Classification of Hydrothermal Alteration Types from Thin-Section Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
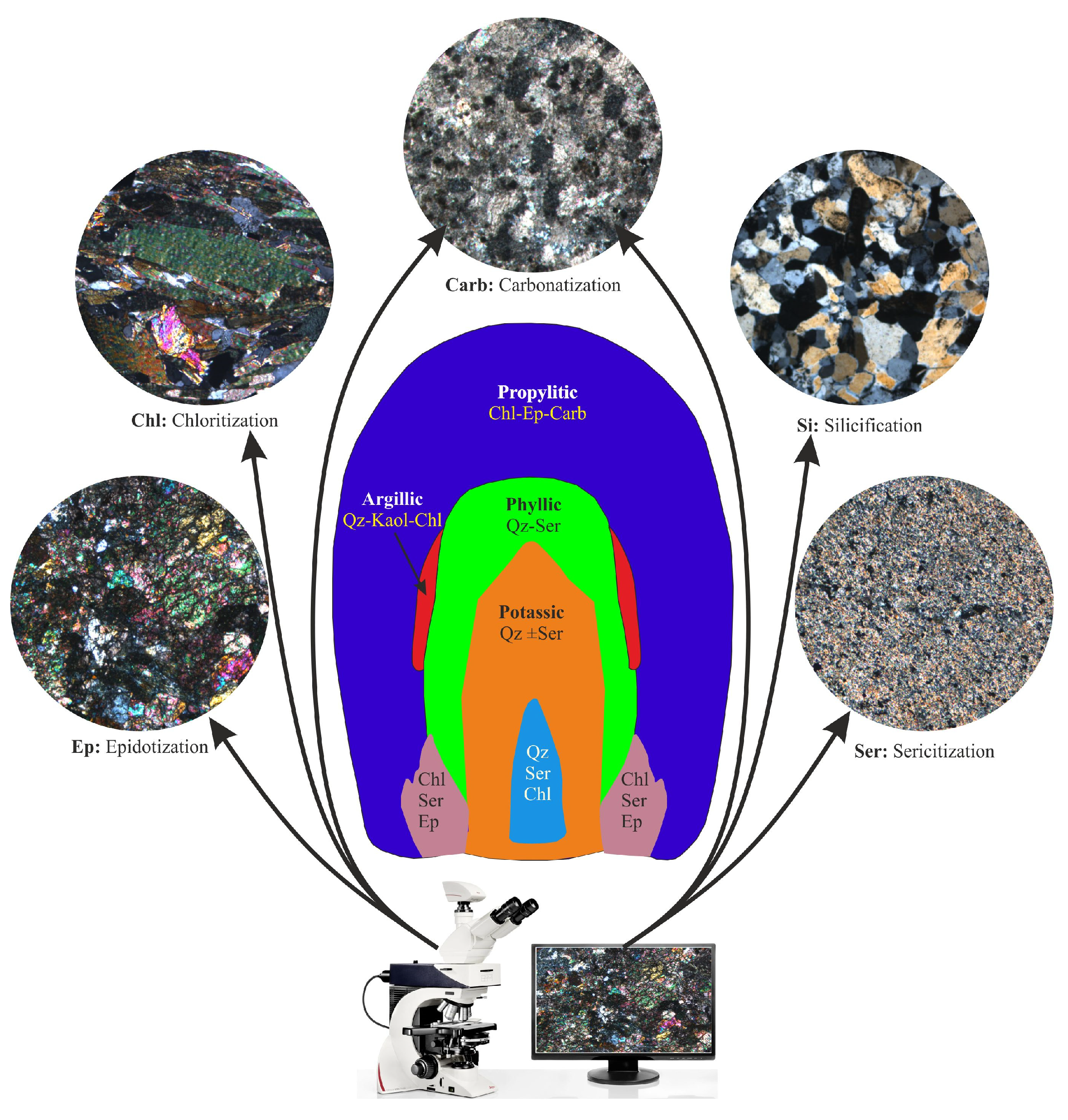
2.1. Hydrothermal Alteration Types
2.2. Preparation and Acquisition of the Thin Section Image Dataset
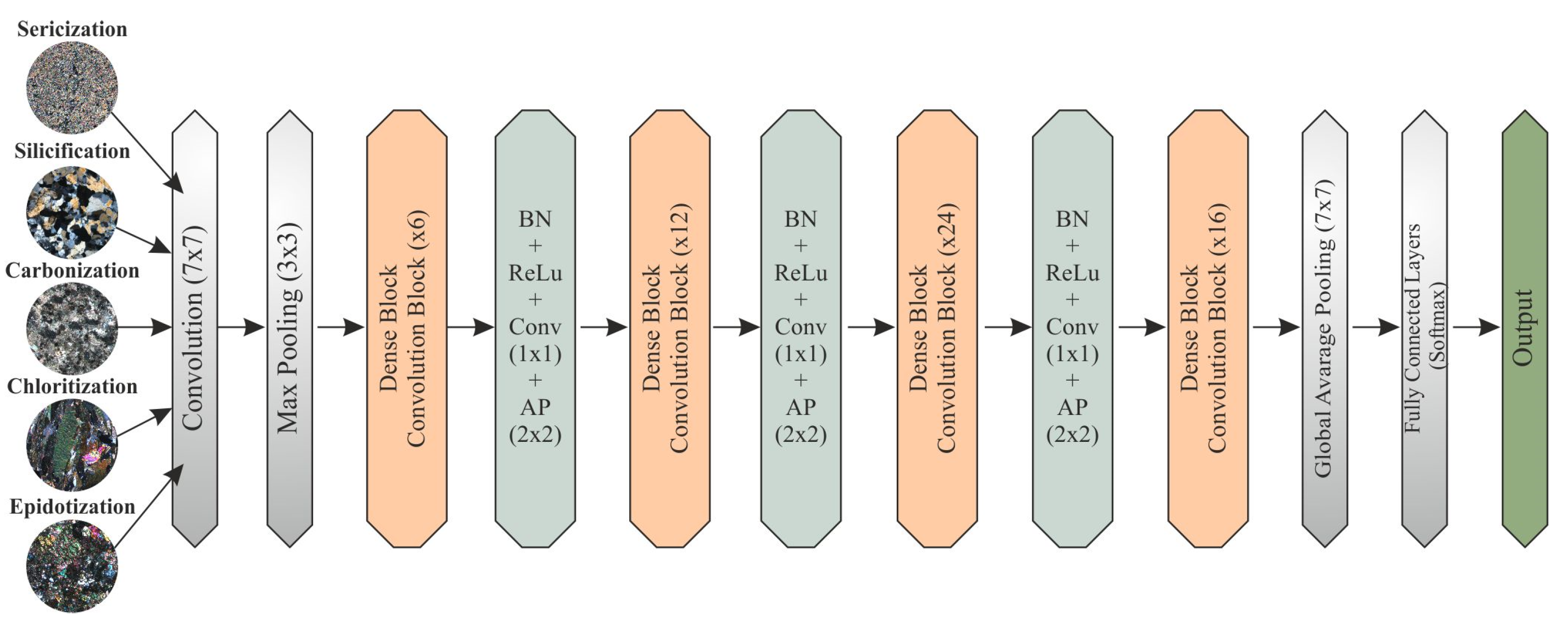
2.3. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
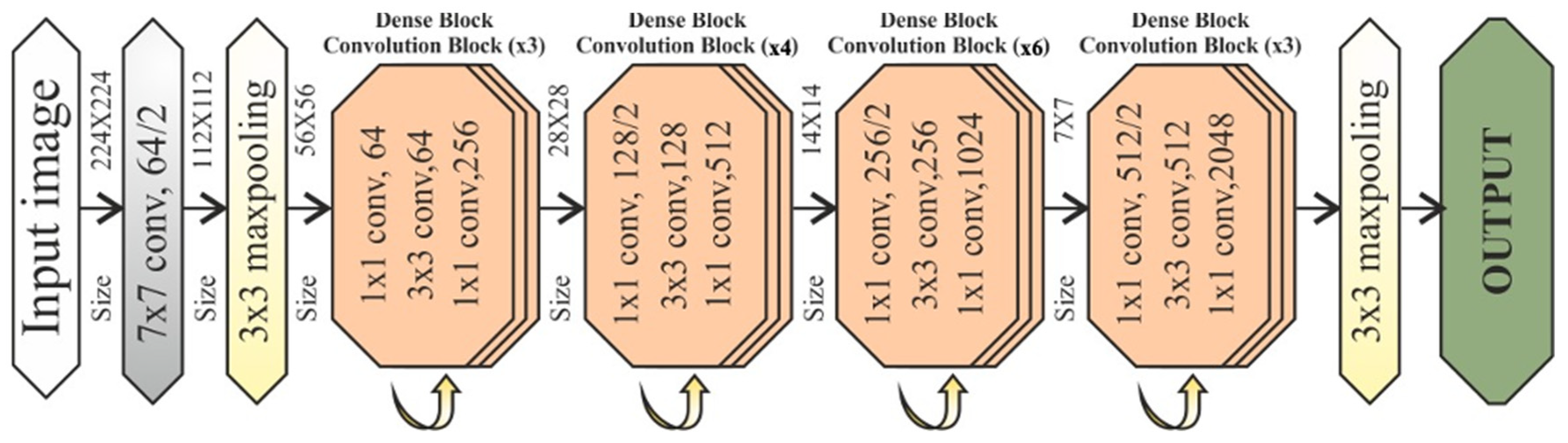
2.3.1. DenseNet121
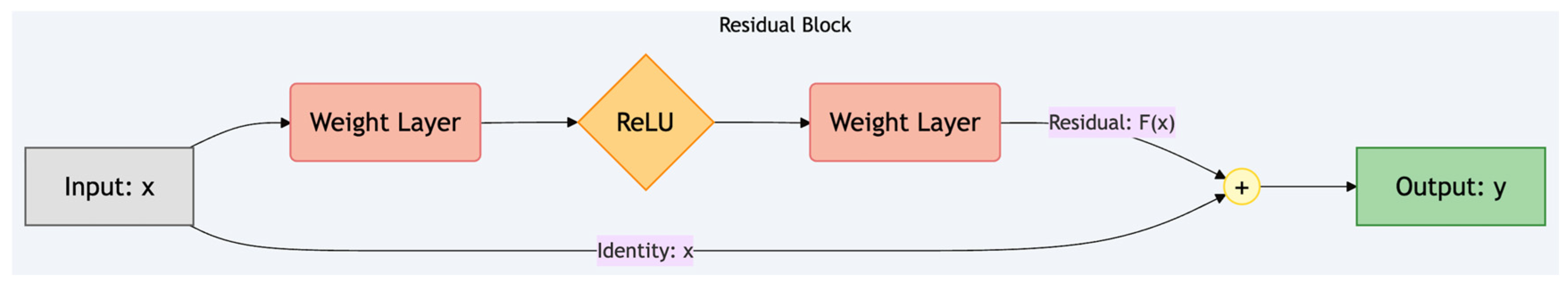
2.3.2. ResNet50
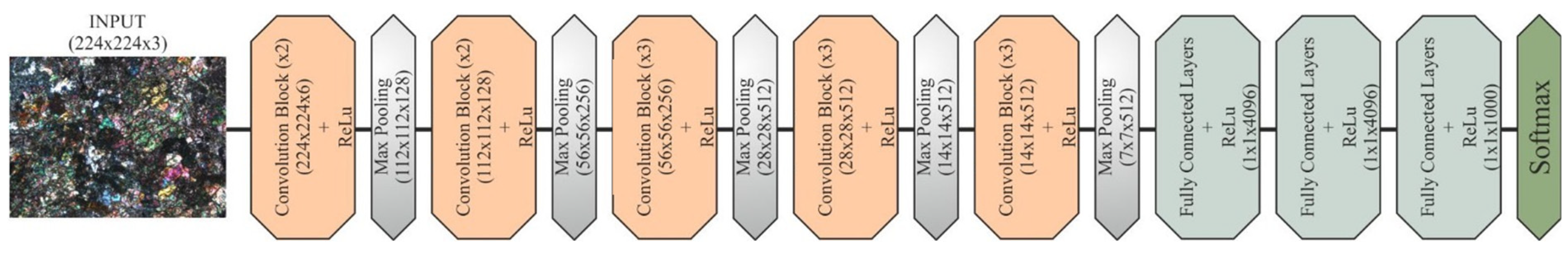
2.3.3. VGG16
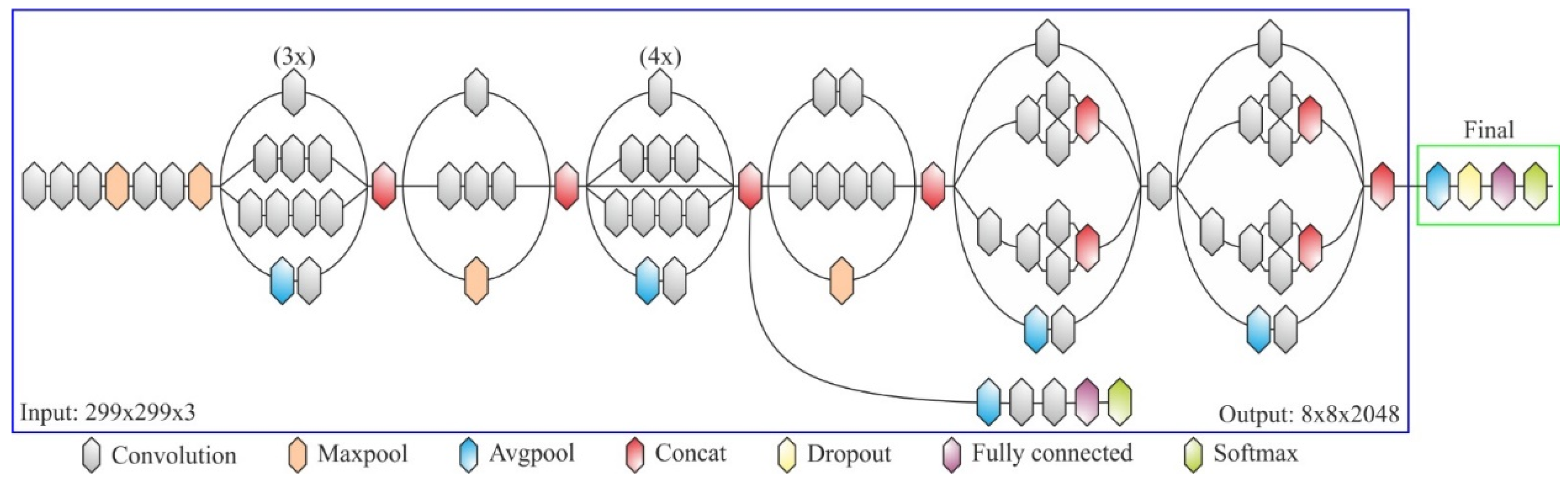
2.3.4. InceptionV3
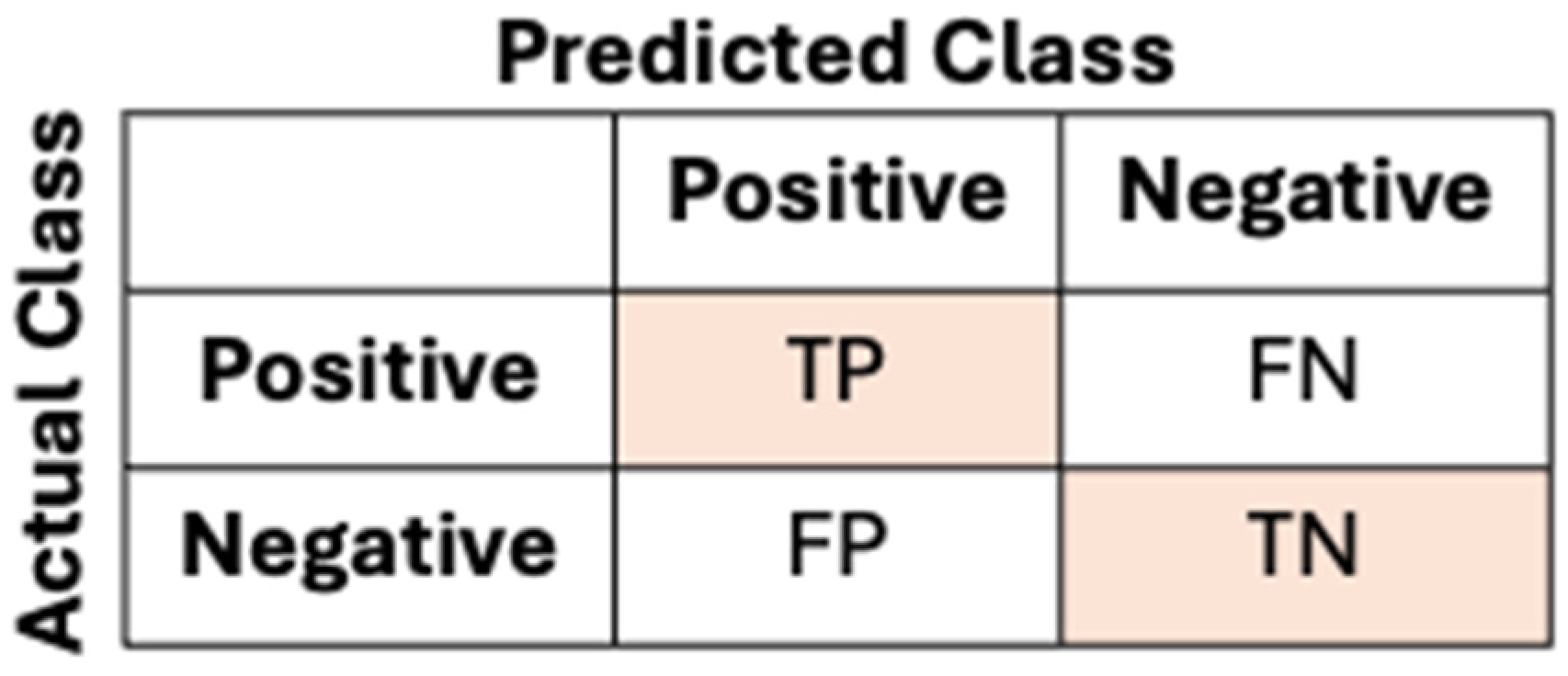
2.4. Performance Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
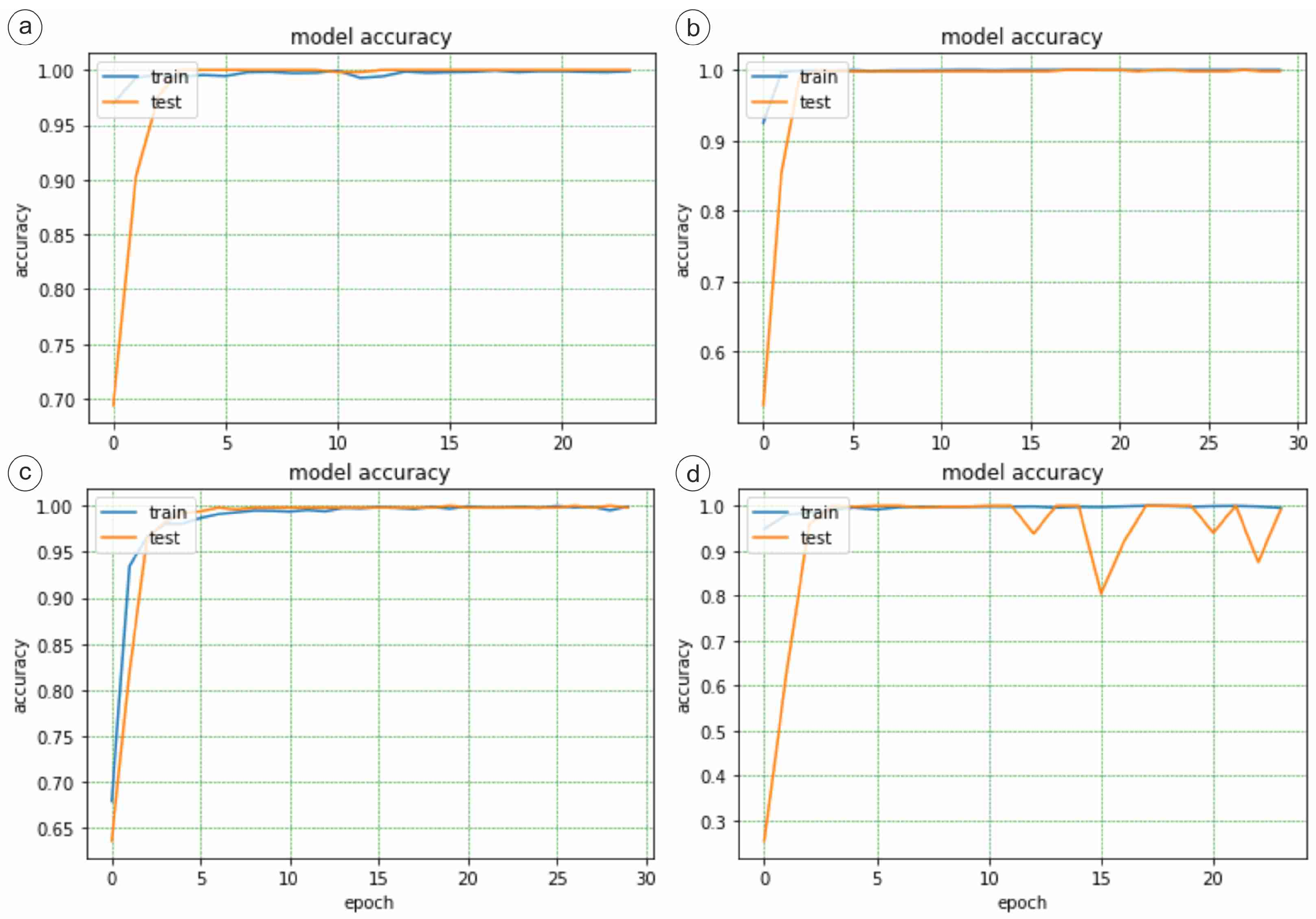
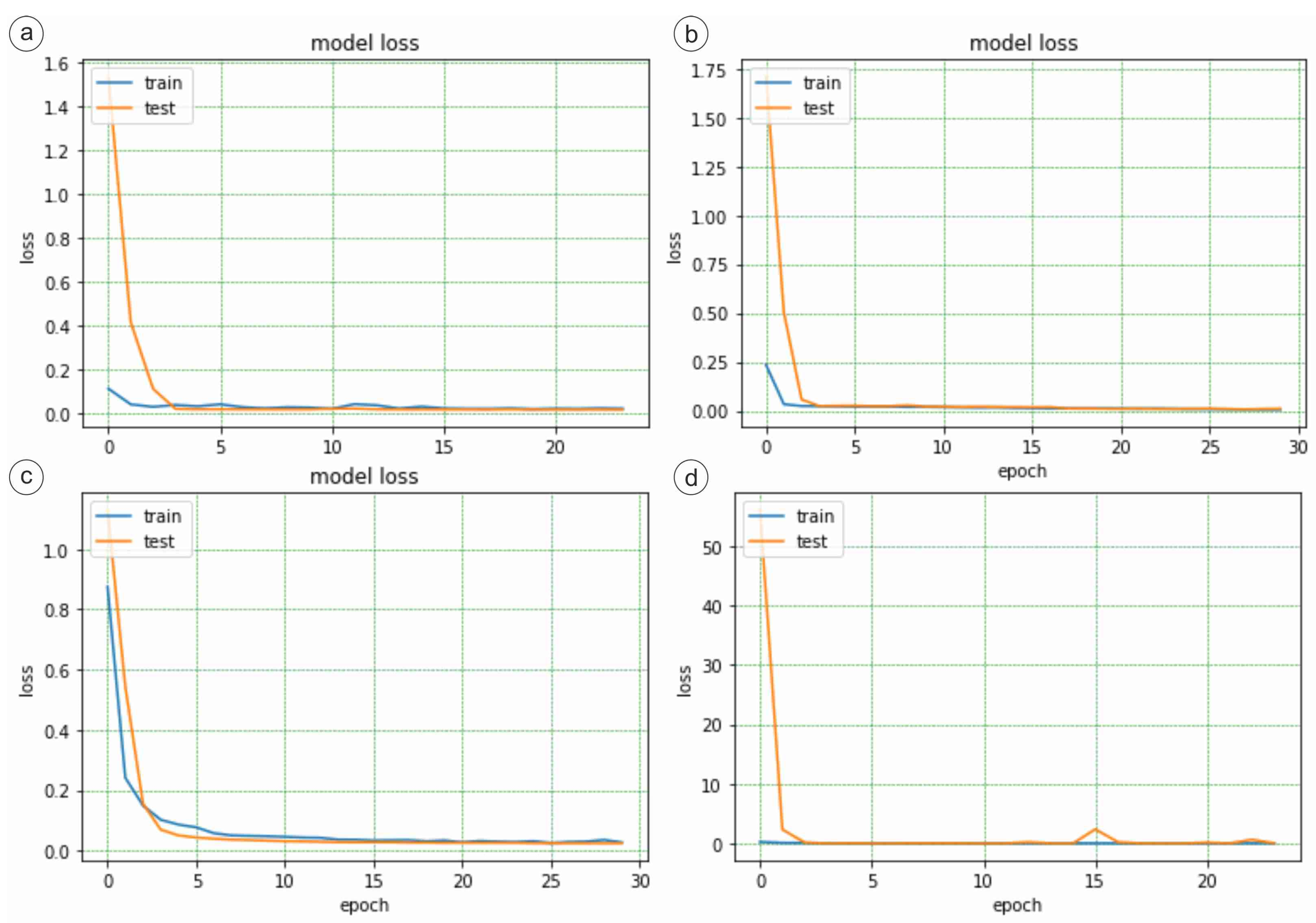
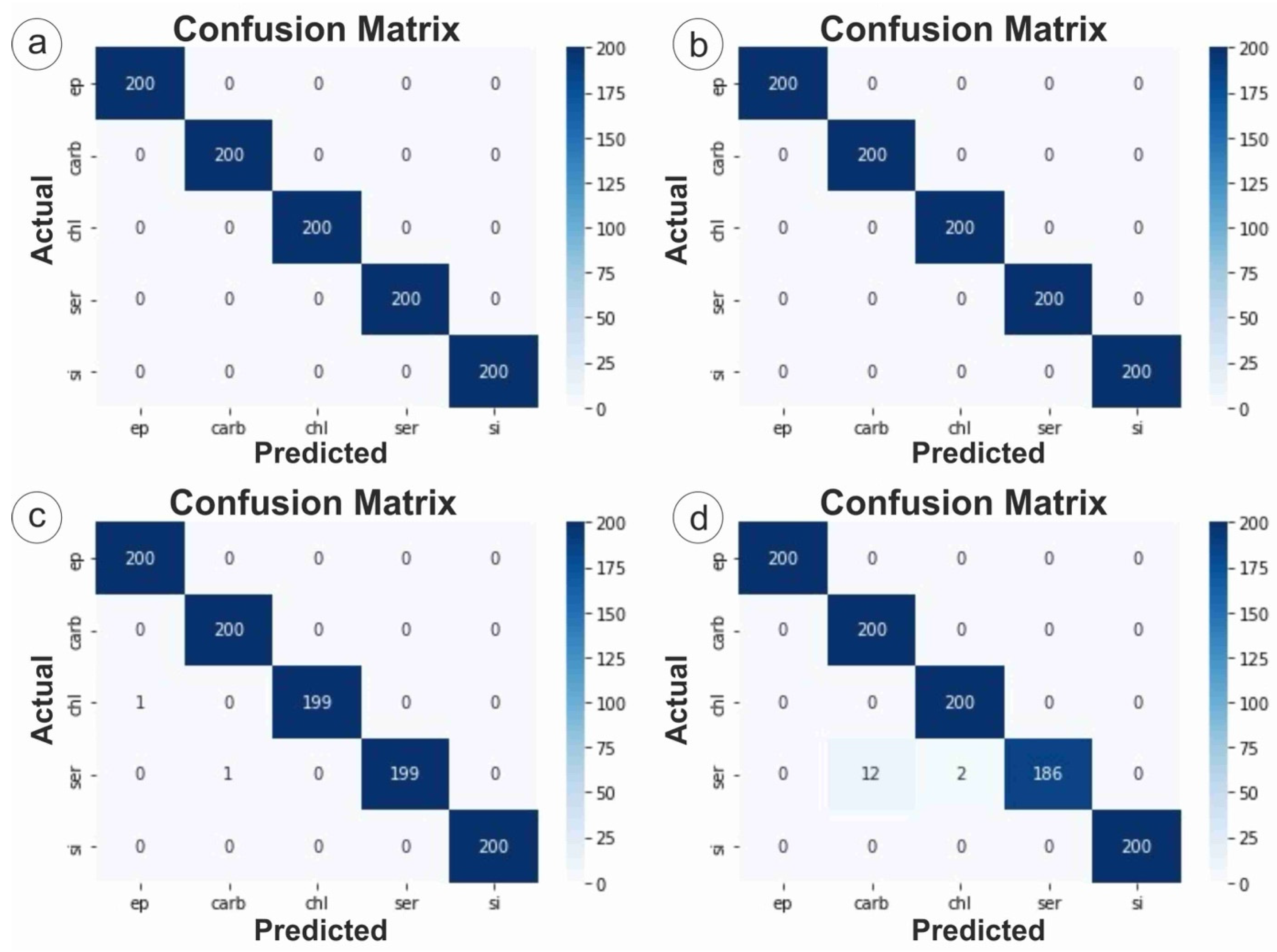
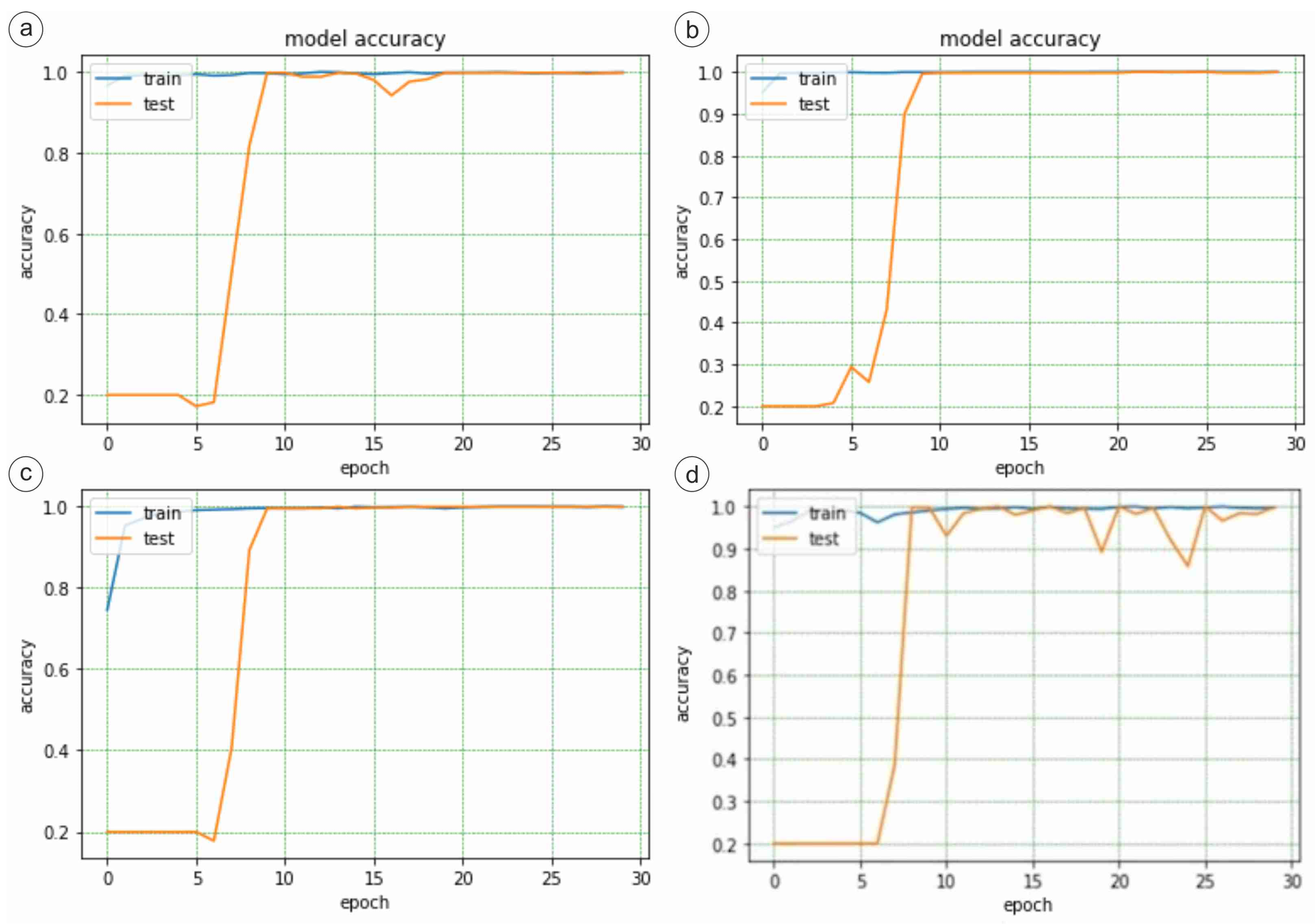
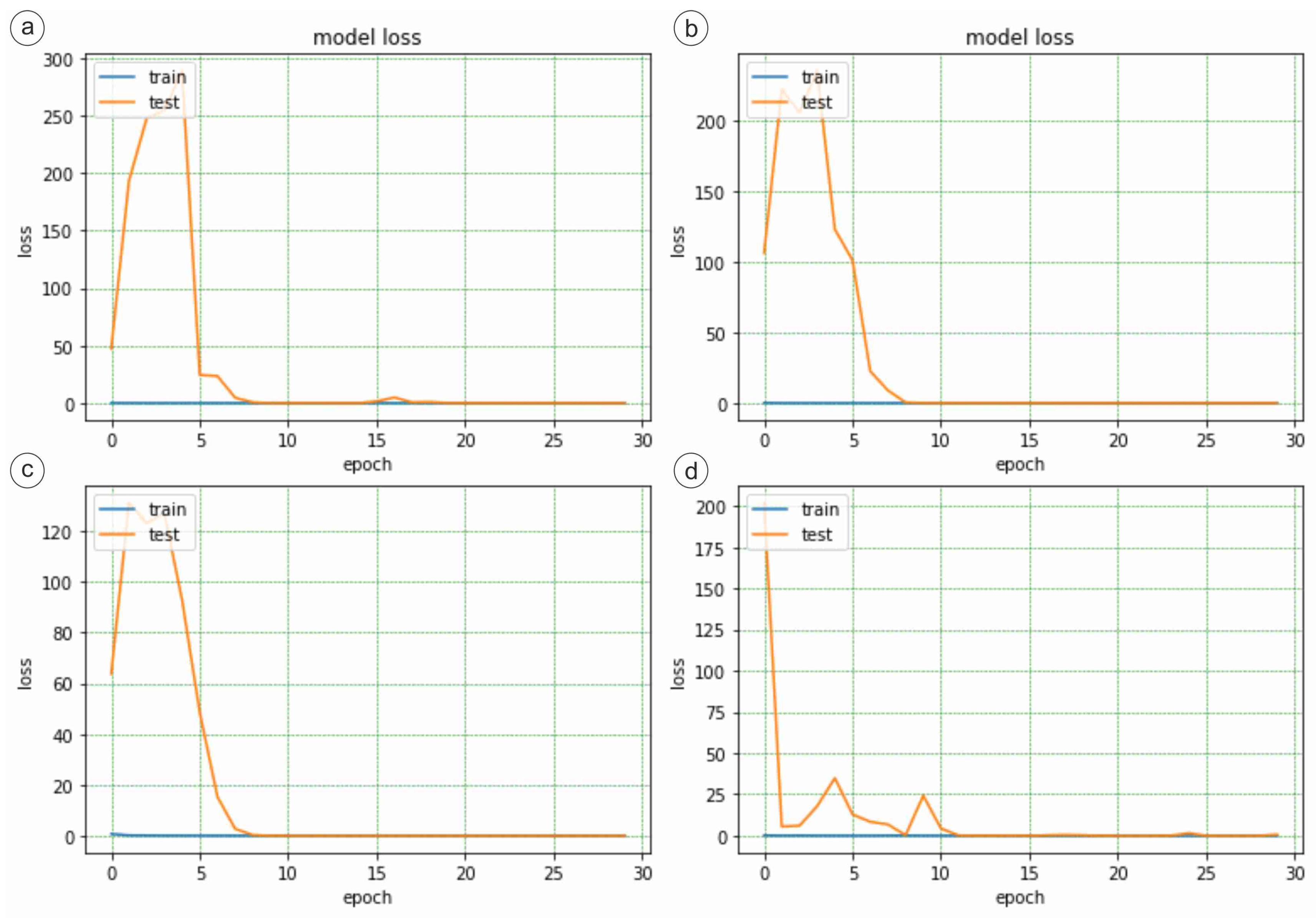
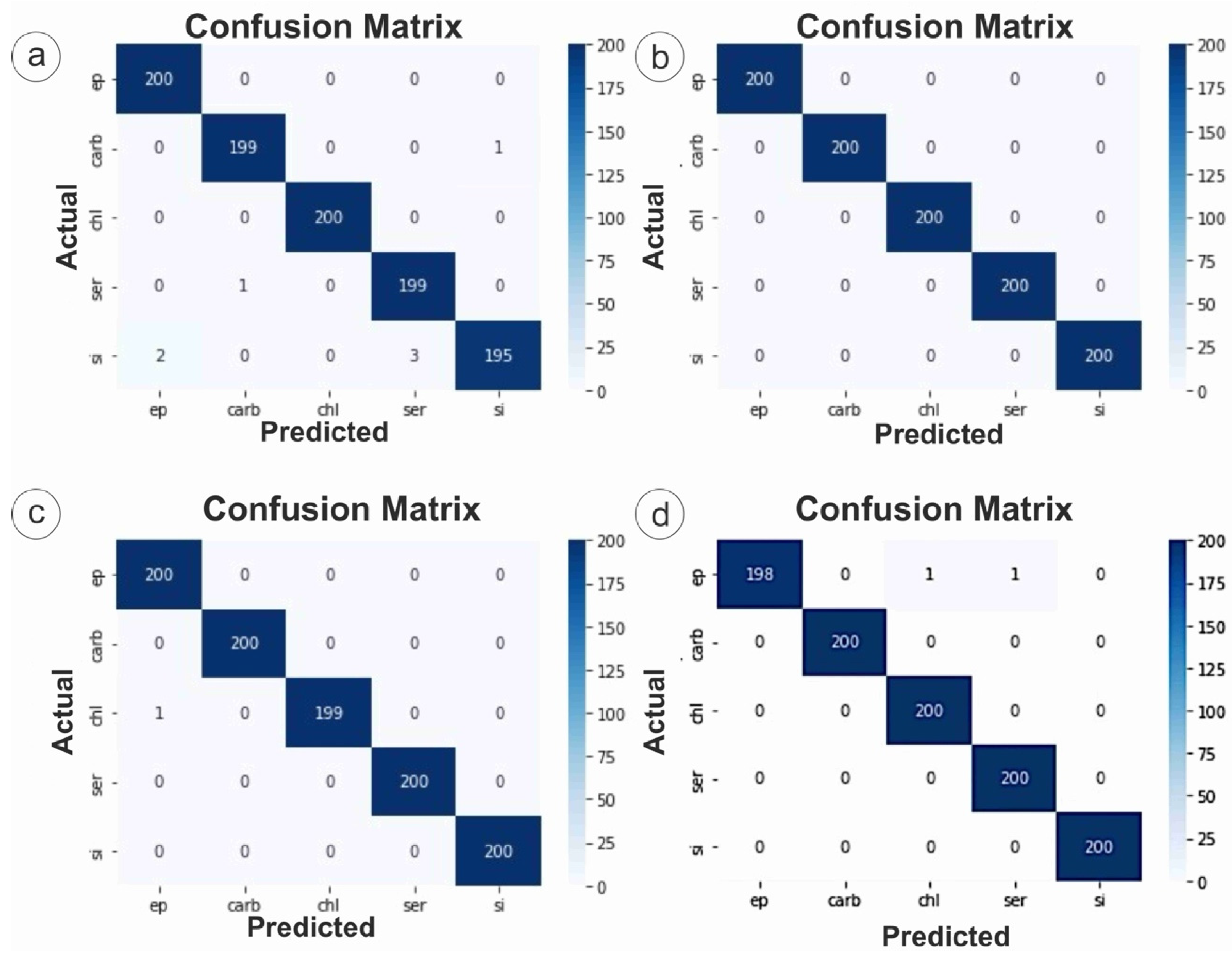
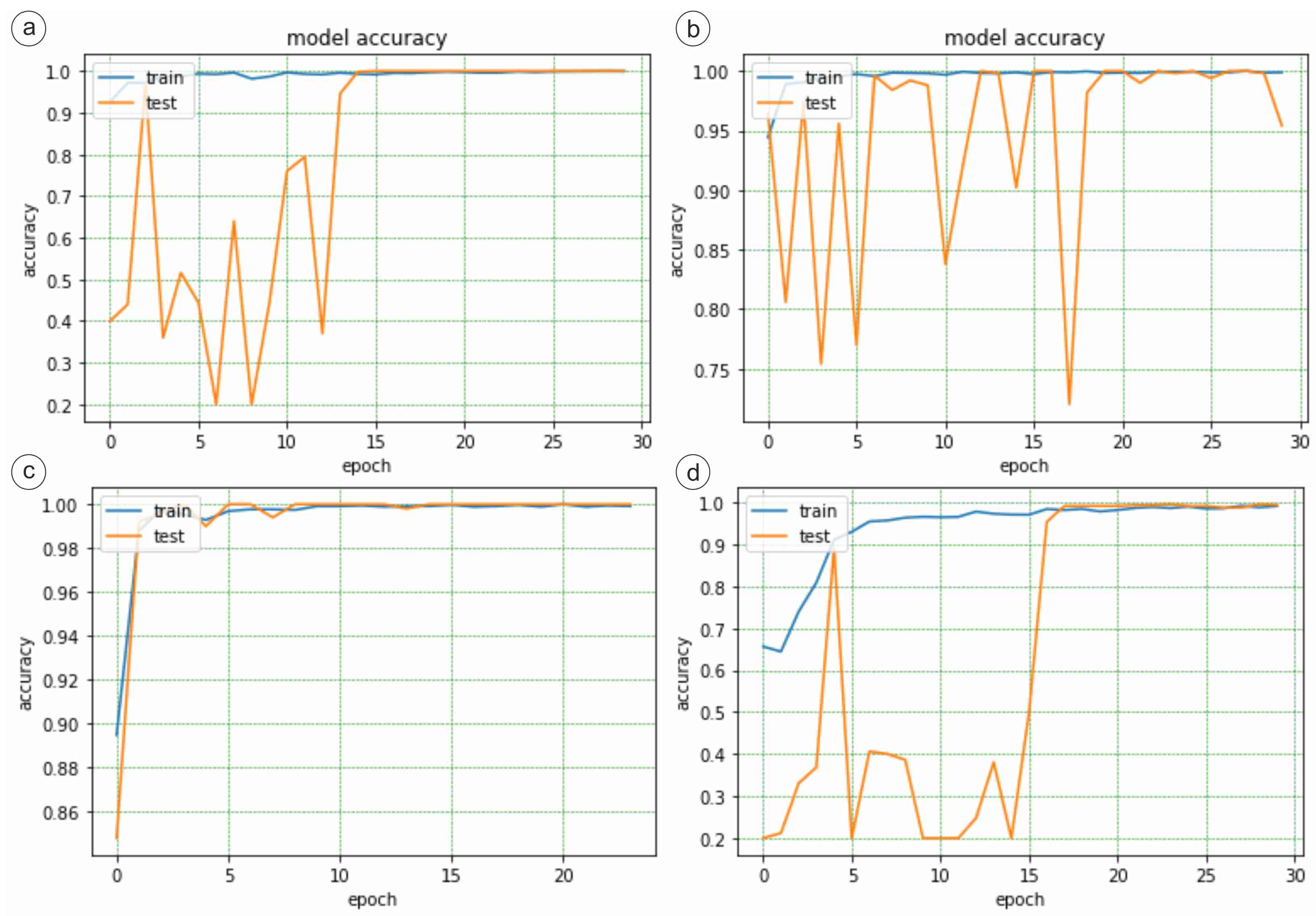
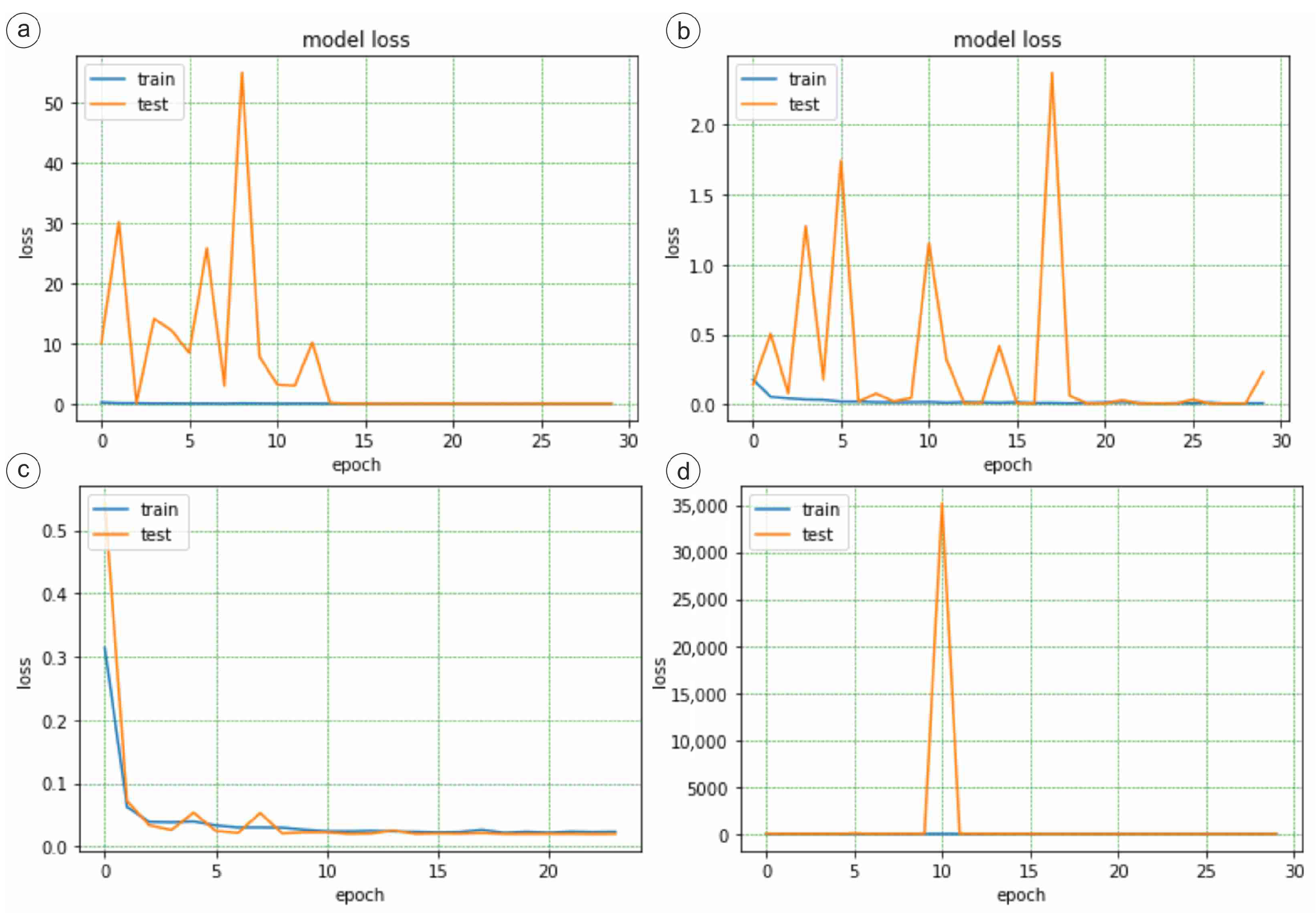
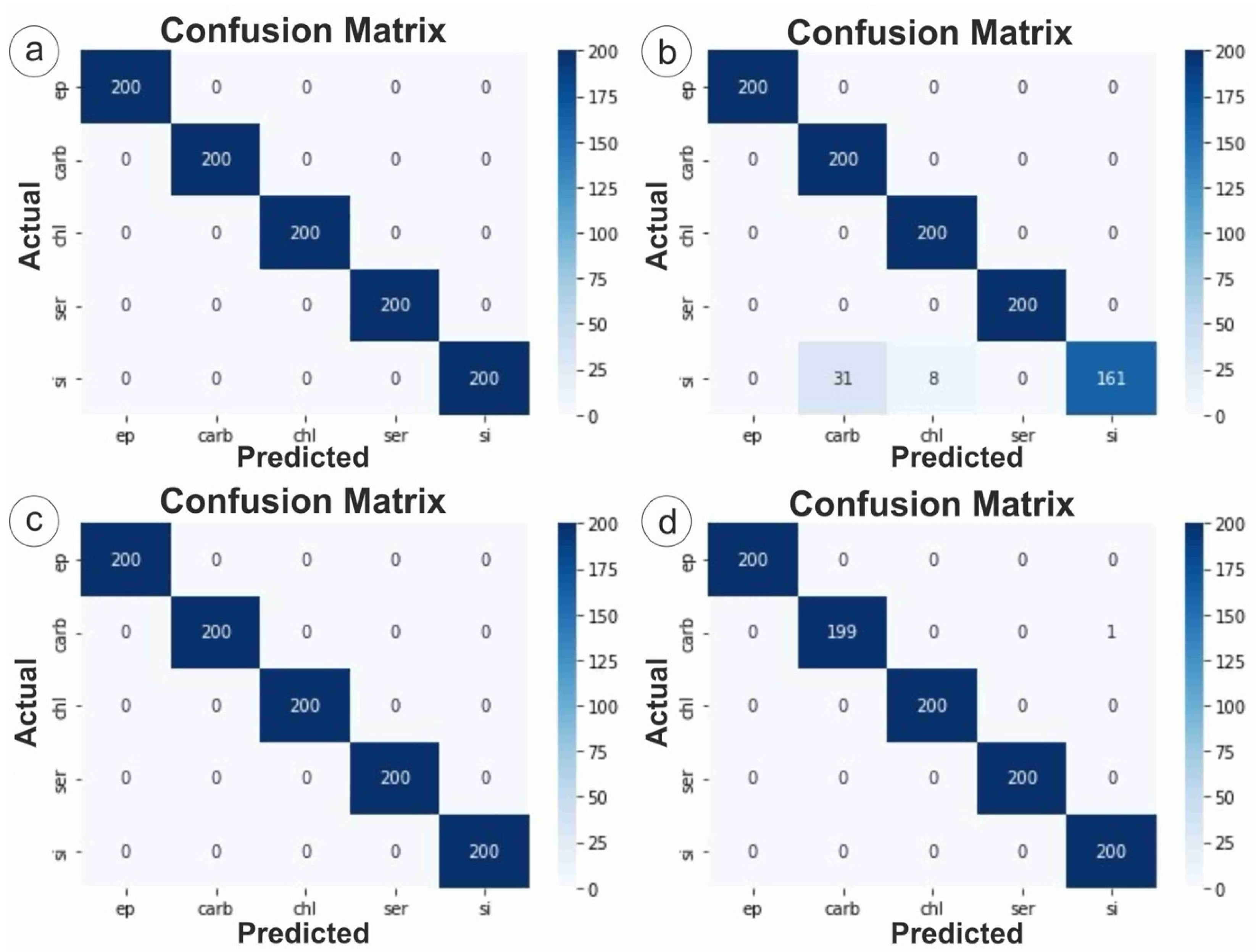
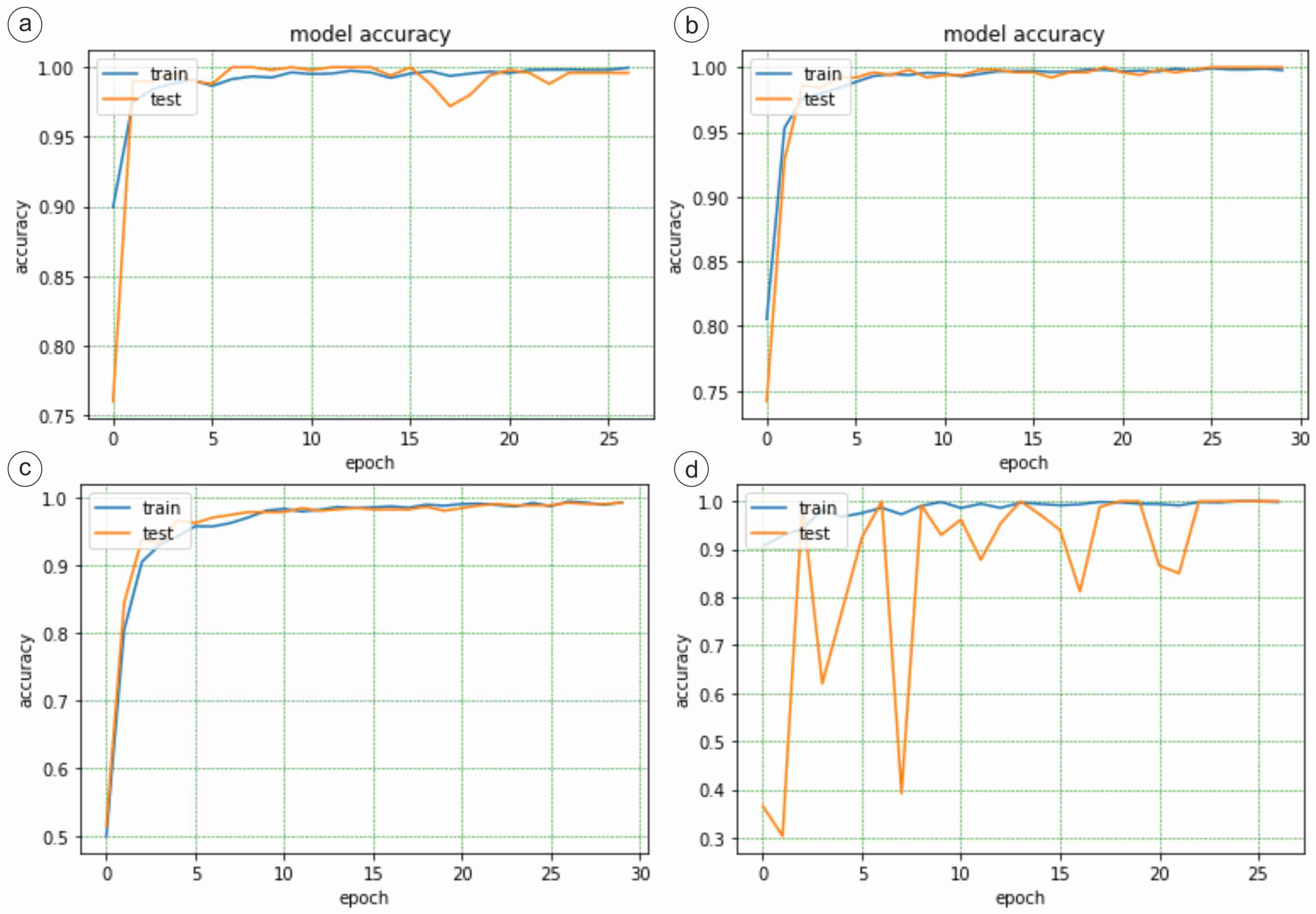
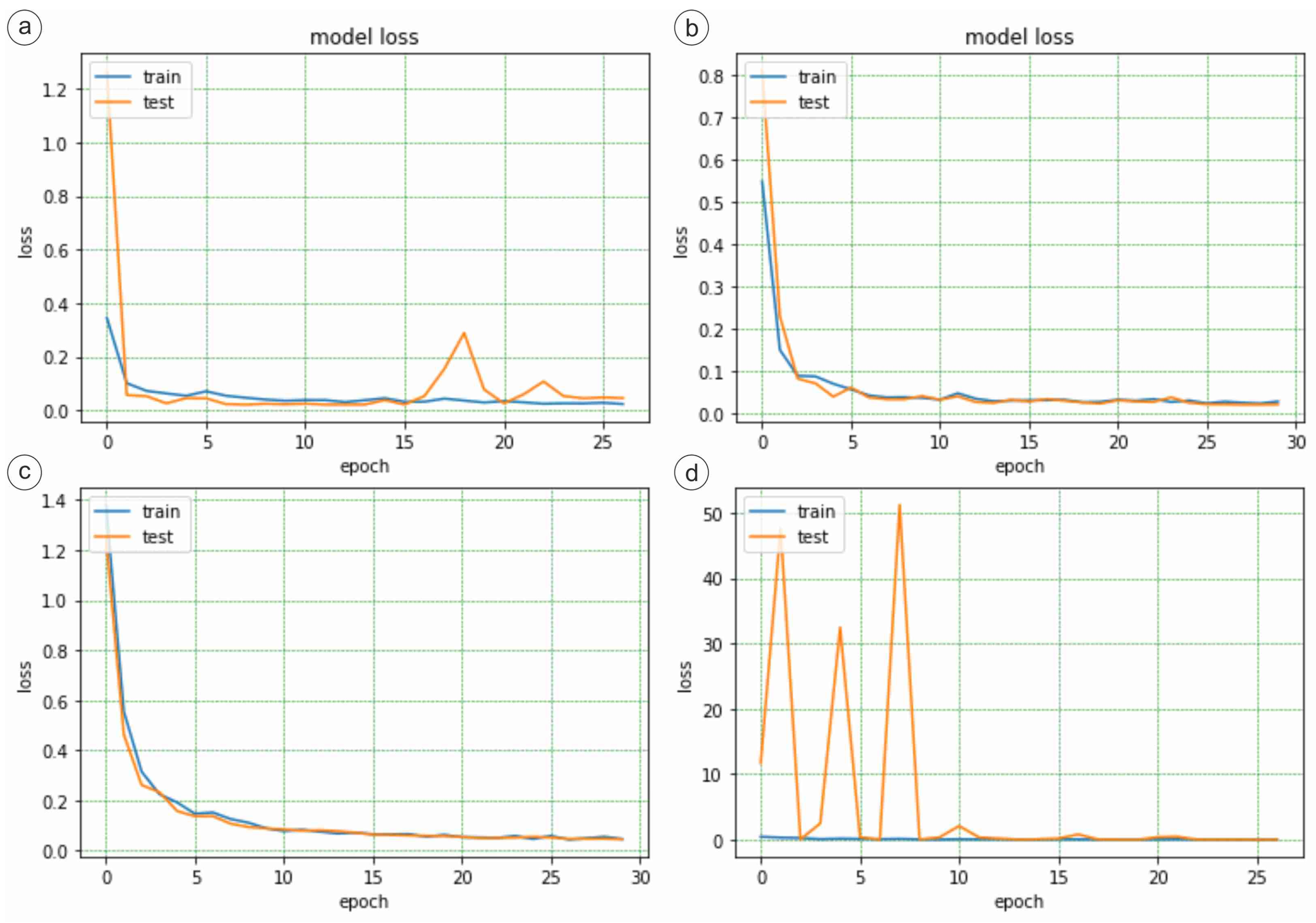
3.1. DenseNet121
3.2. ResNet50
3.3. VGG16
3.4. InceptionV3
3.5. Comparative Evaluation
3.6. Microscopic Interpretation of Misclassification Patterns
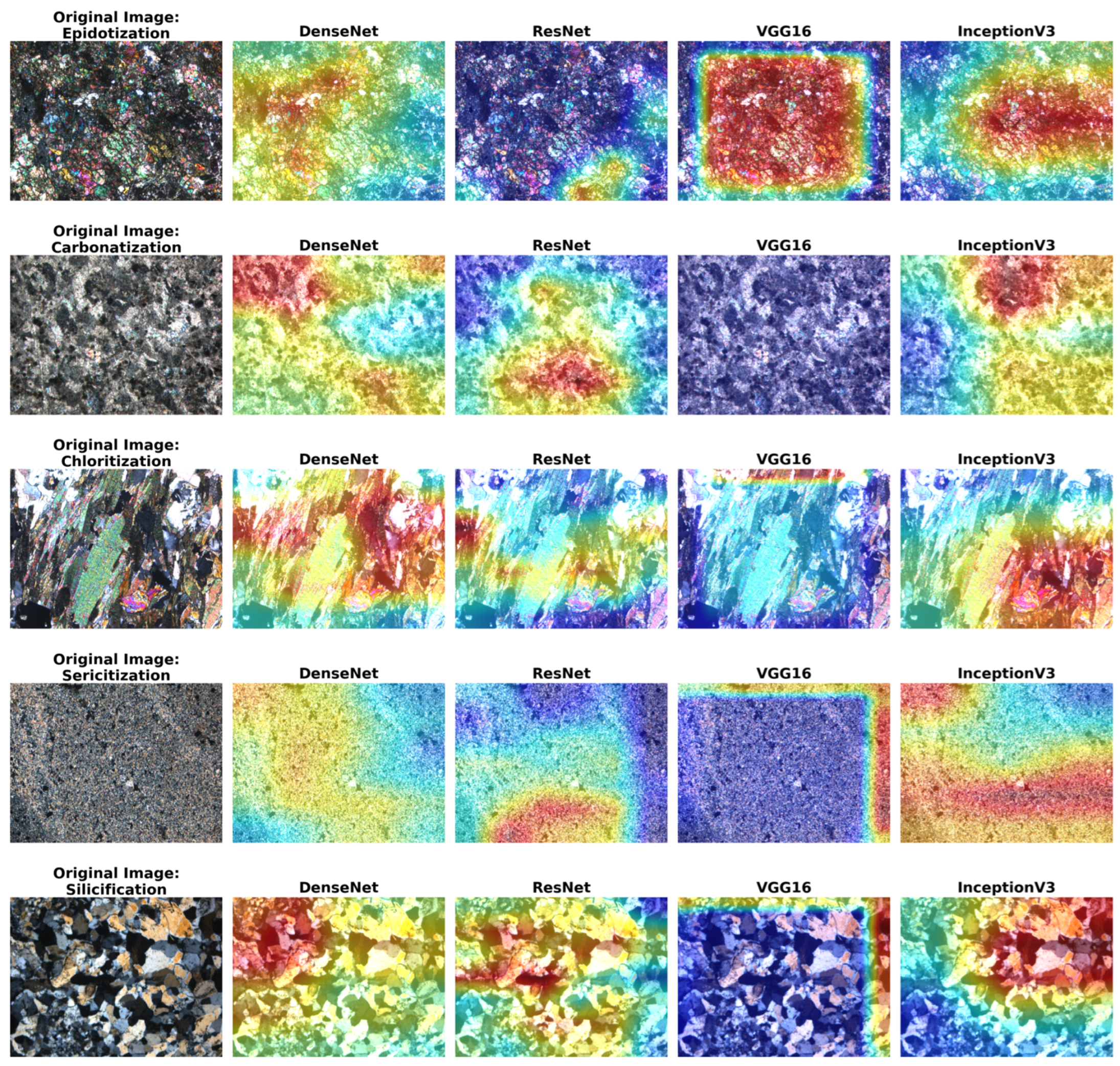
3.7. XAI-Based Visual Validation Using Grad-CAM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Adam | Adaptive Moment Estimation |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DenseNet | Dense Convolutional Network |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| ResNet | Residual Neural Network |
| RMSprop | Root Mean Square Propagation |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| SVMs | Support Vector Machines |
| VGG | Visual Geometry Group |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Pirajno, F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry Copper Systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flügel, E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-03795-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bérubé, C.L.; Olivo, G.R.; Chouteau, M.; Perrouty, S.; Shamsipour, P.; Enkin, R.J.; Morris, W.A.; Feltrin, L.; Thiémonge, R. Predicting Rock Type and Detecting Hydrothermal Alteration Using Machine Learning and Petrophysical Properties of the Canadian Malartic Ore and Host Rocks, Pontiac Subprovince, Québec, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 96, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez-Calderón, J.C.; Gelcich, S. Machine Learning Strategies for Classification and Prediction of Alteration Facies: Examples from the Rosemont Cu-Mo-Ag Skarn Deposit, SE Tucson Arizona. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 194, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, D.; Pires de Lima, R.; Galvis-Portilla, H.; Clarkson, C.R. Generating a Labeled Dataset to Train Machine Learning Algorithms for Lithological Classification of Drill Cuttings. Interpretation 2022, 10, SE85–SE100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.G.; Milliken, K.L.; Spikes, K.T. Machine Learning for Point Counting and Segmentation of Arenite in Thin Section. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 120, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Ojima, H.; Mogi, T.; Kajiwara, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Asanuma, H. Characterization of Hydrothermal Alteration along Geothermal Wells Using Unsupervised Machine-Learning Analysis of X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, İ.; Şener, T.K.; Kılıç, A.D.; Derviş, H. Classification of Thin-Section Rock Images Using a Combined CNN and SVM Approach. Minerals 2025, 15, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budennyy, S.; Pachezhertsev, A.; Bukharev, A.; Erofeev, A.; Mitrushkin, D.; Belozerov, B. Image Processing and Machine Learning Approaches for Petrographic Thin Section Analysis. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers—SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference 2017, Moscow, Russia, 16–18 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Aversana, P. Deep Learning for Automatic Classification of Mineralogical Thin Sections. Bull. Geophys. Oceanogr. 2021, 62, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Xu, S.J.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zhang, X.C. Rock Classification in Petrographic Thin Section Images Based on Concatenated Convolutional Neural Networks. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubo, R.A.; de Carvalho Carneiro, C.; Michelon, M.F.; Gioria, R.d.S. Digital Petrography: Mineralogy and Porosity Identification Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Petrographic Thin Section Images. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 183, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A. Classification Assessment Methods. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 17, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, D.T.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J. Rock Thin Section Image Classification Based on Depth Residuals Shrinkage Network and Attention Mechanism. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, İ.; Kılıç, A.D.; Şener, T.K. Improving Rock Type Identification Through Advanced Deep Learning-Based Segmentation Models: A Comparative Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, P.; Yang, W. Multitarget Intelligent Recognition of Petrographic Thin Section Images Based on Faster RCNN. Minerals 2023, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeshidayatullah, A.; Morsilli, M.; Lehrmann, D.J.; Al-Ramadan, K.; Payne, J.L. Fully Automated Carbonate Petrography Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 122, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Wang, J. Lithology Identification Based on Improved Faster R-CNN. Minerals 2024, 14, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabek, P.; Chudy, K.; Nowak, I.; Zimroz, R. Superpixel-Based Grain Segmentation in Sandstone Thin-Section. Minerals 2023, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, T.N.; Tiwary, A.; Sarkar, K.M. Textural Identification of Basaltic Rock Mass Using Image Processing and Neural Network. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 14, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykan, N.A.; Yılmaz, N. Mineral Identification Using Color Spaces and Artificial Neural Networks. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Mondal, A.; Chakraborty, T.; Ghosh, K. Deep Neural Networks for Automatic Grain-Matrix Segmentation in Plane and Cross-Polarized Sandstone Photomicrographs. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, A.; Haghighi, M.; Zeinijahromi, A. Experiments on Image Data Augmentation Techniques for Geological Rock Type Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, G.; Ma, H.; Zhu, L.; Liang, X.; Lu, X. Rock Thin Sections Identification under Harsh Conditions across Regions Based on Online Transfer Method. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 26, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhong, H.; Camps-Valls, G.; Cao, Z.; Ma, X.; Mills, B.; Hu, X.; Hou, M.; Ma, C. Explainable Deep Learning for Automatic Rock Classification. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 184, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires de Lima, R.; Duarte, D.; Nicholson, C.; Slatt, R.; Marfurt, K.J. Petrographic Microfacies Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 142, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hao, H.; Gu, Q.; Wang, D.; Hu, X. A Transfer Learning Method for Automatic Identification of Sandstone Microscopic Images. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 103, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, Ö.; Polat, A.; Ekici, T. Classification of Plutonic Rock Types Using Thin Section Images with Deep Transfer Learning. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 30, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, Ö.; Polat, A.; Ekici, T. Automatic Classification of Volcanic Rocks from Thin Section Images Using Transfer Learning Networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 11531–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, D.; Kalaiarasan, C. Gradient Propagation Based DenseNet121 with ResNet50 Feature Extraction for Lymphoma Classification. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. B 2025, 106, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raditya, D.I.; Slamet, I.; Sulandari, W.; Susanto, I.; Zukhronah, E.; Isnaini, B. A Comparative Study of Densenet121 And Resnet50 with Grad-Cam for Skin Disease Classification for Improving Good Health. J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev. 2025, 5, e06526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Dai, S. Rock Image Classification Based on Improved EfficientNet. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbaz, O.; Gökce, A. Microthermometric and Stable Isotopic (O and H) Characteristics of Fluid Inclusions in the Porphyry Related Çöpler (İliç-Erzincan) Gold Deposit, Central Eastern Turkey. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2014, 6, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökce, A.; Canbaz, O.; Ünal Çakır, E.; Bozkaya, G.; Bektaş, Ö.; Başdelioğlu, O. Mineralization Characteristics of Lead-Zinc-Copper Deposits in Akdağmadeni Region (Northern Central Anatolia, Türkiye): Integration of Field Study, Geochemical, Isotope, and Geophysical Data. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbaz, O.; Gökce, A. Davulalan A-Type Granitoid-Associated Cu, Mo, Pb, Zn, and REEs Mineralization, Central Anatolia, Turkey. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 196, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbaz, O. Application of Spectral Analysis and Image Processing Methods to Discriminate Hydrothermal Alteration Minerals Around the Tutakdağı (Şebinkarahisar-Giresun) Lead–Zinc Deposits, Northeastern Turkey. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2023, 51, 2019–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, J.D.; Guilbert, J.M. Lateral and Vertical Alteration-Mineralization Zoning in Porphyry Ore Deposits. Econ. Geol. 1970, 65, 373–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Zhao, L.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, J.F. Inception v3 Based Cervical Cell Classification Combined with Artificially Extracted Features. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 93, 106311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sammut, C.; Webb, G.I. Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, 2nd ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4899-7685-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jukes, E. Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining (2nd Edition). Ref. Rev. 2018, 32, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M.N. A Review on Evaluation Metrics for Data Classification Evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, K.M. Confusion Matrix. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining; Sipringer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; p. 260. [Google Scholar]
- Grandini, M.; Bagli, E.; Visani, G. Metrics for Multi-Class Classification: An Overview. arXiv 2008, arXiv:2008.05756. [Google Scholar]

| Adam | RMSprop | SGD | Adadelta | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | |
| ep | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| carb | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.97 |
| chl | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ser | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.96 |
| si | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Adam | RMSprop | SGD | Adadelta | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | |
| ep | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| carb | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| chl | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ser | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| si | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Adam | RMSprop | SGD | Adadelta | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | |
| ep | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| carb | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| chl | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ser | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| si | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Adam | RMSprop | SGD | Adadelta | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | p | r | f1 | |
| ep | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| carb | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| chl | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ser | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| si | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| DenseNet121 | ResNet50 | VGG16 | InceptionV3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acc | loss | time | acc | loss | time | acc | loss | time | acc | loss | time | |
| Adam | 1.00 | 0.018 | 927 | 0.993 | 0.091 | 931 | 1.00 | 0.013 | 1270 | 0.987 | 0.099 | 662 |
| RMSprop | 1.00 | 0.010 | 1382 | 1.00 | 0.009 | 1138 | 0.961 | 0.163 | 1312 | 0.993 | 0.030 | 872 |
| SGD | 0.998 | 0.026 | 1088 | 0.999 | 0.026 | 932 | 1.00 | 0.020 | 1064 | 0.996 | 0.034 | 831 |
| Adadelta | 0.991 | 0.042 | 952 | 0.998 | 0.045 | 973 | 0.999 | 0.024 | 1259 | 1.00 | 0.021 | 674 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çenet, R.; Ünsal, E.; Canbaz, O. Classification of Hydrothermal Alteration Types from Thin-Section Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212274
Çenet R, Ünsal E, Canbaz O. Classification of Hydrothermal Alteration Types from Thin-Section Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212274
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇenet, Rıza, Emre Ünsal, and Oktay Canbaz. 2025. "Classification of Hydrothermal Alteration Types from Thin-Section Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212274
APA StyleÇenet, R., Ünsal, E., & Canbaz, O. (2025). Classification of Hydrothermal Alteration Types from Thin-Section Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212274







