground Mining and the Cumulative Impact of Adjacent Mining Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
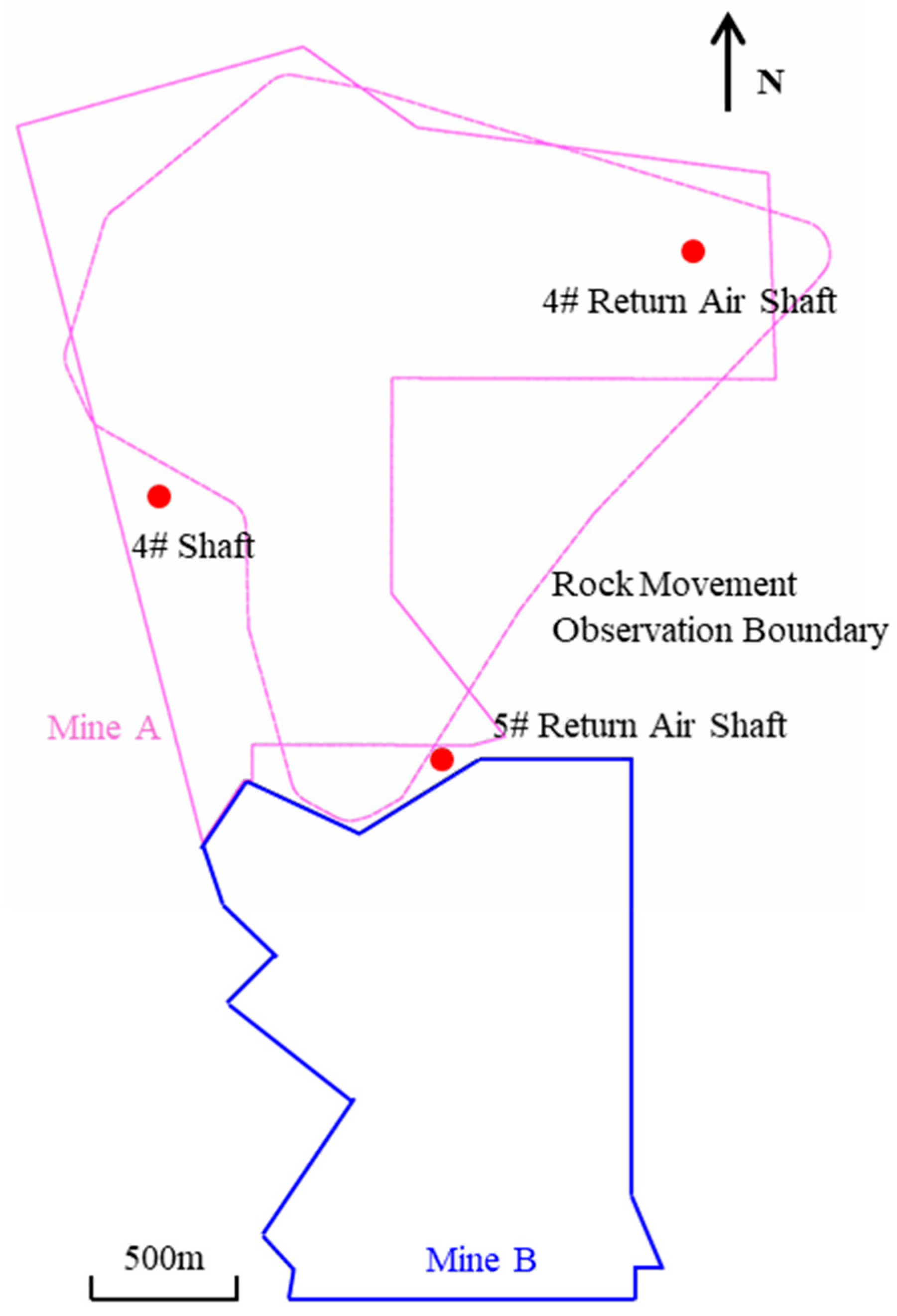
2. Introduction to the Mine
2.1. Overview of the Mining Area and Mining Methods
2.2. Physical and Mechanical Parameters of Rock Mass
2.2.1. Physical and Mechanical Parameters of Rock
2.2.2. Engineering Rock Mass Parameters
3. Theoretical Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining on Surface
3.1. Prediction Methods for Surface Movement and Deformation Induced by Ore Body Extraction
3.1.1. Subsidence Expression for Points on the Surface
3.1.2. Inclination Expression for Points on the Surface
3.1.3. Curvature Expression for Points on the Surface
3.1.4. Horizontal Displacement Expression for Points on the Surface
3.1.5. Horizontal Deformation Expression for Points on the Surface
3.2. Analysis of Surface Movement and Deformation Induced by Ore Body Extraction
4. Numerical Simulation of the Impact of Underground Mining on Surface Facilities
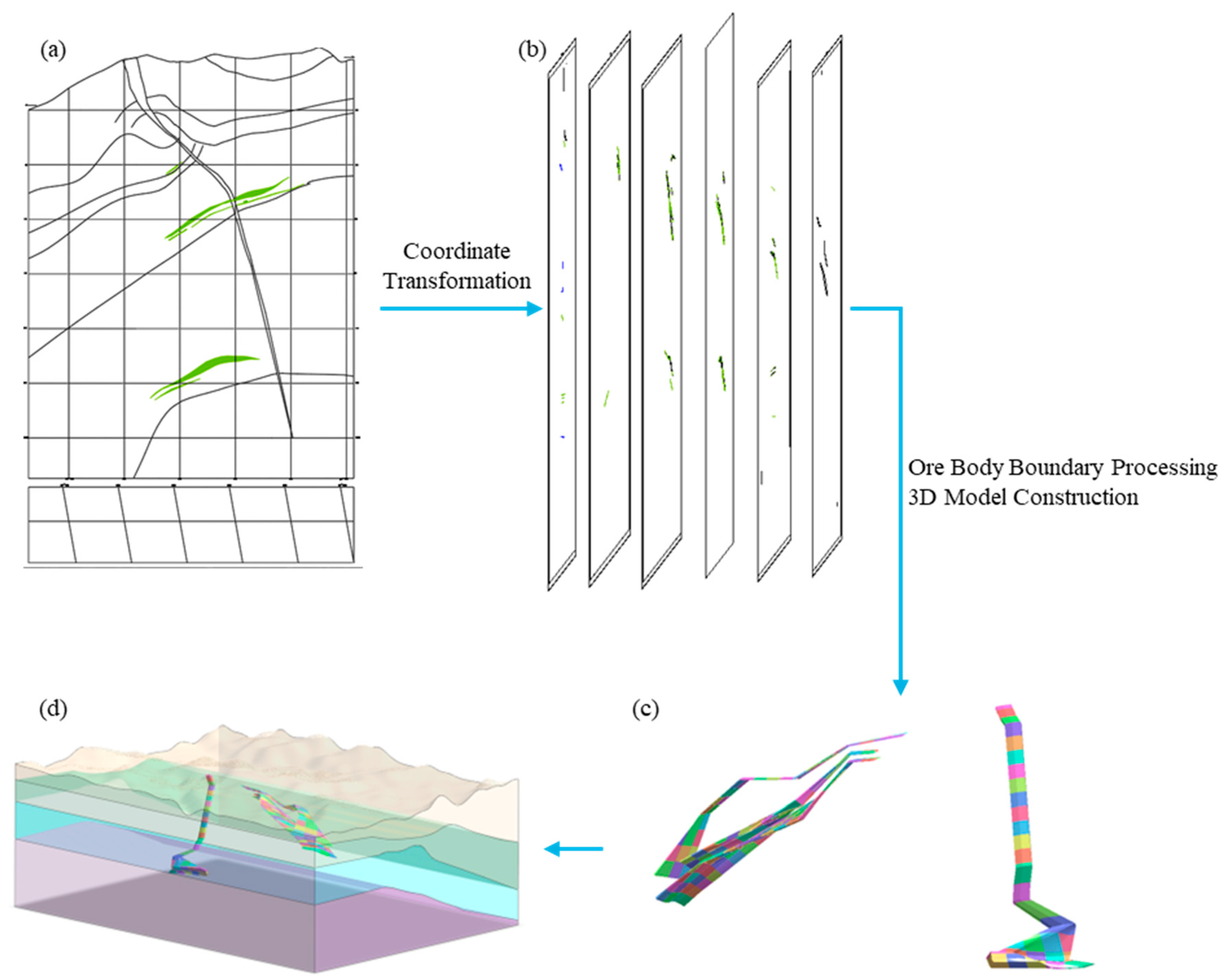
4.1. Simulation Model
4.2. Excavation Method
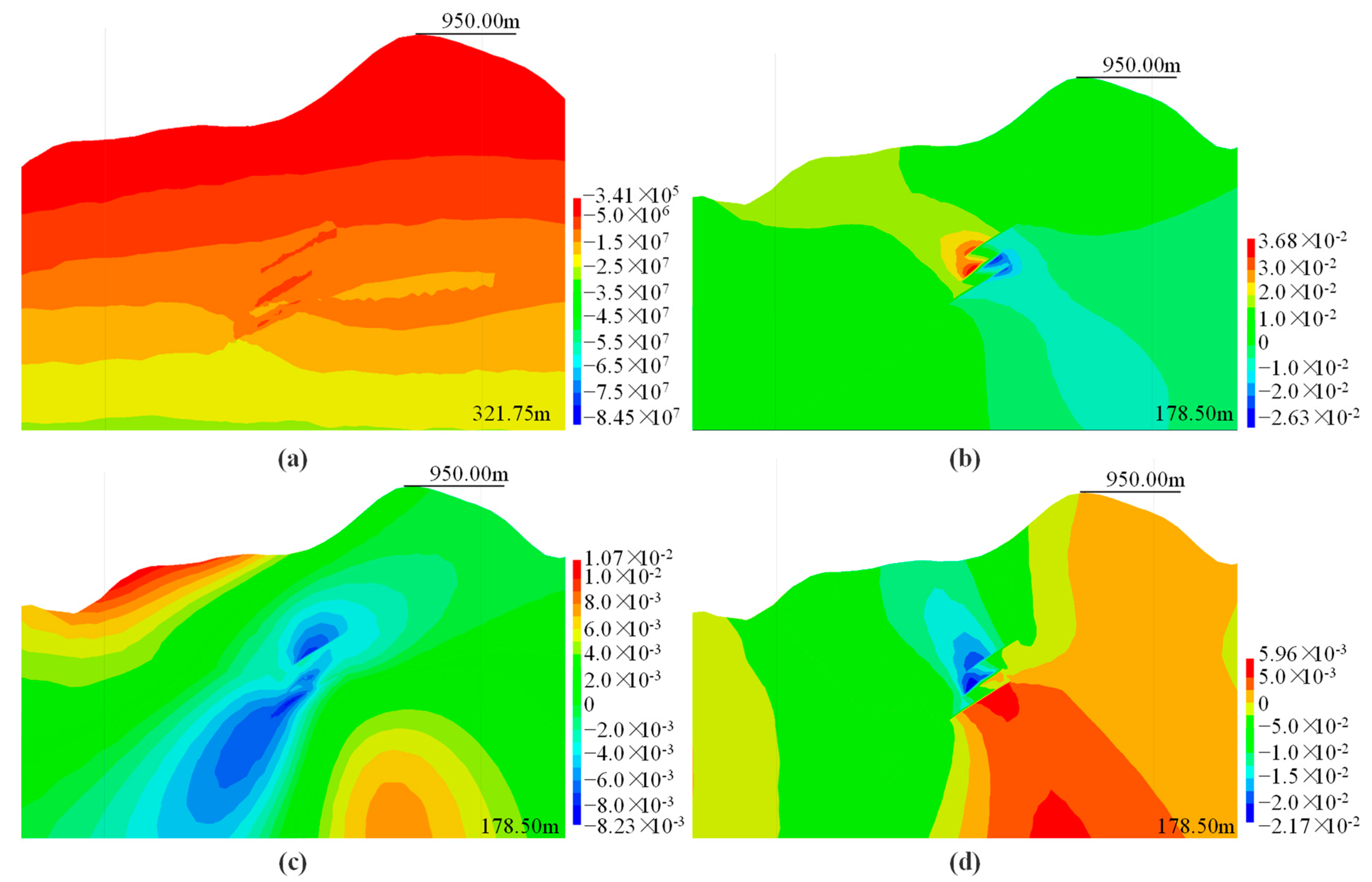
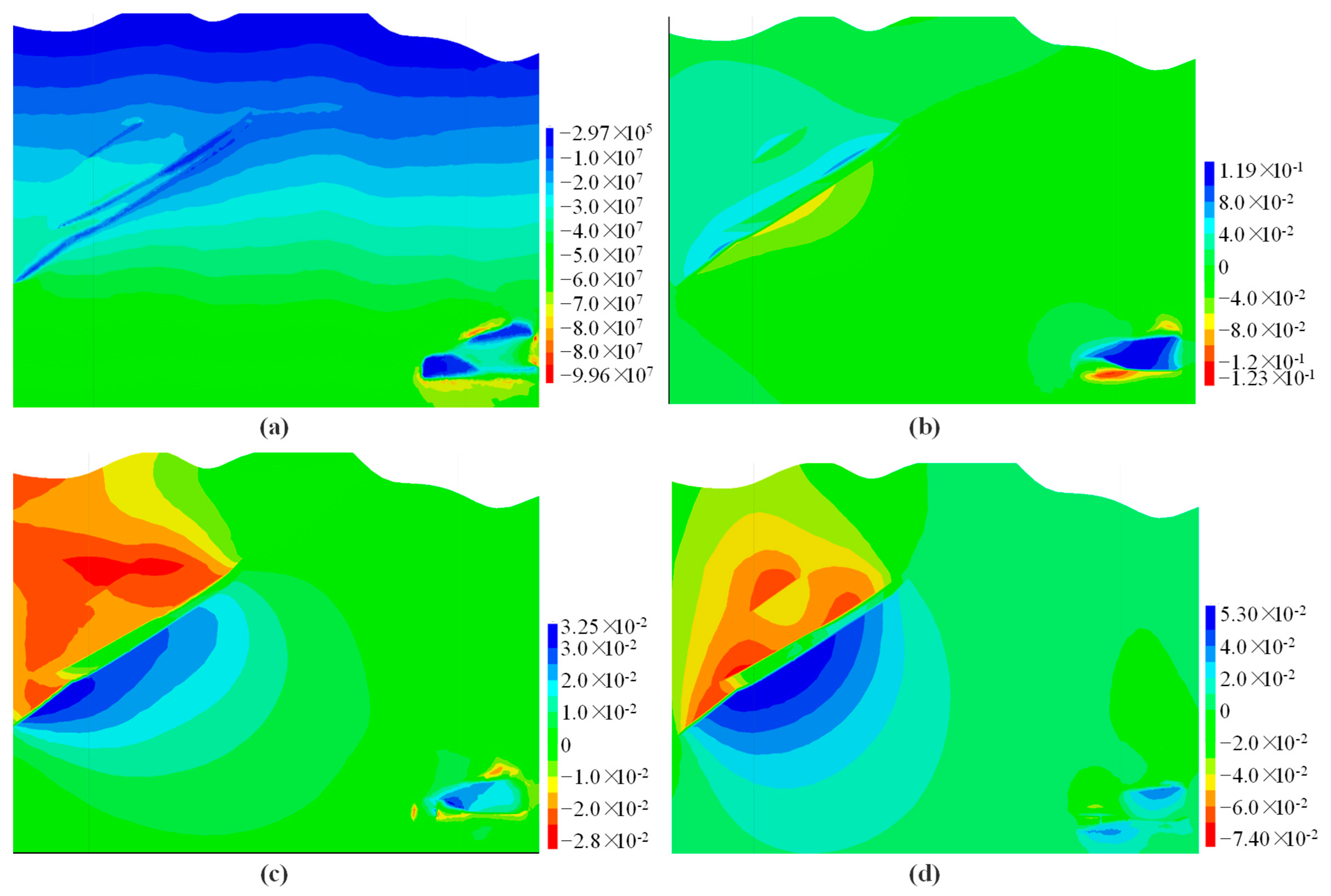
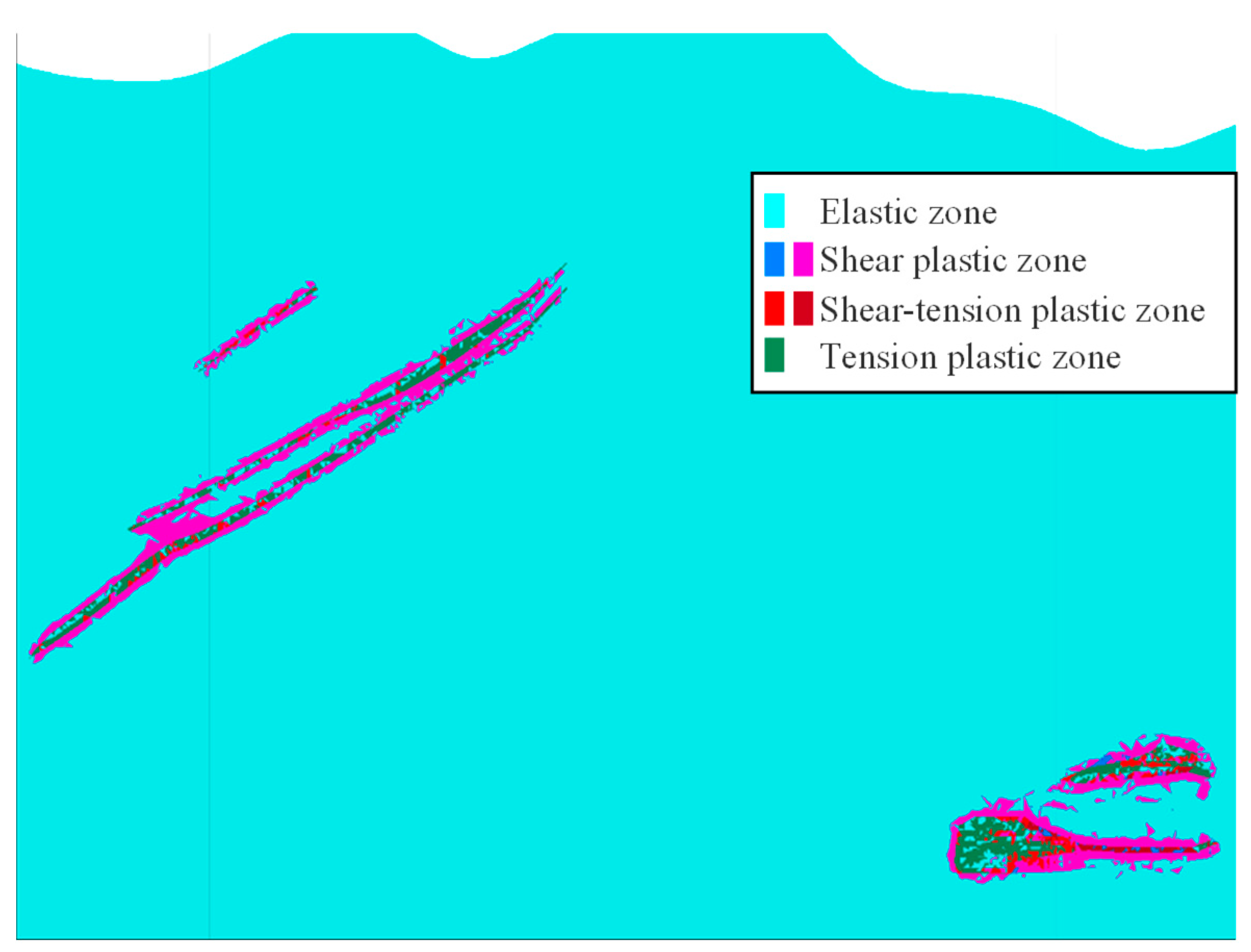
4.3. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining on Surface Deformation
4.3.1. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining on Surface
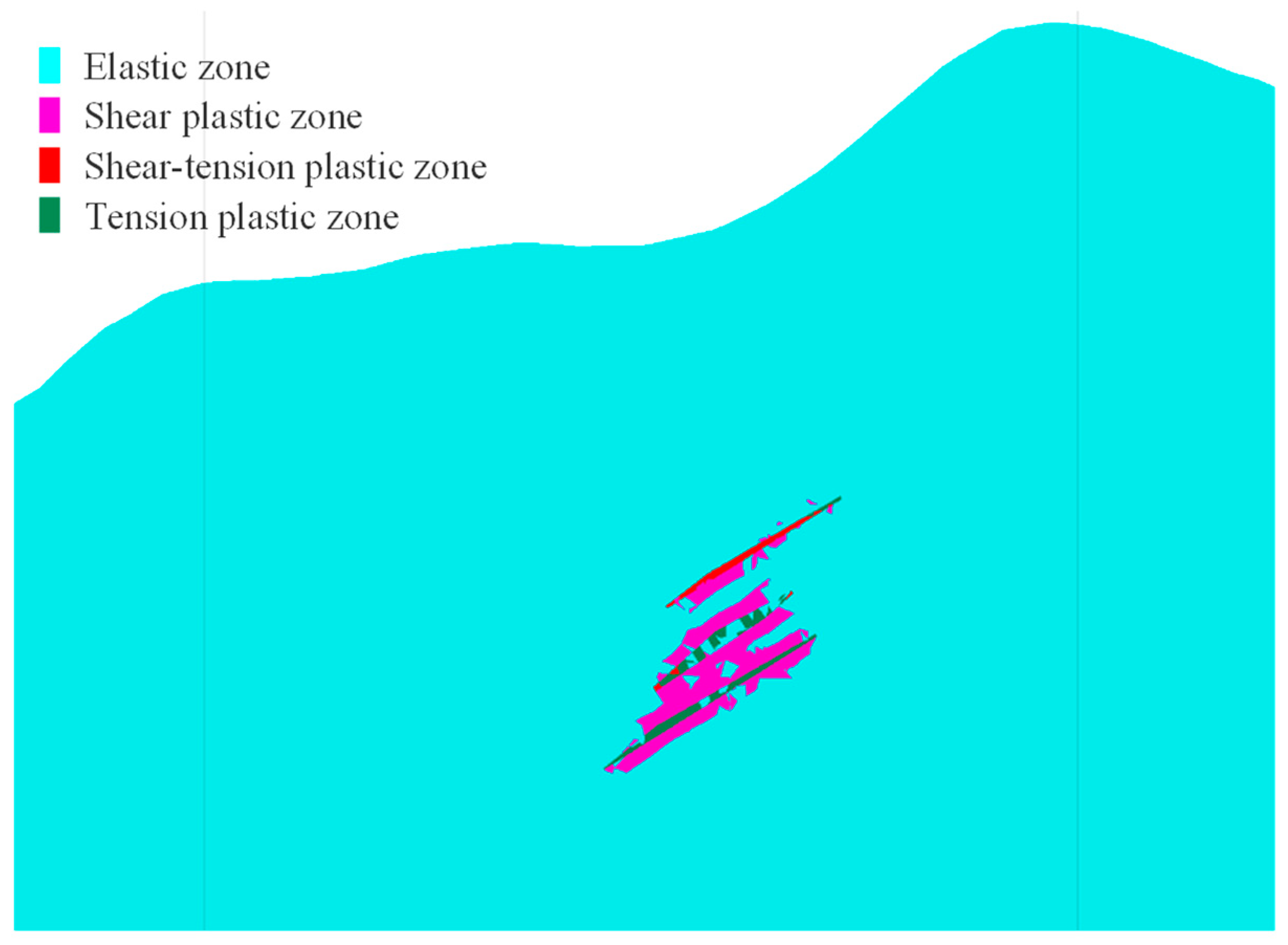
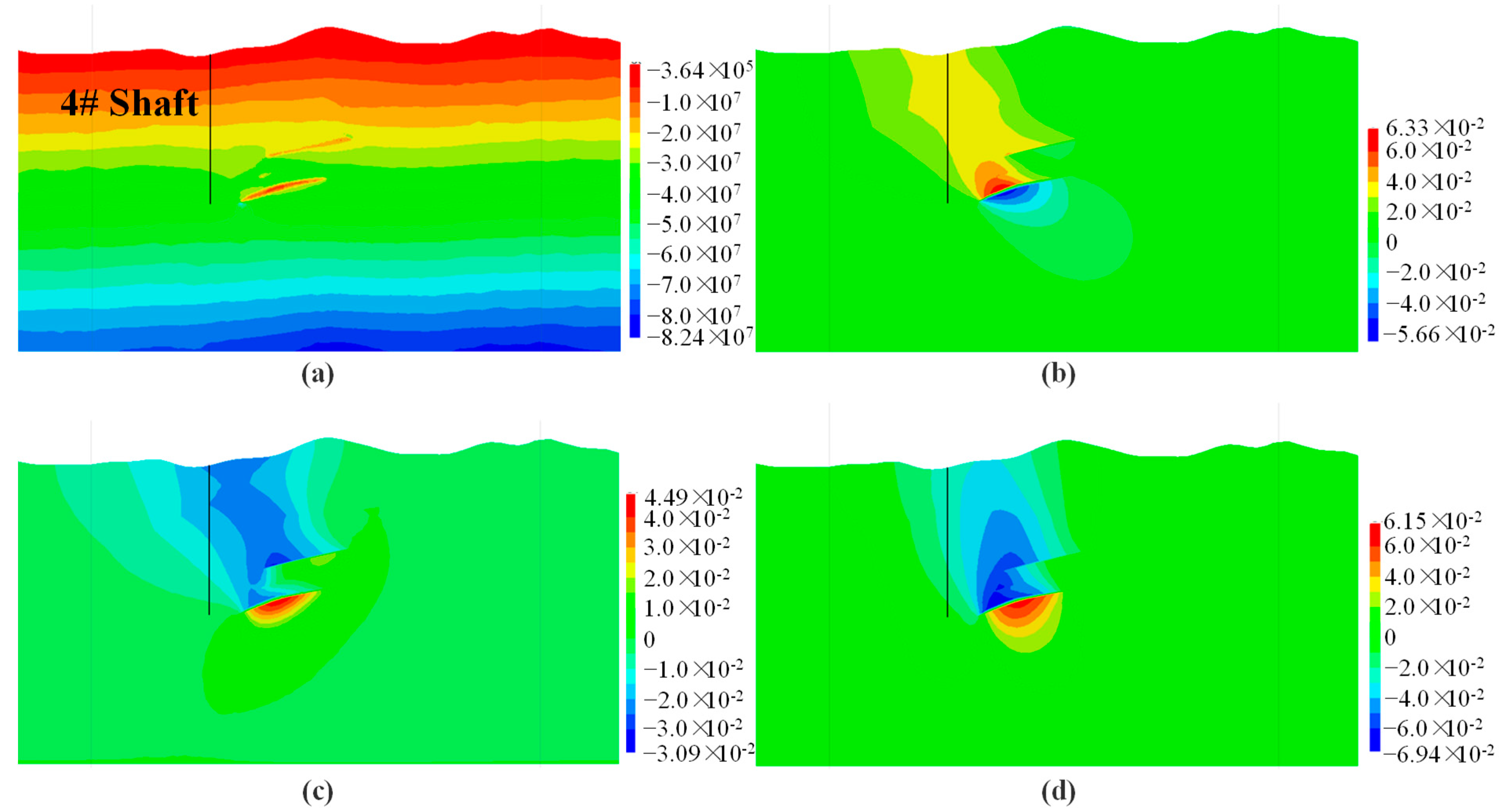
4.3.2. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Ore Body Extraction on 4# Shaft
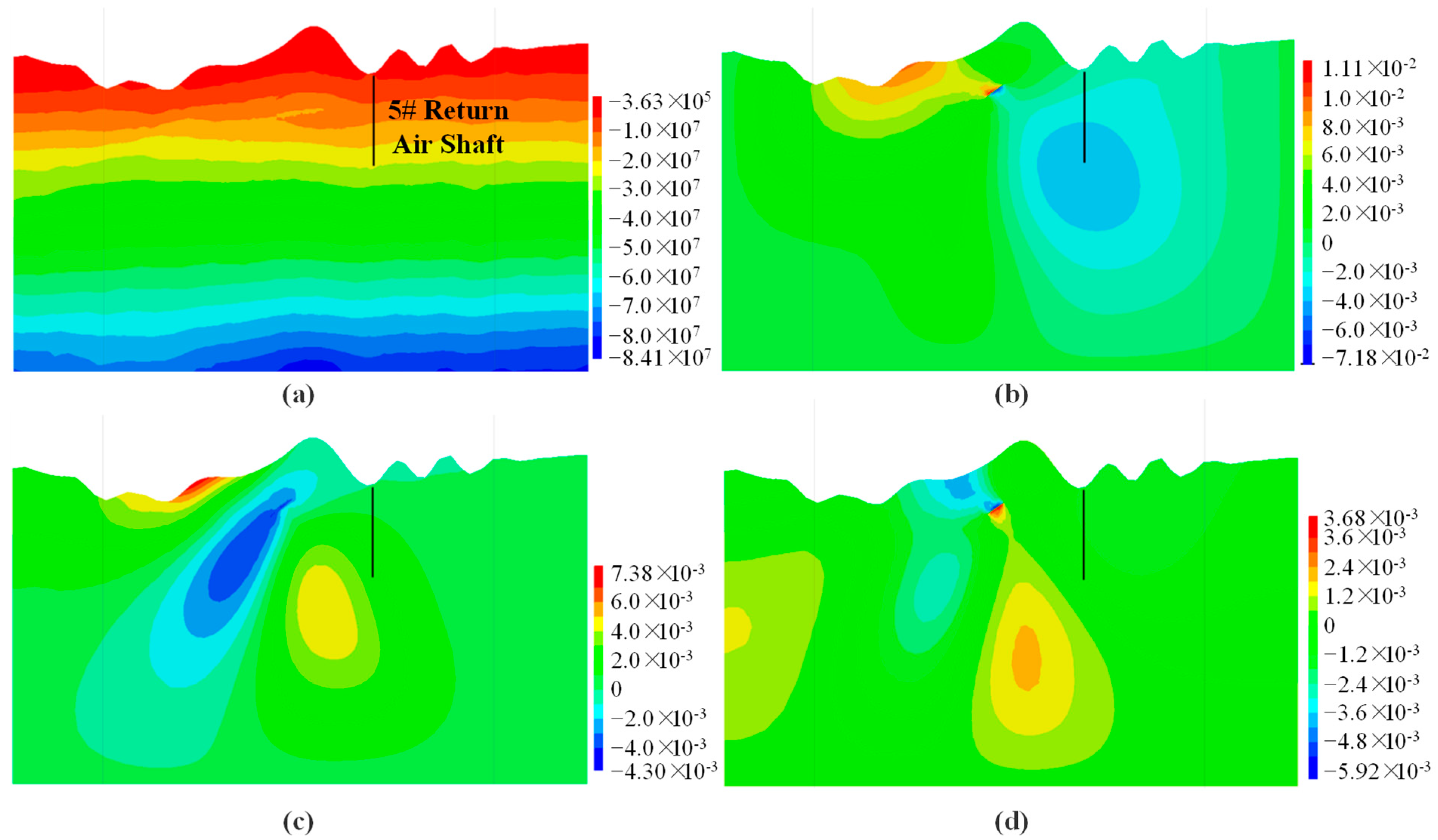
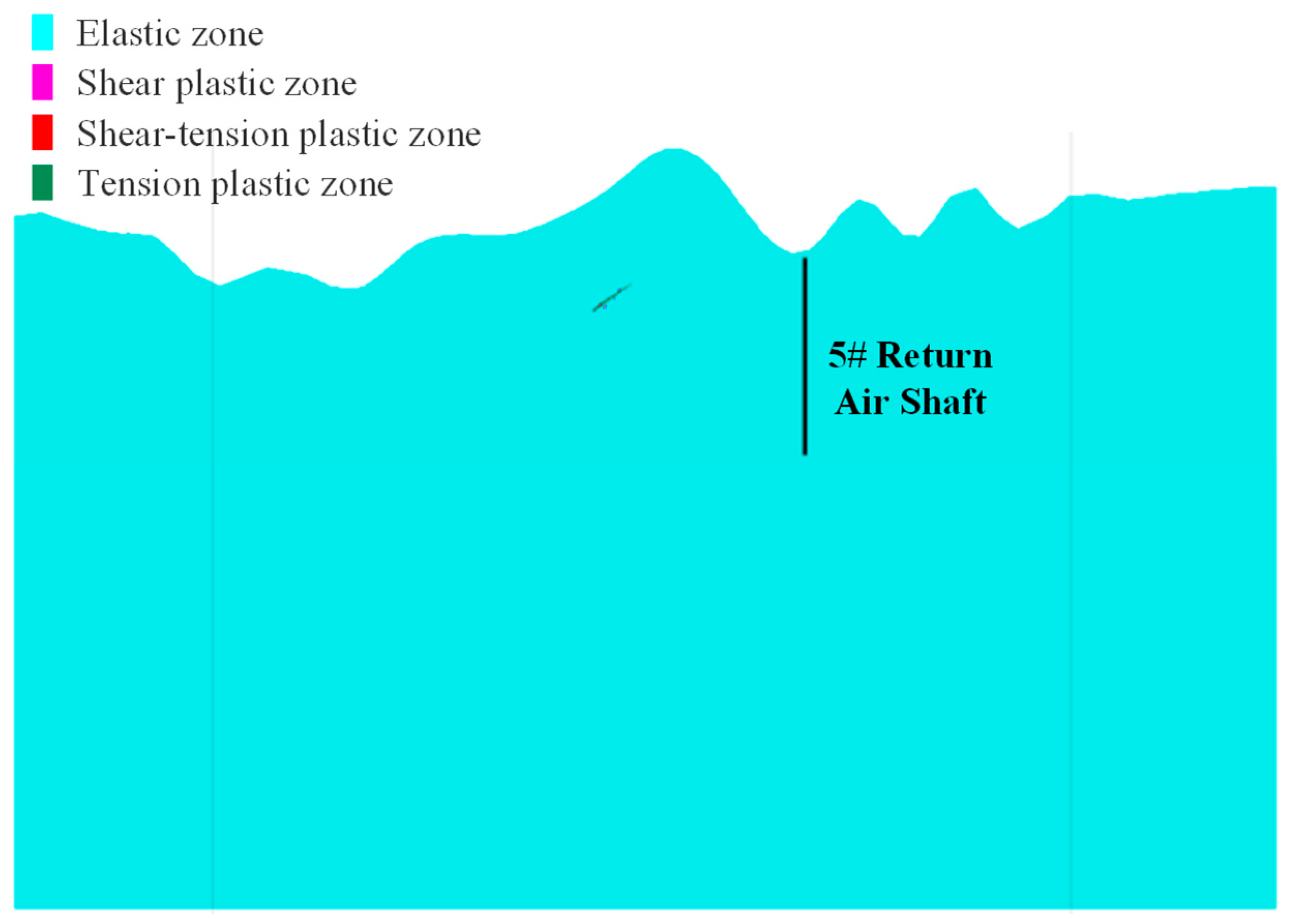
4.3.3. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining on 5# Return Air Shaft
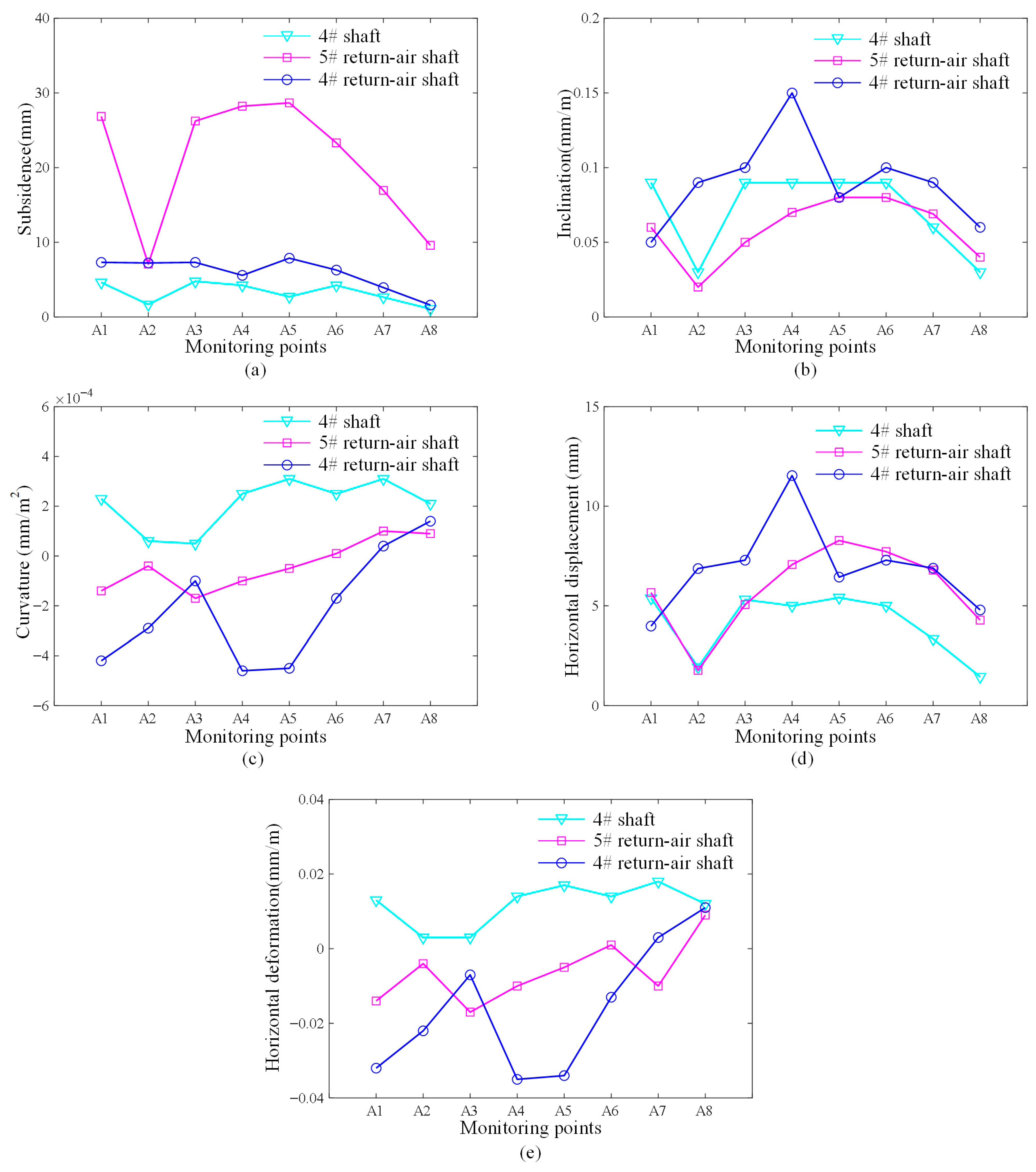
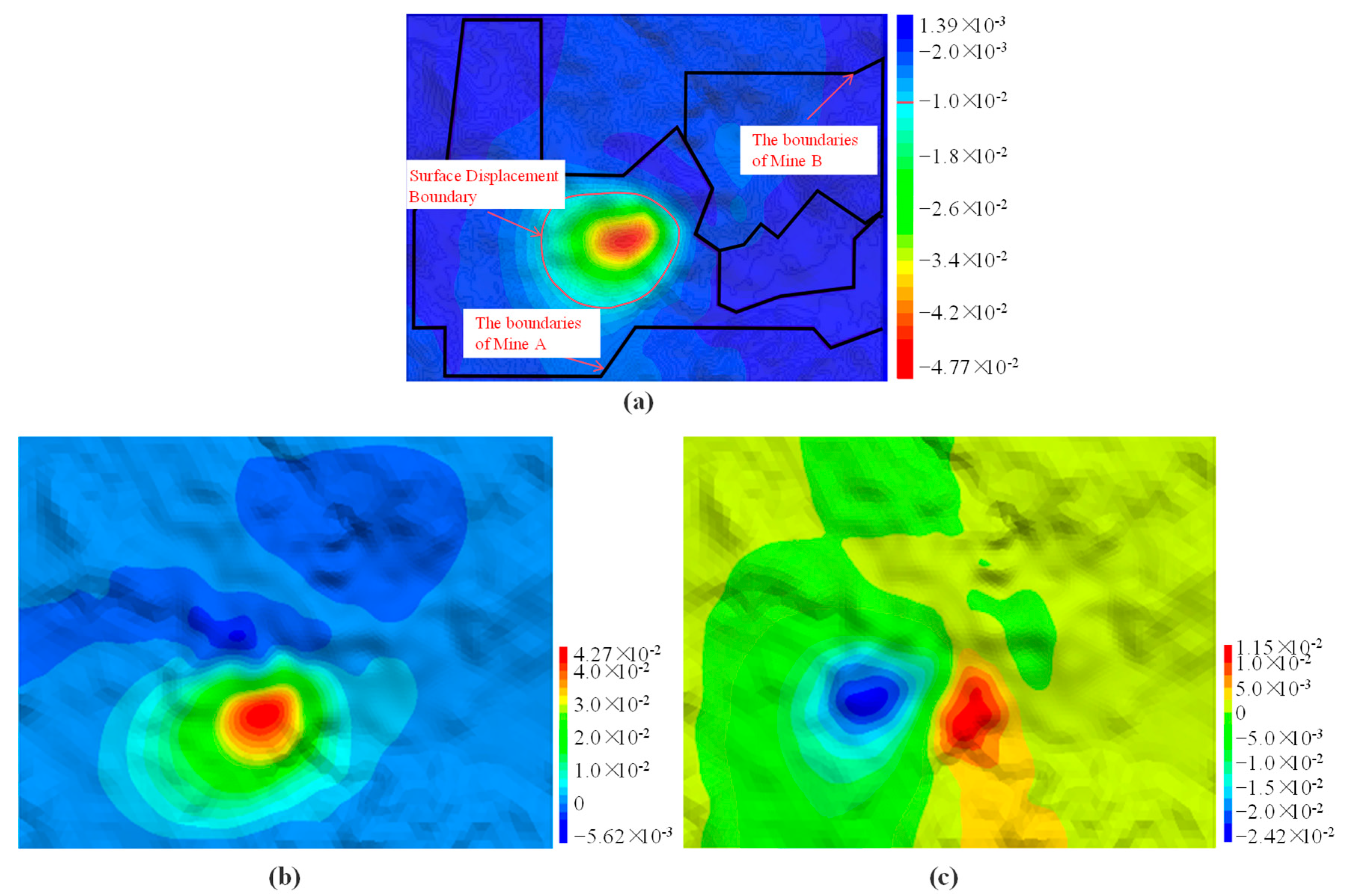
4.3.4. Surface Displacement Analysis
5. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining in Adjacent Mining Areas on Overlying Rock Mass and Surface Deformation
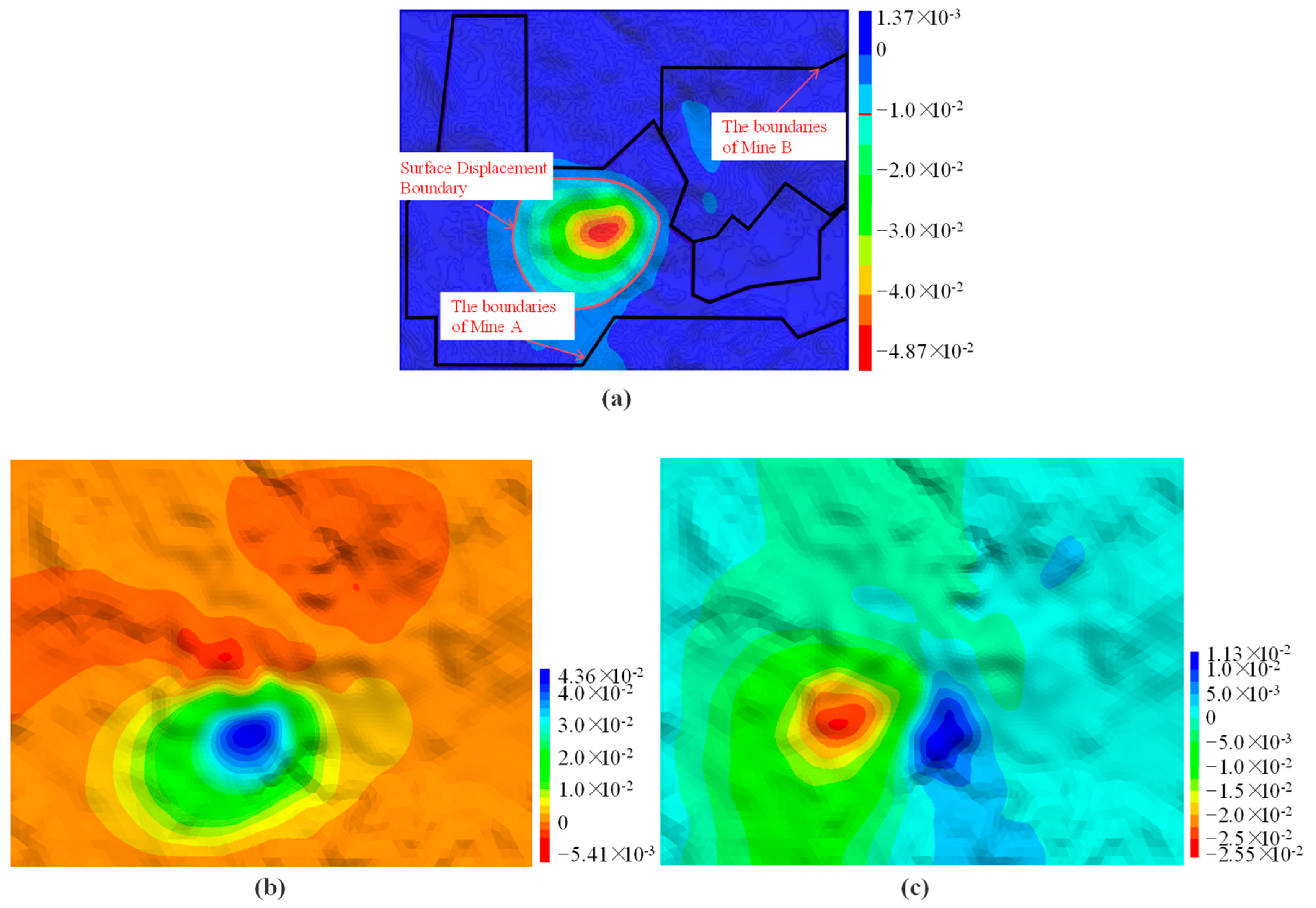
5.1. Analysis of the Impact of Underground Mining in Adjacent Mining Areas on Overlying Rock Mass
5.2. Analysis of the Mutual Impact of Underground Mining in Adjacent Mining Areas on the Surface
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bazaluk, O.; Petlovanyi, M.; Zubko, S.; Lozynskyi, V.; Sai, K. Instability Assessment of Hanging Wall Rocks during Underground Mining of Iron Ores. Minerals 2021, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaryan, A.A.; Batareyev, A.S.; Karamanits, F.I.; Kolosov, B.A.; Morkun, V.S. Ways to Reduce Ore Losses and Dilution in Iron Ore Underground Mining in Kryvbass. Sci. Innov. 2018, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvyj, M.J.; Ivanov, Y.A.; Panteleeva, N.B.; Varakuta, O.M. The Problem of Rational Use of Mineral Resources and Mining Waste in the Context of Sustainable Development of Regions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1254, 012134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaluk, O.; Petlovanyi, M.; Sai, K.; Chebanov, M.; Lozynskyi, V. Comprehensive Assessment of the Earth’s Surface State Disturbed by Mining and Ways to Improve the Situation: Case Study of Kryvyi Rih Iron-Ore Basin, Ukraine. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1480344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Song, W.; Deng, D.; Lei, Y.; Lan, J. Numerical Simulation of Land Subsidence and Verification of Its Character for an Iron Mine Using Sublevel Caving. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Eberhardt, E.; Elmo, D.; Stead, D. Empirical Investigation and Characterization of Surface Subsidence Related to Block Cave Mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 61, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Wang, L. A Novel Analytical Model of Mining Subsidence Considering Time Effect Based on the Probability Integral Theory. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhao, F.; Liu, L.; Shangguan, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X. Subsidence of Strata Overlying Salt Mines: A Case Study in Northern. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, X.; Liu, C. A Prediction Model for the Surface Residual Subsidence in an Abandoned Goaf for Sustainable Development of Resource-Exhausted Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Bai, E.; Zhao, G. Current Status and Progress on Overburden and Surface Damage and Prevention Technology of High-Intensity Mining. Meitan Xuebao J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Ma, F.; Zhao, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, H. Analysis on the Surface Deformation in Jingerquan Mine. J. Eng. Geol. 2016, 24, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Study on Overlying Strata Stability and Surface Subsidence with Effect of Backfilling Method in Luohe Underground Mine; University of Science and Technology Beijing: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G. Mechanism and Application of the Ground Subsidence of Soft Rock; Graduate School of China Coal Research Institute: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guoquan, Z.; Jianlong, S.; Mingwei, S.; Feng, H. Study on the Surface Subsidence Rule in Roof Caving under Complex Conditions Based on UDEC. Met. MINE 2012, 6, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Longbin, D.; Shaoquan, W.; Changyu, J.; Zhaosheng, L.; Yu, Z. Numerical Simulation of Factors Affecting Strata Movement Caused by Caving Method. Met. Mine 2015, 44, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Junen, L.; Zhenhua, G.; Jie, Z. Dynamic Prediction of Mining Subsidence in Ling Long Mine. Mine Surv. 2018, 46, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hao, J. Study on Numerical Models in Predicting Surface Deformation Caused by Underground Coal Mining. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 4457–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wu, D.; Ma, L. Numerical Simulation and Verification of Goaf Morphology Evolution and Surface Subsidence in a Mine. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 144, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, M.; Apel, D.B.; Hall, R.A. Prediction of Mining-Induced Surface Subsidence and Ground Movements at a Canadian Diamond Mine Using an Elastoplastic Finite Element Model. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 100, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, J.; Yu, W. Analysis of the Surface Subsidence Induced by Mining Near-Surface Thick Lead-Zinc Deposit Based on Numerical Simulation. Processes 2021, 9, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hou, K.; Li, T.; Tang, J.; Lu, G. Numerical Simulation of Surface Subsidence and Fracture Evolution Caused by Pulang Copper Mine Mining. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Rupesh, R.; Sharma, S.P.; Ciazela, J. Dynamics of Saltwater Intrusion in a Heterogeneous Coastal Environment: Experimental, DC Resistivity, and Numerical Modeling Approaches. Water 2024, 16, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Guo, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, G.; Fang, Z. Numerical Study on the Surface Movement Regularity of Deep Mining Underlying the Super-Thick and Weak Cementation Overburden: A Case Study in Western China. Sustainablity 2022, 14, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Chen, C.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, G.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Fu, H.; Song, X.; Chen, L. In Situ Monitoring and Analysis of the Mining-Induced Deep Ground Movement in a Metal Mine. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 109, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, A.; Monahan, C.; Roulston, B.; Szostak-Chrzanowski, A. Integrated Monitoring and Modelling of Ground Subsidence in Potash Mines. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1997, 34, 55.e1–55.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, G.J. Using Neural Networks to Discriminate between Genuine and Spurious Seismic Events in Mines. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1999, 154, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Teng, C.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, S. D-InSAR Monitoring Method of Mining Subsidence Based on Boltzmann and Its Application in Building Mining Damage Assessment. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yu, J. Monitoring and Analysis of Surface Subsidence Caused by SBAS-InSAR Technology. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 198–204. [Google Scholar]


| Rock Sample Type | Average Value | Internal Friction Angle/° | Cohesion /MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial Compressive Strength /MPa | Tensile Strength /MPa | Elastic Modulus /GPa | Poisson’s Ratio | |||
| Shallow Siliceous Rock | 124.28 | 8.31 | 33.857 | 0.223 | 36.60 | 16.07 |
| Small Pebble Limestone | 118.94 | 5.23 | 34.577 | 0.313 | 39.78 | 12.47 |
| Deep Siliceous Rock | 84.11 | 6.42 | 30.999 | 0.227 | 35.46 | 11.62 |
| Wide Strip Limestone | 129.55 | 3.47 | 37.378 | 0.257 | 42.85 | 10.60 |
| Ore | 191.37 | 12.09 | 37.934 | 0.299 | 37.07 | 24.05 |
| Tailings Cemented Fill | 1.69 | 0.52 | 1.670 | 0.136 | 19.17 | 0.47 |
| Lithology | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Unit Weight (t/m3) | Cohesion (MPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mudstone | 6.30 | 0.30 | 2.63 | 1.17 | 32 | 1.12 |
| Small Pebble Limestone | 27.20 | 0.26 | 2.66 | 1.90 | 40 | 1.59 |
| Wide Strip Limestone | 27.50 | 0.29 | 2.71 | 2.74 | 43 | 2.39 |
| Siliceous Rock | 28.50 | 0.24 | 2.68 | 2.50 | 42 | 2.10 |
| Reef Limestone | 11.64 | 0.23 | 27.02 | 4.7 | 29.5 | 1.20 |
| Ore Body | 19.76 | 0.14 | 2.80 | 2.45 | 43 | 2.4 |
| Fill Material | 0.88 | 0.28 | 2.26 | 0.17 | 32 | 0.18 |
| ID | Ore Body | Dip Angle/° | Depth | Distance to Buildings/m | Remarks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strike Length/m | Dip Length/m | Ore Body Thickness/m | Lower Boundary/m | Upper Boundary/m | Average/m | ||||
| 94 | 1179 | 637 | 2.15 | 23 | 417 | 210 | 313 | 193 | 5# Return Air Shaft |
| 95 | 800 | 394 | 3.61 | 23 | 548 | 271 | 410 | 200 | 4# Return Air Shaft |
| 96 | 992 | 519 | 3.98 | 23 | 757 | 326 | 541 | 800 | 4# Shaft |
| Surface Structure Expected Displacement Deformation | Subsidence, W (mm) | Inclination, i (mm/m) | Curvature, K (mm/m2) | Horizontal Displacement, U (mm) | Horizontal Deformation, ε (mm/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4# Shaft | 2.71 | 0.09 | 0.0003 | 5.41 | 0.017 | |
| Monitoring Points within the Ore Body Strike Range | A1 | 4.62 | 0.09 | 0.00023 | 5.38 | 0.013 |
| A2 | 1.67 | 0.03 | 0.00006 | 1.93 | 0.003 | |
| A3 | 4.77 | 0.09 | 0.00005 | 5.31 | 0.003 | |
| A4 | 4.23 | 0.09 | 0.00025 | 5.00 | 0.014 | |
| A5 | 2.71 | 0.09 | 0.00031 | 5.41 | 0.017 | |
| A6 | 4.23 | 0.09 | 0.00025 | 5.00 | 0.014 | |
| A7 | 2.65 | 0.06 | 0.00031 | 3.34 | 0.018 | |
| A8 | 1.07 | 0.03 | 0.00021 | 1.45 | 0.012 | |
| 5# Return Air Shaft | 16.95 | 0.07 | 0.0001 | 6.79 | −0.01 | |
| Monitoring Points within the Ore Body Strike Range | A1 | 26.86 | 0.06 | −0.00014 | 5.66 | −0.014 |
| A2 | 7.07 | 0.02 | −0.00004 | 1.77 | −0.004 | |
| A3 | 26.24 | 0.05 | −0.00017 | 5.06 | −0.017 | |
| A4 | 28.23 | 0.07 | −0.00010 | 7.07 | −0.010 | |
| A5 | 28.67 | 0.08 | −0.00005 | 8.28 | −0.005 | |
| A6 | 23.31 | 0.08 | 0.00001 | 7.72 | 0.001 | |
| A7 | 16.95 | 0.07 | 0.0001 | 6.79 | −0.01 | |
| A8 | 9.59 | 0.04 | 0.00009 | 4.28 | 0.009 | |
| 4# Return Air Shaft | 7.31 | 0.08 | −0.00025 | 6.44 | −0.03 | |
| Monitoring Points within the Ore Body Strike Range | A1 | 7.31 | 0.05 | −0.00042 | 3.98 | −0.032 |
| A2 | 7.23 | 0.09 | −0.00029 | 6.87 | −0.022 | |
| A3 | 7.31 | 0.10 | −0.00010 | 7.29 | −0.007 | |
| A4 | 5.57 | 0.15 | −0.00046 | 11.54 | −0.035 | |
| A5 | 7.87 | 0.08 | −0.00045 | 6.44 | −0.034 | |
| A6 | 6.28 | 0.10 | −0.00017 | 7.29 | −0.013 | |
| A7 | 3.93 | 0.09 | 0.00004 | 6.89 | 0.003 | |
| A8 | 1.59 | 0.06 | 0.00014 | 4.79 | 0.011 | |
| Surface Structure Expected Displacement Deformation | Inclination i (mm/m) | Curvature K (mm/m2) | Horizontal Deformation εx (mm/m) | Horizontal Deformation εy (mm/m) | Horizontal Deformation ε (mm/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical Calculation | 0.027 | 0.0001 | 0.0083 | 0.008 | 0.011 |
| Theoretical Analysis | 0.09 | 0.0003 | - | - | 0.017 |
| Error Comparison | 70% | 66.6% | - | - | 35.3% |
| Surface Structure Expected Displacement Deformation | Inclination i (mm/m) | Curvature K (mm/m2) | Horizontal Deformation εx (mm/m) | Horizontal Deformation εy (mm/m) | Horizontal Deformation ε (mm/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical Calculation | 0.045 | 0.00022 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0014 |
| Theoretical Analysis | 0.09 | 0.0003 | - | - | 0.017 |
| Error Comparison | 50% | 26.7% | - | - | 91.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Xie, L. Stability Analysis of Surface Facilities in Underground Mining and the Cumulative Impact of Adjacent Mining Activities. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12424. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312424
Zhang G, Yuan Y, Gao Y, Luo Z, Xie L. Stability Analysis of Surface Facilities in Underground Mining and the Cumulative Impact of Adjacent Mining Activities. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12424. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312424
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guang, Yang Yuan, Yuan Gao, Zhixiong Luo, and Lianku Xie. 2025. "Stability Analysis of Surface Facilities in Underground Mining and the Cumulative Impact of Adjacent Mining Activities" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12424. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312424
APA StyleZhang, G., Yuan, Y., Gao, Y., Luo, Z., & Xie, L. (2025). Stability Analysis of Surface Facilities in Underground Mining and the Cumulative Impact of Adjacent Mining Activities. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12424. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312424






